| This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (February 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

The Zimmer tower (Dutch: Zimmertoren) is a tower in Lier, Belgium, also known as the Cornelius tower, that was originally a keep of Lier's 14th-century city fortifications. In 1930, astronomer and clockmaker Louis Zimmer (1888–1970) built the Jubilee (or Centenary) Clock, which is displayed on the front of the tower, and consists of 12 clocks encircling a central one with 57 dials. These clocks showed time on all continents, phases of the moons, times of tides and many other periodic phenomena.

In 1980 the tower became a state-protected monument.
Tower building

The original tower was built no later than 1425, though the precise date of construction is unknown. In 1812 the tower was sold by the municipal authorities, but after World War I, they repurchased it and slated it for demolition. In 1930 astronomer and clockmaker Louis Zimmer donated a complex clock which was installed in the old tower, which had to be substantially reconstructed for this. In honor of the astronomer the structure was renamed the Zimmer tower.
In 1960 a pavilion for the new clock was built next to the tower to present Zimmer's masterpiece the wonder-clock. (Dutch: Wonderklok). These wonder-clocks were prepared for the 1935 world exhibition in Brussels; later they were demonstrated in the US. Around one of these dials moves the slowest pointer in the world – its complete revolution will take 25800 years, which corresponds to the period of the precession of the Earth's axis. Subsequently, Zimmer attached to the clocks a mechanical planetarium. The wonder-clocks impressed Albert Einstein, who congratulated Zimmer on the creation of these unusual mechanisms.
On the small square at the foot of the tower an exhibition of the Solar System was arranged with the aid of metallic circles and the rings (circles designate the Sun and planets, rings the orbits of planets). These also show asteroids Felix (№ 1664) and Zimmer (№ 3064), which were named after Felix Timmermans and Louis Zimmer when discovered in 1929, and 1984. In 1980 the tower obtained the status of state protected monument. Now the Zimmer tower and pavilion with the wonder-clocks is a museum.
Description of the dials

The Centenary clock has one large dial in the centre, measuring 1.5 metres (4 ft 11 in) in diameter. This dial shows the exact time (UTC+1; during daylight saving time UTC+2 is used instead). The twelve dials around the centre dial show the following (starting from the dial in the 2 o'clock position and going clockwise): the equation of time, the zodiac, the solar cycle and the dominical letter, the week, the globe, the months, the calendar dates, the seasons, the tides, the age of the moon, the phases of the moon and the metonic cycle and the epact.
The equation of time
This dial shows the difference in minutes between the apparent solar time and the mean solar time. Positive values indicate that the apparent solar time is ahead (fast) of the mean solar time, with maxima around 3 November and 15 May. Negative values indicate that the apparent solar time is behind (slow) of the mean solar time, with a maximum lag around 12 February and 27 July.
The difference is zero four times a year; around 16 April 15 June, 1 September and 25 December.
The zodiac
Every year the Sun describes an imaginary circle around the Earth, called the zodiac. The zodiac is divided in twelve segments, each denoted by a sign associated with a constellation. This dial shows the zodiac signs. The signs of spring; Ram, Bull and Twins. The signs of the summer; Crab, Lion and Virgin. The signs of the fall; Balance, Scorpion and Bowman. The signs of winter; Capricorn, Water-bearer and Fishes. One revolution of this dial takes a year.
The solar cycle and the dominical letter
The solar cycle is a 28-year cycle. After the 28 years, dates reappear in the same order. On the inner circle, the hand indicates the current year of the solar cycle. On the outer circle, the hand shows the corresponding dominical letter. The dominical letter gives the day upon which the first Sunday of the year falls. The letter A means that the first Sunday of the year will fall on 1 January. The letter E for example, indicates that the first Sunday will be on 5 January. Leap years have two dominical letters because the dominical letter changes end February. The first letter covers January and February, the second covers March to December. For leap years, the outer circle will show two dominical letters. The cycle of the dominical letters for common years is twice every 11 years and once every 6 years, while for leap years is once every 28 years. 2008 (leap year starting on Tuesday) is the year 1 of the cycle, while 2007 (common year starting on Monday) is the year 28 of the cycle. From 1980 to 2007, respectively, there were:
- 1980 was a leap year starting on Tuesday, those dominical letters hence were FE, was the year 1 of the cycle.
- 1981 was a common year starting on Thursday, that dominical letter hence was D, was the year 2 of the cycle.
- 1982 was a common year starting on Friday, that dominical letter hence was C, was the year 3 of the cycle.
- 1983 was a common year starting on Saturday, that dominical letter hence was B, was the year 4 of the cycle.
- 1984 was a leap year starting on Sunday, those dominical letters hence were AG, was the year 5 of the cycle.
- 1985 was a common year starting on Tuesday, that dominical letter hence was F, was the year 6 of the cycle.
- 1986 was a common year starting on Wednesday, that dominical letter hence was E, was the year 7 of the cycle.
- 1987 was a common year starting on Thursday, that dominical letter hence was D, was the year 8 of the cycle.
- 1988 was a leap year starting on Friday, those dominical letters hence were CB, was the year 9 of the cycle.
- 1989 was a common year starting on Sunday, that dominical letter hence was A, was the year 10 of the cycle.
- 1990 was a common year starting on Monday, that dominical letter hence was G, was the year 11 of the cycle.
- 1991 was a common year starting on Tuesday, that dominical letter hence was F, was the year 12 of the cycle.
- 1992 was a leap year starting on Wednesday, those dominical letters hence were ED, was the year 13 of the cycle.
- 1993 was a common year starting on Friday, that dominical letter hence was C, was the year 14 of the cycle.
- 1994 was a common year starting on Saturday, that dominical letter hence was B, was the year 15 of the cycle.
- 1995 was a common year starting on Sunday, that dominical letter hence was A, was the year 16 of the cycle.
- 1996 was a leap year starting on Monday, those dominical letters hence were GF, was the year 17 of the cycle.
- 1997 was a common year starting on Wednesday, that dominical letter hence was E, was the year 18 of the cycle.
- 1998 was a common year starting on Thursday, that dominical letter hence was D, was the year 19 of the cycle.
- 1999 was a common year starting on Friday, that dominical letter hence was C, was the year 20 of the cycle.
- 2000 was a leap year starting on Saturday, those dominical letters hence were BA, was the year 21 of the cycle.
- 2001 was a common year starting on Monday, that dominical letter hence was G, was the year 22 of the cycle.
- 2002 was a common year starting on Tuesday, that dominical letter hence was F, was the year 23 of the cycle.
- 2003 was a common year starting on Wednesday, that dominical letter hence was E, was the year 24 of the cycle.
- 2004 was a leap year starting on Thursday, those dominical letters hence were DC, was the year 25 of the cycle.
- 2005 was a common year starting on Saturday, that dominical letter hence was B, was the year 26 of the cycle.
- 2006 was a common year starting on Sunday, that dominical letter hence was A, was the year 27 of the cycle.
- 2007 was a common year starting on Monday, that dominical letter hence was G, was the year 28 and final year of the cycle.
The week
This dial marks the seven days of the week, represented by ancient gods and their symbol.
| Day | God | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| Sunday | Apollo | Sun |
| Monday | Diana | Moon |
| Tuesday | Mars | lance |
| Wednesday | Mercurius | golden staff |
| Thursday | Jupiter | flash of lightning |
| Friday | Venus | mirror |
| Saturday | Saturn | sickle and scythe |
The globe
The rotation of the Earth causes day and night. It is day on the part of the globe that is currently visible. The places on Earth that pass under the fixed meridian (the golden belt running from the North Pole to the South Pole) have noon at the same time. The globe rotates once every 24 hours.
The months
This dial depicts the twelve months. The hand shows the current month. One revolution takes a year.
| Number | Month | Alternative name | Days |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | January | Ice-month | 31 |
| 2 | February | Duck-month | 28 (29 days in leap years) |
| 3 | March | Fish-month | 31 |
| 4 | April | Harlequin-month | 30 |
| 5 | May | Flower-month | 31 |
| 6 | June | Shearing-month | 30 |
| 7 | July | Hay-month | 31 |
| 8 | August | Harvest-month | 31 |
| 9 | September | Fruit-month | 30 |
| 10 | October | Wine-month | 31 |
| 11 | November | Slaughter-month | 30 |
| 12 | December | Resting-month | 31 |
The calendar dates
This dial shows the exact date. The numbering goes to 31, the maximum number of days in a month. In months that have fewer days (28, 29 or 30), the hand automatically moves forward to the first day of the following month. The months with 31 days are January, March, May, July, August, October and December, the months with 30 days are April, June, September and November. February is the only month with less than 30 days. February has only 28 days (29 days in leap years).
The seasons
The dial shows four drawings by Felix Timmermans, representing the four seasons. Spring is represented by a child with flowers (upper left). The duration of the season is indicated with Arabic numerals for the days and Roman numerals for the hours. Spring lasts for 92 days and 11 hours. The summer is represented by a mower and lasts 93 days and 8 hours. Autumn is symbolised by a cornucopia and lasts 89 days and 10 hours. Winter is represented by an old lady reading by the fireside. The duration of the winter is exactly 90 days.
On the dividing lines between the drawings is a small globe indicating the part of the globe that is being lit by the Sun at the start of the season. The differences in illumination during the year are caused by the Earth's axial tilt. The hand completes one revolution a year and shows the current season.
The tides
The dial indicates the tides at Lier, Belgium. The biggest ship and the flag without the streamer indicate high water. When the streamer is above the flag it is flood. It is ebb when the streamer is below the flag. At Lier, the water is rising for 3 hours and 53 minutes and falling in the other hours. This dial completes almost two revolutions a day.
The age of the moon
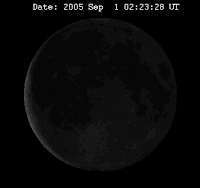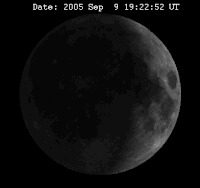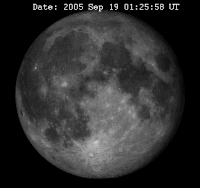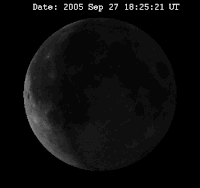
The time between two full moons is about 29 days, 12 hours, 44 minutes. This is the time it takes the Moon to make one orbit around the Earth. The dial shows how many days passed since last new moon, indicating the day in the cycle of the moon and showing on the inner circumference the phases of New Moon (Dutch: Nieuwe Maan, N.M.), First Quarter (Dutch: Eerste Kwartier, E.K.), Full Moon (Dutch: Volle Maan, V.M.) and Last Quarter (Dutch: Laatste Kwartier, L.K.).
The phases of the moon
This globe, colored half-gold and half-blue with golden stars, shows the phases of the moon. The golden part represents the visible part of the Moon.
The metonic cycle and the epact
The hand on this dial revolves once in 19 years. After this period, the different phases of the moon will fall again on the same dates in the year. The Greek astronomer Meton proved this in 432 BC. On the outer ring, the hand points to the golden number, or the number of the current year in the metonic cycle. The inner ring shows the epact, which is the age of the moon on the first of January of the current year.
References
Ceulemans, Luk (1980). Louis Zimmer. vzw Gilde "Heren van Lier"
Zimmertorencomité (1982). Stad Lier, zimmertoren en wonderklok
External links
- Official Website Zimmertower
- The Zimmer Tower
- Louis Zimmer and the Centenary Clock, at Famous Belgians
51°07′45″N 4°34′11″E / 51.12917°N 4.56972°E / 51.12917; 4.56972
| Astronomical clocks | ||
|---|---|---|
| Czech Republic |  | |
| France | ||
| Germany | ||
| Italy | ||
| Switzerland | ||
| United Kingdom | ||
| Other countries | ||
| Clockmakers and designers | ||