Modern railway signalling in Thailand on the mainline employs color light signals and computer-based interlocking. The State Railway of Thailand is currently implementing centralized traffic control to link the whole country’s signalling system together using a fiber optic network. This includes recent double-tracking projects for all mainlines extending from Bangkok.
Early double tracking projects used conventional interlocking systems (Bombardier INTERFLO 200), but later projects are designed for an upgrade to ETCS Level 1, starting from the Red Line commuter project and recent double tracking projects. However, in most rural areas, single track semaphore signals are still in use.
Color Light System
| Distant | Home Outer | Home with Left Indicator | Home with Left/Right Junction Indicator | Starter | Starter with Right Junction Indicator | Main with Shunt Ahead |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
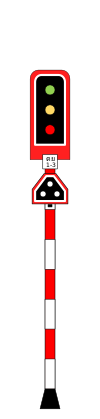
2 Aspects Distant Signal
Distant signals are used to indicate whether the next main signal is red or not. These signals consist of two colored light signals (yellow and green).
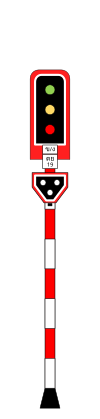
3 Aspects Main / Starter Signal
These consist of three colored light signals (green, yellow and red).
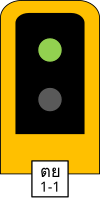
2 Aspects Main / Starter Signal
These consist of two colored light signals (green and red).
Repeater Signal
This signal use when Main Home signal is blocked from driver view (in curve or hills). The signal consists of 3 white signals that display either diagonal, flash diagonal or horizontal that represents green, yellow and red of next signal.
Call-on Signal
Call-on signal, 3 white lamps arranged in triangle pointing up, may installed below or besides Main Signal. Call-on signal use for emergency to allow train or locomotives to pass while signal is red.
| Signal | Meaning | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
White | Call-on | |
Shunt Ahead Signal
Shunt Ahead signal, 3 white lamps arranged in triangle pointing down, may installed below or besides Starter Signal. Shunt Ahead signal use for allow locomotive shunting.
| Signal | Meaning | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
White | Shunt Ahead | |
Ground Shunt Signal
Ground Shunt signal, 2 horizontal red lamps and 2 diagonal white lamps, may installed in shunting area of main tracks (between switches and Home Signal) or in shunting tracks. Ground Shunt signal use for allow locomotive shunting.
| Signal | Meaning | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Diagonal White | Shunt ahead | |
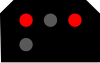 |
Horizontal Red | Stop | |
Junction Indicator
Junction Indicator (5 in-line diagonal white lamps point left or right) may installed above Main or Starter Signal before switches.
If junction indicator is active, the train must proceed at reduce speed. Speed limit indication sign may present at signal to indicate speed limit when passing switches.
| Indicator | Meaning | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
Off | No diverging |
 |
 |
To left | Expect diverging left | |
 |
 |
To right | Expect diverging right | |
Level Crossing Rail Warning Signal
This signal may placed ahead of Level Crossing to indicate road at level crossing ahead been closed engaged and clear to proceed.
Level Crossing Advance Warning Marker Post is placed 1 km ahead of this signal to warn train driver of level crossing ahead. If Signal is not clear driver must slow down the train and proceed with limited speed.
| Signal | Meaning | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Flashing White | Clear | Road barrier of level crossings ahead are closed and clear to pass |
Station Yard Signal Layout

Typical stations which have station yard or siding tracks will have following signal layout.
Distant Signal (Warner Signal)
Distant signal is place before Home Signal of the station yard or signal block.
If signal is yellow, train must prepare to stop at next signal or proceed with limited speed.
Typical distance of Distant Signal from Home Signal is 1000m-1500m.
Home Signal
Home Signal use to protect station's inner area (switching area, passing track, platform track, sidings).
Minimum distance from Home Signal to inner area of station is 850m (650m maximum train length at limit shunt post plus 200m minimum safety distance).
Speed limit sign usually placed along with Home Signal with Junction Indicator to indicate safe passing speed at switches in case of diverging.
In some stations, 2 stages of Home Signal used, this separate Home signal into Home Outer Signal and Home Inner Signal, in this case, Home Inner Signal is placed immediately before station inner area and Home Outer Signal is place at least 850m before Home Inner Signal to allow a train wait on main track before entering station.
Starter Signal
Starter signal use to allow train to leave station or yard.
In large junction station 2 stage of starter signal may exists. Inner Starter Signal use to protect switch and shunting area after leave inner area, Outer Starter Signal use to permit train to leave outer area. I this case, 3 Aspects Signal are use for Inner Starter Signal.
In some stations, If next station are too close (less than 2000m from Home signal of next station), 3 Aspect Signal are use as Starter Signal instead of 2 Aspect Signal and thus, this signal will also act as a Distant Signal for Home Signal of next station.
Block Signal
In case distance between stations is too far (distance from Starter Signal to Home Signal of following station), one or more 2 Aspects Main Signal and corresponding Distant Signal may be placed between station to act as a Block Signal.
This Block Signal usually not controlled by CTC or Station but work automatically using track circuit which is referred to as Automatic Signal
Signal Numbering
Main Signal
Signals numbering in main tracks are based on direction away from Bangkok (Up track) and to Bangkok (Down track). Normally signals on Up direction are given odd number while signals on Down direction are given even number. Signal number always followed by station code that controls the interlocking of the signals.
Main track number is reference by Up track (direction away from Bangkok). In typical cases, leftmost main Up track always track #1 and increasing to the right, so signal on Up main track are number 1 in Up direction and 2 in Down direction, and for track #2 will be 3 and 4, track #3 will be 5 and 6 and so on.
Usually there are more than 1 signal in each track and each direction in station interlocking area. Actual signal number will followed by signal sequence number which also use the same odd/even rules in format A-B, A is signal track number and B is signal sequence number.
So first signal in track #1 Up will be signal number 1-1 following signal will be 1–3, 1-5 and so on. In opposite Down direction of same track #1 number 2-2, 2–4, 2-6 and so on will be used.
Signals on Loop tracks (Siding) or Platform tracks are also follow same rules, since usually only 1 starter signal exists on those tracks, the signal number usually have no sequence number. For Platform tracks, signal start with number 15 on the leftmost side of main Up track followed by 17, 19 and so on and 16, 18, 20 in opposite direction. For Loop tracks signal start with number 31 on the leftmost side of main Up track followed by 33, 35 and so on and 34, 36, 38 in opposite direction up to 50. In some station, multi stage starter signals or Advance starter signals are used and will have sequence number such as 15–1, 15–3.
Automatic Signal
Automatic signal are not controls by station interlocking, numbering on automatic signals use 1/10 of KM as a prefix followed by track number. i.e. KM 25+500 on main Up track will use 255–1, 255–3, 255-5 for automatic signal.
Semaphores System
| This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (January 2021) |
SRT Red Line Signal
Some part of SRT Red Lines tracks will also operate as new SRT mainline tracks which use ETCS Level 1 along with color light signals and new 1 aspect white light signals for Red Lines EMU dedicated tracks.
Tracks of SRT Red Lines use new signal numbering scheme based on Main Line odd/even number system. Signals are prefixed with M for Main signal and B for Automatic signal and two digits number from 01 to 99 (with leading zero), followed by station code that controlled interlocking. i.e. signals number will be M01 M03 and so on in Up direction and M02 M04 and so on in down direction. Since some of the Red Line stations are very close to each other and mostly have no loop tracks, signals in multiple stations may controlled by same Interlocking. In SRT Red Lines signals are more like block signals than station home signals, so sequence number are not used. Instead, signal number will increment from the first signal facing direction of traveling train.
The signal on outer tracks of SRT Dark Red Line in elevated section use white light 1 aspect signal instead of 2/3 aspects color signal because tracks are dedicated for EMU Red Lines. EMU tracks have shorter block length than main track, other trains can use EMU tracks only in Emergency or Shunting.
Signalling in Urban Rapid Transit
BTS Skytrain
BTS Skytrain currently use Bombardier CITYFLO 450 CBTC virtual block for signalling and ATP system. Originally, BTS use Siemens LZB 700M during early operation from 1999 - 2009. In 2009 new extensions to Wongwian Yai are equipped with CITYFLO 450 Signalling, then finally convert the whole system to CITYFLO 450 in 2010.
MRT Blue Line
MRT Blue Line use Siemens LZB 700M for signalling and ATP system.
MRT Purple Line
MRT Purple Line Bombardier CITYFLO 650 CBTC moving block for signalling and ATP system.
Airport Rail Link
Airport Rail Link use Siemens LZB 700M for signalling and ATP system.
References
- "การออกแบบระบบอานัติสัญญาณรถไฟโดยคอมพิวเตอร์" (PDF). thaiscience.info. Retrieved 21 July 2019.
- "SIGNALLING AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS DOUBLE TRACK RAILWAY PROJECTNAKHON PATHOM – CHUMPHON TENDER DOCUMENTS" (PDF). procurement.railway.co.th. Retrieved 24 July 2019.
Notes
- "Worldwide projects". Bombadier. Retrieved 21 July 2019.
- "Bangkok's suburban train will boost its capacity by up to 40% with ThalesBangkok's suburban train will boost its capacity by up to 40% with Thales". Thales. Retrieved 21 July 2019.
- "ประกวดราคาจ้างก่อสร้างโครงการจัดหาและติดตั้งระบบอาณัติสัญญาณและโทรคมนาคม ในโครงการก่อสร้างรถไฟทางคู่ ช่วงมาบกะเบา - ชุมทางถนนจิระ โดยการประกวดราคานานาชาติ". State Railway of Thailand - Procurement. Retrieved 21 July 2019.
- "ประกวดราคาจ้างก่อสร้างโครงการจัดหาและติดตั้งระบบอาณัติสัญญาณและโทรคมนาคม ในโครงการก่อสร้างรถไฟทางคู่ ช่วงลพบุรี - ปากน้ำโพ โดยการประกวดราคานานาชาติ". State Railway of Thailand - Procurement. Retrieved 21 July 2019.
- "ประกวดราคาจ้างก่อสร้างโครงการจัดหาและติดตั้งระบบอาณัติสัญญาณและโทรคมนาคม ในโครงการก่อสร้างรถไฟทางคู่ ช่วงนครปฐม - ชุมพร โดยการประกวดราคานานาชาติ". State Railway of Thailand - Procurement. Retrieved 21 July 2019.
| Major operators |  | |
|---|---|---|
| Lines | ||
| Lists | ||
| Notable trains | ||
| Rolling Stock | ||