| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Ternary plot" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

A ternary plot, ternary graph, triangle plot, simplex plot, or Gibbs triangle is a barycentric plot on three variables which sum to a constant. It graphically depicts the ratios of the three variables as positions in an equilateral triangle. It is used in physical chemistry, petrology, mineralogy, metallurgy, and other physical sciences to show the compositions of systems composed of three species. Ternary plots are tools for analyzing compositional data in the three-dimensional case.
In population genetics, a triangle plot of genotype frequencies is called a de Finetti diagram. In game theory and convex optimization, it is often called a simplex plot.
In a ternary plot, the values of the three variables a, b, and c must sum to some constant, K. Usually, this constant is represented as 1.0 or 100%. Because a + b + c = K for all substances being graphed, any one variable is not independent of the others, so only two variables must be known to find a sample's point on the graph: for instance, c must be equal to K − a − b. Because the three numerical values cannot vary independently—there are only two degrees of freedom—it is possible to graph the combinations of all three variables in only two dimensions.
The advantage of using a ternary plot for depicting chemical compositions is that three variables can be conveniently plotted in a two-dimensional graph. Ternary plots can also be used to create phase diagrams by outlining the composition regions on the plot where different phases exist.
The values of a point on a ternary plot correspond (up to a constant) to its trilinear coordinates or barycentric coordinates.
Reading values on a ternary plot
There are three equivalent methods that can be used to determine the values of a point on the plot:
- Parallel line or grid method. The first method is to use a diagram grid consisting of lines parallel to the triangle edges. A parallel to a side of the triangle is the locus of points constant in the component situated in the vertex opposed to the side. Each component is 100% in a corner of the triangle and 0% at the edge opposite it, decreasing linearly with increasing distance (perpendicular to the opposite edge) from this corner. By drawing parallel lines at regular intervals between the zero line and the corner, fine divisions can be established for easy estimation.
- Perpendicular line or altitude method. For diagrams that do not possess grid lines, the easiest way to determine the values is to determine the shortest (i.e. perpendicular) distances from the point of interest to each of the three sides. By Viviani's theorem, the distances (or the ratios of the distances to the triangle height) give the value of each component.
- Corner line or intersection method. The third method does not require the drawing of perpendicular or parallel lines. Straight lines are drawn from each corner, through the point of interest, to the opposite side of the triangle. The lengths of these lines, as well as the lengths of the segments between the point and the corresponding sides, are measured individually. The ratio of the measured lines then gives the component value as a fraction of 100%.
A displacement along a parallel line (grid line) preserves the sum of two values, while motion along a perpendicular line increases (or decreases) the two values an equal amount, each half of the decrease (increase) of the third value. Motion along a line through a corner preserves the ratio of the other two values.
-
 Figure 1. Altitude method
Figure 1. Altitude method
-
 Figure 2. Intersection method
Figure 2. Intersection method
-
 Figure 3. An example ternary diagram, without any points plotted.
Figure 3. An example ternary diagram, without any points plotted.
-
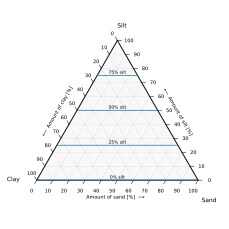 Figure 4. An example ternary diagram, showing increments along the first axis.
Figure 4. An example ternary diagram, showing increments along the first axis.
-
 Figure 5. An example ternary diagram, showing increments along the second axis.
Figure 5. An example ternary diagram, showing increments along the second axis.
-
 Figure 6. An example ternary diagram, showing increments along the third axis.
Figure 6. An example ternary diagram, showing increments along the third axis.
-
 Figure 7. Empty ternary plot
Figure 7. Empty ternary plot
-
 Figure 8. Indication of how the three axes work.
Figure 8. Indication of how the three axes work.
-
 Unlabeled triangle plot with major grid lines
Unlabeled triangle plot with major grid lines
-
 Unlabeled triangle plot with major and minor grid lines
Unlabeled triangle plot with major and minor grid lines
Derivation from Cartesian coordinates
Figure (1) shows an oblique projection of point P(a,b,c) in a 3-dimensional Cartesian space with axes a, b and c, respectively.
If a + b + c = K (a positive constant), P is restricted to a plane containing A(K,0,0), B(0,K,0) and C(0,0,K). If a, b and c each cannot be negative, P is restricted to the triangle bounded by A, B and C, as in (2).
In (3), the axes are rotated to give an isometric view. The triangle, viewed face-on, appears equilateral.
In (4), the distances of P from lines BC, AC and AB are denoted by a′, b′ and c′, respectively.
For any line l = s + t n̂ in vector form (n̂ is a unit vector) and a point p, the perpendicular distance from p to l is
In this case, point P is at
Line BC has
Using the perpendicular distance formula,
Substituting K = a + b + c,
Similar calculation on lines AC and AB gives
This shows that the distance of the point from the respective lines is linearly proportional to the original values a, b and c.
Plotting a ternary plot

Cartesian coordinates are useful for plotting points in the triangle. Consider an equilateral ternary plot where a = 100% is placed at (x,y) = (0,0) and b = 100% at (1,0). Then c = 100% is and the triple (a,b,c) is
Example

This example shows how this works for a hypothetical set of three soil samples:
Sample Clay Silt Sand Notes Sample 1 50% 20% 30% Because clay and silt together make up 70% of this sample, the proportion of sand must be 30% for the components to sum to 100%. Sample 2 10% 60% 30% The proportion of sand is 30% as in Sample 1, but as the proportion of silt rises by 40%, the proportion of clay decreases correspondingly. Sample 3 10% 30% 60% This sample has the same proportion of clay as Sample 2, but the proportions of silt and sand are swapped; the plot is reflected about its vertical axis.
Plotting the points
-
 Plotting Sample 1 (step 1):
Plotting Sample 1 (step 1):
Find the 50% clay line -
 Plotting Sample 1 (step 2):
Plotting Sample 1 (step 2):
Find the 20% silt line -
 Plotting Sample 1 (step 3):
Plotting Sample 1 (step 3):
Being dependent on the first two, the intersect is on the 30% sand line -
 Plotting all the samples
Plotting all the samples
-
 Ternary triangle plot of soil types sand clay and silt programmed with Mathematica
Ternary triangle plot of soil types sand clay and silt programmed with Mathematica
List of notable ternary diagrams
- Chromaticity diagram
- de Finetti diagram
- Dalitz plot
- Flammability diagram
- Jensen cation plot
- Piper diagram, used in hydrochemistry
- UIGS Classification diagram for Ultramafic rock
- USDA Soil texture diagram by particle sizes
See also
- Apparent molar property
- Viviani's theorem
- Barycentric coordinates (mathematics)
- Compositional data
- List of information graphics software
- Earth sciences graphics software
- IGOR Pro
- Origin (data analysis software)
- R has a dedicated package ternary maintained on the Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN)
- Sigmaplot
- Project triangle
- Trilemma
References
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Ternary Diagram". mathworld.wolfram.com. Retrieved 2021-06-05.
- Karl Tuyls, "An evolutionary game-theoretic analysis of poker strategies", Entertainment Computing January 2009 doi:10.1016/j.entcom.2009.09.002, p. 9
- Boyd, S. and Vandenberghe, L., 2004. Convex optimization. Cambridge university press.
- Vaughan, Will (September 5, 2010). "Ternary plots". Archived from the original on December 20, 2010. Retrieved September 7, 2010.
External links
- Printable Ternary Paper at Gridpaper.co.uk
- "Excel Template for Ternary Diagrams". serc.carleton.edu. Science Education Resource Center (SERC) Carleton College. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- "Tri-plot: Ternary diagram plotting software". www.lboro.ac.uk. Loughborough University – Department of Geography / Resources Gateway home > Tri-plot. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- "Ternary Plot Generator – Quickly create ternary diagrams on line". www.ternaryplot.com. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- Holland, Steven (2016). "Data Analysis in the Geosciences – Ternary Diagrams developed in the R language". strata.uga.edu. University of Georgia. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
| Chemical solutions | |
|---|---|
| Solution | |
| Concentration and related quantities | |
| Solubility | |
| Solvent | |







 that of the a and b axes. The cross denotes the point a = b = c.
that of the a and b axes. The cross denotes the point a = b = c. and the triple (a,b,c) is
and the triple (a,b,c) is
