| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Underwater thruster" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
An underwater thruster is a configuration of marine propellers and hydraulic or electric motor built into or mounted to an underwater robot as a propulsion device. These give the robot movement and maneuverability against sea water resistance. The main difference between underwater thrusters and marine thrusters is the ability to work under heavy water pressure, sometime up to full ocean depth.
Types of underwater thrusters
There are three general types of thrust devices: the lateral thruster or tunnel thruster, which consists of a propeller installed in a athwartship tunnel; a jet thruster which consists of a pump taking suction from the keel and discharge to either side; and azimuthal thruster, which can be rotated through 360°
Underwater thrusters can be further divided in two main groups, hydraulic thrusters and electric thrusters. Below are some pros and cons of each type:
| Pros | Cons | |
|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Thrusters |
|
|
| Electric Thrusters |
|
|
Hydraulic Thrusters
Hydraulic thrusters are mainly used on larger work class ROVs, mainly because they take up a lot of space and weight due to the extra components such as valves and pipes. Hydraulic thruster technology is older than the electrical one, they are more rugged and their weight-to-thrust ratio is higher than electric thrusters, but maintenance and piping issues cause some dissatisfaction with users. Weight-to-thrust ratios are higher for hydraulic thrusters than for electric thrusters, but after taking into account the required hydraulic components including valves, hydraulic power units, pipes joints, etc. hydraulic thruster systems come out heavier than electric thrusters.
Electric Thrusters

Electric thrusters are mainly used on battery operated underwater robots such as AUVs, submarines, and electric ROVs. Electric thrusters usually use brushless DC or permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM). These motors may be sealed within air- or oil-filled cavities, or use a flooded design that allows water to come into contact with the motor, providing extra cooling and lubrication.
Components
The main components of an electric thruster are:


- Electric motor: The electric motor is the main component of electric thrusters and drives the propeller. Modern underwater thrusters usually use brush-less permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs). In some low-quality thrusters brushless D.C. motors are used. The gain is lower price and the penalty is lower efficiency. In most modern designs, frameless PMSM motors (mainly produced by Kollmorgen) are used to reduce the weight and increase the thermal efficiency. This improves the power-to-weight ratio, but the penalty is higher assembly cost. Danish based Copenhagen Subsea produces electrical ring thrusters, where the power is applied on the perimeter, and the motor components are integrated with a duct.
- Gearbox: to match propeller torque with motor torque some manufacturers use a gearbox. Most of the time, to reduce the weight and volume of the thruster, the gears are assembled directly inside the thruster shell, which is used as the gearbox housing. In this way the weight is reduced, but repairs become difficult as the spare parts can not be found on the normal market.
- Direct drive: In some modern designs which use PMSM motors, the ratio of motor torque to its diameter is so high that the motor can rotate the propeller without a gearbox. In direct drive underwater thrusters, the motors are heavier than those used in geared thrusters, but lack of a gearbox compensates for this. Direct drive thrusters have higher reliability, lower noise, and higher efficiency, but the prices are higher than geared thrusters.
- Motor driver and electronics: Brushless motors need some electronics to be commutated and control their speed. In early versions the drivers were unreliable and this led to user dissatisfaction when compared with highly reliable hydraulic thrusters. More recently developments in power electronic technology have made the motor driver more efficient and reliable, cheap and small, to be fitted directly to the end of the motor. In modern designs the motor controllers are able not only to control the propeller RPM, but also to control the thrust force in applications that need close control on their positioning.
- Shafting and sealing: Keeping the propeller in the right place and making it reliable in case of impact with external items such as fishes or fishing nets is one of the main concerns in all kinds of thrusters. Many failures have been reported due to this problem. Some manufacturers try to solve it by using magnetic couplings and totally avoiding rotary sealing. This improves reliability of the sealing and shafting, but they lose in efficiency due to limited torque transfer capability of the magnetic coupling and they solve this problem by using a high-speed, low-torque propeller. In most models the efficiency is as low as 25% which is very low for underwater thrusters. Magnetic bearings require the propeller to be rotated on the outer shell surfaces using a layer of water as a lubricant, which may reduce the bearing life considerably in contaminated water. Some other manufacturers use tapered bearings and a multiple sealing system for redundancy. In this design if the main seal (usually a ceramic seal) fails, the others seals keep the motor safe and the thruster can continue operation.
- Propeller: The propeller is the component which converts rotation to thrust. Selection of the right propeller has a considerable influence on the performance a thruster. Each application's hydrodynamic load line needs a matched propeller for maximum efficiency, but there is lack of standard off-the-shelf propeller variation on the market and therefore it is impossible to order the thruster with the best efficiency propeller. Some companies will design and develop custom propellers, but their prices are really high. Other companies try to offer many propellers as options and let the user select the best one using performance charts of their thrusters.
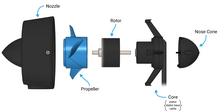
exploded view of a T200 Thruster - a fully flooded, underwater electric motor - Nozzle: Nozzles are used with heavy load, low-speed thrusters. Most ROVs have this type of hydrodynamic loads. In high-speed, light-load robots, such as AUVs, UUVs and submarines, usually the thrusters do not have a nozzle.
- Propeller guards: Propellers may be damaged by impact from fish or other objects, but may vibrate if the flow to the blades is not uniform. The propeller guard design can affect the flow to the propeller and consequently the performance. Some manufacturers leave the design of the propeller guard to the user, but a more efficient solution is to integrate the function with the nozzle support struts.
- Shell: Thruster shells usually must be resistant to seawater corrosion. There are two common version of shells; hard anodized aluminium and stainless steel grade 316. Steel is heavier, more expensive and more resilient. Aluminium is lighter and cheaper.
- Electrical connector: Electrical connectors are important component of underwater thrusters. There is a wide range of reliable components available from third party suppliers.
Performance
Many parameters affect underwater thrusters considerably. Under the sea, energy become more valuable as it is difficult to transfer it (ROVs) or to store it (AUV, UUV, Submarine), Then its very important to have the maximum efficiency. Motor driver, electric motor, shafting, sealing, propeller, nozzle and thruster outer geometry and surface all affect the efficiency.
- Matching the propeller load with motor torque: One of the more difficult design problem of underwater thrusters is to match the propeller load line with the motor power line. If it does not happen the overall efficiency of the thruster will fall well below maximum or only a small percentage of motor power will be used.
- Using the right propeller: Propeller diameter, pitch ratio and type are very important to have the maximum performance. Lots of investigation and engineering must be done before final order of thruster to have the right choice.
- Using low Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) motor and driver: PMSM motors have some efficiency problems with THD. Low-THD motors and drivers are available on the market (Kolmorgen)but their prices are considerably higher than lower efficiency motors. Only high-tech Thrusters on the market using this type of motor and driver (Lian Innovative).
- Streamlined Thruster Shell: Manufacturing of streamlined body and handle have a considerable effects on the efficiency, and manufacturing of the curves in this type of geometry is expensive.
See also
References
- "T200 Thruster". Blue Robotics. Retrieved 2024-01-11.
- seaMarn3 (2023-12-04). "Hydraulic and Electric Thrusters for ROVs". SEAMOR Marine Ltd. Retrieved 2024-01-11.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - "Marine Propulsion Systems".
- "Marine Propulsion Systems".
- "What is a Thruster?". Blue Robotics. Retrieved 2024-01-11.
- Staff. "Reliability first". Home Page. Copenhagen Subsea A/S. Retrieved 20 December 2016.
- Staff. "Underwater Connectors & System Solutions". Home page. Seacon. Retrieved 29 December 2016.
External links
- Advanced Electric Underwater Thruster, Lian innovative is the manufacturer of a range of underwater thrusters.
- Society for Underwater Technology, SUT is an organization of individuals with an interest in underwater technology
- Innerspace Thrusters, Innerspace designs and manufactures underwater thrusters and motors.