| Revision as of 19:54, 4 February 2006 edit70.23.161.113 (talk)No edit summary← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 17:58, 14 December 2024 edit undoTeratingaKevinBaughsNewFriend (talk | contribs)200 editsNo edit summaryTag: Visual edit | ||
| (137 intermediate revisions by 74 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{redirect|Hamburg-Harburg|the railway station|Hamburg-Harburg station}} | |||
| '''Hamburg-Harburg''' (]: DE HBU) is a borough of the city of ], ]. Hamburg-Harburg covers 161 km² (21% of the area of Hamburg), and has a population of 196,000. | |||
| {{Infobox German location | |||
| |name = Harburg | |||
| |image_photo = Hamburg-Harburg Rathaus.jpg | |||
| |image_caption = Harburg town hall (''Harburg Rathaus'') | |||
| |type = Borough | |||
| |City = Hamburg | |||
| |Town = | |||
| |image_flag = Flag of Harburg, Hamburg.png | |||
| |image_coa = Coat of arms of Harburg, Hamburg.svg | |||
| |coordinates = {{coord|53|27|N|9|58|E|format=dms|display=inline,title}} | |||
| |state = Hamburg | |||
| |divisions = 17 quarters | |||
| |area = 161 | |||
| |pop_ref = <ref>{{Population Germany|key=02|datref=QUELLE}}</ref> | |||
| |population = {{Population Germany|key=027}} | |||
| |population_as_of = {{Population Germany|key=02|datref=STAND}} | |||
| |postal_code = | |||
| |area_code = 040 | |||
| |licence = HH | |||
| |year = | |||
| |plantext = Boroughs of Hamburg | |||
| |image_plan = Boroughs of Hamburg.jpg | |||
| }} | |||
| '''Harburg''' is a ] of the city of ], Germany. It is also the name of ] in the borough, which used to be the capital of the ] in ]. The borough of Harburg lies on the southern banks of the river ] and covers parts of the ] as well as residential and rural areas. It had a population of 169,221 as of 2020. | |||
| ==History== | |||
| Hamburg-Harburg lies on the southern shores of the river ] and covers large parts of ] large residential areas and some research institutes. The large ] has a international reputation for its engineering faculties. | |||
| {{Main|Harburg (quarter)#History}} | |||
| Until 1937 Harburg belonged to the ]n ],<ref>{{Cite EB1911 |wstitle=Harburg |volume=12 |page=938}}</ref> where it served as the capital of the ] district. In 1927 it was merged with the nearby city of ] to form the city of ]. Following the ], Harburg was incorporated into the city of Hamburg along with several other independent cities such as ].<ref>Groß-Hamburg-Gesetz</ref> Despite its incorporation into Hamburg, Harburg continued to be the capital of the Hanoverian district of ]. In 1944, the district capital was moved to ]. | |||
| == History == | |||
| On 1 January 2007 the ''Ortsämter'' (Precincts) were dissolved and the organisation of all boroughs of Hamburg was restructured. Previously the quarters of ], ], ], Heimfeld, Langenbek, Marmstorf, ], Rönneburg, Sinstorf and Wilstorf had belonged to the ''Kerngebiet Harburg'' (central area), while the quarters of ], ], ], Hausbruch, ], ] and ] had belonged to the precinct ''Süderelbe'' (south Elbe).<ref>''Verwaltungsreform'' (administrational reform)</ref> | |||
| Until ] Harburg was an independent city, capital of the ]n district of ]. Following the '']'' (Greater Hamburg Act) Harburg, together with other cities such as ], was incorporated into the city of Hamburg. | |||
| On 1 March 2008 Harburg's quarter ] was transferred to the borough Hamburg-Mitte in keeping with civic law.<ref>Act of the areal organisation</ref> | |||
| {{germany-geo-stub}} | |||
| ==Geography== | |||
| ] | |||
| As of 2006, according to the statistical office of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein, the borough of Harburg has a total area of 160.6 km<sup>2</sup>, while the Harburg quarter has an area of 3.9 km<sup>2</sup>. <!-- note including Wilhelmsburg --> | |||
| ===Administrative divisions=== | |||
| ] | |||
| Along with the other boroughs of Hamburg, Harburg is divided into quarters: | |||
| {{div col}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{div col end}} | |||
| ==Demographics== | |||
| In 2006 there were 201,119 inhabitants in the borough. The population density was 1,253 people per km<sup>2</sup>. 18.9% were children under the age of 18, and 18.7% were 65 years of age or older. 20.1% were resident aliens. 12,785 people were registered as unemployed.<ref name="statsB 2006">Residents registration office, source: statistical office Nord of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein (2006)</ref> In 1999 there were 94,273 households, of which 23.9% had children under the age of 18 living in them and 40% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.11.<ref name="stats 1999">Source: statistical office Nord of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein (1999)</ref> | |||
| '''Population by year'''<ref name="statsB 2006"/> | |||
| {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" | |||
| | 1987 || 1988 || 1989 || 1990 || 1991 || 1992 || 1993 || 1994 || 1995 || 1996 || 1997 || 1998 || 1999 | |||
| |- | |||
| | 182,512 || 183,710 || 187,244 || 190,623 || 192,546 || 195,423 || 196,541 || 196,931 || 197,535 || 197,710 || 197,383 || 195,873 || 195,830 | |||
| |} | |||
| {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" | |||
| | 2000 || 2001 || 2002 || 2003 || 2004 || 2005 || 2006 | |||
| |- | |||
| | 196,263 || 198,400 || 198,924 || 199,715 || 200,092 || 200,322 || 201,119 | |||
| |} | |||
| In 2006 there were 24,900 criminal offences in the borough (124 crimes per 1000 people).<ref name="crime 2006">State Investigation Bureaux (]), source: statistical office Nord of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein (2006)</ref> | |||
| These numbers include the ] quarter. | |||
| ==Diet of the borough== | |||
| ] | |||
| {{See also|Boroughs and quarters of Hamburg#Boroughs}} | |||
| Simultaneously with elections to the state parliament (''Bürgerschaft''), the 51-member ''Bezirksversammlung'' is elected to represent the citizens. | |||
| ===Elections=== | |||
| {{Election table|title=District parliament election of Harburg in 2024}} | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="2" style="text-align:left;" | Parties | |||
| ! % | |||
| ! ± | |||
| ! Seats | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="background-color:{{party color|Social Democratic Party of Germany}}" | | |||
| | style="text-align:left;" | ] | |||
| | 28.4 | |||
| | {{increase}} 1.3 | |||
| | style="text-align:center;" | 15 | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="background-color:{{party color|CDU/CSU}}" | | |||
| | style="text-align:left;" | ] | |||
| | 23.0 | |||
| | {{increase}} 3.7 | |||
| | style="text-align:center;" | 12 | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="background-color:{{party color|Alliance 90/The Greens}}" | | |||
| | style="text-align:left;" | ] | |||
| | 15.9 | |||
| | {{decrease}} 9.9 | |||
| | style="text-align:center;" | 8 | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="background-color:{{party color|Alternative for Germany}}" | | |||
| | style="text-align:left;" | ] | |||
| | 14.2 | |||
| | {{increase}} 4.0 | |||
| | style="text-align:center;" | 7 | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="background-color:{{party color|The Left (Germany)}}" | | |||
| | style="text-align:left;" | ] | |||
| | 8.2 | |||
| | {{decrease}} 1.1 | |||
| | style="text-align:center;" | 4 | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="background-color:{{party color|Volt Germany}}" | | |||
| | style="text-align:left;" | ] | |||
| | 5.4 | |||
| | {{increase}} 5.4 | |||
| | style="text-align:center;" | 3 | |||
| |- | |||
| | style="background-color:{{party color|Free Democratic Party (Germany)}}" | | |||
| | style="text-align:left;" | ] | |||
| | 4.8 | |||
| | {{decrease}} 1.3 | |||
| | style="text-align:center;" | 2 | |||
| |- | |||
| ! colspan="2" style="text-align:left;" | Total | |||
| ! style="text-align:center;" colspan="2"| | |||
| ! style="text-align:center;" | 51 | |||
| |} | |||
| ==Education== | |||
| The borough has 32 elementary schools and 26 secondary schools (e.g. ]); 3 elementary schools and 4 secondary schools are situated in the Harburg quarter.<ref name="stats 2006"/> | |||
| The ] is internationally renowned for its engineering faculties. | |||
| ==Infrastructure== | |||
| ===Health systems=== | |||
| There were 316 physicians in private practice and 48 pharmacies in 2006.<ref name="stats 2006"/> | |||
| ===Transportation=== | |||
| ] | |||
| The borough and the quarter are served by the ] ] network which serves several stations. ] is a significant rail hub in the city at which long-distance (IC/ICE) trains also stop. | |||
| According to the Department of Motor Vehicles (Kraftfahrt-Bundesamt), there were 69,262 private cars registered in the borough as of 2006 (346 cars/1000 people).<ref name="stats 2006">Source: statistical office Nord of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein (2006)</ref> | |||
| ==Notes== | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| ===References=== | |||
| {{Refbegin}} | |||
| * Greater Hamburg Act {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180117155225/http://www.verfassungen.de/de/hh/hamburg37.htm |date=17 January 2018 }} Text of the law {{in lang|de}} | |||
| * Statistisches Amt für Hamburg und Schleswig-Holstein, official website {{in lang|de}} | |||
| *Act of the areal organisation, July 6, 2006 {{in lang|de}} | |||
| {{Refend}} | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| {{Commons category|Bezirk Harburg|Harburg}} | |||
| {{Portal|Hamburg}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| {{Hamburg}} | |||
| {{Boroughs of Hamburg}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 17:58, 14 December 2024
"Hamburg-Harburg" redirects here. For the railway station, see Hamburg-Harburg station. Borough of Hamburg in Germany| Harburg | |
|---|---|
| Borough of Hamburg | |
 Harburg town hall (Harburg Rathaus) Harburg town hall (Harburg Rathaus) | |
 Flag Flag Coat of arms Coat of arms | |
Boroughs of Hamburg
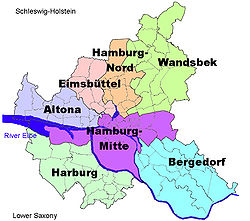 | |
  | |
| Coordinates: 53°27′N 9°58′E / 53.450°N 9.967°E / 53.450; 9.967 | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Hamburg |
| City | Hamburg |
| Subdivisions | 17 quarters |
| Area | |
| • Total | 161 km (62 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 176,868 |
| • Density | 1,100/km (2,800/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Dialling codes | 040 |
| Vehicle registration | HH |
Harburg is a borough of the city of Hamburg, Germany. It is also the name of Harburg quarter in the borough, which used to be the capital of the Harburg district in Lower Saxony. The borough of Harburg lies on the southern banks of the river Elbe and covers parts of the port of Hamburg as well as residential and rural areas. It had a population of 169,221 as of 2020.
History
Main article: Harburg (quarter) § HistoryUntil 1937 Harburg belonged to the Prussian Province of Hanover, where it served as the capital of the Harburg district. In 1927 it was merged with the nearby city of Wilhelmsburg to form the city of Harburg-Wilhelmsburg. Following the Greater Hamburg Act, Harburg was incorporated into the city of Hamburg along with several other independent cities such as Altona. Despite its incorporation into Hamburg, Harburg continued to be the capital of the Hanoverian district of Harburg. In 1944, the district capital was moved to Winsen upon Luhe.
On 1 January 2007 the Ortsämter (Precincts) were dissolved and the organisation of all boroughs of Hamburg was restructured. Previously the quarters of Eißendorf, Gut Moor, Harburg, Heimfeld, Langenbek, Marmstorf, Neuland, Rönneburg, Sinstorf and Wilstorf had belonged to the Kerngebiet Harburg (central area), while the quarters of Altenwerder, Cranz, Francop, Hausbruch, Moorburg, Neuenfelde and Neugraben-Fischbek had belonged to the precinct Süderelbe (south Elbe).
On 1 March 2008 Harburg's quarter Wilhelmsburg was transferred to the borough Hamburg-Mitte in keeping with civic law.
Geography
As of 2006, according to the statistical office of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein, the borough of Harburg has a total area of 160.6 km, while the Harburg quarter has an area of 3.9 km.
Administrative divisions
Along with the other boroughs of Hamburg, Harburg is divided into quarters:
- Altenwerder
- Cranz
- Eißendorf
- Francop
- Gut Moor
- Harburg
- Hausbruch
- Heimfeld
- Langenbek
- Marmstorf
- Moorburg
- Neuenfelde
- Neugraben-Fischbek
- Neuland
- Rönneburg
- Sinstorf
- Wilstorf
Demographics
In 2006 there were 201,119 inhabitants in the borough. The population density was 1,253 people per km. 18.9% were children under the age of 18, and 18.7% were 65 years of age or older. 20.1% were resident aliens. 12,785 people were registered as unemployed. In 1999 there were 94,273 households, of which 23.9% had children under the age of 18 living in them and 40% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.11.
Population by year
| 1987 | 1988 | 1989 | 1990 | 1991 | 1992 | 1993 | 1994 | 1995 | 1996 | 1997 | 1998 | 1999 |
| 182,512 | 183,710 | 187,244 | 190,623 | 192,546 | 195,423 | 196,541 | 196,931 | 197,535 | 197,710 | 197,383 | 195,873 | 195,830 |
| 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 |
| 196,263 | 198,400 | 198,924 | 199,715 | 200,092 | 200,322 | 201,119 |
In 2006 there were 24,900 criminal offences in the borough (124 crimes per 1000 people).
These numbers include the Harburg quarter.
Diet of the borough

Simultaneously with elections to the state parliament (Bürgerschaft), the 51-member Bezirksversammlung is elected to represent the citizens.
Elections
| Parties | % | ± | Seats | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Social Democratic Party | 28.4 | 15 | ||
| Christian Democratic Union | 23.0 | 12 | ||
| Alliance 90/The Greens | 15.9 | 8 | ||
| Alternative for Germany | 14.2 | 7 | ||
| The Left | 8.2 | 4 | ||
| Volt | 5.4 | 3 | ||
| Free Democratic Party | 4.8 | 2 | ||
| Total | 51 | |||
Education
The borough has 32 elementary schools and 26 secondary schools (e.g. Friedrich-Ebert-Gymnasium); 3 elementary schools and 4 secondary schools are situated in the Harburg quarter.
The Hamburg University of Technology is internationally renowned for its engineering faculties.
Infrastructure
Health systems
There were 316 physicians in private practice and 48 pharmacies in 2006.
Transportation

The borough and the quarter are served by the Hamburg S-Bahn rapid transit network which serves several stations. Hamburg-Harburg station is a significant rail hub in the city at which long-distance (IC/ICE) trains also stop.
According to the Department of Motor Vehicles (Kraftfahrt-Bundesamt), there were 69,262 private cars registered in the borough as of 2006 (346 cars/1000 people).
Notes
- "Bevölkerung in Hamburg am 31.12.2023 nach Stadtteilen". Statistisches Amt für Hamburg und Schleswig-Holstein. May 2024.
- Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Harburg" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 12 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 938.
- Groß-Hamburg-Gesetz
- Verwaltungsreform (administrational reform)
- Act of the areal organisation
- ^ Residents registration office, source: statistical office Nord of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein (2006)
- Source: statistical office Nord of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein (1999)
- State Investigation Bureaux (Landeskriminalamt), source: statistical office Nord of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein (2006)
- ^ Source: statistical office Nord of Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein (2006)
References
- Greater Hamburg Act Gesetz über Groß-Hamburg und andere Gebietsbereinigungen (Groß-Hamburg-Gesetz) 26 January 1937 Archived 17 January 2018 at the Wayback Machine Text of the law (in German)
- Statistical office Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein Statistisches Amt für Hamburg und Schleswig-Holstein, official website (in German)
- Act of the areal organisation, July 6, 2006 Gesetz über die räumliche Gliederung der Freien und Hansestadt Hamburg (RäumGiG) (in German)
External links
| Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg | |
| Government and symbols | |
| History and culture | |
| Economy and transport | |