| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Uridine diphosphate" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Uridine 5′-(trihydrogen diphosphate) | |
| Systematic IUPAC name methyl trihydrogen diphosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.372 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| MeSH | Uridine+diphosphate |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C9H14N2O12P2 |
| Molar mass | 404.161 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
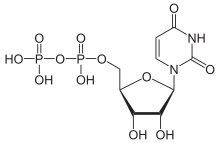
Uridine diphosphate, abbreviated UDP, is an organic compound. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside uridine. UDP consists of the pyrophosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase uracil.
UDP is an important factor in glycogenesis. Before glucose can be stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles, the enzyme UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase forms a UDP-glucose unit by combining glucose 1-phosphate with uridine triphosphate, cleaving a pyrophosphate ion in the process. Then, the enzyme glycogen synthase combines UDP-glucose units to form a glycogen chain. The UDP molecule is cleaved from the glucose ring during this process and can be reused by UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase.
See also
References
- Glycogen Biochemistry
- "Biochemistry Pathways: Polysaccharide Synthesis". Archived from the original on 2015-04-10. Retrieved 2014-09-20.
| Nucleic acid constituents | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleobase | |||||||
| Nucleoside |
| ||||||
| Nucleotide (Nucleoside monophosphate) |
| ||||||
| Nucleoside diphosphate | |||||||
| Nucleoside triphosphate | |||||||
This biochemistry article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |