| Revision as of 12:36, 31 December 2009 editTXiKiBoT (talk | contribs)567,654 editsm robot Adding: yo:Western Europe← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 14:48, 15 December 2024 edit undo2a01:e11:17:40b0:5cdb:7655:2a3d:42ec (talk)No edit summaryTags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Subregion of the European continent}} | |||
| {{Refimprove|date=September 2007}} | |||
| {{distinguish|Western European Union}} | |||
| ].<ref name="National Geographic">{{cite web|url=http://travel.nationalgeographic.com/places/regions/region_westeurope.html|title=Western Europe|date=2009|work=]|publisher=NationalGeographic.com|accessdate=2009-09-28}}</ref>]] | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=November 2022}} | |||
| '''Western Europe''' is the collection of countries in the westernmost region of ], though this definition is ] and carries ] and ] connotations. One definition describes Western Europe as a cultural entity—the region lying west of ]. Another definition was created during the ] and used to describe the non-Communist states of Europe; as a result, geographically central and eastern countries that steered clear of ] during the ] are usually included, while Western members of the former ] are excluded. | |||
| {{EngvarB|date=April 2024}} | |||
| '''Western Europe''' is the western region of ]. The region's extent varies depending on context. | |||
| The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the Western half of the ancient Mediterranean world, the ] of the ], and "]". Beginning with the ] and the ], roughly from the 15th century, the concept of ''Europe'' as "the ]" slowly became distinguished from and eventually replaced the dominant use of "Christendom" as the preferred ] within the area.<ref>{{Cite book|chapter=The Westernisation of Europe|page=30|year=1995|title=Inventing Europe Idea, Identity, Reality|first=Gerard|last=Delanty|isbn=978-0-333-62203-2|doi=10.1057/9780230379657|quote="Until the late fifteenth century the idea of Europe was principally a geographical expression and subordinated to Christendom which was the dominant identity system in the West. The idea of Europe as the West began to be consolidated in the foreign conquests of the age of 'discovery" (...) "Europe then begins to shed itself of its association with Christendom and slowly becomes an autonomous discourse."}}</ref> By the ] and the ], the concepts of "]" and "Western Europe" were more regularly used.<ref>{{Cite journal|url=https://philpapers.org/rec/SUSWIE|title=What Is Eastern Europe? A Philosophical Approach|first=Julia|last=Sushytska|editor-first=Costica|editor-last=Bradatan|journal=]|publisher=]|pages=39–51|year=2012}}</ref> The distinctiveness of Western Europe became most apparent during the ], when Europe was divided for 40 years by the ] into the ] and ], each characterised by distinct political and economical systems.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Key factors in the start of the Cold War upto 1955 - Reasons for the Cold War - Higher History Revision |url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/z8qnsbk/revision/1 |access-date=2024-02-23 |website=BBC Bitesize |language=en-GB}}</ref> | |||
| ==Historical divisions== | |||
| In addition, the term has ], ] and ] aspects. Since the end of ], the term has been used to describe the ] ] of western Europe, characterized by ] political systems, ] combining the ] with aspects of the ], ], and membership in ]. However, the political definition is becoming outdated as these characteristics are not special to Western Europe any more. | |||
| {{original research|date=September 2020|section}} | |||
| ==Classical antiquity and medieval origins== | ===Classical antiquity and medieval origins=== | ||
| ] in ]<ref>{{cite web|url=http://rbedrosian.com/Maps/ahgh66b.htm |title=Atlas of the Historical Geography of the Holy Land |publisher=Rbedrosian.com |access-date=23 February 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130610034842/http://rbedrosian.com/Maps/ahgh66b.htm |archive-date=10 June 2013 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://home.comcast.net/~DiazStudents/MiddleAgesChurchMap1.jpg |title=home.comcast.net |access-date=23 February 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130213233630/http://home.comcast.net/~DiazStudents/MiddleAgesChurchMap1.jpg |archive-date=13 February 2013 }}</ref>]] | |||
| As ] domain expanded a cultural and linguistic division appeared between the mainly ]-speaking eastern provinces which had formed the highly urbanized ]. In contrast, the western territories largely adopted the ]. This cultural and linguistic division was eventually reinforced by the later political east-west division of the ] | |||
| Prior to the ] conquest, a large part of Western Europe had adopted the newly developed ]. As the Roman domain expanded, a cultural and linguistic division appeared between the mainly ]-speaking eastern provinces, which had formed the highly urbanised ], and the western territories, which in contrast largely adopted the ] language. This cultural and linguistic division was eventually reinforced by the later political east–west division of the ]. The ] and the ] controlled the two divergent regions between the 3rd and the 5th centuries. | |||
| The division between these two was enhanced during ] and the ] by a number of events. The ] collapsed starting the ]. By contrast, the Eastern Roman Empire, mostly known as Greek or ], managed to survive and even to thrive for another 1000 years. The rise of the ] in the west, and in particular the ] that formally divided ] and ], enhanced the cultural and religious distinctiveness between Eastern and Western Europe. | |||
| The division between these two was enhanced during ] and the ] by a number of events. The ], starting the ]. By contrast, the Eastern Roman Empire, mostly known as the Greek or ], survived and even thrived for another 1000 years. The rise of the ] in the west, and in particular the ] between ] and ], enhanced the cultural and religious distinctiveness between Eastern and Western Europe. | |||
| The conquest of the Byzantine Empire, center of the ], by the ] ] in the 15th century, and the gradual fragmentation of the ] (which had replaced the ]) led to a change of the importance of ]/] vs. ] concept in Europe. | |||
| After the ], center of the Eastern Orthodox Church, by the ] ] in the 15th century, and the gradual fragmentation of the ] (which had replaced the ]), the division between Roman Catholic and ] became more important in Europe than that with Eastern Orthodoxy. | |||
| Western Europe's significant historical events include the ], the ] by ] and the ] of the ], the ], the ] and the ]. During the final stages of World War II the future of Europe was decided between the ] in the 1945 ], between the ] ], ] ], and the Premier of the ], ]. | |||
| In ], Western Europe was historically known as {{lang|zh|taixi}} in China and {{lang|ja|taisei}} in Japan, which literally translates as the "]". The term Far West became synonymous with Western Europe in China during the ]. The Italian Jesuit priest ] was one of the first writers in China to use the Far West as an Asian counterpart to the European concept of the ]. In Ricci's writings, Ricci referred to himself as "Matteo of the Far West".<ref>{{cite book|first=Matteo|last=Ricci|others=Translated by Timothy Billings|title=On Friendship: One Hundred Maxims for a Chinese Prince|year=1610|orig-year=2009|publisher=Columbia University Press|isbn=978-0-231-14924-2|pages=19, 71, 87}}</ref> The term was still in use in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. | |||
| Post-war Europe would be divided into two major spheres: ], influenced by the United States, and the ], dominated by the Soviet Union. With the onset of the Cold War, Europe was divided by the ]. | |||
| ===Religion=== | |||
| This term had been used during ] by German ] ] and later Count ] in the last days of the war; however, its use was hugely popularised by Winston Churchill, who used it in his famous "Sinews of Peace" address March 5, 1946 at ] in ]: | |||
| ] is the largest religion in Western Europe. According to a 2018 study by the ], 71.0% of Western Europeans identified as Christians.<ref>{{citation|title=Being Christian in Western Europe|work=Pew Research Center |year=2018|url=http://www.pewforum.org/2018/05/29/being-christian-in-western-europe/ |access-date=29 May 2018 |publisher=Pew Research Center}}</ref> | |||
| In 1054, the ] divided Christianity into ] and ]. This split Europe in two, with Western Europe primarily under the ], and ] primarily under the ]. Ever since the ] in the 16th century, ] has also been a major denomination in Europe, with ] and ] denominations also emerging in ]. | |||
| {{cquote|From ] in the ] to ] in the ] an ''iron curtain'' has descended across the Continent. Behind that line lie all the capitals of the ancient states of ] and ]. ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ]; all these famous cities and the populations around them lie in what I must call the Soviet sphere, and all are subject, in one form or another, not only to Soviet influence but to a very high and in some cases increasing measure of control from ].}} | |||
| ===Cold War === | |||
| Although some countries were officially ], they were classified according to the nature of their political and economical systems. This division has largely defined the popular perception and understanding of Western Europe and its borders with Eastern Europe till this day. | |||
| ]; neutral countries (shaded grey or light blue) considered informally Western-oriented but not formally aligned to the West]] | |||
| During the four ] of the ], the definition of East and West was simplified by the existence of the ]. A number of historians and social scientists view the Cold War definition of Western and Eastern Europe as outdated or relegating.<ref name="cotf.edu">"One very common, but now outdated, definition of Eastern Europe was the Soviet-dominated communist countries of Europe."http://www.cotf.edu/earthinfo/balkans/BKdef.html {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171210020555/http://www.cotf.edu/earthinfo/balkans/BKdef.html |date=10 December 2017 }}</ref><ref name="review">"Too much writing on the region has – consciously or unconsciously – clung to an outdated image of 'Eastern Europe', desperately trying to patch together political and social developments from Budapest to Bukhara or Tallinn to Tashkent without acknowledging that this Cold War frame of reference is coming apart at the seams. {{usurped|1=}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last1=Berglund |first1=Sten |last2=Ekman |first2=Joakim |last3=Aarebrot |first3=Frank H. |title=The handbook of political change in Eastern Europe |page=2 |year=2004 |url= https://books.google.com/books?id=HeRzzwzdfPkC&q=Eastern+Europe+term+outdated&pg=PA2 |access-date=5 October 2011 |quote=The term 'Eastern Europe' is ambiguous and in many ways outdated. |isbn=978-1-78195-432-4 }}</ref> | |||
| During the final stages of ], the future of Europe was decided between the ] in the 1945 ], between the ], ], the ], ], and the ], ]. | |||
| ===Eastern Europe=== | |||
| ] member states are marked in blue, ] – green, and ] – red.]] | |||
| Eastern Europe, in the view accepted after the ], was mainly composed of all the European countries occupied by the Soviet army. It included the ], widely known as East Germany, formed by the ] of Germany. All the countries in Eastern Europe had Communist regimes imposed upon them. Most of these countries were officially independent from the Soviet Union, but the practical extent of this independence was quite limited. In some matters many of them were little more than ]s of the Soviet Union. | |||
| Post-war Europe was divided into two major spheres: the ], influenced by the ], and the ], influenced by the ]. With the onset of the Cold War, Europe was divided by the ]. This term had been used during ] by German ] ] and, later, Count ] in the last days of the war; however, its use was hugely popularised by Winston Churchill, who used it in his famous "Sinews of Peace" address on 5 March 1946 at ] in ]: | |||
| Currently, the borders of ] are a topic of debate, especially because of the countries and people of ],<ref>O. Halecki, The Limits and Divisions of European History, Sheed & Ward, London and New York 1950, Chapter VII</ref> identifying themselves with ]. | |||
| {{blockquote|From ] in the ] to ] in the ] an ''iron curtain'' has descended across the Continent. Behind that line lie all the capitals of the ancient states of ]. ], ], ], ], ], ], ] and ]; all these famous cities and the populations around them lie in what I must call the Soviet sphere, and all are subject, in one form or another, not only to Soviet influence but to a very high and in some cases increasing measure of control from Moscow.}} | |||
| *Most of these countries were members of the military ] and its economic twin ]. First and foremost was the Soviet Union (which by itself included ], ], ], ], ], ]). Other countries dominated by the Soviet Union were the ], ], ], ], ], and ]. | |||
| Although some countries were officially ], they were classified according to the nature of their political and economic systems. This division largely defines the popular perception and understanding of Western Europe and its borders with ]. | |||
| *The ] (formed after World War II and before its later dismemberment) was not a member of the ]. It was a founding member of the ], an organization created in an attempt to avoid being assigned to any of the two blocs. It was demonstratively independent from the Soviet Union for most of the Cold War period, but because of its communist regime it was widely regarded part of the ''Eastern/communist bloc''. | |||
| The world changed dramatically with the fall of the ] in 1989. ] peacefully absorbed ], in the ]. ] and the ] were dissolved, and in 1991, the ] ceased to exist. Several countries which had been part of the Soviet Union regained full independence. | |||
| *] broke with the Soviet Union in the early 1960s as a result of the ], aligning itself instead with China. Despite this, it had a communist regime and thus was considered part of the ''Eastern/communist bloc''. | |||
| ===Western |
===Western European Union=== | ||
| ] (1995–2011)]] | |||
| At the end of ] almost all the countries of Western Europe received economic assistance from the United States through the ]. Later, most joined ] and/or the ] or its rival, the ]. | |||
| In 1948 the ] was signed between ], ], ], the ] and the ]. It was further revisited in 1954 at the ], when the ] was established. It was declared defunct in 2011 after the ], and the Treaty of Brussels was terminated. When the Western European Union was dissolved, it had 10 member countries. Additionally, it had 6 associate member countries, 7 associate partner countries and 5 observer countries. | |||
| ==Modern divisions== | |||
| Western Europe is composed of: | |||
| *The ] and ], two of the victors in the war. | |||
| *The ], ], and ], countries which had been occupied by ] and subsequently liberated by the ]. | |||
| *The ], widely known as West Germany, which had been formed by the ] controlled by the ''Western Allies'' (USA, UK, and France). The whole of Germany is now regarded as part of Western Europe. | |||
| *], a former ] which had surrendered and been occupied by the ''Western Allies''. | |||
| *] gained its ] from the United Kingdom in 1922. It remained neutral during the war. It never joined NATO but it joined the European Union in 1973. | |||
| *The ] were special cases. ] and ] had been conquered by Nazi Germany but were not liberated by the allies. During the war ], then still united with Denmark under the kingdom of Denmark, had been ] by the United Kingdom and the United States without any casualties of any nationality. Iceland proclaimed its ] during the war. | |||
| *] had remained neutral throughout the war. | |||
| *] had been invaded by the Soviet Union twice (in the ] and the ]) but the Soviets could not defeat them. After the Winter War on 12 March 1940 the Moscow Peace Treaty was signed and after the Continuation War an armistice between the Soviet Union and Finland was signed on 19 September. (see also: ], ], ]). | |||
| *] and ] were also special cases. Austria had been incorporated into Nazi Germany through the ] before the war, while Switzerland had remained neutral throughout the war. After the war both of them remained neutral, in the case of Austria through the ]. Austria eventually joined the European Union but not NATO. Switzerland declined membership of NATO and the European Union but did join ]. | |||
| ===UN geoscheme classification=== | |||
| *], ], and ], formerly under authoritarian regimes, became parliamentarian democracies in the mid-1970s. They subsequently joined the ]. Spain and Greece joined NATO at around that time, but Portugal had been a founding member of ] (1949) and ] (1960), during the ] regime (1932-1974). | |||
| ].<br>{{legend|#FF8080|]}} | |||
| *The ] of ], ], ], ] and ] are also considered part of ''Western Europe''. Many of these states have special agreements and treaties with the European Union. | |||
| {{legend|#4080FF|]}} | |||
| *The legal status of many of the ] in Europe (including ], the ] and the ]) vary from case to case, but they are also considered part of ''Western Europe''. | |||
| {{legend|#00FF00|]}} | |||
| *] is generally considered part of ''Western Europe''.<ref>United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization: </ref> | |||
| {{legend|#00FFFF|Western Europe}}]] | |||
| The United Nations geoscheme is a system devised by the ] (UNSD) which divides the countries of the world into ]al and ]al groups, based on the ]. The partition is for statistical convenience and does not imply any assumption regarding political or other affiliation of countries or territories.<ref name="m49">{{Cite web|url=https://unstats.un.org/unsd/methodology/m49/|title= Methodology|website=UNSD |access-date=17 June 2019}}</ref> | |||
| ==Later political developments== | |||
| {{Infobox Geopolitical organization | |||
| |name = Western European Union<br />Union de l'Europe occidentale | |||
| |linking_name = the Western European Union | |||
| |image_flag = Western European Union Flag.svg | |||
| |image_map = WEU Map.svg | |||
| |map_caption = | |||
| <span style="color:#e82020;">'''Members'''</span> • <span style="color:#40a800;">'''Associate members'''</span> • <span style="color:#5874a8;">'''Observers'''</span> • <span style="color:#a080a8;">'''Associate partners'''</span> | |||
| |org_type = | |||
| |membership_type = Membership | |||
| |membership = 10 member states <br />6 associate member states<br/>5 observer countries<br/>7 associate partner countries | |||
| |admin_center_type = | |||
| |admin_center = | |||
| |languages_type = | |||
| |languages = | |||
| |leader_title1 = | |||
| |leader_name1 = | |||
| |established = ] | |||
| |established_event1 = Signed | |||
| |established_date1 = 17 March 1948 | |||
| |established_event2 = | |||
| |established_date2 = | |||
| }} | |||
| The world changed dramatically with the fall of the Iron Curtain in 1989. The Federal Republic of Germany peacefully absorbed the Democratic Republic of Germany, leading to the ]. COMECON and the Warsaw Pact were dissolved, and in 1991, the Soviet Union ceased to exist. Several countries which had been part of the Soviet Union regained their full independence. | |||
| In the UN geoscheme, the following countries are classified as Western Europe:<ref name="m49" /> | |||
| Although the term ''Western Europe'' was largely defined of the Cold War, it still remains much in use. The term is commonly used in the media and in everyday use both in "western" and other regions of Europe. | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ===CIA classification=== | |||
| ''Western Europe'' has increasingly less to do with the European Union.{{Citation needed|date=September 2008}} The 1995, 2004, and 2007 ] saw many post-communist countries joining the EU, and a view that Europe is divided strictly into the West and the East is sometimes considered patronising or pejorative by many in the countries of ]{{Citation needed|date=September 2008}}. | |||
| ]'': | |||
| <small>{{legend|#007FFF|Northern Europe}} | |||
| ==Present time== | |||
| ===Definition used by the United Nations Statistics Division=== | |||
| ]s of Europe as delineated by the ] (UN definition of Western Europe marked light blue): | |||
| {{legend|#4080FF|]}} | |||
| {{legend|#00FFFF|Western Europe}} | {{legend|#00FFFF|Western Europe}} | ||
| {{legend|# |
{{legend|#F0DC82|]}} | ||
| {{legend|# |
{{legend|#FF0000|]}} | ||
| {{legend|#66FF00|]}} | |||
| The ] Statistics Division considers Western Europe to consist of the following nine countries,<ref></ref> except in the case of ], in which the term also includes northern and southern Europe: | |||
| {{legend|#D2691E|]}} | |||
| *{{flagcountry|Austria}} | |||
| {{legend|#F88379|]}}</small>]] | |||
| *{{flagcountry|Belgium}} | |||
| *{{flagcountry|France}} | |||
| *{{flagcountry|Germany}} | |||
| *{{flagcountry|Liechtenstein}} | |||
| *{{flagcountry|Luxembourg}} | |||
| *{{flagcountry|Monaco}} | |||
| *{{flagcountry|Netherlands}} | |||
| *{{flagcountry|Switzerland}} | |||
| The ] classifies seven countries as belonging to "Western Europe":<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2144.html |title=Field listing: Location |publisher=CIA World Factbook |access-date=30 July 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110524151212/https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2144.html |archive-date=24 May 2011 |url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| However, it should be noticed that this statistical division was designed during the ] period. According to the UN Statistics Division, ''the assignment of countries or areas to specific groupings is for statistical convenience and does not imply any assumption regarding political or other affiliation of countries or territories by the United Nations''.<ref>http://unstats.un.org/unsd/methods/m49/m49.htm</ref> | |||
| *] | |||
| ==Population of Western Europe== | |||
| *] | |||
| {{Update|type=section}} | |||
| *] | |||
| Countries of Western Europe as defined by the ].<ref name="National Geographic" /> | |||
| *] | |||
| {| border="1" cellpadding="4" cellspacing="0" class="references-small sortable" style="border:1px solid #aaa; border-collapse:collapse" | |||
| *] | |||
| |- bgcolor="#ECECEC" | |||
| *] | |||
| ! Name of country, with ] | |||
| *] | |||
| ! Population <br/>(2009 est.) | |||
| ! Population <br/> (2000 est.) | |||
| The CIA also classifies three countries as belonging to "Southwestern Europe": | |||
| ! -/+ of Population | |||
| ! Percent change | |||
| *] | |||
| ! ] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| === EuroVoc classification=== | |||
| ]: | |||
| <small>{{legend|#0076D3|]}} | |||
| {{legend|#67E863|Western Europe}} | |||
| {{legend|#FCFC00|]}} | |||
| {{legend|#E62121|]}}</small>]] | |||
| ] is a multilingual thesaurus maintained by the ]. In this thesaurus, the countries of Europe are grouped into sub-regions.<ref name="EuroVoc">{{cite web|title=EuroVoc: 7206 Europe|url=https://op.europa.eu/en/web/eu-vocabularies/concept-scheme/-/resource?uri=http://eurovoc.europa.eu/100277|accessdate=9 February 2021}}</ref> The following countries are included in the sub-group Western Europe:<ref name="WE">{{cite web|title=EuroVoc: Western Europe|url=https://op.europa.eu/en/web/eu-vocabularies/concept/-/resource?uri=http://eurovoc.europa.eu/913&lang=en|accessdate=9 February 2021}}</ref> | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ===UN regional groups: Western European and Others Group=== | |||
| ] | |||
| The ] is one of several unofficial ] in the ] that act as ]s and negotiation forums. Regional voting blocs were formed in 1961 to encourage voting to various UN bodies from different regional groups. The European members of the group are:<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110109143548/http://data.unaids.org/pub/Manual/2009/jc1682_governancehandbook_lr_en.pdf |date=9 January 2011 }} (p. 29).</ref> | |||
| {{colbegin|colwidth=12em}} | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| {{colend}} | |||
| In addition, ], ], ] and ] are members of the group, with the ] as observer. | |||
| ==Population== | |||
| Using the CIA classification strictly would give the following calculation of Western Europe's population. All figures based on the projections for 2018 by the Population Division of the ].<ref name="unpop">{{cite web | url=https://esa.un.org/unpd/wpp/DataQuery/ | title=World Population Prospects 2018 | access-date=14 October 2018 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160919061238/https://esa.un.org/unpd/wpp/DataQuery/ | archive-date=19 September 2016 | url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| {| class="wikitable sortable" style="border:1px solid #aaa;" | |||
| ! Rank | |||
| ! Country or territory | |||
| ! Population<br>(most recent estimates) | |||
| ! Languages | |||
| ! Capital | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! 1 | |||
| |{{flagicon|Austria}} ] | |||
| | align= |
| align=left|United Kingdom | ||
| | align= |
| align=right|{{nts|66040229}} | ||
| | align= |
| align=center|] | ||
| | align= |
| align=center|] | ||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! 2 | |||
| |{{flagicon|Belgium}} ] | |||
| | align= |
| align=left|France (metropolitan) | ||
| | align= |
| align=right|{{nts|65058000}} | ||
| | align= |
| align=center|] | ||
| | align= |
| align=center|] | ||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! 3 | |||
| | {{flagicon|Denmark}} ] | |||
| | align= |
| align=left|Netherlands | ||
| | align= |
| align=right|{{nts|17889600}} | ||
| | align=center|], ] | |||
| | align="right" | 181,431 | |||
| | align= |
| align=center|] <sup>'''1'''</sup> | ||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! 4 | |||
| | {{flagicon|Finland}} ] | |||
| | align= |
| align=left|Belgium | ||
| | align= |
| align=right|{{nts|11420163}} | ||
| | align=center|], ] and ] | |||
| | align="right" | 77,263 | |||
| | align= |
| align=center|] | ||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! 5 | |||
| | {{flagicon|France}} ] | |||
| | align= |
| align=left|Ireland | ||
| | align= |
| align=right|{{nts|5123536}} | ||
| | align=center|], ] | |||
| | align="right" | 3,813,023 | |||
| | align= |
| align=center|] | ||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! 6 | |||
| | {{flagicon|Germany}} ] | |||
| | align= |
| align=left|Luxembourg | ||
| | align= |
| align=right|{{nts|602005}} | ||
| | align=center|], ] and ] | |||
| | align="right" | -161,119 | |||
| | align= |
| align=center|] | ||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! 7 | |||
| | {{flagicon|Iceland}} ] | |||
| | align= |
| align=left|Monaco | ||
| | align= |
| align=right|{{nts|38300}} | ||
| | align= |
| align=center|] | ||
| | align= |
| align=center|] (city-state) | ||
| |- class="sortbottom" | |||
| | ] | |||
| ! Total | |||
| ! | |||
| ! {{nts|165265329}} | |||
| ! | |||
| ! | |||
| |} | |||
| Using the CIA classification a little more liberally and including "South-Western Europe", would give the following calculation of Western Europe's population.<ref name="unpop"/> | |||
| {| class="wikitable sortable" style="border:1px solid #aaa;" | |||
| |- style="background:#ececec;" | |||
| ! Rank | |||
| ! Country or territory | |||
| ! Population<br>(most recent estimates) | |||
| ! Languages | |||
| ! Capital | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! 1 | |||
| | {{flagicon|Ireland}} ] | |||
| | align= |
| align=left|United Kingdom | ||
| | align= |
| align=right|{{nts|66040229}} | ||
| | align= |
| align=center|] | ||
| | align= |
| align=center|] | ||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! 2 | |||
| | {{flagicon|Italy}} ] | |||
| | align= |
| align=left|France (metropolitan) | ||
| | align= |
| align=right|{{nts|65058000}} | ||
| | align= |
| align=center|] | ||
| | align= |
| align=center|] | ||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! 3 | |||
| | {{flagicon|Luxembourg}} ] | |||
| | align= |
| align=left|Spain | ||
| | align= |
| align=right|{{nts|46700000}} | ||
| | align= |
| align=center|] | ||
| | align= |
| align=center|] | ||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! 4 | |||
| | {{flagicon|Netherlands}} ] | |||
| | align= |
| align=left|Netherlands | ||
| | align= |
| align=right|{{nts|17889600}} | ||
| | align=center|], ] | |||
| | align="right" | 622,637 | |||
| | align= |
| align=center|]<sup>1</sup> | ||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |||
| |{{flagicon|Norway}} ] | |||
| | align="right" | 4,799,252 | |||
| | align="right" | 4,478,497 | |||
| | align="right" | 320,755 | |||
| | align="right" | 6.79% | |||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! 5 | |||
| | {{flagicon|Portugal}} ] | |||
| | align= |
| align=left|Belgium | ||
| | align= |
| align=right|{{nts|11420163}} | ||
| | align=center|], ] and German | |||
| | align="right" | 432,236 | |||
| | align= |
| align=center|] | ||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! 6 | |||
| | {{flagicon|Spain}} ] | |||
| | align= |
| align=left|Portugal | ||
| | align= |
| align=right|{{nts|10291027}} | ||
| | align=center|] | |||
| | align="right" | 6,612,242 | |||
| | align= |
| align=center|] | ||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! 7 | |||
| | {{flagicon|Sweden}} ] | |||
| | align= |
| align=left|Ireland | ||
| | align= |
| align=right|{{nts|5123536}} | ||
| | align=center|], ] | |||
| | align="right" | 394,921 | |||
| | align= |
| align=center|] | ||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! 8 | |||
| | {{flagicon|Switzerland}} ] | |||
| | align= |
| align=left|Luxembourg | ||
| | align= |
| align=right|{{nts|602005}} | ||
| | align=center|], ] and ] | |||
| | align="right" | 535,758 | |||
| | align= |
| align=center|] | ||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! 9 | |||
| | {{flagicon|United Kingdom}} ] | |||
| | align= |
| align=left|Andorra | ||
| | align= |
| align=right|{{nts|78264}} | ||
| | align= |
| align=center|] | ||
| | align= |
| align=center|] | ||
| | ] | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| ! 10 | |||
| |- style=" font-weight:bold; " | |||
| | align=left|Monaco | |||
| | Total | |||
| | align= |
| align=right|{{nts|38300}} | ||
| | align= |
| align=center|] | ||
| | align= |
| align=center|] (city-state) | ||
| |- class="sortbottom" | |||
| | align="right" | 4.82% | |||
| ! Total | |||
| | align="right" | | |||
| ! | |||
| ! {{nts|222293922}} | |||
| ! | |||
| ! | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| <sup>1</sup> <small>The Hague is the seat of government</small><ref>{{Cite web|title=Europe :: Netherlands — The World Factbook |url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/netherlands/|access-date=6 October 2020|website=Central Intelligence Agency }}</ref> | |||
| ==Climate== | |||
| ] map is presented by the Climatic Research Unit of the University of East Anglia and the Global Precipitation Climatology Center of the Deutscher Wetterdienst.]] | |||
| The climate of Western Europe varies from ] in the coasts of ], ] and ] to ] in the ] and the ]. The ] of the south is dry and warm. The western and northwestern parts have a mild, generally humid climate, influenced by the ]. Western Europe is a ] hotspot, exhibiting upward trends that are three-to-four times faster compared to the rest of the northern midlatitudes.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Rousi |first1=Efi |last2=Kornhuber |first2=Kai |last3=Beobide-Arsuaga |first3=Goratz |last4=Luo |first4=Fei |last5=Coumou |first5=Dim |date=4 July 2022 |title=Accelerated western European heatwave trends linked to more-persistent double jets over Eurasia |journal=Nature Communications |language=en |volume=13 |issue=1 |pages=3851 |doi=10.1038/s41467-022-31432-y |pmid=35788585 |pmc=9253148 |bibcode=2022NatCo..13.3851R |s2cid=250282752 |issn=2041-1723|doi-access=free }}</ref> | |||
| ==Languages== | |||
| {{See also|Languages of Europe|Indo-European languages|List of Indo-European languages}} | |||
| Western European languages mostly fall within two ] families: the ], descended from the ] of the ]; and the ], whose ancestor language (]) came from southern ].<ref name="Encyclopædia Britannica">{{cite encyclopedia|url=http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9106055|title=Europe|year=2007|encyclopedia=]|access-date=10 June 2008}}</ref> | |||
| Romance languages are spoken primarily in the southern and central part of Western Europe, Germanic languages in the northern part (the ] and the ]), as well as a large part of ] and ].<ref name="Encyclopædia Britannica" /> | |||
| Other Western European languages include the ] group (that is, ], ], ], ], ] and ]<ref name="Encyclopædia Britannica" />) and ], the only currently living European ].<ref>{{Cite web|title=Basque language|url=https://www.britannica.com/topic/Basque-language|access-date=16 June 2020|website=Encyclopedia Britannica|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| Multilingualism and the protection of regional and minority languages are recognised political goals in Western Europe today. The ] ] and the Council of Europe's ] set up a legal framework for language rights in Europe.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.coe.int/en/web/european-charter-regional-or-minority-languages/a-word-from-the-chair |title= A Word from the Chair of the Committee of Experts|last=Oszmiańska-Pagett |first=Aleksandra |date=January 2022 |website= |publisher=Council of Europe |access-date=10 November 2023 |quote=}}</ref> | |||
| ==Economy== | |||
| Western Europe is one of the richest regions of the world. ] has the highest ] in Europe and the largest financial surplus of any country, ] has the world's highest GDP per capita, and Germany has the highest ] of any European state.<ref>{{Cite web|title=GDP (current US$) - European Union {{!}} Data|url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.CD?locations=EU|access-date=12 March 2021|website=data.worldbank.org}}</ref> | |||
| ] and Luxembourg have the highest ] in the world, in nominal and ], respectively. ] ranks highest in the world on the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.socialprogress.org/index/global/results|title=2020 Social Progress Index|publisher=The Social Progress Imperative|access-date=29 December 2020}}</ref> | |||
| == Global impact == | |||
| {{See also|Age of Discovery|History of colonialism|New Imperialism|Industrial Revolution}} | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| {{portal|Geography<!-- |Eurasia -->|Europe<!-- |Western Europe -->}} | |||
| *] | |||
| <!-- {{Misplaced Pages books}} --> | |||
| *] | |||
| <!-- {{main|Outline of Western Europe|Index of Western Europe-related articles}} --> | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | <!-- *] --> | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *{{section link|EuroVoc|Western Europe}} | |||
| *] | |||
| == References == | |||
| ==References and notes== | |||
| === Citations === | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| {{Reflist|30em}} | |||
| *''The Making of Europe'', ISBN 0-14-015409-4, by Robert Bartlett | |||
| *''Crescent and Cross'', ISBN 1-84212-753-5, by ] | |||
| === Sources === | |||
| *''The Normans'', ISBN 0-7524-2881-0, by Trevor Rowley | |||
| {{refbegin}} | |||
| *''1066 The Year of the Three Battles'', ISBN 0-7126-6672-9, by Frank McLynn | |||
| * ''The Making of Europe'', {{ISBN|978-0-14-015409-2}}, by ] | |||
| * ''Crescent and Cross'', {{ISBN|978-1-84212-753-7}}, by ] | |||
| * ''The Normans'', {{ISBN|978-0-7524-2881-9}}, by Trevor Rowley | |||
| * ''1066: The Year of the Three Battles'', {{ISBN|978-0-7126-6672-5}}, by ] | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{Commons and category}} | |||
| * | * | ||
| * | * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060601210634/http://www.ericdigests.org/pre-9217/europe.htm |date=1 June 2006 }} | ||
| * | |||
| {{Regions of the world}} | {{Regions of the world}} | ||
| {{Europe topics (small)}} | {{Europe topics (small)}} | ||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:48, 15 December 2024
Subregion of the European continent Not to be confused with Western European Union.Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's extent varies depending on context. The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the Western half of the ancient Mediterranean world, the Latin West of the Roman Empire, and "Western Christendom". Beginning with the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery, roughly from the 15th century, the concept of Europe as "the West" slowly became distinguished from and eventually replaced the dominant use of "Christendom" as the preferred endonym within the area. By the Age of Enlightenment and the Industrial Revolution, the concepts of "Eastern Europe" and "Western Europe" were more regularly used. The distinctiveness of Western Europe became most apparent during the Cold War, when Europe was divided for 40 years by the Iron Curtain into the Western Bloc and Eastern Bloc, each characterised by distinct political and economical systems.
Historical divisions
| This section possibly contains original research. Please improve it by verifying the claims made and adding inline citations. Statements consisting only of original research should be removed. (September 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Classical antiquity and medieval origins

Prior to the Roman conquest, a large part of Western Europe had adopted the newly developed La Tène culture. As the Roman domain expanded, a cultural and linguistic division appeared between the mainly Greek-speaking eastern provinces, which had formed the highly urbanised Hellenistic civilisation, and the western territories, which in contrast largely adopted the Latin language. This cultural and linguistic division was eventually reinforced by the later political east–west division of the Roman Empire. The Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire controlled the two divergent regions between the 3rd and the 5th centuries.
The division between these two was enhanced during late antiquity and the Middle Ages by a number of events. The Western Roman Empire collapsed, starting the Early Middle Ages. By contrast, the Eastern Roman Empire, mostly known as the Greek or Byzantine Empire, survived and even thrived for another 1000 years. The rise of the Carolingian Empire in the west, and in particular the Great Schism between Eastern Orthodoxy and Roman Catholicism, enhanced the cultural and religious distinctiveness between Eastern and Western Europe.
After the conquest of the Byzantine Empire, center of the Eastern Orthodox Church, by the Muslim Ottoman Empire in the 15th century, and the gradual fragmentation of the Holy Roman Empire (which had replaced the Carolingian Empire), the division between Roman Catholic and Protestant became more important in Europe than that with Eastern Orthodoxy.
In East Asia, Western Europe was historically known as taixi in China and taisei in Japan, which literally translates as the "Far West". The term Far West became synonymous with Western Europe in China during the Ming dynasty. The Italian Jesuit priest Matteo Ricci was one of the first writers in China to use the Far West as an Asian counterpart to the European concept of the Far East. In Ricci's writings, Ricci referred to himself as "Matteo of the Far West". The term was still in use in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Religion
Christianity is the largest religion in Western Europe. According to a 2018 study by the Pew Research Center, 71.0% of Western Europeans identified as Christians.
In 1054, the East–West Schism divided Christianity into Western Christianity and Eastern Christianity. This split Europe in two, with Western Europe primarily under the Catholic Church, and Eastern Europe primarily under the Eastern Orthodox Church. Ever since the Reformation in the 16th century, Protestantism has also been a major denomination in Europe, with Eastern Protestant and Eastern Catholic denominations also emerging in Central and Eastern Europe.
Cold War

During the four decades of the Cold War, the definition of East and West was simplified by the existence of the Eastern Bloc. A number of historians and social scientists view the Cold War definition of Western and Eastern Europe as outdated or relegating.
During the final stages of World War II, the future of Europe was decided between the Allies in the 1945 Yalta Conference, between the British Prime Minister, Winston Churchill, the U.S. President, Franklin D. Roosevelt, and the Premier of the Soviet Union, Joseph Stalin.
Post-war Europe was divided into two major spheres: the Western Bloc, influenced by the United States, and the Eastern Bloc, influenced by the Soviet Union. With the onset of the Cold War, Europe was divided by the Iron Curtain. This term had been used during World War II by German Propaganda Minister Joseph Goebbels and, later, Count Lutz Schwerin von Krosigk in the last days of the war; however, its use was hugely popularised by Winston Churchill, who used it in his famous "Sinews of Peace" address on 5 March 1946 at Westminster College in Fulton, Missouri:
From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic an iron curtain has descended across the Continent. Behind that line lie all the capitals of the ancient states of Central and Eastern Europe. Warsaw, Berlin, Prague, Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade, Bucharest and Sofia; all these famous cities and the populations around them lie in what I must call the Soviet sphere, and all are subject, in one form or another, not only to Soviet influence but to a very high and in some cases increasing measure of control from Moscow.
Although some countries were officially neutral, they were classified according to the nature of their political and economic systems. This division largely defines the popular perception and understanding of Western Europe and its borders with Eastern Europe.
The world changed dramatically with the fall of the Iron Curtain in 1989. West Germany peacefully absorbed East Germany, in the German reunification. Comecon and the Warsaw Pact were dissolved, and in 1991, the Soviet Union ceased to exist. Several countries which had been part of the Soviet Union regained full independence.
Western European Union

In 1948 the Treaty of Brussels was signed between Belgium, France, Luxembourg, the Netherlands and the United Kingdom. It was further revisited in 1954 at the Paris Conference, when the Western European Union was established. It was declared defunct in 2011 after the Treaty of Lisbon, and the Treaty of Brussels was terminated. When the Western European Union was dissolved, it had 10 member countries. Additionally, it had 6 associate member countries, 7 associate partner countries and 5 observer countries.
Modern divisions
UN geoscheme classification

Eastern Europe Northern Europe Southern Europe Western Europe
The United Nations geoscheme is a system devised by the United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD) which divides the countries of the world into regional and subregional groups, based on the M49 coding classification. The partition is for statistical convenience and does not imply any assumption regarding political or other affiliation of countries or territories.
In the UN geoscheme, the following countries are classified as Western Europe:
CIA classification
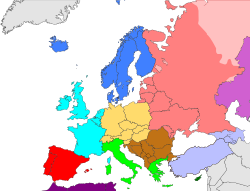
The CIA classifies seven countries as belonging to "Western Europe":
The CIA also classifies three countries as belonging to "Southwestern Europe":
EuroVoc classification
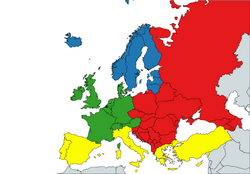
EuroVoc is a multilingual thesaurus maintained by the Publications Office of the European Union. In this thesaurus, the countries of Europe are grouped into sub-regions. The following countries are included in the sub-group Western Europe:
- Andorra
- Austria
- Belgium
- France
- Germany
- Ireland
- Liechtenstein
- Luxembourg
- Monaco
- Netherlands
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom
UN regional groups: Western European and Others Group

The Western European and Others Group is one of several unofficial Regional Groups in the United Nations that act as voting blocs and negotiation forums. Regional voting blocs were formed in 1961 to encourage voting to various UN bodies from different regional groups. The European members of the group are:
- Andorra
- Austria
- Belgium
- Denmark
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Liechtenstein
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Monaco
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Portugal
- San Marino
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- United Kingdom
In addition, Australia, Canada, Israel and New Zealand are members of the group, with the United States as observer.
Population
Using the CIA classification strictly would give the following calculation of Western Europe's population. All figures based on the projections for 2018 by the Population Division of the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs.
| Rank | Country or territory | Population (most recent estimates) |
Languages | Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | United Kingdom | 66,040,229 | English | London |
| 2 | France (metropolitan) | 65,058,000 | French | Paris |
| 3 | Netherlands | 17,889,600 | Dutch, Frisian | Amsterdam |
| 4 | Belgium | 11,420,163 | Dutch, French and German | Brussels |
| 5 | Ireland | 5,123,536 | English, Irish | Dublin |
| 6 | Luxembourg | 602,005 | French, Luxembourgish and German | Luxembourg City |
| 7 | Monaco | 38,300 | French | Monaco (city-state) |
| Total | 165,265,329 |
Using the CIA classification a little more liberally and including "South-Western Europe", would give the following calculation of Western Europe's population.
| Rank | Country or territory | Population (most recent estimates) |
Languages | Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | United Kingdom | 66,040,229 | English | London |
| 2 | France (metropolitan) | 65,058,000 | French | Paris |
| 3 | Spain | 46,700,000 | Spanish | Madrid |
| 4 | Netherlands | 17,889,600 | Dutch, Frisian | Amsterdam |
| 5 | Belgium | 11,420,163 | Dutch, French and German | Brussels |
| 6 | Portugal | 10,291,027 | Portuguese | Lisbon |
| 7 | Ireland | 5,123,536 | English, Irish | Dublin |
| 8 | Luxembourg | 602,005 | French, Luxembourgish and German | Luxembourg City |
| 9 | Andorra | 78,264 | Catalan | Andorra la Vella |
| 10 | Monaco | 38,300 | French | Monaco (city-state) |
| Total | 222,293,922 |
The Hague is the seat of government
Climate

The climate of Western Europe varies from Mediterranean in the coasts of Italy, Portugal and Spain to alpine in the Pyrenees and the Alps. The Mediterranean climate of the south is dry and warm. The western and northwestern parts have a mild, generally humid climate, influenced by the North Atlantic Current. Western Europe is a heatwave hotspot, exhibiting upward trends that are three-to-four times faster compared to the rest of the northern midlatitudes.
Languages
See also: Languages of Europe, Indo-European languages, and List of Indo-European languagesWestern European languages mostly fall within two Indo-European language families: the Romance languages, descended from the Latin of the Roman Empire; and the Germanic languages, whose ancestor language (Proto-Germanic) came from southern Scandinavia. Romance languages are spoken primarily in the southern and central part of Western Europe, Germanic languages in the northern part (the British Isles and the Low Countries), as well as a large part of Northern and Central Europe.
Other Western European languages include the Celtic group (that is, Irish, Scottish Gaelic, Manx, Welsh, Cornish and Breton) and Basque, the only currently living European language isolate.
Multilingualism and the protection of regional and minority languages are recognised political goals in Western Europe today. The Council of Europe Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities and the Council of Europe's European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages set up a legal framework for language rights in Europe.
Economy
Western Europe is one of the richest regions of the world. Germany has the highest gross domestic product in Europe and the largest financial surplus of any country, Luxembourg has the world's highest GDP per capita, and Germany has the highest net national wealth of any European state.
Switzerland and Luxembourg have the highest average wage in the world, in nominal and PPP, respectively. Norway ranks highest in the world on the Social Progress Index.
Global impact
See also: Age of Discovery, History of colonialism, New Imperialism, and Industrial RevolutionSee also
- Atlantic Europe
- Central Europe
- Eastern Europe
- Northern Europe
- Southern Europe
- Far West
- Marshall Plan
- EuroVoc § Western Europe
- Western world
References
Citations
- Delanty, Gerard (1995). "The Westernisation of Europe". Inventing Europe Idea, Identity, Reality. p. 30. doi:10.1057/9780230379657. ISBN 978-0-333-62203-2.
Until the late fifteenth century the idea of Europe was principally a geographical expression and subordinated to Christendom which was the dominant identity system in the West. The idea of Europe as the West began to be consolidated in the foreign conquests of the age of 'discovery" (...) "Europe then begins to shed itself of its association with Christendom and slowly becomes an autonomous discourse.
- Sushytska, Julia (2012). Bradatan, Costica (ed.). "What Is Eastern Europe? A Philosophical Approach". Angelaki. Routledge: 39–51.
- "Key factors in the start of the Cold War upto 1955 - Reasons for the Cold War - Higher History Revision". BBC Bitesize. Retrieved 23 February 2024.
- "Atlas of the Historical Geography of the Holy Land". Rbedrosian.com. Archived from the original on 10 June 2013. Retrieved 23 February 2013.
- "home.comcast.net". Archived from the original on 13 February 2013. Retrieved 23 February 2013.
- Ricci, Matteo (1610) . On Friendship: One Hundred Maxims for a Chinese Prince. Translated by Timothy Billings. Columbia University Press. pp. 19, 71, 87. ISBN 978-0-231-14924-2.
- "Being Christian in Western Europe", Pew Research Center, Pew Research Center, 2018, retrieved 29 May 2018
- "One very common, but now outdated, definition of Eastern Europe was the Soviet-dominated communist countries of Europe."http://www.cotf.edu/earthinfo/balkans/BKdef.html Archived 10 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- "Too much writing on the region has – consciously or unconsciously – clung to an outdated image of 'Eastern Europe', desperately trying to patch together political and social developments from Budapest to Bukhara or Tallinn to Tashkent without acknowledging that this Cold War frame of reference is coming apart at the seams. Central Europe Review: Re-Viewing Central Europe By Sean Hanley, Kazi Stastna and Andrew Stroehlein, 1999
- Berglund, Sten; Ekman, Joakim; Aarebrot, Frank H. (2004). The handbook of political change in Eastern Europe. p. 2. ISBN 978-1-78195-432-4. Retrieved 5 October 2011.
The term 'Eastern Europe' is ambiguous and in many ways outdated.
- ^ "Methodology". UNSD. Retrieved 17 June 2019.
- "Field listing: Location". CIA World Factbook. Archived from the original on 24 May 2011. Retrieved 30 July 2017.
- "EuroVoc: 7206 Europe". Retrieved 9 February 2021.
- "EuroVoc: Western Europe". Retrieved 9 February 2021.
- UNAIDS, The Governance Handbook, January 2010 Archived 9 January 2011 at the Wayback Machine (p. 29).
- ^ "World Population Prospects 2018". Archived from the original on 19 September 2016. Retrieved 14 October 2018.
- "Europe :: Netherlands — The World Factbook". Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 6 October 2020.
- Rousi, Efi; Kornhuber, Kai; Beobide-Arsuaga, Goratz; Luo, Fei; Coumou, Dim (4 July 2022). "Accelerated western European heatwave trends linked to more-persistent double jets over Eurasia". Nature Communications. 13 (1): 3851. Bibcode:2022NatCo..13.3851R. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-31432-y. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 9253148. PMID 35788585. S2CID 250282752.
- ^ "Europe". Encyclopædia Britannica. 2007. Retrieved 10 June 2008.
- "Basque language". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 16 June 2020.
- Oszmiańska-Pagett, Aleksandra (January 2022). "A Word from the Chair of the Committee of Experts". Council of Europe. Retrieved 10 November 2023.
- "GDP (current US$) - European Union | Data". data.worldbank.org. Retrieved 12 March 2021.
- "2020 Social Progress Index". The Social Progress Imperative. Retrieved 29 December 2020.
Sources
- The Making of Europe, ISBN 978-0-14-015409-2, by Robert Bartlett
- Crescent and Cross, ISBN 978-1-84212-753-7, by Hugh Bicheno
- The Normans, ISBN 978-0-7524-2881-9, by Trevor Rowley
- 1066: The Year of the Three Battles, ISBN 978-0-7126-6672-5, by Frank McLynn
External links
- The European sub-regions according to the UN
- Teaching about Western Europe Archived 1 June 2006 at the Wayback Machine
| Europe articles | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History |
| ||||||||
| Geography | |||||||||
| Politics |
| ||||||||
| Economy |
| ||||||||
| Society |
| ||||||||