| |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | USS Chillicothe |
| Namesake | Chillicothe, Ohio |
| Commissioned | 5 September 1862 |
| Stricken | 29 November 1865 |
| Fate |
|
| General characteristics | |
| Type | River gunboat |
| Displacement | 395 long tons (401 t) |
| Length | 162 ft (49 m) |
| Draft | 4 ft (1.2 m) |
| Depth of hold | 5 ft (1.5 m) |
| Speed | 7 knots (13 km/h; 8.1 mph) |
| Armament | 2 × 11 in (280 mm) smoothbore guns |
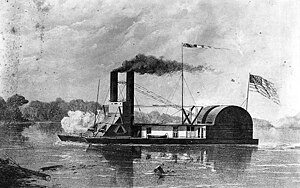
USS Chillicothe was an ironclad river gunboat of the United States Navy. She was named for the capital of Ohio from 1803 to 1810.
Chillicothe was laid down at Cincinnati, Ohio. She was commissioned on 5 September 1862 at Jeffersonville, Indiana, with Acting Lieutenant J. P. Sanford in command. Necessary alterations and repairs and lack of sufficient water to pass over the falls detained her in the Ohio River until early January 1863.
Service history
From 8 January 1863, when she sailed from Cairo, Illinois, until the end of the American Civil War, Chillicothe was constantly employed in the Mississippi River and its tributaries. She joined in the expeditions to the White River in Arkansas in January 1863 and contributed to the capture of Fort Hindman, Arkansas. She then joined the Yazoo Pass Expedition, from 20 February to 10 April. Coming under enemy's fire with Baron DeKalb in the Yazoo expedition, Chillicothe was heavily damaged and lost several men. She was sent to Mound City, Illinois, for repairs and returned to duty on the Mississippi River on 6 September 1863.
On 24 February 1864 she entered the Red River for the expedition of 7 March to 15 May in which her commanding officer, Lieutenant Joseph P. Couthouy, was mortally wounded by rifle fire on 3 April. From 22 May 1864 until 26 May 1865 she lay off Fort Adams, Mississippi, on 8 June 1864 assisting in the capture of a Confederate battery at Simmesport, Louisiana.
Chillicothe arrived at Cairo, Illinois, on 13 July 1865, and on 29 November 1865 was sold at auction at Mound City, Illinois. As a civilian-owned ship, she was destroyed by fire in September 1872.
References
![]() This article incorporates text from the public domain Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships. The entry can be found here.
This article incorporates text from the public domain Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships. The entry can be found here.
| Ironclads of the United States | |
|---|---|
| Coastal monitors | |
| River and harbor monitors | |
| Ocean-going monitors | |
| Riverine casemate ironclads | |
| Ocean-going casemate ironclads | |
| Commissioned ironclads | |
| Never-commissioned ironclads | |
| Miscellaneous ironclads | |