You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in Russian. (March 2017) Click for important translation instructions.
|
 N7001U, the prototype Boeing 727, similar to the aircraft involved in the accident N7001U, the prototype Boeing 727, similar to the aircraft involved in the accident | |
| Accident | |
|---|---|
| Date | August 16, 1965 |
| Summary | Controlled flight into terrain after misread three pointer altimeter. |
| Site | Lake Michigan, United States 42°15′2″N 87°27′56″W / 42.25056°N 87.46556°W / 42.25056; -87.46556 |
| Aircraft | |
| Aircraft type | Boeing 727-22 |
| Operator | United Airlines |
| IATA flight No. | UA389 |
| ICAO flight No. | UAL389 |
| Call sign | UNITED 389 |
| Registration | N7036U |
| Flight origin | LaGuardia Airport, New York City, New York |
| Destination | O'Hare International Airport, Chicago, Illinois |
| Occupants | 30 |
| Passengers | 24 |
| Crew | 6 |
| Fatalities | 30 |
| Survivors | 0 |
United Airlines Flight 389 was a scheduled flight from LaGuardia Airport, New York City, New York, to O'Hare International Airport, Chicago, Illinois. On August 16, 1965, at approximately 21:21 EST, the Boeing 727 crashed into Lake Michigan 20 miles (17 nmi; 32 km) east of Fort Sheridan, near Lake Forest, while descending from 35,000 feet (11,000 m) mean sea level (MSL). There was no indication of any unusual problem prior to impact. All 30 persons aboard, including six crew members and 24 passengers, were killed.
A definitive cause was not determined by National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) investigators. However, it was believed that the crash was most likely the result of the pilots misreading their three-pointer (3p) altimeters by 10,000 feet.
At the time of the accident, United Airlines had 39 other 727s in its fleet (of the 247 Boeing 727s ordered), all of which were 727-100 (727-22).
The accident was both the first hull-loss and first fatal accident of a Boeing 727.
Aircraft

The aircraft involved was a United Airlines Boeing 727-100 (727-22), registration N7036U. With serial number 18328, and line number 146, the aircraft had its maiden flight on May 18, 1965 with delivery to United Airlines on June 3, 1965 meaning it had been in passenger service for two and a half months before it crashed. The aircraft had completed 138 cycles (take offs and landings) before the accident, was equipped with three Pratt & Whitney JT8D-7 engines for propulsion and had no major mechanical problems reported in the time leading up to the accident.
Before the crash Boeing 727s had been operating commercially for approximately two years and N7036U was the first 727 to be written off. It was also one of two United Airlines 727s to crash that year, the other later that year being United Airlines Flight 227, a fatal crash landing attributed to poor decision made by the captain.
Crew
The Captain of the aircraft was Melville W. Towle. Born on September 11, 1922, he started working for United Air Lines on February 12, 1946. He was certified on the Douglas DC-3, DC-4, Vickers Viscount and Boeing 727 aircraft and his last checks for the 727 took place in July 1965. His total flight time was 17,142 hours as a pilot, of which 59 hours were as a captain on the 727, including 22 hours 39 minutes of training flights. At the time of the accident, he had been on duty for about 2 and a half hours, counting from the end of the last rest.
The co-pilot, Roger Marshall Whitezell, born on September 6, 1930, was newer to United than Captain Towle. Whitezell was qualified on the Douglas DC-6, DC-7 aircraft, as well as single- and multi-engine small aircraft. He qualified as a co-pilot 727 on November 1, 1964 and his total flight time was 8,466 hours, of which 363 hours were as a co-pilot on the 727. At the time of the accident, he had been on duty for about 2 and a half hours, counting from the end of the last rest.
The Second Officer (Flight Engineer), Maurice L. Femmer, was born on March 26, 1939, started work at United Air Lines on March 26, 1956. He was qualified as a flight engineer, as well as a pilot of single-engine aircraft. He was certified for the 727 on December 3, 1964. His total flight time experience was 649 hours, of which 303 hours was as a second officer on the 727. At the time of the disaster, he had been on duty for about 2 and a half hours, counting from the end of the last rest.
Accident sequence
The flight was cleared to an altitude of 6,000 feet MSL by air traffic control (ATC), but the plane never leveled off at 6,000 feet (1,800 m). Instead, it continued its descent, at an uninterrupted rate of approximately 2,000 feet per minute, until it hit the waters of Lake Michigan, which is 577 feet (176 m) MSL.
The control tower at O'Hare lost radio contact with the plane as it approached the western shore of Lake Michigan. A tower crewman at O'Hare said the pilot had just received landing instructions and had replied "Roger" when communication with the plane failed. Wallace Whigam, a lifeguard for the Chicago Park District, reported from the North Avenue Beach House that he had seen an orange flash on the horizon. Three seconds later, he reported, there was a "thundering roar." Other reports of the crash flooded police and Coast Guard from the North Side and North Shore.
The Coast Guard reported that skin divers had assembled at the North Shore Yacht Club in Highland Park, which was used as an informal search base. After a search of several hours there were no signs of survivors, though the area was kept ready in case any were found. Hours after the crash, members of the Civil Aeronautics Board (the predecessor to the NTSB) were on scene to begin investigating the accident.
The most likely explanation is the pilots thought they were descending through 16,000 feet (4,900 m) MSL when they were actually descending through only 6,000 feet MSL. Time and radar-image analyses indicated the plane was already down to an altitude of between 1,000 and 2,500 feet (300 and 760 m) MSL when it was again given the 6,000-foot (1,800 m) clearance limit. That final clearance was acknowledged by the captain, and was the last communication with ATC prior to impact with the water.
The captain of a 707 which was 30 miles (26 nmi; 48 km) behind the accident flight stated their descent was in instrument conditions until they broke out of the cloud layer at about 8,000 to 10,000 feet (2,400 to 3,000 m) and approximately 15 to 20 miles (13 to 17 nmi; 24 to 32 km) east of the shoreline. The night visibility was "fuzzy and unclear", and lights on the shoreline were the only ones visible.
Altimeter study
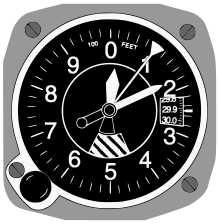
A study by the Naval Research Laboratory published in January 1965 found that, of four different designs of pilot altimeters, the three-pointer design was the one most prone to misreading by pilots. The study revealed that the three-pointer design was misread almost eight times more often than the best-designed of the four altimeters tested. It was also noted that it took the pilots considerably longer to decipher the correct reading of the three-pointer than with the other altimeters.
Investigation
The NTSB estimated the plane was traveling at a speed of approximately 200 knots (230 mph; 370 km/h) when it impacted the water. The investigation was hampered by the fact that the flight data recorder (FDR) was not recovered from the wreckage, which was in muddy water 250 feet (76 m) deep. The FDR casing was recovered, but the device internals including recording media was never found.
Probable cause
"The Board is unable to determine the reason for the aircraft not being leveled off at its assigned altitude of 6,000 feet (1,800 m)."
The first proven case of a crash caused by a pilot misreading the altimeter by 10,000 feet (3,000 m) was of a BEA Vickers Viscount outside Ayr, Scotland, on April 28, 1958. The second proven case was the 1958 Bristol Britannia 312 crash near Christchurch, Dorset, in the south of England, on December 24, 1958. While the former carried only a flight crew, all seven passengers and two of the crew members perished in the latter accident, and surviving crew members helped to pinpoint the cause.
See also
- Iberia Airlines Flight 062 - another incident where altimeter misreading is suspected, but not proven
- 1958 BOAC Bristol Britannia crash
- Air safety
- List of unrecovered flight recorders
References
- ^ "AIRCRAFT ACCIDENT REPORT UNITED AIR LINES, INC. B-727, N7036U In Lake Michigan August 16, 1965" (PDF). National Transportation Safety Board. December 19, 1967. AAR-67-AA. Retrieved June 2, 2019.
- "United Airlines - Fleet". www.planelogger.com. Retrieved 2019-06-02.
- Ranter, Harro. "ASN Aircraft accident Boeing 727-22 N7036U Lake Michigan, MI". aviation-safety.net. Retrieved 2019-09-15.
- "FAA Registry (N7036U)". Federal Aviation Administration.
- "Registration Details For N7036U (United Airlines) 727-22 - PlaneLogger". www.planelogger.com. Retrieved 2019-06-02.
- Ranter, Harro. "ASN Aircraft accident Boeing 727-22 N7030U Salt Lake City International Airport, UT (SLC)". aviation-safety.net. Retrieved 2019-09-15.
- NRL Report 6242, "Altimeter Display Evaluation, Final Report," January 26, 1965
- ICAO Accident Digest Circular 59-AN/54 (129-132)
- ICAO Accident Digest Circular 62-AN/57 (44-47)
External links
| Flight instruments | |
|---|---|
| Pitot-static | |
| Gyroscopic | |
| Navigational | |
| Related topics | |
| United Airlines Holdings | |
|---|---|
| Current airlines | |
| Current marketing brands | |
| Former airlines | |
| Former marketing brands | |
| Former holding companies | |
| Frequent flyer services | |
| People | |
| Legal and public relations | |
| United Airlines accidents and incidents |
|
| United Express accidents and incidents |
|
| Continental Airlines accidents and incidents |
|
| Continental Express / Connection accidents and incidents |
|
| Facilities |
|
- Aviation accidents and incidents in the United States in 1965
- 1965 in Illinois
- Airliner accidents and incidents in Illinois
- History of Chicago
- Airliner accidents and incidents involving controlled flight into terrain
- Accidents and incidents involving the Boeing 727
- United Airlines accidents and incidents
- August 1965 events in the United States