| This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (September 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
 | |
| General | |
|---|---|
| Designers | Roger Needham, David Wheeler |
| First published | 1997 |
| Derived from | TEA |
| Successors | Corrected Block TEA |
| Cipher detail | |
| Key sizes | 128 bits |
| Block sizes | 64 bits |
| Structure | Feistel cipher |
| Rounds | variable; recommended 64 Feistel rounds (32 cycles) |
| Best public cryptanalysis | |
| A related-key rectangle attack on 36 rounds of XTEA (Lu, 2009) | |
In cryptography, XTEA (eXtended TEA) is a block cipher designed to correct weaknesses in TEA. The cipher's designers were David Wheeler and Roger Needham of the Cambridge Computer Laboratory, and the algorithm was presented in an unpublished technical report in 1997 (Needham and Wheeler, 1997). It is not subject to any patents.
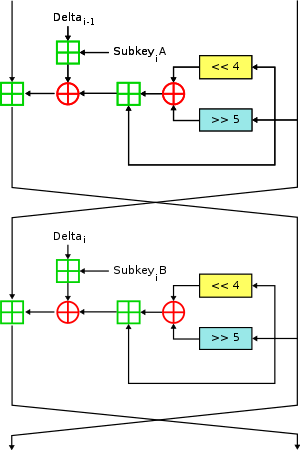
Like TEA, XTEA is a 64-bit block Feistel cipher with a 128-bit key and a suggested 64 rounds. Several differences from TEA are apparent, including a somewhat more complex key-schedule and a rearrangement of the shifts, XORs, and additions.
Implementations
This standard C source code, adapted from the reference code released into the public domain by David Wheeler and Roger Needham, encrypts and decrypts using XTEA:
#include <stdint.h>
/* take 64 bits of data in v and v and 128 bits of key - key */
void encipher(unsigned int num_rounds, uint32_t v, uint32_t const key) {
unsigned int i;
uint32_t v0=v, v1=v, sum=0, delta=0x9E3779B9;
for (i=0; i < num_rounds; i++) {
v0 += (((v1 << 4) ^ (v1 >> 5)) + v1) ^ (sum + key);
sum += delta;
v1 += (((v0 << 4) ^ (v0 >> 5)) + v0) ^ (sum + key);
}
v=v0; v=v1;
}
void decipher(unsigned int num_rounds, uint32_t v, uint32_t const key) {
unsigned int i;
uint32_t v0=v, v1=v, delta=0x9E3779B9, sum=delta*num_rounds;
for (i=0; i < num_rounds; i++) {
v1 -= (((v0 << 4) ^ (v0 >> 5)) + v0) ^ (sum + key);
sum -= delta;
v0 -= (((v1 << 4) ^ (v1 >> 5)) + v1) ^ (sum + key);
}
v=v0; v=v1;
}
The changes from the reference source code are minor:
- The reference source code used the
unsigned longtype rather than the 64-bit cleanuint32_t. - The reference source code did not use
consttypes. - The reference source code omitted redundant parentheses, using C precedence to write the round function as e.g.
v1 += (v0<<4 ^ v0>>5) + v0 ^ sum + k;
The recommended value for the "num_rounds" parameter is 32, not 64, as each iteration of the loop does two Feistel-cipher rounds. To additionally improve speed, the loop can be unrolled by pre-computing the values of sum+key.
Cryptanalysis
See also: cryptanalysisIn 2004, Ko et al. presented a related-key differential attack on 27 out of 64 rounds of XTEA, requiring 2 chosen plaintexts and a time complexity of 2.
In 2009, Lu presented a related-key rectangle attack on 36 rounds of XTEA, breaking more rounds than any previously published cryptanalytic results for XTEA. The paper presents two attacks, one without and with a weak key assumption, which corresponds to 2 bytes of data and 2 operations, and 2 bytes of data and 2 operations respectively.
Block TEA
Presented along with XTEA was a variable-width block cipher termed Block TEA, which uses the XTEA round function, but Block TEA applies it cyclically across an entire message for several iterations. Because it operates on the entire message, Block TEA has the property that it does not need a mode of operation. An attack on the full Block TEA was described by Saarinen, which also details a weakness in Block TEA's successor, XXTEA.
See also
- Ascon — A NIST-select lightweight authenticated cipher.
- RC4 — A stream cipher that, just like XTEA, is designed to be very simple to implement.
- TEA — Block TEA's precursor.
- XXTEA — Block TEA's successor.
References
- Roger M. Needham; David J. Wheeler (October 1997). Tea extensions (PDF). Computer Laboratory, University of Cambridge (Technical report).
- Ko, Youngdai; Hong, Seokhie; Lee, Wonil; Lee, Sangjin; Kang, Ju-Sung (2004). "Related Key Differential Attacks on 27 Rounds of XTEA and Full-Round GOST" (PDF). In Roy, B.; Meier, W. (eds.). Fast Software Encryption. FSE 2004. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Vol. 3017. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer. pp. 299–316. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-25937-4_19. ISBN 978-3-540-22171-5. Retrieved October 10, 2018.
- Hong, Seokhie; Hong, Deukjo; Ko, Youngdai; Chang, Donghoon; Lee, Wonil; Lee, Sangjin (2004). "Differential Cryptanalysis of TEA and XTEA". In Lim, JI.; Lee, DH. (eds.). Information Security and Cryptology. ICISC 2003. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Vol. 2971. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer. pp. 402–417. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-24691-6_30. ISBN 978-3-540-21376-5.
- Lu, Jiqiang (July 2, 2008). "Related-key rectangle attack on 36 rounds of the XTEA block cipher". International Journal of Information Security. 8 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1007/s10207-008-0059-9. ISSN 1615-5262. S2CID 26794956.
- Saarinen, Markku-Juhani (October 20, 1998). "Cryptanalysis of Block Tea". ResearchGate. Retrieved October 10, 2018.
Further reading
- Sekar, Gautham; Mouha, Nicky; Velichkov, Vesselin; Preneel, Bart (2011). "Meet-in-the-Middle Attacks on Reduced-Round XTEA". In Kiayias, A. (ed.). Topics in Cryptology – CT-RSA 2011. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Vol. 6558. pp. 250–267. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-19074-2_17. ISBN 978-3-642-19073-5. Retrieved October 10, 2018.
- Moon, Dukjae; Hwang, Kyungdeok; Lee, Wonil; Lee, Sangjin; Lim, Jongin (2002). "Impossible Differential Cryptanalysis of Reduced Round XTEA and TEA". Fast Software Encryption. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Vol. 2365. pp. 49–60. doi:10.1007/3-540-45661-9_4. ISBN 978-3-540-44009-3. Retrieved October 10, 2018.
- Andem, Vikram Reddy (2003). A cryptanalysis of the Tiny Encryption Algorithm (PDF) (Masters thesis). The University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa. Retrieved October 10, 2018.
External links
- DataFlow Diagram
- A web page advocating TEA and XTEA and providing a variety of implementations
- Test vectors for TEA and XTEA
- A Cryptanalysis of the Tiny Encryption Algorithm
- A C implementation of XTEA Archived February 24, 2023, at the Wayback Machine
- PHP implementation of XTEA
- Pascal/Delphi implementation of XTEA Archived October 22, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- Java implementation of XTEA (32 rounds)
- JavaScript implementation of XTEA (32 rounds)
- Python implementation of XTEA
- Linden Scripting Language (LSL) implementation of XTEA for Second Life scripting
- Verilog implementation of XTEA
- Smalltalk implementation of XTEA Archived March 4, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- PostgreSQL implementation of XTEA