| Revision as of 21:18, 26 September 2009 view sourceDaveSDCali (talk | contribs)130 editsmNo edit summary← Previous edit | Revision as of 22:28, 24 December 2024 view source JacktheBrown (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers76,485 edits →Cuisine: WP:NOTBROKENTags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit Advanced mobile editNext edit → | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Country in North America}} | |||
| {{Dablink|This article is about the United States of America. For other uses of terms redirecting here, see ], ], and ].}} | |||
| {{Redirect|America|the landmass comprising North and South America|Americas|5=America (disambiguation)}} | |||
| {{pp-semi-protected|small=yes}} | |||
| {{Redirect-several|US|USA|United States|The United States of America}} | |||
| {{Infobox Country | |||
| {{pp-move}} | |||
| |conventional_long_name=United States of America | |||
| {{pp-extended|small=yes}} | |||
| |common_name=the United States | |||
| {{Use American English|date=January 2024}} | |||
| |image_flag=Flag of the United States.svg | |||
| {{Use mdy dates|date=August 2024}} | |||
| |image_coat=US-GreatSeal-Obverse.svg | |||
| {{Infobox country | |||
| |length=1776–Present | |||
| | conventional_long_name = United States of America | |||
| |symbol_type=Great Seal | |||
| | common_name = United States | |||
| |national_motto=<!--Please read the talk page before editing these mottoes:-->]{{spaces|2}}<small>(official)</small><br />{{lang|la|'']''}}{{spaces|2}}<small>(]; traditional)</small><br /><small>(Out of Many, One)</small> | |||
| | |
| image_flag = Flag of the United States (DoS ECA Color Standard).svg | ||
| | alt_flag = {{nbsp}} <!--Used to denote purely decorative images--> | |||
| |map_width=220px | |||
| | flag_type_article = Flag of the United States | |||
| |national_anthem="]" | |||
| | image_coat = Greater coat of arms of the United States.svg | |||
| |official_languages=None at federal level{{smallsup|1}} | |||
| | coat_alt = {{nbsp}} <!--Used to denote purely decorative images--> | |||
| |languages_type=] | |||
| | symbol_type_article = Great Seal of the United States#Obverse | |||
| |languages=] ('']''){{smallsup|2}} | |||
| | national_motto = "]"<ref>{{USC|36|302}}</ref>{{collapsible list | |||
| |capital=] | |||
| |title={{nowrap|Other traditional mottos:<ref name="de facto Motto">{{cite web|publisher=], ]|year=2003|url= https://2009-2017.state.gov/documents/organization/27807.pdf|title=The Great Seal of the United States|access-date=February 12, 2020}}</ref>}} | |||
| |largest_city=] | |||
| |titlestyle=background:transparent;color:inherit;text-align:center;line-height:1.15em; | |||
| |latd=38|latm=53|latNS=N|longd=77|longm=01|longEW=W | |||
| |liststyle=text-align:center;white-space:nowrap; | |||
| |]=] | |||
| |{{native phrase|la|"]"|italics=off}}<br />"Out of many, one" | |||
| |government_type=] ] ] | |||
| |{{native phrase|la|"]"|italics=off}}<br />"Providence favors our undertakings" | |||
| |leader_title1=] | |||
| |{{native phrase|la|"]"|italics=off}}<br />"New order of the ages" | |||
| |leader_name1=] (]) | |||
| }} | |||
| |leader_title2=] | |||
| | national_anthem = "]"<ref>{{cite act|date=March 3, 1931|article=14|article-type=H.R.|legislature=]|title=An Act To make The Star-Spangled Banner the national anthem of the United States of America|url=https://uscode.house.gov/statviewer.htm?volume=46&page=1508}}</ref><div style="display:inline-block;margin-top:0.4em;">]</div> | |||
| |leader_name2=] (]) | |||
| <!-- Commented out, as not ] for lead. | |||
| |leader_title3={{nowrap|]}} | |||
| | march="]"<ref name="urluscode.house.gov">{{cite web|url=https://uscode.house.gov/statviewer.htm?volume=112&page=1263|title=uscode.house.gov|date=August 12, 1999|website=Public Law 105-225|publisher=uscode.house.gov|pages=112 Stat. 1263|quote=Section 304. "The composition by John Philip Sousa entitled 'The Stars and Stripes Forever' is the national march."|access-date=September 10, 2017}}</ref><div style="display:inline-block;margin-top:0.4em;">]</div> | |||
| |leader_name3=] (]) | |||
| --> | |||
| |leader_title4=] | |||
| <!-- Consensus map, see talk page. --> | |||
| |leader_name4=] | |||
| | image_map = {{Switcher|]|Show globe (] and ] only)|]|Show the U.S. and ]|]|Show territories with ]|default=1}} | |||
| |sovereignty_type=] {{nobold|from the ]}} | |||
| | map_width = 220px | |||
| |established_event1=] | |||
| | capital = ]<br />{{coord|38|53|N|77|1|W|display=inline}} | |||
| |established_date1=July 4, 1776 | |||
| | largest_city = ]<br />{{coord|40|43|N|74|0|W|display=inline}} | |||
| |established_event2=] | |||
| | official_languages = None at the ]{{efn|name=officiallanguage|Twenty-eight of the 50 states recognize only English as an official language. The ] recognizes both ] and English as official languages, the ] officially recognizes 20 ] alongside English, and the ] recognizes English and ] as official languages. Nineteen states and the District of Columbia have no official language.}} | |||
| |established_date2=September 3, 1783 | |||
| | languages_type = ] | |||
| |established_event3=] | |||
| | languages = ]{{efn|English is the ] language. For more information, see ].}} | |||
| |established_date3=June 21, 1788 | |||
| <!-- NOTE: For English, don't add "American English" --> | |||
| |area_footnote=<ref name="WF"/> | |||
| | ethnic_groups = {{plainlist|''By race:'' | |||
| |area_sq_mi=3794066 | |||
| * 61.6% ] | |||
| |area_km2=9826630 | |||
| * 12.4% ] | |||
| |area_rank=3rd/4th{{smallsup|3}} | |||
| * 6% ] | |||
| |area_magnitude=1 E12 | |||
| * 1.1% ] | |||
| |percent_water=6.76 | |||
| * 0.2% ] | |||
| |population_estimate={{uspop commas}}<ref name="POP"/> | |||
| * 10.2% ] | |||
| |population_estimate_year={{CURRENTYEAR}} | |||
| * 8.4% ] | |||
| |population_estimate_rank=3rd{{smallsup|4}} | |||
| }} | |||
| |population_census=281,421,906<ref>{{cite web|url=http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/SAFFPopulation?_submenuId=population_0&_sse=on|title=Population Finder: United States|publisher=U.S. Census Bureau|accessdate=2007-12-20|year =2000}}</ref> | |||
| {{plainlist|''By origin:'' | |||
| |population_census_year=2000 | |||
| * 81.3% non-] | |||
| |population_density_km2=31 | |||
| * 18.7% Hispanic or Latino | |||
| |population_density_sq_mi=80 | |||
| }} | |||
| |population_density_rank=180th | |||
| | ethnic_groups_year = 2020 | |||
| |GDP_PPP_year=2008 | |||
| | ethnic_groups_ref = <ref name="2020CensusData">{{cite web|url=https://www.census.gov/library/stories/2021/08/improved-race-ethnicity-measures-reveal-united-states-population-much-more-multiracial.html|title=2020 Census Illuminates Racial and Ethnic Composition of the Country|work=]|access-date=August 13, 2021}}</ref><ref name="2020InteractiveCensusData">{{cite web|url=https://www.census.gov/library/visualizations/interactive/race-and-ethnicity-in-the-united-state-2010-and-2020-census.html?linkId=100000060666476|title=Race and Ethnicity in the United States: 2010 Census and 2020 Census|work=]|access-date=August 13, 2021}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.npr.org/2021/08/13/1014710483/2020-census-data-us-race-ethnicity-diversity|title=A Breakdown of 2020 Census Demographic Data|date=August 13, 2021|publisher=NPR|access-date=}}</ref> | |||
| |GDP_PPP=$14.264 trillion<ref name=IMF_GDP>{{cite web|url=http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2009/01/weodata/weorept.aspx?sy=2006&ey=2009&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=111&s=NGDPD%2CNGDPDPC%2CPPPGDP%2CPPPPC%2CLP&grp=0&a=&pr.x=60&pr.y=9|title=United States|publisher=International Monetary Fund|accessdate=2009-04-22}}</ref> | |||
| | demonym = ]{{efn|name=demonym|The historical and informal demonym ] has been applied to Americans, New Englanders, or northeasterners since the 18th century.}}<ref>{{cite book|title=Compton's Pictured Encyclopedia and Fact-index: Ohio|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=uV5tvKPO684C&q=%22national+nicknames%22+Yankee|year=1963|page=336}}</ref> | |||
| |GDP_PPP_rank=1st | |||
| | government_type = ] presidential republic | |||
| |GDP_PPP_per_capita=$46,859<ref name="IMF_GDP"/> | |||
| <!-- Consensus is to list President, Vice President, Chief Justice, and Speaker of the House --> | |||
| |GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank=6th | |||
| | leader_title1 = ] | |||
| |GDP_nominal=$14.264 trillion<ref name="IMF GDP"/> | |||
| | leader_name1 = ]<!--]--> | |||
| |GDP_nominal_rank=1st | |||
| | leader_title2 = ] | |||
| |GDP_nominal_year=2008 | |||
| | leader_name2 = ]<!--]--> | |||
| |GDP_nominal_per_capita=$46,859<ref name="IMF_GDP"/> | |||
| | leader_title3 = ] | |||
| |GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank=17th | |||
| | leader_name3 = ] | |||
| |HDI_year=2006 | |||
| | leader_title4 = ] | |||
| |HDI={{steady}} 0.950<ref> The United Nations. Retrieved 10 July 2009.</ref> | |||
| | leader_name4 = ] | |||
| |HDI_rank=15th | |||
| | legislature = ] | |||
| |HDI_category=<span style="color:#090;">high</span> | |||
| | upper_house = ] | |||
| |Gini=45.0<ref name="WF"/> | |||
| | lower_house = ] | |||
| |Gini_rank=38th | |||
| | sovereignty_type = ] | |||
| |Gini_year=2007 | |||
| | sovereignty_note = from ] | |||
| |currency=] ($) | |||
| | established_event1 = ] | |||
| |currency_code=USD | |||
| | established_date1 = {{Start date|1776|7|4}} | |||
| |country_code=USA | |||
| | established_event2 = ] | |||
| |utc_offset=-5 to -10 | |||
| | established_date2 = {{Start date|1781|3|1}} | |||
| |utc_offset_DST=-4 to -10 | |||
| | established_event3 = ] | |||
| |cctld=] ] ] ] | |||
| | established_date3 = {{Start date|1783|9|3}} | |||
| |calling_code= ] | |||
| | established_event4 = ] | |||
| |drives_on=Right | |||
| | established_date4 = {{Start date|1788|6|21}} | |||
| |demonym=] | |||
| | area_link = Geography of the United States | |||
| |footnote1=English is the official language of at least 28 states—some sources give a higher figure, based on differing definitions of "official".<ref name=ILW/> English and ] are both official languages in the state of Hawaii. | |||
| | area_label = Total area | |||
| |footnote2=English is the ''de facto'' language of American government and the sole language spoken at home by 81% of Americans age five and older. Spanish is the ]. | |||
| | area_footnote = <ref name="CensusGov2010HTML">Areas of the 50 states and the District of Columbia but not Puerto Rico nor other island territories per {{cite web| date = August 2010| title = State Area Measurements and Internal Point Coordinates| work = ]| url = https://www.census.gov/geographies/reference-files/2010/geo/state-area.html| access-date = March 31, 2020| quote = reflect base feature updates made in the MAF/TIGER database through August, 2010.}}</ref>{{efn|name=largestcountry}} | |||
| |footnote3=Whether the United States or the People's Republic of China is larger is ]. The figure given is from the U.S. ]'s '']''. Other sources give smaller figures. All authoritative calculations of the country's size include only the 50 states and the District of Columbia, not the territories. | |||
| | area_rank = 3rd | |||
| |footnote4=The population estimate includes people whose usual residence is in the fifty states and the District of Columbia, including noncitizens. It does not include either those living in the territories, amounting to more than 4 million U.S. citizens (most in ]), or U.S. citizens living outside the United States. | |||
| | area_sq_mi = 3,796,742 | |||
| | percent_water = 7.0<ref>{{cite web|title=The Water Area of Each State|access-date=January 29, 2024|publisher=]|url=https://www.usgs.gov/special-topics/water-science-school/science/how-wet-your-state-water-area-each-state|year=2018}}</ref> (2010) | |||
| | area_label2 = Land area | |||
| | area_data2 = {{convert|3,531,905|sqmi|km2|abbr=on}} (3rd) | |||
| | population_census = {{IncreaseNeutral}} 331,449,281{{efn|name="pop"}}<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.census.gov/library/stories/2021/04/2020-census-data-release.html|title=U.S. Census Bureau Today Delivers State Population Totals for Congressional Apportionment|work=]|access-date=April 26, 2021}} The 2020 census is as of April 1, 2020.</ref> | |||
| | population_census_year = 2020 | |||
| | population_estimate = {{IncreaseNeutral}} 340,110,988<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.census.gov/data/tables/time-series/demo/popest/2020s-national-total.html | title=National Population Totals and Components of Change: April 1, 2020 to July 1, 2024 |publisher=] (USCB) |website=www.census.gov |access-date=20 December 2024}}</ref> | |||
| | population_estimate_year = 2024 | |||
| | population_census_rank = 3rd | |||
| | population_density_sq_mi = 87<!-- Figure uses (population/land + water area) as of July 2019. --> | |||
| | population_density_rank = 185th | |||
| | GDP_PPP = {{increase}} $29.168 trillion<ref name="IMFWEO.US">{{cite web |url=https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2024/October/weo-report?c=111,&s=NGDPD,PPPGDP,NGDPDPC,PPPPC,&sy=2022&ey=2029&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1 |title=World Economic Outlook Database, October 2024 Edition. (United States) |publisher=] |website=www.imf.org |date=October 22, 2024 |access-date=October 22, 2024}}</ref> | |||
| | GDP_PPP_year = 2024 | |||
| | GDP_PPP_rank = 2nd | |||
| | GDP_PPP_per_capita = {{increase}} $86,601<ref name="IMFWEO.US" /> | |||
| | GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 8th | |||
| | GDP_nominal = {{increase}} $29.168 trillion<ref name="IMFWEO.US" /> | |||
| | GDP_nominal_year = 2024 | |||
| | GDP_nominal_rank = 1st | |||
| | GDP_nominal_per_capita = {{increase}} $86,601<ref name="IMFWEO.US" /> | |||
| | GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = 6th | |||
| | Gini = 41.6<!-- Number only. --> | |||
| | Gini_year = 2023 | |||
| | Gini_change = decrease | |||
| | Gini_ref = {{efn|After adjustment for taxes and transfers}}<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.census.gov/library/publications/2024/demo/p60-282.html|title=Income in the United States: 2023|newspaper=Census.gov |page=53|access-date=December 15, 2024}}</ref> | |||
| | HDI = 0.927<!-- Number only. --> | |||
| | HDI_year = 2022<!-- Please use the year to which the data refers, not the publication year. --> | |||
| | HDI_change = increase<!-- Increase/decrease/steady. --> | |||
| | HDI_ref = <ref name="UNHDR">{{cite web|url=https://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2023-24reporten.pdf|title=Human Development Report 2023/24|language=en|publisher=]|date=March 13, 2024|access-date=March 13, 2024}}</ref> | |||
| | HDI_rank = 20th | |||
| | currency = ] (]) | |||
| | currency_code = USD | |||
| | utc_offset = −4 to −12, +10, +11 | |||
| | utc_offset_DST = −4 to −10{{efn|name="time"}} | |||
| | date_format = mm/dd/yyyy{{efn|See ].}} | |||
| | drives_on = Right{{efn|name="drive"}} | |||
| | calling_code = ] | |||
| | iso3166code = US | |||
| | cctld = ]<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://cozab.com/the-difference-between-us-vs-com/|title=The Difference Between .us vs .com|date=January 3, 2022|website=Cozab|access-date=August 11, 2023|archive-date=April 16, 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230416200528/https://cozab.com/the-difference-between-us-vs-com/|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| | religion = {{ublist|item_style=white-space:nowrap; | |||
| |{{Tree list}} | |||
| * 67% ] | |||
| ** 33% ] | |||
| ** 22% ] | |||
| ** 1% ] | |||
| ** 11% other ] | |||
| {{Tree list/end}} | |||
| |22% ] | |||
| |2% ] | |||
| |6% ] | |||
| |3% unanswered | |||
| }} | |||
| | religion_year = 2023 | |||
| | religion_ref = <ref name="Staff-2007">{{Cite web |last=Staff |date= June 8, 2007|title=In Depth: Topics A to Z (Religion) |url=https://news.gallup.com/poll/1690/Religion.aspx |access-date=July 1, 2024 |website=] |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| <!--The following opening paragraphs on this subject are a topic of great debate. Check the discussion page before editing. In particular, do NOT add mention of the territories to the first sentence: they are possessions of the United States, not part of it.--> | |||
| The '''United States of America''' (commonly referred to as the '''United States''', the '''U.S.''', the '''USA''', the '''States''', or '''America''') is a ] ] comprising ] and a ]. The country is situated mostly in central ], where its ] and ], the ], lie between the ] and ]s, ] by ] to the north and ] to the south. The state of ] is in the northwest of the continent, with Canada to its east and ] to the west across the ]. The state of ] is an ] in the mid-Pacific. The country also possesses ], or ]s, in the ] and Pacific. | |||
| The '''United States of America''' ('''USA'''), commonly known as the '''United States''' ('''U.S.''') or '''America''', is a country primarily located in ]. It is a ] of 50 ] and a federal capital district, ] The ] border ] to the north and ] to the south, with the states of ] to the northwest and the ] ] in the ]. The United States also asserts sovereignty over five ] and ].{{efn|The five major territories outside the union of states are ], ], the ], ], and the ]. The seven undisputed island areas without permanent populations are ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]. U.S. sovereignty over the unpopulated ], ], ], and ] is disputed.<ref name="HRI-2012">{{multiref2|{{Cite web|publisher=U.S. State Department |url=https://2009-2017.state.gov/j/drl/rls/179780.htm |title=Common Core Document to U.N. Committee on Human Rights|date=December 30, 2011 |at=Item 22, 27, 80 |access-date=April 6, 2016}}|{{Cite web|publisher=U.S. General Accounting Office Report |url=https://www.gao.gov/archive/1998/og98005.pdf |title=U.S. Insular Areas: application of the U.S. Constitution |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131103093032/https://www.gao.gov/archive/1998/og98005.pdf |archive-date=November 3, 2013 |date=November 1997 |pages=1, 6, 39n |access-date=April 6, 2016}}}}</ref>}} The country has the world's ],{{efn|At {{cvt|9,147,590|km2|order=flip}}, the United States is the third-largest country in the world by land area, behind ] and ]. By total area (land and water), it is the third-largest, behind Russia and ], if its coastal and territorial water areas are included. However, if only its internal waters are included (bays, sounds, rivers, lakes, and the ]), the U.S. is the fourth-largest, after Russia, Canada, and China. | |||
| At 3.79 million square miles (9.83 million km<sup>2</sup>) and with about 307 million people, the United States is the ] largest country by total area, and the third largest by land area and ]. The United States is one of the world's most ] and ] nations, the product of large-scale ].<ref name="DD">Adams, J.Q., and Pearlie Strother-Adams (2001). ''Dealing with Diversity''. Chicago: Kendall/Hunt. ISBN 078728145X.</ref> The ] is the largest national economy in the world, with an estimated 2008 ] (GDP) of ]14.3 trillion (23% of the world total based on nominal GDP and almost 21% at ]).<ref name="IMF GDP">{{cite web|url=http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2008/02/weodata/index.aspx|publisher=International Monetary Fund|title=World Economic Outlook Database|month=October|year=2008|accessdate=2008-10-27}}</ref><ref>The ] has a larger collective economy, but is not a single nation.</ref> | |||
| <br /> | |||
| Coastal/territorial waters included: {{cvt|9,833,517|km2|order=flip}}<ref>{{cite web|title=China|url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/china/|access-date=June 10, 2016|website=]}}</ref> | |||
| <br /> | |||
| Only internal waters included: {{cvt|9,572,900|km2|order=flip}}<ref>{{cite web|title=United States|url=https://www.britannica.com/topic/616563/United-States-quick-facts|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131219194413/https://www.britannica.com/topic/616563/United-States-quick-facts|archive-date=December 19, 2013|access-date=January 31, 2010|website=]}}</ref>|name=largestcountry}} ], and ], exceeding 340 million.{{efn|The ]'s latest official population estimate of 340,110,988 residents (2024) is for the 50 states and the District of Columbia; it excludes the 3.6 million residents of the five major ] and outlying islands. The Census Bureau also provides a continuously updated but unofficial population clock: |name=pop clock}} Its three ] are ], ], and ], and its three ] are ], ], and ]. | |||
| ] migrated across the ] more than 12,000 years ago, and formed ]. ] led to the first settlement of the ] in ] in 1607, with the beginning of the ] of ] following soon after. Clashes with the ] over taxation and ] sparked the ], with the ] formally ] on July 4, 1776. Following its victory in the 1775–1783 ], the country continued to ], resulting in the dispossession of ]. As more states ], a ] over slavery led to the secession of the ], which fought states remaining in ] in the 1861–1865 ]. With the victory and preservation of the United States, ]. By 1900, the country had established itself as a ], a status solidified after its involvement in ]. After ]'s ] in December 1941, the U.S. ]. ] left the U.S. and the ] as the world's two ] and led to the ], during which both countries struggled for ] and ]. Following the ] and the ] in 1991, the U.S. ], wielding ]. | |||
| The nation was founded by ] of ] located along the ]. On July 4, 1776, they issued the ], which proclaimed their independence from Great Britain and their formation of a cooperative union. The rebellious states defeated Great Britain in the ], the first successful ].<ref>Dull, Jonathan R. (2003). "Diplomacy of the Revolution, to 1783," p. 352, chap. in ''A Companion to the American Revolution'', ed. Jack P. Greene and J. R. Pole. Maiden, Mass.: Blackwell, pp. 352–361. ISBN 1405116749.</ref> The ] adopted the current ] on September 17, 1787; its ratification the following year made the states part of a single republic with a strong central government. The ], comprising ten ] guaranteeing many fundamental civil rights and freedoms, was ratified in 1791. | |||
| The ] is a ] ] ] and ] with ]: ], ], and ]. It has a ] national legislature composed of the ], a ] based on population, and the ], an ] based on equal representation for each state. ] to the 50 states, while American values are based on a democratic political tradition that draws its inspiration from the ]. | |||
| In the 19th century, the United States acquired land from ], ], the ], ], and ], and ] the ] and the ]. Disputes between the ] and ] over ] and the expansion of the ] provoked the ] of the 1860s. The North's victory prevented a permanent split of the country and led to the ] in the United States. By the 1870s, the national economy was the world's largest.<ref>{{cite web|author=Maddison, Angus|url=http://www.ggdc.net/maddison/Historical_Statistics/horizontal-file_09-2008.xls|title=Historical Statistics for the World Economy|publisher=The Groningen Growth and Development Centre, Economics Department of the University of Groningen|year=2006|accessdate=2008-11-06}}</ref> The ] and ] confirmed the country's status as a military power. In 1945, the United States emerged from ] as the ], a permanent member of the ], and a founding member of ]. The end of the ] and the ] left the United States as the sole ]. The country accounts for ] and is a leading economic, political and cultural force in the world.<ref>{{cite web|author=Cohen, Eliot A.|url=http://www.foreignaffairs.org/20040701faessay83406/eliot-a-cohen/history-and-the-hyperpower.html|title=History and the Hyperpower|work=Foreign Affairs|date=July/August 2004|accessdate=2006-07-14}} {{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/americas/country_profiles/1217752.stm|title=Country Profile: United States of America|publisher=BBC News|date=2008-04-22|accessdate=2008-05-18}}</ref> | |||
| One of the world's ], the United States has had the ] and accounted for over 15% of the ] in 2023.{{efn|Based on ]}} It possesses by far the ] and has the ] among ] countries. The U.S. ] in ], ], ], ], and ]. Its ] and ] have a global reach. The U.S. is a founding member of the ], the ], ], and the ],{{Efn|Including agencies such as the ] and the ]}} as well as a ]. | |||
| ==Etymology== | |||
| {{See also|Names for U.S. citizens}} | |||
| In 1507, German ] ] produced a world map on which he named the lands of the Western Hemisphere ] after Italian explorer and cartographer ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.usatoday.com/news/nation/2007-04-24-america-turns-500_N.htm?csp=34|title=Cartographer Put 'America' on the Map 500 years Ago|work=USA Today|date=2007-04-24|accessdate=2008-11-30}}</ref> The former British colonies first used the country's modern name in the ], which was the "unanimous Declaration of the thirteen united States of America" adopted by the "Representatives of the united States of America" on July 4, 1776.<!--Do not uppercase "united" here: it is unambiguously lowercased in the Declaration--><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.archives.gov/exhibits/charters/charters.html|title=The Charters of Freedom|publisher=National Archives|accessdate=2007-06-20}}</ref> The current name was finalized on November 15, 1777, when the ] adopted the ], the first of which states, "The Stile of this Confederacy shall be 'The United States of America.'" The short form ''United States'' is also standard. Other common forms include the ''U.S.'', the ''USA'', and ''America''. Colloquial names include the ''U.S. of A.'' and ''the States''. '']'', a once popular name for the United States, was derived from ]. It appears in the name "]". | |||
| == Etymology == | |||
| The standard way to refer to a citizen of the United States is as an '']''. Though ''United States'' is the formal adjective, ''American'' and ''U.S.'' are the most common adjectives used to refer to the country ("American values," "U.S. forces"). ''American'' is rarely used in English to refer to people not connected to the United States.<ref>Wilson, Kenneth G. (1993). ''The Columbia Guide to Standard American English''. New York: Columbia University Press, pp. 27–28. ISBN 0231069898.</ref> | |||
| {{Further|Names of the United States|Demonyms for the United States|United Colonies}} | |||
| The first documented use of the phrase "United States of America" is a letter from January 2, 1776. ], a ] aide to General ], wrote to ], Washington's ], seeking to go "with full and ample powers from the United States of America to Spain" to seek assistance in the ] effort.<ref name="DeLear-2013">{{cite news |last=DeLear |first=Byron |date=July 4, 2013 |title=Who coined 'United States of America'? Mystery might have intriguing answer |url=https://www.csmonitor.com/USA/Politics/2013/0704/Who-coined-United-States-of-America-Mystery-might-have-intriguing-answer |work=The Christian Science Monitor |location=Boston, Massachusetts}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |last=Fay |first=John |date=July 15, 2016 |url=https://www.irishcentral.com/roots/history/The-forgotten-Irishman-who-named-the-United-States-of-America.html |title=The forgotten Irishman who named the 'United States of America' |quote=According to the NY Historical Society, Stephen Moylan was the man responsible for the earliest documented use of the phrase 'United States of America'. But who was Stephen Moylan? |work=IrishCentral.com}}</ref> The first known public usage is an ] published in the ] newspaper, '']'', on April 6, 1776.<ref name="DeLear-2013"/><ref>{{cite news|newspaper=The Virginia Gazette|title=To the inhabitants of Virginia |author=((A PLANTER)) |date=April 6, 1776 |location=Williamsburg, Virginia |publisher=Dixon and Hunter's |url=https://research.history.org/DigitalLibrary/VirginiaGazette/VGIssueThumbs.cfm?IssueIDNo=76.DH.16|issue=1287|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141219053616/https://research.history.org/DigitalLibrary/VirginiaGazette/VGIssueThumbs.cfm?IssueIDNo=76.DH.16|archive-date=December 19, 2014|volume=5}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=A Planter' s Address to the Inhabitants of Virginia |url=https://digital.lib.niu.edu/islandora/object/niu-amarch%3A87440 |website=American Archives |publisher=Northern Illinois University |access-date=May 25, 2024}}</ref> By June 1776, the "United States of America" appeared in the ]{{sfn|Safire|2003|p=199}}{{sfn|Mostert|2005|p=18}} and the ].{{sfn|Safire|2003|p=199}} The ] adopted the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776.<ref name="Davis7">], p. 7.</ref> | |||
| The phrase "the United States" was originally treated as plural—e.g., "the United States are"—including in the ], ratified in 1865. It became common to treat it as singular—e.g., "the United States is"—after the end of the Civil War. The singular form is now standard; the plural form is retained in the idiom "these United States."<ref>{{cite web|url=http://itre.cis.upenn.edu/~myl/languagelog/archives/002663.html|author=Zimmer, Benjamin|date=2005-11-24|title=Life in These, Uh, This United States|publisher=University of Pennsylvania—Language Log|accessdate=2008-02-22}}</ref> | |||
| The term "United States" and the initialism "U.S.", used as nouns or as adjectives in English, are common short names for the country. The initialism "USA", a noun, is also common.<ref>{{cite web |title=Is USA A Noun Or Adjective? |url=https://www.dictionary.com/e/is-usa-a-noun/ |website=Dictionary.com |date=9 March 2017}}</ref> "United States" and "U.S." are the established terms throughout the ], with prescribed rules.{{efn|The official ] has prescribed specific usages for "U.S." and "United States" as part of official names. In "formal writing (treaties, Executive orders, proclamations, etc.); congressional bills; legal citations and courtwork; and covers and title pages",<ref name="gpo-stylemanual" /> "United States" is always used. In a sentence containing the name of another country, "United States" must be used. Otherwise, "U.S." is used preceding a government organization or as an adjective, but "United States" is used as an adjective preceding non-governmental organizations (e.g. ]).<ref name="gpo-stylemanual">{{cite book |title=U.S. Government Publishing Office Style Manual |date=January 12, 2017 |pages=222–223 |url=https://www.govinfo.gov/app/details/GPO-STYLEMANUAL-2016/ |access-date=3 September 2020}}</ref>}} In English, the term "America" rarely refers to topics unrelated to the United States, despite the usage of "the ]" as the totality of North and South America.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Wilson |first1=Kenneth G. |title=The Columbia guide to standard American English |date=1993 |publisher=Columbia University Press |location=New York |isbn=978-0-231-06989-2}}</ref> "The States" is an established colloquial shortening of the name, used particularly from abroad;<ref>{{cite web|website=Longman dictionary|title="The States"|url=https://www.ldoceonline.com/dictionary/the-states|accessdate=September 27, 2024}}</ref> "stateside" is the corresponding adjective or adverb.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2024-09-27 |title=Definition of STATESIDE |url=https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/stateside |access-date=2024-10-04 |website=www.merriam-webster.com |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| ==Geography, climate, and environment== | |||
| {{Main|Geography of the United States|Climate of the United States|Environment of the United States}} | |||
| ] of the ]]] | |||
| The total land area of the ] is approximately 1.9 billion acres. Alaska, separated from the contiguous United States by Canada, is the largest state at 365 million acres. Hawaii, occupying an archipelago in the central Pacific, southwest of North America, has just over 4 million acres.<ref>{{cite web|author=Lubowski, Ruben, Marlow Vesterby, and Shawn Bucholtz|url=http://www.ers.usda.gov/publications/arei/eib16/chapter1/1.1/|title=AREI Chapter 1.1: Land Use|publisher=Economic Research Service|date=2006-07-21|accessdate=2009-03-09}}</ref> After Russia and Canada, the United States is the world's third or fourth ], ranking just above or below ]. The ranking varies depending on how two territories disputed by China and ] are counted and how the total size of the United States is calculated: the CIA ''World Factbook'' gives {{convert|3794083|sqmi|km2|0|abbr=on}},<ref name="WF">{{cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/us.html|title=United States|publisher=CIA|work=The World Factbook|date=2007-05-31|accessdate=2008-10-14}}</ref> the United Nations Statistics Division gives {{convert|3717813|sqmi|km2|0|abbr=on}},<ref>{{cite web|url=http://unstats.un.org/unsd/demographic/products/dyb/DYB2005/Table03.pdf|title=Population by Sex, Rate of Population Increase, Surface Area and Density|publisher=UN Statistics Division|work=Demographic Yearbook 2005|accessdate=2008-03-25}}</ref> and the ''Encyclopedia Britannica'' gives {{convert|3676486|sqmi|km2|0|abbr=on}}.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://209.85.165.104/search?q=cache:2lOa44xXcrgJ:www.britannica.com/eb/article-9111233/United-States+United+States+Area+encyclopedia+britannica&hl=en&ct=clnk&cd=1&gl=us|title=United States|publisher=Encyclopedia Britannica|accessdate=2008-03-25}}</ref> Including only land area, the United States is third in size behind Russia and China, just ahead of Canada.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://education.yahoo.com/reference/factbook/countrycompare/area/3d.html;_ylt=As1XMsN8kgSx746VWazy_s7PecYF|title=World Factbook: Area Country Comparison Table|publisher=Yahoo Education|accessdate=2007-02-28}}</ref> | |||
| ], part of the ]]] | |||
| The name "America" is the Latinized form of the first name of Italian explorer ]. He first proposed that the ] discovered by ] in 1492 were part of a previously unknown landmass and not among the Indies at the eastern limit of ].<ref>{{cite book |first=Sandra |last=Sider |title=Handbook to Life in Renaissance Europe |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=JtYy67FsRosC&pg=PA226 |page=226 |year=2007 |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-533084-7}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |last1=Szalay |first1=Jessie |title=Amerigo Vespucci: Facts, Biography & Naming of America |url=https://www.livescience.com/42510-amerigo-vespucci.html |publisher=] |access-date=June 23, 2019 |date=September 20, 2017}}</ref><ref name="locnamingofamerica">{{cite web |last1=Allen |first1=Erin |title=How Did America Get Its Name?|url=https://blogs.loc.gov/loc/2016/07/how-did-america-get-its-name/#:~:text=America%20is%20named%20after%20Amerigo,part%20of%20a%20separate%20continent |website=Library of Congress Blog |access-date=3 September 2020 |date=4 July 2016}}</ref> | |||
| The coastal plain of the Atlantic seaboard gives way further inland to ] forests and the rolling hills of the ]. The ] divide the eastern seaboard from the ] and the grasslands of the ]. The ]–], the world's ], runs mainly north–south through the heart of the country. The flat, fertile ] of the ] stretches to the west, interrupted by ] in the southeast. The ], at the western edge of the Great Plains, extend north to south across the country, reaching altitudes higher than 14,000 feet (4,300 m) in ]. Farther west are the rocky ] and deserts such as the ]. The ] and ] mountain ranges run close to the ]. At 20,320 feet (6,194 m), Alaska's ] is the country's tallest peak. Active ]es are common throughout Alaska's ] and ], and Hawaii consists of volcanic islands. The ] underlying ] in the Rockies is the continent's largest volcanic feature.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://dsc.discovery.com/convergence/supervolcano/under/under.html|title=Supervolcano: What's Under Yellowstone?|author=O'Hanlon, Larry|publisher=Discovery Channel|accessdate=2007-06-13}}</ref> | |||
| ], national bird of the United States since 1782]] | |||
| The United States, with its large size and geographic variety, includes most climate types. To the east of the ], the climate ranges from ] in the north to ] in the south. The southern tip of ] is tropical, as is Hawaii. The Great Plains west of the 100th meridian are semi-arid. Much of the Western mountains are ]. The climate is arid in the Great Basin, desert in the Southwest, ] in ], and ] in coastal ] and ] and southern Alaska. Most of Alaska is subarctic or polar. Extreme weather is not uncommon—the states bordering the ] are prone to ], and most of the world's ]es occur within the country, mainly in the Midwest's ].<ref>{{cite web|author=Perkins, Sid|url=http://www.sciencenews.org/articles/20020511/bob9.asp|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20070701131631/http://www.sciencenews.org/articles/20020511/bob9.asp|archivedate=2007-07-01|title=Tornado Alley, USA|accessdate=2006-09-20|date=2002-05-11|work=Science News}}</ref> | |||
| == History == | |||
| The U.S. ecology is considered "]": about 17,000 species of ] occur in the contiguous United States and Alaska, and over 1,800 species of ]s are found in Hawaii, few of which occur on the mainland.<ref>{{cite web|author=Morin, Nancy|url=http://www.fungaljungal.org/papers/National_Biological_Service.pdf|title=Vascular Plants of the United States|publisher=National Biological Service|work=Plants|accessdate=2008-10-27}}</ref> The United States is home to more than 400 mammal, 750 bird, and 500 reptile and amphibian species.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sdi.gov/curtis/TxTab4x1.html|title=Global Significance of Selected U.S. Native Plant and Animal Species|publisher=SDI Group|date=2001-02-09|accessdate=2009-01-20}}</ref> About 91,000 insect species have been described.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.si.edu/Encyclopedia_SI/nmnh/buginfo/bugnos.htm|title=Numbers of Insects (Species and Individuals)|publisher=Smithsonian Institution|accessdate=2009-01-20}}</ref> The ] of 1973 protects threatened and endangered species and their habitats, which are monitored by the ]. There are fifty-eight ] and hundreds of other federally managed parks, forests, and ]s.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://home.nps.gov/applications/release/Detail.cfm?ID=639|title=National Park Service Announces Addition of Two New Units|publisher=National Park Service|date=2006-02-28|accessdate=2006-06-13}}</ref> Altogether, the government owns 28.8% of the country's land area.<ref name=FL>{{cite web|url=http://johnshadegg.house.gov/rsc/Federal%20Land%20Ownership--May%202005.pdf|title=Federal Land and Buildings Ownership|publisher=Republican Study Committee|date=2005-05-19|accessdate=2009-03-09}}</ref> Most of this is ], though some is leased for oil and gas drilling, mining, logging, or cattle ranching; 2.4% is used for military purposes.<ref name=FL/> | |||
| ==History== | |||
| {{Main|History of the United States}} | {{Main|History of the United States}} | ||
| {{For outline|Outline of the history of the United States}} | |||
| ===Native Americans and European settlers=== | |||
| {{seealso|Native Americans in the United States|European colonization of the Americas|Thirteen Colonies}} | |||
| The ] of the U.S. mainland, including ], are believed to have ]. They began arriving at least 12,000 and as many as 40,000 years ago.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://anthropology.si.edu/HumanOrigins/faq/americas.htm|title=Peopling of Americas|publisher=Smithsonian Institution, National Museum of Natural History|month=June|year=2004|accessdate=2007-06-19}}</ref> Some, such as the ] ], developed advanced agriculture, grand architecture, and state-level societies. After Europeans began settling the Americas, ] from epidemics of imported diseases such as ].<ref>{{Cite journal|author=Meltzer, D.J.|year=1992|title=How Columbus Sickened the New World: Why Were Native Americans So Vulnerable to the Diseases European Settlers Brought With Them?|journal=New Scientist|pages=38|url=http://www.newscientist.com/article/mg13618424.700-how-columbus-sickened-the-new-world-why-were-nativeamericans-so-vulnerable-to-the-diseases-european-settlers-brought-with-them.html}}</ref> | |||
| === Indigenous peoples === | |||
| ]'' transported ] to the New World in 1620, as depicted in William Halsall's ''The Mayflower in Plymouth Harbor'', 1882]] | |||
| {{Main|History of Native Americans in the United States}} | |||
| In 1492, ] explorer ], under contract to the Spanish crown, reached several Caribbean islands, making ] with the indigenous people. On April 2, 1513, Spanish ] ] landed on what he called "]"—the first documented European arrival on what would become the U.S. mainland. Spanish settlements in the region were followed by ones in the present-day ] that drew thousands through Mexico. French ]rs established outposts of ] around the ]; France eventually claimed much of the North American interior, down to the Gulf of Mexico. The first successful English settlements were the ] in ] in 1607 and the ]s' ] in 1620. The 1628 chartering of the ] resulted in a wave of migration; by 1634, ] had been settled by some 10,000 ]s. Between the late 1610s and the American Revolution, about 50,000 convicts were shipped to Britain's American colonies.<ref>{{cite web|work=Butler, James Davie|url=http://www.dinsdoc.com/butler-1.htm|title=British Convicts Shipped to American Colonies|publisher=Smithsonian Institution, National Museum of Natural History|work=American Historical Review 2|month=October|year=1896|accessdate=2007-06-21}}</ref> Beginning in 1614, the Dutch settled along the lower ], including ] on ]. | |||
| {{Further|Native Americans in the United States|Pre-Columbian era}} | |||
| ], a settlement of ] the ] ] in present-day ], built between {{Circa|1200 and 1275}}<ref> at Colorado Encyclopedia. Retrieved January 31, 2024</ref>]] | |||
| In 1674, the Dutch ceded their American territory to England; the province of ] was renamed New York. Many new immigrants, especially to ], were ]s—some two-thirds of all Virginia immigrants between 1630 and 1680.<ref>Russell, David Lee (2005). ''The American Revolution in the Southern Colonies''. Jefferson, N.C., and London: McFarland, p. 12. ISBN 0786407832.</ref> By the turn of the century, ] were becoming the primary source of bonded labor. With the 1729 division of ] and the 1732 colonization of ], the thirteen British colonies that would become the United States of America were established. All had local governments with elections open to most free men, with a growing devotion to the ancient ] and a sense of self-government stimulating support for ]. All legalized the ]. With high birth rates, low death rates, and steady immigration, the colonial population grew rapidly. The ]ist movement of the 1730s and 1740s known as the ] fueled interest in both religion and religious liberty. In the ], British forces seized Canada from the French, but the ] population remained politically isolated from the southern colonies. Excluding the ] (popularly known as "American Indians"), who were being displaced, those thirteen colonies had a population of 2.6 million in 1770, about one-third that of Britain; nearly one in five Americans were black slaves.<ref>Blackburn, Robin (1998). ''The Making of New World Slavery: From the Baroque to the Modern, 1492–1800''. London and New York: Verso, p. 460. ISBN 1859841953.</ref> Though ], the American colonials had no representation in the ]. | |||
| The ] migrated from ] across the ] about 12,000 years ago;{{sfn|Erlandson|Rick|Vellanoweth|2008|p=19}}{{sfn|Savage|2011|page=55}} the ], which appeared around 11,000 BC, is believed to be the first widespread culture in the Americas.{{sfn|Waters|Stafford|2007|pages=1122–1126}}{{sfn|Flannery|2015|pages=173–185}} Over time, indigenous North American cultures grew increasingly sophisticated, and some, such as the ], developed ], ], and ].{{sfn|Lockard|2010|page=315}} In the ], the Mississippian cultures were located in the ], ], and ] regions, and the ] in the ] and along the ], while the ] and ] inhabited the ].<ref>{{cite book |last=Johansen |first=Bruce |title=The Native Peoples of North America: A History, Volume 1 |year=2006 |publisher=Rutgers University Press |isbn=978-0-8135-3899-0 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=yiKgBuSUPUIC&dq=native+american+history+archaic+period&pg=PA51}}</ref> ] of what is now the United States before the arrival of European immigrants range from around 500,000{{sfn|Thornton|1998|page=34}}{{sfn|Perdue|Green|2005|page=40}} to nearly 10 million.{{sfn|Perdue|Green|2005|page=40}}{{sfn|Haines|Haines|Steckel|2000|page=12}} | |||
| === European settlement and conflict (1607–1765) === | |||
| ===Independence and expansion=== | |||
| {{Main|Colonial history of the United States|Colonial American military history}} | |||
| {{seealso|American Revolution|American Revolutionary War|Manifest Destiny}} | |||
| {{See also|European colonization of the Americas}} | |||
| ]'', by ], 1817–18]] | |||
| ] of ] (in pink and purple), ] (in blue), and ] (in orange) in present-day ] and the United States]] | |||
| Tensions between American colonials and the British during the ] of the 1760s and early 1770s led to the ], fought from 1775 through 1781. On June 14, 1775, the ], convening in ], established a ] under the command of ]. Proclaiming that "]" and endowed with "certain ]," the Congress adopted the ], drafted largely by ], on July 4, 1776. That date is now celebrated annually as America's ]. In 1777, the ] established a weak federal government that operated until 1789. | |||
| ] began exploring the ] for Spain in 1492, leading to ] from Puerto Rico and Florida to ] and ].<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Davis |first1=Frederick T. |year=1932 |title=The Record of Ponce de Leon's Discovery of Florida, 1513 |url=http://palmm.digital.flvc.org/islandora/object/ucf%3A21231 |journal=The QUARTERLY Periodical of THE FLORIDA HISTORICAL SOCIETY |volume=XI |issue=1 |pages=5–6}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |author=Florida Center for Instructional Technology |url=https://fcit.usf.edu/florida/lessons/menendz/menendz1.htm |title=A Short History of Florida |date=2002 |publisher=University of South Florida |chapter=Pedro Menendez de Aviles Claims Florida for Spain}}<!--Online textbook for Florida public schools.--></ref><ref>{{cite web |date=February 28, 2015 |title=Not So Fast, Jamestown: St. Augustine Was Here First |url=https://www.npr.org/2015/02/28/389682893/not-so-fast-jamestown-st-augustine-was-here-first |access-date=March 5, 2021 |publisher=NPR |language=en}}</ref> ] established ] along the ], ] and ].<ref name="Petto20072">{{cite book |author=Petto |first=Christine Marie |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9ZiaAAAAQBAJ&pg=PA125 |title=When France Was King of Cartography: The Patronage and Production of Maps in Early Modern France |publisher=Lexington Books |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-7391-6247-7 |page=125}}</ref> ] of the ] began with the ] (1607) and ] (1620).<ref name="Jr.Selby20182">{{cite book |last1=Seelye |first1=James E. Jr. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=YgVnDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA344 |title=Shaping North America: From Exploration to the American Revolution [3 volumes] |last2=Selby |first2=Shawn |publisher=ABC-CLIO |year=2018 |isbn=978-1-4408-3669-5 |page=344}}</ref><ref name="BellahSullivan20062">{{cite book |last1=Bellah |first1=Robert Neelly |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=5DQHmykT6u4C&pg=PA220 |title=Habits of the Heart: Individualism and Commitment in American Life |last2=Madsen |first2=Richard |last3=Sullivan |first3=William M. |last4=Swidler |first4=Ann |last5=Tipton |first5=Steven M. |publisher=University of California Press |year=1985 |isbn=978-0-520-05388-5 |page=220 |ol=7708974M}}</ref> The ] and the ] established precedents for representative ] and ] that would develop throughout the American colonies.<ref name="Remini2–32">{{Harvard citation no brackets|Remini|2007|pp=2–3}}</ref><ref name="Johnson26–302">{{Harvard citation no brackets|Johnson|1997|pp=26–30}}</ref> While European settlers in what is now the United States experienced conflicts with Native Americans, they also engaged in trade, exchanging European tools for food and animal pelts.<ref>], p. 6</ref>{{efn|From the late 15th century, the ] had been catastrophic for native populations throughout the Americas. It is estimated ], especially in the Caribbean, ];<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Ehrenpreis |first1=Jamie E. |last2=Ehrenpreis |first2=Eli D. |date=April 2022 |title=A Historical Perspective of Healthcare Disparity and Infectious Disease in the Native American Population |journal=The American Journal of the Medical Sciences |volume=363 |issue=4 |pages=288–294 |doi=10.1016/j.amjms.2022.01.005 |issn=0002-9629 |pmc=8785365 |pmid=35085528}}</ref> remaining populations were often displaced by European expansion.{{sfn|Joseph|2016|page=590}}<ref>] p. ]</ref>}} Relations ranged from close cooperation to warfare and massacres. The colonial authorities often pursued policies that forced Native Americans to adopt European lifestyles, including conversion to Christianity.<ref>] p. 5</ref><ref>], p. 55</ref> Along the eastern seaboard, settlers ] through the ].<ref>{{Cite book |last=Thomas |first=Hugh |url=https://archive.org/details/slavetradestoryo00thom/page/516 |title=The Slave Trade: The Story of the Atlantic Slave Trade: 1440{{ndash}}1870 |publisher=Simon and Schuster |year=1997 |isbn=0-684-83565-7 |pages= |url-access=registration}}</ref> | |||
| After the ] by American forces ], Great Britain ] and the states' ] over American territory west to the ]. A ] was organized in 1787 by those wishing to establish a strong national government, with powers of taxation. The ] was ratified in 1788, and the new republic's ], and ]—George Washington—took office in 1789. The ], forbidding federal restriction of personal freedoms and guaranteeing a range of legal protections, was adopted in 1791. | |||
| The original ]{{efn|], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]}} that would later found the United States were administered as possessions of ],<ref name="BilhartzElliott20072">{{cite book |author1=Bilhartz, Terry D. |url=https://archive.org/details/currentsinameric0000bilh |title=Currents in American History: A Brief History of the United States |author2=Elliott, Alan C. |publisher=M.E. Sharpe |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-7656-1817-7 |url-access=registration}}</ref> and had ].<ref name="Wood19982">{{cite book |author=Wood |first=Gordon S. |url=https://archive.org/details/creationofameric0000wood_r7v4 |title=The Creation of the American Republic, 1776–1787 |publisher=UNC Press Books |year=1998 |isbn=978-0-8078-4723-7 |page=263}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last=Ratcliffe |first=Donald |year=2013 |title=The Right to Vote and the Rise of Democracy, 1787–1828 |journal=Journal of the Early Republic |volume=33 |issue=2 |page=220 |doi=10.1353/jer.2013.0033 |s2cid=145135025 | issn=0275-1275}}</ref> The colonial population grew rapidly, eclipsing Native American populations;<ref>], pp. 38–39</ref> by the 1770s, the natural increase of the population was such that only a small minority of Americans had been born overseas.<ref>], p. 35</ref> The colonies' distance from Britain allowed for the development of self-governance,<ref>{{cite book |author=Otis |first=James |url=https://archive.org/details/cihm_52678 |title=The Rights of the British Colonies Asserted and Proved |year=1763 |isbn=978-0-665-52678-7}}</ref> and the ], a series of ]s, fueled colonial interest in ].<ref>{{cite book |last1=Foner |first1=Eric |url=https://archive.org/details/storyofamericanf00fone |title=The Story of American Freedom |date=1998 |publisher=W.W. Norton |isbn=978-0-393-04665-6 |edition=1st |pages=–5 |quote=story of American freedom. |url-access=registration}}</ref> | |||
| Attitudes toward ] were shifting; a ] protected the African slave trade only until 1808. The Northern states abolished slavery between 1780 and 1804, leaving the ]s of the South as defenders of the "]." The ], beginning about 1800, made ] a force behind various social ]s, including ]. | |||
| For a century, the American colonists ], especially France, and the Americans had begun to develop a sense of self-defense and self-reliance separate from Britain. The ] (1754–1763) took on new significance for all North American colonists after Parliament under ] concluded that major military resources needed to be devoted to North America to win the war against France. The British colonies' position as an integral part of the ] became more apparent during the war, with British military and civilian officials becoming a more significant presence in American life. | |||
| ] | |||
| Americans' eagerness to ] prompted a long series of ] and an ] policy that stripped the native peoples of their land. The ] of French-claimed territory under President Thomas Jefferson in 1803 almost doubled the nation's size. The ], declared against Britain over various grievances and fought to a draw, strengthened U.S. ]. A series of U.S. military incursions into Florida led ] it and other Gulf Coast territory in 1819. The United States annexed the ] in 1845. The concept of ] was popularized during this time.<ref>Morrison, Michael A. (1999). ''Slavery and the American West: The Eclipse of Manifest Destiny and the Coming of the Civil War''. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, pp. 13–21. ISBN 0807847968.</ref> The 1846 ] with Britain led to U.S. control of the present-day ]. The U.S. victory in the ] resulted in the 1848 ] of ] and much of the present-day ]. The ] of 1848–49 further spurred western migration. ] made relocation easier for settlers and increased conflicts with Native Americans. Over a half-century, up to 40 million ], or buffalo, were slaughtered for skins and meat and to ease the railways' spread. The loss of the buffalo, a primary resource for the ], was an existential blow to many native cultures. | |||
| ===American Revolution and the early republic (1765–1800)=== | |||
| ===Civil War and industrialization=== | |||
| {{ |
{{Main|American Revolution|American Revolutionary War}} | ||
| {{Further|History of the United States (1776–1789)|History of the United States (1789–1815)}} | |||
| ]'', lithograph by ], ca. 1863]] | |||
| ]'', a portrait by ] depicting the ] presenting the draft of ] to the ] on June 28, 1776, in ]]] | |||
| ] between slave and ] mounted with arguments over the relationship between the ], as well as ] over the spread of slavery into new states. ], candidate of the largely antislavery ], was elected president in 1860. Before he took office, seven slave states declared their ]—which the federal government maintained was illegal—and formed the ]. With the Confederate ], the ] began and four more slave states joined the Confederacy. Lincoln's ] committed the ] to ending slavery. Following the Union victory in 1865, three amendments to the U.S. Constitution ] for the nearly four million ]s who had been slaves,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www2.census.gov/prod2/decennial/documents/1860a-02.pdf|title=1860 Census|publisher=U.S. Census Bureau|accessdate=2007-06-10}} Page 7 lists a total slave population of 3,953,760.</ref> ], and ]. The war and its resolution led to a substantial increase in ].<ref>De Rosa, Marshall L. (1997). ''The Politics of Dissolution: The Quest for a National Identity and the American Civil War''. Edison, NJ: Transaction, p. 266. ISBN 1560003499.</ref> | |||
| Following their victory in the French and Indian War, Britain began to assert greater control over local colonial affairs, resulting in ]; one of the primary colonial grievances was a denial of their ], particularly the right to ]. To demonstrate their dissatisfaction and resolve, the ] met in 1774 and passed the ], a colonial boycott of British goods that proved effective. The British attempt to then disarm the colonists resulted in the 1775 ], igniting the ]. At the ], the colonies appointed ] commander-in-chief of the ], and created ] that named ] to draft the ]. Two days after passing the ] to create an independent nation the Declaration was adopted on July 4, 1776.<ref name="YoungNash20112">{{cite book |author1=Fabian Young, Alfred |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=QEzaLJ4u_MEC&pg=PA4 |title=Revolutionary Founders: Rebels, Radicals, and Reformers in the Making of the Nation |author2=Nash, Gary B. |author3=Raphael, Ray |publisher=Random House Digital |year=2011 |isbn=978-0-307-27110-5 |pages=4–7}}</ref> The ] included ]'','' ]; and the ];<ref>Yick Wo vs. Hopkins, 118 U.S. 356, 370</ref> supporting ] and rejecting ], ], and all hereditary political power; ]; and vilification of ].<ref>Richard Buel, ''Securing the Revolution: Ideology in American Politics, 1789–1815'' (1972)</ref> The ], who included Washington, Jefferson, ], ], ], ], ], ], and many others, were inspired by ], ], and ] philosophies and ideas.<ref>Becker et al (2002), ch 1</ref><ref name="SEoP-2006">{{cite web |date=June 19, 2006 |title=Republicanism |url=https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/republicanism/ |access-date=September 20, 2022 |website=Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy}}</ref> | |||
| The ] ] were ratified in 1781 and established a decentralized government that operated until 1789.<ref name="YoungNash20112" /> After the British surrender at the ] in 1781 American sovereignty was internationally recognized by the ] (1783), through which the U.S. gained territory stretching west to the Mississippi River, north to present-day Canada, and south to ].<ref>{{cite web |editor-last=Miller |editor-first=Hunter |title=British-American Diplomacy: The Paris Peace Treaty of September 30, 1783 |url=http://avalon.law.yale.edu/18th_century/paris.asp |publisher=The Avalon Project at Yale Law School}}</ref> The ] (1787) established the precedent by which the country's territory would expand with the ], rather than the expansion of existing states.<ref>Shōsuke Satō, '''', Johns Hopkins University, (1886), p. 352</ref> The ] was drafted at the 1787 ] to overcome the limitations of the Articles. It went into effect in 1789, creating a ] governed by ] that together ensured a system of ].{{sfn|Foner|2020|p=524}} George Washington ] the country's first president under the Constitution, and the ] was adopted in 1791 to allay skeptics' concerns about the power of the more centralized government.{{sfn|OpenStax|2014|loc=§ }}{{sfn|Foner|2020|pp=538-540}} ] after the Revolutionary War and his later refusal to run for a third term as the country's first president established a precedent for the supremacy of civil authority in the United States and the ].<ref name="BoyerJr.20072">], pp. 192–193</ref>{{sfn|OpenStax|2014|loc=§ }} | |||
| ], New York, 1902]] | |||
| After the war, the ] ] ] policies aimed at reintegrating and rebuilding the Southern states while ensuring the rights of the newly freed slaves. The resolution of the disputed ] by the ] ended Reconstruction; ] soon ]. In the North, urbanization and an unprecedented ] from ] and ] hastened the ]. The wave of immigration, lasting until 1929, provided labor and transformed American culture. National infrastructure development spurred economic growth. The 1867 ] from Russia completed the country's mainland expansion. The ] in 1890 was the last major armed conflict of the Indian Wars. In 1893, the ] of the Pacific ] was overthrown in a coup led by American residents; the United States annexed the archipelago in 1898. Victory in the ] the same year demonstrated that the United States was a ] and led to the annexation of Puerto Rico, Guam, and the ].<ref>{{cite web|author=Gates, John M.|url=http://www3.wooster.edu/History/jgates/book-ch3.html|title=War-Related Deaths in the Philippines|work=Pacific Historical Review|publisher=College of Wooster|date=August 1984|accessdate=2007-09-27}}</ref> The Philippines gained independence a half-century later; Puerto Rico and Guam remain U.S. territories. | |||
| === |
===Westward expansion and Civil War (1800–1865)=== | ||
| {{ |
{{Further||History of the United States (1815–1849)|History of the United States (1849–1865)}} | ||
| ]]] | |||
| ] during the ], 1936]] | |||
| ]: | |||
| At the outbreak of ] in 1914, the United States remained neutral. Most Americans sympathized with the British and French, although many opposed intervention.<ref>Foner, Eric, and John A. Garraty (1991). ''The Reader's Companion to American History.'' New York: Houghton Mifflin, p. 576. ISBN 0395513723.</ref> In 1917, the United States joined the ], turning the tide against the ]. After the war, the Senate did not ratify the ], which established the ]. The country pursued a policy of ], verging on ].<ref>McDuffie, Jerome, Gary Wayne Piggrem, and Steven E. Woodworth (2005). ''U.S. History Super Review''. Piscataway, NJ: Research & Education Association, p. 418. ISBN 0738600709.</ref> In 1920, the ] movement won passage of a ] granting ]. The prosperity of the ] ended with the ] that triggered the ]. After his election as president in 1932, ] responded with the ], a range of policies increasing government intervention in the economy. The ] of the mid-1930s impoverished many farming communities and spurred a new wave of western migration. | |||
| {{legend|#204A87|]}} | |||
| ] ] ] on ], June 6, 1944]] | |||
| {{legend|#729FCF|]}} | |||
| The United States, effectively neutral during ]'s early stages after ]'s ] in September 1939, began supplying ] to the ] in March 1941 through the ] program. On December 7, 1941, the ] launched a surprise ], prompting the United States to join the Allies against the ]. Participation in the war spurred capital investment and industrial capacity. Among the major combatants, the United States was the only nation to become richer—indeed, far richer—instead of poorer because of the war.<ref>Kennedy, Paul (1989). ''The Rise and Fall of the Great Powers''. New York: Vintage, p. 358. ISBN 0670728197.</ref> Allied conferences at ] and ] outlined a new system of international organizations that placed the ] and ] at the center of world affairs. As ], a 1945 ] held in ] produced the ], which became active after the war.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.state.gov/r/pa/ho/pubs/fs/55407.htm|title=The United States and the Founding of the United Nations, August 1941–October 1945|month=October|year=2005|accessdate=2007-06-11|publisher=U.S. Dept. of State, Bureau of Public Affairs, Office of the Historian}}</ref> The United States, having ], used them on the Japanese cities of ] in August. ] on September 2, ending the war.<ref>Pacific War Research Society (2006). ''Japan's Longest Day''. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 4770028873.</ref> | |||
| {{legend|#A40000|]}} | |||
| {{legend|#D3D7CF|]}}]] | |||
| The ] of 1803 from France nearly doubled the territory of the United States.<ref>{{cite web |title=Louisiana Purchase |url=https://www.nps.gov/jeff/historyculture/upload/louisiana_purchase.pdf |access-date=March 1, 2011 |publisher=National Park Service}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Harriss |first=Joseph A. |title=How the Louisiana Purchase Changed the World |url=https://www.smithsonianmag.com/history/how-the-louisiana-purchase-changed-the-world-79715124/ |access-date=June 25, 2024 |website=Smithsonian Magazine |language=en}}</ref> ], leading to the ], which was fought to a draw.<ref name="Wait19992">{{cite book |last=Wait |first=Eugene M. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=puuQ30N0EsIC&pg=PA78 |title=America and the War of 1812 |publisher=Nova Publishers |year=1999 |isbn=978-1-56072-644-9 |page=78}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=April 10, 2024 |title=War of 1812 |url=http://public2.nhhcaws.local/browse-by-topic/wars-conflicts-and-operations/1812.html |access-date=June 25, 2024 |website=] |language=en-US }}{{Dead link|date=November 2024 |bot=InternetArchiveBot |fix-attempted=yes }}</ref> ] and its Gulf Coast territory in 1819.<ref name="KloseJones19942">{{cite book |author1=Klose, Nelson |url=https://archive.org/details/unitedstateshist00klos_0/page/150 |title=United States History to 1877 |author2=Jones, Robert F. |publisher=Barron's Educational Series |year=1994 |isbn=978-0-8120-1834-9 |page=}}</ref> In the late 18th century, American settlers began to ], many with a sense of ].<ref name="MD20072">{{Cite book |last1=Carlisle |first1=Rodney P. |url=https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/659807062 |title=Manifest destiny and the expansion of America |last2=Golson |first2=J. Geoffrey |date=2007 |publisher=ABC-CLIO |isbn=978-1-85109-834-7 |series=Turning Points in History Series |location=Santa Barbara, Calif. |page=238 |oclc=659807062}}</ref>{{Sfn|McPherson|1988|p=41–46}} The ] attempted to balance the desire of northern states to prevent the expansion of slavery into new territories with that of southern states to extend it, admitting ] as a ] and ] as a free state. It further prohibited slavery in all other lands of the Louisiana Purchase north of the ].<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Hammond|first=John Craig|date=March 2019|title=President, Planter, Politician: James Monroe, the Missouri Crisis, and the Politics of Slavery|journal=Journal of American History|volume=105|issue=4|pages=843–867|doi=10.1093/jahist/jaz002}}</ref> As Americans expanded further into land inhabited by Native Americans, the federal government often applied ] of ] or ].<ref>{{Cite book |last=Frymer |first=Paul |url=https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/981954623 |title=Building an American empire : the era of territorial and political expansion |date=2017 |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-4008-8535-0 |location=Princeton, New Jersey |oclc=981954623}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Calloway |first=Colin G. |url=https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/1035393060 |title=First peoples : a documentary survey of American Indian history |date=2019 |publisher=Bedford/St. Martin's, Macmillan Learning |isbn=978-1-319-10491-7 |edition=6th |location=Boston |oclc=1035393060}}</ref> The ] (1830–1850) was a U.S. government policy that forcibly removed and displaced most Native Americans living east of the ] to lands far to the west.{{Sfn|McPherson|1988|p=45}} These and earlier organized displacements prompted a long series of ] west of the Mississippi.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Michno |first=Gregory |title=Encyclopedia of Indian Wars: Western Battles and Skirmishes, 1850–1890 |date=2003 |publisher=Mountain Press Publishing |isbn=978-0-87842-468-9}}</ref><ref name="BillingtonRidge2001j2">{{cite book |author1=Billington, Ray Allen |url=https://archive.org/details/westwardexpansio00bill/page/22 |title=Westward Expansion: A History of the American Frontier |author2=Ridge, Martin |publisher=UNM Press |year=2001 |isbn=978-0-8263-1981-4 |page= |author-link2=Martin Ridge (historian)}}</ref> The ] was ] in 1845,<ref name="Morrison19992">{{cite book |author=Morrison, Michael A. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=YTaxzMlkVEMC&pg=PA13 |title=Slavery and the American West: The Eclipse of Manifest Destiny and the Coming of the Civil War |date=April 28, 1997 |publisher=University of North Carolina Press |isbn=978-0-8078-4796-1 |pages=13–21}}</ref> and the 1846 ] led to U.S. control of the present-day ].<ref name="Kemp20102">{{cite book |author=Kemp, Roger L. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=JHawgM-WnlUC&pg=PA180 |title=Documents of American Democracy: A Collection of Essential Works |publisher=McFarland |year=2010 |isbn=978-0-7864-4210-2 |page=180 |access-date=October 25, 2015}}</ref> Victory in the ] resulted in the 1848 ] of California, Nevada, Utah, and much of present-day Colorado and the ].<ref name="MD20072" /><ref name="McIlwraithMuller20012">{{cite book |author1=McIlwraith, Thomas F. |url=https://archive.org/details/northamericahist00mcil/page/61 |title=North America: The Historical Geography of a Changing Continent |author2=Muller, Edward K. |publisher=Rowman & Littlefield |year=2001 |isbn=978-0-7425-0019-8 |page= |access-date=October 25, 2015}}</ref> The ] of 1848–1849 spurred a huge migration of white settlers to the Pacific coast, leading to even more confrontations with Native populations. One of the most violent, the ] of thousands of Native inhabitants, lasted into the early 1870s,<ref> | |||
| ===Cold War and protest politics=== | |||
| * {{harvnb|Meyer|Snow|Snow|Cohen|Meyer|Thornton|Grinde|Dilworth|2001|loc=From 1800 to 1900}}: "The discovery of gold in California in 1848 proved a momentous watershed for native people in the West. Hordes of single men stampeded to find fortune. Unrestrained by family, community, or church, they decimated the native population near the goldfields. California natives suffered the most complete genocide in U.S. history." | |||
| {{seealso|Cold War|African-American Civil Rights Movement (1955–1968)|Vietnam War}} | |||
| * {{cite web|url=https://newsroom.ucla.edu/stories/revealing-the-history-of-genocide-against-californias-native-americans|title=Revealing the history of genocide against California's Native Americans|last=Wolf|first=Jessica|website=UCLA Newsroom|language=en|access-date=July 8, 2018}} | |||
| ] delivering his "]" speech, 1963]] | |||
| * {{Cite book|last=Madley |first=Benjamin |date=2016 |title=An American Genocide: The United States and the California Indian Catastrophe, 1846-1873. |publisher=Yale University Press |url=https://archive.org/details/americangenocide0000madl |url-access=registration |isbn= 9780300230697}} | |||
| The United States and Soviet Union jockeyed for power after World War II during the ], dominating the military affairs of Europe through ] and the ]. The United States promoted ] and capitalism, while the Soviet Union promoted communism and a centrally ]. Both supported dictatorships and engaged in ]s. American troops fought ] forces in the ] of 1950–53. The ] pursued a series of investigations into suspected leftist subversion, while Senator ] became the figurehead of anticommunist sentiment. | |||
| * {{harvnb|Smithers|2012|p=339}}: "The genocidal intent of California settlers and government officials was acted out in numerous battles and massacres (and aided by technological advances in weaponry, especially after the Civil War), in the abduction and sexual abuse of Indian women, and in the economic exploitation of Indian child labourers" | |||
| * {{harvnb|Blackhawk|2023|p=38}}: "With these works, a near consensus emerged. By most scholarly definitions and consistent with the UN Convention, these scholars all asserted that genocide against at least some Indigenous peoples had occurred in North America following colonisation, perpetuated first by colonial empires and then by independent nation-states"</ref> just as additional western territories and states were created.<ref name="Rawls1999">{{cite book|author=Rawls, James J.|title=A Golden State: Mining and Economic Development in Gold Rush California|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=UPUsIaHZTm0C&pg=PA20|year=1999|publisher=University of California Press|isbn=978-0-520-21771-3|page=20}}</ref> | |||
| During the colonial period, ], though the practice began to be significantly questioned during the American Revolution.{{sfnm|1a1=Walker Howe|1y=2007|1p=52–54|2a1=Wright|2y=2022}} States in ] enacted ],{{sfnm|1a1=Walker Howe|1y=2007|1p=52–54|2a1=Rodriguez|2y=2015|2p=XXXIV|3a1=Wright|3y=2022}} though support for slavery strengthened in ], as inventions such as the ] made the institution increasingly profitable for ].<ref>], p. 43</ref><ref>], pp. 27, 29</ref>{{sfn|Walker Howe|2007|p=478, 481–482, 587–588}} This ] regarding slavery ] in the ] (1861–1865).<ref>{{cite book |last=Murray |first=Stuart |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bJ_sy7mmmxQC&pg=PA76 |title=Atlas of American Military History |publisher=Infobase Publishing |year=2004 |isbn=978-1-4381-3025-5 |page=76 |access-date=October 25, 2015}} {{cite book |last=Lewis |first=Harold T. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=kr-xNru5vZkC&pg=PA53 |title=Christian Social Witness |publisher=Rowman & Littlefield |year=2001 |isbn=978-1-56101-188-9 |page=53}}</ref><ref name="Woods 2012 pp. 415–4392">{{cite journal |last=Woods |first=Michael E. |year=2012 |title=What Twenty-First-Century Historians Have Said about the Causes of Disunion: A Civil War Sesquicentennial Review of the Recent Literature |url=http://www.jstor.org/stable/44306803 |journal=The Journal of American History |publisher= |volume=99 |issue=2 |pages=415–439 |doi=10.1093/jahist/jas272 |issn=0021-8723 |jstor=44306803 |access-date=April 29, 2023}}</ref> Eleven slave states ] and formed the ], while the other states remained in ].<ref name="Silkenat 2019 p. 252">{{cite book |last=Silkenat |first=D. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=nHWKDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA25 |title=Raising the White Flag: How Surrender Defined the American Civil War |publisher=University of North Carolina Press |year=2019 |isbn=978-1-4696-4973-3 |series=Civil War America |page=25 |access-date=April 29, 2023}}</ref>{{Sfn|McPherson|1988|p=236}} War broke out in April 1861 after the Confederates ].<ref>{{cite book |last=Vinovskis |first=Maris |title=Toward A Social History of the American Civil War: Exploratory Essays |date=1990 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |isbn=978-0-521-39559-5 |location=Cambridge; New York |page=4}}</ref>{{Sfn|McPherson|1988|pp=273–274}} After the January 1863 ], many freed slaves joined the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.archives.gov/education/lessons/blacks-civil-war/ |title=The Fight for Equal Rights: Black Soldiers in the Civil War|work=]|date=August 15, 2016|quote=By the end of the Civil War, roughly 179,000 black men (10% of the Union army) served as soldiers in the U.S. Army and another 19,000 served in the Navy.}}</ref> The war ] following the 1863 ] and ], and the Confederacy surrendered in 1865 after the Union's victory in the ].<ref>Davis, Jefferson. , 1890, 2010. {{ISBN|978-1-175-82358-8}}. Available free online as an ebook. Chapter LXXXVIII, "Re-establishment of the Union by force", p. 503. Retrieved March 14, 2012.</ref> The ] followed the war. After ] of President ], ] were passed to ]. National infrastructure, including ] and ], spurred growth in the ].<ref name="Black2011kj2">{{cite book |last=Black |first=Jeremy |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=EIst_CSWOqIC&pg=PA275 |title=Fighting for America: The Struggle for Mastery in North America, 1519–1871 |publisher=Indiana University Press |year=2011 |isbn=978-0-253-35660-4 |page=275 |author-link=Jeremy Black (historian)}}</ref> | |||
| The 1961 Soviet launch of the ] prompted President ]'s call for the United States to be first to land ] achieved in 1969. Kennedy also faced a ] with Soviet forces in Cuba. Meanwhile, the United States experienced sustained economic expansion. A growing ], led by African Americans such as ] and ], fought segregation and discrimination. Following ] in 1963, the ] and ] were passed under President ]. Johnson and his successor, ], expanded a proxy war in Southeast Asia into the unsuccessful ]. A widespread ] grew, fueled by ], ], and the ]. ], ], and others led a ] that sought political, social, and economic equality for women. | |||
| === Post–Civil War era (1865–1917) === | |||
| As a result of the ], in 1974 Nixon became the first U.S. president to resign, to avoid being ] on charges including obstruction of justice and abuse of power; he was ] by Vice President ]. The ] administration of the late 1970s was marked by ] and the ]. The election of ] as president in 1980 heralded a ], reflected in major changes in ]. His second term in office brought both the ] and significant ]. The subsequent Soviet collapse ended the Cold War. | |||
| {{Main|History of the United States (1865–1917)}} | |||
| ] film showing immigrants arriving at ] in ], a major point of entry for European ] in the late 19th and early 20th centuries<ref name="PriceBenton-Short2008">{{cite book|first1=Marie|last1=Price|first2=Lisa|last2=Benton-Short|title=Migrants to the Metropolis: The Rise of Immigrant Gateway Cities|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=_Tb5HMB63xAC&pg=PA51|year=2008|publisher=Syracuse University Press|isbn=978-0-8156-3186-6|page=51}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=March 4, 2020 |title=Overview + History {{!}} Ellis Island |url=https://www.statueofliberty.org/ellis-island/overview-history/ |access-date=September 10, 2021 |website=Statue of Liberty & Ellis Island |language=en}}</ref>]] | |||
| From 1865 through 1917, an unprecedented stream of immigrants arrived in the United States, including 24.4 million from Europe.<ref>U.S. Bureau of the Census, ''Historical Statistics of the United States'' (1976) series C89–C119, pp. 105–109</ref> Most came through the ], and New York City and other large cities on the ] became home to large ], ], and ] populations, while many ] and Central Europeans moved to the ]. At the same time, about one million ] migrated from ] to ].<ref>Stephan Thernstrom, ed., ''Harvard Encyclopedia of American Ethnic Groups'' (1980) covers the history of all the main groups</ref> During the ], millions of African Americans ] for urban areas in the North.<ref>{{Cite web |date=May 20, 2021 |title=The Great Migration (1910–1970) |url=https://www.archives.gov/research/african-americans/migrations/great-migration |publisher=National Archives}}</ref> ] from ] in 1867.<ref>{{cite web |title=Purchase of Alaska, 1867 |url=https://history.state.gov/milestones/1866-1898/alaska-purchase |access-date=December 23, 2014 |website=Office of the Historian |publisher=U.S. Department of State}}</ref> | |||
| ===Contemporary era=== | |||
| {{seealso|September 11 attacks|Iraq War|Late 2000s recession}} | |||
| ] on the morning of ]]] | |||
| The leadership role taken by the United States and its allies in the UN–sanctioned ], under President ], and the ], under President ], helped to preserve its position as a superpower. The longest economic expansion in modern U.S. history—from March 1991 to March 2001—encompassed the Clinton administration and the ].<ref>{{cite web|author=Voyce, Bill|url=http://iwin.iwd.state.ia.us/iowa/ArticleReader?itemid=00003700&print=1|title=Why the Expansion of the 1990s Lasted So Long|publisher=Iowa Workforce Information Network|date=2006-08-21|accessdate=2007-08-16}}</ref> A ] and ] led to ] in 1998, but he remained in office. The ], one of the closest in U.S. history, was resolved by a ]—], son of George H. W. Bush, became president. | |||
| The ] effectively ended Reconstruction and ].<ref>{{cite book |last=Woodward |first=C. Vann |title=Reunion and Reaction: The Compromise of 1877 and the End of Reconstruction |date=1991 |publisher=Oxford University Press |location=United Kingdom}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |author1=Drew Gilpin Faust |author-link=Drew Gilpin Faust |author2=Eric Foner |author2-link=Eric Foner |author3=Clarence E. Walker |author3-link=Clarence E. Walker |title=White Southern Responses to Black Emancipation |url=http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/americanexperience/features/reconstruction-white-southern-responses-black-emancipation/ |work=]}}</ref> African Americans endured a period of heightened, overt racism following Reconstruction, a time often called the ].<ref name="ReferenceA2">{{cite book |last=Trelease |first=Allen W. |title=White Terror: The Ku Klux Klan Conspiracy and Southern Reconstruction |publisher=Harper & Row |year=1979 |isbn=0-313-21168-X |location=New York}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |author=Shearer Davis Bowman |url=https://archive.org/details/masterslordsmid10000bowm |title=Masters and Lords: Mid-19th-Century U.S. Planters and Prussian Junkers |publisher=Oxford UP |year=1993 |isbn=978-0-19-536394-4 |page= |url-access=registration}}</ref> A series of Supreme Court decisions, including '']'', emptied the Fourteenth and Fifteenth Amendments of their force, allowing ] in the South to remain unchecked, ]s in the Midwest, and ], which would be reinforced by the policy of ] later adopted by the federal ].<ref>{{cite journal |title=Plessy's Legacy: The Government's Role in the Development and Perpetuation of Segregated Neighborhoods |last=Ware |first=Leland |journal=RSF: The Russell Sage Foundation Journal of the Social Sciences |date=February 2021 |pages=92–109 |volume=7 |issue=1 |doi=10.7758/rsf.2021.7.1.06 |s2cid=231929202 }}</ref> | |||
| On ], ] terrorists struck the ] in New York City and ] near Washington, D.C., killing nearly three thousand people. In response, the ] launched a "]". In late 2001, U.S. forces led an ], removing the ] government and al-Qaeda training camps. Taliban insurgents continue to fight a guerrilla war. In 2002, the Bush administration began to press for ] in Iraq on ].<ref>{{cite web|title=Many Europeans Oppose War in Iraq|work=USA Today|url=http://www.usatoday.com/news/world/2003-02-14-eu-survey.htm|date=2003-02-14|accessdate=2008-09-01}}{{cite web|author=Springford, John|title='Old’ and ‘New’ Europeans United: Public Attitudes Towards the Iraq War and US Foreign Policy|publisher=Centre for European Reform|url=http://www.cer.org.uk/pdf/back_brief_springford_dec03.pdf|month=December|year=2003|accessdate=2008-09-01}}</ref> Lacking the support of NATO or an explicit UN mandate for military intervention, Bush organized a ]; coalition forces ] ] in 2003, removing dictator and former U.S. ally ]. In 2005, ] caused severe destruction along much of the ], devastating ]. On November 4, 2008, amid a global ], ] was elected president. He is the first African American to hold the office. | |||
| ] accompanied by the exploitation of cheap immigrant labor<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Hirschman |first1=Charles |last2=Mogford |first2=Elizabeth |date=December 1, 2009 |title=Immigration and the American Industrial Revolution From 1880 to 1920 |journal=Social Science Research |volume=38 |issue=4 |pages=897–920 |doi=10.1016/j.ssresearch.2009.04.001 |issn=0049-089X |pmc=2760060 |pmid=20160966}}</ref> led to ], allowing the United States to outpace the economies of England, France, and Germany combined.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Carson |first1=Thomas |last2=Bonk |first2=Mary |title=Gale Encyclopedia of U.S. Economic History |date=1999 |publisher=Gale |chapter=Industrial Revolution}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Riggs |first1=Thomas |title=Gale Encyclopedia of U.S. Economic History Vol. 3 |date=2015 |publisher=Gale |page=1179 |edition=2}}</ref> This fostered the amassing of power by ], largely by their formation of ] and ] to prevent competition.<ref name="Atlantic2">{{Cite journal |last=Dole |first=Charles F. |year=1907 |title=The Ethics of Speculation |journal=] |volume=C |issue=December 1907 |pages=812–818}}</ref> ]s led the nation's expansion in the ], ], and ] industries. The United States emerged as a pioneer of the ].<ref>{{cite web |author1=The Pit Boss |date=February 26, 2021 |title=The Pit Stop: The American Automotive Industry Is Packed With History |url=https://pitstop.rumbleon.com/american-automotive-history |access-date=December 5, 2021 |website=Rumble On}}</ref> These changes were accompanied by significant increases in ], ], and ], creating the environment for ].<ref>Tindall, George Brown and Shi, David E. (2012). ''America: A Narrative History (Brief Ninth Edition) (Vol. 2).'' ]. {{ISBN|978-0-393-91267-8}}, p. 589</ref><ref>], pp. 321–357</ref><ref name="Fraser2">{{cite book |last=Fraser |first=Steve |title=The Age of Acquiescence: The Life and Death of American Resistance to Organized Wealth and Power |publisher=] |year=2015 |isbn=978-0-316-18543-1 |page=66}}</ref> This period eventually ended with the advent of the ], which was characterized by significant reforms.<ref name="Aldrich2">Aldrich, Mark. ''Safety First: Technology, Labor and Business in the Building of Work Safety, 1870-1939.'' Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 1997. {{ISBN|0-8018-5405-9}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Progressive Era to New Era, 1900-1929 {{!}} U.S. History Primary Source Timeline {{!}} Classroom Materials at the Library of Congress {{!}} Library of Congress |url=https://www.loc.gov/classroom-materials/united-states-history-primary-source-timeline/progressive-era-to-new-era-1900-1929/overview/ |access-date=November 11, 2023 |website=Library of Congress, Washington, D.C. 20540 USA}}</ref> | |||
| ==Government and elections== | |||
| {{Main|Federal government of the United States|Elections in the United States}} | |||
| ], which houses the ]]] | |||
| The United States is the world's oldest surviving ]. It is a ], "in which ] is tempered by ] protected by ]."<ref>Scheb, John M., and John M. Scheb II (2002). ''An Introduction to the American Legal System''. Florence, KY: Delmar, p. 6. ISBN 0766827593.</ref> It is fundamentally structured as a ], though U.S. citizens residing in the territories are excluded from voting for federal officials.<ref>Raskin, James B. (2003). ''Overruling Democracy: The Supreme Court Vs. the American People''. London and New York: Routledge, pp. 36–38. ISBN 0415934397.</ref> The government is regulated by a system of ] defined by the U.S. Constitution, which serves as the country's supreme legal document. In the ], citizens are usually subject to ], federal, state, and local; the ]'s duties are commonly split between ] and municipal governments. In almost all cases, executive and legislative officials are elected by a ] of citizens by district. There is no ] at the federal level, and it is very rare at lower levels. Federal and state judicial and ] officials are typically nominated by the executive branch and approved by the legislature, although some state judges and officials are elected by popular vote. | |||
| ], home and workplace of the ]]] | |||
| The federal government is composed of three branches: | |||
| *]: The ] ], made up of the ] and the ], makes ], ], approves treaties, has the ], and has the power of ], by which it can remove sitting members of the government. | |||
| *]: The ] is the ] of the military, can veto ] before they become law, and appoints the ] and other officers, who administer and enforce federal laws and policies. | |||
| *]: The ] and lower ], whose judges are appointed by the president with Senate approval, interpret laws and overturn those they find ]. | |||
| ]]] | |||
| The House of Representatives has 435 members, each representing a ] for a two-year term. House seats are ] among the states by population every tenth year. As of the ], seven states have the minimum of one representative, while California, the most populous state, has fifty-three. The Senate has 100 members with each state having two senators, elected ] to six-year terms; one third of Senate seats are up for election every other year. The president serves a four-year term and may be elected to the office ]. The president is ], but by an indirect ] system in which the determining votes are apportioned by state. The Supreme Court, led by the ], has nine members, who serve for life. The state governments are structured in roughly similar fashion; ] uniquely has a ] legislature. The ] (chief executive) of each state is directly elected. | |||
| Pro-American elements in Hawaii ]; the islands ] in 1898. That same year, ], ], and ] were ceded to the U.S. by Spain after the latter's defeat in the ]. (The Philippines was granted full independence from the U.S. on July 4, 1946, following World War II. Puerto Rico and Guam have remained U.S. territories.)<ref>{{cite web |title=The Spanish–American War, 1898 |url=https://history.state.gov/milestones/1866-1898/spanish-american-war |access-date=December 24, 2014 |website=Office of the Historian |publisher=U.S. Department of State}}</ref> ] was acquired by the United States in 1900 after the ].<ref>Ryden, George Herbert. ''The Foreign Policy of the United States in Relation to Samoa''. New York: Octagon Books, 1975.</ref> The ] were purchased from ] in 1917.<ref>{{cite web |title=Virgin Islands History |url=https://www.vinow.com/general_usvi/history/ |access-date=January 5, 2018 |publisher=Vinow.com}}</ref> | |||
| All laws and procedures of both state and federal governments are subject to review, and any law ruled in violation of the Constitution by the judiciary is voided. The original text of the Constitution establishes the structure and responsibilities of the federal government and its relationship with the individual states. ] protects the right to the "great writ" of ], and ] guarantees the ] in all criminal cases. ] require the approval of three-fourths of the states. The Constitution has been amended twenty-seven times; the first ten amendments, which make up the ], and the ] form the central basis of Americans' individual rights. | |||
| === Rise as a superpower (1917–1945) === | |||
| ===Parties, ideology, and politics=== | |||
| {{Main| |
{{Main|History of the United States (1917–1945)}} | ||
| ] in 1945, part of the ] and the first detonation of a ]. The World Wars permanently ended ] and left it as a ].]] | |||
| ] taking the ] from U.S. Chief Justice ], January 20, 2009]] | |||
| The United States has operated under a ] for most of its history. For elective offices at all levels, state-administered ]s choose the major party nominees for subsequent ]s. Since the ], the major parties have been the ], ], and the ], ]. Since the Civil War, only one ] presidential candidate—former president ], running as a ] in ]—has won as much as 20% of the popular vote. | |||
| The United States ] alongside the ], helping to turn the tide against the ].<ref>McDuffie, Jerome; Piggrem, Gary Wayne; Woodworth, Steven E. (2005). ''U.S. History Super Review''. Piscataway, NJ: Research & Education Association. p. 418. {{ISBN|978-0-7386-0070-3}}.</ref> In 1920, ] granted nationwide ].<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Larson |first1=Elizabeth C. |last2=Meltvedt |first2=Kristi R. |year=2021 |title=Women's suffrage: fact sheet |url=https://crsreports.congress.gov/product/details?prodcode=R45805 |journal=CRS Reports (Library of Congress. Congressional Research Service) |series=Report / Congressional Research Service |access-date=August 9, 2023}}</ref> During the 1920s and '30s, radio for ] and the invention of early television transformed communications nationwide.{{sfn|Winchester|2013|pp=410–411}} The ] triggered the ], which President ] responded to with the ], a series of ] and ] combined with financial reforms and ]. All were intended to protect against future economic depressions.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Axinn |first1=June |title=Social Welfare: A History of the American Response to Need |last2=Stern |first2=Mark J. |publisher=Allyn & Bacon |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-205-52215-6 |edition=7th |location=Boston}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |author=James Noble Gregory |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qNdtGwnXYrIC |title=American Exodus: The Dust Bowl Migration and Okie Culture in California |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=1991 |isbn=978-0-19-507136-8 |access-date=October 25, 2015}} {{cite web |author=<!-- Staff writer(s); no by-line. --> |year=2013 |title=Mass Exodus From the Plains |url=https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/americanexperience/features/general-article/dustbowl-mass-exodus-plains/ |access-date=October 5, 2014 |website=American Experience |publisher=WGBH Educational Foundation}} {{cite web |last1=Fanslow |first1=Robin A. |date=April 6, 1997 |title=The Migrant Experience |url=https://memory.loc.gov/ammem/afctshtml/tsme.html |access-date=October 5, 2014 |website=American Folklore Center |publisher=Library of Congress}} {{cite book |last=Stein |first=Walter J. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hGuGAAAAIAAJ |title=California and the Dust Bowl Migration |publisher=Greenwood Press |year=1973 |isbn=978-0-8371-6267-6 |access-date=October 25, 2015}}</ref> | |||
| Within American ], the Republican Party is considered center-right or "]" and the Democratic Party is considered center-left or "]". The states of the ] and ] and some of the ] states, known as "]", are relatively liberal. The "]" of the ] and parts of the ] and ] are relatively conservative. | |||
| ] during ], the U.S. began ] to the ] in March 1941 and ] in December after the ]'s attack on ].<ref>The official WRA record from 1946 states that it was 120,000 people. See {{cite book |author=] |url=https://ddr.densho.org/ddr-densho-282-5/ |title=The Evacuated People: A Quantitative Study |year=1946 |page=8}} This number does not include people held in other camps such as those run by the DoJ or U.S. Army. Other sources may give numbers slightly more or less than 120,000.</ref><ref name="Pearl Harbor2">{{cite web |last1=Yamasaki |first1=Mitch |title=Pearl Harbor and America's Entry into World War II: A Documentary History |url=https://www.hawaiiinternment.org/static/ush_yamasaki_documentary_history.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141213122046/https://www.hawaiiinternment.org/static/ush_yamasaki_documentary_history.pdf |archive-date=December 13, 2014 |access-date=January 14, 2015 |publisher=World War II Internment in Hawaii}}</ref> The U.S. ] and ] in August 1945, ending the war.<ref>{{Cite news |title=Why did Japan surrender in World War II? |language=en |newspaper=The Japan Times |url=https://www.japantimes.co.jp/opinion/2016/08/06/commentary/japan-surrender-world-war-ii/ |access-date=February 8, 2017}}</ref><ref>Pacific War Research Society (2006). ''Japan's Longest Day''. New York: Oxford University Press. {{ISBN|978-4-7700-2887-7}}.</ref> The United States was one of the "]" who met to plan the ], alongside the ], ], and ].{{sfn|Hoopes|Brinkley|1997|p=100}}{{sfn|Gaddis|1972|p=25}} The U.S. emerged relatively unscathed from the war, with even greater ] and ].<ref>Kennedy, Paul (1989). ''The Rise and Fall of the Great Powers''. New York: Vintage. p. 358. {{ISBN|978-0-679-72019-5}}</ref> | |||
| The winner of the ], Democrat ], is the ] and the first African American to hold the office. All previous presidents were men of solely European descent. The 2008 elections also saw the Democratic Party strengthen its control of both the ] and the ]. In the ], the Senate comprises 58 Democrats, two ] who caucus with the Democrats, and 40 Republicans; the House comprises 256 Democrats and 177 Republicans (two seats are vacant). | |||
| === Cold War (1945–1991) === | |||
| ==Political divisions== | |||
| {{Main| |
{{Main|Cold War}} | ||
| {{ |
{{Further|History of the United States (1945–1964)|History of the United States (1964–1980)|History of the United States (1980–1991)}} | ||
| ] and ] sign the ] at the ] in 1987.]] | |||
| The United States is a ] of fifty states. The original thirteen states were the successors of the ] that rebelled against British rule. Early in the country's history, three new states were organized on territory separated from the claims of the existing states: ] from ]; ] from ]; and ] from ]. Most of the other states have been carved from territories obtained through war or purchase by the U.S. government. One set of exceptions comprises ], ], and ]: each was an independent republic before joining the union. During the ], ] broke away from Virginia. The most recent state—Hawaii—achieved statehood on August 21, 1959. The states ] to ] from the union. | |||
| After World War II, the United States entered the Cold War, where geopolitical tensions between the U.S. and the Soviet Union led the two countries to ].<ref name="Blakemore-20192">{{cite web |last=Blakemore |first=Erin |date=March 22, 2019 |title=What was the Cold War? |url=https://www.nationalgeographic.com/culture/topics/reference/cold-war/ |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190401192349/https://www.nationalgeographic.com/culture/topics/reference/cold-war/ |archive-date=April 1, 2019 |access-date=August 28, 2020 |website=National Geographic |language=en}}</ref><ref>Mark Kramer, "The Soviet Bloc and the Cold War in Europe," in {{Cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=EyNcCwAAQBAJ&pg=PT174 |title=A Companion to Europe Since 1945 |publisher=Wiley |year=2014 |isbn=978-1-118-89024-0 |editor-last=Larresm |editor-first=Klaus |page=79}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Sempa |first=Francis |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Px4uDwAAQBAJ |title=Geopolitics: From the Cold War to the 21st Century |date=July 12, 2017 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1-351-51768-3}}</ref> The U.S. utilized the policy of ] to limit the USSR's sphere of influence, and prevailed in the ], which culminated with the ] in 1969.<ref>], </ref><ref name="Proxy2">{{cite book |last=Collins |first=Michael |url=https://archive.org/details/liftoff00coll |title=Liftoff: The Story of America's Adventure in Space |publisher=Grove Press |year=1988 |isbn=978-0-8021-1011-4 |location=New York |author-link=Michael Collins (astronaut) |url-access=registration}}</ref> Domestically, the U.S. ], ], and ].{{sfn|Winchester|2013|pp=305–308}} The ] emerged, with ] becoming a prominent leader in the early 1960s.<ref>{{cite web |title=The Civil Rights Movement |url=https://www.pbs.org/johngardner/chapters/4b.html |access-date=January 5, 2019 |publisher=PBS}}</ref> The ] plan of President ]'s administration resulted in groundbreaking and broad-reaching laws, policies and a constitutional amendment to counteract some of the worst effects of lingering ].<ref>{{cite book|first= Alan|last=Brinkley|chapter= Great Society |title=The Reader's Companion to American History|date=January 24, 1991 |editor1=Eric Foner|editor2=John Arthur Garraty|isbn=0-395-51372-3|publisher=Houghton Mifflin Books|page=472}}</ref> The ] in the U.S. brought significant social changes, including the liberalization of attitudes toward ] and ].<ref>{{Cite web |date=August 25, 2022 |title=Playboy: American Magazine |url=https://www.britannica.com/topic/Playboy |access-date=February 2, 2023 |website=] |quote=...the so-called sexual revolution in the United States in the 1960s, marked by greatly more permissive attitudes toward sexual interest and activity than had been prevalent in earlier generations.}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |author=Svetlana Ter-Grigoryan |date=February 12, 2022 |title=The Sexual Revolution Origins and Impact |url=https://study.com/learn/lesson/sexual-liberation-movement-origin-timeline-impact-revolution.html |access-date=April 27, 2023 |website=study.com}}</ref> It also encouraged ] (leading to the ] in 1973) and ] to ] (with the U.S. totally withdrawing in 1975).<ref>{{cite magazine |last=Levy |first=Daniel |date=January 19, 2018 |title=Behind the Protests Against the Vietnam War in 1968 |url=https://time.com/5106608/protest-1968/?amp=true |magazine=] |access-date=May 5, 2021}}</ref> A ] was significantly responsible for the large increase in female paid labor participation during the 1970s, and by 1985 the majority of American women aged 16 and older were employed.<ref>{{cite web|title=Women in the Labor Force: A Databook|url=https://www.bls.gov/cps/wlf-databook-2012.pdf|publisher=U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics|access-date=March 21, 2014|page=11|year=2013}}</ref> The late 1980s and early 1990s saw the ] and the ], which marked the end of the Cold War and ].<ref name="Gaidar2">{{cite book |last=Gaĭdar |first=E.T. |url={{GBUrl|bDSfnxYjVwAC|pg=PA102}} |title=Collapse of an Empire: Lessons for Modern Russia |publisher=] |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-8157-3114-6 |location=Washington, D.C. |pages=190–205}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=Howell |first=Buddy Wayne |title=The Rhetoric of Presidential Summit Diplomacy: Ronald Reagan and the U.S.-Soviet Summits, 1985–1988 |publisher=Texas A&M University |year=2006 |isbn=978-0-549-41658-6 |page=352}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=Kissinger |first=Henry |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=0IZboamhb5EC&pg=PA731 |title=Diplomacy |publisher=Simon & Schuster |year=2011 |isbn=978-1-4391-2631-8 |pages=781–784 |author-link=Henry Kissinger |access-date=October 25, 2015}} {{cite book |last=Mann |first=James |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=BgZyXNIrvB4C&pg=PT12 |title=The Rebellion of Ronald Reagan: A History of the End of the Cold War |publisher=Penguin |year=2009 |isbn=978-1-4406-8639-9 |page=432}}</ref><ref>]</ref> | |||
| === Contemporary (1991–present) === | |||
| The states compose the vast bulk of the U.S. land mass; the two other areas considered integral parts of the country are the District of Columbia, the ] where the capital, Washington, is located; and ], an uninhabited but ] in the Pacific Ocean. The United States also possesses five major overseas territories: ] and the ] in the Caribbean; and ], ], and the ] in the Pacific. Those born in the territories (except for American Samoa) possess ]. | |||
| {{Main|History of the United States (1991–2008)|History of the United States (2008–present)}} | |||
| ] in New York City during the ] in 2001]] | |||
| The 1990s saw the ], a dramatic ], and ]. Throughout this decade, technological innovations such as the ], the evolution of the ] in accordance with ], rechargeable ], the first ] trial, and ] either emerged in the U.S. or were improved upon there. The ] was formally launched in 1990, while ] became the first stock market in the United States to trade online in 1998.<ref>{{Cite web |last=((CFI Team)) |title=NASDAQ |url=https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/career-map/sell-side/capital-markets/nasdaq/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231211163114/https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/career-map/sell-side/capital-markets/nasdaq/ |archive-date=December 11, 2023 |access-date=December 11, 2023 |website=Corporate Finance Institute |language=en-US}}</ref> | |||
| {{USA midsize imagemap with state names}} | |||
| In the ] of 1991, an ] expelled an ] invasion force that had occupied neighboring ].<ref>{{cite book|last=Holsti|first=Ole R.|author-link=Ole R. Holsti|title=American Public Opinion on the Iraq War|page=20|chapter=The United States and Iraq before the Iraq War|date=November 7, 2011|publisher=]|isbn=978-0-472-03480-2}}</ref> The ] on the United States in 2001 by the ] militant organization ] led to the ], and subsequent ] and ].<ref>{{cite news |author=Walsh, Kenneth T. |date=December 9, 2008 |title=The 'War on Terror' Is Critical to President George W. Bush's Legacy |newspaper=U.S. News & World Report |url=https://www.usnews.com/news/articles/2008/12/09/the-war-on-terror-is-critical-to-president-george-w-bushs-legacy |access-date=March 6, 2013}} {{cite book |last=Atkins |first=Stephen E. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=PDDIgWRN_HQC&pg=PA210 |title=The 9/11 Encyclopedia: Second Edition |publisher=ABC-CLIO |year=2011 |isbn=978-1-59884-921-9 |page=872 |access-date=October 25, 2015}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |last=Wong |first=Edward |date=February 15, 2008 |title=Overview: The Iraq War |newspaper=The New York Times |url=https://www.nytimes.com/ref/timestopics/topics_iraq.html |access-date=March 7, 2013}} {{cite book |last=Johnson |first=James Turner |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=SF7U27JsLC4C&q=iraq+invasion+removes+hussein |title=The War to Oust Saddam Hussein: Just War and the New Face of Conflict |publisher=Rowman & Littlefield |year=2005 |isbn=978-0-7425-4956-2 |page=159 |access-date=October 25, 2015}} {{cite news |author=Durando, Jessica |author2=Green, Shannon Rae |date=December 21, 2011 |title=Timeline: Key moments in the Iraq War |newspaper=USA Today |agency=Associated Press |url=https://usatoday30.usatoday.com/news/world/iraq/story/2011-12-21/iraq-war-timeline/52147680/1 |url-status=dead |access-date=March 7, 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200904084312/https://usatoday30.usatoday.com/news/world/iraq/story/2011-12-21/iraq-war-timeline/52147680/1 |archive-date=September 4, 2020}}</ref> The ] was profound and long-lasting. | |||
| ==Foreign relations and military== | |||
| {{Main|Foreign policy of the United States|United States armed forces}} | |||
| ] ] of the ] and President Obama]] | |||
| The United States exercises global economic, political, and military influence. It is a permanent member of the ] and New York City hosts the ]. Almost all countries have ] in Washington, D.C., and many have ] around the country. Likewise, nearly all nations host ]. However, ], ], ], ], ], and the ] (Taiwan) do not have formal diplomatic relations with the United States. | |||
| The ] culminated in 2007 with the ], the largest economic contraction since the Great Depression.<ref>{{Cite news |last1=Hilsenrath |first1=Jon |last2=Ng |first2=Serena |last3=Paletta |first3=Damian |date=September 18, 2008 |title=Worst Crisis Since '30s, With No End Yet in Sight |work=] |url=https://www.wsj.com/articles/SB122169431617549947 |url-status=live |url-access=subscription |access-date=July 28, 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141225040616/https://www.wsj.com/articles/SB122169431617549947 |archive-date=December 25, 2014 |issn=1042-9840 |oclc=781541372}}</ref> Coming to a head in the 2010s, ] increased between liberal and conservative factions.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Geiger |first=Abigail |date=June 12, 2014 |title=Political Polarization in the American Public |url=https://www.pewresearch.org/politics/2014/06/12/political-polarization-in-the-american-public/ |access-date=June 30, 2024 |website=Pew Research Center |language=en-US}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last1=Murray |first1=Mark |last2=Marquez |first2=Alexandra |date=June 15, 2023 |title=Here's what's driving America's increasing political polarization|url=https://www.nbcnews.com/meet-the-press/meetthepressblog/s-s-driving-americas-increasing-political-polarization-rcna89559 |access-date=June 30, 2024 |website=NBC News |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Hamid |first=Shadi |date=January 8, 2022 |title=The Forever Culture War |url=https://www.theatlantic.com/ideas/archive/2022/01/republicans-democrats-forever-culture-war/621184/ |access-date=October 1, 2023 |website=] |language=en}}</ref> This polarization was capitalized upon in the ],<ref name="Kleinfeld-2023">{{cite web |last1=Kleinfeld |first1=Rachel |title=Polarization, Democracy, and Political Violence in the United States: What the Research Says |url=https://carnegieendowment.org/research/2023/09/polarization-democracy-and-political-violence-in-the-united-states-what-the-research-says?lang=en |website=Carnegie Endowment for International Peace |access-date=13 September 2024 |date=September 5, 2023}}</ref> when a mob of insurrectionists<ref name="Pape-2022">{{cite web |last1=Pape|first1=Robert|author1-link=Robert Pape|title=American Face of Insurrection: Analysis of Individuals Charged for Storming the US Capitol on January 6, 2021|url=https://cpost.uchicago.edu/publications/american_face_of_insurrection/ |website=cpost.uchicago.edu |publisher=University of Chicago, Chicago Project on Security and Threats|access-date=13 September 2024 |date=January 5, 2022}}</ref> entered the ] and sought to prevent the peaceful transfer of power<ref>{{cite news |last1=Rutenberg |first1=Jim |last2=Becker |first2=Jo |last3=Lipton |first3=Eric |last4=Haberman |first4=Maggie |last5=Martin |first5=Jonathan |last6=Rosenberg |first6=Matthew |last7=Schmidt |first7=Michael S. |title=77 Days: Trump's Campaign to Subvert the Election |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2021/01/31/us/trump-election-lie.html |work=The New York Times |date=January 31, 2021 |archiveurl=https://archive.today/20220618170015/https://www.nytimes.com/2021/01/31/us/trump-election-lie.html |archivedate=June 18, 2022 |url-status=live}}</ref> in an ].<ref name="Multiple Sources">{{multiref2|{{Cite book |last=Harvey |first=Michael |url=https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.4324/9781003110361-1/introduction-michael-harvey |title=Donald Trump in Historical Perspective |date=2022 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1-003-11036-1 |editor-last=Harvey |editor-first=Michael |chapter=Introduction: History's Rhymes |doi=10.4324/9781003110361-1 |quote = As with the Beer Hall Putsch, a would-be leader tried to take advantage of an already scheduled event (in Hitler's case, Kahr's speech; in Trump's, Congress's tallying of the electoral votes) to create a dramatic moment with himself at the center of attention, calling for bold action to upend the political order. Unlike Hitler's coup attempt, Trump already held top of office, so he was attempting to hold onto power, not seize it (the precise term for Trump's intended action is a 'self-coup' or 'autogolpe'). Thus, Trump was able to plan for the event well in advance, and with much greater control, including developing the legal arguments that could be used to justify rejecting the election's results. (p. 3)}}|{{cite journal |last1=Pion-Berlin |first1=David |last2=Bruneau |first2=Thomas |last3=Goetze |first3=Richard B. Jr.|date=2022-04-07 |title=The Trump self-coup attempt: comparisons and civil–military relations |journal=Government and Opposition |volume=FirstView |issue=4 |pages=789–806 |doi=10.1017/gov.2022.13 |s2cid=248033246 |doi-access=free }}|{{cite journal |author1-last=Castañeda |author1-first=Ernesto |author2-last=Jenks |author2-first=Daniel |date=April 17, 2023 |title=January 6th and De-Democratization in the United States |editor-last1=Costa |editor-first1=Bruno Ferreira |editor-last2=Parton|editor-first2=Nigel|journal=Social Sciences |publisher=] |volume=12 |issue=4 |pages=238 |doi=10.3390/socsci12040238 |doi-access=free |issn=2076-0760|quote=What the United States went through on January 6th was an attempt at a self-coup, where Trump would use force to stay as head of state even if abandoning democratic practices in the U.S. Some advised Trump to declare martial law to create a state of emergency and use that as an excuse to stay in power.}}|{{Cite report |url=https://www.brookings.edu/research/trump-on-trial/ |title=Trump on Trial: A Guide to the January 6 Hearings and the Question of Criminality |last1=Eisen |first1=Norman |last2=Ayer |first2=Donald |date=2022-06-06 |publisher=Brookings Institution |language=en-US |quote= tried to delegitimize the election results by disseminating a series of far fetched and evidence-free claims of fraud. Meanwhile, with a ring of close confidants, Trump conceived and implemented unprecedented schemes to{{snd}}in his own words{{snd}}"overturn" the election outcome. Among the results of this "Big Lie" campaign were the terrible events of January 6, 2021{{snd}}an inflection point in what we now understand was nothing less than an attempted coup. |last3=Perry |first3=Joshua |last4=Bookbinder |first4=Noah |last5=Perry |first5=E. Danya |access-date=December 16, 2023}}|{{cite court|litigants=Eastman v Thompson, et al. |opinion= 8:22-cv-00099-DOC-DFM Document 260 |pinpoint=44 |court=S.D. Cal. |date=May 28, 2022 |url=https://storage.courtlistener.com/recap/gov.uscourts.cacd.841840/gov.uscourts.cacd.841840.260.0.pdf |access-date=December 16, 2023 |quote=Dr. Eastman and President Trump launched a campaign to overturn a democratic election, an action unprecedented in American history. Their campaign was not confined to the ivory tower{{snd}}it was a coup in search of a legal theory. The plan spurred violent attacks on the seat of our nation's government, led to the deaths of several law enforcement officers, and deepened public distrust in our political process... If Dr. Eastman and President Trump's plan had worked, it would have permanently ended the peaceful transition of power, undermining American democracy and the Constitution. If the country does not commit to investigating and pursuing accountability for those responsible, the Court fears January 6 will repeat itself.}}|{{Cite web |last=Graham |first=David A. |date=January 6, 2021 |title=This Is a Coup |url=https://www.theatlantic.com/ideas/archive/2021/01/attempted-coup/617570/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210106224049/https://www.theatlantic.com/ideas/archive/2021/01/attempted-coup/617570/ |archive-date=January 6, 2021 |access-date=December 16, 2023 |website=] }}|{{Cite web|last=Musgrave|first=Paul|date=January 6, 2021|title=This Is a Coup. Why Were Experts So Reluctant to See It Coming?|url=https://foreignpolicy.com/2021/01/06/coup-america-capitol-electoral-college-2020-election/|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210106235812/https://foreignpolicy.com/2021/01/06/coup-america-capitol-electoral-college-2020-election/|archive-date=January 6, 2021|access-date=December 16, 2023|website=Foreign Policy}}|{{Cite web|last=Solnit|first=Rebecca|date=January 6, 2021|title=Call it what it was: a coup attempt|url=https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2021/jan/06/trump-mob-storm-capitol-washington-coup-attempt|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210107000436/https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2021/jan/06/trump-mob-storm-capitol-washington-coup-attempt|archive-date=January 7, 2021|access-date=December 16, 2023|website=The Guardian}}|{{Cite web|last=Coleman|first=Justine|date=January 6, 2021|title=GOP lawmaker on violence at Capitol: 'This is a coup attempt'|url=https://thehill.com/homenews/house/532944-gop-lawmaker-on-violence-at-capitol-this-is-a-coup-attempt|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210106212600/https://thehill.com/homenews/house/532944-gop-lawmaker-on-violence-at-capitol-this-is-a-coup-attempt|archive-date=January 6, 2021|access-date=December 16, 2023|website=] }}|{{Cite web|last=Jacobson|first=Louis|date=January 6, 2021|title=Is this a coup? Here's some history and context to help you decide|url=https://www.politifact.com/article/2021/jan/06/coup-heres-some-history-and-context-help-you-decid/|access-date=January 7, 2021|website=] |quote=A good case can be made that the storming of the Capitol qualifies as a coup. It's especially so because the rioters entered at precisely the moment when the incumbent's loss was to be formally sealed, and they succeeded in stopping the count.}}|{{Cite news|last1=Barry|first1=Dan|last2=Frenkel|first2=Sheera|date=January 7, 2021|title='Be There. Will Be Wild!': Trump All but Circled the Date|work=] |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2021/01/06/us/politics/capitol-mob-trump-supporters.html |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/archive/20211228/https://www.nytimes.com/2021/01/06/us/politics/capitol-mob-trump-supporters.html |archive-date=2021-12-28 |url-access=registration |url-status=live |access-date=December 16, 2023}}|{{cite encyclopedia |last=Duignan |first=Brian |date=2021-08-04 |title=January 6 U.S. Capitol attack |url=https://www.britannica.com/event/January-6-U-S-Capitol-attack |url-status=live |access-date=2021-09-22 |encyclopedia=] |quote=Because its object was to prevent a legitimate president-elect from assuming office, the attack was widely regarded as an insurrection or attempted coup d'état.|language=en |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230117232629/https://www.britannica.com/event/January-6-U-S-Capitol-attack |archive-date=2023-01-17}} | |||
| The United States enjoys a ] with the ] and strong ties with ], ], ], ], ], ], and fellow ] members. It also works closely with its neighbors through the ] and ] such as the trilateral ] with Canada and ]. In 2005, the United States spent $27 billion on ], the most in the world. However, as a share of ] (GNI), the U.S. contribution of 0.22% ranked twentieth of twenty-two donor states. Nongovernmental sources such as private foundations, corporations, and educational and religious institutions donated $96 billion. The combined total of $123 billion is also the most in the world and seventh as a percentage of GNI.<ref>{{cite web|title=Americans Favor Private Giving, People-to-People Contacts|date=2007-05-24|publisher=U.S. Dept. of State, International Information Programs|url=http://usinfo.state.gov/xarchives/display.html?p=washfile-english&y=2007&m=May&x=20070524165115zjsredna0.2997553|accessdate=2007-06-17}}</ref> | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| == Geography == | |||
| ] ]]] | |||
| {{Main|Geography of the United States}} | |||
| ] of the United States]] | |||
| The United States is the world's ] by total area behind Russia and Canada.{{efn|name=largestcountry}}<ref name="CIA-2018" /><ref name="CIA Factbook Area">{{cite web|title=Area|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2147.html|website=The World Factbook|publisher=Central Intelligence Agency|access-date=January 15, 2015|archive-date=January 31, 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140131115000/https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2147.html|url-status=dead }}</ref> The 48 ] occupy a combined area of {{convert|3,119,885|sqmi|km2|abbr=}}.<ref name="CensusGov2010HTML"/><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/279.html#as|work=The World Factbook|publisher=cia.gov|title=Field Listing: Area|access-date=April 21, 2020|archive-date=July 7, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200707180005/https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/279.html#as|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name="urlState Area Measurements and Internal Point Coordinates—Geography—U.S. Census Bureau">{{cite web|url=https://www.census.gov/geographies/reference-files/2010/geo/state-area.html|title=State Area Measurements and Internal Point Coordinates—Geography—U.S. Census Bureau|website=State Area Measurements and Internal Point Coordinates|publisher=U.S. Department of Commerce|access-date=September 11, 2017}}</ref> ] of the ] seaboard gives way to inland forests and rolling hills in the ] plateau region.<ref>{{cite web|title=Geographic Regions of Georgia|url=https://georgiainfo.galileo.usg.edu/topics/geography/article/geographic-regions-of-georgia|website=Georgia Info|publisher=Digital Library of Georgia|access-date=December 24, 2014}}</ref> | |||
| The president holds the title of commander-in-chief of the nation's armed forces and appoints its leaders, the ] and the ]. The ] administers the armed forces, including the ], ], ], and ]. The ] is run by the ] in peacetime and the ] in time of war. In 2005, the military had 1.38 million personnel on active duty,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.globalpolicy.org/empire/tables/2005/1231militarypersonnel.pdf|title=Department of Defense Active Duty Military Personnel Strengths by Regional Area and by Country (309A)|date=2005-12-31|publisher=Global Policy Forum|accessdate=2007-06-21}}</ref> along with several hundred thousand each in the ] and the ] for a total of ]. The Department of Defense also employs about 700,000 civilians, not including contractors. Military service is voluntary, though ] may occur in wartime through the ]. American forces can be rapidly deployed by the Air Force's large fleet of transport aircraft and aerial refueling tankers, the Navy's fleet of eleven active aircraft carriers, and ]s at sea in the Navy's ] ]. Outside of the United States, the military is ], on every continent ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.globalpolicy.org/empire/intervention/2005/basestructurereport.pdf|title=Department of Defense Base Structure Report, Fiscal Year 2005 Baseline|publisher=Global Policy Forum|accessdate=2007-06-21}}</ref> The extent of this global military presence has prompted some scholars to describe the United States as maintaining an "empire of bases."<ref>{{cite web|author=Ikenberry, G. John|url=http://people.cas.sc.edu/rosati/ttp.ikenberry.empirereviews.fa.march04.htm|title=Illusions of Empire: Defining the New American Order|work=Foreign Affairs|date=March/April 2004}} {{cite web|author=Kreisler, Harry, and Chalmers Johnson|url=http://globetrotter.berkeley.edu/people4/CJohnson/cjohnson-con3.html|title=Conversations with History|publisher=University of California at Berkeley|date=2004-01-29|accessdate=2007-06-21}}</ref> | |||
| The ] and the ] massif separate the ] from the ] and the grasslands of ].<ref name="NAU">{{cite web|last=Lew|first=Alan|title=PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY OF THE US|url=https://www.geog.nau.edu/courses/alew/gsp220/text/chapters/ch2.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160409112252/https://www.geog.nau.edu/courses/alew/gsp220/text/chapters/ch2.html|archive-date=April 9, 2016|website=GSP 220—Geography of the United States|publisher=North Arizona University|access-date=December 24, 2014}}</ref> The ], the world's ], runs predominantly north–south through the heart of the country. The flat and fertile ] of the ] stretches to the west, interrupted by ] in the southeast.<ref name="NAU" /> | |||
| Total U.S. military spending in 2006, over $528 billion, was 46% of global military spending and greater than the next fourteen largest national military expenditures combined. (In ] terms, it was larger than the next six such expenditures combined.) The per capita spending of $1,756 was about ten times the world average.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.sipri.org/contents/milap/milex/mex_major_spenders.pdf/download|title=The Fifteen Major Spender Countries in 2006|publisher=Stockholm International Peace Research Institute|year=2007|accessdate=2007-06-20}}</ref> At 4.06% of GDP, U.S. military spending is ranked 27th out of 172 nations.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2034rank.html|title=Rank Order—Military Expenditures—Percent of GDP|publisher=CIA|work=The World Factbook|date=2007-05-31|accessdate=2007-06-13}}</ref> The proposed base ] for 2009, $515.4 billion, is a 7% increase over 2008 and a nearly 74% increase over 2001.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.whitehouse.gov/omb/budget/fy2009/defense.html|title=Department of Defense|publisher=Office of Management and Budget|work=Budget of the United States Government, FY 2009|accessdate=2008-03-02}}</ref> The cost of the ] to the United States has been estimated to reach $2.7 trillion.<ref>{{cite web|author=Goldman, David|url=http://money.cnn.com/2008/06/11/news/economy/iraq_war_hearing/|title=Iraq War Could Cost Taxpayers $2.7 Trillion|publisher=CNNMoney|date=2008-06-12|accessdate=2009-03-10}}</ref> As of May 3, 2009, the United States had suffered 4,284 military fatalities during the war and over 31,000 wounded.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://icasualties.org/Iraq/index.aspx|title=Iraq Coalition Casualties|publisher=Iraq Coalition Casualty Count|date=2009-05-03|accessdate=2009-05-03}}</ref> | |||
| ] in Arizona]] | |||
| ==Economy== | |||
| The ], west of the Great Plains, extend north to south across the country, peaking at over {{convert|14000|ft}} in ].<ref>{{cite web|last=Harms|first=Nicole|title=Facts About the Rocky Mountain Range|url=https://traveltips.usatoday.com/rocky-mountain-range-11967.html|work=USA Today|access-date=December 24, 2014|archive-date=February 12, 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220212094150/https://traveltips.usatoday.com/rocky-mountain-range-11967.html|url-status=dead}}</ref> Farther west are the rocky ] and ], ], and ] deserts.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Tinkham|first=Ernest R.|title=Biological, Taxonomic and Faunistic Studies on the Shield-Back Katydids of the North American Deserts|jstor=2421073|doi=10.2307/2421073|journal=]|volume=31|number=2|date=March 1944|pages=257–328|publisher=The ]}}</ref> In the northwest corner of ], carved by the ] over millions of years, is the ], a steep-sided canyon and popular tourist destination known for its overwhelming visual size and intricate, colorful landscape. | |||
| The ] and ] mountain ranges run close to the ]. The ] are in the State of California,<ref>{{cite web|title=Mount Whitney, California|url=https://www.peakbagger.com/peak.aspx?pid=2829|publisher=Peakbagger|access-date=December 24, 2014}}</ref> about {{convert|84|mi|km}} apart.<ref>{{cite web|title=Find Distance and Azimuths Between 2 Sets of Coordinates (Badwater 36-15-01-N, 116-49-33-W and Mount Whitney 36-34-43-N, 118-17-31-W)|url=https://transition.fcc.gov/fcc-bin/distance?dlat=36&mlat=15&slat=01&ns=1&dlon=116&mlon=49&slon=33&ew=1&dlat2=36&mlat2=34&slat2=43&sn=1&dlon2=118&mlon2=17&slon2=31&we=1&iselec=1|publisher=Federal Communications Commission|access-date=December 24, 2014}}</ref> At an elevation of {{convert|20310|ft|1}}, Alaska's ] is the highest peak in the country and continent.<ref>{{cite web|last=Poppick|first=Laura|title=US Tallest Mountain's Surprising Location Explained|date=August 28, 2013|url=https://www.livescience.com/39245-us-tallest-mountain-location-explained.html|publisher=LiveScience|access-date=May 2, 2015}}</ref> Active ] are common throughout Alaska's ] and ], and Hawaii consists of volcanic islands. The ] underlying ] in the Rocky Mountains, the ], is the continent's largest volcanic feature.<ref>{{cite web|last=O'Hanlon|first=Larry|title=America's Explosive Park|url=https://dsc.discovery.com/convergence/supervolcano/under/under.html|date=March 14, 2005|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20050314034001/https://dsc.discovery.com/convergence/supervolcano/under/under.html|archive-date=March 14, 2005|publisher=Discovery Channel|access-date=April 5, 2016}}</ref> In 2021, the United States had 8% of global permanent meadows and pastures and 10% of cropland.<ref name="Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations-2023">{{Cite book |title=World Food and Agriculture – Statistical Yearbook 2023 |publisher=Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations |url=https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en?details=cc8166en |access-date=December 13, 2023 | date=2023 |language=en |doi=10.4060/cc8166en| isbn=978-92-5-138262-2 }}</ref> | |||
| === Climate === | |||
| {{Main|Climate of the United States}} | |||
| {{See also|Climate change in the United States}} | |||
| ] of the United States]] | |||
| With its large size and geographic variety, the United States includes most climate types. East of the ], the climate ranges from ] in the north to ] in the south.<ref>{{cite web|last=Boyden|first=Jennifer|title=Climate Regions of the United States|url=https://traveltips.usatoday.com/climate-regions-united-states-21570.html|work=USA Today|access-date=December 24, 2014|archive-date=February 12, 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220212094152/https://traveltips.usatoday.com/climate-regions-united-states-21570.html|url-status=dead}}</ref> The western Great Plains are ].<ref>{{cite journal |author=McGranahan, Devan Allen; Wonkka, Carissa L. |title=Pyrogeography of the Western Great Plains: A 40-Year History of Fire in Semi-Arid Rangelands |journal=Fire |volume=7 |issue=1 |pages=32 |year=2024 |url=https://www.mdpi.com/2571-6255/7/1/32}}</ref> Many mountainous areas of the American West have an ]. The climate is ] in the Southwest, ] in ], and ] in coastal ], ], and southern ]. Most of Alaska is ] or ]. ], the ] and U.S. territories in the ] and ] are ].<ref>{{cite web|title=World Map of Köppen–Geiger Climate Classification|url=https://koeppen-geiger.vu-wien.ac.at/pdf/kottek_et_al_2006_A4.pdf|access-date=August 19, 2015|archive-date=January 26, 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220126115149/http://koeppen-geiger.vu-wien.ac.at/pdf/kottek_et_al_2006_A4.pdf|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| States bordering the ] are prone to hurricanes, and most of the world's tornadoes ], mainly in ].<ref>{{cite news|author=Perkins, Sid|url=https://www.sciencenews.org/articles/20020511/bob9.asp|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070701131631/https://www.sciencenews.org/articles/20020511/bob9.asp|archive-date=July 1, 2007|title=Tornado Alley, USA|access-date=September 20, 2006|date=May 11, 2002|work=Science News}}</ref> Overall, the United States receives more high-impact extreme weather incidents than any other country.<ref>{{cite web|title=USA has the world's most extreme weather|url=https://www.usatoday.com/story/weather/2013/05/16/extreme-weather-north-america/2162501/|last=Rice|first=Doyle|website=USA Today|language=en|access-date=May 17, 2020}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Borenstein |first=Seth |date=April 2, 2023 |title=Why the U.S. is leading the world in extreme weather catastrophes |url=https://www.pbs.org/newshour/science/why-the-u-s-is-leading-the-world-in-extreme-weather-catastrophes |access-date=June 25, 2024 |website=PBS News |language=en-us}}</ref> Extreme weather became more frequent in the U.S. in the 21st century, with three times the number of reported ] as in the 1960s. In the ], droughts became more persistent and more severe.<ref>{{Cite web|last=US EPA|first=OAR|date=June 27, 2016|title=Climate Change Indicators: Weather and Climate|url=https://www.epa.gov/climate-indicators/weather-climate|access-date=June 19, 2022|website=Epa.gov|language=en}}</ref> The regions considered as the most attractive to the population are the most vulnerable.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Waldron |first1=Lucas |last2=Lustgarten |first2=Abrahm |title=Climate Change Will Make Parts of the U.S. Uninhabitable. Americans Are Still Moving There. |url=https://www.propublica.org/article/climate-change-will-make-parts-of-the-u-s-uninhabitable-americans-are-still-moving-there |website=Propublica |date=November 10, 2020 |publisher=Rhodium Group |access-date=25 November 2024}}</ref> | |||
| === Biodiversity and conservation === | |||
| {{Main|Fauna of the United States|Flora of the United States}} | |||
| {{Anchor|Wildlife and conservation}} | |||
| ], the ] since 1782<ref name="McDougall2004">{{cite book|first=Len|last=McDougall|title=The Encyclopedia of Tracks and Scats: A Comprehensive Guide to the Trackable Animals of the United States and Canada|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9XOc2_u7z6cC&pg=PA325|year=2004|publisher=Lyons Press|isbn=978-1-59228-070-4|page=325}}</ref>]] | |||
| The U.S. is one of 17 ] containing large numbers of ]: about 17,000 species of ]s occur in the contiguous United States and Alaska, and over 1,800 species of ]s are found in Hawaii, few of which occur on the mainland.<ref>{{cite web|author=Morin, Nancy|url=https://www.fungaljungal.org/papers/National_Biological_Service.pdf|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130724222726/https://www.fungaljungal.org/papers/National_Biological_Service.pdf|title=Vascular Plants of the United States|website=Plants|publisher=National Biological Service|access-date=October 27, 2008|archive-date=July 24, 2013}}</ref> The United States is home to 428 ] species, 784 birds, 311 reptiles, 295 ]s,<ref name="Current Results # of native species in the US">{{cite web|last1=Osborn|first1=Liz|title=Number of Native Species in United States|url=https://www.currentresults.com/Environment-Facts/Plants-Animals/number-of-native-species-in-united-states.php|publisher=Current Results Nexus|access-date=January 15, 2015}}</ref> and around 91,000 insect species.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.si.edu/Encyclopedia_SI/nmnh/buginfo/bugnos.htm|title=Numbers of Insects (Species and Individuals)|publisher=Smithsonian Institution|access-date=January 20, 2009}}</ref> | |||
| There are ], and ] parks, forests, and ], managed by the ] and other agencies.<ref>{{cite web|title= National Park FAQ|url=https://www.nps.gov/aboutus/national-park-system.htm/|website=nps|publisher=National Park Service|access-date=May 8, 2015}}</ref> About 28% of the country's land is publicly owned and federally managed,<ref name="NYTimes Federal Land">{{cite news|last1=Lipton|first1=Eric|last2=Krauss|first2=Clifford|title=Giving Reins to the States Over Drilling|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2012/08/24/us/romney-would-give-reins-to-states-on-drilling-on-federal-lands.html?pagewanted=2&_r=0|access-date=January 18, 2015|newspaper=The New York Times|date=August 23, 2012}}</ref> primarily in the ].<ref name="AKLeg CRS Federal Land">{{Cite report|url=https://www.akleg.gov/basis/get_documents.asp?session=31&docid=47224|title=Federal Land Ownership: Overview and Data|publisher=Congressional Research Service|date=March 3, 2017|access-date=June 18, 2020|last1=Vincent|first1=Carol H.|last2=Hanson|first2=Laura A.|last3=Argueta|first3=Carla N.|page=2}}</ref> ], though some is leased for commercial use, and less than one percent is used for military purposes.<ref name="Federal Land Ownership">{{cite web|last1=Gorte|first1=Ross W.|last2=Vincent|first2=Carol Hardy.|last3=Hanson|first3=Laura A.|last4=Marc R.|first4=Rosenblum|title=Federal Land Ownership: Overview and Data|url=https://fas.org/sgp/crs/misc/R42346.pdf|website=fas.org|publisher=Congressional Research Service|access-date=January 18, 2015}}</ref><ref name="Fed Land Uses">{{cite web|title=Chapter 6: Federal Programs to Promote Resource Use, Extraction, and Development|url=https://www.doi.gov/pmb/oepc/wetlands2/v2ch6.cfm|website=doi.gov|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150318005744/https://www.doi.gov/pmb/oepc/wetlands2/v2ch6.cfm|publisher=U.S. Department of the Interior|access-date=January 19, 2015|archive-date=March 18, 2015}}</ref> | |||
| ] include debates on ]s and ], ], ], logging and ],<ref>{{cite web|author=The National Atlas of the United States of America|url=https://www.nationalatlas.gov/articles/biology/a_forest.html|title=Forest Resources of the United States|publisher=Nationalatlas.gov|date=January 14, 2013|access-date=January 13, 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090507195541/https://www.nationalatlas.gov/articles/biology/a_forest.html|archive-date=May 7, 2009 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.fs.fed.us/pnw/pubs/gtr587.pdf|title=Land Use Changes Involving Forestry in the United States: 1952 to 1997, With Projections to 2050|year=2003|access-date=January 13, 2014}}</ref> and ].<ref>], pp. 3, 72, 74–76, 78</ref><ref>Hays, Samuel P. (2000). ''A History of Environmental Politics since 1945''.</ref> The ] (EPA) is the federal agency charged with ].<ref name="Collin2006">{{cite book|last=Collin|first=Robert W.|title=The Environmental Protection Agency: Cleaning Up America's Act|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=OVPoqXeTYTwC&pg=PA1|year=2006|publisher=Greenwood Publishing Group|isbn=978-0-313-33341-5|page=1|access-date=October 25, 2015}}</ref> The ] has shaped the management of public lands since 1964, with the ].<ref>Turner, James Morton (2012). ''The Promise of Wilderness'', pp. 29–32</ref> The ] provides a way to protect threatened and endangered species and their habitats. The ] implements and enforces the Act.<ref name="Office">{{cite book|title=Endangered species Fish and Wildlife Service|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=a8BEuUPJb58C&pg=PA1|publisher=General Accounting Office, Diane Publishing|isbn=978-1-4289-3997-4|pages=1–3, 42|access-date=October 25, 2015|year=2003 }}</ref> In 2024, the U.S. ranked 35th among 180 countries in the ].<ref>{{Cite web |date=July 10, 2024 |title=Environmental Performance Index |url=https://epi.yale.edu/measure/2024/EPI |access-date=July 10, 2024 |website=epi.yale.edu}}</ref> The country joined the ] on climate change in 2016.<ref>{{cite web | |||
| |url=https://treaties.un.org/pages/viewdetails.aspx?src=treaty&mtdsg_no=xxvii-7-d&chapter=27&clang=_en#7 | |||
| |title=United Nations Treaty Collection-The Paris Agreement | |||
| |access-date=2024-12-03}}</ref> | |||
| == Government and politics == | |||
| {{Main|Politics of the United States}} | |||
| {{Further|Elections in the United States|Political ideologies in the United States|Americanism (ideology)|}} | |||
| ], the seat of legislative government, is home to both chambers of the ]: the ] (in left wing of building) and the ] (right wing).]] | |||
| ], the residence and workplace of the U.S. president and the offices of ]]] | |||
| ], which houses the ]]] | |||
| The United States is a ] of 50 ] and a separate federal capital district, ] It also asserts sovereignty over five ] and ].<ref name="HRI-2012"/>{{sfn|Onuf|2010|p=xvii}} The U.S. is the world's oldest surviving federation,<ref>{{Cite web |last=Desjardins |first=Jeff |date=August 8, 2019 |title=Mapped: The world's oldest democracies |url=https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2019/08/countries-are-the-worlds-oldest-democracies/ |access-date=June 25, 2024 |website=]}}</ref> and its ] has been adopted, in whole or in part, by many newly independent states worldwide following their ].<ref>{{cite book |last1=Ryan |first1=David |editor-first1=David |editor-first2=Victor |editor-last1=Ryan |editor-last2=Pungong |title=The United States and Decolonization |year=2000 |publisher=Springer |doi=10.1057/9780333977958 |hdl=1887/72726 |isbn=978-1-349-40644-9 |url=https://link.springer.com/book/10.1057/9780333977958}}</ref> It is a liberal ] "in which ] by ] protected ]".<ref name="Scheb">Scheb, John M.; Scheb, John M. II (2002). ''An Introduction to the American Legal System''. Florence, Kentucky: Delmar, p. 6. {{ISBN|978-0-7668-2759-2}}.</ref> The ] serves as ], also establishing the structure and responsibilities of the national federal government and its relationship with the individual states. The U.S. Constitution is the world's oldest national constitution still in effect (from March 4, 1789). | |||
| === National government === | |||
| {{Main|Federal government of the United States}} | |||
| Composed of three branches, all headquartered in Washington, D.C., the federal government is the national government of the United States. It is regulated by a strong system of ].<ref>{{cite web |author=Killian, Johnny H. Ed|title=Constitution of the United States |url=https://www.senate.gov/civics/constitution_item/constitution.htm |access-date=February 11, 2012 |publisher=The Office of the Secretary of the Senate}}</ref> | |||
| * The ], a ] made up of the ] and the ], makes ], ], approves treaties, has the ],<ref>{{cite web|title=The Legislative Branch|publisher=United States Diplomatic Mission to Germany|url=https://usa.usembassy.de/government-legislative.htm|access-date=August 20, 2012}}</ref> and has ].<ref>{{cite web|title=The Process for impeachment|publisher=ThinkQuest|url=https://library.thinkquest.org/25673/process.htm|access-date=August 20, 2012|archive-date=April 8, 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130408102119/https://library.thinkquest.org/25673/process.htm|url-status=dead }}</ref> The Senate has 100 members (2 from each state), elected for a six-year term. The House of Representatives has 435 members, each elected for a two-year term; all representatives serve one ] of equivalent population. Congressional districts are drawn by each state legislature and are contiguous within the state.<ref>{{cite web |title=The Senate and the House of Representatives: lesson overview (article) |url=https://www.khanacademy.org/humanities/us-government-and-civics/us-gov-interactions-among-branches/us-gov-congress-the-senate-and-the-house-of-representatives/a/lesson-summary-the-senate-and-the-house-of-representatives |website=Khan Academy |language=en}}</ref> The Congress also organizes a collection of ], each of which handles a specific task or duty. One of Congress's foremost non-legislative functions is the power to ] and oversee the executive branch.<ref name="tws2010Sep11t11">{{cite news |author=Broder |first=David S. |date=March 18, 2007 |title=Congress's Oversight Offensive |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/03/16/AR2007031601989.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110501115602/http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2007/03/16/AR2007031601989.html |archive-date=May 1, 2011 |access-date=September 11, 2010 |newspaper=The Washington Post}}</ref> ] is usually delegated to committees and is facilitated by Congress's subpoena power.<ref name="tws2010Sep11t13">{{cite news |author=Ferraro |first=Thomas |date=April 25, 2007 |title=House committee subpoenas Rice on Iraq |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/idUSN2518728220070425 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114214442/https://www.reuters.com/article/idUSN2518728220070425 |archive-date=January 14, 2021 |access-date=September 11, 2010 |work=Reuters}}</ref> Appointment to a committee enables a member to develop specialized knowledge of the matters under its purview. The various committees monitor ongoing governmental operations, identify issues suitable for legislative review, gather and evaluate information, and recommend courses of action to the U.S. Congress, including but not limited to new legislation. The two major political parties have appointment power in deciding each committee's membership. Committee chairs are assigned to a member of the majority party. | |||
| * The U.S. president is the ], ] of the military, chief executive of the federal government, and has the ability to veto ] from the U.S. Congress before they become law. However, ] can be overridden by a two-thirds ] vote in both chambers of Congress. The president appoints the ], subject to Senate approval, and names other officials who administer and enforce federal laws through ].<ref>{{cite web|title=The Executive Branch|url=https://www.whitehouse.gov/about-the-white-house/our-government/the-executive-branch/|website=The White House|access-date=February 11, 2017}}</ref> The president also has clemency power for federal crimes and ]. Finally, the president has the right to issue expansive "]", subject to ], in a number of policy areas. Candidates for president campaign with a vice-presidential ]. Both candidates are elected together, or defeated together, in a presidential election. Unlike other votes in American politics, this is technically an ] in which the winner will be determined by the ]. There, votes are officially cast by individual electors selected by ].<ref>{{cite web |title=Interpretation: Article II, Section 1, Clauses 2 and 3 {{!}} Constitution Center |url=https://constitutioncenter.org/the-constitution/articles/article-ii/clauses/350 |website=National Constitution Center – constitutioncenter.org |language=en}}</ref> In practice, however, each of the 50 states chooses a group of presidential electors who are required to confirm the winner of their state's popular vote. Each state is allocated two electors plus one additional elector for each ], which in effect combines to equal the number of elected officials that state sends to Congress. The District of Columbia, with no representatives or senators, is allocated three electoral votes. Both the president and the vice president serve a four-year term, and the president may be ], for one additional four-year term.{{efn|Per the ], proposed by the U.S. Congress on June 16, 1960, and ratified by the States on March 29, 1961}} | |||
| * The ], whose judges are all appointed for life by the president with Senate approval, consists primarily of the ], the ], and the ]. The U.S. Supreme Court interprets laws and ].<ref name=FedJud>{{multiref2 | |||
| |{{cite book|first1=Kermit L.|last1=Hall|first2=Kevin T.|last2=McGuire|title=Institutions of American Democracy: The Judicial Branch|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=6rWCaMAdUzgC|year=2005|publisher=Oxford University Press|isbn=978-0-19-988374-5}} | |||
| |{{cite book|author=U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services|title=Learn about the United States: Quick Civics Lessons for the Naturalization Test|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=8X1CzvBXHksC&pg=PA4|date=2013|publisher=Government Printing Office|isbn=978-0-16-091708-0|page=4}} | |||
| |{{cite book|first=Bryon|last=Giddens-White|title=The Supreme Court and the Judicial Branch|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mbZw3bJsWtUC|year=2005|publisher=Heinemann Library|isbn=978-1-4034-6608-2}} | |||
| |{{cite book|first=Charles L.|last=Zelden|title=The Judicial Branch of Federal Government: People, Process, and Politics|url=https://archive.org/details/judicialbranchof0000zeld|url-access=registration|year=2007|publisher=ABC-CLIO|isbn=978-1-85109-702-9|access-date=October 25, 2015}} | |||
| |{{cite web|url=https://www.uscourts.gov/FederalCourts.aspx|title=Federal Courts|author=<!-- Staff writer(s); no by-line. -->|publisher=United States Courts|access-date=October 19, 2014}} }}</ref> The Supreme Court has nine members led by the ]. The members are appointed by the sitting president when a vacancy becomes available.<ref>{{cite news|title=Beyond politics: Why Supreme Court justices are appointed for life|first=Roger|last=Cossack|url=https://archives.cnn.com/2000/LAW/07/columns/cossack.scotus.07.12/|publisher=CNN|date=July 13, 2000|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120712085825/https://archives.cnn.com/2000/LAW/07/columns/cossack.scotus.07.12|archive-date=July 12, 2012 }}</ref> In a number of ways the federal court system operates differently than state courts. For ]s that is apparent in the types of cases that can be heard in the federal system. Their ] restricts them to cases authorized by the United States Constitution or ]s. In criminal cases, states may only bring criminal prosecutions in state courts, and the federal government may only bring criminal prosecutions in federal court. The first level in the federal courts is ] for any case under "]", such as federal statutes, the Constitution, or ]. There are twelve ]s that divide the country into different regions for federal appeals courts. After a federal district court has decided a case, it can then be ] to a United States court of appeal. The next and highest court in the system is the Supreme Court of the United States. It has the power to decide appeals on all cases brought in federal court or those brought in state court but dealing with federal law. Unlike circuit court appeals, however, the Supreme Court is usually not required to hear the appeal. A "]" may be submitted to the court, asking it to hear the case. If it is granted, the Supreme Court will take ] and conduct ]s. If it is not granted, the opinion of the lower court stands. Certiorari is not often granted, and less than 1% of appeals to the Supreme Court are actually heard by it. Usually, the Court only hears cases when there are conflicting decisions across the nation on a particular issue, or when there is an obvious error in a case. | |||
| The three-branch system is known as the ], in contrast to the ], where the executive is part of the legislative body. Many countries around the world imitated this aspect of the 1789 ], especially in the Americas.<ref name="Sundquist">{{Cite book |last=Sundquist |first=James L. |title=Designs for Democratic Stability: Studies in Viable Constitutionalism |publisher=] |year=1997 |isbn=0765600528 |editor-last=Baaklini |editor-first=Abdo I. |pages=53–72 |language=en |chapter=The U.S. Presidential System as a Model for the World |editor-last2=Desfosses |editor-first2=Helen}}</ref> | |||
| === Political parties === | |||
| {{main|Political parties in the United States|List of political parties in the United States}} | |||
| {{See also|Political party strength in U.S. states}} | |||
| ] (governor and legislature) by party control, {{as of|2024|lc=y}}: | |||
| {{legend|#33f|] control}} | |||
| {{legend|#f33|] control}} | |||
| {{legend|#829|Split control}}]] | |||
| The Constitution is silent on political parties. However, they developed independently in the 18th century with the ] and ] parties.<ref name="Hofstadter-1969-iv">{{cite book |last1=Hofstadter |first1=Richard |title=The Idea of a Party System : The Rise of Legitimate Opposition in the United States, 1780-1840 |date=1969 |publisher=University of California Press |page=iv |isbn=9780520013896 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=wG5rCKm8SmAC&q=%E2%80%9Cdid+not+believe+in+parties+as+such,+scorned+those+that+they+were+conscious+of+as+historical+models%22 |access-date=October 5, 2022}}</ref> Since then, the United States has operated as a de facto ], though the parties in that system have been different at different times.<ref name="Blake-2021">{{cite news |last1=Blake |first1=Aaron |title=Why are there only two parties in American politics? |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/the-fix/wp/2016/04/27/why-are-there-only-two-parties-in-american-politics/ |access-date=May 4, 2024 |newspaper=Washington Post |date=November 25, 2021}}</ref> The two main national parties are presently the ] and the ]. The former is perceived as ] in its ] while the latter is perceived as ].<ref>], ''The Partisan Sort: How Liberals Became Democrats and Conservatives Became Republicans'' (U Chicago Press, 2009)</ref> | |||
| === Subdivisions === | |||
| {{Main|U.S. state|County (United States)}} | |||
| {{See also|State governments of the United States| Local government in the United States}} | |||
| {{Further|List of states and territories of the United States|Indian reservation|Territories of the United States|Territorial evolution of the United States}} | |||
| In the ], sovereign powers are shared between two levels of elected government: national and state. People in the states are also represented by ], which are administrative divisions of the states.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Levy |first1=Robert A. |title=Rights, Powers, Dual Sovereignty, and Federalism |url=https://www.cato.org/policy-report/september/october-2011/rights-powers-dual-sovereignty-federalism# |website=Cato Institute |access-date=January 13, 2024 |date=October 2011}}</ref> States are subdivided into ], and ]. The District of Columbia is a ] containing the U.S. capital, ]<ref>{{usc|8|1101}}(a)(36) and {{usc|8|1101}}(a)(38) U.S. Federal Code, Immigration and Nationality Act. {{USC|8|1101a}}</ref> The federal district is an administrative division of the federal government.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Feldstein |first=Martin |date=March 2017 |title=Why is Growth Better in the United States Than in Other Industrial Countries? |url=http://dx.doi.org/10.3386/w23221 |journal=] |location=Cambridge, Massachusetts |doi=10.3386/w23221}}</ref> ] govern 326 ].<ref>{{Cite web |title=What is a federal Indian reservation? |url=https://www.bia.gov/faqs/what-federal-indian-reservation#:~:text=There%20are%20approximately%20326%20Indian,%2C%20communities%2C%20etc.). |access-date=August 26, 2023 |website=bia.gov | date=August 19, 2017 |publisher=]}}</ref> | |||
| {{USA image map}} | |||
| === Foreign relations === | |||
| {{Main|Foreign relations of the United States|Foreign policy of the United States}} | |||
| ] has been situated along the ] in ] since 1952; in 1945, the United States was a ].|alt=see caption]] | |||
| The United States has an established structure of foreign relations, and it has the world's ] {{As of|2024|lc=y}}. It is a ],<ref>{{cite web|url= https://www.un.org/securitycouncil/content/current-members|title=Current Members|work=]|access-date=July 15, 2022}}</ref> and home to the ].<ref>{{cite journal|title=United Nations Headquarters Agreement|journal=The American Journal of International Law |volume=42|number=2|date=April 1948|pages=445–447|publisher=]|doi=10.2307/2193692|jstor=2193692|s2cid=246008694 }}</ref> The United States is a member of the ],<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.cfr.org/backgrounder/where-g7-headed|title=Where is the G7 Headed?|work=]|location=New York City|date=June 28, 2022}}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite web|url= https://www.state.gov/the-united-states-and-g20-building-a-more-peaceful-stable-and-prosperous-world-together/|title=The United States and G20: Building a More Peaceful, Stable, and Prosperous World Together|date=July 6, 2022|work=]|access-date=July 15, 2022}}</ref> and ] intergovernmental organizations.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.oecd.org/about/members-and-partners/|title=Our global reach|work=]|access-date=July 15, 2022}}</ref> Almost all countries have ] and many have ] (official representatives) in the country. Likewise, nearly all countries host formal ]s with the United States, except ],<ref>{{cite report |last1=Fialho |first1=Livia Pontes |last2=Wallin |first2=Matthew |title=Reaching for an Audience: U.S. Public Diplomacy Towards Iran |date=August 1, 2013 |publisher=American Security Project |jstor=resrep06070}}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-42351336|title=Which are the countries still talking to North Korea?|newspaper=]|location=London|date=December 19, 2017|access-date=July 15, 2022|last1=Oliver|first1=Alex|last2=Graham|first2=Euan}}</ref> and ].<ref>{{cite news|url=https://thediplomat.com/2014/12/the-case-for-a-stronger-bhutanese-american-relationship/|title=The Case for Stronger Bhutanese-American Ties|newspaper=]|date=December 22, 2014|last=Ferraro|first=Matthew F.|access-date=July 15, 2022}}</ref> Though ] does not have formal diplomatic relations with the U.S., it maintains close unofficial relations.<ref>{{Cite web |date=September 28, 2022 |title=US will continue to strengthen 'unofficial ties' with Taiwan, says Harris |url=https://www.scmp.com/news/china/diplomacy/article/3194126/us-will-continue-strengthen-unofficial-ties-taiwan-vice |access-date=September 28, 2022 |website=South China Morning Post |language=en}}</ref> The United States regularly ] to deter potential Chinese aggression.<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.npr.org/2020/09/22/915818283/formal-ties-with-u-s-not-for-now-says-taiwan-foreign-minister|title=Formal Ties With U.S.? Not For Now, Says Taiwan Foreign Minister|publisher=]|date=September 22, 2020|last=Ruwitch|first=John|access-date=July 15, 2022}}</ref> Its geopolitical attention also turned to the ] when the United States joined the ] with Australia, India, and Japan.<ref name="kobara">{{cite news |last1=Kobara |first1=Junnosuke |last2=Moriyasu |first2=Ken |date=March 27, 2021 |title=Japan will turn to Quad in 'nealsow Cold War': Defense Ministry think tank |url=https://asia.nikkei.com/Politics/International-relations/Japan-will-turn-to-Quad-in-new-Cold-War-Defense-Ministry-think-tank |access-date=April 13, 2021 |work=Nikkei Asia}}</ref> | |||
| The United States has a "]" ]<ref>{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=jLy-NKnQitIC&q=uk+us+special+relationship&pg=PA45|title=America's 'Special Relationships': Foreign and Domestic Aspects of the Politics of Alliance|page=45|first1=John|first2=Axel|last2=Schäfer|last1=Dumbrell|year=2009|publisher=Taylor & Francis |isbn=978-0-203-87270-3|access-date=October 25, 2015}}</ref> and strong ties ],<ref>{{cite web|url=https://fas.org/sgp/crs/row/96-397.pdf|title=Canada–U.S. Relations|author1=Ek, Carl|first2=Ian F.|last2=Fergusson|name-list-style=amp|publisher=Congressional Research Service|date=September 3, 2010|access-date=August 28, 2011}}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite book|title=Australia: Background and U.S. Relations|author=Vaughn, Bruce|publisher=Congressional Research Service|date=August 8, 2008|oclc = 70208969}}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite web|url=https://fas.org/sgp/crs/row/RL32876.pdf|title=New Zealand: Background and Bilateral Relations with the United States|author=Vaughn, Bruce|publisher=Congressional Research Service|date=May 27, 2011|access-date=August 28, 2011}}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite web|url=https://fas.org/sgp/crs/row/RL33233.pdf|title=The Republic of the Philippines and U.S. Interests|author=Lum, Thomas|publisher=Congressional Research Service|date=January 3, 2011|access-date=August 3, 2011}}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite web|url=https://fas.org/sgp/crs/row/RL33436.pdf|title=Japan-U.S. Relations: Issues for Congress|author=Chanlett-Avery, Emma|publisher=Congressional Research Service|date=June 8, 2011|access-date=August 28, 2011|display-authors=etal}}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite web|url=https://fas.org/sgp/crs/row/R41481.pdf|title=U.S.–South Korea Relations: Issues for Congress|first1=Mark E.|last1=Manyin|first2=Emma|last2=Chanlett-Avery|first3=Mary Beth|last3=Nikitin|publisher=Congressional Research Service|date=July 8, 2011|access-date=August 28, 2011}}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite web|url=https://fas.org/sgp/crs/mideast/RL33476.pdf|title=Israel: Background and U.S. Relations|author=Zanotti, Jim|publisher=Congressional Research Service|date=July 31, 2014|access-date=September 12, 2014}}</ref> and several ] (], ], ], ], and ]).<ref>{{Cite web|date=January 20, 2021|url=https://www.state.gov/u-s-relations-with-poland/|title=U.S. Relations With Poland|website=State.gov|access-date=June 19, 2023}}</ref> The U.S. works closely with its ] allies on military and ] issues, and with countries in the Americas through the ] and the ]. In South America, ] is traditionally considered to be the closest ally of the United States.<ref>{{cite news|title=The Untapped Potential of the US-Colombia Partnership|url=https://www.atlanticcouncil.org/in-depth-research-reports/report/untapped-potential-us-colombia-partnership/|date=September 26, 2019|website=Atlantic Council|language=en|access-date=May 30, 2020|last1=Kimer |first1=James }}</ref> The U.S. exercises full international defense authority and responsibility for ], the ], and ] through the ].<ref name=FedJud/> It has increasingly conducted strategic cooperation ],<ref>{{cite web |title=INDO- PACIFIC STRATEGY OF THE UNITED STATES |url=https://www.whitehouse.gov/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/U.S.-Indo-Pacific-Strategy.pdf |publisher=White House |access-date=February 3, 2022}}</ref> but ] have steadily deteriorated.<ref>{{cite report |last=Meidan |first=Michal |title=US-China: The Great Decoupling |date=July 1, 2019 |publisher=] |jstor=resrep33982}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Bala |first=Sumathi |title=U.S.-China relations are going downhill with 'no trust' on either side, Stephen Roach says |url=https://www.cnbc.com/2023/03/28/us-china-ties-on-dangerous-path-with-no-trust-on-both-sides-roach-cohen.html |access-date=May 7, 2023 |publisher=CNBC |date=March 28, 2023 |language=en}}</ref> Since 2014, the U.S. has ];<ref>{{cite news|last1=Rumer|first1=Eugene|last2=Sokolsky|first2=Richard|url=https://carnegieendowment.org/2019/06/20/thirty-years-of-u.s.-policy-toward-russia-can-vicious-circle-be-broken-pub-79323|title=Thirty Years of U.S. Policy Toward Russia: Can the Vicious Circle Be Broken?|newspaper=]|location=Washington, D.C.|date=June 20, 2019|access-date=July 14, 2022}}</ref> it has also provided the country with significant military equipment and other support in response to ].<ref>{{Cite web |last=Macias |first=Amanda |title=Here's a look at the $5.6 billion in firepower the U.S. has committed to Ukraine in its fight against Russia |url=https://www.cnbc.com/2022/06/17/russia-ukraine-war-summary-of-weapons-us-has-given-to-ukraine.html |access-date=September 28, 2022 |publisher=CNBC |date=June 17, 2022 |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| === Military === | |||
| {{Main|United States Armed Forces}} | |||
| {{See also|Military history of the United States}} | |||
| ], the headquarters of the ] in ], is one of the world's largest office buildings with over {{convert|6.5|e6ft2|m2}} of ].]] | |||
| The president is the ] of the United States Armed Forces and appoints its leaders, the ] and the ]. The ], which is headquartered at ] near Washington, D.C., administers five of the six service branches, which are made up of the ], ], ], ], and ].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.defense.gov/about/our-forces|title=Our Forces|publisher=]|access-date=July 12, 2024}}</ref> The ] is administered by the ] in peacetime and can be transferred to the ] in wartime.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.cfr.org/blog/happy-231st-birthday-united-states-coast-guard|title=Happy 231st Birthday to the United States Coast Guard!|last=Lindsay|first=James M.|publisher=]|location=New York City|date=August 4, 2021|access-date=July 16, 2022|quote=During peacetime it is part of the Department of Homeland Security. During wartime, or when the president or Congress so direct, it becomes part of the Department of Defense and is included in the Department of the Navy.}}</ref> | |||
| The United States ] in 2023, which is by far the ], making up 37% of global military spending and accounting for 3.4% of the country's GDP.'''''<ref name="SIPRI-2020">{{Cite web |date=April 2024 |title=Trends in Military Expenditure 2023 |url=https://www.sipri.org/sites/default/files/2024-04/2404_fs_milex_2023.pdf#page=2 |access-date=April 22, 2024 |publisher=]}}</ref>'''''<ref>{{cite web| url=https://sipri.org/sites/default/files/Data%20for%20all%20countries%20from%201988%E2%80%932020%20in%20constant%20%282019%29%20USD%20%28pdf%29.pdf| title=Data for all countries from 1988–2020 in constant (2019) USD (pdf)| publisher=SIPRI| access-date=April 28, 2021| archive-date=April 28, 2021| archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210428180002/https://sipri.org/sites/default/files/Data%20for%20all%20countries%20from%201988%E2%80%932020%20in%20constant%20(2019)%20USD%20(pdf).pdf| url-status=live}}</ref> The U.S. ]—the second-largest share after Russia.<ref name="Stockholm International Peace Research Institute-2024">{{Cite web |date=June 17, 2024 |title=Role of nuclear weapons grows as geopolitical relations deteriorate—new SIPRI Yearbook out now {{!}} SIPRI |url=https://www.sipri.org/media/press-release/2024/role-nuclear-weapons-grows-geopolitical-relations-deteriorate-new-sipri-yearbook-out-now |access-date=June 18, 2024 |website=Stockholm International Peace Research Institute |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| The United States has the ] in the world, behind the ] and ].<ref>{{cite book |last1=Hackett |first1=James |title=The military balance. 2023 |date=2023 |publisher=Routledge |location=London |isbn=978-1032508955}}</ref> The military operates about 800 bases and facilities abroad,<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.vox.com/2015/5/18/8600659/military-bases-united-states|title=Why does the US have 800 military bases around the world?|last=Harris|first=Johnny|date=May 18, 2015|website=Vox|access-date=September 23, 2020|url-status=dead|archive-date=September 24, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200924114313/https://www.vox.com/2015/5/18/8600659/military-bases-united-states}}</ref> and maintains ] in 25 foreign countries.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://siadapp.dmdc.osd.mil/personnel/MILITARY/history/hst1003.pdf|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130724211511/https://siadapp.dmdc.osd.mil/personnel/MILITARY/history/hst1003.pdf|title=Active Duty Military Personnel Strengths by Regional Area and by Country (309A)|publisher=Department of Defense|date=March 31, 2010|access-date=October 7, 2010|archive-date=July 24, 2013}}</ref> | |||
| ] (SDFs) are military units that operate under the sole authority of a state government. SDFs are authorized by state and federal law but are under the command of ].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://statedefenseforce.com/|title=StateDefenseForce.com|date=September 17, 2024|website=StateDefenseForce.com}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://sgaus.org/|title=State Guard Association of the United States – Supporting the State Defense Forces of the United States|website=sgaus.org}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=32 U.S. Code § 109 – Maintenance of other troops |url=https://www.law.cornell.edu/uscode/text/32/109}}</ref> | |||
| They are distinct from the state's ] units in that they cannot become federalized entities. A state's National Guard personnel, however, may be federalized under the ], which created the Guard and provides for the integration of ] units and personnel into the U.S. Army and (since 1947) the U.S. Air Force.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.arng.army.mil/aboutus/history/Pages/ConstitutionalCharteroftheGuard.aspx |title=Legal Basis of the National Guard |publisher=Army National Guard |year=2013 |access-date=17 May 2013 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130521130934/http://www.arng.army.mil/aboutus/history/Pages/ConstitutionalCharteroftheGuard.aspx |archive-date=21 May 2013 }}</ref> | |||
| === Law enforcement and criminal justice === | |||
| {{Main|Law of the United States|Law enforcement in the United States|Crime in the United States}} | |||
| {{See also|Censorship in the United States|Race and crime in the United States}} | |||
| ], the headquarters of the ] (FBI), in ]]] | |||
| There are about 18,000 U.S. police agencies from local to national level in the United States.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Banks |first1=Duren |last2=Hendrix |first2=Joshua |last3=Hickman |first3=Mathhew |date=October 4, 2016 |title=National Sources of Law Enforcement Employment Data |url=https://bjs.ojp.gov/content/pub/pdf/nsleed.pdf |journal=] |pages=1}}</ref> Law in the United States is mainly enforced by local police departments and ] in their municipal or county jurisdictions. ] departments ], and ] such as the ] (FBI) and the ] have national jurisdiction and specialized duties, such as protecting ], ] and enforcing ]' rulings and federal laws.<ref>{{cite web|title=U.S. Federal Law Enforcement Agencies, Who Governs & What They Do|publisher=Chiff.com|url=https://www.chiff.com/police/federal-police-agencies.htm|access-date=November 10, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140210040432/https://www.chiff.com/police/federal-police-agencies.htm|archive-date=February 10, 2014|url-status= }}</ref> ] conduct most civil and criminal trials,<ref>{{cite book|last1=Manweller|first1=Mathew|editor1-last=Hogan|editor1-first=Sean O.|title=The Judicial Branch of State Government: People, Process, and Politics|date=2006|publisher=]|location=]|isbn=978-1-85109-751-7|pages=37–96|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ong5k8n97P4C&pg=PA55|access-date=October 5, 2020|chapter=Chapter 2, The Roles, Functions, and Powers of State Courts}}</ref> and federal courts handle designated crimes and ].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.justice.gov/usao/justice-101/federal-courts|title=Introduction To The Federal Court System|work=]|date=November 7, 2014 |publisher=]|access-date=July 14, 2022|location=Washington, D.C.}}</ref> | |||
| There is no unified "criminal justice system" in the United States. The ] is largely heterogenous, with thousands of relatively independent systems operating across federal, state, local, and tribal levels. In 2023, "these systems almost 2 million people in 1,566 state prisons, 98 federal prisons, 3,116 local jails, 1,323 juvenile correctional facilities, 181 immigration detention facilities, and 80 Indian country jails, as well as in ], civil commitment centers, state psychiatric hospitals, and prisons in the U.S. territories."<ref name="Sawyer-2023">{{Cite web |last1=Sawyer |first1=Wendy |last2=Wagner |first2=Peter |title=Mass Incarceration: The Whole Pie 2023 |url=https://www.prisonpolicy.org/reports/pie2023.html |date=July 6, 2023 |access-date=August 23, 2024| website=Prison Policy Initiative |language=en}}</ref> Despite disparate systems of confinement, four main institutions dominate: ], ], local jails, and ].<ref name="National Academies Press-2014">{{Cite book |url=http://www.nap.edu/catalog/18613 |title=The Growth of Incarceration in the United States: Exploring Causes and Consequences |date=April 24, 2014 |publisher=National Academies Press |isbn=978-0-309-29801-8 |location=Washington, D.C.|doi=10.17226/18613 }}</ref> Federal prisons are run by the ] and hold people who have been convicted of federal crimes, including pretrial detainees.<ref name="National Academies Press-2014" /> State prisons, run by the official department of correction of each state, hold sentenced people serving prison time (usually longer than one year) for felony offenses.<ref name="National Academies Press-2014" /> Local jails are county or municipal facilities that incarcerate defendants prior to trial; they also hold those serving short sentences (typically under a year).<ref name="National Academies Press-2014" /> Juvenile correctional facilities are operated by local or state governments and serve as longer-term placements for any minor adjudicated as delinquent and ordered by a judge to be confined.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Foundation |first=The Annie E. Casey |date=November 14, 2020 |title=Juvenile Detention Explained |url=https://www.aecf.org/blog/what-is-juvenile-detention |access-date=2023-07-06 |website=The Annie E. Casey Foundation |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| As of January 2023, the United States has the ] in the world—531 people per 100,000 inhabitants—and the largest prison and jail population in the world, with ].<ref name="Sawyer-2023" /><ref>. ].</ref><ref name="WorldPrisonBrief">. ] (WPB). Use the dropdown menu to choose lists of countries by region or the whole world. Use the menu to select highest-to-lowest lists of prison population totals, prison population rates, percentage of pre-trial detainees/remand prisoners, percentage of female prisoners, percentage of foreign prisoners, and occupancy rate. Column headings in WPB tables can be clicked to reorder columns lowest to highest, or alphabetically. For detailed information for each country click on any country name in lists. See the and click on the map links or the sidebar links to get to the region and country desired.</ref> An analysis of the ] Mortality Database from 2010 showed U.S. homicide rates "were 7 times higher than in other high-income countries, driven by ] that was 25 times higher".<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Grinshteyn|first1=Erin|last2=Hemenway|first2=David|date=March 2016|title=Violent Death Rates: The US Compared with Other High-income OECD Countries, 2010|url=https://www.amjmed.com/article/S0002-9343(15)01030-X/fulltext|journal=]|volume=129|issue=3|pages=226–273|doi=10.1016/j.amjmed.2015.10.025|pmid=26551975|access-date=June 18, 2017|doi-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| == Economy == | |||
| {{Main|Economy of the United States}} | {{Main|Economy of the United States}} | ||
| {{further|Economic history of the United States|Tourism in the United States}} | |||
| {|class="wikitable" border="1" table style="border:1px black; float:right; margin-left:1em;" | |||
| ], the most-used currency ] and the world's foremost ]<ref name="federalreserve.gov">{{cite web |title=The Implementation of Monetary Policy – The Federal Reserve in the International Sphere |url=http://www.federalreserve.gov/pf/pdf/pf_4.pdf |access-date=August 24, 2010}}</ref>]] | |||
| |- | |||
| ! style="background:#f99;" colspan="2"|Economic indicators | |||
| |- | |||
| |]||9.4%<sup>July 2009</sup><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.bls.gov/news.release/empsit.nr0.htm|title=Employment Situation Summary|publisher=U.S. Dept. of Labor|date=2009-08-07|accessdate=2009-08-09}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |GDP growth||−1.0%<sup>2Q 2009</sup> <ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.bea.gov/national/xls/gdpchg.xls|title=Gross Domestic Product|publisher=Bureau of Economic Analysis|date=2009-07-31|accessdate=2009-08-06}} Change is based on ]. Quarterly growth is expressed as an annualized rate.</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |] inflation||−2.1%<sup>{{as of|date=2009|June|alt=July 2008 – July 2009}}</sup><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.bls.gov/news.release/cpi.nr0.htm|title=Consumer Price Index: July 2009|publisher=Bureau of Labor Statistics|date=2009-08-14|accessdate=2009-08-23}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |]||$11.808 trillion<sup>September 18, 2009</sup><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.treasurydirect.gov/NP/BPDLogin?application=np|title=Debt Statistics|publisher=U.S. Dept. of the Treasury|accessdate=2009-09-21}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |]||13.2%<sup>2008</sup><ref name="CBPR08">{{cite web|url=http://www.census.gov/prod/2009pubs/p60-236.pdf|title=Income, Poverty and Health Insurance Coverage in the United States: 2008|publisher=U.S. Census Bureau|date=2009-09-10|accessdate=2009-09-16}}</ref> | |||
| |} | |||
| The United States has a ] ], which is fueled by abundant ]s, a well-developed infrastructure, and high productivity.<ref>{{cite book|title=Natural Resources: Neither Curse Nor Destiny|author=Lederman, Daniel, and William Maloney|publisher=World Bank|year=2007|isbn=0821365452|page=185}}</ref> According to the ], the U.S. GDP of $14.3 trillion constitutes 23% of the ] at market exchange rates and almost 21% of the gross world product at ] (PPP).<ref name="IMF GDP"/> The largest national GDP in the world, it was about 4% less than the combined GDP of the ] at PPP in 2007.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2001rank.html|title=Rank Order—GDP (Purchasing Power Parity)|publisher=CIA|work=World Factbook|date=2008-10-09|accessdate=2008-10-21}}</ref> The country ranks seventeenth in the world in ] and sixth in ].<ref name="IMF GDP"/> The United States is the largest importer of goods and third largest exporter, though ] are relatively low. Canada, China, Mexico, Japan, and Germany are its top trading partners.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/top/dst/current/balance.html|title=U.S. Top Trading Partners, 2006|publisher=U.S. Census Bureau|accessdate=2007-03-26}}</ref> The leading export commodity is electrical machinery, while vehicles constitute the leading import.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.census.gov/prod/2006pubs/07statab/foreign.pdf|title=Table 1289. U.S. Exports and General Imports by Selected SITC Commodity Groups: 2002 to 2005|publisher=U.S. Census Bureau|work=Statistical Abstract of the United States 2007|month=October|year=2006|accessdate=2007-08-26}}</ref> China is the largest foreign holder of U.S. public debt.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.reuters.com/article/newsOne/idUSTRE58M25U20090923|title=Factbox: U.S.-China Interdependence Outweighs Trade Spat|publisher=Reuters|date=2009-09-23|accessdate=2007-09-25}}</ref> After an expansion that lasted just over six years, the U.S. economy has been in ] since December 2007.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.nytimes.com/2008/12/02/business/02markets.html|author=Grynbaum, Michael A.|title=Dow Plunges 680 Points as Recession Is Declared|work=New York Times|date=2008-12-01|accessdate=2008-12-01}}</ref> The United States ranks second in the ].<ref name=Rank2009>{{Cite web| url=http://www.weforum.org/pdf/GCR09/GCR20092010fullrankings.pdf|title = Table 4: The Global Competitiveness Index 2009–2010 rankings and 2008–2009 comparisons| author = World Economic Forum|accessdate=2009-09-09}}</ref> | |||
| ], on ]]] | |||
| In 2009, the ] is estimated to constitute 55.3% of the economy, with federal government activity accounting for 24.1% and state and local government activity (including federal transfers) the remaining 20.6%.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.usgovernmentspending.com/index.php|title=Government Spending Overview|publisher=usgovernmentspending.com|accessdate=2009-05-09}}</ref> The economy is ], with the ] contributing 67.8% of GDP.<ref name="Econ">{{cite web|url=http://usinfo.state.gov/products/pubs/economy-in-brief/page3.html|accessdate=2008-03-12|title=USA Economy in Brief|publisher=U.S. Dept. of State, International Information Programs}}</ref> The leading business field by gross business receipts is wholesale and retail trade; by net income it is finance and insurance.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.census.gov/prod/2006pubs/07statab/business.pdf|title=Table 726. Number of Returns, Receipts, and Net Income by Type of Business and Industry: 2003|publisher=U.S. Census Bureau|work=Statistical Abstract of the United States 2007|month=October|year=2006|accessdate=2007-08-26}}</ref> The United States remains an industrial power, with chemical products the leading manufacturing field.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.census.gov/prod/2006pubs/07statab/manufact.pdf|title=Table 971. Gross Domestic Product in Manufacturing in Current and Real (2000) Dollars by Industry: 2000 to 2005 (2004)|publisher=U.S. Census Bureau|work=Statistical Abstract of the United States 2007|month=October|year=2006|accessdate=2007-08-26}}</ref> The United States is the third largest producer of oil in the world, as well as its largest importer.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2173rank.html|title=Rank Order—Oil (Production)|publisher=CIA|work=The World Factbook|date=2007-09-06|accessdate=2007-09-14}}{{cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2174rank.html|title=Rank Order—Oil (Consumption)|publisher=CIA|work=The World Factbook|date=2007-09-06|accessdate=2007-09-14}}{{cite web|url=http://www.eia.doe.gov/pub/oil_gas/petroleum/data_publications/company_level_imports/current/import.html|title=Crude Oil and Total Petroleum Imports Top 15 Countries|publisher=U.S. Energy Information Administration|date=2008-08-26|accessdate=2008-09-10}}</ref> It is the world's number one producer of electrical and nuclear energy, as well as liquid natural gas, sulfur, phosphates, and salt. While ] accounts for just under 1% of GDP,<ref name="Econ"/> the United States is the world's top producer of corn<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.grains.org/page.ww?section=Barley,+Corn+%26+Sorghum&name=Corn|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20080112182404/http://www.grains.org/page.ww?section=Barley,+Corn+%26+Sorghum&name=Corn|archivedate=2008-01-12|title=Corn|publisher=U.S. Grains Council|accessdate=2008-03-13}}</ref> and soybeans.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.worldwatch.org/node/5442|title=Soybean Demand Continues to Drive Production|publisher=Worldwatch Institute|date=2007-11-06|accessdate=2008-03-13}}</ref> The ] is the world's largest by dollar volume.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://ir.nyse.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=129145&p=irol-newsArticle&ID=1036503&highlight=|title=New Release/Ultra Petroleum Corp.,|publisher=NYSE Euronext|date=2007-07-03|accessdate=2007-08-03}}</ref> ] and ] are the two most recognized brands in the world.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cheskin.com/view_news.php?id=2|title=Sony, LG, Wal-Mart among Most Extendible Brands|publisher=Cheskin|date=2005-06-06|accessdate=2007-06-19}}</ref> | |||
| The U.S. has been the world's ].<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Fordham |first=Benjamin |date=October 2017 |title=Protectionist Empire: Trade, Tariffs, and United States Foreign Policy, 1890–1914 |url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/s0898588x17000116 |journal=Studies in American Political Development |volume=31 |issue=2 |pages=170–192 |doi=10.1017/s0898588x17000116 |s2cid=148917255 |issn=0898-588X}}</ref> The 2023 nominal U.S. ] (GDP) of more than $27 trillion was the highest in the world, constituting over 25% of the global economy or 15% at ] (PPP).<ref name="IMFWEO.US" /><ref name="IMF-2023">{{cite web |title=Report for Selected Countries and Subjects |url=https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2023/April/weo-report?c=111,&s=NGDP_R,NGDP_RPCH,NGDP,NGDPD,PPPGDP,NGDP_D,NGDPRPC,NGDPRPPPPC,NGDPPC,NGDPDPC,PPPPC,NGAP_NPGDP,PPPSH,PPPEX,NID_NGDP,NGSD_NGDP,PCPI,PCPIPCH,PCPIE,PCPIEPCH,FLIBOR6,TM_RPCH,TMG_RPCH,TX_RPCH,TXG_RPCH,LUR,LE,LP,GGR,GGR_NGDP,GGX,GGX_NGDP,GGXCNL,GGXCNL_NGDP,GGSB,GGSB_NPGDP,GGXONLB,GGXONLB_NGDP,GGXWDN,GGXWDN_NGDP,GGXWDG,GGXWDG_NGDP,NGDP_FY,BCA,BCA_NGDPD,&sy=2021&ey=2023&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1 |website=Imf.org}}</ref> From 1983 to 2008, U.S. real compounded annual GDP growth was 3.3%, compared to a 2.3% weighted average for the rest of the ].<ref name="Hagopian">{{cite journal |author=Hagopian |first1=Kip |last2=Ohanian |first2=Lee |date=August 1, 2012 |title=The Mismeasure of Inequality |url=https://www.hoover.org/publications/policy-review/article/123566 |url-status=dead |journal=Policy Review |issue=174 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131203012353/https://www.hoover.org/publications/policy-review/article/123566 |archive-date=December 3, 2013 |access-date=January 23, 2020 }}</ref> The country ranks ],<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.bea.gov/news/2023/gross-domestic-product-fourth-quarter-and-year-2022-third-estimate-gdp-industry-and|title=Gross Domestic Product, Fourth Quarter and Year 2022 (Third Estimate), GDP by Industry, and Corporate Profits|publisher=]}}</ref> ] (PPP),<ref name="IMFWEO.US" /> and ].<ref name="IMFWEO.US" /> It possesses the ] among ] countries.<ref>{{cite web |title=Household disposable income |url=https://data.oecd.org/hha/household-disposable-income.htm |website=OECD Data |language=en}}</ref> As of February 2024, the total ] was $34.4 trillion.<ref>{{cite news|last=Fox|first=Michelle|date=March 1, 2024|title=The U.S. national debt is rising by $1 trillion about every 100 days|publisher=CNBC|url=https://www.cnbc.com/2024/03/01/the-us-national-debt-is-rising-by-1-trillion-about-every-100-days.html}}</ref> | |||
| In 2005, 155 million persons were employed with earnings, of whom 80% had full-time jobs.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://pubdb3.census.gov/macro/032006/perinc/new05_001.htm|title=Labor Force and Earnings, 2005|publisher=U.S. Census Bureau|accessdate=2007-05-29}}</ref> The majority, 79%, were employed in the service sector.<ref name="WF" /> With about 15.5 million people, health care and social assistance is the leading field of employment.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.census.gov/prod/2006pubs/07statab/business.pdf|title=Table 739. Establishments, Employees, and Payroll by Employment-Size Class and Industry: 2000 to 2003|publisher=U.S. Census Bureau|work=Statistical Abstract of the United States 2007|month=October|year=2006|accessdate=2007-08-26}}</ref> About 12% of workers are ], compared to 30% in Western Europe.<ref>{{cite web|author=Fuller, Thomas|url=http://www.iht.com/articles/2005/06/14/news/europe.php|title=In the East, Many EU Work Rules Don't Apply|date=2005-06-15|work=International Herald Tribune|accessdate=2007-06-28}}</ref> The World Bank ranks the United States first in the ease of hiring and firing workers.<ref name="EDBI">{{cite web|url=http://www.doingbusiness.org/ExploreEconomies/?economyid=197|accessdate=2007-06-28|title=Doing Business in the United States (2006)|publisher=World Bank}}</ref> Between 1973 and 2003, a year's work for the average American grew by 199 hours.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.usnews.com/usnews/opinion/articles/031110/10dobbs.htm|author=Dobbs, Lou|title=The Perils of Productivity|work=U.S. News & World Report|date=2003-11-02|accessdate=2007-06-30}}</ref> Partly as a result, the United States maintains the highest labor productivity in the world. However, it no longer leads in productivity per hour as it did from the 1950s through the early 1990s; workers in Norway, France, Belgium and ] are now more productive per hour.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://kilm.ilo.org/2005/press/download/ExSumEN.pdf|title=Highlights of Current Labour Market trends|publisher=International Labour Organization|work=Key Indicators of the Labour Market Programme|date=2005-12-09|accessdate=2007-12-20}}</ref> Compared to Europe, U.S. property and corporate ] are generally higher, while labor and, particularly, consumption tax rates are lower.<ref>{{cite news|author=Gumbel, Peter|url=http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,662737-2,00.html|title=Escape from Tax Hell|date=2004-07-11|work=Time|accessdate=2007-06-28}}</ref> | |||
| ], the world's ],<ref>{{Cite web |date=June 21, 2024 |title=Microsoft back as most valuable listed company as Nvidia slips |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/c8884389l35o |access-date=August 6, 2024 |website=] |language=en-GB}}</ref> has its global headquarters in ], north of Seattle.]] | |||
| Of the world's ], ] as of 2023,<ref name="Fortune-2022">{{Cite web |title=Global 500 |url=https://fortune.com/ranking/global500/ |access-date=August 3, 2023 |website=] |language=en}}</ref> which is the highest number of any country.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Hyam |first=Benji |date=November 29, 2023 |title=Most Profitable Companies: U.S. vs. Rest of the World, 2023 |url=https://www.growandconvert.com/research/most-profitable-fortune-500-companies-in-2023/ |access-date=July 16, 2024 |website=www.growandconvert.com |language=en-US}}</ref> The ] is the currency most used ] and is the world's foremost ], backed by the country's dominant economy, ], the ] system, and its linked ] and large ].<ref name="federalreserve.gov" /> ], and in others it is the ].<ref name="Benjamin J. Cohen 2006, p. 17">Benjamin J. Cohen, ''The Future of Money'', Princeton University Press, 2006, {{ISBN|0691116660}}; ''cf''. "the dollar is the de facto currency in Cambodia", Charles Agar, ''] Vietnam'', 2006, {{ISBN|0471798169}}, p. 17.</ref><ref>{{cite web |date=March 31, 2014 |title=US GDP Growth Rate by Year |url=http://www.multpl.com/us-gdp-growth-rate/table/by-year |access-date=June 18, 2014 |website=multpl.com |publisher=US Bureau of Economic Analysis}}</ref> It has ] with ], including the ].<ref>{{cite web |title=United States free trade agreements |url=https://ustr.gov/trade-agreements/free-trade-agreements |access-date=May 31, 2019 |work=]}}</ref> The U.S. ranked second in the ] in 2019, after Singapore.<ref name="World Economic Forum">{{cite web |title=Rankings: Global Competitiveness Report 2013–2014 |url=http://www3.weforum.org/docs/GCR2013-14/GCR_Rankings_2013-14.pdf |access-date=June 1, 2014 |publisher=World Economic Forum}}</ref> Although the United States has reached a ]<ref name="Collins-2023">{{Cite web |last=Collins |first=Michael |date=August 11, 2023 |title=The Post-Industrial Service Economy Isn't Working for the Middle Class |url=https://www.industryweek.com/the-economy/data-and-statistics/article/21271497/the-post-industrial-service-economy-isnt-working |access-date=August 10, 2024 |website=] |language=en}}</ref> and is often described as having a ],<ref name="Collins-2023" /><ref name="Econ">{{cite web |title=USA Economy in Brief |url=https://usinfo.state.gov/products/pubs/economy-in-brief/page3.html |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080312123609/https://usinfo.state.gov/products/pubs/economy-in-brief/page3.html |archive-date=March 12, 2008 |publisher=U.S. Dept. of State, International Information Programs}}</ref> it ].<ref>{{cite web |date=July 2010 |title=The State of Manufacturing in the United States |url=http://trade.gov/manufactureamerica/facts/tg_mana_003019.asp |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130226011512/http://trade.gov/manufactureamerica/facts/tg_mana_003019.asp |archive-date=February 26, 2013 |access-date=March 10, 2013 |publisher=International Trade Administration }}</ref> {{As of|2021}}, the U.S. is the ] after China.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Manufacturing, Value Added (Current US$) |url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NV.IND.MANF.CD?most_recent_value_desc=true |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200107135049/https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NV.IND.MANF.CD?most_recent_value_desc=true |archive-date=January 7, 2020 |access-date=July 14, 2021 |publisher=]}}</ref> | |||
| ] on ], the world's ]<ref name=NYSEhighestcap>{{cite web|url=https://www.forbes.com/advisor/investing/nyse-new-york-stock-exchange/|title=NYSE: What Is The New York Stock Exchange|author= Kat Tretina and Benjamin Curry|work=Forbes|date=April 9, 2021|access-date=July 24, 2022}}</ref>]] | |||
| ] is the world's principal ]<ref>{{cite news |last1=Jones |first1=Huw |date=March 24, 2022 |title=New York widens lead over London in top finance centres index |url=https://www.reuters.com/business/new-york-widens-lead-over-london-top-finance-centres-index-2022-03-24/ |access-date=July 29, 2022 |website=]}}</ref><ref name=NYCFintechAndFinancialCapitalWorld>{{cite web |url = https://www.longfinance.net/publications/long-finance-reports/the-global-financial-centres-index-35/|title = The Global Financial Centres Index 35|date = March 21, 2024|publisher = Long Finance|access-date = May 1, 2024}}</ref> and the epicenter of the world's ].<ref name="NYCEpicenterUSMetroEconomy">{{cite web |author=Ghosh |first=Iman |date=September 24, 2020 |title=This 3D map shows the U.S. cities with the highest economic output |url=https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2020/09/united-states-america-economic-output-new-york-la/ |access-date=March 5, 2023 |publisher=World Economic Forum |quote=The New York metro area dwarfs all other cities for economic output by a large margin.}}</ref> The ] and ], both located in New York City, are the world's two ] by ] and ].<ref>{{cite web |title=Monthly Reports – World Federation of Exchanges |url=https://www.world-exchanges.org/our-work/statistics |publisher=WFE}}</ref><ref name="sfc.hk">. Securities and Exchange Commission (China).</ref> The United States is at or near the forefront of ] and ]<ref>{{Cite book |last=WIPO |url=https://www.wipo.int/global_innovation_index/en/2022/index.html |title=Global Innovation Index 2022, 15th Edition |publisher=World Intellectual Property Organization |year=2022 |isbn=9789280534320 |language=en |doi=10.34667/tind.46596 |access-date=February 25, 2023}}</ref> in many economic fields, especially in ]; ] and ]s; ]; and medical, ] and ].<ref name="CIA-2018" /> The country's economy is fueled by abundant ]s, a well-developed ], and ].<ref name="Wright, Gavin 2007 p. 185">Wright, Gavin, and Jesse Czelusta, "Resource-Based Growth Past and Present", in ''Natural Resources: Neither Curse Nor Destiny'', ed. Daniel Lederman and William Maloney (World Bank, 2007), p. 185. {{ISBN|0821365452}}.</ref> The ] are the ], Mexico, Canada, China, Japan, South Korea, the United Kingdom, Vietnam, India, and Taiwan.<ref>{{cite web |date=October 2022 |title=Top Trading Partners – October 2022 |url=https://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/statistics/highlights/top/top1612yr.html |access-date=May 12, 2023 |publisher=U.S. Census Bureau}}</ref> The United States is the world's ] and the ].{{efn|A country's total exports are usually understood to be goods and services. Based on this, the U.S. is the world's second-largest exporter, after China.<ref>{{cite web |title=World Trade Statistical Review 2019 |url=https://www.wto.org/english/res_e/statis_e/wts2019_e/wts2019_e.pdf |access-date=May 31, 2019 |work=] |page=100}}</ref> However, if primary income is included, the U.S. is the world's largest exporter.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Exports of goods, services and primary income (BoP, current US$) |url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/BX.GSR.TOTL.CD?most_recent_value_desc=true |access-date=May 24, 2024 |website=data.worldbank.org}}</ref>}} It is by far the world's ].<ref>{{Cite web |title=Service exports (BoP, current US$) |url=https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/BX.GSR.NFSV.CD?most_recent_value_desc=true&year_high_desc=false |access-date=August 4, 2023 |publisher=World Bank}}</ref> | |||
| Americans have the highest average ] and ] among ] member states,<ref>{{cite web |title=Income |url=http://www.oecdbetterlifeindex.org/topics/income/ |access-date=September 28, 2019 |work=Better Life Index |publisher=OECD |quote=In the United States, the average household net adjusted disposable income per capita is USD 45 284 a year, much higher than the OECD average of USD 33 604 and the highest figure in the OECD.}}</ref> and the fourth-highest ] as of 2023,<ref>{{Cite web |title=Median Income by Country 2023 |url=https://wisevoter.com/country-rankings/median-income-by-country/ |access-date=July 28, 2023 |website=Wisevoter |language=en-US}}</ref> up from sixth-highest in 2013.<ref name="Household Income">{{cite journal |date=March 18, 2014 |url=http://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/social-issues-migration-health/society-at-a-glance-2014_soc_glance-2014-en |journal=Society at a Glance 2014: OECD Social Indicators |publisher=OECD Publishing |doi=10.1787/soc_glance-2014-en |isbn=9789264200722 |access-date=May 29, 2014 |doi-access=free |title=Society at a Glance 2014 }}</ref> With personal ] of over $18.5 trillion in 2023,<ref>{{Cite web |date=March 28, 2024 |title=Personal Consumption Expenditures |url=https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/PCECA |access-date=July 24, 2024 |website=fred.stlouisfed.org |language=en}}</ref> the U.S. has a heavily ] and is by far the world's ].<ref>{{Cite web |last=Rocha |first=Laura |date=August 18, 2023 |title=Playing To Win In The U.S. Market |url=https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbeseq/2023/08/18/playing-to-win-in-the-us-market/ |access-date=July 24, 2024 |website=] |language=en}}</ref> ] is ]; the richest 10% of the adult population own 72% of the country's household wealth, while the bottom 50% own just 2%.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Piketty|first1=Thomas|title=Capital in the Twenty-First Century|title-link=Capital in the Twenty-First Century|date=2014|publisher=Belknap Press|page=|author-link1=Thomas Piketty}} {{ISBN|978-0-674-43000-6}}</ref> ] remains at record highs,<ref>{{Cite news |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/business/2019/09/26/income-inequality-america-highest-its-been-since-census-started-tracking-it-data-show/ |title=Income inequality in America is the highest it's been since Census Bureau started tracking it, data shows |newspaper=] |access-date=July 27, 2020}}</ref> with the top fifth of earners taking home more than half of all income<ref>{{Cite news|last=Long|first=Heather|date=September 12, 2017|title=U.S. middle-class incomes reached highest-ever level in 2016, Census Bureau says|newspaper=The Washington Post|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/business/economy/us-middle-class-incomes-reached-highest-ever-level-in-2016-census-bureau-says/2017/09/12/7226905e-97de-11e7-b569-3360011663b4_story.html|access-date=November 11, 2019}}</ref> and giving the U.S. one of the widest income distributions among OECD members.<ref name="Sme">{{cite journal |last1=Smeeding |first1=T. M. |year=2005 |title=Public Policy: Economic Inequality and Poverty: The United States in Comparative Perspective |journal=Social Science Quarterly |volume=86 |pages=955–983 |doi=10.1111/j.0038-4941.2005.00331.x |s2cid=154642286}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=Hopkin|first=Jonathan|author-link=Jonathan Hopkin|date=2020 |title=Anti-System Politics: The Crisis of Market Liberalism in Rich Democracies|chapter=American Nightmare: How Neoliberalism Broke US Democracy|url=|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=IyXTDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA87|location= |publisher=]|pages=87–88 |isbn=978-0190699765|doi=10.1093/oso/9780190699765.003.0004}}</ref> The U.S. ] and ], with 735 billionaires and nearly 22 million millionaires as of 2023.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Here's How Many Billionaires And Millionaires Live In The U.S. – Forbes Advisor |url=https://www.forbes.com/advisor/retirement/how-many-billionaires-and-millionaires-live-in-the-u-s/#:~:text=As%20of%202023,%20there%20are,your%20own%20definition%20of%20wealth. |access-date=November 20, 2023 |website=Forbes| date=October 20, 2023 }}</ref> There were about 582,500 sheltered and unsheltered ] in 2022, with 60% staying in an emergency shelter or transitional housing program.<ref>{{cite web |url= https://www.huduser.gov/portal/sites/default/files/pdf/2022-AHAR-Part-1.pdf|title=The 2022 Annual Homelessness Assessment Report (AHAR) to Congress|date= December 2022|website= |publisher=The U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development|access-date=June 16, 2023 }}</ref> In 2022, 6.4 million children experienced food insecurity.<ref name="ers.usda.gov">{{Cite web|url=https://www.ers.usda.gov/topics/food-nutrition-assistance/food-security-in-the-us/key-statistics-graphics.aspx|title=USDA ERS – Key Statistics & Graphics|website= ers.usda.gov|access-date=December 4, 2019}}</ref> ] estimates that around one in five, or approximately 13 million, ] and do not know where they will get their next meal or when.<ref name="FactsAbout">{{Cite web|title= Facts About Child Hunger in America {{!}} Feeding America|url= https://www.feedingamerica.org/hunger-in-america/child-hunger-facts| access-date=December 4, 2019|website= feedingamerica.org}}</ref> {{as of|2022|post=,}} 37.9 million people, or 11.5% of the U.S. population, were ].<ref>{{Cite web |last= |first= |title=National Poverty in America Awareness Month: January 2023 |url=https://www.census.gov/newsroom/stories/poverty-awareness-month.html |website=Census.gov}}</ref> | |||
| ===Income and human development=== | |||
| {{Main|Income in the United States}} | |||
| {{seealso|Income inequality in the United States|Poverty in the United States|Affluence in the United States}} | |||
| ] | |||
| The United States has a smaller ] and redistributes less income through government action than most other ].<ref>{{cite web|first1=Isabelle|last1=Joumard|first2=Mauro|last2=Pisu|first3=Debbie|last3=Bloch|title=Tackling income inequality The role of taxes and transfers|url=https://www.oecd.org/eco/public-finance/TacklingincomeinequalityTheroleoftaxesandtransfers.pdf|publisher=OECD|access-date=May 21, 2015|year=2012}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=Rank|first=Mark Robert |author-link=Mark Robert Rank|date=2023|title=The Poverty Paradox: Understanding Economic Hardship Amid American Prosperity|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hGewEAAAQBAJ&pg=PA116|location= |publisher=]|pages=116–117 |isbn= 978-0190212636}}</ref> It is the only ] that does not ] nationally<ref>{{cite news |last=Min |first=Sarah |date=May 24, 2019 |title=1 in 4 workers in U.S. don't get any paid vacation time or holidays|url=https://www.cbsnews.com/news/one-in-four-workers-in-us-dont-get-any-paid-vacation-time-or-holidays/|publisher=CBS News |access-date=July 15, 2022|quote=The United States is the only advanced economy that does not federally mandate any paid vacation days or holidays. }}</ref> and is one of a few countries in the world without federal ] as a legal right.<ref>{{cite news |last=Bernard |first=Tara Siegel |date=February 22, 2013 |title=In Paid Family Leave, U.S. Trails Most of the Globe |newspaper=The New York Times |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2013/02/23/your-money/us-trails-much-of-the-world-in-providing-paid-family-leave.html |access-date=August 27, 2013}}</ref> The United States has a higher percentage of low-income ] than almost any other developed country, largely because of a weak ] system and lack of government support for at-risk workers.<ref>{{cite news|last=Van Dam|first=Andrew|date=July 4, 2018|title=Is it great to be a worker in the U.S.? Not compared with the rest of the developed world.|newspaper=The Washington Post|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/wonk/wp/2018/07/04/is-it-great-to-be-a-worker-in-the-u-s-not-compared-to-the-rest-of-the-developed-world/?noredirect=on|access-date=July 12, 2018}}</ref> | |||
| According to the ], the pretax ] in 2007 was $50,233. The median ranged from $68,080 in ] to $36,338 in ].<ref name="CBPR08"/> Using ] exchange rates, the overall median is similar to the most affluent cluster of ]. After declining sharply during the middle of the 20th century, ] have plateaued since the early 1970s, with 11–15% of Americans below the ] every year, and 58.5% spending at least one year in poverty between the ages of 25 and 75.<ref name="USCB IP&HIC 2007">{{cite web|author=DeNavas-Walt, Carmen, Bernadette D. Proctor, and Jessica Smith|url=http://www.census.gov/prod/2008pubs/p60-235.pdf|format=PDF|title=Income, Poverty, and Health Insurance Coverage in the United States: 2007|publisher=U.S. Census Bureau|month=August|year=2008|accessdate=2008-11-13}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book|last=Hacker|first=Jacob S.|year=2006|title=The Great Risk Shift: The New Economic Insecurity and the Decline of the American Dream|location=New York|publisher=Oxford University Press|isbn=0195335341}}</ref> In 2007, 37.3 million Americans lived in poverty.<ref name="CBPR08"/> The U.S. welfare state is now among the most austere in the developed world, reducing both ] and ] by considerably less than the mean for rich nations.<ref name="Sme">Smeeding, T. M. (2005). "Public Policy: Economic Inequality and Poverty: The United States in Comparative Perspective." ''Social Science Quarterly'' 86, 955–983.</ref><ref>Kenworthy, L. (1999). "Do Social-Welfare Policies Reduce Poverty? A Cross-National Assessment" ''Social Forces'' 77(3), 1119–1139. Bradley, D., E. Huber, S. Moller, F. Nielsen, and J. D. Stephens (2003). "Determinants of Relative Poverty in Advanced Capitalist Democracies" ''American Sociological Review'' 68(1), 22–51.</ref> While the American welfare state does well in reducing poverty among the elderly,<ref>Orr, D. (November–December, 2004). "Social Security Isn't Broken: So Why the Rush to 'Fix' It?" In C. Sturr and R. Vasudevan, eds. (2007). ''Current Economic Issues''. Boston: Economic Affairs Bureau.</ref> the young receive relatively little assistance.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.prospect.org/cs/articles?article=a_new_deal_of_their_own|author=Starr, Paul|date=2008-02-25|title=A New Deal of Their Own|work=American Prospect|accessdate=2008-07-24}}</ref> A 2007 ] study of children's well-being in twenty-one industrialized nations ranked the United States next to last.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/nol/shared/bsp/hi/pdfs/13_02_07_nn_unicef.pdf|title=Child Poverty in Perspective: An Overview of Child Well-Being in Rich Countries|author=UNICEF|work=BBC|year=2007|accessdate=2007-09-10}}</ref> | |||
| === Science, technology, spaceflight and energy === | |||
| Despite strong increases in productivity, low unemployment, and low inflation, income gains since 1980 have been slower than in previous decades, less widely shared, and accompanied by increased economic insecurity. Between 1947 and 1979, ] rose by over 80% for all classes, with the incomes of poor Americans rising faster than those of the rich.<ref name="Bar">Bartels, L. M. (2008). ''Unequal Democracy: The Political Economy of the New Gilded Age''. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.demos.org/inequality/numbers.cfm#1|author=Hartman, C.|year=2008|title=By the Numbers: Income|accessdate=2008-07-24}}</ref> ] has increased for all classes since 1980,<ref>{{cite web|author=Henderson, David R.|url=http://www.hoover.org/publications/digest/3522596.html|title=The Rich—and Poor—Are Getting Richer|work=Hoover Digest|year=1998|accessdate=2007-06-19}}</ref> largely owing to more dual-earner households, the closing of the gender gap, and longer work hours, but growth has been slower and strongly tilted toward the very top (see graph).<ref name="Sme"/><ref name="Bar"/><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.frbsf.org/news/speeches/2006/1106.html|author=Yellen, J.|year=2006|title=Speech to the Center for the Study of Democracy 2006–2007 Economics of Governance Lecture University of California, Irvine|publisher=Federal Reserve Board|location=San Francisco|accessdate=2008-07-24}}{{cite web|author=Shapiro, Isaac|url=http://www.cbpp.org/10-17-05inc.htm|title=New IRS Data Show Income Inequality Is Again on the Rise|date=2005-10-17|publisher=Center on Budget and Policy Priorities|accessdate=2007-05-16}} Gilbert, D. (1998). ''The American Class Structure''. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth. ISBN 0534505201.</ref> Consequently, the share of income of the top 1%—21.8% of total reported income in 2005—has more than doubled since 1980,<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.nytimes.com/2007/03/29/business/29tax.html?ex=1332820800&en=fb472e72466c34c8&ei=5088&partner=rssnyt&emc=rss|title=Income Gap Is Widening, Data Shows|author=Johnston, David Cay|work=New York Times|date=2007-03-29|accessdate=2007-05-16}}</ref> leaving the United States with the greatest income inequality among developed nations.<ref name="Sme"/><ref>{{cite web|url=http://elsa.berkeley.edu/~saez/TabFig2005prel.xls|author=Saez, E.|title=Table A1: Top Fractiles Income Shares (Excluding Capital Gains) in the U.S., 1913–2005|publisher=UC Berkeley|month=October|year=2007|accessdate=2008-07-24}}{{cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2172.html|title=Field Listing—Distribution of Family Income—Gini Index|publisher=CIA|work=The World Factbook|date=2007-06-14|accessdate=2007-06-17}}</ref> The top 1% pays 27.6% of all federal taxes; the top 10% pays 54.7%.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cbo.gov/ftpdocs/88xx/doc8885/EffectiveTaxRates.shtml|title=Shares of Federal Tax Liabilities, 2004 and 2005|publisher=Congressional Budget Office|accessdate=2008-11-02}}</ref> Wealth, like income, is highly concentrated: The richest 10% of the adult population possesses 69.8% of the country's household wealth, the second-highest share among developed nations.<ref>{{cite web|author=Domhoff, G. William|url=http://sociology.ucsc.edu/whorulesamerica/power/wealth.html|title=Table 4: Percentage of Wealth Held by the Top 10% of the Adult Population in Various Western Countries|publisher=University of California at Santa Cruz, Sociology Dept.|work=Power in America|month=December|year=2006|accessdate=2006-08-21}}</ref> The top 1% possesses 33.4% of net wealth.<ref>{{cite web|author=Kennickell, Arthur B.|url=http://www.federalreserve.gov/pubs/oss/oss2/papers/concentration.2004.5.pdf|title=Table11a: Amounts (Billions of 2004 Dollars) and Shares of Net Worth and Components Distributed by Net Worth Groups, 2004|publisher=Federal Reserve Board|work=Currents and Undercurrents: Changes in the Distribution of Wealth, 1989–2004|date=2006-08-02|accessdate=2007-06-24}}</ref> | |||
| {{Main|Science and technology in the United States|Space policy of the United States|Energy in the United States}} | |||
| {{See also|Communications in the United States}} | |||
| The United States ] and scientific research since the mid-20th century.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Mowery |first=David |title=Technological Change and the Evolution of the U.S. "National Innovation System", 1880-1990 |url=https://www.bbvaopenmind.com/en/articles/technological-change-and-the-evolution-of-the-u-s-national-innovation-system-1880-1990/ |access-date=July 10, 2024 |website=OpenMind |language=en-US}}</ref> Methods for producing ] and the establishment of a ] industry enabled ] of U.S. consumer products in the late 19th century.<ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Goodfriend |first1=Marvin |last2=McDermott |first2=John |date=February 24, 2021 |title=The American System of economic growth |url= |journal=Journal of Economic Growth |language=en |volume=26 |issue=1 |pages= 31–75|doi=10.1007/s10887-021-09186-x |issn=1573-7020 |pmc=7902180 |pmid=33642936}}</ref> By the early 20th century, factory ], the introduction of the ], and other ] created the system of ].<ref>{{Hounshell1984}}</ref> The United States is widely considered to be the leading country in the development of ] technology.<ref>{{cite web |year=2021 |title=Measuring trends in AI |url=https://aiindex.stanford.edu/report |website=Artificial Intelligence Index |publisher=Stanford University}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Espinel |first=Victoria |title=America leads the world in AI–but we could fall behind on AI regulation by the end of 2023 |url=https://fortune.com/europe/2023/09/11/america-leads-world-artificial-intelligence-fall-behind-ai-regulation-2023-tech-victoria-espinel/ |access-date=July 30, 2024 |website=Fortune Europe |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Radu |first=Sintia |date=August 19, 2019 |title=Despite Chinese Efforts, the U.S. Still Leads in AI |url=https://www.usnews.com/news/best-countries/articles/2019-08-19/the-us-is-still-the-global-leader-in-artificial-intelligence |access-date=July 30, 2024 |website=]}}</ref> In 2022, the United States was (after China) the country with the ].<ref>{{Cite web |title=SJR – International Science Ranking |url=https://www.scimagojr.com/countryrank.php?order=itp&ord=desc&year=2020 |access-date=February 5, 2022 |website=Scimagojr.com |language=en-uk}}</ref> In 2021, the U.S. ranked second (also after China) by the number of patent applications, and third by trademark and industrial design applications (after China and Germany), according to ].<ref>{{cite book |author1=World Intellectual Property Organization. |url=https://www.wipo.int/publications/en/details.jsp?id=4571&plang=EN |title=World Intellectual Property Indicators 2021 |publisher=World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) |year=2021 |isbn=9789280533293 |series=World IP Indicators (WIPI) |language=en |doi=10.34667/tind.44461 |access-date=April 27, 2022}}</ref> In 2023 and 2024, the United States ranked third (after Switzerland and Sweden) in the ].<ref>{{Cite web |title=Global Innovation Index 2024 : Unlocking the Promise of Social Entrepreneurship |url=https://www.wipo.int/web-publications/global-innovation-index-2024/en/ |access-date=2024-11-29 |website=www.wipo.int |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=WIPO |url=https://www.wipo.int/global_innovation_index/en/2023/index.html |title=Global Innovation Index 2023, 15th Edition |date=December 28, 2023 |publisher=World Intellectual Property Organization |isbn=9789280534320 |language=en |doi=10.34667/tind.46596 |access-date=October 17, 2023}}</ref> The U.S. has the ]<ref>{{Cite web |last=Desjardins |first=Jeff |date=December 18, 2018 |title=Innovators wanted: these countries spend the most on R&D |url=https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2018/12/how-much-countries-spend-on-r-d/ |access-date=May 22, 2024 |website=www.weforum.org}}</ref> and ranks ninth as a percentage of GDP.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Fleming |first=Sean |date=November 16, 2020 |title=These countries spend the most on research and development |url=https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2020/11/countries-spending-research-development-gdp/ |access-date=May 22, 2024 |website=www.weforum.org}}</ref> In 2023, the United States was ranked the second most technologically advanced country in the world (after South Korea) by ] magazine.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Getzoff |first=Marc |date=December 1, 2023 |title=Most Technologically Advanced Countries In The World 2023 |url=https://gfmag.com/data/non-economic-data/most-advanced-countries-in-the-world/ |access-date=July 29, 2024 |website=Global Finance Magazine |language=en-US}}</ref> | |||
| ] saluting the ] on the ] during the 1969 ] mission; the United States is the only country that has ].]] | |||
| The United States has maintained a space program since the late 1950s, beginning with the establishment of the ] (NASA) in 1958.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2023-07-26 |title=65 Years Ago: The National Aeronautics and Space Act of 1958 Creates NASA – NASA |url=https://www.nasa.gov/history/65-years-ago-the-national-aeronautics-and-space-act-of-1958-creates-nasa/#:~:text=President%20Eisenhower%20signed%20the%20National,of%20the%20International%20Geophysical%20Year. |access-date=2024-09-06 |language=en-US}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=2024-09-04 |title=National Aeronautics and Space Administration {{!}} US Space Agency & Exploration Achievements {{!}} Britannica |url=https://www.britannica.com/topic/NASA |access-date=2024-09-05 |website=www.britannica.com |language=en}}</ref> NASA's ] (1961–1972) achieved the first crewed ] with the 1969 ] mission; it remains one of the agency's most significant milestones.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2024-08-29 |title=Apollo {{!}} History, Missions, Significance, & Facts {{!}} Britannica |url=https://www.britannica.com/science/Apollo-space-program |access-date=2024-09-05 |website=www.britannica.com |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=2019-07-04 |title=The Apollo Missions |url=https://www.ibm.com/thought-leadership/the-apollo-missions/ |access-date=2024-09-05 |website=The Apollo Missions |language=en-US}}</ref> Other major endeavors by NASA include the ] (1981–2011),<ref>{{Cite web |title=Space Shuttle – NASA |url=https://www.nasa.gov/space-shuttle/ |access-date=2024-09-05 |language=en-US}}</ref> the ] (1972–present), the ] and ] ]s (launched in 1990 and 2021, respectively),<ref>{{Cite web |title=Quick Facts |url=https://hubblesite.org/quick-facts |access-date=2024-09-05 |website=HubbleSite |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Quick Facts |url=https://webbtelescope.org/quick-facts |access-date=2024-09-05 |website=Webb |language=en}}</ref> and the multi-mission ] ('']'' and '']'', ''],'' and '']'').<ref>{{Cite web |title=Mars Exploration – NASA Science |url=https://science.nasa.gov/planetary-science/programs/mars-exploration/ |access-date=2024-09-05 |website=science.nasa.gov |language=en-US}}</ref> NASA is one of five agencies collaborating on the ] (ISS);<ref>{{Cite web |title=International Space Station Facts and Figures – NASA |url=https://www.nasa.gov/international-space-station/space-station-facts-and-figures/ |access-date=2024-09-05 |language=en-US}}</ref> U.S. contributions to the ISS include several modules, including '']'' (2001), '']'' (2007), and '']'' (2010), as well as ongoing logistical and operational support.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Howell |first=Elizabeth |date=2022-08-24 |title=International Space Station: Facts, History & Tracking |url=https://www.space.com/16748-international-space-station.html |access-date=2024-09-05 |website=Space.com |language=en |edition=updated, last}}</ref> The United States ] dominates the global ].<ref>{{Cite news |date=2022-01-11 |title=Analysis {{!}} Companies are commercializing outer space. Do government programs still matter? |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/politics/2022/01/11/companies-are-commercializing-outer-space-do-government-programs-still-matter/ |access-date=2024-09-05 |newspaper=Washington Post |language=en-US |issn=0190-8286}}</ref> Prominent American spaceflight contractors include ], ], ], ], and ]. NASA programs such as the ], ], ], and ] have facilitated growing private-sector involvement in American spaceflight.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Commercial Space – NASA |url=https://www.nasa.gov/humans-in-space/commercial-space/ |access-date=2024-09-05 |language=en-US}}</ref><!-- Info needed about the Artemis program as it is a major component of contemporary American space policy --> | |||
| {{as of|2023}}, the United States receives approximately 84% of its energy from fossil fuel, and the largest source of the country's energy came from ] (38%), followed by ] (36%), ] (9%), ] (9%), and ] (9%).<ref>{{Cite web |title=U.S. energy facts explained – consumption and production – U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) |url=https://www.eia.gov/energyexplained/us-energy-facts/ |access-date=November 21, 2023 |website=eia.gov}}</ref><ref name="visu">{{cite web |date= March 2022|title=Energy Flow Charts: Charting the Complex Relationships among Energy, Water, and Carbon |url=https://flowcharts.llnl.gov/ |access-date=May 16, 2023 |publisher=Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory}}</ref><!--Numbers do not add up to 100 due to rounding errors. --> The United States constitutes less than 4% of the ], but consumes around 16% of the world's energy.<ref>{{cite news |date=November 5, 2021 |title=What is the United States' share of world energy consumption? |work=] |url=https://www.eia.gov/tools/faqs/faq.php?id=87&t=1}}</ref> The U.S. ranks as the ].<ref>{{cite web |last=US Environmental Protection Agency |first=OAR |date=February 8, 2017 |title=Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks |url=https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/inventory-us-greenhouse-gas-emissions-and-sinks |access-date=December 3, 2020 |website=US EPA |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| ===Science and technology=== | |||
| {{Main|Science and technology in the United States}} | |||
| {{seealso|Technological and industrial history of the United States}} | |||
| ] during the first human ], 1969]] | |||
| The United States has been a leader in scientific research and technological innovation since the late 19th century. In 1876, ] was awarded the first U.S. ]. ]'s laboratory developed the ], the first ], and the first viable ]. ] pioneered ], the ], and ]. In the early 20th century, the automobile companies of ] and ] promoted the ]. The ], in 1903, made the ].<ref>{{cite web|author=Benedetti, François| url =http://www.fai.org/news_archives/fai/000295.asp| title =100 Years Ago, the Dream of Icarus Became Reality| publisher =Fédération Aéronautique Internationale (FAI)|date=2003-12-17|accessdate=2007-08-15}}</ref> The rise of ] in the 1930s led many European scientists, including ] and ], to immigrate to the United States. During World War II, the ] developed nuclear weapons, ushering in the ]. The ] produced rapid advances in rocketry, ], and computers. The United States largely developed the ] and its successor, the ]. Today, the bulk of research and development funding, 64%, comes from the private sector.<ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.census.gov/compendia/statab/tables/08s0775.xls | title = Research and Development (R&D) Expenditures by Source and Objective: 1970 to 2004 | publisher = U.S. Census Bureau | accessdate = 2007-06-19 }}{{Dead link|date=May 2009}}</ref> The United States leads the world in scientific research papers and ].<ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.guardian.co.uk/education/2006/mar/21/highereducation.uk4 |author=MacLeod, Donald| title = Britain Second in World Research Rankings | date=2006-03-21 | work = Guardian | accessdate = 2006-05-14 }}</ref> Americans possess high levels of technological consumer goods,<ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.nationmaster.com/graph/med_tel_percap-media-televisions-per-capita | title = Media Statistics > Televisions (per capita) by Country | publisher = NationMaster |month=December | year=2003}} {{cite web | url = http://www.nationmaster.com/graph/med_per_com_percap-media-personal-computers-per-capita | title = Media Statistics > Personal Computers (per capita) by Country | publisher = NationMaster |month=December | year=2003}} {{cite web | url = http://www.nationmaster.com/graph/med_rad_percap-media-radios-per-capita | title = Media Statistics > Radios (per capita) by Country | publisher = NationMaster | month = December | year = 2003 | accessdate = 2007-06-03 }}</ref> and almost half of U.S. households have ].<ref>{{cite web | url = http://adage.com/digital/article?article_id=116136 | title = Download 2007 Digital Fact Pack | date=2007-04-23| work = Advertising Age | accessdate = 2007-06-10 }}</ref> The country is the primary developer and grower of ]; more than half of the world's land planted with biotech crops is in the United States.<ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.isaaa.org/Resources/Publications/briefs/35/executivesummary/default.html | title = ISAAA Brief 35-2006: Executive Summary—Global Status of Commercialized Biotech/GM Crops: 2006 | publisher = International Service for the Acquisition of Agri-Biotech Applications | accessdate = 2007-06-19 }}</ref> | |||
| ===Transportation=== | === Transportation === | ||
| {{Main|Transportation in the United States}} | {{Main|Transportation in the United States}} | ||
| ], serving the ], is the world's ] with over 75 million passengers in 2021.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.cnn.com/travel/article/worlds-busiest-airports-2021/index.html|title=This US airport has reclaimed its title as the world's busiest|publisher=CNN|first=Marnie|last=Hunter|date=April 11, 2022}}</ref>]] | |||
| ], which extends {{convert|46876|mi|km}}<ref>{{cite web |title=Interstate FAQ (Question #3) |publisher=Federal Highway Administration |year=2006 |url=http://www.fhwa.dot.gov/interstate/faq.htm#question3 |accessdate=2009-03-04}}</ref>]] | |||
| Everyday personal transportation in America is dominated by the automobile. As of 2003, there were 759 automobiles per 1,000 Americans, compared to 472 per 1,000 inhabitants of the European Union the following year.<ref>{{cite web | url =http://europa.eu/rapid/pressReleasesAction.do?reference=STAT/06/125| title =Car Free Day 2006: Nearly One Car per Two Inhabitants in the EU25 in 2004| date=2006-09-19|publisher =Europa, Eurostat Press Office| accessdate = 2007-08-15 }}</ref> About 40% of ] are vans, ], or light trucks.<ref>{{cite web|url =http://www.bts.gov/publications/highlights_of_the_2001_national_household_travel_survey/html/section_01.html| title =Household, Individual, and Vehicle Characteristics|publisher =U.S. Dept. of Transportation, Bureau of Transportation Statistics|work =2001 National Household Travel Survey|accessdate = 2007-08-15}}</ref> The average American adult (accounting for all drivers and nondrivers) spends 55 minutes driving every day, traveling {{convert|29|mi|km|0}}.<ref>{{cite web|url =http://www.bts.gov/publications/highlights_of_the_2001_national_household_travel_survey/html/section_02.html| title =Daily Passenger Travel|publisher =U.S. Dept. of Transportation, Bureau of Transportation Statistics|work =2001 National Household Travel Survey|accessdate = 2007-08-15}}</ref> The civil airline industry is entirely privatized, while most major airports are publicly owned. The four largest airlines in the world by passengers carried are American; ] is number one.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.iata.org/ps/publications/wats-passenger-carried.htm| title =Scheduled Passengers Carried (2008 data)|publisher=International Air Transport Association (IATA)|accessdate=2009-06-27}}</ref> Of the world's thirty busiest passenger airports, sixteen are in the United States, including ].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.airports.org/cda/aci_common/display/main/aci_content07_c.jsp?zn=aci&cp=1-5-54-55_666_2__|title=Passenger Traffic 2006 Final|publisher=Airports Council International|date=2007-07-18|accessdate=2007-08-15}}</ref> While transport of goods by rail is extensive, relatively few people use rail to travel, within or between cities.<ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.gao.gov/products/GAO-07-15 | title = Intercity Passenger Rail: National Policy and Strategies Needed to Maximize Public Benefits from Federal Expenditures| date=2006-11-13| publisher = U.S. Government Accountability Office| accessdate = 2007-06-20 }}</ref> Only 9% of total U.S. work trips use ], compared to 38.8% in Europe.<ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.policy.rutgers.edu/vtc/documents/TOD.Euro-Style_Planning-Renne-Wells.pdf |format=PDF|author=Renne, John L., and Jan S. Wells| title = Emerging European-Style Planning in the United States: Transit-Oriented Development (p. 2) | year=2003 | publisher = Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey | accessdate = 2007-06-11}}</ref> Bicycle usage is minimal, well below European levels.<ref>{{cite web | url =http://www.transalt.org/files/resources/other/010901TQpdf021.pdf|author=Pucher, John, and Lewis Dijkstra| title = Making Walking and Cycling Safer: Lessons from Europe | month=February | year=2000| publisher = Transportation Alternatives |work=Transportation Quarterly | accessdate = 2007-08-15}}</ref> | |||
| The ] and its divisions provide regulation, supervision, and funding for all aspects of transportation except for customs, immigration, and security. (The latter remain the responsibility of the ].) Each U.S. state has ], which builds and maintains state highways. Depending upon the state, this department might also directly operate or supervise other modes of transportation. | |||
| ===Energy=== | |||
| {{Main|Energy in the United States}} | |||
| {{seealso|Energy policy of the United States}} | |||
| The United States energy market is 29,000 ] per year. ] is 7.8 tons of oil equivalent per year, compared to Germany's 4.2 tons and Canada's 8.3 tons. In 2005, 40% of this energy came from petroleum, 23% from coal, and 22% from natural gas. The remainder was supplied by nuclear power and ] sources.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.eia.doe.gov/emeu/aer/pdf/pages/sec1_3.pdf|title= Diagram 1: Energy Flow, 2007|work=EIA Annual Energy Review 2007 |publisher=U.S. Dept. of Energy, Energy Information Administration|accessdate=2008-06-25}}</ref> The United States is the world's largest consumer of petroleum.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2174rank.html|title= Rank Order—Oil (Consumption)|publisher=CIA|work=The World Factbook|date=2007-09-06|accessdate=2007-09-14}}</ref> For decades, ] has played a limited role relative to many other developed countries. In 2007, several applications for new nuclear plants were filed.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.economist.com/science/displaystory.cfm?story_id=9762843|title= Atomic Renaissance|work=Economist|accessdate=2007-09-06}}</ref> | |||
| ] is almost entirely the jurisdiction of the federal government; the ] regulates all aspects of ], ], certification and compliance, and ]. Vehicle traffic laws, however, are enacted and enforced by state and local authorities, with the exception of roads located on federal property (national parks, military bases) or in the ]. The ] is the primary enforcer of law and security on U.S. waterways, inland as well as coastal, but economic jurisdiction over coastal ] is shared between state and federal governments. The ] are the world's ], totaling {{convert|41009|km|0|abbr=on}}.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/field/waterways/country-comparison |title=Waterways – The World Factbook |work=] |publisher=] |access-date=July 14, 2022}}</ref> | |||
| ==Demographics== | |||
| {{Main|Demographics of the United States}} | |||
| {{seealso|Immigration to the United States}} | |||
| ] | |||
| The United States population is projected by the U.S. Census Bureau to be {{uspop commas}},<ref name="POP">{{cite web|url=http://www.census.gov/population/www/popclockus.html|publisher=U.S. Census Bureau|title=U.S. POPClock Projection}} Figure updated automatically.</ref> including an estimated 11.2 million ].<ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.cis.org/articles/2008/back808.pdf| author =Camarota, Steven A., and Karen Jensenius | title = Homeward Bound: Recent Immigration Enforcement and the Decline in the Illegal Alien Population | month =July | year =2008| publisher = Center for Immigration Studies | accessdate = 2008-08-06}}</ref> The United States is the third most populous nation in the world, after China and India. Its ] rate is 0.89%,<ref name="WF"/> compared to the European Union's 0.16%.<ref>{{cite web | url = https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ee.html | title = European Union| publisher = CIA|work=The World Factbook | date = 2007-05-31| accessdate = 2007-06-15}}</ref> The ] of 14.16 per 1,000, 30% below the world average, is higher than any European country's except ] and ].<ref>{{cite web | url = https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2054rank.html | title = Rank Order—Birth Rate| publisher = CIA|work=The World Factbook | date =2007-05-31| accessdate = 2007-06-13}}</ref> In fiscal year 2008, 1.1 million immigrants were granted ].<ref>. ] ''Annual Flow Report.''</ref> Mexico has been the leading source of new residents for over two decades; since 1998, China, India, and the Philippines have been in the top four sending countries every year.<ref>{{cite web|url = http://www.dhs.gov/ximgtn/statistics/publications/LPR07.shtm|title=Persons Obtaining Legal Permanent Resident Status by Region and Country of Birth: Fiscal Years 1998 to 2007 (Table 3)|publisher=U.S. Dept. of Homeland Security|accessdate=2008-09-06}}</ref> The United States is the only industrialized nation in which large population increases are projected.<ref name="PRC">{{cite web|url=http://www.prcdc.org/summaries/uspopperspec/uspopperspec.html|title=Executive Summary: A Population Perspective of the United States|publisher=Population Resource Center|month=May|year=2000|accessdate=2007-12-20|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20070604165856/http://www.prcdc.org/summaries/uspopperspec/uspopperspec.html|archivedate=2007-06-04}}</ref> | |||
| Passenger and freight rail systems, bus systems, water ferries, and dams may be under either public or private ownership and operation. U.S. civilian airlines are all privately owned. Most U.S. airports are owned and operated by local government authorities, and there are also some private airports. The ] has provided security at most major airports since 2001. | |||
| The United States has a very ]—thirty-one ] have more than a million members.<ref name="An2000">{{cite web|url=http://www.census.gov/prod/2004pubs/c2kbr-35.pdf|title=Ancestry 2000|publisher=U.S.Census Bureau|month=June|year=2004|accessdate=2007-06-13}}</ref> ] are the largest ], with ]s, ]s, and ]s constituting three of the country's four largest ancestry groups.<ref name="An2000"/> ]s are the nation's largest ] and third largest ancestry group.<ref name="An2000"/><ref name="Cen2008">{{cite web|url=http://www.census.gov/popest/national/asrh/NC-EST2008-srh.html|title=Annual Estimates of the Population by Sex, Race, and Hispanic Origin for the United States: April 1, 2000 to July 1, 2008 (NC-EST2008-03)| publisher = U.S. Census Bureau, Population Division | date = 2009-05-01| accessdate = 2009-07-23}}</ref> ]s are the country's second largest racial minority; the two largest Asian American ethnic groups are ] and ].<ref name="An2000"/> In 2008, the U.S. population included an estimated 4.9 million people with some ] or ] ancestry (3.1 million exclusively of such ancestry) and 1.1 million with some ] or ] ancestry (0.6 million exclusively).<ref name="Cen2008"/> | |||
| ] and ] in ]]] | |||
| <div style="font-size: 90%"> | |||
| Commercial railroads and trains were the dominant ] in the U.S. until the mid-twentieth century. The introduction of jet airplanes and airports serving the same major routes accelerated a decline in demand for interstate and intercity rail passenger service by the 1960s. The completion of the ] also hastened the sharp curtailment of passenger service by the railroads. These significant developments led to the creation of the National Railroad Passenger Corporation, now called ], by the ] in 1971. Amtrak helps to maintain limited intercity rail passenger service in most parts of the country. It serves most major U.S. cities, but outside the ], ], and ] it typically runs only a few trains per day. More frequent Amtrak service is available in regional corridors between certain major cities, particularly the ] between ], ], ] and ]; between New York City and ]; in metropolitan ]; and in parts of California and the ]. Amtrak does not serve several major U.S. destinations, including ] and ]. | |||
| {| class="wikitable" border="1" table style="border:1px black; float:right; margin-left:1em;" | |||
| |- | |||
| ! style="background:#f99;" colspan="2"|Race/Ethnicity (2008)<ref name="Cen2008"/> | |||
| |- | |||
| |]||79.8% | |||
| |- | |||
| |]||12.8% | |||
| |- | |||
| |]||4.5% | |||
| |- | |||
| |]||1.0% | |||
| |- | |||
| |]||0.2% | |||
| |- | |||
| |]|| 1.7% | |||
| |- | |||
| |] (''of any race'')||15.4% | |||
| |} | |||
| </div> | |||
| The ] is entirely owned by corporations and has been largely ], while ] are publicly owned.<ref>{{cite web|last=Edwards|first=Chris|date=July 12, 2020|title=Privatization|url=https://www.downsizinggovernment.org/privatization|access-date=January 23, 2021|website=Downsizing the Federal Government|publisher=Cato Institute|language=en}}</ref> The three largest airlines in the world by passengers carried are U.S.-based; ] is number one after its 2013 acquisition by ].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.iata.org/publications/pages/wats-passenger-carried.aspx|title=Scheduled Passengers Carried|publisher=International Air Transport Association (IATA)|year=2011|access-date=February 17, 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150102034843/https://www.iata.org/publications/pages/wats-passenger-carried.aspx|archive-date=January 2, 2015}}</ref> Of the world's ], 16 are in the United States, including the top five and the busiest, ].<ref name="PANYNJ 2021 report">{{cite web|url=https://www.panynj.gov/content/dam/airports/statistics/statistics-general-info/annual-atr/ATR_2021.pdf|title=2021 Airport Traffic Report|work=Port Authority of New York and New Jersey|date=April 2022|page=32}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.aci.aero/News/Releases/Most-Recent/2014/03/31/Preliminary-World-Airport-Traffic-and-Rankings-2013--High-Growth-Dubai-Moves-Up-to-7th-Busiest-Airport-|title=Preliminary World Airport Traffic and Rankings 2013—High Growth Dubai Moves Up to 7th Busiest Airport|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140401052319/https://www.aci.aero/News/Releases/Most-Recent/2014/03/31/Preliminary-World-Airport-Traffic-and-Rankings-2013--High-Growth-Dubai-Moves-Up-to-7th-Busiest-Airport-|archive-date=April 1, 2014|date=March 31, 2014|access-date=May 17, 2014}}</ref> {{As of|2022}}, there are 19,969 airports in the U.S., of which 5,193 are designated as "public use", including for ] and other activities.<ref>{{cite web |title=Number of U.S. Airports |url=https://www.bts.gov/content/number-us-airportsa |publisher=Bureau of Transportation Statistics |access-date=December 15, 2023}}</ref> | |||
| The population growth of ] (the terms are officially interchangeable) is a major ]. The 46.9 million Americans of Hispanic descent<ref name="Cen2008"/> are identified as sharing a distinct "]" by the Census Bureau; 64% of Hispanic Americans are of ].<ref name=CB2007>{{cite web | url = http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/DTTable?_bm=y&-ds_name=ACS_2007_1YR_G00_&-CONTEXT=dt&-mt_name=ACS_2007_1YR_G2000_B03001&-redoLog=true&-geo_id=01000US&-geo_id=04000US48&-format=&-_lang=en&-SubjectID=15233304 | title = B03001. Hispanic or Latino Origin by Specific Origin | work = 2007 American Community Survey | publisher = U.S. Census Bureau | accessdate = 2008-09-26}}</ref> Between 2000 and 2008, the country's Hispanic population increased 32% while the non-Hispanic population rose just 4.3%.<ref name="Cen2008"/> Much of this growth is from immigration; as of 2007, 12.4% of the U.S. population was foreign-born, with 54% of that figure born in ].<ref>{{cite web | url = http://www.census.gov/compendia/statab/cats/population/native_and_foreignborn_populations.html | archiveurl = http://web.archive.org/web/20071225193714/http://www.census.gov/compendia/statab/cats/population/native_and_foreignborn_populations.html | archivedate = 2007-12-25| title = Population: Native and Foreign-born Populations (Tables 42 and 43)| publisher = U.S. Census Bureau|work=2009 Statistical Abstract | date = 2008-12-23| accessdate = 2009-01-21}}</ref> Fertility is also a factor; the average Hispanic woman gives birth to three children in her lifetime. The comparable fertility rate is 2.2 for non-Hispanic black women and 1.8 for non-Hispanic white women (below the ] of 2.1).<ref name="PRC"/> ] (as defined by the Census Bureau, all those beside non-Hispanic, non-multiracial whites) constitute 34% of the population; they are projected to be the majority by 2042.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.census.gov/Press-Release/www/releases/archives/population/012496.html|title=An Older and More Diverse Nation by Midcentury|publisher=U.S. Census Bureau|date=2008-08-14|accessdate=2008-09-06}}</ref> | |||
| The overwhelming majority of roads in the United States are owned and maintained by state and local governments. Roads maintained only by the U.S. federal government are generally only found on ] (such as ]) or at federal facilities (like military bases). The ], with its large, open ] linking the states, is partly funded by the federal government but owned and maintained by the state government hosting its section of the interstate. Some states fund and build their own large expressways—often called "]" or "]"—that generally use tolls to pay for construction and maintenance. Likewise, some privately owned roads may use tolls for this purpose. | |||
| About 79% of Americans live in ] (as defined by the Census Bureau, such areas include the ]s); about half of those reside in cities with populations over 50,000.<ref>{{cite web | url = http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/GCTTable?_bm=y&-state=gct&-ds_name=DEC_2000_SF1_U&-_box_head_nbr=GCT-P1&-mt_name=&-_caller=geoselect&-geo_id=&-format=US-1&-_lang=en| title = United States—Urban/Rural and Inside/Outside Metropolitan Area (GCT-P1. Population, Housing Units, Area, and Density: 2000)| publisher = U.S. Census Bureau | date =2000-04-01| accessdate = 2008-09-23 }}</ref> In 2006, 254 ] had populations over 100,000, nine cities had more than 1 million residents, and four ] had over 2 million (], ], ], and ]).<ref name=PopEstBigCities>{{cite web | url = http://www.census.gov/Press-Release/www/2007/cb07-91table1.pdf|format=PDF| title =Table 1: Population Estimates for the 25 Largest U.S. Cities Based on July 1, 2006, Population Estimates: April 1, 2000 to July 1, 2006 | work = 2006 Population Estimates | publisher = U.S. Census Bureau, Population Division | date =2007-06-28| accessdate = 2007-09-08}}</ref> There are fifty ] with populations greater than 1 million.<ref name="PopEstMSA">{{cite web | url = http://www.census.gov/Press-Release/www/releases/archives/cb07-51tbl2.pdf |format=PDF| title = Table 2. Population Estimates for the 100 Most Populous Metropolitan Statistical Areas Based on July 1, 2006, Population Estimates | work = 2006 Population Estimates | publisher = U.S. Census Bureau| date =2007-04-05| accessdate = 2007-06-17}}</ref> Of the fifty fastest-growing metro areas, twenty-three are in the West and twenty-five in the South. The metro areas of ], ], Houston, ], and California's ] all grew by more than three-quarters of a million people between 2000 and 2006.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.census.gov/Press-Release/www/releases/archives/population/009865.html|title=50 Fastest-Growing Metro Areas Concentrated in West and South|publisher=U.S. Census Bureau|date=2007-04-05|accessdate=2007-01-26}}</ref> | |||
| {{Largest cities of the United States}} | |||
| {{-}} | |||
| ] includes ], ], ], and sometimes ] service. Public transit systems serve areas of higher population density where demand is greatest. Many U.S. cities, towns, and suburbs are car-dependent, however, and suburban public transit is less common and service far less frequent. Most U.S. urban areas have some form of public transit, notably city buses, while the largest (e.g. New York, Chicago, Atlanta, Philadelphia, Boston, San Francisco, and Portland, Oregon) operate extensive systems that also include ] or ].<ref name=":0">{{Cite book|title=Urban mass transportation planning|author=Black, Alan|date=1995|publisher=McGraw-Hill|isbn=978-0070055575|location=New York|oclc=31045097}}</ref> Most public transit service in the United States is run by local governments, but national and regional commuter lines serve major U.S. urban corridors. | |||
| ===Language=== | |||
| Personal transportation in the United States is ],<ref>{{Cite web |date=May 19, 2022 |title=Cars still dominate the American commute |url=https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2022/05/commute-america-sustainability-cars/ |access-date=May 21, 2023 |website=World Economic Forum |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Humes |first=Edward |date=April 12, 2016 |title=The Absurd Primacy of the Automobile in American Life |url=https://www.theatlantic.com/business/archive/2016/04/absurd-primacy-of-the-car-in-american-life/476346/ |access-date=July 12, 2023 |website=The Atlantic |language=en}}</ref> which operate on a network of {{convert|4|e6mi|abbr=off|sp=us}} of public roads, making it the ] in the world.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Roadways – The World Factbook |url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/field/roadways/country-comparison |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210712201909/https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/field/roadways/country-comparison |archive-date=July 12, 2021 |access-date=July 15, 2021 |website=Cia.gov}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Public Road and Street Mileage in the United States by Type of Surface|url=https://www.rita.dot.gov/bts/sites/rita.dot.gov.bts/files/publications/national_transportation_statistics/html/table_01_04.html|website=United States Department of Transportation|access-date=January 13, 2015|archive-date=January 2, 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150102141414/https://www.rita.dot.gov/bts/sites/rita.dot.gov.bts/files/publications/national_transportation_statistics/html/table_01_04.html|url-status =dead }}</ref> The ], also the ] in the world at {{cvt|293564.2|km|order=flip}},<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/field/railways/country-comparison|title=Railways – The World Factbook|work=]|publisher=]|access-date=July 14, 2022}}</ref> handles mostly ].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.transtats.bts.gov/osea/seasonaladjustment/?PageVar=RAIL_PM|title=Seasonally Adjusted Transportation Data|publisher=Bureau of Transportation Statistics|location=Washington, D.C.|year=2021|access-date=February 16, 2021|archive-date=April 22, 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210422132507/https://www.transtats.bts.gov/osea/seasonaladjustment/?PageVar=RAIL_PM|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |last=Fitzsimmons |first=Emma G. |date=April 24, 2017 |title=Amtrak at a Junction: Invest in Improvements, or Risk Worsening Problems |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2017/04/24/nyregion/amtrak-infrastructure-crisis.html |newspaper=The New York Times |access-date=April 16, 2023}}</ref> Of the ], four are located in the United States. The busiest in the U.S. is the ].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.worldshipping.org/top-50-ports|title=The Top 50 Container Ports|work=]|location=Washington, D.C.|access-date=July 14, 2022}}</ref> | |||
| The ] and the ], both American cars, are considered the first mass-produced<ref>{{Cite news |date= January 26, 1986 |title=SOME MILESTONES OF THE AUTO AGE |language= en-US |work=The New York Times |url= https://www.nytimes.com/1986/01/26/automobiles/some-milestones-of-the-auto-age.html |access-date=June 1, 2023 |issn=0362-4331}}</ref> and mass-affordable<ref>{{Cite news |date =September 1, 2002|title=1926 Ford Model T Sports Touring Car |language= en-US |newspaper=The Washington Post |url =https://www.washingtonpost.com/archive/business/2002/09/01/1926-ford-model-t-sports-touring-car/810e313f-4370-44b7-bb76-3282f9de945e/ |access-date=June 1, 2023 |issn=0190-8286}}</ref> cars, respectively. As of 2023, the United States is the ]<ref>{{Cite web |title=2023 production statistics |url=https://www.oica.net/category/production-statistics/2023-statistics/ |access-date=July 1, 2024 |website=International Organization of Motor Vehicle Manufacturers}}</ref> and is home to ], the world's most valuable car company.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Klebnikov | first=Sergei |title=Tesla Is Now The World's Most Valuable Car Company With A $208 Billion Valuation |url= https://www.forbes.com/sites/sergeiklebnikov/2020/07/01/tesla-is-now-the-worlds-most-valuable-car-company-with-a-valuation-of-208-billion/ |access-date=April 14, 2023 |website=Forbes |language=en}}</ref> American automotive company ] held the title of the world's best-selling automaker from 1931 to 2008.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Bunkley |first=Nick |date=January 21, 2009 |title=Toyota Ahead of G.M. in 2008 Sales |language=en-US |work=The New York Times |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2009/01/22/business/22auto.html |access-date=April 14, 2023 |issn=0362-4331}}</ref> The ] is the world's second-largest automobile market by sales, having been overtaken by China in 2010,<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.theguardian.com/business/2010/jan/08/china-us-car-sales-overtakes|title=China overtakes US in car sales|newspaper=The Guardian|date=January 8, 2010|access-date=July 10, 2011|location=London}}</ref> and the U.S. has the ] in the world,<ref>{{cite web|date=January 30, 2017|title=Fact #962: Vehicles per Capita: Other Regions/Countries Compared to the United States|url=https://www.energy.gov/eere/vehicles/fact-962-january-30-2017-vehicles-capita-other-regionscountries-compared-united-states|access-date=January 23, 2021|website=Energy.gov|language=en}}</ref> with 910 vehicles per 1000 people.<ref name="USBTS">{{cite web|url=https://capitol-tires.com/how-many-cars-per-capita-in-the-us.html|title=Vehicle Statistics: Cars Per Capita|date=August 2017 |publisher=Capitol Tires}}</ref> By value, the U.S. was the world's largest importer and third-largest exporter of cars in 2022.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Cars |url=https://oec.world/en/profile/hs/cars |access-date=July 27, 2024 |website=]}}</ref> | |||
| == Demographics == | |||
| {{Main|Demographics of the United States}} | |||
| === Population === | |||
| <!--As prose text is preferred, overly detailed statistical charts and diagrams such as economic trends, weather boxes, historical population charts, past elections results, etc. should be reserved for main sub articles on the topic as per WP:DETAIL as outlined at WP:NOTSTATS.--> | |||
| {{Main|Americans|Race and ethnicity in the United States}} | |||
| {{See also|List of U.S. states by population}} | |||
| {{Bar chart | |||
| | float = right | |||
| | title = The 10 most populous U.S. states <br> (2024 estimates){{efn|These population figures are official 2024 annual estimates (rounded off) from the U.S. Census Bureau.}}<ref name="CensusEst2024">{{cite web |title=Annual and cumulative estimates of residential population change for the United States, regions, states, District of Columbia, Puerto Rico |url=https://www.census.gov/newsroom/press-kits/2024/national-state-population-estimates.html|website=U.S. Census Bureau|access-date=December 20, 2024}}</ref> | |||
| | label_type = State | |||
| | data_type = Population (millions) | |||
| | bar_width = 10 | |||
| | width_units = em | |||
| | data_max = 40 | |||
| | label1 = ] | |||
| | data1 = 39.4 | |||
| | label2 = ] | |||
| | data2 = 31.3 | |||
| | label3 = ] | |||
| | data3 = 23.4 | |||
| | label4 = ] | |||
| | data4 = 19.9 | |||
| | label5 = ] | |||
| | data5 = 13.1 | |||
| | label6 = ] | |||
| | data6 = 12.7 | |||
| | label7 = ] | |||
| | data7 = 11.9 | |||
| | label8 = ] | |||
| | data8 = 11.2 | |||
| | label9 = ] | |||
| | data9 = 11.0 | |||
| | label10 = ] | |||
| | data10 = 10.1 | |||
| }} | |||
| The ] reported 331,449,281 residents as of April 1, 2020,{{efn|This figure, like most official data for the United States as a whole, excludes the five unincorporated territories (], ], the ], ], and the ]) and minor island possessions.}}<ref name=2020CENSUS>{{cite web|url=https://www.census.gov/newsroom/press-releases/2021/2020-census-apportionment-results.htmlpid=2020CENSUS&src=pt|title=Census Bureau's 2020 Population Count|work=]|access-date=April 26, 2021}}</ref> making the United States the ] in the world, after China and India.<ref name="CIA-2018">{{cite web|title=The World Factbook: United States|url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/united-states/|access-date=November 10, 2018|publisher=Central Intelligence Agency}}</ref> The Census Bureau's official 2024 population estimate was 340,110,988, an increase of 2.6% since the 2020 census.<ref name="Vintage 2024">{{cite web |url=https://www.census.gov/data/tables/time-series/demo/popest/2020s-national-total.html | title=National Population Totals and Components of Change: 2020-2024}}</ref> According to the Bureau's ], on July 1, 2024, the U.S. population had a net gain of one person every 16 seconds, or about 5400 people per day.<ref>{{cite web|title=Population Clock|url=https://www.census.gov/popclock/|website=Census.gov}}</ref> In 2023, 51% of Americans age 15 and over were married, 6% were ], 10% were divorced, and 34% had never been married.<ref>{{cite web|title=Table MS-1. Marital Status of the Population 15 Years Old and Over, by Sex, Race and Hispanic Origin: 1950 to Present|url=https://www.census.gov/data/tables/time-series/demo/families/marital.html|access-date=September 11, 2019|website=Historical Marital Status Tables|publisher=U.S. Census Bureau}}</ref> In 2023, the ] for the U.S. stood at 1.6 children per woman,<ref>{{Cite web |last=Saric |first=Ivana |date=April 25, 2024 |title=Births dropped in 2023, ending pandemic baby boom |url=https://www.axios.com/2024/04/25/us-births-drop-2023 |access-date=July 1, 2024 |publisher=Axios |language=en}}</ref> and, at 23%, it had the world's highest rate of children living in ] households in 2019.<ref>{{cite web|title=U.S. has world's highest rate of children living in single-parent households|url=https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2019/12/12/u-s-children-more-likely-than-children-in-other-countries-to-live-with-just-one-parent/|access-date=March 17, 2020|website=Pew Research Center|date=December 12, 2019 |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| The United States has a diverse population; 37 ] have more than one million members.<ref name="An2000">{{cite web|title=Ancestry 2000|url=https://www.census.gov/prod/2004pubs/c2kbr-35.pdf|date=June 2004|publisher=U.S. Census Bureau|url-status=live|archive-url=http://webarchive.loc.gov/all/20041204015245/https://www.census.gov/prod/2004pubs/c2kbr-35.pdf|archive-date=December 4, 2004|access-date=December 2, 2016}}</ref> ] with ancestry from Europe, the Middle East, or North Africa form the largest ] and ] at 57.8% of the United States population.<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.census.gov/library/stories/2021/08/2020-united-states-population-more-racially-ethnically-diverse-than-2010.html | title=The Chance That Two People Chosen at Random Are of Different Race or Ethnicity Groups Has Increased Since 2010 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Table 52. Population by Selected Ancestry Group and Region: 2009|url=https://www.census.gov/compendia/statab/2012/tables/12s0052.pdf|year=2009|publisher=U.S. Census Bureau|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20121225031832/https://www.census.gov/compendia/statab/2012/tables/12s0052.pdf|archive-date=December 25, 2012|access-date=February 11, 2017}}</ref> ] form the second-largest group and are 18.7% of the United States population. ] constitute the country's third-largest ancestry group and are 12.1% of the total U.S. population.<ref name="An2000" /> Asian Americans are the country's fourth-largest group, composing 5.9% of the United States population. The country's 3.7 million Native Americans account for about 1%,<ref name="An2000" /> and some 574 native tribes are recognized by the federal government.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Federally recognized American Indian tribes and Alaska Native entities {{!}} USAGov |url=https://www.usa.gov/indian-tribes-alaska-native |access-date=April 5, 2024 |website=www.usa.gov |language=en}}</ref> In 2022, the ] of the United States population was 38.9 years.<ref>{{Cite web |date=June 22, 2023 |title=America Is Getting Older |url=https://www.census.gov/newsroom/press-releases/2023/population-estimates-characteristics.html |access-date=June 30, 2024 |website=Census.gov}}</ref> | |||
| === Language === | |||
| {{Main|Languages of the United States}} | {{Main|Languages of the United States}} | ||
| ] | |||
| {{seealso|Language Spoken at Home (U.S. Census)}} | |||
| While many languages are spoken in the United States, ] is by far the most commonly spoken and written.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Kaur |first=Harmeet |date=May 20, 2018 |title=FYI: English isn't the official language of the United States |url=https://www.cnn.com/2018/05/20/us/english-us-official-language-trnd/index.html |access-date=May 11, 2023 |publisher=CNN |language=en}}</ref> Although there is no ] at the federal level, some laws, such as ], standardize English, and most states have declared it the official language.<ref>{{cite news|date=August 12, 2014|title=States Where English Is the Official Language|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/blogs/govbeat/wp/2014/08/12/states-where-english-is-the-official-language/|access-date=September 12, 2020|newspaper=The Washington Post}}</ref> Three states and four U.S. territories have recognized local or indigenous languages in addition to English, including Hawaii (]),<ref>{{cite web|date=November 7, 1978|title=The Constitution of the State of Hawaii, Article XV, Section 4|url=https://www.hawaii.gov/lrb/con/conart15.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130724231656/https://hawaii.gov/lrb/con/conart15.html|archive-date=July 24, 2013|access-date=June 19, 2007|publisher=Hawaii Legislative Reference Bureau}}</ref> Alaska (]),{{efn|], ], ], ], ] (Aleut), ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]}}<ref>{{cite news|last1=Chapel|first1=Bill|date=April 21, 2014|title=Alaska OKs Bill Making Native Languages Official|url=https://www.npr.org/sections/thetwo-way/2014/04/21/305688602/alaska-oks-bill-making-native-languages-official|publisher=NPR}}</ref> South Dakota (]),<ref name="LakotaCommon">{{cite web|title=South Dakota recognizes official indigenous language|url=https://eu.argusleader.com/story/news/politics/2019/03/22/south-dakota-recognizes-official-indigenous-language-governor-noem/3245113002/|access-date=March 26, 2019|publisher=]}}</ref> American Samoa (]), Puerto Rico (]), Guam (]), and the Northern Mariana Islands (] and Chamorro). In total, 169 Native American languages are spoken in the United States.<ref>{{Cite web |last1=Siebens |first1=Julie |last2=Julian |first2=Tiffany |date=December 2011 |title=Native North American Languages Spoken at Home in the United States and Puerto Rico: 2006–2010 |url=https://www2.census.gov/library/publications/2011/acs/acsbr10-10.pdf |access-date=April 5, 2024 |website=United States Census Bureau}}</ref> In Puerto Rico, Spanish is more widely spoken than English.<ref name="PuertoRicoTranslation">{{cite web|title=Translation in Puerto Rico|url=https://www.puertorico.com/translation/|access-date=December 29, 2013|website=Puerto Rico Channel|archive-date=December 30, 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131230233259/http://www.puertorico.com/translation/|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| <div style="font-size: 90%"> | |||
| {| class="wikitable" border="1" table style="border:1px black; float:right; margin-left:1em;" | |||
| ! style="background:#f99;" colspan="2"|Languages (2005)<ref name="USCB Lang">{{cite web|url=http://www.census.gov/prod/2007pubs/08statab/pop.pdf|publisher=U.S. Census Bureau|work=Statistical Abstract of the United States 2006| title=Table 52—Languages Spoken at Home by Language: 2005|accessdate = 2008-10-18}}</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |English (''only'')||216.2 million | |||
| |- | |||
| |Spanish, incl. ]||32.2 million | |||
| |- | |||
| |Chinese||2.3 million | |||
| |- | |||
| |French, incl. ]||1.9 million | |||
| |- | |||
| |]||1.4 million | |||
| |- | |||
| |]||1.1 million | |||
| |- | |||
| |German||1.1 million | |||
| |} | |||
| </div> | |||
| ] is the de facto ]. Although there is no ] at the federal level, some laws—such as ]—standardize English. In 2005, about 216 million, or 81% of the population aged five years and older, spoke only English at home. ], spoken by 12% of the population at home, is the second most common language and the most widely taught second language.<ref name="USCB Lang"/><ref>{{cite web| url = http://www.adfl.org/resources/enrollments.pdf| title = Foreign Language Enrollments in United States Institutions of Higher Learning|date=fall 2002| publisher = MLA| accessdate = 2006-10-16}}</ref> Some Americans advocate making English the country's official language, as it is in at least twenty-eight states.<ref name=ILW>{{cite web|author=Feder, Jody| url = http://www.ilw.com/immigdaily/news/2007,0515-crs.pdf| title = English as the Official Language of the United States—Legal Background and Analysis of Legislation in the 110th Congress|date=2007-01-25| publisher = ILW.COM (Congressional Research Service)| accessdate = 2007-06-19}}</ref> Both ] and English are official languages in Hawaii by state law.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.hawaii.gov/lrb/con/conart15.html|title=The Constitution of the State of Hawaii, Article XV, Section 4| publisher=Hawaii Legislative Reference Bureau|date=1978-11-07|accessdate=2007-06-19}}</ref> While neither has an official language, ] has laws providing for the use of both English and Spanish, as ] does for English and French.<ref>{{cite book| author =Dicker, Susan J. | title = Languages in America: A Pluralist View |year=2003|pages=216, 220–25 | location =Clevedon, UK| publisher = Multilingual Matters|isbn=1853596515}}</ref> Other states, such as ], mandate the publication of Spanish versions of certain government documents including court forms.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.leginfo.ca.gov/cgi-bin/waisgate?WAISdocID=90544325063+0+0+0&WAISaction=retrieve|title=California Code of Civil Procedure, Section 412.20(6)| publisher=Legislative Counsel, State of California|accessdate=2007-12-17}} {{cite web|url=http://www.courtinfo.ca.gov/forms/allforms.htm|title=California Judicial Council Forms| publisher=Judicial Council, State of California|accessdate=2007-12-17}}</ref> Several insular territories grant official recognition to their native languages, along with English: ] and ] are recognized by American Samoa and Guam, respectively; ] and Chamorro are recognized by the Northern Mariana Islands; Spanish is an official language of Puerto Rico. | |||
| According to the ] (2020),<ref name="ACS2021">{{cite web |title=ACS B16001 |url=https://data.census.gov/table?q=B16001:+LANGUAGE+SPOKEN+AT+HOME+BY+ABILITY+TO+SPEAK+ENGLISH+FOR+THE+POPULATION+5+YEARS+AND+OVER&g=0100000US&tid=ACSDT1Y2021.B16001&moe=true |website=ACS B16001 |publisher=U.S. Census Bureau |access-date=26 December 2022}}</ref> some 245.4 million people out of the total U.S. population of 334 million spoke only English at home. About 41.2 million spoke Spanish at home, making it the second most commonly used language. Other languages spoken at home by one million people or more include ] (3.40 million), ] (1.71 million), ] (1.52 million), ] (1.39 million), ] (1.18 million), ] (1.07 million), and ] (1.04 million). ], spoken by 1 million people at home in 2010, fell to 857,000 total speakers in 2020.<ref>{{cite web |last= |first= |title=American FactFinder—Results |url=https://factfinder.census.gov/faces/tableservices/jsf/pages/productview.xhtml?pid=ACS_10_1YR_B16001&prodType=table |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://archive.today/20200212213140/https://factfinder.census.gov/faces/tableservices/jsf/pages/productview.xhtml?pid=ACS_10_1YR_B16001&prodType=table |archive-date=February 12, 2020 |access-date=May 29, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| ===Religion=== | |||
| === Immigration === | |||
| {{Main|Immigration to the United States}} | |||
| {{See also|United States Border Patrol}} | |||
| ] between ] (left) and ] (right)]] | |||
| America's immigrant population is by far the world's ].<ref name="UNdef">{{Cite web |author=((United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division)) |title=International Migrant Stock 2019 Documentation |url= https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/migration/data/estimates2/docs/MigrationStockDocumentation_2019.pdf |date=August 2019 |publisher=United Nations |access-date=June 19, 2023}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/migration/data/estimates2/data/UN_MigrantStockTotal_2019.xlsx|title=UN Migrant Stock Total 2019|publisher=United Nations|access-date=June 19, 2023}}</ref> In 2022, there were 87.7 million immigrants and ] in the United States, accounting for nearly 27% of the overall U.S. population.<ref>{{cite news|date=March 14, 2019|title=Frequently Requested Statistics on Immigrants and Immigration in the United States|work=]|url=https://www.migrationpolicy.org/article/frequently-requested-statistics-immigrants-and-immigration-united-states}}</ref> In 2017, out of the U.S. foreign-born population, some 45% (20.7 million) were naturalized citizens, 27% (12.3 million) were lawful permanent residents, 6% (2.2 million) were temporary lawful residents, and 23% (10.5 million) were unauthorized immigrants.<ref name="KeyFindings">{{cite web|date=June 17, 2019|title= Key findings about U.S. immigrants| url=https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2019/06/17/key-findings-about-u-s-immigrants/|publisher=Pew Research Center}}</ref> In 2019, the top countries of origin for immigrants were Mexico (24% of immigrants), India (6%), China (5%), the Philippines (4.5%), and El Salvador (3%).<ref>{{Cite web |date= September 21, 2021|title=Immigrants in the United States |url= https://www.americanimmigrationcouncil.org/sites/default/files/research/immigrants_in_the_united_states_0.pdf |access-date=August 18, 2023 |website =americanimmigrationcouncil.org}}</ref> In fiscal year 2022, over one million immigrants (most of whom entered through ]) were granted ].<ref>{{cite news |title=Who Are America's Immigrants? |url=https://www.prb.org/articles/who-are-americas-immigrants/ |work=] |date=May 22, 2024}}</ref> The United States led the world in ] for decades, admitting more refugees than the rest of the world combined.<ref name="PewRefugees">{{cite web |author=Krogstad |first=Jens Manuel |date=October 7, 2019 |title=Key facts about refugees to the U.S. |url=https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2019/10/07/key-facts-about-refugees-to-the-u-s/ |publisher=Pew Research Center}}</ref> | |||
| === Religion === | |||
| {{Main|Religion in the United States}} | {{Main|Religion in the United States}} | ||
| {{ |
{{See also|List of religious movements that began in the United States}} | ||
| {{Pie chart | |||
| ] church; most Americans identify as Christian.]] | |||
| | thumb = right | |||
| | caption = Religious affiliation in the U.S., according to a 2023 ] poll:<ref name="Staff-2007"/> | |||
| | label1 = ] | |||
| | value1 = 33 | |||
| | color1 = DarkBlue | |||
| | label2 = ] | |||
| | value2 = 22 | |||
| | color2 = Blue | |||
| | label3 = ] | |||
| | value3 = 11 | |||
| | color3 = SkyBlue | |||
| | label4 = ] | |||
| | value4 = 2 | |||
| | color4 = Pink | |||
| | label5 = ] | |||
| | value5 = 1 | |||
| | color5 = #468fEA | |||
| | label6 = Other religion | |||
| | value6 = 6 | |||
| | color6 = Green | |||
| | label7 = ] | |||
| | value7 = 22 | |||
| | color7 = White | |||
| | label8 = Unanswered | |||
| | value8 = 3 | |||
| | color8 = Black | |||
| }} | |||
| The ] guarantees the ] and forbids Congress from passing laws respecting ].<ref name="Donadio-2021">{{Cite web |last=Donadio |first=Rachel |date=November 22, 2021 |title=Why Is France So Afraid of God? |url=https://www.theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/2021/12/france-god-religion-secularism/620528/ |access-date=March 25, 2023 |website=The Atlantic |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=First Amendment |url=https://constitution.congress.gov/constitution/amendment-1/#:~:text=Congress%20shall%20make%20no%20law,for%20a%20redress%20of%20grievances. |work=Constitution Annotated |publisher=]}}</ref> Religious practice is widespread, among the ] in the world,<ref name="alesina1">{{cite journal |last=Alesina |first=Alberto |display-authors=etal |year=2003 |title=Fractionalization |url=http://www.economics.harvard.edu/faculty/alesina/files/fractionalization.pdf |url-status=dead |journal=Journal of Economic Growth |volume=8 |issue=2 |pages=155–194 |doi=10.1023/a:1024471506938 |s2cid=260685524 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120831221230/http://www.economics.harvard.edu/faculty/alesina/files/fractionalization.pdf |archive-date=August 31, 2012 |access-date=September 13, 2012}}</ref> and profoundly vibrant.<ref name="pewreligion">{{cite web |last=Fahmy |first=Dalia |date=July 31, 2018 |title=Americans are far more religious than adults in other wealthy nations |url=https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2018/07/31/americans-are-far-more-religious-than-adults-in-other-wealthy-nations/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200109160911/https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2018/07/31/americans-are-far-more-religious-than-adults-in-other-wealthy-nations/ |archive-date=January 9, 2020 |access-date=January 23, 2020 |work=Pew Research Center }}</ref> The country has the world's ].<ref name="Global Christianity">{{cite web|author=ANALYSIS|url=https://www.pewforum.org/Christian/Global-Christianity-exec.aspx|title=Global Christianity|publisher=Pewforum.org|date=December 19, 2011|access-date=August 17, 2012|archive-date=July 30, 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130730062627/http://www.pewforum.org/christian/global-christianity-exec.aspx|url-status=dead }}</ref> Other notable faiths include ], ], ], ], many ] movements, and ].<ref>{{Cite book |last=Sewell |first=Elizabeth |title=The Oxford Handbook of Church and State in the United States |publisher=] |year=2010 |isbn=9780199892228 |editor-last=Davis |editor-first=Derek |pages=249–275 |chapter=Religious Liberty and Religious Minorities in the United States}}</ref> Religious practice varies significantly by region.<ref name="Williams-2023">{{Cite web |last=Williams |first=Daniel |date=March 1, 2023 |title='Christian America' Isn't Dying. It's Dividing. |url=https://www.christianitytoday.com/ct/2023/february-web-only/christianity-america-pew-research-statistics-minority.html |access-date=March 25, 2023 |website=] |language=en}}</ref> "]" is common in American culture.<ref>{{Cite web |last1=Merriam |first1=Jesse |last2=Lupu |first2=Ira |last3=Elwood |first3=F |last4=Davis |first4=Eleanor |date=August 28, 2008 |title=On Ceremonial Occasions, May the Government Invoke a Deity? |url=https://www.pewresearch.org/religion/2008/08/28/on-ceremonial-occasions-may-the-government-invoke-a-deity/ |access-date=March 31, 2023 |website=Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project |language=en-US}}</ref> | |||
| The overwhelming majority of ] believe in a ] or spiritual force, engage in ]s such as prayer, and consider themselves religious or ].<ref name="Kallo-2023">{{Cite web |last=Kallo |display-authors=etal |first=Becka|date=December 7, 2023 |title=Spirituality Among Americans |url=https://www.pewresearch.org/religion/2023/12/07/spirituality-among-americans/ |access-date=December 8, 2023 |website=Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project |language=en-US}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last1=Froese |first1=Paul |last2=Uecker |first2=Jeremy E. |date=September 2022 |title=Prayer in America: A Detailed Analysis of the Various Dimensions of Prayer |url=https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jssr.12810 |journal=Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion |language=en |volume=61 |issue=3–4 |pages=663–689 |doi=10.1111/jssr.12810 |s2cid=253439298 |issn=0021-8294}}</ref> In the "]", located within the Southern United States, ] plays a significant role culturally, whereas ] and the Western United States ].<ref name="Williams-2023" /> ]—a ] movement, whose members migrated westward from Missouri and Illinois under the leadership of ] in 1847 after the assassination of ]{{sfn|Howe|2008|pp=727–728}}—remains the predominant religion in Utah to this day.<ref>{{cite web|website=World Population Review|title=Mormon Population by State|date=June 2023|url=https://worldpopulationreview.com/state-rankings/mormon-population-by-state}}</ref> | |||
| === Urbanization === | |||
| {{Main|Urbanization in the United States|List of United States cities by population}} | |||
| About 82% of Americans live in ], including suburbs;<ref name="CIA-2018" /> about half of those reside in cities with populations over 50,000.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/GCTTable?_bm=y&-state=gct&-ds_name=DEC_2000_SF1_U&-_box_head_nbr=GCT-P1&-mt_name=&-_caller=geoselect&-geo_id=&-format=US-1&-_lang=en|title=United States—Urban/Rural and Inside/Outside Metropolitan Area|publisher=U.S. Census Bureau|archive-url=http://webarchive.loc.gov/all/20090403024532/https://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/GCTTable?_bm=y&-state=gct&-ds_name=DEC_2000_SF1_U&-_box_head_nbr=GCT-P1&-mt_name=&-_caller=geoselect&-geo_id=&-format=US-1&-_lang=en|archive-date=April 3, 2009|access-date=September 23, 2008|url-status=dead }}</ref> In 2022, 333 ] had populations over 100,000, nine cities had more than one million residents, and four cities—], ], ], and ]—had populations exceeding two million.<ref>{{Cite web |title=City and Town Population Totals: 2020-2022 |url=https://www.census.gov/data/tables/time-series/demo/popest/2020s-total-cities-and-towns.html |access-date=November 26, 2023 |website=Census.gov}}</ref> Many U.S. metropolitan populations are growing rapidly, particularly in the South and West.<ref>{{cite web|date=April 18, 2019|title=Counties in South and West Lead Nation in Population Growth|url=https://www.census.gov/newsroom/press-releases/2019/estimates-county-metro.html|access-date=August 29, 2020|website=The United States Census Bureau|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| {{Largest metropolitan areas of the United States}} | |||
| === Health === | |||
| {{See also|Healthcare in the United States|Healthcare reform in the United States|Health insurance in the United States}} | |||
| ] in ] is the largest medical complex in the world.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.tmc.edu/about-tmc/|title=About Us}}</ref><ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.newsweek.com/texas-medical-center-largest-medical-complex-world-reaches-98-percent-icu-capacity-1526180 | title=Texas Medical Center, largest medical complex in the world, reaches 98 percent ICU capacity | website=] | date=August 19, 2020 }}</ref> In 2018, it employed 120,000 people and treated 10 million patients.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.tmc.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/TMC_FactsFiguresOnePager_07052018-1.pdf|title=TMC Facts & Figures}}</ref>]] | |||
| According to the ] (CDC), average American life expectancy at birth was 77.5 years in 2022 (74.8 years for men and 80.2 years for women). This was a gain of 1.1 years from 76.4 years in 2021, but the CDC noted that the new average "didn't fully offset the loss of 2.4 years between 2019 and 2021". Higher overall mortality due especially to the ] as well as ] and ] were held mostly responsible for the previous drop in life expectancy.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Mayes-Osterman |first=Cybele |date=November 30, 2023 |title=Americans are living longer but there's a catch: CDC report on life expectancy |url=https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/nation/2023/11/29/average-us-life-expectancy-increased-not-pre-covid/71738611007/ |access-date=December 18, 2024 |publisher=USA Today |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=McPhillips |first=Deidre |date=November 29, 2023 |title=US life expectancy rebounded in 2022 but not back to pre-pandemic levels |url=https://www.cnn.com/2023/11/29/health/life-expectancy-us-2022-cdc-report/index.html |access-date=February 12, 2024 |publisher=CNN |language=en}}</ref> The same report stated that the 2022 gains in average U.S. life expectancy were especially significant for men, Hispanics, and American Indian–Alaskan Native people (AIAN). Starting in 1998, the life expectancy in the U.S. fell ], and Americans' "health disadvantage" gap has been increasing ever since.<ref>{{cite news|last=Achenbach|first=Joel|date=November 26, 2019|title='There's something terribly wrong': Americans are dying young at alarming rates|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/health/theres-something-terribly-wrong-americans-are-dying-young-at-alarming-rates/2019/11/25/d88b28ec-0d6a-11ea-8397-a955cd542d00_story.html|newspaper=]|access-date=December 19, 2019}}</ref> The U.S. has one of the ] among ].<ref>{{cite web|date=January 30, 2020|title=New International Report on Health Care: U.S. Suicide Rate Highest Among Wealthy Nations {{!}} Commonwealth Fund|url=https://www.commonwealthfund.org/press-release/2020/new-international-report-health-care-us-suicide-rate-highest-among-wealthy|access-date=March 17, 2020|website=Commonwealthfund.org|language=en}}</ref> ] and another third is overweight.<ref>{{cite web|title=Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity Among Adults: United States, 2003–2004|url=https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/pubs/pubd/hestats/overweight/overwght_adult_03.htm|access-date=June 5, 2007|publisher=Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics}}</ref> The U.S. healthcare system far ], measured both in per capita spending and as a percentage of GDP, but attains worse healthcare outcomes when compared to peer countries for reasons that are debated.<ref>{{cite web|year=2001|title=The U.S. Healthcare System: The Best in the World or Just the Most Expensive?|url=https://dll.umaine.edu/ble/U.S.+HCweb.pdf|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/20070309142240/https://dll.umaine.edu:80/ble/U.S.%20HCweb.pdf|archive-date=March 9, 2007|access-date=November 29, 2006|publisher=University of Maine}}{{cbignore}}</ref> The United States is the only developed country ], and ].<ref>{{cite journal|last=Vladeck|first=Bruce|title=Universal Health Insurance in the United States: Reflections on the Past, the Present, and the Future|date=January 2003|volume=93|number=1|pages=16–19|pmid=12511377|doi=10.2105/ajph.93.1.16|journal=]|pmc=1447684 }}</ref> Government-funded healthcare coverage for the poor (]) and for those age 65 and older (]) is available to Americans who meet the programs' income or age qualifications. In 2010, former President Obama passed the ].{{efn|Also known less formally as Obamacare}}<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Oberlander|first=Jonathan|date=June 1, 2010| title=Long Time Coming: Why Health Reform Finally Passed|journal=Health Affairs|language=en|volume=29|issue=6|pages=1112–1116|doi=10.1377/hlthaff.2010.0447| pmid=20530339|issn=0278-2715|doi-access=free}}</ref> ] is not federally protected, and is illegal or restricted in 17 states.<ref>{{Cite web |last1=Glenza |first1=Jessica |last2=Noor |first2=Poppy |title=Tracking abortion laws across the United States |url=https://www.theguardian.com/us-news/ng-interactive/2024/jul/29/abortion-laws-bans-by-state |access-date=August 14, 2024 |website=The Guardian |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| The United States is officially a ]; the ] of the U.S. Constitution guarantees the ] and forbids the establishment of any religious governance. In a 2002 study, 59% of Americans said that religion played a "very important role in their lives," a far higher figure than that of any other wealthy nation.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://pewglobal.org/reports/display.php?ReportID=167|title=Among Wealthy Nations…U.S. Stands Alone in its Embrace of Religion| publisher=Pew Research Center|work=Pew Global Attitudes Project|date=2002-12-19|accessdate=2008-10-23}}</ref> According to a 2007 survey, 78.4% of adults identified themselves as ],<ref name="Pew">{{cite web|url=http://religions.pewforum.org/pdf/affiliations-all-traditions.pdf|title=Religious Composition of the U.S.| publisher=Pew Forum on Religion & Public Life|work=U.S. Religious Landscape Survey|year=2007|accessdate=2008-10-23}}</ref> down from 86.4% in 1990.<ref name="ARIS">{{cite web|url=http://www.gc.cuny.edu/faculty/research_briefs/aris/key_findings.htm|title=American Religious Identification Survey| publisher=CUNY Graduate Center|year=2001|accessdate=2007-06-17}}</ref> ] denominations accounted for 51.3%, while ], at 23.9%, was the largest individual denomination. The study categorizes white ], 26.3% of the population, as the country's largest religious cohort;<ref name="Pew"/> another study estimates evangelicals of all races at 30–35%.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.uakron.edu/bliss/docs/Religious_Landscape_2004.pdf|author=Green, John C|title=The American Religious Landscape and Political Attitudes: A Baseline for 2004| publisher=University of Akron|Ray C. Bliss Institute of Applied Politics|accessdate=2007-06-18}}</ref> The total reporting non-Christian religions in 2007 was 4.7%, up from 3.3% in 1990.<ref name="ARIS"/> The leading non-Christian faiths were ] (1.7%), ] (0.7%), ] (0.6%), ] (0.4%), and ] (0.3%).<ref name="Pew"/> From 8.2% in 1990,<ref name="ARIS"/> 16.1% in 2007 described themselves as ], ], or simply having ].<ref name="Pew"/> | |||
| ===Education=== | === Education === | ||
| {{Main|Education in the United States}} | {{Main|Education in the United States}} | ||
| ]. "". Accessed July 29, 2024.</ref> such as the ], founded by ] in 1819.|alt=Photograph of the University of Virginia]] | |||
| {{seealso|Educational attainment in the United States|Higher education in the United States}} | |||
| American primary and secondary education (known in the U.S. as ], "kindergarten through 12th grade") is decentralized. School systems are operated by state, territorial, and sometimes municipal governments and regulated by the ]. In general, children are required to attend school or ] from the age of five or six (] or ]) until they are 18 years old. This often brings students through the ], the final year of a U.S. high school, but some states and territories allow them to leave school earlier, at age 16 or 17.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://nces.ed.gov/programs/digest/d02/dt150.asp|title=Ages for Compulsory School Attendance ...|access-date=June 10, 2007|publisher=U.S. Dept. of Education, National Center for Education Statistics}}</ref> The U.S. spends more on education per student than any country in the world,<ref>{{Cite news|last=Rushe|first=Dominic|date=September 7, 2018|title=The US spends more on education than other countries. Why is it falling behind?|language=en-GB|work=The Guardian|url=https://www.theguardian.com/us-news/2018/sep/07/us-education-spending-finland-south-korea|access-date=August 29, 2020|issn=0261-3077}}</ref> an average of $18,614 per year per public elementary and secondary school student in 2020–2021.<ref>{{cite web|date=April 2020|title=Fast Facts: Expenditures|url=https://nces.ed.gov/fastfacts/display.asp?id=66|access-date=August 29, 2020|website=nces.ed.gov|language=EN}}</ref> Among Americans age 25 and older, 92.2% graduated from high school, 62.7% attended some college, 37.7% earned a ], and 14.2% earned a graduate degree.<ref>{{cite web |title=Educational Attainment in the United States: 2022 |url=https://www.census.gov/data/tables/2022/demo/educational-attainment/cps-detailed-tables.html |access-date=July 20, 2024 |publisher=U.S. Census Bureau}}</ref> The ] is near-universal.<ref name="CIA-2018" /><ref>For more detail on U.S. literacy, see , U.S. Department of Education (2003).</ref> The country has the ], with ] (having won 413 awards).<ref>{{Cite web |title=All Nobel Prizes |url=https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/lists/all-nobel-prizes |publisher=Nobel Foundation}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=2022–2023 Best Global Universities Rankings |url=https://www.usnews.com/education/best-global-universities/rankings |access-date=April 27, 2023 |website=]}}</ref> | |||
| ] such as the ], a ] founded by ].<ref>{{cite web |title=Public Education for the Common Good |author=Rosenstone, Steven J. |publisher=University of Minnesota |url=http://cla.umn.edu/news/clatoday/summer2002/dean.php |date=2009-12-17 |accessdate=2009-03-06}}</ref>]] | |||
| American ] is operated by state and local governments, regulated by the ] through restrictions on federal grants. Children are required in most states to attend school from the age of six or seven (generally, ] or ]) until they turn eighteen (generally bringing them through ], the end of ]); some states allow students to leave school at sixteen or seventeen.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://nces.ed.gov/programs/digest/d02/dt150.asp |title=Ages for Compulsory School Attendance... |accessdate = 2007-06-10 |publisher=U.S. Dept. of Education, National Center for Education Statistics}}</ref> About 12% of children are enrolled in ] or ] ]s. Just over 2% of children are ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ed.gov/about/offices/list/oii/nonpublic/statistics.html |title=Statistics About Non-Public Education in the United States |accessdate = 2007-06-05 |publisher=U.S. Dept. of Education, Office of Non-Public Education}}</ref> The United States has many competitive private and public ], as well as local ]s with open admission policies. Of Americans twenty-five and older, 84.6% graduated from high school, 52.6% attended some college, 27.2% earned a ], and 9.6% earned graduate degrees.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.census.gov/prod/2004pubs/p20-550.pdf|title=Educational Attainment in the United States: 2003|publisher=U.S. Census Bureau|accessdate = 2006-08-01}}</ref> The basic ] is approximately 99%.<ref name="WF" /><ref>For more detail on U.S. literacy, see , U.S. Department of Education (2003).</ref> The United Nations assigns the United States an Education Index of 0.97, tying it for 12th in the world.<ref>{{cite web|title=Human Development Indicators|year=2005|publisher=United Nations Development Programme, Human Development Reports|accessdate = 2008-01-14|url=http://hdr.undp.org/reports/global/2005/pdf/HDR05_HDI.pdf|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20070620235428/http://hdr.undp.org/reports/global/2005/pdf/HDR05_HDI.pdf|archivedate=2007-06-20}}</ref> | |||
| ] has earned a global reputation. Many of the world's top universities, as listed by various ranking organizations, are in the United States, including 19 of the top 25.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Fink |first=Jenni |date=October 22, 2019 |title=U.S. Schools Take 8 of 10 Top Spots on U.S. News' Best Global Universities |url=https://www.newsweek.com/us-news-best-global-universities-american-schools-dominate-top-10-1466768 |access-date=April 18, 2023 |website=Newsweek |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |date=April 19, 2023 |title=Best Countries for Education: North American and European countries are seen as offering the best opportunities for education. |url=https://www.usnews.com/news/best-countries/best-countries-for-education |website=U.S. News & World Report}}</ref> American higher education is dominated by ]s, although ] enroll about 20% of all American students. Local ]s generally offer coursework and degree programs covering the first two years of college study. They often have more open admission policies, shorter academic programs, and lower tuition.<ref>{{cite web|last1=Pannoni|first1=Alexandra|last2=Kerr|first2=Emma|url=https://www.usnews.com/education/community-colleges/articles/2015/02/06/frequently-asked-questions-community-college|title=Everything You Need to Know About Community Colleges: FAQ|work=]|date=July 14, 2020|access-date=July 9, 2022}}</ref> | |||
| ===Health=== | |||
| {{seealso|Health care in the United States|Health care reform in the United States|Health insurance in the United States}} | |||
| The United States ] of 77.8 years at birth<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hus/hus06.pdf#027|title=Health, United States, 2006|month=November | year=2006|publisher=Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics|accessdate = 2007-08-15}}</ref> is a year shorter than the overall figure in Western Europe, and three to four years lower than that of Norway, Switzerland, and Canada.<ref>{{cite web |author=Eberstadt, Nicholas, and Hans Groth|url=http://www.iht.com/articles/2007/04/19/opinion/edeber.php |title=Healthy Old Europe|date=2007-04-19|work=International Herald Tribune|accessdate = 2007-06-19 }}</ref> Over the past two decades, the country's rank in life expectancy has dropped from 11th to 42nd in the world.<ref>{{cite web|author=MacAskill, Ewen|url=http://www.guardian.co.uk/world/2007/aug/13/usa.ewenmacaskill |title=US Tumbles Down the World Ratings List for Life Expectancy|date=2007-08-13 |work= Guardian|accessdate = 2007-08-15}}</ref> The ] of 6.37 per thousand likewise places the United States 42nd out of 221 countries, behind all of Western Europe.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2091rank.html |title=Rank Order—Infant Mortality Rate|date=2007-06-14|publisher =CIA|work=The World Factbook|accessdate = 2007-06-19}}</ref> U.S. cancer survival rates are the highest in the world.<ref> | |||
| {{cite news| first = Nicole| last = Martin| title = UK Cancer Survival Rate Lowest in Europe| url = http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/uknews/1560849/UK-cancer-survival-rate-lowest-in-Europe.html | work = The Daily Telegraph| date = 2007-08-24}} {{cite journal| last = Gatta| first = Gemma | year = 2006| month = February| title = Survival from Rare Cancer in Adults: A Population-Based Study| journal = The Lancet Oncology| volume = 7| issue = 2| pages = 132–140| doi = 10.1016/S1470-2045(05)70471-X}}</ref> Approximately one-third of the adult population is ] and an additional third is overweight;<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/pubs/pubd/hestats/overweight/overwght_adult_03.htm |title=Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity Among Adults: United States, 2003–2004 |accessdate = 2007-06-05 |publisher=Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics}}</ref> the obesity rate, the highest in the industrialized world, has more than doubled in the last quarter-century.<ref>{{cite book | author= Schlosser, Eric | year = 2002 | title = Fast Food Nation | publisher = Perennial | location = New York| isbn = 0060938455 |page = 240 }}</ref> Obesity-related ] is considered ] by health care professionals.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://atvb.ahajournals.org/cgi/content/full/25/12/2451#R3-101329 |title=Fast Food, Central Nervous System Insulin Resistance, and Obesity|year=2005 |accessdate = 2007-06-17|work= ]|publisher=American Heart Association}}</ref> The U.S. adolescent pregnancy rate, 79.8 per 1,000 women, is nearly four times that of France and five times that of Germany.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.advocatesforyouth.org/PUBLICATIONS/factsheet/fsest.htm |title=Adolescent Sexual Health in Europe and the U.S.—Why the Difference?|month=October | year=2001 |accessdate = 2007-06-17 |publisher=Advocates for Youth}}</ref> ], legal on demand, is highly controversial. Many states ban public funding of the procedure and restrict late-term abortions, require parental notification for minors, and mandate a waiting period. While the abortion rate is falling, the abortion ratio of 241 per 1,000 live births and abortion rate of 15 per 1,000 women aged 15–44 remain higher than those of most Western nations.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/ss5511a1.htm|author=Strauss, Lilo T., et al.|title=Abortion Surveillance—United States, 2003|accessdate = 2007-06-17 |publisher=Centers for Disease Control, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Division of Reproductive Health|work=MMWR|date=2006-11-24}}</ref> | |||
| As for ]s on higher education, the U.S. spends more per student than the ] average, and Americans spend more than all nations in combined public and private spending.<ref name="education spending">{{cite news|date=June 25, 2013|title=U.S. education spending tops global list, study shows|publisher=CBS|agency=Associated Press|url=https://www.cbsnews.com/news/us-education-spending-tops-global-list-study-shows/|access-date=October 5, 2013|archive-date=July 26, 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130726002619/http://www.cbsnews.com/8301-202_162-57590921/u.s-education-spending-tops-global-list-study-shows|url-status=live}}</ref> Colleges and universities directly funded by the federal government do not charge tuition and are limited to military personnel and government employees, including: the ], the ], and ]. Despite some student ] programs in place,<ref>{{Cite web |title=The Biden administration cancelled $9.5B in student loan debt. Here's who it affects. |url=https://usafacts.org/articles/the-biden-administration-cancelled-95b-in-student-loan-debt-heres-who-it-affects/ |access-date=July 15, 2022 |website=USAFacts |language=en}}</ref> ] increased by 102% between 2010 and 2020,<ref>{{cite news|last=Hess|first=Abigail Johnson|date=December 22, 2020|title=U.S. student debt has increased by more than 100% over the past 10 years|publisher=CNBC|url=https://www.cnbc.com/2020/12/22/us-student-debt-has-increased-by-more-than-100percent-over-past-10-years.html|access-date=January 8, 2022}}</ref> and exceeded $1.7 trillion as of 2022.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Dickler|first1=Jessica|last2=Nova|first2=Annie|date=May 6, 2022|title=This is how student loan debt became a $1.7 trillion crisis|url=https://www.cnbc.com/2022/05/06/this-is-how-student-loan-debt-became-a-1point7-trillion-crisis.html|publisher=CNBC|access-date=July 8, 2022}}</ref> | |||
| ] in ], the world's largest medical center<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.texmedctr.tmc.edu/root/en/GetToKnow/FactsandFigures/Facts+and+Figures.htm|title=2007 Facts & Figures|accessdate = 2008-11-07|publisher=Texas Medical Center}}</ref>]] | |||
| == Culture and society == | |||
| The U.S. health care system far ] any other nation's, measured in both per capita spending and percentage of GDP.<ref>''OECD Health Data 2000: A Comparative Analysis of 29 Countries'' (OECD: Paris, 2000). See also {{cite web |url=http://dll.umaine.edu/ble/U.S.%20HCweb.pdf|title=The U.S. Healthcare System: The Best in the World or Just the Most Expensive?|year=2001|accessdate = 2006-11-29 |publisher=University of Maine}}</ref> The ] ranked the U.S. health care system in 2000 as first in responsiveness, but 37th in overall performance. The United States is a leader in medical innovation. In 2004, the nonindustrial sector spent three times as much as Europe per capita on biomedical research.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Groves, Trish| year=2008|month=February |title=Stronger European Medical Research |journal=British Medical Journal |volume=336 |pages=341–342| doi=10.1136/bmj.39489.505208.80 |pmid=18276671 |first1=T |issue=7640 |issn=0959-8138}}</ref> | |||
| {{Main|Culture of the United States|Society of the United States}} | |||
| ] (''Liberty Enlightening the World'') on ] in ] was an 1866 gift from France that has become an iconic symbol of the ].<ref>{{cite web| title = Statue of Liberty| website=World Heritage| publisher=UNESCO| url = https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/307| access-date = January 4, 2022}}</ref>|alt=The Statue of Liberty, a large teal bronze sculpture on a stone pedestal]] | |||
| Americans have traditionally ] by a unifying political belief in an "]" emphasizing ], ], ], ], ], ], and a preference for ].<ref>{{cite book |last=Huntington |first=Samuel P. |url=https://archive.org/details/whoarewechalleng00hunt |title=Who are We?: The Challenges to America's National Identity |publisher=Simon & Schuster |year=2004 |isbn=978-0-684-87053-3 |chapter=Chapters 2–4 |author-link=Samuel P. Huntington |access-date=October 25, 2015 |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=6xiYiybkE8kC&q=core}}: see ], written by ] and adopted by Congress in 1918.</ref><ref>Hoeveler, J. David, ''Creating the American Mind: Intellect and Politics in the Colonial Colleges'', Rowman & Littlefield, {{ISBN|978-0742548398}}, 2007, p. xi</ref> Culturally, the country has been described as having the values of ] and ],<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Grabb |first1=Edward |last2=Baer |first2=Douglas |last3=Curtis |first3=James |year=1999 |title=The Origins of American Individualism: Reconsidering the Historical Evidence |journal=] |publisher=] |volume=24 |pages=511–533 |doi=10.2307/3341789 |issn=0318-6431 |jstor=3341789 |number=4}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |last=Marsh |first=Abigail |date=May 26, 2021 |title=Everyone Thinks Americans Are Selfish. They're Wrong. |language=en-US |work=The New York Times |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2021/05/26/opinion/individualism-united-states-altruism.html |access-date=July 16, 2023 |issn=0362-4331}}</ref> as well as having a strong ],<ref>{{cite journal |last=Porter |first=Gayle |date=November 2010 |title=Work Ethic and Ethical Work: Distortions in the American Dream |journal=] |publisher=] |volume=96 |pages=535–550 |doi=10.1007/s10551-010-0481-6 |jstor=29789736 |s2cid=143991044 |number=4}}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite journal |last=Stephens |first=R. H. |date=September 1952 |title=The Role Of Competition In American Life |journal=] |publisher=] |volume=24 |pages=9–14 |jstor=41317686 |number=3}}</ref> and voluntary ] towards others.<ref>{{cite web |date=September 9, 2022|url=https://good2give.ngo/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/2022-CAF-World-Giving-Index.pdf |title=World Giving Index 2022 |website=] |access-date=April 27, 2023}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Country-level estimates of altruism |url=https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/cross-country-variation-in-altruism |access-date=March 14, 2023 |website=Our World in Data}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Marsh |first=Abigail |date=February 5, 2018 |title=Could A More Individualistic World Also Be A More Altruistic One? |url=https://www.npr.org/sections/13.7/2018/02/05/581873428/could-a-more-individualistic-world-also-be-a-more-altruistic-one |access-date=March 14, 2023 |publisher=]}}</ref> According to a 2016 study by the ], Americans donated 1.44% of total GDP to charity—the ] in the world by a large margin.<ref>{{cite web |date=January 2016 |title=GROSS DOMESTIC PHILANTHROPY: An international analysis of GDP, tax and giving |url=https://www.cafonline.org/docs/default-source/about-us-policy-and-campaigns/gross-domestic-philanthropy-feb-2016.pdf |access-date=July 18, 2022 |publisher=]}}</ref> The United States is home to a ].<ref>{{Cite news |last=Volokh |first=Eugene |date=January 17, 2015 |title=The American tradition of multiculturalism |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/volokh-conspiracy/wp/2015/01/27/the-american-tradition-of-multiculturalism/ |access-date=July 30, 2024 |newspaper=]}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Jackson |first=Lucas |date=August 22, 2014 |title=America's Tipping Point: Most Of U.S. Now Multicultural, Says Group |url=https://www.nbcnews.com/news/latino/americas-tipping-point-most-u-s-now-multicultural-says-group-n186206 |access-date=July 30, 2024 |website=] |language=en}}</ref> It has acquired ] and economic ].<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Berghahn |first=Volker R. |date=February 1, 2010 |title=The debate on 'Americanization' among economic and cultural historians |url=https://doi.org/10.1080/14682740903388566 |journal=Cold War History |volume=10 |issue=1 |pages=107–130 |doi=10.1080/14682740903388566 |s2cid=144459911 |issn=1468-2745}}</ref><ref>{{Cite magazine |last1=Fergie |first1=Dexter |date=March 24, 2022 |title=How American Culture Ate the World |url=https://newrepublic.com/article/165836/american-culture-ate-world-righteous-smokescreen-globalization-review |magazine=The New Republic |issn=0028-6583 |access-date=July 3, 2022}}</ref> | |||
| Unlike in all other developed countries, health care coverage in the United States is not ]. In 2004, private insurance paid for 36% of personal health expenditures, private out-of-pocket payments covered 15%, and federal, state, and local governments paid for 44%.<ref name="CDC H">{{cite web |url=http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hus/hus06.pdf|title=Health, United States, 2006|accessdate = 2006-11-24 |publisher=Centers for Disease Control, National Center for Health Statistics}}</ref> In 2005, 46.6 million Americans, 15.9% of the population, were uninsured, 5.4 million more than in 2001. The main cause of this rise is the drop in the number of Americans with employer-sponsored health insurance.<ref name="CBPP">{{cite web|url=http://www.cbpp.org/8-29-06pov.htm|title=Poverty Remains Higher, and Median Income for Non-Elderly Is Lower, Than When Recession Hit Bottom: Poor Performance Unprecedented for Four-Year Recovery Period|publisher=Center for Budget and Policy Priorities|date =2006-09-01|accessdate = 2007-06-24}}</ref> The subject of uninsured and underinsured Americans—estimates of which vary widely—is a major political issue.<ref>{{cite news|author=Abelson, Reed|url=http://www.nytimes.com/2008/06/10/health/policy/10health.html|title=Ranks of Underinsured Are Rising, Study Finds|date= 2008-06-10|work=New York Times|accessdate=2008-10-25}} {{cite journal|author=Blewett, Lynn A. et al.|title=How Much Health Insurance Is Enough? Revisiting the Concept of Underinsurance|year= 2006|work=Medical Care Research and Review|volume=63|issue=6|pages=663–700|doi=10.1177/1077558706293634|journal=Medical Care Research and Review|pmid=17099121|month=Dec|first1=LA|first2=A|first3=TJ|issn=1077-5587}}</ref> A Harvard-based study released in the ] estimates that nearly 45,000 deaths a year in the United States are associated with the lack of health insurance.<ref>. CNN.com. September 18, 2009.</ref> In 2006, ] became the first state to mandate universal health insurance.<ref>{{cite web|author=Fahrenthold, David A.|url=http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2006/04/04/AR2006040401937.html|title= Mass. Bill Requires Health Coverage|date= 2006-04-05|work=Washington Post|accessdate=2007-06-19}}</ref> | |||
| Nearly all present Americans or their ancestors came from ] (the "]") within the past five centuries.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Fiorina|first1=Morris P.|author-link1=Morris P. Fiorina|last2=Peterson|first2=Paul E.|title=The New American democracy|date=2010|publisher=Longman|location=London|isbn=978-0-205-78016-7|page=97|edition=7th}}</ref> ] American culture is a ] largely derived from the ] with influences from many other sources, such as ].<ref>{{multiref2 | |||
| ===Crime and law enforcement=== | |||
| |{{cite book|last1=Holloway|first1=Joseph E.|title=Africanisms in American culture|date=2005|publisher=Indiana University Press|location=Bloomington|isbn=978-0-253-21749-3|pages=18–38|edition=2nd}} | |||
| {{Main|Policing in the United States|Crime in the United States}} | |||
| |{{cite book|last1=Johnson|first1=Fern L.|title=Speaking culturally : language diversity in the United States|publisher=Sage Publications|isbn=978-0-8039-5912-5|page=116|year=2000 }} }}</ref> More recent immigration from ] and especially ] has added to a cultural mix that has been described as a homogenizing ], and a heterogeneous ], with immigrants contributing to, and often ] into, mainstream American culture. The ], or the perception that Americans enjoy high ], plays a key role in attracting immigrants.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.gallup.com/poll/161435/100-million-worldwide-dream-life.aspx|title=More Than 100 Million Worldwide Dream of a Life in the U.S. More than 25% in Liberia, Sierra Leone, Dominican Republic want to move to the U.S.|last=Clifton|first=Jon|date=March 21, 2013|publisher=Gallup|access-date=January 10, 2014}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Kulkarni |first=Jay |date=January 12, 2022 |title=Attracting Immigrant Talent With A New American Dream |url=https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbesbusinesscouncil/2022/01/12/attracting-immigrant-talent-with-a-new-american-dream/ |access-date=July 24, 2024 |website=] |language=en}}</ref> Whether this perception is accurate has been a topic of debate.<ref name="socialmobility">{{cite web|url=https://www.oecd.org/tax/public-finance/chapter%205%20gfg%202010.pdf|title=A Family Affair: Intergenerational Social Mobility across OECD Countries|website=Economic Policy Reforms: Going for Growth|publisher=OECD|year=2010|access-date=September 20, 2010}}</ref><ref name="CAP">{{cite web|title=Understanding Mobility in America|url=https://www.americanprogress.org/issues/economy/news/2006/04/26/1917/understanding-mobility-in-america/|website=Center for American Progress|date=April 26, 2006}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|last1=Gould|first1=Elise|title=U.S. lags behind peer countries in mobility|url=https://www.epi.org/publication/usa-lags-peer-countries-mobility/|website=]|access-date=July 15, 2013|date=October 10, 2012}}</ref> While mainstream culture holds that the United States is a ],<ref>{{cite book|last=Gutfeld|first=Amon|year=2002|title=American Exceptionalism: The Effects of Plenty on the American Experience|publisher=Sussex Academic Press|location=Brighton and Portland|page=65|isbn=978-1-903900-08-6}}</ref> scholars identify significant differences between ], affecting ], language, and values.<ref>{{cite book|last=Zweig|first=Michael|year=2004|title=What's Class Got To Do With It, American Society in the Twenty-First Century|publisher=Cornell University Press|location=Ithaca, NY|isbn=978-0-8014-8899-3}}</ref><ref>{{cite report | last=Hoff-Ginsberg | first=Erika | date=April 1989 | title=Effects of Social Class and Interactive Setting on Maternal Speech | publication-place=Bethesda, MD | publisher=National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NIH) | via=Education Resource Information Center | url=https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED309843}} Republished with revisions as {{cite journal | last=Hoff-Ginsberg | first=Erika | title=Mother-Child Conversation in Different Social Classes and Communicative Settings | journal=Child Development | volume=62 | issue=4 | date=1991 | issn=0009-3920 | doi=10.1111/j.1467-8624.1991.tb01569.x | pages=782–796| pmid=1935343 }}</ref> Americans tend to greatly value ] achievement, but ] is promoted by some as a noble condition as well.<ref>{{cite book|last=O'Keefe|first=Kevin|year=2005|title=The Average American|publisher=PublicAffairs|location=New York|isbn=978-1-58648-270-1|url=https://archive.org/details/averageamericant00okee }}</ref> | |||
| {{seealso|Law of the United States|Incarceration in the United States|Capital punishment in the United States}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Law enforcement in the United States is primarily the responsibility of local police and ]'s departments, with ] providing broader services. Federal agencies such as the ] (FBI) and the ] have specialized duties. At the federal level and in almost every state, jurisprudence operates on a ] system. State courts conduct most criminal trials; ] handle certain designated crimes as well as ]s from state systems. | |||
| The ] is an agency of the United States federal government that was established in 1965 with the purpose to "develop and promote a broadly conceived national policy of support for the humanities and the arts in the United States, and for institutions which preserve the cultural heritage of the United States."<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.federalregister.gov/agencies/national-foundation-on-the-arts-and-the-humanities|title=National Foundation on the Arts and the Humanities|work=Federal Register|access-date=October 1, 2022}}</ref> It is composed of four sub-agencies: | |||
| Among ], the United States has above-average levels of violent crime and particularly high levels of ] and ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.unodc.org/pdf/crime/eighthsurvey/8sv.pdf|title=Eighth United Nations Survey of Crime Trends and Operations of Criminal Justice Systems (2001–2002) |publisher=United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) |date = 2005-03-31|accessdate=2008-05-18}} {{cite journal |author=Krug, E.G, K.E. Powell, and L.L. Dahlberg |year=1998 |title=Firearm-Related Deaths in the United States and 35 Other High- and Upper-Middle Income Countries |journal=International Journal of Epidemiology |volume=7|issue=2 |pages=214–221 |url=http://ije.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/27/2/214 |doi=10.1093/ije/27.2.214 |pmid=9602401 |month=Apr |first1=EG |first2=KE |first3=LL |issn=0300-5771}}</ref> In 2007, there were 5.6 murders per 100,000 persons,<ref name="Crime 2007">{{cite web|url=http://www.fbi.gov/ucr/cius2007/data/table_01.html|title=Crime in the United States by Volume and Rate per 100,000 Inhabitants, 1988–2007|work=Crime in the United States 2007|publisher=FBI|month=September | year=2008|accessdate=2008-10-26}}</ref> three times the rate in neighboring Canada.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www40.statcan.ca/l01/cst01/legal02.htm?sdi=crimes|title=Crimes by Type of Offence|publisher=Statistics Canada|date=2008-07-17|accessdate=2008-10-26}}</ref> The U.S. homicide rate, which decreased by 42% between 1991 and 1999, has been roughly steady since.<ref name="Crime 2007"/> ] are the subject of ]. | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| The United States is considered to have the ] under the ],<ref name="Coleman-2013">{{Cite book |last=Coleman |first=Gabriella |title=Coding Freedom |publisher=] |year=2013 |isbn=978-0-691-14461-0 |pages=10, 201 |author-link=Gabriella Coleman}}</ref> which protects ], ], ], and ] as forms of protected expression.<ref>{{Cite web |date=September 19, 2012 |title=Held Dear In U.S., Free Speech Perplexing Abroad |url=https://www.npr.org/2012/09/19/161439562/held-dear-in-u-s-free-speech-perplexing-abroad |access-date=March 4, 2023 |publisher=]}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |last=Liptak |first=Adam |date=June 11, 2008 |title=Hate speech or free speech? What much of West bans is protected in U.S. |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2008/06/11/world/americas/11iht-hate.4.13645369.html |url-access=limited |access-date=February 21, 2023 |work=]}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Durkee |first=Alison |date=April 25, 2018 |title=What if we didn't... have the First Amendment? |url=https://www.mic.com/articles/188402/what-if-we-didnt-have-the-first-amendment |access-date=February 6, 2023 |website=Mic |language=en}}</ref> A 2016 ] poll found that Americans were the most supportive of free expression of any polity measured.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Wike |first=Richard |title=Americans more tolerant of offensive speech than others in the world |url=https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2016/10/12/americans-more-tolerant-of-offensive-speech-than-others-in-the-world/ |access-date=February 6, 2023 |website=Pew Research Center |date=October 12, 2016 |language=en-US}}</ref> They are the "most supportive of ] and the ] without government censorship."<ref>{{Cite web |last=Gray |first=Alex |date=November 8, 2016 |title=Freedom of speech: which country has the most? |url=https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2016/11/freedom-of-speech-country-comparison/ |access-date=February 6, 2023 |website=World Economic Forum |language=en}}</ref> The U.S. is a ] country<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Norris |first=Pippa |author-link=Pippa Norris |date=February 2023 |title=Cancel Culture: Myth or Reality? |url=http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/00323217211037023 |journal=Political Studies |language=en |volume=71 |issue=1 |pages=145–174 |doi=10.1177/00323217211037023 |s2cid=238647612 |issn=0032-3217 |quote=As predicted, in post-industrial societies, characterized by predominately liberal social cultures, like the US, Sweden, and UK...}}</ref> with ] attitudes surrounding ].<ref name="Derks-2020">{{Cite book |last1=Derks |first1=Marco |title=Public Discourses About Homosexuality and Religion in Europe and Beyond |last2=van den Berg |first2=Mariecke |publisher=] |year=2020 |isbn=978-3-030-56326-4 |pages=338 |quote=...(the United States and Europe) as "already in crisis" for their permissive attitudes toward nonnormative sexualities...}}</ref> ] are advanced by global standards.<ref name="Derks-2020" /><ref>{{Cite web |last=Leveille |first=Dan |date=December 4, 2009 |title=LGBT Equality Index: The most LGBT-friendly countries in the world |url=https://www.equaldex.com/equality-index |access-date=January 26, 2023 |website=] |quote=13.) United States}}</ref><ref>{{Cite book |last=Garretson |first=Jeremiah |title=The Path to Gay Rights: How Activism and Coming Out Changed Public Opinion |publisher=] |year=2018 |isbn=978-1-4798-5007-5 |page= |chapter=A Transformed Society: LGBT Rights in the United States |quote=In the late 1980s and early 1990s, a dramatic wave began to form in the waters of public opinion: American attitudes involving homosexuality began to change... The transformation of America's response to homosexuality has been — and continues to be — one of the most rapid and sustained shifts in mass attitudes since the start of public polling.}}</ref> | |||
| The United States has the highest documented ] rate<ref name="SP">{{cite web |url=http://www.sentencingproject.org/Admin/Documents/publications/inc_newfigures.pdf|title=New Incarceration Figures: Thirty-Three Consecutive Years of Growth |month=December | year=2006 |accessdate = 2007-06-10 |publisher=Sentencing Project}}</ref> and total prison population<ref>{{cite web| author=Walmsley, Roy |url=http://www.kcl.ac.uk/depsta/rel/icps/world-prison-population-list-2005.pdf |format=PDF|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20070628215935/http://www.kcl.ac.uk/depsta/rel/icps/world-prison-population-list-2005.pdf |archivedate=2007-06-28|title=World Prison Population List |year=2005|accessdate = 2007-10-19|publisher=King's College London, International Centre for Prison Studies}} For the latest data, see {{cite web|url=http://www.kcl.ac.uk/depsta/rel/icps/worldbrief/north_america_records.php?code=190|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20070804061423/http://www.kcl.ac.uk/depsta/rel/icps/worldbrief/north_america_records.php?code=190|archivedate=2007-08-04|title=Prison Brief for United States of America|date=2006-06-21|accessdate = 2007-10-19|publisher=King's College London, International Centre for Prison Studies}} For other estimates of the incarceration rate in China and North Korea see {{cite web|author=Adams, Cecil|url=http://www.straightdope.com/columns/read/2494/does-the-united-states-lead-the-world-in-prison-population |title=Does the United States Lead the World in Prison Population? |date=2004-02-06|accessdate = 2007-10-11 |publisher=The Straight Dope}}</ref> in the world. At the start of 2008, more than 2.3 million people were incarcerated, more than one in every 100 adults.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.pewcenteronthestates.org/news_room_detail.aspx?id=35912 |title=Pew Report Finds More than One in 100 Adults are Behind Bars|date=2008-02-28|accessdate = 2008-03-02|publisher=Pew Center on the States}}</ref> The current rate is about seven times the 1980 figure.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ojp.usdoj.gov/bjs/glance/tables/incrttab.htm |title=Incarceration Rate, 1980–2005 |year=2006|accessdate = 2007-06-10 |publisher=U.S. Dept. of Justice, Bureau of Justice Statistics}}</ref> African American males are jailed at about six times the rate of white males and three times the rate of Hispanic males.<ref name="SP"/> In 2006, the U.S. incarceration rate was over three times the figure in Poland, the ] (OECD) country with the next highest rate.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.kcl.ac.uk/depsta/rel/icps/worldbrief/highest_to_lowest_rates.php|archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20070824173340/http://www.kcl.ac.uk/depsta/rel/icps/worldbrief/highest_to_lowest_rates.php|archivedate=2007-08-24|title=Entire World—Prison Population Rates per 100,000 of the National Population|year=2007|accessdate = 2007-10-19|publisher=King's College London, International Centre for Prison Studies}}</ref> The country's high rate of incarceration is largely due to ] and ].<ref name="SP"/><ref name="HRW">{{cite web |url=http://www.hrw.org/reports/2000/usa/Rcedrg00-05.htm |title=The Impact of the War on Drugs on U.S. Incarceration |month=May | year=2000 |accessdate = 2007-06-10 |publisher=Human Rights Watch}}</ref> Though it has been abolished in most Western nations, ] is sanctioned in the United States for certain federal and military crimes, and in thirty-six states. Since 1976, when the U.S. Supreme Court ] after a four-year moratorium, there have been more than 1,000 executions.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.deathpenaltyinfo.org/executions-united-states-2007 |title=Executions in the United States in 2007|accessdate = 2007-06-15 |publisher=Death Penalty Information Center}}</ref> In 2006, the country had the sixth highest number of executions in the world, following China, Iran, ], Iraq, and ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.deathpenaltyinfo.org/death-penalty-international-perspective |title=Executions Around the World|accessdate = 2007-06-15|year=2007 |publisher=Death Penalty Information Center}}</ref> In 2007, ] became the first state to legislatively abolish the death penalty since the 1976 Supreme Court decision, followed by ] in 2009. | |||
| == |
=== Literature === | ||
| {{Main|American literature|American philosophy}} | |||
| {{Main|Culture of the United States}} | |||
| {{ |
{{see also|List of American novelists|List of playwrights from the United States}} | ||
| ], whom ] called "the father of American literature"<ref name="faulkner">{{cite book |last=Jelliffe |first=Robert A. |title=Faulkner at Nagano |year=1956 |publisher=Kenkyusha, Ltd |location=Tokyo}}</ref>|alt=Photograph of Mark Twain]] | |||
| ], ], and the ]]] | |||
| Colonial American authors were influenced by ] and various other ] philosophers.{{sfn|Baym|Levine|2013|pp=157-159}}{{sfn|Lauter|1994a|pp=503-509}} ] (1765–1783) is notable for the political writings of ], ], ], and ]. Shortly before and after the ], the newspaper rose to prominence, filling a demand for anti-British national literature.{{sfn|Baym|Levine|2013|p=163}}<ref>Mulford, Carla. In {{harvnb|Lauter|1994a|pp=705–707}}.</ref> An early novel is ]'s '']'', published in 1791. Writer and critic ] in the early- to mid-nineteenth century helped advance America toward a unique literature and culture by criticizing predecessors such as ] for imitating their British counterparts, and by influencing writers such as ],<ref>{{Cite book | publisher = University of Chicago Press | isbn = 0-226-46969-7 | last = Lease | first = Benjamin | title = That Wild Fellow John Neal and the American Literary Revolution | location = Chicago, Illinois | year = 1972 | page = 80}}</ref> who took American poetry and short fiction in new directions. ] and ] pioneered the influential ] movement;<ref>{{cite web|last1=Finseth|first1=Ian Frederick|title=The Emergence of Transcendentalism|url=http://xroads.virginia.edu/~ma95/finseth/trans.html|website= American Studies @ The University of Virginia|publisher=]|access-date=November 9, 2014|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230718205554/http://xroads.virginia.edu/~MA95/finseth/trans.html |archive-date=July 18, 2023}}</ref><ref name=Coviello>{{cite book |last=Coviello |first=Peter |chapter=Transcendentalism |title=The Oxford Encyclopedia of American Literature |publisher=Oxford University Press |date=2005 |via=Oxford Reference Online |access-date=October 23, 2011 |url=https://www.oxfordreference.com/display/10.1093/acref/9780195156539.001.0001/acref-9780195156539-e-0294?rskey=lw57LH&result=1 |isbn=9780195307726}}</ref> ], author of '']'', was influenced by this movement. The conflict surrounding ] inspired writers, like ], and authors of slave narratives, such as ]. ]'s '']'' (1850) explored the dark side of American history, as did ]'s '']'' (1851). Major American poets of the nineteenth century ] include ], Melville, and ].{{sfn|Baym|Levine|2013|pp=444-447}}{{sfn|Lauter|1994a|pp=1228, 1233, 1260}} ] was the first major American writer to be born in the West. ] achieved international recognition with novels like '']'' (1881). As literacy rates rose, periodicals published more stories centered around industrial workers, women, and the rural poor.{{sfn|Baym|Levine|2013|pp=1269-1270}}{{sfn|Lauter|1994b|pp=8-10}} ], ], and ] were the major literary movements of the period.{{sfn|Baym|Levine|2013|pp=1271-1273}}{{sfn|Lauter|1994b|p=12}} | |||
| The United States is a ] nation, home to a wide variety of ethnic groups, traditions, and values.<ref name="DD"/><ref name="Society in Focus">Thompson, William, and Joseph Hickey (2005). ''Society in Focus''. Boston: Pearson. ISBN 020541365X.</ref> Aside from the now small ] and ] populations, nearly all Americans or their ancestors immigrated within the past five centuries.<ref>Fiorina, Morris P., and Paul E. Peterson (2000). ''The New American Democracy''. London: Longman, p. 97. ISBN 0321070585.</ref> The culture held in common by most Americans—mainstream American culture—is a ] largely derived from the ] with influences from many other sources, such as ].<ref name="DD"/><ref>Holloway, Joseph E. (2005). ''Africanisms in American Culture'', 2d ed. Bloomington: Indiana University Press, pp. 18–38. ISBN 0253344794. Johnson, Fern L. (1999). ''Speaking Culturally: Language Diversity in the United States''. Thousand Oaks, Calif., London, and New Delhi: Sage, p. 116. ISBN 0803959125.</ref> More recent immigration from ] and especially ] has added to a cultural mix that has been described as both a homogenizing ] and a heterogeneous ] in which immigrants and their descendants retain distinctive cultural characteristics.<ref name="DD"/> | |||
| While ] generally took on an international character, modernist authors working within the United States more often rooted their work in specific regions, peoples, and cultures.{{sfn|Baym|Levine|2013|pp=1850-1851}} Following the Great Migration to northern cities, African-American and black ] authors of the ] developed an independent tradition of literature that rebuked a history of inequality and celebrated black culture. An important cultural export during the ], these writings were a key influence on '']'', a philosophy emerging in the 1930s among francophone writers of the ].<ref>]. In {{harvnb|Lauter|1994b|pp=1579–1585}}.</ref><ref>{{Cite journal |last=Philipson |first=Robert |title=The Harlem Renaissance as Postcolonial Phenomenon |journal=African American Review |volume=40 |issue=1 |year=2006 |pages=145–160 |jstor=40027037}}</ref> In the 1950s, an ideal of homogeneity led many authors to attempt to write the ],{{sfn|Baym|Levine|2013|pp=2260-2261}} while the ] rejected this conformity, using styles that elevated the impact of the ] over mechanics to describe drug use, sexuality, and the failings of society.{{sfn|Baym|Levine|2013|p=2262}}<ref>{{harvnb|Lauter|1994b|pp=1975–1977}}. "".</ref> Contemporary literature is more pluralistic than in previous eras, with the closest thing to a unifying feature being a trend toward self-conscious ].{{sfn|Baym|Levine|2013|pp=2266-2267}} As of 2024, there have been 12 American laureates for the ].<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/lists/all-nobel-prizes-in-literature/all/ |title=All Nobel Prizes in Literature |author=<!--Not stated--> |date= |website=The Nobel Prize |publisher= Nobel Prize Outreach AB 2024 |access-date=August 6, 2024 |quote=}}</ref> | |||
| According to ]'s cultural dimensions analysis, the United States has the highest ] score of any country studied.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.clearlycultural.com/geert-hofstede-cultural-dimensions/individualism/|title=Individualism| publisher = Clearly Cultural|accessdate=2009-02-28}}</ref> While the mainstream culture holds that the United States is a ],<ref>{{cite book |last=Gutfield |first=Amon |year=2002 |title=American Exceptionalism: The Effects of Plenty on the American Experience |publisher=Sussex Academic Press |location=Brighton and Portland |page=65 |isbn=1903900085}}</ref> scholars identify significant differences between the country's social classes, affecting ], language, and values.<ref>{{cite book |last=Zweig |first=Michael |year=2004 |title=What's Class Got To Do With It, American Society in the Twenty-First Century |publisher=Cornell University Press |location=Ithaca, NY |isbn=0801488990}} {{cite web |url=http://eric.ed.gov/ERICWebPortal/Home.portal?_nfpb=true&_pageLabel=RecordDetails&ERICExtSearch_SearchValue_0=ED309843&ERICExtSearch_SearchType_0=eric_accno&objectId=0900000b800472a5 |title=Effects of Social Class and Interactive Setting on Maternal Speech |publisher=Education Resource Information Center |accessdate=2007-01-27}}</ref> The ] has initiated many contemporary social trends such as ], ], and multiculturalism.<ref>{{cite book |last=Ehrenreich |first=Barbara |year=1989 |title=Fear of Falling, The Inner Life of the Middle Class |publisher=HarperCollins |location=New York |isbn=0060973331}}</ref> Americans' self-images, social viewpoints, and cultural expectations are associated with their occupations to an unusually close degree.<ref>{{cite book |last=Eichar |first=Douglas |year=1989 |title=Occupation and Class Consciousness in America |publisher=Greenwood Press |location=Westport, CT |isbn=0313261113}}</ref> While Americans tend greatly to value socioeconomic achievement, being ] is generally seen as a positive attribute.<ref>{{cite book |last=O'Keefe |first=Kevin |year=2005 |title=The Average American |publisher=PublicAffairs |location=New York |id=ISBN 158648270X |isbn=158648270X}}</ref> Though the ], or the perception that Americans enjoy high ], plays a key role in attracting immigrants, some analysts find that the United States has less social mobility than Western Europe and Canada.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.economist.com/world/unitedstates/displayStory.cfm?story_id=3518560|title=Ever Higher Society, Ever Harder to Ascend: Whatever Happened to the Belief That Any American Could Get to the Top| work = Economist|date=2004-12-29 |accessdate=2006-08-21}} {{cite web|url=http://www.suttontrust.com/reports/IntergenerationalMobility.pdf|title=Intergenerational Mobility in Europe and North America|author=Blanden, Jo, Paul Gregg, and Stephen Malchin| publisher = Centre for Economic Performance|month=April | year=2005 |accessdate=2006-08-21}}</ref> | |||
| === Mass media === | |||
| Women now mostly work outside the home and receive a majority of ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.iserp.columbia.edu/news/articles/female_college.html |title=Women's Advances in Education |publisher=Columbia University, Institute for Social and Economic Research and Policy |year=2006 |accessdate=2007-06-06}}{{Dead link|url=http://www.iserp.columbia.edu/news/articles/female_college.html|date=May 2009}}</ref> In 2005, ] were married childless couples, the most common arrangement.<ref>Williams, Brian, Stacey C. Sawyer, and Carl M. Wahlstrom (2005). ''Marriages, Families and Intimate Relationships''. Boston: Pearson. ISBN 0205366740.</ref> ] is contentious. ] permit ] in lieu of marriage. Since 2003, four state supreme courts have ruled bans on same-sex marriage unconstitutional, while voters in more than a dozen states approved constitutional bans on the practice. In 2009, ], ], and ] became the first states to permit same-sex marriage through legislative action. | |||
| {{Main|Mass media in the United States}} | |||
| {{See also|Newspapers in the United States|Television in the United States|Broadcasting in the United States|Public broadcasting in the United States|Internet in the United States|Radio in the United States|Video games in the United States}} | |||
| ] in ], headquarters of ], one of the world's ] and media conglomerates]] | |||
| Media is ], with the ] providing significant protections, as reiterated in '']''.<ref name="Coleman-2013" /> The four major broadcasters in the U.S. are the ] (NBC), ] (CBS), ] (ABC), and ] (FOX). The four major broadcast television networks are all commercial entities. ] offers hundreds of channels catering to a variety of niches.<ref>{{cite news|title=Streaming TV Services: What They Cost, What You Get|url=https://www.nytimes.com/aponline/2015/10/12/business/ap-us-streaming-tv-options.html|access-date=October 12, 2015|work=]|agency=Associated Press|date=October 12, 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151015023520/https://www.nytimes.com/aponline/2015/10/12/business/ap-us-streaming-tv-options.html|archive-date=October 15, 2015}}</ref> {{as of|2021}}, about 83% of Americans over age 12 listen to ], while about 40% listen to ]s.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.pewresearch.org/journalism/fact-sheet/audio-and-podcasting/|title=Audio and Podcasting Fact Sheet|publisher=]|location=Washington, D.C.|date=June 29, 2021|access-date=July 3, 2022}}</ref> {{As of|2020}}, there were 15,460 licensed full-power radio stations in the U.S. according to the ] (FCC).<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://docs.fcc.gov/public/attachments/DOC-367270A1.pdf|title=BROADCAST STATION TOTALS AS OF SEPTEMBER 30, 2020}}</ref> Much of the public radio broadcasting is supplied by ], incorporated in February 1970 under the ].<ref>{{Cite news|date=June 20, 2013|title=History: NPR|publisher=NPR|url=https://www.npr.org/about-npr/192827079/overview-and-history|access-date=May 5, 2021}}</ref> | |||
| ===Popular media=== | |||
| {{Main|Cinema of the United States|Television in the United States|Music of the United States}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| The world's first commercial motion picture exhibition was given in New York City in 1894, using ]'s ]. The next year saw the first commercial screening of a projected film, also in New York, and the United States was in the forefront of ]'s development in the following decades. Since the early 20th century, the U.S. film industry has largely been based in and around ]. Director ] was central to the development of ] and ]'s '']'' (1941) is frequently cited as the greatest film of all time.<ref>. Filmsite.org; . BFI. Retrieved on 2007-06-19.</ref> American screen actors like ] and ] have become iconic figures, while producer/entrepreneur ] was a leader in both ] and movie ]. The ]s of Hollywood have produced the most commercially successful movies in history, such as '']'' (1977) and '']'' (1997), and the products of Hollywood today dominate the global film industry.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.unesco.org/bpi/eng/unescopress/2000/00-120e.shtml |title=World Culture Report 2000 Calls for Preservation of Intangible Cultural Heritage |date=2000-11-17 |publisher=UNESCO |accessdate=2007-09-14}} {{cite web |url=http://www1.worldbank.org/economicpolicy/globalization/thwart.html |title=Summary: Does Globalization Thwart Cultural Diversity? |publisher=World Bank Group |accessdate=2007-09-14}}</ref> | |||
| U.S. newspapers with a global reach and reputation include '']'', '']'', '']'', and '']''.<ref name="Shaffer2006">{{cite book|first=Brenda|last=Shaffer|title=The Limits of Culture: Islam and Foreign Policy|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=uEOd-cDWVwQC&pg=PA116|year=2006|publisher=MIT Press|isbn=978-0-262-19529-4|page=116}}</ref> ] are produced in Spanish.<ref>{{cite web|title=Spanish Newspapers in United States|url=https://www.w3newspapers.com/usa/spanish|access-date=August 5, 2014|publisher=W3newspapers}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Spanish Language Newspapers in the USA : Hispanic Newspapers : Periódiscos en Español en los EE.UU|url=https://www.onlinenewspapers.com/usstate/spanish-language-newspapers-usa.htm|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140626114455/https://www.onlinenewspapers.com/usstate/spanish-language-newspapers-usa.htm|archive-date=June 26, 2014|access-date=August 5, 2014|publisher=Onlinenewspapers.com}}</ref> With few exceptions, newspapers are privately owned, either by large chains such as ] or ], which own dozens or even hundreds of newspapers; by small chains that own a handful of papers; or, in an increasingly rare situation, by individuals or families. Major cities often have ]s to complement the mainstream daily papers, such as '']'' in New York City and '']'' in Los Angeles. The five most popular websites used in the U.S. are ], ], ], ], and ]—all of them American-owned.<ref name="alexa-topsitesus">{{cite web|year=2021|title=Top Sites in United States|url=https://www.alexa.com/topsites/countries/US|access-date=October 6, 2021|publisher=Alexa|archive-date=June 21, 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200621221154/https://www.alexa.com/topsites/countries/US|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| Americans are the heaviest television viewers in the world,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nationmaster.com/graph/med_tel_vie-media-television-viewing |title=Media Statistics > Television Viewing by Country |publisher=NationMaster |accessdate=2007-06-03}}</ref> and the average viewing time continues to rise, reaching five hours a day in 2006.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.emarketer.com/Article.aspx?id=1005003 |title=Broadband and Media Consumption |date=2007-06-07|publisher=eMarketer |accessdate=2007-06-10}}</ref> The four major broadcast networks are all commercial entities. Americans listen to radio programming, also largely commercialized, on average just over two-and-a-half hours a day.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.emarketer.com/Article.aspx?id=1004830 |title=TV Fans Spill into Web Sites |date=2007-06-07|publisher=eMarketer |accessdate = 2007-06-10}}</ref> Aside from ]s and ]s, the most popular websites are ], ], ], ], ], and ].<ref name="alexa-topsitesus">{{cite web |url=http://www.alexa.com/topsites/countries/US |title=Top Sites in United States |year=2009 |publisher=Alexa |accessdate=2009-05-01}}</ref> | |||
| {{As of|2022}}, the video game market of the United States is the world's ].<ref>{{cite web|title= Top countries and markets by video game revenues|url=https://newzoo.com/resources/rankings/top-10-countries-by-game-revenues |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230326135814/https://newzoo.com/resources/rankings/top-10-countries-by-game-revenues |archive-date=March 26, 2023|access-date=October 6, 2023|website=Newzoo}}</ref> There are 444 publishers, developers, and hardware companies in California alone.<ref>{{Cite web |title=California (CA) |url=https://www.theesa.com/video-game-impact-map/state/california/ |access-date=December 14, 2022 |website=ESA Impact Map |date=July 20, 2017 |language=en-US}}</ref> | |||
| The rhythmic and lyrical styles of ] have deeply influenced ] at large, distinguishing it from European traditions. Elements from ] idioms such as the ] and what is now known as ] were adopted and transformed into ] with global audiences. ] was developed by innovators such as ] and ] early in the 20th century. ], ], and ] emerged between the 1920s and 1950s. In the 1960s, ] emerged from the ] to become one of America's greatest songwriters and ] led the development of ]. More recent American creations include ] and ]. American pop stars such as ], ], and ] have become global celebrities.<ref>Biddle, Julian (2001). ''What Was Hot!: Five Decades of Pop Culture in America''. New York: Citadel, p. ix. ISBN 0806523115.</ref> | |||
| === Theater === | |||
| ===Literature, philosophy, and the arts=== | |||
| {{Main |
{{Main|Theater in the United States}} | ||
| ]s in ]]] | |||
| The United States is well known for its theater. Mainstream theater in the United States derives from the old European theatrical tradition and has been heavily influenced by the ].<ref name="Saxon2011">{{cite book| first = Theresa| last = Saxon| date = October 11, 2011| title = American Theatre: History, Context, Form| publisher = Edinburgh University Press| pages = 7–| isbn = 978-0-7486-3127-8| oclc = 1162047055| url = https://books.google.com/books?id=2-AkDQAAQBAJ&pg=PA7}}</ref> By the middle of the 19th century America had created new distinct dramatic forms in the ], the ] and the ].<ref>Meserve, Walter J. An Outline History of American Drama, New York: Feedback/Prospero, 1994.</ref> The central hub of the American theater scene is the ], with its divisions of ], ], and ].<ref name="LondréWatermeier1998">{{cite book| first1 = Felicia Hardison | last1 = Londré| first2 = Daniel J.| last2 = Watermeier| date = 1998| title = The History of North American Theater: From Pre-Columbian Times to the Present| publisher = Continuum| pages =| isbn = 978-0-8264-1079-5| oclc = 1024855967}}</ref> | |||
| ], one of the best-known figures of the ]]] | |||
| In the eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries, American art and literature took most of its cues from Europe. Writers such as ], ], and ] established a distinctive American literary voice by the middle of the 19th century. ] and poet ] were major figures in the century's second half; ], virtually unknown during her lifetime, is now recognized as an essential American poet.<ref>]. 1999. ''Emily Dickinson''. Broomall, PA: Chelsea House Publishers. p. 9. ISBN 0791051064.</ref> A work seen as capturing fundamental aspects of the national experience and character—such as ]'s '']'' (1851), Twain's '']'' (1885), and ]'s '']'' (1925)—may be dubbed the "]." | |||
| Many movie and television ] have gotten their big break working in New York productions. Outside New York City, many cities have professional ] that produce their own seasons. The biggest-budget theatrical productions are musicals. U.S. theater has an active ] culture.<ref>Stephen Watt, and Gary A. Richardson, ''American Drama: Colonial to Contemporary'' (1994).</ref> | |||
| Eleven U.S. citizens have won the ], most recently ] in 1993. ], the 1954 Nobel laureate, is often named as one of the most influential writers of the 20th century.<ref>Meyers, Jeffrey (1999). ''Hemingway: A Biography''. New York: Da Capo, p. 139. ISBN 0306808900.</ref> Popular literary genres such as the ] and ] developed in the United States. The ] writers opened up new literary approaches, as have ] authors such as ], ], and ]. | |||
| The ] recognizes excellence in live Broadway theater and are presented at an annual ceremony in ]. The awards are given for Broadway productions and performances. One is also given for ]. Several discretionary non-competitive awards are given as well, including a ], the ], and the ].<ref>Staff (undated). . {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161223002914/http://www.tonyawards.com/en_US/about/index.html|date=December 23, 2016}}. tonyawards.com. Retrieved September 13, 2013.</ref> | |||
| The ], led by Thoreau and ], established the first major American ]. After the Civil War, ] and then ] and ] were leaders in the development of ]. In the 20th century, the work of ] and ] brought ] to the fore of U.S. academics. ] and ] led a revival of ]. | |||
| === Visual arts === | |||
| In the visual arts, the ] was a mid-19th-century movement in the tradition of European ]. The 1913 ] in New York City, an exhibition of European ], shocked the public and transformed the U.S. art scene.<ref>Brown, Milton W. (1988 1963). ''The Story of the Armory Show''. New York: Abbeville. ISBN 0896597954.</ref> ], ], and others experimented with new styles, displaying a highly individualistic sensibility. Major artistic movements such as the ] of ] and ] and the ] of ] and ] developed largely in the United States. The tide of modernism and then ] has brought fame to American architects such as ], ], and ]. | |||
| {{Main|Visual art of the United States|Architecture of the United States}} | |||
| ], host to many shows]] | |||
| ]'' (1930) by ] is one of the most famous ] and is widely ].<ref name=BBC>{{cite web|url=http://www.bbc.com/culture/story/20170208-how-american-gothic-became-an-icon|title=How American Gothic became an icon|first=Fisun|last=Güner|date=February 8, 2017|publisher=BBC|access-date=March 2, 2017}}</ref>]] | |||
| ] in ] grew out of artisanal craftsmanship in communities that allowed commonly trained people to individually express themselves. It was distinct from Europe's tradition of ], which was less accessible and generally less relevant to early American settlers.<ref>American folk art the art of the common man in America, 1750-1900. New York, N.Y.: The Museum of Modern Art. 1932.</ref> Cultural movements in art and craftsmanship in colonial America generally lagged behind those of Western Europe. For example, the prevailing medieval style of ] and primitive ] became integral to early American folk art, despite the emergence of ] in England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. The new English styles would have been early enough to make a considerable impact on American folk art, but American styles and forms had already been firmly adopted. Not only did styles change slowly in early America, but there was a tendency for rural artisans there to continue their traditional forms longer than their urban counterparts did—and far longer than those in Western Europe.<ref name="Coleman-2013" /> | |||
| One of the first major promoters of American theater was impresario ], who began operating a lower ] entertainment complex in 1841. The team of ] produced a series of popular ] comedies in New York starting in the late 1870s. In the 20th century, the modern musical form emerged on ]; the songs of musical theater composers such as ], ], and ] have become ]. Playwright ] won the Nobel literature prize in 1936; other acclaimed U.S. dramatists include multiple ] winners ], ], and ]. | |||
| The ] was a mid-19th-century movement in the visual arts tradition of European ]. The 1913 ] in New York City, an exhibition of European ], shocked the public and transformed the U.S. art scene.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Brown|first1=Milton W.|title=The Story of the Armory Show|date=1963|publisher=Abbeville Press|location=New York|isbn=978-0-89659-795-2|edition=2nd|url=https://archive.org/details/storyofarmorysho00brow }}</ref> | |||
| Though largely overlooked at the time, ]'s work of the 1910s established him as the first major U.S. composer in the classical tradition; other experimentalists such as ] and ] created an American approach to classical composition. ] and ] developed a unique synthesis of popular and classical music. ] ] and ] helped create ], while ] and ] were leaders in 20th century ballet. Americans have long been important in the modern artistic medium of ], with major photographers including ], ], and ]. The newspaper ] and the ] are both U.S. innovations. ], the quintessential comic book ], has become an American icon.<ref>{{cite book | last=Daniels | first=Les | authorlink=Les Daniels | year=1998 | title=Superman: The Complete History | page=11 | edition=1st | publisher=] | isbn=1-85286-988-7 }}</ref> | |||
| ], ], and others experimented with new and individualistic styles, which would become known as ]. Major artistic movements such as the ] of ] and ] and the ] of ] and ] developed largely in the United States. Major photographers include ], ], ], ], ], ], and ].<ref name="Davenport1991">{{cite book|last=Davenport|first=Alma|title=The History of Photography: An Overview|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hca5H_rJZnUC&pg=PA67|year=1991|publisher=UNM Press|isbn=978-0-8263-2076-6|page=67}}</ref> | |||
| ===Food=== | |||
| {{Main|Cuisine of the United States}} | |||
| ], with restaurants featuring Mexican- and Chinese-based food]] | |||
| Mainstream American ]s are similar to those in other Western countries. ] is the primary ] grain. Traditional American cuisine uses ingredients such as ], ] ], ]es, ]es, ], ], and ], indigenous foods employed by Native Americans and early European settlers. Slow-cooked pork and beef ], ]s, ]s, and ]s are distinctively American styles. ], developed by African slaves, is popular around the South and among many African Americans elsewhere. ] cuisines such as ], ], and ] are regionally important. Characteristic dishes such as ], ], ], ]s, and ]s derive from the recipes of various immigrants. ], Mexican dishes such as ]s and ]s, and ] dishes freely adapted from Italian sources are widely consumed.<ref name="IFT">{{cite web |url=http://www.ift.org/cms/?pid=1000496 |author=Klapthor, James N. |title=What, When, and Where Americans Eat in 2003 |publisher=Institute of Food Technologists |date=2003-08-23|accessdate=2007-06-19}}</ref> Americans generally prefer coffee to tea. Marketing by U.S. industries is largely responsible for making orange juice and milk ubiquitous breakfast beverages.<ref>Smith, Andrew F. (2004). ''The Oxford Encyclopedia of Food and Drink in America''. New York: Oxford University Press, pp. 131–32. ISBN 0195154371. Levenstein, Harvey (2003). ''Revolution at the Table: The Transformation of the American Diet''. Berkeley, Los Angeles, and London: University of California Press, pp. 154–55. ISBN 0520234391.</ref> During the 1980s and 1990s, Americans' caloric intake rose 24%;<ref name="IFT" /> frequent dining at ] outlets is associated with what health officials call the American "obesity epidemic." Highly sweetened ]s are widely popular; sugared beverages account for 9% of the average American's caloric intake.<ref>{{cite web |title=Fast Food, Central Nervous System Insulin Resistance, and Obesity |publisher=American Heart Association |year=2005 |work=] |url=http://atvb.ahajournals.org/cgi/content/full/25/12/2451#R3-101329 |accessdate=2007-06-09}} {{cite web |title=Let's Eat Out: Americans Weigh Taste, Convenience, and Nutrition |publisher=U.S. Dept. of Agriculture |url=http://www.ers.usda.gov/publications/eib19/eib19_reportsummary.pdf|accessdate=2007-06-09}}</ref> | |||
| The tide of ] and then ] has brought global fame to American architects, including ], ], and ].<ref name="JansonJanson2003">{{cite book|last1=Janson|first1=Horst Woldemar|last2=Janson|first2=Anthony F.|title=History of Art: The Western Tradition|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=MMYHuvhWBH4C&pg=PT955|year=2003|publisher=Prentice Hall Professional|isbn=978-0-13-182895-7|page=955}}</ref> The ] in ] is the largest ] in the United States<ref name="METLargestArtMuseum">{{cite news |author=Lester |first=Alfred |date=December 6, 1993 |title=Letter: The Louvre: tourism on the grand scale |url=https://www.independent.co.uk/voices/letter-the-louvre-tourism-on-the-grand-scale-1465736.html |access-date=December 2, 2023 |newspaper=]}}</ref> and the ] in the world. | |||
| ===Sports=== | |||
| === Music === | |||
| <!---Misplaced Pages:WikiProject Countries. Caution should be taken to ensure that the section is not simply a listing of names or mini biographies.--> | |||
| {{Main|Music of the United States}} | |||
| ] encompasses numerous music genres, variously known as traditional music, traditional ], contemporary folk music, or roots music. Many traditional songs have been sung within the same family or folk group for generations, and sometimes trace back to such origins as the ], ], or ].<ref name=afc>{{Cite web|url=https://www.loc.gov/folklife/guide/folkmusicandsong.html|title=Folk Music and Song: American Folklife Center: An Illustrated Guide (Library of Congress)|website=Loc.gov}}</ref> The rhythmic and lyrical styles of African-American music in particular have influenced American music.<ref>{{cite web |date=September 22, 2016 |title=Musical Crossroads: African American Influence on American Music |url=https://music.si.edu/story/musical-crossroads |access-date=April 14, 2023 |website=Smithsonian}}</ref> ]s were brought to America through the slave trade. ]s incorporating the instrument into their acts led to its increased popularity and widespread production in the 19th century.<ref>{{cite journal|title=The Folk, the Stage, and the Five-String Banjo in the Nineteenth Century |first=Robert B. |last=Winans |journal=The Journal of American Folklore |year=1976 |volume=89 |issue=354 | pages=407–437 |publisher=American Folklore Society |doi=10.2307/539294 |jstor=539294 }}</ref>{{sfn|Shi|2016|p=378}} The ], first invented in the 1930s, and mass-produced by the 1940s, had an enormous influence on popular music, in particular due to the development of ].<ref name="axe">{{cite web|title=The Invention of the Electric Guitar |date=April 18, 2014 |url=https://invention.si.edu/invention-electric-guitar |website=Lemelson Center Studies in Invention and Innovation |publisher=Smithsonian Institution}}</ref> | |||
| ] in ]]] | |||
| Elements from folk idioms such as the ] and ] were adopted and transformed into ] with global audiences. ] grew from blues and ] in the early 20th century, developing from the innovations and recordings of composers such as ] and ]. ] and ] increased its popularity early in the 20th century.<ref name="Biddle-2001">{{cite book|last1=Biddle|first1=Julian|title=What Was Hot!: Five Decades of Pop Culture in America|date=2001|publisher=Citadel|location=New York|isbn=978-0-8065-2311-8|page=|url=https://archive.org/details/whatwashotroller00bidd/page/ }}</ref> ] developed in the 1920s,<ref>{{Cite web|website=OUP blog |title=Early blues and country music |last=Stoia |first=Nicholas |date=October 21, 2014 |url=https://blog.oup.com/2014/10/early-blues-country-music/ |publisher=Oxford University Press}}</ref> rock and roll in the 1930s,<ref name="axe" /> and ]<ref>{{cite web |title=Bluegrass music |url=https://www.britannica.com/art/bluegrass-music |website=Encyclopædia Britannica |access-date=June 19, 2020 |language=en}}</ref> and ] in the 1940s.{{sfn|OpenStax|2014|loc=§ }} In the 1960s, ] emerged from the ] to become one of the country's most celebrated songwriters.<ref>{{cite magazine |date=April 10, 2020 |title=No. 1 Bob Dylan |url=https://www.rollingstone.com/interactive/lists-100-greatest-songwriters/#bob-dylan |magazine=Rolling Stone |access-date=January 29, 2021}}</ref> The musical forms of ] and ] both originated in the United States in the 1970s.<ref>{{cite book |author=Funk |first=Clayton |url=https://ohiostate.pressbooks.pub/artandmusicbiographies/chapter/reading-9-neo-expressionism-and-music-reaching-into-the-1980s/ |title=A Quick and Dirty Guide to Art, Music, and Culture |date=August 16, 2016 |publisher=The Ohio State University |chapter=9. Neo-Expressionism, Punk, and Hip Hop Emerge}}</ref> | |||
| The United States has the world's ] with a total retail value of $15.9 billion in 2022.<ref>{{Cite web |title=2022 Year-End Music Industry Revenue Report |url=https://www.riaa.com/reports/2022-year-end-music-industry-revenue-report-riaa/ |access-date=November 26, 2023 |publisher=Record Industry Association of America |language=en-US}}</ref> Most of the world's ] are based in the U.S.; they are represented by the ] (RIAA).<ref>{{cite web |author=Hennessy |first=Eoin |date=March 27, 2014 |title=How American Music Took Over the World |url=https://universitytimes.ie/2014/03/how-american-music-took-over-the-world/ |access-date=April 28, 2023 |website=]}}</ref> Mid-20th-century American pop stars, such as ]<ref>{{cite web|date=December 8, 2015|title=10 ways that Frank Sinatra changed the world|url=https://www.usatoday.com/story/life/music/2015/12/08/10-ways-frank-sinatra-changed-world/76381754/|access-date=June 24, 2021|website=USA Today}}</ref> and ],<ref>{{cite news|url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-universal-music-elvis-idCAKCN2M40UH|title=Universal Music can't help falling for Elvis Presley, to manage song catalog|date=April 12, 2022|work=]|access-date=April 12, 2022}}</ref> became ] and ],<ref name="Biddle-2001" /> as have artists of the late 20th century, such as ],<ref name="RIAA">{{cite web|title= Michael Jackson's 'Thriller' First Ever 30X Multi-Platinum RIAA Certification |date= December 16, 2015 |access-date= December 17, 2021 |publisher= Recording Industry Association of America |url= https://www.riaa.com/michael-jacksons-thriller-first-ever-30x-multi-platinum-riaa-certification/}}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite news|url=https://english.elpais.com/culture/2022-08-17/madonna-has-been-scandalizing-people-for-40-years-and-nobodys-going-to-stop-her.html|title=Madonna has been scandalizing people for 40 years, and nobody's going to stop her|date=August 17, 2022|first=Carlos|last=Marcos|work=]|access-date=August 17, 2022}}</ref> ],<ref name="Rolling Stone-2023">{{cite magazine |date=January 1, 2023 |title=The 200 Greatest Singers of All Time |url=https://www.rollingstone.com/music/music-lists/best-singers-all-time-1234642307/whitney-houston-11-1234643211/ |magazine=Rolling Stone |access-date=January 2, 2023}}</ref> and ],<ref name="ReferenceA">{{Cite magazine |date=April 28, 2016 |title=Prince Tribute: The Greatest Musical Talent of His Generation |url=https://www.billboard.com/articles/news/magazine-feature/7348527/prince-tribute-greatest-musical-talent-of-his-generation |magazine=Billboard |access-date=March 17, 2020}}</ref> and the early 21st century, such as ] and ].<ref>{{cite news|url=https://news.sky.com/story/taylor-swift-and-beyonce-reporters-wanted-by-biggest-newspaper-chain-in-us-12960828|title=Taylor Swift and Beyoncé reporters wanted by biggest newspaper chain in US|publisher=]|date=September 14, 2023|access-date=November 8, 2023|archive-date=November 9, 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231109015600/https://news.sky.com/story/taylor-swift-and-beyonce-reporters-wanted-by-biggest-newspaper-chain-in-us-12960828|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| === Fashion === | |||
| {{main|Fashion in the United States}} | |||
| ] ]s on the ] during ]]] | |||
| The United States is the world's largest ] market by revenue.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2024-06-19 |title=Global Apparel Industry Statistics (2024) |url=https://www.uniformmarket.com/statistics/global-apparel-industry-statistics |access-date=2024-08-25 |website=uniformmarket.com |language=en-US}}</ref> Apart from professional ], American fashion is eclectic and predominantly informal. Americans' diverse cultural roots are reflected in their clothing; however, ]s, ], T-shirts, and ]s are emblematic of American styles.<ref name=AmericanClassicFashion>{{cite web|url=https://www.cnn.com/interactive/2019/01/style/american-style-classics/|title= American Classics How seven everyday clothing items became American style staples.|publisher=]|access-date=December 4, 2023}}</ref> New York, with ], is considered to be one of the "Big Four" global ]s, along with ], ], and ]. A study demonstrated that general proximity to ] has been synonymous with American fashion since its inception in the early 20th century.<ref name="GarmentDistrictNYCFashionSymbolUS">{{cite web |author=Caplin |first=John |date=September 1, 2021 |title=Made In New York: The Future Of New York City's Historic Garment District |url=https://www.forbes.com/sites/johncaplan/2021/09/01/made-in-new-york-the-future-of-new-york-citys-historic-garment-district/amp/ |access-date=December 5, 2023 |work=] |quote=Spanning just about 20 square blocks between ] and ] along ] (also known as "Fashion Avenue"), the vibrant and always-busy neighborhood has a long and rich history that has become synonymous with American fashion since its inception more than a century ago.}}</ref> | |||
| The headquarters of many ]s reside in ]. Labels cater to ]s, such as preteens. New York Fashion Week is one of the most influential fashion weeks in the world, and occurs twice a year;<ref name="USNYCFashionWeekGlobalIndustryTonesetter">{{cite news |author=Juarez |first=Diana |date=October 4, 2023 |title=The Economic Impact of New York Fashion Week |url=https://thefordhamram.com/93053/news/fashion-week/ |access-date=December 5, 2023 |newspaper=The Fordham Ram}}</ref> while the annual ] in Manhattan is commonly known as the fashion world's "biggest night".<ref name="MetGalaFashion'sBiggestNight1">{{cite web |author=Bauman |first=Ali |date=May 1, 2023 |title=Met Gala 2023: Fashion's biggest night honors Karl Lagerfeld |url=https://www.cbsnews.com/amp/newyork/news/met-gala-2023-red-carpet/ |access-date=April 30, 2024 |publisher=]}}</ref><ref name="MetGalaFashion'sBiggestNight2">{{cite web|url=https://www.glamour.com/story/met-gala-2024-how-to-watch|title=Met Gala 2024: How to Watch Fashion's Biggest Night|publisher=]|date=April 29, 2024|access-date=April 30, 2024}}</ref> | |||
| === Cinema === | |||
| {{Main|Cinema of the United States}} | |||
| ] in the ], often regarded as the symbol of the ]]] | |||
| The U.S. film industry has ]. ], a district in northern Los Angeles, the nation's second-most populous city, is also metonymous for the American filmmaking industry.<ref>{{cite book|title=Annual Report of the Controller of the City of Los Angeles, California|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1VbOAAAAMAAJ&q=Hollywood+merged+with+City+of+Los+Angeles+in+1910&pg=PA193|publisher=By] Los Angeles, CA (1914)|access-date=February 22, 2014|year = 1914}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|title=Report of the Auditor of the City of Los Angeles California of the Financial Affairs of the Corporation in Its Capacity as a City for the Fiscal Year|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=cPo2AQAAMAAJ&q=Hollywood+merged+with+City+of+Los+Angeles+in+1910&pg=PA173|publisher=By ] of Los Angeles, CA (1913)|access-date=February 22, 2014|year = 1913}}</ref><ref>{{cite press release|url=https://www.un.org/apps/news/story.asp?NewsID=30707|title=Nigeria surpasses Hollywood as world's second-largest film producer|publisher=United Nations|date=May 5, 2009|access-date=February 17, 2013}}</ref> The ] of the United States are the primary source of the ] and most ticket-selling movies in the world.<ref name="Kerrigan_Page_18">{{cite book |last1=Kerrigan |first1=Finola |title=Film Marketing |date=2010 |publisher=Butterworth-Heinemann |location=Oxford |isbn=978-0-7506-8683-9 |page=18 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ufMdvuuTQ7MC&pg=PA18 |access-date=February 4, 2022}}</ref><ref name="Davis">{{cite book |last1=Davis |first1=Glyn |last2=Dickinson |first2=Kay |last3=Patti |first3=Lisa |last4=Villarejo |first4=Amy |title=Film Studies: A Global Introduction |date=2015 |publisher=Routledge |location=Abingdon |isbn=978-1-317-62338-0 |page=299 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=dnXABgAAQBAJ&pg=PA299 |access-date=August 24, 2020}}</ref> Since the early 20th century, the U.S. film industry has largely been based in and around Hollywood, although in the 21st century an increasing number of films are not made there, and film companies have been subject to the forces of globalization.<ref>{{cite magazine|url=https://www.hollywoodreporter.com/news/john-landis-rails-studios-theyre-659222|title=John Landis Rails Against Studios: 'They're Not in the Movie Business Anymore'|magazine=The Hollywood Reporter|access-date=January 24, 2015}}</ref> The ], popularly known as the Oscars, have been held annually by the ] since 1929,<ref name="DrowneHuber2004">{{cite book |last1=Drowne |first1=Kathleen Morgan |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=CecCHiI95dYC&pg=PA236 |title=The 1920s |last2=Huber |first2=Patrick |publisher=Greenwood Publishing Group |year=2004 |isbn=978-0-313-32013-2 |page=236}}</ref> and the ]s have been held annually since January 1944.<ref name="Kroon2014">{{cite book |last=Kroon |first=Richard W. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=HjmNAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA338 |title=A/V A to Z: An Encyclopedic Dictionary of Media, Entertainment and Other Audiovisual Terms |publisher=McFarland |year=2014 |isbn=978-0-7864-5740-3 |page=338}}</ref> | |||
| The industry peaked in what is commonly referred to as the "]", from the early sound period until the early 1960s,<ref>{{cite news|last1=Matthews|first1=Charles|title=Book explores Hollywood 'Golden Age' of the 1960s-'70s|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/entertainment/books/book-explores-hollywood-golden-age-of-the-1960s-70s/2011/02/10/AGh5xJIH_story.html|newspaper=The Washington Post|access-date=August 6, 2015|date=June 3, 2011}}</ref> with screen actors such as ] and ] becoming iconic figures.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Banner|first1=Lois|title=Marilyn Monroe, the eternal shape shifter|url=https://www.latimes.com/opinion/la-xpm-2012-aug-05-la-oe-0805-banner-marilyn-monroe-icon-biography-20120805-story.html|newspaper=Los Angeles Times|access-date=August 6, 2015|date=August 5, 2012}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|last1=Rick|first1=Jewell|title=John Wayne, an American Icon|url=https://www.usc.edu/uscnews/stories/15465.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080822102812/https://www.usc.edu/uscnews/stories/15465.html|archive-date=August 22, 2008|publisher=University of Southern California|access-date=August 6, 2015|date=August 8, 2008}}</ref> In the 1970s, "]", or the "Hollywood Renaissance",<ref name="Greven2013">{{cite book|last=Greven|first=David|title=Psycho-Sexual: Male Desire in Hitchcock, De Palma, Scorsese, and Friedkin|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=QIyNBQAAQBAJ&pg=PT23|year=2013|publisher=University of Texas Press|isbn=978-0-292-74204-8|page=23}}</ref> was defined by grittier films influenced by French and Italian realist pictures of the ].<ref name="Morrison1998">{{cite book|last=Morrison|first=James|title=Passport to Hollywood: Hollywood Films, European Directors|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=dWRif68I3igC&pg=PA11|year=1998|publisher=SUNY Press|isbn=978-0-7914-3938-8|page=11}}</ref> The 21st century has been marked by the rise of American streaming platforms, which came to rival traditional cinema.<ref name="RE">{{cite news |last=Seitz|first=Matt Zoller|author-link=Matt Zoller Seitz|title=What's Next: Avengers, MCU, Game of Thrones, and the Content Endgame|url=https://www.rogerebert.com/mzs/avengers-mcu-and-the-content-endgame|access-date=July 21, 2021|work=]|publisher=Ebert Digital LLC|date=April 29, 2019}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |author=Avery |first=Hannah |date=January 18, 2023 |title=US streaming market growth continues, despite changes in the industry |url=https://www.kantar.com/inspiration/technology/us-streaming-market-growth-continues-despite-changes-in-the-industry |access-date=April 29, 2023 |website=]}}</ref> | |||
| === Cuisine === | |||
| {{Main|American cuisine}} | |||
| {{further|List of American regional and fusion cuisines}} | |||
| ] with ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ]]] | |||
| Early settlers were introduced by Native Americans to foods such as ], ]es, ], ], and ]. Of the most enduring and pervasive examples are variations of the native dish called ]. Early settlers and later immigrants combined these with foods they were familiar with, such as ],<ref name="Wheat">{{cite web|title=Wheat Info|url=https://www.wheatworld.org/wheat-info/fast-facts/|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091011012758/https://www.wheatworld.org/wheat-info/fast-facts/|archive-date=October 11, 2009|website=Wheatworld.org|access-date=January 15, 2015 }}</ref> beef, and milk, to create a distinctive American cuisine.<ref>{{cite web|title=Traditional Indigenous Recipes|url=https://aihd.ku.edu/recipes/index.html|publisher=American Indian Health and Diet Project|access-date=September 15, 2014}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|last=Akenuwa|first=Ambrose|title=Is the United States Still the Land of the Free and Home to the Brave?|url=https://books.apple.com/us/book/is-the-united-states-still-the-land-of-the/id1017814038|date=July 1, 2015|pages=92–94|publisher=Lulu Press|isbn=978-1-329-26112-9|access-date=November 20, 2020}}</ref> ], especially ], corn, ], and turkey as the main course are part of a shared national menu on ], when many Americans prepare or purchase traditional dishes to celebrate the occasion.<ref name="Mintz1996">{{cite book |author=Mintz |first=Sidney Wilfred |url=https://archive.org/details/tastingfoodtasti00mint_0 |title=Tasting Food, Tasting Freedom: Excursions Into Eating, Culture, and the Past |publisher=Beacon Press |year=1996 |isbn=978-0-8070-4629-6 |pages=– |access-date=October 25, 2015 |url-access=registration}}</ref> | |||
| Characteristic American dishes such as ], ], ]s, ], ], ], ]s, ]s, and ] derive from the recipes of various immigrant groups.<ref>{{cite book|first=Hasia|last=Diner|title=Hungering for America: Italian, Irish, and Jewish Foodways in the Age of Migration|publisher= Harvard University Press|place=Cmabridge|date=2001|page=1}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last=Poe |first=Tracy N. |date=February 1999 |title=The Origins of Soul Food in Black Urban Identity: Chicago, 1915–1947 |journal=American Studies International |volume=37 |issue=1 |page=5}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.bizjournals.com/louisville/news/2020/12/31/consumer-spending-data-kfc-is-the-most-popular.html|title=KFC is America's favorite fried chicken, data suggests|last=Cawthon|first=Haley|date=December 31, 2020|website=The Business Journals|access-date=May 8, 2021}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.pastemagazine.com/food/america/the-history-of-the-pizza/|title=How Pizza Became America's Favorite Food|last=Russell|first=Joan|date=May 23, 2016|website=Paste|access-date=May 8, 2021}}</ref> ] such as ] and ] preexisted the United States in areas later annexed from Mexico, and ] as well as ] are all widely consumed.<ref name="IFT">{{cite web|url=https://www.newswise.com/articles/what-when-and-where-americans-eat-in-2003|author=Klapthor, James N.|title=What, When, and Where Americans Eat in 2003|publisher=Newswise/Institute of Food Technologists|date=August 23, 2003|access-date=June 19, 2007}}</ref> American ]s have had a significant impact on society both domestically and internationally. In 1946, the ] was founded by ] and ]. This would become the United States' most prestigious culinary school, where many of the most talented American chefs would study prior to successful careers.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Our Story: CIA History {{!}} Culinary Institute of America |url=https://www.ciachef.edu/our-story/ |access-date=October 11, 2022 |website=ciachef.edu |language=en}}</ref><ref name="FTfbs">{{cite news|last=Averbuch|first=Bonnie|title=Attention Food Entrepreneurs: School's Back in Business|publisher=]|url=https://foodtank.com/news/2015/09/attention-food-entrepreneurs-its-time-to-head-back-to-school/|date=September 2015|access-date=June 19, 2017}}</ref> | |||
| The ] was projected at $899 billion in sales for 2020,<ref name=":p">{{Cite web|url=https://www.bizjournals.com/cincinnati/news/2020/03/20/cincinnati-restaurants-ask-feds-for-coronavirus.html|title=Cincinnati restaurants ask feds for coronavirus bailout|last=Brownfield|first=Andy|date=March 20, 2020|website=login.research.cincinnatilibrary.org|access-date=March 22, 2020}}</ref><ref name="Ramirez">{{Cite web|url=https://www.forbes.com/sites/elvaramirez/2020/03/19/the-restaurant-industry-needs-a-coronavirus-bailout-will-they-get-it/|title=The Restaurant Industry Needs A Coronavirus Bailout. Will They Get It?|last=Ramirez|first=Elva|website=]|language=en|access-date=March 22, 2020}}</ref> and employed more than 15 million people, representing 10% of the nation's workforce directly.<ref name=":p" /> It is the country's second-largest private employer and the third-largest employer overall.<ref name="Noguchi-2020">{{Cite web|url=https://www.npr.org/2020/03/22/819189939/closed-all-at-once-restaurant-industry-faces-collapse|title=Closed All At Once: Restaurant Industry Faces Collapse|last=Noguchi|first=Yuki|date=March 22, 2020|publisher=]|language=en|access-date=March 22, 2020}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.msnbc.com/stephanie-ruhle/watch/restaurant-industry-reeling-from-coronavirus-80967237571|title=Restaurant industry reeling from coronavirus|publisher=]|language=en|access-date=March 22, 2020}}</ref> The United States is home to over 220 ]-rated restaurants, 70 of which are in New York City alone.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Restaurants|url=https://guide.michelin.com/en/us/new-york-state/new-york/restaurants/1-star-michelin/2-stars-michelin/3-stars-michelin|access-date=August 30, 2023|website=Michelin Guide|language=en}}</ref> ] has been produced in what is now the United States since the 1500s, with the ] in 1628.<ref>United States Department of Agriculture " {{webarchive |url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080408235146/http://www.fas.usda.gov/agx/ISMG/Global%20Wine%20Report%20Final%20Aug2006.pdf |date=April 8, 2008 }}", pp. 7-9.</ref><ref name="Birchell Steel 2013 p.">{{cite book |last1=Birchell |first1=D.B. |last2=Steel |first2=G. |title=New Mexico Wine: An Enchanting History |publisher=American Palate |series=American Palate Series |year=2013 |isbn=978-1-60949-643-2 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=5f0kvgAACAAJ | language=it |access-date=November 15, 2019}}</ref><ref name="New Mexico. Office of Cultural Affairs 1995 p.">{{cite book | author=New Mexico. Office of Cultural Affairs | title=Enchanted Lifeways: The History, Museums, Arts & Festivals of New Mexico | publisher=New Mexico Magazine | year=1995 | isbn=978-0-937206-39-3 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=nvoRAQAAIAAJ | access-date=November 15, 2019}}</ref> In the modern U.S., wine production is undertaken in all fifty states, with ]. With more than {{convert|1100000|acre|km2}} under vine, the United States is the ] in the world, after ], ], and ].<ref name="Sotheby, p. 462">T. Stevenson, ''The Sotheby's Wine Encyclopedia'' Fourth Edition, p. 462, Dorling Kindersly, 2005, {{ISBN|0-7566-1324-8}}.</ref><ref name="Oxford, p. 719">J. Robinson, ed. ''The Oxford Companion to Wine'', Third Edition, p. 719; Oxford University Press, 2006, {{ISBN|0-19-860990-6}}.</ref> | |||
| The American ] industry developed alongside the nation's ].<ref>{{cite web |title=America's Love Of Drive-thrus |url=https://www.npr.org/2023/12/11/1198909271/1a-draft-12-11-2023 |website=NPR |access-date=May 4, 2024 |date=December 11, 2023}}</ref> American restaurants developed the ] format in the 1920s, which they began to replace with the ] format by the 1940s.<ref name="drivethru">{{cite web|title=When Was the First Drive-Thru Restaurant Created?|url=https://www.wisegeek.org/when-was-the-first-drive-thru-restaurant-created.htm|website=Wisegeek.org|access-date=January 15, 2015}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |last1=Sheldon |first1=Andrew |title=The History of the Drive-Thru in America |url=https://magazine.northeast.aaa.com/daily/life/cars-trucks/auto-history/history-of-the-drive-thru/ |website=Your AAA Network |date=July 23, 2020}}</ref> American ] chains, such as ], ], ] and ], have numerous outlets around the world.<ref name="Pavlova-2019">{{cite magazine |last=Pavlova |first=Rada |title=Globalization of American Fast-Food Chains: the Pinnacle of Effective Management and Adaptability – The Yale Globalist |url=https://globalist.yale.edu/in-the-magazine/globalization-of-american-fast-food-chains-the-pinnacle-of-effective-management-and-adaptability/ |access-date=May 4, 2024 |date=April 8, 2019 |magazine=The Yale Globalist}}</ref> | |||
| === Sports === | |||
| {{Main|Sports in the United States}} | {{Main|Sports in the United States}} | ||
| {{See also|Professional sports leagues in the United States|National Collegiate Athletic Association|United States at the Olympics}} | |||
| ] ] looking to ]]] | |||
| ] is the most popular sport in the United States; in this September 2022 ] game, the ] play the ] at ].]] | |||
| Since the late 19th century, ] has been regarded as the ]; ], ], and ] are the country's three other leading professional team sports. ] and ] attract large audiences. Football is now by several measures the most popular ].<ref>{{cite web |author=Krane, David K. |title=Professional Football Widens Its Lead Over Baseball as Nation's Favorite Sport |url=http://www.harrisinteractive.com/harris_poll/index.asp?PID=337 |publisher=Harris Interactive |date=2002-10-30|accessdate=2007-09-14}} Maccambridge, Michael (2004). ''America's Game: The Epic Story of How Pro Football Captured a Nation''. New York: Random House. ISBN 0375504540.</ref> ] and ] were once the most watched individual sports, but they have been eclipsed by ] and ], particularly ]. ] is played widely at the youth and amateur levels. ] and many outdoor sports are popular as well. | |||
| The most popular spectator sports in the U.S. are ], ], ], ], and ].<ref>{{cite web |date=September 25, 2007 |title=Sports |url=https://news.gallup.com/poll/4735/sports.aspx |access-date=April 16, 2023 |publisher=Gallup, Incorporated}}</ref> While most major U.S. sports such as baseball and American football have evolved out of European practices, basketball, ], ], and ] are American inventions, many of which have become popular worldwide.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Krasnoff |first=Lindsay Sarah |date=December 26, 2017 |title=How the NBA went global |newspaper=] |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/made-by-history/wp/2017/12/26/how-the-nba-went-global/ |url-status=live |url-access=subscription |access-date=September 14, 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171226153302/https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/made-by-history/wp/2017/12/26/how-the-nba-went-global/ |archive-date=December 26, 2017 |issn=0190-8286 |oclc=2269358}}</ref> ] and ] arose from Native American and Native Hawaiian activities that predate European contact.<ref name="liss">Liss, Howard. ''Lacrosse'' (Funk & Wagnalls, 1970), p. 13.</ref> The ] was approximately $69 billion in July 2013, roughly 50% larger than that of all of Europe, the Middle East, and Africa combined.<ref>{{cite web|date=June 18, 2008|title=Global sports market to hit $141 billion in 2012|url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-pwcstudy-idUSN1738075220080618|access-date=July 24, 2013|work=Reuters}}</ref> | |||
| While most major U.S. sports have evolved out of European practices, basketball, ], ], ], and ] are American inventions. ] and ] arose from Native American and Native Hawaiian activities that predate Western contact. Eight ] have ] The United States has won 2,301 medals at the ], more than any other country,<ref>{{cite web|title=All-Time Medal Standings, 1896–2004 | publisher = Information Please|url=http://www.infoplease.com/ipsa/A0115108.html | accessdate=2007-06-14}} {{cite web|title=Distribution of Medals—2008 Summer Games| publisher = Fact Monster|url=http://www.factmonster.com/sports/olympics/2008/distribution-medals-summer-games.html| accessdate=2008-09-02}}</ref> and 216 in the ], the second most.<ref>{{cite web|title=All-Time Medal Standings, 1924–2006|publisher=Information Please|url=http://www.infoplease.com/ipsa/A0115207.html|accessdate=2007-06-14}} Norway is first; the Soviet Union is third, and would be second if its medal count was combined with Russia's.</ref>{{clear}} | |||
| American football is by several measures the most popular spectator sport in the United States;<ref>{{cite web|author=Krane, David K.|title=Professional Football Widens Its Lead Over Baseball as Nation's Favorite Sport|url=https://www.harrisinteractive.com/Insights/HarrisVault8482.aspx?PID=337|publisher=Harris Interactive|date=October 30, 2002|access-date=September 14, 2007|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100709111448/https://www.harrisinteractive.com/Insights/HarrisVault8482.aspx?PID=337|archive-date=July 9, 2010}} MacCambridge, Michael (2004). ''America's Game: The Epic Story of How Pro Football Captured a Nation''. New York: Random House. {{ISBN|978-0-375-50454-9}}.</ref> the ] has the highest average attendance of any sports league in the world, and the ] is watched by tens of millions globally.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.espn.com/nfl/story/_/id/27321898/how-nfl-took-america-100-years|title=How the NFL took over America in 100 years|last=Guliza|first=Anthony|date=August 14, 2019|publisher=]|access-date=May 8, 2021}}</ref> However, baseball has been regarded as the U.S. "]" since the late 19th century. After American football, the next four most popular professional team sports are basketball, baseball, soccer, and ice hockey. Their premier leagues are, respectively, the ], ], ], and the ]. The most-watched ]s in the U.S. are ] and ], particularly ] and ].<ref>{{cite web|date=January 16, 2014|title=As American as Mom, Apple Pie and Football? Football continues to trump baseball as America's Favorite Sport|url=https://www.harrisinteractive.com/vault/Harris%20Poll%205%20-%202014%20Fave%20Sport_1.16.14.pdf|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140309053431/https://www.harrisinteractive.com/vault/Harris%20Poll%205%20-%202014%20Fave%20Sport_1.16.14.pdf|archive-date=March 9, 2014|access-date=July 2, 2014|website=Harris Interactive}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|author1=Cowen, Tyler|author2=Grier, Kevin|date=February 9, 2012|title=What Would the End of Football Look Like?|url=https://www.grantland.com/story/_/id/7559458/cte-concussion-crisis-economic-look-end-football|access-date=February 12, 2012|publisher=Grantland/ESPN}}</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| {{portal|United States|Flag of the United States.svg}} | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| <!--Please place links to all topics directly related to the United States of America in ].--> | |||
| On the ], earnings for the member institutions exceed $1 billion annually,<ref name="si">{{Cite news|url=https://www.si.com/college-basketball/2018/03/07/ncaa-1-billion-revenue|title=Sports Illustrated: NCAA Reports $1.1 Billion in Revenues|newspaper=Sports Illustrated |date=March 7, 2018 }}</ref> and ] and ] attract large audiences, as the ] and the ] are some of the most watched national sporting events.<ref>{{cite web|date=March 19, 2013|title=Passion for College Football Remains Robust|url=https://www.footballfoundation.org/tabid/567/Article/53380/Passion-for-College-Football-Remains-Robust.aspx|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140407075223/https://www.footballfoundation.org/tabid/567/Article/53380/Passion-for-College-Football-Remains-Robust.aspx|archive-date=April 7, 2014|access-date=April 1, 2014|publisher=National Football Foundation}}</ref> In the U.S., the intercollegiate sports level serves as a feeder system for professional sports. This differs greatly from practices in nearly all other countries, where publicly and privately funded sports organizations serve this function.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Rosandich|first= Thomas|title=Collegiate Sports Programs: A Comparative Analysis|page= 471|journal= Education|year=2002|volume=122|issue=3|publisher=Project Innovation Austin LLC.}}</ref> | |||
| ==References== | |||
| <!--Please DO NOT use a scroll template or form/table for the reflink, please read warning on the scroll template page ].--> | |||
| {{reflist|colwidth=30em}} | |||
| Eight ] have taken place in the United States. The ] in ], were the first-ever Olympic Games held outside of Europe.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Schaus|first1=Gerald P.|last2=Wenn|first2=Stephen R.|title=Onward to the Olympics: Historical Perspectives on the Olympic Games|date=February 9, 2007|publisher=]|page=224|isbn=978-0-88920-505-5}}</ref> The Olympic Games will be held in the U.S. for a ninth time when Los Angeles hosts the ]. ] have won a total of 2,968 medals (1,179 gold) at the Olympic Games, the most of any country.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://greatestsportingnation.com/|title=Greatest Sporting Nation|website=greatestsportingnation.com}}</ref><ref>{{cite news| url = https://www.washingtonpost.com/graphics/sports/olympics/the-1000-medals-of-the-united-states/| title = 1,000 times gold – The thousand medals of Team USA – Washington Post| newspaper = ]}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=The 10 most fascinating facts about the all-time Winter Olympics medal standings|first=Chris|last=Chase|date=February 7, 2014|work=USA Today|url=https://ftw.usatoday.com/2014/02/winter-olympics-medal-count-sochi-all-time-facts/|access-date=February 28, 2014}} {{cite news|title=With Sochi Olympics approaching, a history of Winter Olympic medals|date=February 6, 2014|first=Dan|last=Loumena|work=Los Angeles Times|url=https://www.latimes.com/la-sp-a-history-of-the-winter-olympic-medals-20140206-story.html|access-date=February 28, 2014}}</ref> | |||
| ==External links== | |||
| {{sisterlinks|United States}} | |||
| <!--Please: | |||
| 1)Follow the ] guideline where possible and consider discussing on the talk page; | |||
| 2)Do not turn these bullets into headers! They expand the TOC too much--> | |||
| {{Misplaced Pages-Books}} | |||
| ;Government | |||
| * Gateway to government sites | |||
| * Official site of the United States House of Representatives | |||
| * Official site of the United States Senate | |||
| * Official site of the President of the United States | |||
| * Official site of the Supreme Court of the United States | |||
| ;Overviews and Data | |||
| *{{CIA World Factbook link|us|United States}} | |||
| * Portal to U.S. Information Agency resources | |||
| * Official site of the U.S. ] | |||
| * Statistics from the Population Reference Bureau | |||
| * Collected informational links for each state | |||
| *] from ] | |||
| * ''Encyclopaedia Britannica'' entry | |||
| *{{dmoz|Regional/North_America/United_States}} | |||
| * Wide-ranging data from the ] | |||
| * Official government site | |||
| * Population, employment, income, and farm data from the U.S. ] | |||
| * Economic, environmental, and energy data for each state from the U.S. ] | |||
| ;History | |||
| * Collected by the National Center for Public Policy Research | |||
| * Analysis by the Ontario Consultants on Religious Tolerance | |||
| * Collected links to historical data | |||
| ;Maps | |||
| * Official maps from the U.S. Department of the Interior | |||
| * Satellite view at ] (not affiliated with Misplaced Pages/]) | |||
| *{{wikiatlas|the United States}} | |||
| In international professional competition, the ] has qualified for ], while the ] has ] the ] and ] four times each.<ref>{{cite web|last=Carlisle|first=Jeff|date=April 6, 2020|title=MLS Year One, 25 seasons ago: The Wild West of training, travel, hockey shootouts and American soccer|url=https://www.espn.com/soccer/major-league-soccer/story/4082408/mls-year-one25-seasons-ago-the-wild-west-of-trainingtravelhockey-shootouts-and-american-soccer|access-date=May 5, 2021|publisher=]}}</ref> The United States hosted the ] and will co-host, along with Canada and Mexico, the ].<ref>{{cite news |last=Wamsley |first=Laurel |date=June 16, 2022 |title=The U.S. cities hosting the 2026 World Cup are announced |url=https://www.npr.org/2022/06/16/1105562734/us-cities-hosting-2026-world-cup-announcement |publisher=] |access-date=April 16, 2023}}</ref> The ] was also hosted by the United States. ] was watched by 90,185, setting the world record for most-attended women's sporting event at the time.<ref>{{cite news |last=Gerson |first=Aria |date=July 10, 2020 |title=Impact of 1999 Women's World Cup went far beyond Brandi Chastain's iconic goal |url=https://www.usatoday.com/story/sports/soccer/2020/07/10/1999-womens-world-cup-uswnt-iconic-moments-brandi-chastain/5405459002/ |work=USA Today |access-date=February 14, 2024}}</ref> | |||
| {{-}} | |||
| == See also == | |||
| {{Navboxes | |||
| * ] | |||
| |title=Articles Related to the United States of America | |||
| * ] | |||
| |list1= | |||
| {{United States Template Group}} | |||
| == Notes == | |||
| {{Anglophone states}} | |||
| {{notelist | |||
| {{English official language clickable map}} | |||
| | colwidth = | |||
| {{United States topics}} | |||
| | notes = | |||
| {{National personifications}} | |||
| {{efn | |||
| | name = pop | |||
| | Excludes ] and the other ] because they are counted separately in ] statistics | |||
| }} | |||
| {{efn | |||
| | name = time | |||
| | See ] for details about laws governing time zones in the United States. | |||
| }} | |||
| {{efn | |||
| | name = drive | |||
| | The ] use left-hand traffic. | |||
| }} | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| == References == | |||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| === Sources === | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor1-last=Baym |editor1-first=Nina |editor2-last=Levine |editor2-first=Robert S. |date=2013 |title=The Norton Anthology of American Literature |publisher=W.W. Norton |location=New York, New York |isbn=978-0-393-91885-4 |edition=Shorter eighth}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Bianchine |first1=Peter J. |last2=Russo |first2=Thomas A. |year=1992 |title=The Role of Epidemic Infectious Diseases in the Discovery of America |volume=13 |issue=5 |pages=225–232 |ref=Bianchine |doi=10.2500/108854192778817040 |pmid=1483570 |journal=Allergy and Asthma Proceedings}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Blackhawk |first1=Ned |author1-link=Ned Blackhawk |chapter='The Centrality of Dispossession': Native American Genocide and Settler Colonialism |year=2023 |pages=23–45 |doi=10.1017/9781108765480.002 |editor1-last=Blackhawk |editor1-first=Ned |editor2-last=Kiernan |editor2-first=Ben |editor2-link=Ben Kiernan |editor3-last=Madley |editor3-first=Benjamin |editor4-last=Taylor |editor4-first=Rebe |editor4-link=Rebe Taylor |title=The Cambridge World History of Genocide |volume=2: Genocide in the Indigenous, Early Modern and Imperial Worlds, from c.1535 to World War One |publisher=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Blakeley |first=Ruth |date=2009 |title=State Terrorism and Neoliberalism: The North in the South |url=https://www.routledge.com/books/details/9780415462402/ |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-0-415-68617-4 |ref=Blakeley}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Boyer |first1=Paul S. |last2=Clark Jr. |first2=Clifford E. |last3=Kett |first3=Joseph F. |last4=Salisbury |first4=Neal |last5=Sitkoff |first5=Harvard |last6=Woloch |first6=Nancy |title=The Enduring Vision: A History of the American People |ref=Boyer |year=2007 |volume=1 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9KT3lI76-0cC |publisher=Cengage Learning |page=588 |isbn=978-0-618-80161-9}} | |||
| * {{cite book |first=Colin G. |last=Calloway |title=New Worlds for All: Indians, Europeans, and the Remaking of Early America |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=edYbAZ7ECEoC |publisher=] |ref=Calloway 1998 |page=229 |isbn=978-0-8018-5959-5 |year=1998}} | |||
| * {{cite magazine |last=Cohen |first=Eliot A. |ref=Cohen |location=Washington, D.C. |url=https://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/59919/eliot-a-cohen/history-and-the-hyperpower |title=History and the Hyperpower |website=Foreign Affairs |date=July–August 2004 |access-date=July 14, 2006}} | |||
| * {{cite book |ref={{sfnref|OpenStax2014}} |first1=P. Scott |last1=Corbett |first2=Volker |last2=Janssen |first3=John M. |last3=Lund |first4=Todd |last4=Pfannestiel |first5=Sylvie |last5=Waskiewicz |first6=Paul |last6=Vickery |publisher=OpenStax at Rice University |date=2014 |title=U.S. History |location=Houston, Texas |url=https://openstax.org/books/us-history/pages/1-introduction}} | |||
| * {{cite news |url=https://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/americas/country_profiles/1217752.stm |title=Country Profile: United States of America |ref=BBC18may |work=BBC News |location=London |date=April 22, 2008 |access-date=May 18, 2008}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Davis |first=Kenneth C. |title=Don't know much about the Civil War |ref=Davis96 |publisher=William Marrow and Company |location=New York |year=1996 |url=https://archive.org/details/dontknowmuchabou00davi_1/page/518 |isbn=978-0-688-11814-3 |page=}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Daynes |first1=Byron W. |last2=Sussman |first2=Glen |title=White House Politics and the Environment: Franklin D. Roosevelt to George W. Bush |ref=Daynes |publisher=] |year=2010 |page=320 |url=https://archive.org/details/whitehousepoliti0000dayn |url-access=registration |isbn=978-1-60344-254-1 |oclc=670419432 |quote=Presidential environmental policies, 1933–2009}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Foner |first1=Eric |title=Give Me Liberty: An American History |date=2020 |publisher=W.W. Norton |location=New York, New York; London, England |isbn=978-0-393-44123-9 |edition=6th |volume=1 |url=https://archive.org/details/give-me-liberty-an-american-history-eric-foner-z-lib.org_20220819}} Ebook. | |||
| * {{cite book |first1=Jon M. |last1=Erlandson |first2=Torben C. |last2=Rick |first3=Rene L. |last3=Vellanoweth |title=A Canyon Through Time: Archaeology, History, and Ecology of the Tecolote Canyon Area, Santa Barbara County |location=California |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=GeTv2lmb79UC&pg=PA19 |year=2008 |publisher=University of Utah Press |isbn=978-0-87480-879-7}} | |||
| * {{cite book |first1=Sylvan G. |last1=Feldstein |first2=Frank J. |last2=Fabozzi |title=The Handbook of Municipal Bonds |ref=Feldstein |publisher=] |year=2011 |page=1376 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Juc4fb1Fx1cC |isbn=978-1-118-04494-0}} | |||
| * {{cite book |first=Tim |last=Flannery |title=The Eternal Frontier: An Ecological History of North America and Its Peoples |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mkkyBgAAQBAJ |date=2015 |publisher=Open Road + Grove/Atlantic |isbn=978-0-8021-9109-0}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Fraser |first1=Steve |first2=Gary |last2=Gerstle |author-link2=Gary Gerstle |ref=Fraser |title=The Rise and Fall of the New Deal Order: 1930–1980 |series=American History: Political science |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=yd4GqkP5XYgC&pg=PA229 |year=1989 |publisher=Princeton University Press |isbn=978-0-691-00607-9 |page=311}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Gaddis |first=John Lewis |title=The United States and the Origins of the Cold War, 1941–1947 |year=1972 |publisher=Columbia University Press |isbn=978-0-231-12239-9}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Gordon |first=John Steele |author-link=John Steele Gordon |ref=Gordon |title=An Empire of Wealth: The Epic History of American Economic Power |year=2004 |publisher=HarperCollins |url=https://archive.org/details/empireofwealthth00gord |url-access=registration |isbn=978-0-06-009362-4}} | |||
| * {{cite book |first1=Michael Robert |last1=Haines |first2=Michael R. |last2=Haines |first3=Richard H. |last3=Steckel |title=A Population History of North America |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=BPdgiysIVcgC&pg=PA12 |date=2000 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |isbn=978-0-521-49666-7}} | |||
| * {{cite news |title=Looking back 20 years: Who deserves credit for ending the Cold War? |first=Nick |last=Hayes |ref=Hayes |url=https://www.minnpost.com/politics-policy/2009/11/looking-back-20-years-who-deserves-credit-ending-cold-war |newspaper=MinnPost |date=November 6, 2009 |access-date=March 11, 2013}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Hoopes |first1=Townsend |last2=Brinkley |first2=Douglas |title=FDR and the Creation of the U.N |url=https://archive.org/details/fdrcreationofun00hoop |url-access=registration |year=1997 |publisher=Yale University Press |isbn=978-0-300-08553-2}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Howe |first=Daniel Walker |title=What Hath God Wrought: The Transformation of America, 1815–1848 |date=2008 |location=New York |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0195078947 |url=https://archive.org/details/whathathgodwroug00howe |url-access=registration}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Johnson |first=Paul |title=A History of the American People |year=1997 |publisher=HarperCollins |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=RXSVQjz1_tMC |isbn=978-0-06-195213-5}} | |||
| * {{cite book |first=Paul |last=Joseph |title=The Sage Encyclopedia of War: Social Science Perspectives |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=idw0DQAAQBAJ&pg=PA590 |date=2016 |publisher=Sage Publications |isbn=978-1-4833-5988-5}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor-last=Lauter |editor-first=Paul |year=1994a |volume=1 |edition=2nd |url=https://archive.org/details/heathanthologyof00v1unse_e3d7 |title=The Heath Anthology of American Literature |publisher=D.C. Heath and Company |location=Lexington, Massachusetts |isbn=0-669-32972-X}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor-last=Lauter |editor-first=Paul |year=1994b |volume=2 |edition=2nd |url=https://archive.org/details/heathanthologyof02laut/page/n2/mode/1up |title=The Heath Anthology of American Literature |publisher=D.C. Heath and Company |location=Lexington, Massachusetts |isbn=0-669-32973-8}} | |||
| * {{cite book |first=Craig |last=Lockard |title=Societies, Networks, and Transitions, Volume B: From 600 to 1750 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=k91sCgAAQBAJ&pg=PA315 |year=2010 |publisher=Cengage Learning |isbn=978-1-111-79083-7}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Lien |first=Arnold Johnson |title=Studies in History, Economics, and Public Law |volume=54 |ref=Lien |publisher=Columbia University |location=New York |year=1913 |page=604 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=UYpVAAAAYAAJ}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Meyer |first1=M. |last2=Snow |first2=D. |last3=Snow |first3=D. |last4=Cohen |first4=C. |last5=Meyer |first5=M. |last6=Thornton |first6=R. |last7=Grinde |first7=D. |last8=Dilworth |first8=L. |year=2001 |chapter=Indian History and Culture |chapter-url=https://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/acref/9780195082098.001.0001/acref-9780195082098-e-0758 |editor-last1=Boyer |editor-first1=Paul S. |title=The Oxford Companion to United States History |publisher=] |editor-link1=Paul Boyer (historian) |doi=10.1093/acref/9780195082098.001.0001 |isbn=978-0-19-508209-8}} | |||
| * {{cite book |first=Mary |last=Mostert |title=The Threat of Anarchy Leads to the Constitution of the United States |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=jntSQ-yn66AC&pg=PA18 |year=2005 |publisher=CTR Publishing, Inc. |isbn=978-0-9753851-4-2}} | |||
| * {{cite book |first=Peter S. |last=Onuf |title=The Origins of the Federal Republic: Jurisdictional Controversies in the United States, 1775–1787 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=WcUgLPqmfuYC |year=2010 |publisher=University of Pennsylvania Press |isbn=978-0-8122-0038-6}} | |||
| * {{cite book |first1=Theda |last1=Perdue |first2=Michael D. |last2=Green |title=The Columbia Guide to American Indians of the Southeast |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=-RBJCyp2bFIC&pg=PA40 |date=2005 |publisher=Columbia University Press |isbn=978-0-231-50602-1}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Quirk |first=Joel |title=The Anti-Slavery Project: From the Slave Trade to Human Trafficking |ref=Quirk |year=2011 |publisher=University of Pennsylvania Press |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qqxK4KlqKYMC |isbn=978-0-8122-4333-8 |page=344}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Remini |first=Robert V. |title=The House: The History of the House of Representatives |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=CAM6J6IoQFQC |year=2007 |publisher=HarperCollins |isbn=978-0-06-134111-3}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Ripper |first=Jason |title=American Stories: To 1877 |year=2008 |ref=Ripper2008 |publisher=M.E. Sharpe |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=vX-fYvoAeHwC |page=299 |isbn=978-0-7656-2903-6}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Rodriguez |first=Junius |title=Encyclopedia of Emancipation and Abolition in the Transatlantic World |publisher=] (]) |year=2015 |isbn=978-1-317-47180-6 |edition=Illustrated |pages=}} | |||
| * {{cite book |first=William |last=Safire |title=No Uncertain Terms: More Writing from the Popular "On Language" Column in The New York Times Magazine |url=https://archive.org/details/nouncertainterms00safi |url-access=registration |page= |year=2003 |publisher=Simon and Schuster |isbn=978-0-7432-4955-3}} | |||
| * {{cite book |first=Candace |last=Savage |title=Prairie: A Natural History |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=X1u9BwAAQBAJ&pg=PA55 |date=2011 |publisher=Greystone Books |isbn=978-1-55365-899-3}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Schultz |first=David Andrew |title=Encyclopedia of the United States Constitution |ref=Schultz |year=2009 |publisher=Infobase Publishing |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=f7m713xwK58C |page=904 |isbn=978-1-4381-2677-7}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Shi |first=David Emory |title=America: A Narrative History |date=2016 |location=New York |publisher=W.W. Norton |volume=1 |edition=Brief 10th |isbn=978-0393265941 |url=https://archive.org/details/americanarrative0001shid}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Smithers |first1=Gregory D. |author-link=Gregory D. Smithers |chapter=Rethinking Genocide in North America |year=2012 |pages=322–342 |doi=10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199232116.013.0017 |editor-last1=Bloxham |editor-first1=Donald |editor-link1=Donald Bloxham |editor2-last=Moses |editor2-first=A. Dirk |editor-link2=A. Dirk Moses |title=The Oxford Handbook of Genocide Studies |publisher=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Soss |first=Joe |editor-last=Hacker |editor-first=Jacob S. |editor2-last=Mettler |editor2-first=Suzanne |ref=Soss |title=Remaking America: Democracy and Public Policy in an Age of Inequality |year=2010 |publisher=Russell Sage Foundation |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=JttyjBoyb3AC |isbn=978-1-61044-694-5}} | |||
| * {{cite book |ref=Stannard |last=Stannard |first=David E. |author-link=David Stannard |title=American Holocaust: The Conquest of the New World |year=1993 |publisher=Oxford University Press |location=New York |url=https://archive.org/details/americanholocaus00stan |isbn=978-0-19-508557-0}} | |||
| * {{cite book |title=The New York Times Guide to Essential Knowledge: A Desk Reference for the Curious Mind |edition=2nd |url=https://archive.org/details/newyorktimesguid00 |year=2007 |publisher=St. Martin's Press |isbn=978-0-312-37659-8}} | |||
| * {{cite book |first=Russell |last=Thornton |title=Studying Native America: Problems and Prospects |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=_EA-UwvN_HUC&pg=PA34 |year=1998 |publisher=Univ of Wisconsin Press |isbn=978-0-299-16064-7}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Walker Howe |first=Daniel |title=] |publisher=] |year=2007 |isbn=978-0-19-972657-8 |author-link=Daniel Walker Howe}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Walton |first1=Gary M. |last2=Rockoff |first2=Hugh |title=History of the American Economy |year=2009 |ref=Walton |publisher=Cengage Learning |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=lyhI1q_E4G0C |isbn=978-0-324-78662-0}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Waters |first1=M. R. |last2=Stafford |first2=T. W. |title=Redefining the Age of Clovis: Implications for the Peopling of the Americas |journal=Science |volume=315 |issue=5815 |year=2007 |pages=1122–1126 |issn=0036-8075 |doi=10.1126/science.1137166 |pmid=17322060 |bibcode=2007Sci...315.1122W |s2cid=23205379}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Winchester |first=Simon |title=The men who United the States |url=https://archive.org/details/isbn_9780062079602 |url-access=registration |year=2013 |publisher=Harper Collins |isbn=978-0-06-207960-2 |pages=, 216, 251, 253}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last=Wright |first=Gavin |year=2022 |title=Slavery and the Rise of the Nineteenth-Century American Economy |url=https://www.aeaweb.org/articles?id=10.1257/jep.36.2.123 |journal=] |volume=36 |issue=2 |pages=123–148 |doi=10.1257/jep.36.2.123 |s2cid=248716718}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Zinn |first=Howard |author-link=Howard Zinn |title=A People's History of the United States |ref=Zinn |year=2005 |publisher=] Modern Classics |isbn=978-0-06-083865-2 |title-link=A People's History of the United States}} | |||
| *{{Cite book |last=McPherson |first=James M. |author-link=James M. McPherson |title=Battle Cry of Freedom: The Civil War Era |title-link=Battle Cry of Freedom: The Civil War Era |publisher=] |year=1988 |isbn=978-0-19-503863-7 |location=Oxford, England; New York, New York}} | |||
| *{{Free-content attribution | |||
| | title = World Food and Agriculture – Statistical Yearbook 2023 | |||
| | author = FAO | |||
| | publisher = FAO | |||
| | documentURL = https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en?details=cc8166en | |||
| | license statement URL = https://commons.wikimedia.org/whttps://commons.wikimedia.org/File:World_Food_and_Agriculture_-_Statistical_Yearbook_2023.pdf | |||
| | license = CC BY-SA IGO 3.0 | |||
| }}{{refend}} | |||
| == External links == | |||
| {{Library resources box}} | |||
| <!-- Please: | |||
| 1) Follow the ] guideline and discuss on the talk page. The MediaWiki software that powers Misplaced Pages has parameters that limit the complexity of a page, thus limiting the number of templates that can be included. | |||
| 2) Do not turn these bullets into headers! They expand the TOC too much. --> | |||
| * from ] | |||
| === Government === | |||
| * – gateway to government sites | |||
| * – official website of the United States House of Representatives | |||
| * – official website of the United States Senate | |||
| * – official website of the president of the United States | |||
| * – official website of the Supreme Court of the United States | |||
| === History === | |||
| * – website from the ] | |||
| * . Religious Tolerance. Analysis by the ]. | |||
| * – links to U.S. historical data | |||
| === Maps === | |||
| * – official maps from the ] | |||
| * {{wikiatlas|the United States}} | |||
| * {{osmrelation-inline|148838}} | |||
| * – a variety of mapped information relating to health, education, income, safety and demographics in the United States | |||
| {{Anchor|Related information}} <!-- Target for Navbox link at See also section --> | |||
| {{United States topics}} | |||
| {{United States political divisions}} | |||
| {{North America topic}} | |||
| {{Subject bar|United States|North America|Countries|auto=yes|voy=United States}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| {{Coord|40|-100|dim:10000000_region:region:US_type:country|name=United States of America|display=title}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Link FA|ceb}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Link FA|eu}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Link FA|fa}} | |||
| {{Link FA|fo}} | |||
| {{Link FA|lv}} | |||
| {{Link FA|ml}} | |||
| {{Link FA|sl}} | |||
| {{Link FA|sq}} | |||
| {{Link FA|vi}} | |||
| {{Link FA|zh}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Revision as of 22:28, 24 December 2024
Country in North America "America" redirects here. For the landmass comprising North and South America, see Americas. For other uses, see America (disambiguation). Several terms redirect here. For other uses, see US (disambiguation), USA (disambiguation), United States (disambiguation), and The United States of America (disambiguation).
| United States of America | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Flag
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |
Motto: "In God We Trust"
Other traditional mottos:
| |
| Anthem: "The Star-Spangled Banner" | |
 Show globe (states and D.C. only) Show globe (states and D.C. only)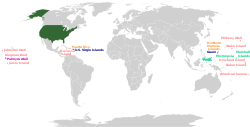 Show the U.S. and its territories Show the U.S. and its territories Show territories with their exclusive economic zone Show territories with their exclusive economic zone | |
| Capital | Washington, D.C. 38°53′N 77°1′W / 38.883°N 77.017°W / 38.883; -77.017 |
| Largest city | New York City 40°43′N 74°0′W / 40.717°N 74.000°W / 40.717; -74.000 |
| Official languages | None at the federal level |
| National language | English |
| Ethnic groups (2020) | By race:
|
| Religion (2023) |
|
| Demonym(s) | American |
| Government | Federal presidential republic |
| • President | Joe Biden |
| • Vice President | Kamala Harris |
| • House Speaker | Mike Johnson |
| • Chief Justice | John Roberts |
| Legislature | Congress |
| • Upper house | Senate |
| • Lower house | House of Representatives |
| Independence from Great Britain | |
| • Declaration | July 4, 1776 (1776-07-04) |
| • Confederation | March 1, 1781 (1781-03-01) |
| • Recognized | September 3, 1783 (1783-09-03) |
| • Constitution | June 21, 1788 (1788-06-21) |
| Area | |
| • Total area | 3,796,742 sq mi (9,833,520 km) (3rd) |
| • Water (%) | 7.0 (2010) |
| • Land area | 3,531,905 sq mi (9,147,590 km) (3rd) |
| Population | |
| • 2024 estimate | |
| • 2020 census | |
| • Density | 87/sq mi (33.6/km) (185th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
| • Total | |
| • Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
| • Total | |
| • Per capita | |
| Gini (2023) | medium inequality |
| HDI (2022) | very high (20th) |
| Currency | U.S. dollar ($) (USD) |
| Time zone | UTC−4 to −12, +10, +11 |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 to −10 |
| Date format | mm/dd/yyyy |
| Drives on | Right |
| Calling code | +1 |
| ISO 3166 code | US |
| Internet TLD | .us |
The United States of America (USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal union of 50 states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous states border Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, with the states of Alaska to the northwest and the archipelagic Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The United States also asserts sovereignty over five major island territories and various uninhabited islands. The country has the world's third-largest land area, largest exclusive economic zone, and third-largest population, exceeding 340 million. Its three largest metropolitan areas are New York, Los Angeles, and Chicago, and its three most populous states are California, Texas, and Florida.
Paleo-Indians migrated across the Bering land bridge more than 12,000 years ago, and formed various civilizations and societies. British colonization led to the first settlement of the Thirteen Colonies in Virginia in 1607, with the beginning of the forced migration of enslaved Africans following soon after. Clashes with the British Crown over taxation and political representation sparked the American Revolution, with the Second Continental Congress formally declaring independence on July 4, 1776. Following its victory in the 1775–1783 Revolutionary War, the country continued to expand westward across North America, resulting in the dispossession of native inhabitants. As more states were admitted, a North–South division over slavery led to the secession of the Confederate States of America, which fought states remaining in the Union in the 1861–1865 American Civil War. With the victory and preservation of the United States, slavery was abolished nationally. By 1900, the country had established itself as a great power, a status solidified after its involvement in World War I. After Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor in December 1941, the U.S. entered World War II. Its aftermath left the U.S. and the Soviet Union as the world's two superpowers and led to the Cold War, during which both countries struggled for ideological dominance and international influence. Following the Soviet Union's collapse and the end of the Cold War in 1991, the U.S. emerged as the world's sole superpower, wielding significant geopolitical influence globally.
The U.S. national government is a presidential constitutional federal republic and liberal democracy with three separate branches: legislative, executive, and judicial. It has a bicameral national legislature composed of the House of Representatives, a lower house based on population, and the Senate, an upper house based on equal representation for each state. Federalism provides substantial autonomy to the 50 states, while American values are based on a democratic political tradition that draws its inspiration from the European Enlightenment movement.
One of the world's most developed countries, the United States has had the largest nominal GDP since about 1890 and accounted for over 15% of the global economy in 2023. It possesses by far the largest amount of wealth of any country and has the highest disposable household income per capita among OECD countries. The U.S. ranks among the world's highest in economic competitiveness, productivity, innovation, human rights, and higher education. Its hard power and cultural influence have a global reach. The U.S. is a founding member of the World Bank, the Organization of American States, NATO, and the United Nations, as well as a permanent member of the UN Security Council.
Etymology
Further information: Names of the United States, Demonyms for the United States, and United ColoniesThe first documented use of the phrase "United States of America" is a letter from January 2, 1776. Stephen Moylan, a Continental Army aide to General George Washington, wrote to Joseph Reed, Washington's aide-de-camp, seeking to go "with full and ample powers from the United States of America to Spain" to seek assistance in the Revolutionary War effort. The first known public usage is an anonymous essay published in the Williamsburg newspaper, The Virginia Gazette, on April 6, 1776. By June 1776, the "United States of America" appeared in the Articles of Confederation and the Declaration of Independence. The Second Continental Congress adopted the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776.
The term "United States" and the initialism "U.S.", used as nouns or as adjectives in English, are common short names for the country. The initialism "USA", a noun, is also common. "United States" and "U.S." are the established terms throughout the U.S. federal government, with prescribed rules. In English, the term "America" rarely refers to topics unrelated to the United States, despite the usage of "the Americas" as the totality of North and South America. "The States" is an established colloquial shortening of the name, used particularly from abroad; "stateside" is the corresponding adjective or adverb.
The name "America" is the Latinized form of the first name of Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci. He first proposed that the West Indies discovered by Christopher Columbus in 1492 were part of a previously unknown landmass and not among the Indies at the eastern limit of Asia.
History
Main article: History of the United States For a topical guide, see Outline of the history of the United States.Indigenous peoples
Main article: History of Native Americans in the United States Further information: Native Americans in the United States and Pre-Columbian era
The first inhabitants of North America migrated from Siberia across the Bering land bridge about 12,000 years ago; the Clovis culture, which appeared around 11,000 BC, is believed to be the first widespread culture in the Americas. Over time, indigenous North American cultures grew increasingly sophisticated, and some, such as the Mississippian culture, developed agriculture, architecture, and complex societies. In the post-archaic period, the Mississippian cultures were located in the midwestern, eastern, and southern regions, and the Algonquian in the Great Lakes region and along the Eastern Seaboard, while the Hohokam culture and Ancestral Puebloans inhabited the southwest. Native population estimates of what is now the United States before the arrival of European immigrants range from around 500,000 to nearly 10 million.
European settlement and conflict (1607–1765)
Main articles: Colonial history of the United States and Colonial American military history See also: European colonization of the Americas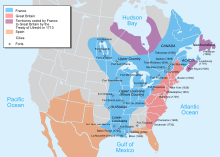
Christopher Columbus began exploring the Caribbean for Spain in 1492, leading to Spanish-speaking settlements and missions from Puerto Rico and Florida to New Mexico and California. France established its own settlements along the Great Lakes, Mississippi River and Gulf of Mexico. British colonization of the East Coast began with the Virginia Colony (1607) and Plymouth Colony (1620). The Mayflower Compact and the Fundamental Orders of Connecticut established precedents for representative self-governance and constitutionalism that would develop throughout the American colonies. While European settlers in what is now the United States experienced conflicts with Native Americans, they also engaged in trade, exchanging European tools for food and animal pelts. Relations ranged from close cooperation to warfare and massacres. The colonial authorities often pursued policies that forced Native Americans to adopt European lifestyles, including conversion to Christianity. Along the eastern seaboard, settlers trafficked African slaves through the Atlantic slave trade.
The original Thirteen Colonies that would later found the United States were administered as possessions of Great Britain, and had local governments with elections open to most white male property owners. The colonial population grew rapidly, eclipsing Native American populations; by the 1770s, the natural increase of the population was such that only a small minority of Americans had been born overseas. The colonies' distance from Britain allowed for the development of self-governance, and the First Great Awakening, a series of Christian revivals, fueled colonial interest in religious liberty.
For a century, the American colonists had been providing their own troops and materiel in conflicts with indigenous peoples allied with Britain's colonial rivals, especially France, and the Americans had begun to develop a sense of self-defense and self-reliance separate from Britain. The French and Indian War (1754–1763) took on new significance for all North American colonists after Parliament under William Pitt the Elder concluded that major military resources needed to be devoted to North America to win the war against France. The British colonies' position as an integral part of the British Empire became more apparent during the war, with British military and civilian officials becoming a more significant presence in American life.
American Revolution and the early republic (1765–1800)
Main articles: American Revolution and American Revolutionary War Further information: History of the United States (1776–1789) and History of the United States (1789–1815)
Following their victory in the French and Indian War, Britain began to assert greater control over local colonial affairs, resulting in colonial political resistance; one of the primary colonial grievances was a denial of their rights as Englishmen, particularly the right to representation in the British government that taxed them. To demonstrate their dissatisfaction and resolve, the First Continental Congress met in 1774 and passed the Continental Association, a colonial boycott of British goods that proved effective. The British attempt to then disarm the colonists resulted in the 1775 Battles of Lexington and Concord, igniting the American Revolutionary War. At the Second Continental Congress, the colonies appointed George Washington commander-in-chief of the Continental Army, and created a committee that named Thomas Jefferson to draft the Declaration of Independence. Two days after passing the Lee Resolution to create an independent nation the Declaration was adopted on July 4, 1776. The political values of the American Revolution included liberty, inalienable individual rights; and the sovereignty of the people; supporting republicanism and rejecting monarchy, aristocracy, and all hereditary political power; civic virtue; and vilification of political corruption. The Founding Fathers of the United States, who included Washington, Jefferson, John Adams, Benjamin Franklin, Alexander Hamilton, John Jay, James Madison, Thomas Paine, and many others, were inspired by Greco-Roman, Renaissance, and Enlightenment philosophies and ideas.
The Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union were ratified in 1781 and established a decentralized government that operated until 1789. After the British surrender at the siege of Yorktown in 1781 American sovereignty was internationally recognized by the Treaty of Paris (1783), through which the U.S. gained territory stretching west to the Mississippi River, north to present-day Canada, and south to Spanish Florida. The Northwest Ordinance (1787) established the precedent by which the country's territory would expand with the admission of new states, rather than the expansion of existing states. The U.S. Constitution was drafted at the 1787 Constitutional Convention to overcome the limitations of the Articles. It went into effect in 1789, creating a federal republic governed by three separate branches that together ensured a system of checks and balances. George Washington was elected the country's first president under the Constitution, and the Bill of Rights was adopted in 1791 to allay skeptics' concerns about the power of the more centralized government. His resignation as commander-in-chief after the Revolutionary War and his later refusal to run for a third term as the country's first president established a precedent for the supremacy of civil authority in the United States and the peaceful transfer of power.
Westward expansion and Civil War (1800–1865)
Further information: History of the United States (1815–1849) and History of the United States (1849–1865)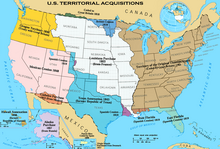
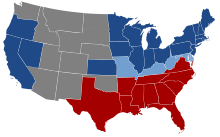
The Louisiana Purchase of 1803 from France nearly doubled the territory of the United States. Lingering issues with Britain remained, leading to the War of 1812, which was fought to a draw. Spain ceded Florida and its Gulf Coast territory in 1819. In the late 18th century, American settlers began to expand westward, many with a sense of manifest destiny. The Missouri Compromise attempted to balance the desire of northern states to prevent the expansion of slavery into new territories with that of southern states to extend it, admitting Missouri as a slave state and Maine as a free state. It further prohibited slavery in all other lands of the Louisiana Purchase north of the 36°30′ parallel. As Americans expanded further into land inhabited by Native Americans, the federal government often applied policies of Indian removal or assimilation. The Trail of Tears (1830–1850) was a U.S. government policy that forcibly removed and displaced most Native Americans living east of the Mississippi River to lands far to the west. These and earlier organized displacements prompted a long series of American Indian Wars west of the Mississippi. The Republic of Texas was annexed in 1845, and the 1846 Oregon Treaty led to U.S. control of the present-day American Northwest. Victory in the Mexican–American War resulted in the 1848 Mexican Cession of California, Nevada, Utah, and much of present-day Colorado and the American Southwest. The California gold rush of 1848–1849 spurred a huge migration of white settlers to the Pacific coast, leading to even more confrontations with Native populations. One of the most violent, the California genocide of thousands of Native inhabitants, lasted into the early 1870s, just as additional western territories and states were created.
During the colonial period, slavery had been legal in the American colonies, though the practice began to be significantly questioned during the American Revolution. States in the North enacted abolition laws, though support for slavery strengthened in Southern states, as inventions such as the cotton gin made the institution increasingly profitable for Southern elites. This sectional conflict regarding slavery culminated in the American Civil War (1861–1865). Eleven slave states seceded and formed the Confederate States of America, while the other states remained in the Union. War broke out in April 1861 after the Confederates bombarded Fort Sumter. After the January 1863 Emancipation Proclamation, many freed slaves joined the Union army. The war began to turn in the Union's favor following the 1863 Siege of Vicksburg and Battle of Gettysburg, and the Confederacy surrendered in 1865 after the Union's victory in the Battle of Appomattox Court House. The Reconstruction era followed the war. After the assassination of President Abraham Lincoln, Reconstruction Amendments were passed to protect the rights of African Americans. National infrastructure, including transcontinental telegraph and railroads, spurred growth in the American frontier.
Post–Civil War era (1865–1917)
Main article: History of the United States (1865–1917)From 1865 through 1917, an unprecedented stream of immigrants arrived in the United States, including 24.4 million from Europe. Most came through the port of New York City, and New York City and other large cities on the East Coast became home to large Jewish, Irish, and Italian populations, while many Germans and Central Europeans moved to the Midwest. At the same time, about one million French Canadians migrated from Quebec to New England. During the Great Migration, millions of African Americans left the rural South for urban areas in the North. Alaska was purchased from Russia in 1867.
The Compromise of 1877 effectively ended Reconstruction and white supremacists took local control of Southern politics. African Americans endured a period of heightened, overt racism following Reconstruction, a time often called the nadir of American race relations. A series of Supreme Court decisions, including Plessy v. Ferguson, emptied the Fourteenth and Fifteenth Amendments of their force, allowing Jim Crow laws in the South to remain unchecked, sundown towns in the Midwest, and segregation in communities across the country, which would be reinforced by the policy of redlining later adopted by the federal Home Owners' Loan Corporation.
An explosion of technological advancement accompanied by the exploitation of cheap immigrant labor led to rapid economic expansion during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, allowing the United States to outpace the economies of England, France, and Germany combined. This fostered the amassing of power by a few prominent industrialists, largely by their formation of trusts and monopolies to prevent competition. Tycoons led the nation's expansion in the railroad, petroleum, and steel industries. The United States emerged as a pioneer of the automotive industry. These changes were accompanied by significant increases in economic inequality, slum conditions, and social unrest, creating the environment for labor unions to begin to flourish. This period eventually ended with the advent of the Progressive Era, which was characterized by significant reforms.
Pro-American elements in Hawaii overthrew the Hawaiian monarchy; the islands were annexed in 1898. That same year, Puerto Rico, the Philippines, and Guam were ceded to the U.S. by Spain after the latter's defeat in the Spanish–American War. (The Philippines was granted full independence from the U.S. on July 4, 1946, following World War II. Puerto Rico and Guam have remained U.S. territories.) American Samoa was acquired by the United States in 1900 after the Second Samoan Civil War. The U.S. Virgin Islands were purchased from Denmark in 1917.
Rise as a superpower (1917–1945)
Main article: History of the United States (1917–1945)
The United States entered World War I alongside the Allies, helping to turn the tide against the Central Powers. In 1920, a constitutional amendment granted nationwide women's suffrage. During the 1920s and '30s, radio for mass communication and the invention of early television transformed communications nationwide. The Wall Street Crash of 1929 triggered the Great Depression, which President Franklin D. Roosevelt responded to with the New Deal, a series of sweeping programs and public works projects combined with financial reforms and regulations. All were intended to protect against future economic depressions.
Initially neutral during World War II, the U.S. began supplying war materiel to the Allies of World War II in March 1941 and entered the war in December after the Empire of Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor. The U.S. developed the first nuclear weapons and used them against the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945, ending the war. The United States was one of the "Four Policemen" who met to plan the post-war world, alongside the United Kingdom, Soviet Union, and China. The U.S. emerged relatively unscathed from the war, with even greater economic power and international political influence.
Cold War (1945–1991)
Main article: Cold War Further information: History of the United States (1945–1964), History of the United States (1964–1980), and History of the United States (1980–1991)
After World War II, the United States entered the Cold War, where geopolitical tensions between the U.S. and the Soviet Union led the two countries to dominate world affairs. The U.S. utilized the policy of containment to limit the USSR's sphere of influence, and prevailed in the Space Race, which culminated with the first crewed Moon landing in 1969. Domestically, the U.S. experienced economic growth, urbanization, and population growth following World War II. The civil rights movement emerged, with Martin Luther King Jr. becoming a prominent leader in the early 1960s. The Great Society plan of President Lyndon B. Johnson's administration resulted in groundbreaking and broad-reaching laws, policies and a constitutional amendment to counteract some of the worst effects of lingering institutional racism. The counterculture movement in the U.S. brought significant social changes, including the liberalization of attitudes toward recreational drug use and sexuality. It also encouraged open defiance of the military draft (leading to the end of conscription in 1973) and wide opposition to U.S. intervention in Vietnam (with the U.S. totally withdrawing in 1975). A societal shift in the roles of women was significantly responsible for the large increase in female paid labor participation during the 1970s, and by 1985 the majority of American women aged 16 and older were employed. The late 1980s and early 1990s saw the fall of communism and the collapse of the Soviet Union, which marked the end of the Cold War and left the United States as the world's sole superpower.
Contemporary (1991–present)
Main articles: History of the United States (1991–2008) and History of the United States (2008–present)
The 1990s saw the longest recorded economic expansion in American history, a dramatic decline in U.S. crime rates, and advances in technology. Throughout this decade, technological innovations such as the World Wide Web, the evolution of the Pentium microprocessor in accordance with Moore's law, rechargeable lithium-ion batteries, the first gene therapy trial, and cloning either emerged in the U.S. or were improved upon there. The Human Genome Project was formally launched in 1990, while Nasdaq became the first stock market in the United States to trade online in 1998.
In the Gulf War of 1991, an American-led international coalition of states expelled an Iraqi invasion force that had occupied neighboring Kuwait. The September 11 attacks on the United States in 2001 by the pan-Islamist militant organization al-Qaeda led to the war on terror, and subsequent military interventions in Afghanistan and Iraq. The cultural impact of the attacks was profound and long-lasting.
The U.S. housing bubble culminated in 2007 with the Great Recession, the largest economic contraction since the Great Depression. Coming to a head in the 2010s, political polarization in the country increased between liberal and conservative factions. This polarization was capitalized upon in the January 2021 Capitol attack, when a mob of insurrectionists entered the U.S. Capitol and sought to prevent the peaceful transfer of power in an attempted self-coup d'état.
Geography
Main article: Geography of the United States
The United States is the world's third-largest country by total area behind Russia and Canada. The 48 contiguous states and the District of Columbia occupy a combined area of 3,119,885 square miles (8,080,470 km). The coastal plain of the Atlantic seaboard gives way to inland forests and rolling hills in the Piedmont plateau region.
The Appalachian Mountains and the Adirondack massif separate the East Coast from the Great Lakes and the grasslands of the Midwest. The Mississippi River System, the world's fourth-longest river system, runs predominantly north–south through the heart of the country. The flat and fertile prairie of the Great Plains stretches to the west, interrupted by a highland region in the southeast.

The Rocky Mountains, west of the Great Plains, extend north to south across the country, peaking at over 14,000 feet (4,300 m) in Colorado. Farther west are the rocky Great Basin and Chihuahua, Sonoran, and Mojave deserts. In the northwest corner of Arizona, carved by the Colorado River over millions of years, is the Grand Canyon, a steep-sided canyon and popular tourist destination known for its overwhelming visual size and intricate, colorful landscape.
The Sierra Nevada and Cascade mountain ranges run close to the Pacific coast. The lowest and highest points in the contiguous United States are in the State of California, about 84 miles (135 km) apart. At an elevation of 20,310 feet (6,190.5 m), Alaska's Denali is the highest peak in the country and continent. Active volcanoes are common throughout Alaska's Alexander and Aleutian Islands, and Hawaii consists of volcanic islands. The supervolcano underlying Yellowstone National Park in the Rocky Mountains, the Yellowstone Caldera, is the continent's largest volcanic feature. In 2021, the United States had 8% of global permanent meadows and pastures and 10% of cropland.
Climate
Main article: Climate of the United States See also: Climate change in the United States
With its large size and geographic variety, the United States includes most climate types. East of the 100th meridian, the climate ranges from humid continental in the north to humid subtropical in the south. The western Great Plains are semi-arid. Many mountainous areas of the American West have an alpine climate. The climate is arid in the Southwest, Mediterranean in coastal California, and oceanic in coastal Oregon, Washington, and southern Alaska. Most of Alaska is subarctic or polar. Hawaii, the southern tip of Florida and U.S. territories in the Caribbean and Pacific are tropical.
States bordering the Gulf of Mexico are prone to hurricanes, and most of the world's tornadoes occur in the country, mainly in Tornado Alley. Overall, the United States receives more high-impact extreme weather incidents than any other country. Extreme weather became more frequent in the U.S. in the 21st century, with three times the number of reported heat waves as in the 1960s. In the American Southwest, droughts became more persistent and more severe. The regions considered as the most attractive to the population are the most vulnerable.
Biodiversity and conservation
Main articles: Fauna of the United States and Flora of the United States

The U.S. is one of 17 megadiverse countries containing large numbers of endemic species: about 17,000 species of vascular plants occur in the contiguous United States and Alaska, and over 1,800 species of flowering plants are found in Hawaii, few of which occur on the mainland. The United States is home to 428 mammal species, 784 birds, 311 reptiles, 295 amphibians, and around 91,000 insect species.
There are 63 national parks, and hundreds of other federally managed parks, forests, and wilderness areas, managed by the National Park Service and other agencies. About 28% of the country's land is publicly owned and federally managed, primarily in the Western States. Most of this land is protected, though some is leased for commercial use, and less than one percent is used for military purposes.
Environmental issues in the United States include debates on non-renewable resources and nuclear energy, air and water pollution, biodiversity, logging and deforestation, and climate change. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is the federal agency charged with addressing most environmental-related issues. The idea of wilderness has shaped the management of public lands since 1964, with the Wilderness Act. The Endangered Species Act of 1973 provides a way to protect threatened and endangered species and their habitats. The United States Fish and Wildlife Service implements and enforces the Act. In 2024, the U.S. ranked 35th among 180 countries in the Environmental Performance Index. The country joined the Paris Agreement on climate change in 2016.
Government and politics
Main article: Politics of the United States Further information: Elections in the United States, Political ideologies in the United States, and Americanism (ideology)


The United States is a federal republic of 50 states and a separate federal capital district, Washington, D.C. It also asserts sovereignty over five unincorporated territories and several uninhabited island possessions. The U.S. is the world's oldest surviving federation, and its presidential system of national government has been adopted, in whole or in part, by many newly independent states worldwide following their decolonization. It is a liberal representative democracy "in which majority rule is tempered by minority rights protected by law". The Constitution of the United States serves as the country's supreme legal document, also establishing the structure and responsibilities of the national federal government and its relationship with the individual states. The U.S. Constitution is the world's oldest national constitution still in effect (from March 4, 1789).
National government
Main article: Federal government of the United StatesComposed of three branches, all headquartered in Washington, D.C., the federal government is the national government of the United States. It is regulated by a strong system of checks and balances.
- The U.S. Congress, a bicameral legislature made up of the Senate and the House of Representatives, makes federal law, declares war, approves treaties, has the power of the purse, and has the power of impeachment. The Senate has 100 members (2 from each state), elected for a six-year term. The House of Representatives has 435 members, each elected for a two-year term; all representatives serve one congressional district of equivalent population. Congressional districts are drawn by each state legislature and are contiguous within the state. The Congress also organizes a collection of committees, each of which handles a specific task or duty. One of Congress's foremost non-legislative functions is the power to investigate and oversee the executive branch. Congressional oversight is usually delegated to committees and is facilitated by Congress's subpoena power. Appointment to a committee enables a member to develop specialized knowledge of the matters under its purview. The various committees monitor ongoing governmental operations, identify issues suitable for legislative review, gather and evaluate information, and recommend courses of action to the U.S. Congress, including but not limited to new legislation. The two major political parties have appointment power in deciding each committee's membership. Committee chairs are assigned to a member of the majority party.
- The U.S. president is the head of state, commander-in-chief of the military, chief executive of the federal government, and has the ability to veto legislative bills from the U.S. Congress before they become law. However, presidential vetoes can be overridden by a two-thirds supermajority vote in both chambers of Congress. The president appoints the members of the Cabinet, subject to Senate approval, and names other officials who administer and enforce federal laws through their respective agencies. The president also has clemency power for federal crimes and can issue pardons. Finally, the president has the right to issue expansive "executive orders", subject to judicial review, in a number of policy areas. Candidates for president campaign with a vice-presidential running mate. Both candidates are elected together, or defeated together, in a presidential election. Unlike other votes in American politics, this is technically an indirect election in which the winner will be determined by the U.S. Electoral College. There, votes are officially cast by individual electors selected by their state legislature. In practice, however, each of the 50 states chooses a group of presidential electors who are required to confirm the winner of their state's popular vote. Each state is allocated two electors plus one additional elector for each congressional district, which in effect combines to equal the number of elected officials that state sends to Congress. The District of Columbia, with no representatives or senators, is allocated three electoral votes. Both the president and the vice president serve a four-year term, and the president may be reelected to the office only once, for one additional four-year term.
- The U.S. federal judiciary, whose judges are all appointed for life by the president with Senate approval, consists primarily of the U.S. Supreme Court, the U.S. courts of appeals, and the U.S. district courts. The U.S. Supreme Court interprets laws and overturn those they find unconstitutional. The Supreme Court has nine members led by the Chief Justice of the United States. The members are appointed by the sitting president when a vacancy becomes available. In a number of ways the federal court system operates differently than state courts. For civil cases that is apparent in the types of cases that can be heard in the federal system. Their limited jurisdiction restricts them to cases authorized by the United States Constitution or federal statutes. In criminal cases, states may only bring criminal prosecutions in state courts, and the federal government may only bring criminal prosecutions in federal court. The first level in the federal courts is federal district court for any case under "original jurisdiction", such as federal statutes, the Constitution, or treaties. There are twelve federal circuits that divide the country into different regions for federal appeals courts. After a federal district court has decided a case, it can then be appealed to a United States court of appeal. The next and highest court in the system is the Supreme Court of the United States. It has the power to decide appeals on all cases brought in federal court or those brought in state court but dealing with federal law. Unlike circuit court appeals, however, the Supreme Court is usually not required to hear the appeal. A "petition for writ of certiorari" may be submitted to the court, asking it to hear the case. If it is granted, the Supreme Court will take briefs and conduct oral arguments. If it is not granted, the opinion of the lower court stands. Certiorari is not often granted, and less than 1% of appeals to the Supreme Court are actually heard by it. Usually, the Court only hears cases when there are conflicting decisions across the nation on a particular issue, or when there is an obvious error in a case.
The three-branch system is known as the presidential system, in contrast to the parliamentary system, where the executive is part of the legislative body. Many countries around the world imitated this aspect of the 1789 Constitution of the United States, especially in the Americas.
Political parties
Main articles: Political parties in the United States and List of political parties in the United States See also: Political party strength in U.S. states
The Constitution is silent on political parties. However, they developed independently in the 18th century with the Federalist and Anti-Federalist parties. Since then, the United States has operated as a de facto two-party system, though the parties in that system have been different at different times. The two main national parties are presently the Democratic and the Republican. The former is perceived as relatively liberal in its political platform while the latter is perceived as relatively conservative.
Subdivisions
Main articles: U.S. state and County (United States) See also: State governments of the United States and Local government in the United States Further information: List of states and territories of the United States, Indian reservation, Territories of the United States, and Territorial evolution of the United StatesIn the American federal system, sovereign powers are shared between two levels of elected government: national and state. People in the states are also represented by local elected governments, which are administrative divisions of the states. States are subdivided into counties or county equivalents, and further divided into municipalities. The District of Columbia is a federal district containing the U.S. capital, Washington, D.C. The federal district is an administrative division of the federal government. Federally recognized tribes govern 326 Indian reservations.

Foreign relations
Main articles: Foreign relations of the United States and Foreign policy of the United States
The United States has an established structure of foreign relations, and it has the world's second-largest diplomatic corps as of 2024. It is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council, and home to the United Nations headquarters. The United States is a member of the G7, G20, and OECD intergovernmental organizations. Almost all countries have embassies and many have consulates (official representatives) in the country. Likewise, nearly all countries host formal diplomatic missions with the United States, except Iran, North Korea, and Bhutan. Though Taiwan does not have formal diplomatic relations with the U.S., it maintains close unofficial relations. The United States regularly supplies Taiwan with military equipment to deter potential Chinese aggression. Its geopolitical attention also turned to the Indo-Pacific when the United States joined the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue with Australia, India, and Japan.
The United States has a "Special Relationship" with the United Kingdom and strong ties with Canada, Australia, New Zealand, the Philippines, Japan, South Korea, Israel, and several European Union countries (France, Italy, Germany, Spain, and Poland). The U.S. works closely with its NATO allies on military and national security issues, and with countries in the Americas through the Organization of American States and the United States–Mexico–Canada Free Trade Agreement. In South America, Colombia is traditionally considered to be the closest ally of the United States. The U.S. exercises full international defense authority and responsibility for Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and Palau through the Compact of Free Association. It has increasingly conducted strategic cooperation with India, but its ties with China have steadily deteriorated. Since 2014, the U.S. has become a key ally of Ukraine; it has also provided the country with significant military equipment and other support in response to Russia's 2022 invasion.
Military
Main article: United States Armed Forces See also: Military history of the United States
The president is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces and appoints its leaders, the secretary of defense and the Joint Chiefs of Staff. The Department of Defense, which is headquartered at the Pentagon near Washington, D.C., administers five of the six service branches, which are made up of the U.S. Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, and Space Force. The Coast Guard is administered by the Department of Homeland Security in peacetime and can be transferred to the Department of the Navy in wartime.
The United States spent $916 billion on its military in 2023, which is by far the largest amount of any country, making up 37% of global military spending and accounting for 3.4% of the country's GDP. The U.S. has 42% of the world's nuclear weapons—the second-largest share after Russia.
The United States has the third-largest combined armed forces in the world, behind the Chinese People's Liberation Army and Indian Armed Forces. The military operates about 800 bases and facilities abroad, and maintains deployments greater than 100 active duty personnel in 25 foreign countries.
State defense forces (SDFs) are military units that operate under the sole authority of a state government. SDFs are authorized by state and federal law but are under the command of the state's governor. They are distinct from the state's National Guard units in that they cannot become federalized entities. A state's National Guard personnel, however, may be federalized under the National Defense Act Amendments of 1933, which created the Guard and provides for the integration of Army National Guard units and personnel into the U.S. Army and (since 1947) the U.S. Air Force.
Law enforcement and criminal justice
Main articles: Law of the United States, Law enforcement in the United States, and Crime in the United States See also: Censorship in the United States and Race and crime in the United States
There are about 18,000 U.S. police agencies from local to national level in the United States. Law in the United States is mainly enforced by local police departments and sheriff departments in their municipal or county jurisdictions. The state police departments have authority in their respective state, and federal agencies such as the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and the U.S. Marshals Service have national jurisdiction and specialized duties, such as protecting civil rights, national security and enforcing U.S. federal courts' rulings and federal laws. State courts conduct most civil and criminal trials, and federal courts handle designated crimes and appeals of state court decisions.
There is no unified "criminal justice system" in the United States. The American prison system is largely heterogenous, with thousands of relatively independent systems operating across federal, state, local, and tribal levels. In 2023, "these systems almost 2 million people in 1,566 state prisons, 98 federal prisons, 3,116 local jails, 1,323 juvenile correctional facilities, 181 immigration detention facilities, and 80 Indian country jails, as well as in military prisons, civil commitment centers, state psychiatric hospitals, and prisons in the U.S. territories." Despite disparate systems of confinement, four main institutions dominate: federal prisons, state prisons, local jails, and juvenile correctional facilities. Federal prisons are run by the Federal Bureau of Prisons and hold people who have been convicted of federal crimes, including pretrial detainees. State prisons, run by the official department of correction of each state, hold sentenced people serving prison time (usually longer than one year) for felony offenses. Local jails are county or municipal facilities that incarcerate defendants prior to trial; they also hold those serving short sentences (typically under a year). Juvenile correctional facilities are operated by local or state governments and serve as longer-term placements for any minor adjudicated as delinquent and ordered by a judge to be confined.
As of January 2023, the United States has the sixth-highest per capita incarceration rate in the world—531 people per 100,000 inhabitants—and the largest prison and jail population in the world, with almost 2 million people incarcerated. An analysis of the World Health Organization Mortality Database from 2010 showed U.S. homicide rates "were 7 times higher than in other high-income countries, driven by a gun homicide rate that was 25 times higher".
Economy
Main article: Economy of the United States Further information: Economic history of the United States and Tourism in the United States
The U.S. has been the world's largest economy nominally since about 1890. The 2023 nominal U.S. gross domestic product (GDP) of more than $27 trillion was the highest in the world, constituting over 25% of the global economy or 15% at purchasing power parity (PPP). From 1983 to 2008, U.S. real compounded annual GDP growth was 3.3%, compared to a 2.3% weighted average for the rest of the G7. The country ranks first in the world by nominal GDP, second when adjusted for purchasing power parities (PPP), and ninth by PPP-adjusted GDP per capita. It possesses the highest disposable household income per capita among OECD countries. As of February 2024, the total U.S. federal government debt was $34.4 trillion.

Of the world's 500 largest companies by revenue, 136 are headquartered in the U.S. as of 2023, which is the highest number of any country. The U.S. dollar is the currency most used in international transactions and is the world's foremost reserve currency, backed by the country's dominant economy, its military, the petrodollar system, and its linked eurodollar and large U.S. treasuries market. Several countries use it as their official currency, and in others it is the de facto currency. It has free trade agreements with several countries, including the USMCA. The U.S. ranked second in the Global Competitiveness Report in 2019, after Singapore. Although the United States has reached a post-industrial level of development and is often described as having a service economy, it remains a major industrial power. As of 2021, the U.S. is the second-largest manufacturing country after China.

New York City is the world's principal financial center and the epicenter of the world's largest metropolitan economy. The New York Stock Exchange and Nasdaq, both located in New York City, are the world's two largest stock exchanges by market capitalization and trade volume. The United States is at or near the forefront of technological advancement and innovation in many economic fields, especially in artificial intelligence; electronics and computers; pharmaceuticals; and medical, aerospace and military equipment. The country's economy is fueled by abundant natural resources, a well-developed infrastructure, and high productivity. The largest trading partners of the United States are the European Union, Mexico, Canada, China, Japan, South Korea, the United Kingdom, Vietnam, India, and Taiwan. The United States is the world's largest importer and the second-largest exporter. It is by far the world's largest exporter of services.
Americans have the highest average household and employee income among OECD member states, and the fourth-highest median household income as of 2023, up from sixth-highest in 2013. With personal consumption expenditures of over $18.5 trillion in 2023, the U.S. has a heavily consumer-driven economy and is by far the world's largest consumer market. Wealth in the United States is highly concentrated; the richest 10% of the adult population own 72% of the country's household wealth, while the bottom 50% own just 2%. Income inequality in the U.S. remains at record highs, with the top fifth of earners taking home more than half of all income and giving the U.S. one of the widest income distributions among OECD members. The U.S. ranks first in the number of dollar billionaires and millionaires, with 735 billionaires and nearly 22 million millionaires as of 2023. There were about 582,500 sheltered and unsheltered homeless persons in the U.S. in 2022, with 60% staying in an emergency shelter or transitional housing program. In 2022, 6.4 million children experienced food insecurity. Feeding America estimates that around one in five, or approximately 13 million, children experience hunger in the U.S. and do not know where they will get their next meal or when. As of 2022, 37.9 million people, or 11.5% of the U.S. population, were living in poverty.
The United States has a smaller welfare state and redistributes less income through government action than most other high-income countries. It is the only advanced economy that does not guarantee its workers paid vacation nationally and is one of a few countries in the world without federal paid family leave as a legal right. The United States has a higher percentage of low-income workers than almost any other developed country, largely because of a weak collective bargaining system and lack of government support for at-risk workers.
Science, technology, spaceflight and energy
Main articles: Science and technology in the United States, Space policy of the United States, and Energy in the United States See also: Communications in the United StatesThe United States has been a leader in technological innovation since the late 19th century and scientific research since the mid-20th century. Methods for producing interchangeable parts and the establishment of a machine tool industry enabled the large-scale manufacturing of U.S. consumer products in the late 19th century. By the early 20th century, factory electrification, the introduction of the assembly line, and other labor-saving techniques created the system of mass production. The United States is widely considered to be the leading country in the development of artificial intelligence technology. In 2022, the United States was (after China) the country with the second-highest number of published scientific papers. In 2021, the U.S. ranked second (also after China) by the number of patent applications, and third by trademark and industrial design applications (after China and Germany), according to World Intellectual Property Indicators. In 2023 and 2024, the United States ranked third (after Switzerland and Sweden) in the Global Innovation Index. The U.S. has the highest total research and development expenditure of any country and ranks ninth as a percentage of GDP. In 2023, the United States was ranked the second most technologically advanced country in the world (after South Korea) by Global Finance magazine.

The United States has maintained a space program since the late 1950s, beginning with the establishment of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) in 1958. NASA's Apollo program (1961–1972) achieved the first crewed Moon landing with the 1969 Apollo 11 mission; it remains one of the agency's most significant milestones. Other major endeavors by NASA include the Space Shuttle program (1981–2011), the Voyager program (1972–present), the Hubble and James Webb space telescopes (launched in 1990 and 2021, respectively), and the multi-mission Mars Exploration Program (Spirit and Opportunity, Curiosity, and Perseverance). NASA is one of five agencies collaborating on the International Space Station (ISS); U.S. contributions to the ISS include several modules, including Destiny (2001), Harmony (2007), and Tranquility (2010), as well as ongoing logistical and operational support. The United States private sector dominates the global commercial spaceflight industry. Prominent American spaceflight contractors include Blue Origin, Boeing, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, and SpaceX. NASA programs such as the Commercial Crew Program, Commercial Resupply Services, Commercial Lunar Payload Services, and NextSTEP have facilitated growing private-sector involvement in American spaceflight.
As of 2023, the United States receives approximately 84% of its energy from fossil fuel, and the largest source of the country's energy came from petroleum (38%), followed by natural gas (36%), renewable sources (9%), coal (9%), and nuclear power (9%). The United States constitutes less than 4% of the world's population, but consumes around 16% of the world's energy. The U.S. ranks as the second-highest emitter of greenhouse gases.
Transportation
Main article: Transportation in the United States
The U.S. Department of Transportation and its divisions provide regulation, supervision, and funding for all aspects of transportation except for customs, immigration, and security. (The latter remain the responsibility of the U.S. Department of Homeland Security.) Each U.S. state has its own department of transportation, which builds and maintains state highways. Depending upon the state, this department might also directly operate or supervise other modes of transportation.
Aviation law is almost entirely the jurisdiction of the federal government; the Federal Aviation Administration regulates all aspects of civil aviation, air traffic management, certification and compliance, and aviation safety. Vehicle traffic laws, however, are enacted and enforced by state and local authorities, with the exception of roads located on federal property (national parks, military bases) or in the unorganized U.S. territories. The United States Coast Guard is the primary enforcer of law and security on U.S. waterways, inland as well as coastal, but economic jurisdiction over coastal tidelands is shared between state and federal governments. The country's inland waterways are the world's fifth-longest, totaling 41,009 km (25,482 mi).
Passenger and freight rail systems, bus systems, water ferries, and dams may be under either public or private ownership and operation. U.S. civilian airlines are all privately owned. Most U.S. airports are owned and operated by local government authorities, and there are also some private airports. The Transportation Security Administration has provided security at most major airports since 2001.

Commercial railroads and trains were the dominant mode of transportation in the U.S. until the mid-twentieth century. The introduction of jet airplanes and airports serving the same major routes accelerated a decline in demand for interstate and intercity rail passenger service by the 1960s. The completion of the Interstate Highway System also hastened the sharp curtailment of passenger service by the railroads. These significant developments led to the creation of the National Railroad Passenger Corporation, now called Amtrak, by the U.S. federal government in 1971. Amtrak helps to maintain limited intercity rail passenger service in most parts of the country. It serves most major U.S. cities, but outside the Northeast, California, and Illinois it typically runs only a few trains per day. More frequent Amtrak service is available in regional corridors between certain major cities, particularly the Northeast Corridor between Washington, D.C., Philadelphia, New York City and Boston; between New York City and Albany; in metropolitan Chicago; and in parts of California and the Pacific Northwest. Amtrak does not serve several major U.S. destinations, including Las Vegas and Phoenix, Arizona.
The American civil airline industry is entirely owned by corporations and has been largely deregulated since 1978, while most major airports are publicly owned. The three largest airlines in the world by passengers carried are U.S.-based; American Airlines is number one after its 2013 acquisition by US Airways. Of the world's 50 busiest passenger airports, 16 are in the United States, including the top five and the busiest, Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport. As of 2022, there are 19,969 airports in the U.S., of which 5,193 are designated as "public use", including for general aviation and other activities.
The overwhelming majority of roads in the United States are owned and maintained by state and local governments. Roads maintained only by the U.S. federal government are generally only found on federal lands (such as national parks) or at federal facilities (like military bases). The Interstate Highway System, with its large, open freeways linking the states, is partly funded by the federal government but owned and maintained by the state government hosting its section of the interstate. Some states fund and build their own large expressways—often called "parkways" or "turnpikes"—that generally use tolls to pay for construction and maintenance. Likewise, some privately owned roads may use tolls for this purpose.
Public transportation in the United States includes bus, commuter rail, ferry, and sometimes airline service. Public transit systems serve areas of higher population density where demand is greatest. Many U.S. cities, towns, and suburbs are car-dependent, however, and suburban public transit is less common and service far less frequent. Most U.S. urban areas have some form of public transit, notably city buses, while the largest (e.g. New York, Chicago, Atlanta, Philadelphia, Boston, San Francisco, and Portland, Oregon) operate extensive systems that also include subways or light rail. Most public transit service in the United States is run by local governments, but national and regional commuter lines serve major U.S. urban corridors.
Personal transportation in the United States is dominated by automobiles, which operate on a network of 4 million miles (6.4 million kilometers) of public roads, making it the longest in the world. The country's rail transport network, also the longest in the world at 182,412.3 mi (293,564.2 km), handles mostly freight. Of the world's 50 busiest container ports, four are located in the United States. The busiest in the U.S. is the Port of Los Angeles.
The Oldsmobile Curved Dash and the Ford Model T, both American cars, are considered the first mass-produced and mass-affordable cars, respectively. As of 2023, the United States is the second-largest manufacturer of motor vehicles and is home to Tesla, the world's most valuable car company. American automotive company General Motors held the title of the world's best-selling automaker from 1931 to 2008. The American automotive industry is the world's second-largest automobile market by sales, having been overtaken by China in 2010, and the U.S. has the highest vehicle ownership per capita in the world, with 910 vehicles per 1000 people. By value, the U.S. was the world's largest importer and third-largest exporter of cars in 2022.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of the United StatesPopulation
Main articles: Americans and Race and ethnicity in the United States See also: List of U.S. states by population| State | Population (millions) |
|---|---|
| California | 39.4 |
| Texas | 31.3 |
| Florida | 23.4 |
| New York | 19.9 |
| Pennsylvania | 13.1 |
| Illinois | 12.7 |
| Ohio | 11.9 |
| Georgia | 11.2 |
| North Carolina | 11.0 |
| Michigan | 10.1 |
The U.S. Census Bureau reported 331,449,281 residents as of April 1, 2020, making the United States the third-most-populous country in the world, after China and India. The Census Bureau's official 2024 population estimate was 340,110,988, an increase of 2.6% since the 2020 census. According to the Bureau's U.S. Population Clock, on July 1, 2024, the U.S. population had a net gain of one person every 16 seconds, or about 5400 people per day. In 2023, 51% of Americans age 15 and over were married, 6% were widowed, 10% were divorced, and 34% had never been married. In 2023, the total fertility rate for the U.S. stood at 1.6 children per woman, and, at 23%, it had the world's highest rate of children living in single-parent households in 2019.
The United States has a diverse population; 37 ancestry groups have more than one million members. White Americans with ancestry from Europe, the Middle East, or North Africa form the largest racial and ethnic group at 57.8% of the United States population. Hispanic and Latino Americans form the second-largest group and are 18.7% of the United States population. African Americans constitute the country's third-largest ancestry group and are 12.1% of the total U.S. population. Asian Americans are the country's fourth-largest group, composing 5.9% of the United States population. The country's 3.7 million Native Americans account for about 1%, and some 574 native tribes are recognized by the federal government. In 2022, the median age of the United States population was 38.9 years.
Language
Main article: Languages of the United States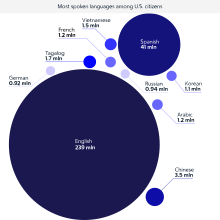
While many languages are spoken in the United States, English is by far the most commonly spoken and written. Although there is no official language at the federal level, some laws, such as U.S. naturalization requirements, standardize English, and most states have declared it the official language. Three states and four U.S. territories have recognized local or indigenous languages in addition to English, including Hawaii (Hawaiian), Alaska (twenty Native languages), South Dakota (Sioux), American Samoa (Samoan), Puerto Rico (Spanish), Guam (Chamorro), and the Northern Mariana Islands (Carolinian and Chamorro). In total, 169 Native American languages are spoken in the United States. In Puerto Rico, Spanish is more widely spoken than English.
According to the American Community Survey (2020), some 245.4 million people out of the total U.S. population of 334 million spoke only English at home. About 41.2 million spoke Spanish at home, making it the second most commonly used language. Other languages spoken at home by one million people or more include Chinese (3.40 million), Tagalog (1.71 million), Vietnamese (1.52 million), Arabic (1.39 million), French (1.18 million), Korean (1.07 million), and Russian (1.04 million). German, spoken by 1 million people at home in 2010, fell to 857,000 total speakers in 2020.
Immigration
Main article: Immigration to the United States See also: United States Border Patrol
America's immigrant population is by far the world's largest in absolute terms. In 2022, there were 87.7 million immigrants and U.S.-born children of immigrants in the United States, accounting for nearly 27% of the overall U.S. population. In 2017, out of the U.S. foreign-born population, some 45% (20.7 million) were naturalized citizens, 27% (12.3 million) were lawful permanent residents, 6% (2.2 million) were temporary lawful residents, and 23% (10.5 million) were unauthorized immigrants. In 2019, the top countries of origin for immigrants were Mexico (24% of immigrants), India (6%), China (5%), the Philippines (4.5%), and El Salvador (3%). In fiscal year 2022, over one million immigrants (most of whom entered through family reunification) were granted legal residence. The United States led the world in refugee resettlement for decades, admitting more refugees than the rest of the world combined.
Religion
Main article: Religion in the United States See also: List of religious movements that began in the United StatesReligious affiliation in the U.S., according to a 2023 Gallup poll:
Protestantism (33%) Catholicism (22%) Non-specific Christian (11%) Judaism (2%) Mormonism (1%) Other religion (6%) Unaffiliated (22%) Unanswered (3%)The First Amendment guarantees the free exercise of religion in the country and forbids Congress from passing laws respecting its establishment. Religious practice is widespread, among the most diverse in the world, and profoundly vibrant. The country has the world's largest Christian population. Other notable faiths include Judaism, Buddhism, Hinduism, Islam, many New Age movements, and Native American religions. Religious practice varies significantly by region. "Ceremonial deism" is common in American culture.
The overwhelming majority of Americans believe in a higher power or spiritual force, engage in spiritual practices such as prayer, and consider themselves religious or spiritual. In the "Bible Belt", located within the Southern United States, evangelical Protestantism plays a significant role culturally, whereas New England and the Western United States tend to be more secular. Mormonism—a Restorationist movement, whose members migrated westward from Missouri and Illinois under the leadership of Brigham Young in 1847 after the assassination of Joseph Smith—remains the predominant religion in Utah to this day.
Urbanization
Main articles: Urbanization in the United States and List of United States cities by populationAbout 82% of Americans live in urban areas, including suburbs; about half of those reside in cities with populations over 50,000. In 2022, 333 incorporated municipalities had populations over 100,000, nine cities had more than one million residents, and four cities—New York City, Los Angeles, Chicago, and Houston—had populations exceeding two million. Many U.S. metropolitan populations are growing rapidly, particularly in the South and West.
| Largest metropolitan areas in the United States 2023 MSA population estimates from the U.S. Census Bureau | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Region | Pop. | Rank | Name | Region | Pop. | ||
 New York  Los Angeles |
1 | New York | Northeast | 19,498,249 | 11 | Boston | Northeast | 4,919,179 |  Chicago  Dallas–Fort Worth |
| 2 | Los Angeles | West | 12,799,100 | 12 | Riverside–San Bernardino | West | 4,688,053 | ||
| 3 | Chicago | Midwest | 9,262,825 | 13 | San Francisco | West | 4,566,961 | ||
| 4 | Dallas–Fort Worth | South | 8,100,037 | 14 | Detroit | Midwest | 4,342,304 | ||
| 5 | Houston | South | 7,510,253 | 15 | Seattle | West | 4,044,837 | ||
| 6 | Atlanta | South | 6,307,261 | 16 | Minneapolis–Saint Paul | Midwest | 3,712,020 | ||
| 7 | Washington, D.C. | South | 6,304,975 | 17 | Tampa–St. Petersburg | South | 3,342,963 | ||
| 8 | Philadelphia | Northeast | 6,246,160 | 18 | San Diego | West | 3,269,973 | ||
| 9 | Miami | South | 6,183,199 | 19 | Denver | West | 3,005,131 | ||
| 10 | Phoenix | West | 5,070,110 | 20 | Baltimore | South | 2,834,316 | ||
Health
See also: Healthcare in the United States, Healthcare reform in the United States, and Health insurance in the United States
According to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), average American life expectancy at birth was 77.5 years in 2022 (74.8 years for men and 80.2 years for women). This was a gain of 1.1 years from 76.4 years in 2021, but the CDC noted that the new average "didn't fully offset the loss of 2.4 years between 2019 and 2021". Higher overall mortality due especially to the health impact of the COVID-19 pandemic as well as opioid overdoses and suicides were held mostly responsible for the previous drop in life expectancy. The same report stated that the 2022 gains in average U.S. life expectancy were especially significant for men, Hispanics, and American Indian–Alaskan Native people (AIAN). Starting in 1998, the life expectancy in the U.S. fell behind that of other wealthy industrialized countries, and Americans' "health disadvantage" gap has been increasing ever since. The U.S. has one of the highest suicide rates among high-income countries. Approximately one-third of the U.S. adult population is obese and another third is overweight. The U.S. healthcare system far outspends that of any other country, measured both in per capita spending and as a percentage of GDP, but attains worse healthcare outcomes when compared to peer countries for reasons that are debated. The United States is the only developed country without a system of universal healthcare, and a significant proportion of the population that does not carry health insurance. Government-funded healthcare coverage for the poor (Medicaid) and for those age 65 and older (Medicare) is available to Americans who meet the programs' income or age qualifications. In 2010, former President Obama passed the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act. Abortion in the United States is not federally protected, and is illegal or restricted in 17 states.
Education
Main article: Education in the United States
American primary and secondary education (known in the U.S. as K-12, "kindergarten through 12th grade") is decentralized. School systems are operated by state, territorial, and sometimes municipal governments and regulated by the U.S. Department of Education. In general, children are required to attend school or an approved homeschool from the age of five or six (kindergarten or first grade) until they are 18 years old. This often brings students through the 12th grade, the final year of a U.S. high school, but some states and territories allow them to leave school earlier, at age 16 or 17. The U.S. spends more on education per student than any country in the world, an average of $18,614 per year per public elementary and secondary school student in 2020–2021. Among Americans age 25 and older, 92.2% graduated from high school, 62.7% attended some college, 37.7% earned a bachelor's degree, and 14.2% earned a graduate degree. The U.S. literacy rate is near-universal. The country has the most Nobel Prize winners of any country, with 411 (having won 413 awards).
U.S. tertiary or higher education has earned a global reputation. Many of the world's top universities, as listed by various ranking organizations, are in the United States, including 19 of the top 25. American higher education is dominated by state university systems, although the country's many private universities and colleges enroll about 20% of all American students. Local community colleges generally offer coursework and degree programs covering the first two years of college study. They often have more open admission policies, shorter academic programs, and lower tuition.
As for public expenditures on higher education, the U.S. spends more per student than the OECD average, and Americans spend more than all nations in combined public and private spending. Colleges and universities directly funded by the federal government do not charge tuition and are limited to military personnel and government employees, including: the U.S. service academies, the Naval Postgraduate School, and military staff colleges. Despite some student loan forgiveness programs in place, student loan debt increased by 102% between 2010 and 2020, and exceeded $1.7 trillion as of 2022.
Culture and society
Main articles: Culture of the United States and Society of the United States
Americans have traditionally been characterized by a unifying political belief in an "American Creed" emphasizing consent of the governed, liberty, equality under the law, democracy, social equality, property rights, and a preference for limited government. Culturally, the country has been described as having the values of individualism and personal autonomy, as well as having a strong work ethic, competitiveness, and voluntary altruism towards others. According to a 2016 study by the Charities Aid Foundation, Americans donated 1.44% of total GDP to charity—the highest rate in the world by a large margin. The United States is home to a wide variety of ethnic groups, traditions, and values. It has acquired significant cultural and economic soft power.
Nearly all present Americans or their ancestors came from Europe, Africa, or Asia (the "Old World") within the past five centuries. Mainstream American culture is a Western culture largely derived from the traditions of European immigrants with influences from many other sources, such as traditions brought by slaves from Africa. More recent immigration from Asia and especially Latin America has added to a cultural mix that has been described as a homogenizing melting pot, and a heterogeneous salad bowl, with immigrants contributing to, and often assimilating into, mainstream American culture. The American Dream, or the perception that Americans enjoy high social mobility, plays a key role in attracting immigrants. Whether this perception is accurate has been a topic of debate. While mainstream culture holds that the United States is a classless society, scholars identify significant differences between the country's social classes, affecting socialization, language, and values. Americans tend to greatly value socioeconomic achievement, but being ordinary or average is promoted by some as a noble condition as well.
The National Foundation on the Arts and the Humanities is an agency of the United States federal government that was established in 1965 with the purpose to "develop and promote a broadly conceived national policy of support for the humanities and the arts in the United States, and for institutions which preserve the cultural heritage of the United States." It is composed of four sub-agencies:
- National Endowment for the Arts
- National Endowment for the Humanities
- Institute of Museum and Library Services
- Federal Council on the Arts and the Humanities
The United States is considered to have the strongest protections of free speech of any country under the First Amendment, which protects flag desecration, hate speech, blasphemy, and lese-majesty as forms of protected expression. A 2016 Pew Research Center poll found that Americans were the most supportive of free expression of any polity measured. They are the "most supportive of freedom of the press and the right to use the Internet without government censorship." The U.S. is a socially progressive country with permissive attitudes surrounding human sexuality. LGBT rights in the United States are advanced by global standards.
Literature
Main articles: American literature and American philosophy See also: List of American novelists and List of playwrights from the United States
Colonial American authors were influenced by John Locke and various other Enlightenment philosophers. The American Revolutionary Period (1765–1783) is notable for the political writings of Benjamin Franklin, Alexander Hamilton, Thomas Paine, and Thomas Jefferson. Shortly before and after the Revolutionary War, the newspaper rose to prominence, filling a demand for anti-British national literature. An early novel is William Hill Brown's The Power of Sympathy, published in 1791. Writer and critic John Neal in the early- to mid-nineteenth century helped advance America toward a unique literature and culture by criticizing predecessors such as Washington Irving for imitating their British counterparts, and by influencing writers such as Edgar Allan Poe, who took American poetry and short fiction in new directions. Ralph Waldo Emerson and Margaret Fuller pioneered the influential Transcendentalism movement; Henry David Thoreau, author of Walden, was influenced by this movement. The conflict surrounding abolitionism inspired writers, like Harriet Beecher Stowe, and authors of slave narratives, such as Frederick Douglass. Nathaniel Hawthorne's The Scarlet Letter (1850) explored the dark side of American history, as did Herman Melville's Moby-Dick (1851). Major American poets of the nineteenth century American Renaissance include Walt Whitman, Melville, and Emily Dickinson. Mark Twain was the first major American writer to be born in the West. Henry James achieved international recognition with novels like The Portrait of a Lady (1881). As literacy rates rose, periodicals published more stories centered around industrial workers, women, and the rural poor. Naturalism, regionalism, and realism were the major literary movements of the period.
While modernism generally took on an international character, modernist authors working within the United States more often rooted their work in specific regions, peoples, and cultures. Following the Great Migration to northern cities, African-American and black West Indian authors of the Harlem Renaissance developed an independent tradition of literature that rebuked a history of inequality and celebrated black culture. An important cultural export during the Jazz Age, these writings were a key influence on Négritude, a philosophy emerging in the 1930s among francophone writers of the African diaspora. In the 1950s, an ideal of homogeneity led many authors to attempt to write the Great American Novel, while the Beat Generation rejected this conformity, using styles that elevated the impact of the spoken word over mechanics to describe drug use, sexuality, and the failings of society. Contemporary literature is more pluralistic than in previous eras, with the closest thing to a unifying feature being a trend toward self-conscious experiments with language. As of 2024, there have been 12 American laureates for the Nobel Prize in Literature.
Mass media
Main article: Mass media in the United States See also: Newspapers in the United States, Television in the United States, Broadcasting in the United States, Public broadcasting in the United States, Internet in the United States, Radio in the United States, and Video games in the United States
Media is broadly uncensored, with the First Amendment providing significant protections, as reiterated in New York Times Co. v. United States. The four major broadcasters in the U.S. are the National Broadcasting Company (NBC), Columbia Broadcasting System (CBS), American Broadcasting Company (ABC), and Fox Broadcasting Company (FOX). The four major broadcast television networks are all commercial entities. Cable television offers hundreds of channels catering to a variety of niches. As of 2021, about 83% of Americans over age 12 listen to broadcast radio, while about 40% listen to podcasts. As of 2020, there were 15,460 licensed full-power radio stations in the U.S. according to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC). Much of the public radio broadcasting is supplied by NPR, incorporated in February 1970 under the Public Broadcasting Act of 1967.
U.S. newspapers with a global reach and reputation include The Wall Street Journal, The New York Times, The Washington Post, and USA Today. About 800 publications are produced in Spanish. With few exceptions, newspapers are privately owned, either by large chains such as Gannett or McClatchy, which own dozens or even hundreds of newspapers; by small chains that own a handful of papers; or, in an increasingly rare situation, by individuals or families. Major cities often have alternative newspapers to complement the mainstream daily papers, such as The Village Voice in New York City and LA Weekly in Los Angeles. The five most popular websites used in the U.S. are Google, YouTube, Amazon, Yahoo, and Facebook—all of them American-owned.
As of 2022, the video game market of the United States is the world's largest by revenue. There are 444 publishers, developers, and hardware companies in California alone.
Theater
Main article: Theater in the United States
The United States is well known for its theater. Mainstream theater in the United States derives from the old European theatrical tradition and has been heavily influenced by the British theater. By the middle of the 19th century America had created new distinct dramatic forms in the Tom Shows, the showboat theater and the minstrel show. The central hub of the American theater scene is the Theater District in Manhattan, with its divisions of Broadway, off-Broadway, and off-off-Broadway.
Many movie and television celebrities have gotten their big break working in New York productions. Outside New York City, many cities have professional regional or resident theater companies that produce their own seasons. The biggest-budget theatrical productions are musicals. U.S. theater has an active community theater culture.
The Tony Awards recognizes excellence in live Broadway theater and are presented at an annual ceremony in Manhattan. The awards are given for Broadway productions and performances. One is also given for regional theater. Several discretionary non-competitive awards are given as well, including a Special Tony Award, the Tony Honors for Excellence in Theatre, and the Isabelle Stevenson Award.
Visual arts
Main articles: Visual art of the United States and Architecture of the United States
Folk art in colonial America grew out of artisanal craftsmanship in communities that allowed commonly trained people to individually express themselves. It was distinct from Europe's tradition of high art, which was less accessible and generally less relevant to early American settlers. Cultural movements in art and craftsmanship in colonial America generally lagged behind those of Western Europe. For example, the prevailing medieval style of woodworking and primitive sculpture became integral to early American folk art, despite the emergence of Renaissance styles in England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. The new English styles would have been early enough to make a considerable impact on American folk art, but American styles and forms had already been firmly adopted. Not only did styles change slowly in early America, but there was a tendency for rural artisans there to continue their traditional forms longer than their urban counterparts did—and far longer than those in Western Europe.
The Hudson River School was a mid-19th-century movement in the visual arts tradition of European naturalism. The 1913 Armory Show in New York City, an exhibition of European modernist art, shocked the public and transformed the U.S. art scene.
Georgia O'Keeffe, Marsden Hartley, and others experimented with new and individualistic styles, which would become known as American modernism. Major artistic movements such as the abstract expressionism of Jackson Pollock and Willem de Kooning and the pop art of Andy Warhol and Roy Lichtenstein developed largely in the United States. Major photographers include Alfred Stieglitz, Edward Steichen, Dorothea Lange, Edward Weston, James Van Der Zee, Ansel Adams, and Gordon Parks.
The tide of modernism and then postmodernism has brought global fame to American architects, including Frank Lloyd Wright, Philip Johnson, and Frank Gehry. The Metropolitan Museum of Art in Manhattan is the largest art museum in the United States and the fourth-largest in the world.
Music
Main article: Music of the United StatesAmerican folk music encompasses numerous music genres, variously known as traditional music, traditional folk music, contemporary folk music, or roots music. Many traditional songs have been sung within the same family or folk group for generations, and sometimes trace back to such origins as the British Isles, mainland Europe, or Africa. The rhythmic and lyrical styles of African-American music in particular have influenced American music. Banjos were brought to America through the slave trade. Minstrel shows incorporating the instrument into their acts led to its increased popularity and widespread production in the 19th century. The electric guitar, first invented in the 1930s, and mass-produced by the 1940s, had an enormous influence on popular music, in particular due to the development of rock and roll.

Elements from folk idioms such as the blues and old-time music were adopted and transformed into popular genres with global audiences. Jazz grew from blues and ragtime in the early 20th century, developing from the innovations and recordings of composers such as W.C. Handy and Jelly Roll Morton. Louis Armstrong and Duke Ellington increased its popularity early in the 20th century. Country music developed in the 1920s, rock and roll in the 1930s, and bluegrass and rhythm and blues in the 1940s. In the 1960s, Bob Dylan emerged from the folk revival to become one of the country's most celebrated songwriters. The musical forms of punk and hip hop both originated in the United States in the 1970s.
The United States has the world's largest music market with a total retail value of $15.9 billion in 2022. Most of the world's major record companies are based in the U.S.; they are represented by the Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA). Mid-20th-century American pop stars, such as Frank Sinatra and Elvis Presley, became global celebrities and best-selling music artists, as have artists of the late 20th century, such as Michael Jackson, Madonna, Whitney Houston, and Prince, and the early 21st century, such as Taylor Swift and Beyoncé.
Fashion
Main article: Fashion in the United States
The United States is the world's largest apparel market by revenue. Apart from professional business attire, American fashion is eclectic and predominantly informal. Americans' diverse cultural roots are reflected in their clothing; however, sneakers, jeans, T-shirts, and baseball caps are emblematic of American styles. New York, with its fashion week, is considered to be one of the "Big Four" global fashion capitals, along with Paris, Milan, and London. A study demonstrated that general proximity to Manhattan's Garment District has been synonymous with American fashion since its inception in the early 20th century.
The headquarters of many designer labels reside in Manhattan. Labels cater to niche markets, such as preteens. New York Fashion Week is one of the most influential fashion weeks in the world, and occurs twice a year; while the annual Met Gala in Manhattan is commonly known as the fashion world's "biggest night".
Cinema
Main article: Cinema of the United States
The U.S. film industry has a worldwide influence and following. Hollywood, a district in northern Los Angeles, the nation's second-most populous city, is also metonymous for the American filmmaking industry. The major film studios of the United States are the primary source of the most commercially successful and most ticket-selling movies in the world. Since the early 20th century, the U.S. film industry has largely been based in and around Hollywood, although in the 21st century an increasing number of films are not made there, and film companies have been subject to the forces of globalization. The Academy Awards, popularly known as the Oscars, have been held annually by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences since 1929, and the Golden Globe Awards have been held annually since January 1944.
The industry peaked in what is commonly referred to as the "Golden Age of Hollywood", from the early sound period until the early 1960s, with screen actors such as John Wayne and Marilyn Monroe becoming iconic figures. In the 1970s, "New Hollywood", or the "Hollywood Renaissance", was defined by grittier films influenced by French and Italian realist pictures of the post-war period. The 21st century has been marked by the rise of American streaming platforms, which came to rival traditional cinema.
Cuisine
Main article: American cuisine Further information: List of American regional and fusion cuisines
Early settlers were introduced by Native Americans to foods such as turkey, sweet potatoes, corn, squash, and maple syrup. Of the most enduring and pervasive examples are variations of the native dish called succotash. Early settlers and later immigrants combined these with foods they were familiar with, such as wheat flour, beef, and milk, to create a distinctive American cuisine. New World crops, especially pumpkin, corn, potatoes, and turkey as the main course are part of a shared national menu on Thanksgiving, when many Americans prepare or purchase traditional dishes to celebrate the occasion.
Characteristic American dishes such as apple pie, fried chicken, doughnuts, french fries, macaroni and cheese, ice cream, hamburgers, hot dogs, and American pizza derive from the recipes of various immigrant groups. Mexican dishes such as burritos and tacos preexisted the United States in areas later annexed from Mexico, and adaptations of Chinese cuisine as well as pasta dishes freely adapted from Italian sources are all widely consumed. American chefs have had a significant impact on society both domestically and internationally. In 1946, the Culinary Institute of America was founded by Katharine Angell and Frances Roth. This would become the United States' most prestigious culinary school, where many of the most talented American chefs would study prior to successful careers.
The United States restaurant industry was projected at $899 billion in sales for 2020, and employed more than 15 million people, representing 10% of the nation's workforce directly. It is the country's second-largest private employer and the third-largest employer overall. The United States is home to over 220 Michelin star-rated restaurants, 70 of which are in New York City alone. Wine has been produced in what is now the United States since the 1500s, with the first widespread production beginning in what is now New Mexico in 1628. In the modern U.S., wine production is undertaken in all fifty states, with California producing 84 percent of all U.S. wine. With more than 1,100,000 acres (4,500 km) under vine, the United States is the fourth-largest wine-producing country in the world, after Italy, Spain, and France.
The American fast-food industry developed alongside the nation's car culture. American restaurants developed the drive-in format in the 1920s, which they began to replace with the drive-through format by the 1940s. American fast-food restaurant chains, such as McDonald's, Kentucky Fried Chicken, Dunkin' Donuts and many others, have numerous outlets around the world.
Sports
Main article: Sports in the United States See also: Professional sports leagues in the United States, National Collegiate Athletic Association, and United States at the Olympics
The most popular spectator sports in the U.S. are American football, basketball, baseball, soccer, and ice hockey. While most major U.S. sports such as baseball and American football have evolved out of European practices, basketball, volleyball, skateboarding, and snowboarding are American inventions, many of which have become popular worldwide. Lacrosse and surfing arose from Native American and Native Hawaiian activities that predate European contact. The market for professional sports in the United States was approximately $69 billion in July 2013, roughly 50% larger than that of all of Europe, the Middle East, and Africa combined.
American football is by several measures the most popular spectator sport in the United States; the National Football League has the highest average attendance of any sports league in the world, and the Super Bowl is watched by tens of millions globally. However, baseball has been regarded as the U.S. "national sport" since the late 19th century. After American football, the next four most popular professional team sports are basketball, baseball, soccer, and ice hockey. Their premier leagues are, respectively, the National Basketball Association, Major League Baseball, Major League Soccer, and the National Hockey League. The most-watched individual sports in the U.S. are golf and auto racing, particularly NASCAR and IndyCar.
On the collegiate level, earnings for the member institutions exceed $1 billion annually, and college football and basketball attract large audiences, as the NCAA March Madness tournament and the College Football Playoff are some of the most watched national sporting events. In the U.S., the intercollegiate sports level serves as a feeder system for professional sports. This differs greatly from practices in nearly all other countries, where publicly and privately funded sports organizations serve this function.
Eight Olympic Games have taken place in the United States. The 1904 Summer Olympics in St. Louis, Missouri, were the first-ever Olympic Games held outside of Europe. The Olympic Games will be held in the U.S. for a ninth time when Los Angeles hosts the 2028 Summer Olympics. U.S. athletes have won a total of 2,968 medals (1,179 gold) at the Olympic Games, the most of any country.
In international professional competition, the U.S. men's national soccer team has qualified for eleven World Cups, while the women's national team has won the FIFA Women's World Cup and Olympic soccer tournament four times each. The United States hosted the 1994 FIFA World Cup and will co-host, along with Canada and Mexico, the 2026 FIFA World Cup. The 1999 FIFA Women's World Cup was also hosted by the United States. Its final match was watched by 90,185, setting the world record for most-attended women's sporting event at the time.
See also
Notes
- Twenty-eight of the 50 states recognize only English as an official language. The State of Hawaii recognizes both Hawaiian and English as official languages, the State of Alaska officially recognizes 20 Alaska Native languages alongside English, and the State of South Dakota recognizes English and all Sioux dialects as official languages. Nineteen states and the District of Columbia have no official language.
- English is the de facto language. For more information, see Languages of the United States.
- The historical and informal demonym Yankee has been applied to Americans, New Englanders, or northeasterners since the 18th century.
- ^ At 3,531,900 sq mi (9,147,590 km), the United States is the third-largest country in the world by land area, behind Russia and China. By total area (land and water), it is the third-largest, behind Russia and Canada, if its coastal and territorial water areas are included. However, if only its internal waters are included (bays, sounds, rivers, lakes, and the Great Lakes), the U.S. is the fourth-largest, after Russia, Canada, and China.
Coastal/territorial waters included: 3,796,742 sq mi (9,833,517 km)
Only internal waters included: 3,696,100 sq mi (9,572,900 km) - Excludes Puerto Rico and the other unincorporated islands because they are counted separately in U.S. census statistics
- After adjustment for taxes and transfers
- See Time in the United States for details about laws governing time zones in the United States.
- See Date and time notation in the United States.
- The U.S. Virgin Islands use left-hand traffic.
- The five major territories outside the union of states are American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. The seven undisputed island areas without permanent populations are Baker Island, Howland Island, Jarvis Island, Johnston Atoll, Kingman Reef, Midway Atoll, and Palmyra Atoll. U.S. sovereignty over the unpopulated Bajo Nuevo Bank, Navassa Island, Serranilla Bank, and Wake Island is disputed.
- The U.S. Census Bureau's latest official population estimate of 340,110,988 residents (2024) is for the 50 states and the District of Columbia; it excludes the 3.6 million residents of the five major U.S. territories and outlying islands. The Census Bureau also provides a continuously updated but unofficial population clock: www.census.gov/popclock
- Based on purchasing power
- Including agencies such as the International Monetary Fund and the World Health Organization
- The official U.S. Government Publishing Office Style Manual has prescribed specific usages for "U.S." and "United States" as part of official names. In "formal writing (treaties, Executive orders, proclamations, etc.); congressional bills; legal citations and courtwork; and covers and title pages", "United States" is always used. In a sentence containing the name of another country, "United States" must be used. Otherwise, "U.S." is used preceding a government organization or as an adjective, but "United States" is used as an adjective preceding non-governmental organizations (e.g. United States Steel Corporation).
- From the late 15th century, the Columbian exchange had been catastrophic for native populations throughout the Americas. It is estimated that up to 95 percent of the indigenous populations, especially in the Caribbean, perished from infectious diseases during the years following European colonization; remaining populations were often displaced by European expansion.
- New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Connecticut, Rhode Island, New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia
- Per the U.S. Constitution, Amendment Twenty-three, proposed by the U.S. Congress on June 16, 1960, and ratified by the States on March 29, 1961
- A country's total exports are usually understood to be goods and services. Based on this, the U.S. is the world's second-largest exporter, after China. However, if primary income is included, the U.S. is the world's largest exporter.
- These population figures are official 2024 annual estimates (rounded off) from the U.S. Census Bureau.
- This figure, like most official data for the United States as a whole, excludes the five unincorporated territories (Puerto Rico, Guam, the U.S. Virgin Islands, American Samoa, and the Northern Mariana Islands) and minor island possessions.
- Inupiaq, Siberian Yupik, Central Alaskan Yup'ik, Alutiiq, Unanga (Aleut), Denaʼina, Deg Xinag, Holikachuk, Koyukon, Upper Kuskokwim, Gwichʼin, Tanana, Upper Tanana, Tanacross, Hän, Ahtna, Eyak, Tlingit, Haida, and Tsimshian
- Also known less formally as Obamacare
References
- 36 U.S.C. § 302
- "The Great Seal of the United States" (PDF). U.S. Department of State, Bureau of Public Affairs. 2003. Retrieved February 12, 2020.
- An Act To make The Star-Spangled Banner the national anthem of the United States of America (H.R. 14). 71st United States Congress. March 3, 1931.
- "2020 Census Illuminates Racial and Ethnic Composition of the Country". United States Census. Retrieved August 13, 2021.
- "Race and Ethnicity in the United States: 2010 Census and 2020 Census". United States Census. Retrieved August 13, 2021.
- "A Breakdown of 2020 Census Demographic Data". NPR. August 13, 2021.
- ^ Staff (June 8, 2007). "In Depth: Topics A to Z (Religion)". Gallup, Inc. Retrieved July 1, 2024.
- Compton's Pictured Encyclopedia and Fact-index: Ohio. 1963. p. 336.
- "The Water Area of Each State". United States Geological Survey. 2018. Retrieved January 29, 2024.
- ^ Areas of the 50 states and the District of Columbia but not Puerto Rico nor other island territories per "State Area Measurements and Internal Point Coordinates". Census.gov. August 2010. Retrieved March 31, 2020.
reflect base feature updates made in the MAF/TIGER database through August, 2010.
- "National Population Totals and Components of Change: April 1, 2020 to July 1, 2024". www.census.gov. United States Census Bureau (USCB). Retrieved December 20, 2024.
- "U.S. Census Bureau Today Delivers State Population Totals for Congressional Apportionment". United States Census. Retrieved April 26, 2021. The 2020 census is as of April 1, 2020.
- ^ "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2024 Edition. (United States)". www.imf.org. International Monetary Fund. October 22, 2024. Retrieved October 22, 2024.
- "Income in the United States: 2023". Census.gov. p. 53. Retrieved December 15, 2024.
- "Human Development Report 2023/24" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. March 13, 2024. Retrieved March 13, 2024.
- "The Difference Between .us vs .com". Cozab. January 3, 2022. Archived from the original on April 16, 2023. Retrieved August 11, 2023.
- ^
- "Common Core Document to U.N. Committee on Human Rights". U.S. State Department. December 30, 2011. Item 22, 27, 80. Retrieved April 6, 2016.
- "U.S. Insular Areas: application of the U.S. Constitution" (PDF). U.S. General Accounting Office Report. November 1997. pp. 1, 6, 39n. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 3, 2013. Retrieved April 6, 2016.
- "China". The World Factbook. Retrieved June 10, 2016.
- "United States". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on December 19, 2013. Retrieved January 31, 2010.
- ^ DeLear, Byron (July 4, 2013). "Who coined 'United States of America'? Mystery might have intriguing answer". The Christian Science Monitor. Boston, Massachusetts.
- Fay, John (July 15, 2016). "The forgotten Irishman who named the 'United States of America'". IrishCentral.com.
According to the NY Historical Society, Stephen Moylan was the man responsible for the earliest documented use of the phrase 'United States of America'. But who was Stephen Moylan?
- A PLANTER (April 6, 1776). "To the inhabitants of Virginia". The Virginia Gazette. Vol. 5, no. 1287. Williamsburg, Virginia: Dixon and Hunter's. Archived from the original on December 19, 2014.
- "A Planter' s Address to the Inhabitants of Virginia". American Archives. Northern Illinois University. Retrieved May 25, 2024.
- ^ Safire 2003, p. 199.
- Mostert 2005, p. 18.
- Davis 1996, p. 7.
- "Is USA A Noun Or Adjective?". Dictionary.com. March 9, 2017.
- ^ U.S. Government Publishing Office Style Manual. January 12, 2017. pp. 222–223. Retrieved September 3, 2020.
- Wilson, Kenneth G. (1993). The Columbia guide to standard American English. New York: Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-06989-2.
- ""The States"". Longman dictionary. Retrieved September 27, 2024.
- "Definition of STATESIDE". www.merriam-webster.com. September 27, 2024. Retrieved October 4, 2024.
- Sider, Sandra (2007). Handbook to Life in Renaissance Europe. Oxford University Press. p. 226. ISBN 978-0-19-533084-7.
- Szalay, Jessie (September 20, 2017). "Amerigo Vespucci: Facts, Biography & Naming of America". Live Science. Retrieved June 23, 2019.
- Allen, Erin (July 4, 2016). "How Did America Get Its Name?". Library of Congress Blog. Retrieved September 3, 2020.
- "Cliff Palace" at Colorado Encyclopedia. Retrieved January 31, 2024
- Erlandson, Rick & Vellanoweth 2008, p. 19.
- Savage 2011, p. 55.
- Waters & Stafford 2007, pp. 1122–1126.
- Flannery 2015, pp. 173–185.
- Lockard 2010, p. 315.
- Johansen, Bruce (2006). The Native Peoples of North America: A History, Volume 1. Rutgers University Press. ISBN 978-0-8135-3899-0.
- Thornton 1998, p. 34.
- ^ Perdue & Green 2005, p. 40.
- Haines, Haines & Steckel 2000, p. 12.
- Davis, Frederick T. (1932). "The Record of Ponce de Leon's Discovery of Florida, 1513". The QUARTERLY Periodical of THE FLORIDA HISTORICAL SOCIETY. XI (1): 5–6.
- Florida Center for Instructional Technology (2002). "Pedro Menendez de Aviles Claims Florida for Spain". A Short History of Florida. University of South Florida.
- "Not So Fast, Jamestown: St. Augustine Was Here First". NPR. February 28, 2015. Retrieved March 5, 2021.
- Petto, Christine Marie (2007). When France Was King of Cartography: The Patronage and Production of Maps in Early Modern France. Lexington Books. p. 125. ISBN 978-0-7391-6247-7.
- Seelye, James E. Jr.; Selby, Shawn (2018). Shaping North America: From Exploration to the American Revolution [3 volumes]. ABC-CLIO. p. 344. ISBN 978-1-4408-3669-5.
- Bellah, Robert Neelly; Madsen, Richard; Sullivan, William M.; Swidler, Ann; Tipton, Steven M. (1985). Habits of the Heart: Individualism and Commitment in American Life. University of California Press. p. 220. ISBN 978-0-520-05388-5. OL 7708974M.
- Remini 2007, pp. 2–3
- Johnson 1997, pp. 26–30
- Ripper, 2008, p. 6
- Ehrenpreis, Jamie E.; Ehrenpreis, Eli D. (April 2022). "A Historical Perspective of Healthcare Disparity and Infectious Disease in the Native American Population". The American Journal of the Medical Sciences. 363 (4): 288–294. doi:10.1016/j.amjms.2022.01.005. ISSN 0002-9629. PMC 8785365. PMID 35085528.
- Joseph 2016, p. 590.
- Stannard, 1993 p. xii
- Ripper, 2008 p. 5
- Calloway, 1998, p. 55
- Thomas, Hugh (1997). The Slave Trade: The Story of the Atlantic Slave Trade: 1440–1870. Simon and Schuster. pp. 516. ISBN 0-684-83565-7.
- Bilhartz, Terry D.; Elliott, Alan C. (2007). Currents in American History: A Brief History of the United States. M.E. Sharpe. ISBN 978-0-7656-1817-7.
- Wood, Gordon S. (1998). The Creation of the American Republic, 1776–1787. UNC Press Books. p. 263. ISBN 978-0-8078-4723-7.
- Ratcliffe, Donald (2013). "The Right to Vote and the Rise of Democracy, 1787–1828". Journal of the Early Republic. 33 (2): 220. doi:10.1353/jer.2013.0033. ISSN 0275-1275. S2CID 145135025.
- Walton, 2009, pp. 38–39
- Walton, 2009, p. 35
- Otis, James (1763). The Rights of the British Colonies Asserted and Proved. ISBN 978-0-665-52678-7.
- Foner, Eric (1998). The Story of American Freedom (1st ed.). W.W. Norton. pp. 4–5. ISBN 978-0-393-04665-6.
story of American freedom.
- ^ Fabian Young, Alfred; Nash, Gary B.; Raphael, Ray (2011). Revolutionary Founders: Rebels, Radicals, and Reformers in the Making of the Nation. Random House Digital. pp. 4–7. ISBN 978-0-307-27110-5.
- Yick Wo vs. Hopkins, 118 U.S. 356, 370
- Richard Buel, Securing the Revolution: Ideology in American Politics, 1789–1815 (1972)
- Becker et al (2002), ch 1
- "Republicanism". Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. June 19, 2006. Retrieved September 20, 2022.
- Miller, Hunter (ed.). "British-American Diplomacy: The Paris Peace Treaty of September 30, 1783". The Avalon Project at Yale Law School.
- Shōsuke Satō, History of the land question in the United States, Johns Hopkins University, (1886), p. 352
- Foner 2020, p. 524.
- OpenStax 2014, § 8.1.
- Foner 2020, pp. 538–540.
- Boyer, 2007, pp. 192–193
- OpenStax 2014, § 8.3.
- "Louisiana Purchase" (PDF). National Park Service. Retrieved March 1, 2011.
- Harriss, Joseph A. "How the Louisiana Purchase Changed the World". Smithsonian Magazine. Retrieved June 25, 2024.
- Wait, Eugene M. (1999). America and the War of 1812. Nova Publishers. p. 78. ISBN 978-1-56072-644-9.
- "War of 1812". Naval History and Heritage Command. April 10, 2024. Retrieved June 25, 2024.
- Klose, Nelson; Jones, Robert F. (1994). United States History to 1877. Barron's Educational Series. p. 150. ISBN 978-0-8120-1834-9.
- ^ Carlisle, Rodney P.; Golson, J. Geoffrey (2007). Manifest destiny and the expansion of America. Turning Points in History Series. Santa Barbara, Calif.: ABC-CLIO. p. 238. ISBN 978-1-85109-834-7. OCLC 659807062.
- McPherson 1988, p. 41–46.
- Hammond, John Craig (March 2019). "President, Planter, Politician: James Monroe, the Missouri Crisis, and the Politics of Slavery". Journal of American History. 105 (4): 843–867. doi:10.1093/jahist/jaz002.
- Frymer, Paul (2017). Building an American empire : the era of territorial and political expansion. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-1-4008-8535-0. OCLC 981954623.
- Calloway, Colin G. (2019). First peoples : a documentary survey of American Indian history (6th ed.). Boston: Bedford/St. Martin's, Macmillan Learning. ISBN 978-1-319-10491-7. OCLC 1035393060.
- McPherson 1988, p. 45.
- Michno, Gregory (2003). Encyclopedia of Indian Wars: Western Battles and Skirmishes, 1850–1890. Mountain Press Publishing. ISBN 978-0-87842-468-9.
- Billington, Ray Allen; Ridge, Martin (2001). Westward Expansion: A History of the American Frontier. UNM Press. p. 22. ISBN 978-0-8263-1981-4.
- Morrison, Michael A. (April 28, 1997). Slavery and the American West: The Eclipse of Manifest Destiny and the Coming of the Civil War. University of North Carolina Press. pp. 13–21. ISBN 978-0-8078-4796-1.
- Kemp, Roger L. (2010). Documents of American Democracy: A Collection of Essential Works. McFarland. p. 180. ISBN 978-0-7864-4210-2. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- McIlwraith, Thomas F.; Muller, Edward K. (2001). North America: The Historical Geography of a Changing Continent. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 61. ISBN 978-0-7425-0019-8. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
-
- Meyer et al. 2001, From 1800 to 1900: "The discovery of gold in California in 1848 proved a momentous watershed for native people in the West. Hordes of single men stampeded to find fortune. Unrestrained by family, community, or church, they decimated the native population near the goldfields. California natives suffered the most complete genocide in U.S. history."
- Wolf, Jessica. "Revealing the history of genocide against California's Native Americans". UCLA Newsroom. Retrieved July 8, 2018.
- Madley, Benjamin (2016). An American Genocide: The United States and the California Indian Catastrophe, 1846-1873. Yale University Press. ISBN 9780300230697.
- Smithers 2012, p. 339: "The genocidal intent of California settlers and government officials was acted out in numerous battles and massacres (and aided by technological advances in weaponry, especially after the Civil War), in the abduction and sexual abuse of Indian women, and in the economic exploitation of Indian child labourers"
- Blackhawk 2023, p. 38: "With these works, a near consensus emerged. By most scholarly definitions and consistent with the UN Convention, these scholars all asserted that genocide against at least some Indigenous peoples had occurred in North America following colonisation, perpetuated first by colonial empires and then by independent nation-states"
- Rawls, James J. (1999). A Golden State: Mining and Economic Development in Gold Rush California. University of California Press. p. 20. ISBN 978-0-520-21771-3.
- Walker Howe 2007, p. 52–54; Wright 2022.
- Walker Howe 2007, p. 52–54; Rodriguez 2015, p. XXXIV; Wright 2022.
- Walton, 2009, p. 43
- Gordon, 2004, pp. 27, 29
- Walker Howe 2007, p. 478, 481–482, 587–588.
- Murray, Stuart (2004). Atlas of American Military History. Infobase Publishing. p. 76. ISBN 978-1-4381-3025-5. Retrieved October 25, 2015. Lewis, Harold T. (2001). Christian Social Witness. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 53. ISBN 978-1-56101-188-9.
- Woods, Michael E. (2012). "What Twenty-First-Century Historians Have Said about the Causes of Disunion: A Civil War Sesquicentennial Review of the Recent Literature". The Journal of American History. 99 (2). : 415–439. doi:10.1093/jahist/jas272. ISSN 0021-8723. JSTOR 44306803. Retrieved April 29, 2023.
- Silkenat, D. (2019). Raising the White Flag: How Surrender Defined the American Civil War. Civil War America. University of North Carolina Press. p. 25. ISBN 978-1-4696-4973-3. Retrieved April 29, 2023.
- McPherson 1988, p. 236.
- Vinovskis, Maris (1990). Toward A Social History of the American Civil War: Exploratory Essays. Cambridge; New York: Cambridge University Press. p. 4. ISBN 978-0-521-39559-5.
- McPherson 1988, pp. 273–274.
- "The Fight for Equal Rights: Black Soldiers in the Civil War". U.S. National Archives and Records Administration. August 15, 2016.
By the end of the Civil War, roughly 179,000 black men (10% of the Union army) served as soldiers in the U.S. Army and another 19,000 served in the Navy.
- Davis, Jefferson. A Short History of the Confederate States of America, 1890, 2010. ISBN 978-1-175-82358-8. Available free online as an ebook. Chapter LXXXVIII, "Re-establishment of the Union by force", p. 503. Retrieved March 14, 2012.
- Black, Jeremy (2011). Fighting for America: The Struggle for Mastery in North America, 1519–1871. Indiana University Press. p. 275. ISBN 978-0-253-35660-4.
- Price, Marie; Benton-Short, Lisa (2008). Migrants to the Metropolis: The Rise of Immigrant Gateway Cities. Syracuse University Press. p. 51. ISBN 978-0-8156-3186-6.
- "Overview + History | Ellis Island". Statue of Liberty & Ellis Island. March 4, 2020. Retrieved September 10, 2021.
- U.S. Bureau of the Census, Historical Statistics of the United States (1976) series C89–C119, pp. 105–109
- Stephan Thernstrom, ed., Harvard Encyclopedia of American Ethnic Groups (1980) covers the history of all the main groups
- "The Great Migration (1910–1970)". National Archives. May 20, 2021.
- "Purchase of Alaska, 1867". Office of the Historian. U.S. Department of State. Retrieved December 23, 2014.
- Woodward, C. Vann (1991). Reunion and Reaction: The Compromise of 1877 and the End of Reconstruction. United Kingdom: Oxford University Press.
- Drew Gilpin Faust; Eric Foner; Clarence E. Walker. "White Southern Responses to Black Emancipation". American Experience.
- Trelease, Allen W. (1979). White Terror: The Ku Klux Klan Conspiracy and Southern Reconstruction. New York: Harper & Row. ISBN 0-313-21168-X.
- Shearer Davis Bowman (1993). Masters and Lords: Mid-19th-Century U.S. Planters and Prussian Junkers. Oxford UP. p. 221. ISBN 978-0-19-536394-4.
- Ware, Leland (February 2021). "Plessy's Legacy: The Government's Role in the Development and Perpetuation of Segregated Neighborhoods". RSF: The Russell Sage Foundation Journal of the Social Sciences. 7 (1): 92–109. doi:10.7758/rsf.2021.7.1.06. S2CID 231929202.
- Hirschman, Charles; Mogford, Elizabeth (December 1, 2009). "Immigration and the American Industrial Revolution From 1880 to 1920". Social Science Research. 38 (4): 897–920. doi:10.1016/j.ssresearch.2009.04.001. ISSN 0049-089X. PMC 2760060. PMID 20160966.
- Carson, Thomas; Bonk, Mary (1999). "Industrial Revolution". Gale Encyclopedia of U.S. Economic History. Gale.
- Riggs, Thomas (2015). Gale Encyclopedia of U.S. Economic History Vol. 3 (2 ed.). Gale. p. 1179.
- Dole, Charles F. (1907). "The Ethics of Speculation". The Atlantic Monthly. C (December 1907): 812–818.
- The Pit Boss (February 26, 2021). "The Pit Stop: The American Automotive Industry Is Packed With History". Rumble On. Retrieved December 5, 2021.
- Tindall, George Brown and Shi, David E. (2012). America: A Narrative History (Brief Ninth Edition) (Vol. 2). W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 978-0-393-91267-8, p. 589
- Zinn, 2005, pp. 321–357
- Fraser, Steve (2015). The Age of Acquiescence: The Life and Death of American Resistance to Organized Wealth and Power. Little, Brown and Company. p. 66. ISBN 978-0-316-18543-1.
- Aldrich, Mark. Safety First: Technology, Labor and Business in the Building of Work Safety, 1870-1939. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 1997. ISBN 0-8018-5405-9
- "Progressive Era to New Era, 1900-1929 | U.S. History Primary Source Timeline | Classroom Materials at the Library of Congress | Library of Congress". Library of Congress, Washington, D.C. 20540 USA. Retrieved November 11, 2023.
- "The Spanish–American War, 1898". Office of the Historian. U.S. Department of State. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- Ryden, George Herbert. The Foreign Policy of the United States in Relation to Samoa. New York: Octagon Books, 1975.
- "Virgin Islands History". Vinow.com. Retrieved January 5, 2018.
- McDuffie, Jerome; Piggrem, Gary Wayne; Woodworth, Steven E. (2005). U.S. History Super Review. Piscataway, NJ: Research & Education Association. p. 418. ISBN 978-0-7386-0070-3.
- Larson, Elizabeth C.; Meltvedt, Kristi R. (2021). "Women's suffrage: fact sheet". CRS Reports (Library of Congress. Congressional Research Service). Report / Congressional Research Service. Retrieved August 9, 2023.
- Winchester 2013, pp. 410–411.
- Axinn, June; Stern, Mark J. (2007). Social Welfare: A History of the American Response to Need (7th ed.). Boston: Allyn & Bacon. ISBN 978-0-205-52215-6.
- James Noble Gregory (1991). American Exodus: The Dust Bowl Migration and Okie Culture in California. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-507136-8. Retrieved October 25, 2015. "Mass Exodus From the Plains". American Experience. WGBH Educational Foundation. 2013. Retrieved October 5, 2014. Fanslow, Robin A. (April 6, 1997). "The Migrant Experience". American Folklore Center. Library of Congress. Retrieved October 5, 2014. Stein, Walter J. (1973). California and the Dust Bowl Migration. Greenwood Press. ISBN 978-0-8371-6267-6. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- The official WRA record from 1946 states that it was 120,000 people. See War Relocation Authority (1946). The Evacuated People: A Quantitative Study. p. 8. This number does not include people held in other camps such as those run by the DoJ or U.S. Army. Other sources may give numbers slightly more or less than 120,000.
- Yamasaki, Mitch. "Pearl Harbor and America's Entry into World War II: A Documentary History" (PDF). World War II Internment in Hawaii. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 13, 2014. Retrieved January 14, 2015.
- "Why did Japan surrender in World War II?". The Japan Times. Retrieved February 8, 2017.
- Pacific War Research Society (2006). Japan's Longest Day. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-4-7700-2887-7.
- Hoopes & Brinkley 1997, p. 100.
- Gaddis 1972, p. 25.
- Kennedy, Paul (1989). The Rise and Fall of the Great Powers. New York: Vintage. p. 358. ISBN 978-0-679-72019-5
- Blakemore, Erin (March 22, 2019). "What was the Cold War?". National Geographic. Archived from the original on April 1, 2019. Retrieved August 28, 2020.
- Mark Kramer, "The Soviet Bloc and the Cold War in Europe," in Larresm, Klaus, ed. (2014). A Companion to Europe Since 1945. Wiley. p. 79. ISBN 978-1-118-89024-0.
- Sempa, Francis (July 12, 2017). Geopolitics: From the Cold War to the 21st Century. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-351-51768-3.
- Blakeley, 2009, p. 92
- Collins, Michael (1988). Liftoff: The Story of America's Adventure in Space. New York: Grove Press. ISBN 978-0-8021-1011-4.
- Winchester 2013, pp. 305–308.
- "The Civil Rights Movement". PBS. Retrieved January 5, 2019.
- Brinkley, Alan (January 24, 1991). "Great Society". In Eric Foner; John Arthur Garraty (eds.). The Reader's Companion to American History. Houghton Mifflin Books. p. 472. ISBN 0-395-51372-3.
- "Playboy: American Magazine". Encyclopædia Britannica. August 25, 2022. Retrieved February 2, 2023.
...the so-called sexual revolution in the United States in the 1960s, marked by greatly more permissive attitudes toward sexual interest and activity than had been prevalent in earlier generations.
- Svetlana Ter-Grigoryan (February 12, 2022). "The Sexual Revolution Origins and Impact". study.com. Retrieved April 27, 2023.
- Levy, Daniel (January 19, 2018). "Behind the Protests Against the Vietnam War in 1968". Time. Retrieved May 5, 2021.
- "Women in the Labor Force: A Databook" (PDF). U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. 2013. p. 11. Retrieved March 21, 2014.
- Gaĭdar, E.T. (2007). Collapse of an Empire: Lessons for Modern Russia. Washington, D.C.: Brookings Institution Press. pp. 190–205. ISBN 978-0-8157-3114-6.
- Howell, Buddy Wayne (2006). The Rhetoric of Presidential Summit Diplomacy: Ronald Reagan and the U.S.-Soviet Summits, 1985–1988. Texas A&M University. p. 352. ISBN 978-0-549-41658-6.
- Kissinger, Henry (2011). Diplomacy. Simon & Schuster. pp. 781–784. ISBN 978-1-4391-2631-8. Retrieved October 25, 2015. Mann, James (2009). The Rebellion of Ronald Reagan: A History of the End of the Cold War. Penguin. p. 432. ISBN 978-1-4406-8639-9.
- Hayes, 2009
- CFI Team. "NASDAQ". Corporate Finance Institute. Archived from the original on December 11, 2023. Retrieved December 11, 2023.
- Holsti, Ole R. (November 7, 2011). "The United States and Iraq before the Iraq War". American Public Opinion on the Iraq War. University of Michigan Press. p. 20. ISBN 978-0-472-03480-2.
- Walsh, Kenneth T. (December 9, 2008). "The 'War on Terror' Is Critical to President George W. Bush's Legacy". U.S. News & World Report. Retrieved March 6, 2013. Atkins, Stephen E. (2011). The 9/11 Encyclopedia: Second Edition. ABC-CLIO. p. 872. ISBN 978-1-59884-921-9. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- Wong, Edward (February 15, 2008). "Overview: The Iraq War". The New York Times. Retrieved March 7, 2013. Johnson, James Turner (2005). The War to Oust Saddam Hussein: Just War and the New Face of Conflict. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 159. ISBN 978-0-7425-4956-2. Retrieved October 25, 2015. Durando, Jessica; Green, Shannon Rae (December 21, 2011). "Timeline: Key moments in the Iraq War". USA Today. Associated Press. Archived from the original on September 4, 2020. Retrieved March 7, 2013.
- Hilsenrath, Jon; Ng, Serena; Paletta, Damian (September 18, 2008). "Worst Crisis Since '30s, With No End Yet in Sight". The Wall Street Journal. ISSN 1042-9840. OCLC 781541372. Archived from the original on December 25, 2014. Retrieved July 28, 2023.
- Geiger, Abigail (June 12, 2014). "Political Polarization in the American Public". Pew Research Center. Retrieved June 30, 2024.
- Murray, Mark; Marquez, Alexandra (June 15, 2023). "Here's what's driving America's increasing political polarization". NBC News. Retrieved June 30, 2024.
- Hamid, Shadi (January 8, 2022). "The Forever Culture War". The Atlantic. Retrieved October 1, 2023.
- Kleinfeld, Rachel (September 5, 2023). "Polarization, Democracy, and Political Violence in the United States: What the Research Says". Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. Retrieved September 13, 2024.
- Pape, Robert (January 5, 2022). "American Face of Insurrection: Analysis of Individuals Charged for Storming the US Capitol on January 6, 2021". cpost.uchicago.edu. University of Chicago, Chicago Project on Security and Threats. Retrieved September 13, 2024.
- Rutenberg, Jim; Becker, Jo; Lipton, Eric; Haberman, Maggie; Martin, Jonathan; Rosenberg, Matthew; Schmidt, Michael S. (January 31, 2021). "77 Days: Trump's Campaign to Subvert the Election". The New York Times. Archived from the original on June 18, 2022.
-
- Harvey, Michael (2022). "Introduction: History's Rhymes". In Harvey, Michael (ed.). Donald Trump in Historical Perspective. Routledge. doi:10.4324/9781003110361-1. ISBN 978-1-003-11036-1.
As with the Beer Hall Putsch, a would-be leader tried to take advantage of an already scheduled event (in Hitler's case, Kahr's speech; in Trump's, Congress's tallying of the electoral votes) to create a dramatic moment with himself at the center of attention, calling for bold action to upend the political order. Unlike Hitler's coup attempt, Trump already held top of office, so he was attempting to hold onto power, not seize it (the precise term for Trump's intended action is a 'self-coup' or 'autogolpe'). Thus, Trump was able to plan for the event well in advance, and with much greater control, including developing the legal arguments that could be used to justify rejecting the election's results. (p. 3)
- Pion-Berlin, David; Bruneau, Thomas; Goetze, Richard B. Jr. (April 7, 2022). "The Trump self-coup attempt: comparisons and civil–military relations". Government and Opposition. FirstView (4): 789–806. doi:10.1017/gov.2022.13. S2CID 248033246.
- Castañeda, Ernesto; Jenks, Daniel (April 17, 2023). Costa, Bruno Ferreira; Parton, Nigel (eds.). "January 6th and De-Democratization in the United States". Social Sciences. 12 (4). MDPI: 238. doi:10.3390/socsci12040238. ISSN 2076-0760.
What the United States went through on January 6th was an attempt at a self-coup, where Trump would use force to stay as head of state even if abandoning democratic practices in the U.S. Some advised Trump to declare martial law to create a state of emergency and use that as an excuse to stay in power.
- Eisen, Norman; Ayer, Donald; Perry, Joshua; Bookbinder, Noah; Perry, E. Danya (June 6, 2022). Trump on Trial: A Guide to the January 6 Hearings and the Question of Criminality (Report). Brookings Institution. Retrieved December 16, 2023.
tried to delegitimize the election results by disseminating a series of far fetched and evidence-free claims of fraud. Meanwhile, with a ring of close confidants, Trump conceived and implemented unprecedented schemes to – in his own words – "overturn" the election outcome. Among the results of this "Big Lie" campaign were the terrible events of January 6, 2021 – an inflection point in what we now understand was nothing less than an attempted coup.
- Eastman v Thompson, et al., 8:22-cv-00099-DOC-DFM Document 260, 44 (S.D. Cal. May 28, 2022) ("Dr. Eastman and President Trump launched a campaign to overturn a democratic election, an action unprecedented in American history. Their campaign was not confined to the ivory tower – it was a coup in search of a legal theory. The plan spurred violent attacks on the seat of our nation's government, led to the deaths of several law enforcement officers, and deepened public distrust in our political process... If Dr. Eastman and President Trump's plan had worked, it would have permanently ended the peaceful transition of power, undermining American democracy and the Constitution. If the country does not commit to investigating and pursuing accountability for those responsible, the Court fears January 6 will repeat itself.").
- Graham, David A. (January 6, 2021). "This Is a Coup". The Atlantic. Archived from the original on January 6, 2021. Retrieved December 16, 2023.
- Musgrave, Paul (January 6, 2021). "This Is a Coup. Why Were Experts So Reluctant to See It Coming?". Foreign Policy. Archived from the original on January 6, 2021. Retrieved December 16, 2023.
- Solnit, Rebecca (January 6, 2021). "Call it what it was: a coup attempt". The Guardian. Archived from the original on January 7, 2021. Retrieved December 16, 2023.
- Coleman, Justine (January 6, 2021). "GOP lawmaker on violence at Capitol: 'This is a coup attempt'". The Hill. Archived from the original on January 6, 2021. Retrieved December 16, 2023.
- Jacobson, Louis (January 6, 2021). "Is this a coup? Here's some history and context to help you decide". PolitiFact. Retrieved January 7, 2021.
A good case can be made that the storming of the Capitol qualifies as a coup. It's especially so because the rioters entered at precisely the moment when the incumbent's loss was to be formally sealed, and they succeeded in stopping the count.
- Barry, Dan; Frenkel, Sheera (January 7, 2021). "'Be There. Will Be Wild!': Trump All but Circled the Date". The New York Times. Archived from the original on December 28, 2021. Retrieved December 16, 2023.
- Duignan, Brian (August 4, 2021). "January 6 U.S. Capitol attack". Encyclopædia Britannica. Archived from the original on January 17, 2023. Retrieved September 22, 2021.
Because its object was to prevent a legitimate president-elect from assuming office, the attack was widely regarded as an insurrection or attempted coup d'état.
- Harvey, Michael (2022). "Introduction: History's Rhymes". In Harvey, Michael (ed.). Donald Trump in Historical Perspective. Routledge. doi:10.4324/9781003110361-1. ISBN 978-1-003-11036-1.
- ^ "The World Factbook: United States". Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved November 10, 2018.
- "Area". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Archived from the original on January 31, 2014. Retrieved January 15, 2015.
- "Field Listing: Area". The World Factbook. cia.gov. Archived from the original on July 7, 2020. Retrieved April 21, 2020.
- "State Area Measurements and Internal Point Coordinates—Geography—U.S. Census Bureau". State Area Measurements and Internal Point Coordinates. U.S. Department of Commerce. Retrieved September 11, 2017.
- "Geographic Regions of Georgia". Georgia Info. Digital Library of Georgia. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- ^ Lew, Alan. "PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY OF THE US". GSP 220—Geography of the United States. North Arizona University. Archived from the original on April 9, 2016. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- Harms, Nicole. "Facts About the Rocky Mountain Range". USA Today. Archived from the original on February 12, 2022. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- Tinkham, Ernest R. (March 1944). "Biological, Taxonomic and Faunistic Studies on the Shield-Back Katydids of the North American Deserts". The American Midland Naturalist. 31 (2). The University of Notre Dame: 257–328. doi:10.2307/2421073. JSTOR 2421073.
- "Mount Whitney, California". Peakbagger. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- "Find Distance and Azimuths Between 2 Sets of Coordinates (Badwater 36-15-01-N, 116-49-33-W and Mount Whitney 36-34-43-N, 118-17-31-W)". Federal Communications Commission. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- Poppick, Laura (August 28, 2013). "US Tallest Mountain's Surprising Location Explained". LiveScience. Retrieved May 2, 2015.
- O'Hanlon, Larry (March 14, 2005). "America's Explosive Park". Discovery Channel. Archived from the original on March 14, 2005. Retrieved April 5, 2016.
- World Food and Agriculture – Statistical Yearbook 2023. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2023. doi:10.4060/cc8166en. ISBN 978-92-5-138262-2. Retrieved December 13, 2023.
- Boyden, Jennifer. "Climate Regions of the United States". USA Today. Archived from the original on February 12, 2022. Retrieved December 24, 2014.
- McGranahan, Devan Allen; Wonkka, Carissa L. (2024). "Pyrogeography of the Western Great Plains: A 40-Year History of Fire in Semi-Arid Rangelands". Fire. 7 (1): 32.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "World Map of Köppen–Geiger Climate Classification" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on January 26, 2022. Retrieved August 19, 2015.
- Perkins, Sid (May 11, 2002). "Tornado Alley, USA". Science News. Archived from the original on July 1, 2007. Retrieved September 20, 2006.
- Rice, Doyle. "USA has the world's most extreme weather". USA Today. Retrieved May 17, 2020.
- Borenstein, Seth (April 2, 2023). "Why the U.S. is leading the world in extreme weather catastrophes". PBS News. Retrieved June 25, 2024.
- US EPA, OAR (June 27, 2016). "Climate Change Indicators: Weather and Climate". Epa.gov. Retrieved June 19, 2022.
- Waldron, Lucas; Lustgarten, Abrahm (November 10, 2020). "Climate Change Will Make Parts of the U.S. Uninhabitable. Americans Are Still Moving There". Propublica. Rhodium Group. Retrieved November 25, 2024.
- McDougall, Len (2004). The Encyclopedia of Tracks and Scats: A Comprehensive Guide to the Trackable Animals of the United States and Canada. Lyons Press. p. 325. ISBN 978-1-59228-070-4.
- Morin, Nancy. "Vascular Plants of the United States" (PDF). Plants. National Biological Service. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 24, 2013. Retrieved October 27, 2008.
- Osborn, Liz. "Number of Native Species in United States". Current Results Nexus. Retrieved January 15, 2015.
- "Numbers of Insects (Species and Individuals)". Smithsonian Institution. Retrieved January 20, 2009.
- "National Park FAQ". nps. National Park Service. Retrieved May 8, 2015.
- Lipton, Eric; Krauss, Clifford (August 23, 2012). "Giving Reins to the States Over Drilling". The New York Times. Retrieved January 18, 2015.
- Vincent, Carol H.; Hanson, Laura A.; Argueta, Carla N. (March 3, 2017). Federal Land Ownership: Overview and Data (Report). Congressional Research Service. p. 2. Retrieved June 18, 2020.
- Gorte, Ross W.; Vincent, Carol Hardy.; Hanson, Laura A.; Marc R., Rosenblum. "Federal Land Ownership: Overview and Data" (PDF). fas.org. Congressional Research Service. Retrieved January 18, 2015.
- "Chapter 6: Federal Programs to Promote Resource Use, Extraction, and Development". doi.gov. U.S. Department of the Interior. Archived from the original on March 18, 2015. Retrieved January 19, 2015.
- The National Atlas of the United States of America (January 14, 2013). "Forest Resources of the United States". Nationalatlas.gov. Archived from the original on May 7, 2009. Retrieved January 13, 2014.
- "Land Use Changes Involving Forestry in the United States: 1952 to 1997, With Projections to 2050" (PDF). 2003. Retrieved January 13, 2014.
- Daynes & Sussman, 2010, pp. 3, 72, 74–76, 78
- Hays, Samuel P. (2000). A History of Environmental Politics since 1945.
- Collin, Robert W. (2006). The Environmental Protection Agency: Cleaning Up America's Act. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 1. ISBN 978-0-313-33341-5. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- Turner, James Morton (2012). The Promise of Wilderness, pp. 29–32
- Endangered species Fish and Wildlife Service. General Accounting Office, Diane Publishing. 2003. pp. 1–3, 42. ISBN 978-1-4289-3997-4. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- "Environmental Performance Index". epi.yale.edu. July 10, 2024. Retrieved July 10, 2024.
- "United Nations Treaty Collection-The Paris Agreement". Retrieved December 3, 2024.
- Onuf 2010, p. xvii.
- Desjardins, Jeff (August 8, 2019). "Mapped: The world's oldest democracies". World Economic Forum. Retrieved June 25, 2024.
- Ryan, David (2000). Ryan, David; Pungong, Victor (eds.). The United States and Decolonization. Springer. doi:10.1057/9780333977958. hdl:1887/72726. ISBN 978-1-349-40644-9.
- Scheb, John M.; Scheb, John M. II (2002). An Introduction to the American Legal System. Florence, Kentucky: Delmar, p. 6. ISBN 978-0-7668-2759-2.
- Killian, Johnny H. Ed. "Constitution of the United States". The Office of the Secretary of the Senate. Retrieved February 11, 2012.
- "The Legislative Branch". United States Diplomatic Mission to Germany. Retrieved August 20, 2012.
- "The Process for impeachment". ThinkQuest. Archived from the original on April 8, 2013. Retrieved August 20, 2012.
- "The Senate and the House of Representatives: lesson overview (article)". Khan Academy.
- Broder, David S. (March 18, 2007). "Congress's Oversight Offensive". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on May 1, 2011. Retrieved September 11, 2010.
- Ferraro, Thomas (April 25, 2007). "House committee subpoenas Rice on Iraq". Reuters. Archived from the original on January 14, 2021. Retrieved September 11, 2010.
- "The Executive Branch". The White House. Retrieved February 11, 2017.
- "Interpretation: Article II, Section 1, Clauses 2 and 3 | Constitution Center". National Constitution Center – constitutioncenter.org.
- ^
- Hall, Kermit L.; McGuire, Kevin T. (2005). Institutions of American Democracy: The Judicial Branch. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-988374-5.
- U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (2013). Learn about the United States: Quick Civics Lessons for the Naturalization Test. Government Printing Office. p. 4. ISBN 978-0-16-091708-0.
- Giddens-White, Bryon (2005). The Supreme Court and the Judicial Branch. Heinemann Library. ISBN 978-1-4034-6608-2.
- Zelden, Charles L. (2007). The Judicial Branch of Federal Government: People, Process, and Politics. ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1-85109-702-9. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- "Federal Courts". United States Courts. Retrieved October 19, 2014.
- Cossack, Roger (July 13, 2000). "Beyond politics: Why Supreme Court justices are appointed for life". CNN. Archived from the original on July 12, 2012.
- Sundquist, James L. (1997). "The U.S. Presidential System as a Model for the World". In Baaklini, Abdo I.; Desfosses, Helen (eds.). Designs for Democratic Stability: Studies in Viable Constitutionalism. Routledge. pp. 53–72. ISBN 0765600528.
- Hofstadter, Richard (1969). The Idea of a Party System : The Rise of Legitimate Opposition in the United States, 1780-1840. University of California Press. p. iv. ISBN 9780520013896. Retrieved October 5, 2022.
- Blake, Aaron (November 25, 2021). "Why are there only two parties in American politics?". Washington Post. Retrieved May 4, 2024.
- Matthew Levendusky, The Partisan Sort: How Liberals Became Democrats and Conservatives Became Republicans (U Chicago Press, 2009)
- Levy, Robert A. (October 2011). "Rights, Powers, Dual Sovereignty, and Federalism". Cato Institute. Retrieved January 13, 2024.
- 8 U.S.C. § 1101(a)(36) and 8 U.S.C. § 1101(a)(38) U.S. Federal Code, Immigration and Nationality Act. 8 U.S.C. § 1101a
- Feldstein, Martin (March 2017). "Why is Growth Better in the United States Than in Other Industrial Countries?". National Bureau of Economic Research. Cambridge, Massachusetts. doi:10.3386/w23221.
- "What is a federal Indian reservation?". bia.gov. Bureau of Indian Affairs. August 19, 2017. Retrieved August 26, 2023.
- "Current Members". United Nations Security Council. Retrieved July 15, 2022.
- "United Nations Headquarters Agreement". The American Journal of International Law. 42 (2). Cambridge University Press: 445–447. April 1948. doi:10.2307/2193692. JSTOR 2193692. S2CID 246008694.
- "Where is the G7 Headed?". Council on Foreign Relations. New York City. June 28, 2022.
- "The United States and G20: Building a More Peaceful, Stable, and Prosperous World Together". United States Department of State. July 6, 2022. Retrieved July 15, 2022.
- "Our global reach". OECD. Retrieved July 15, 2022.
- Fialho, Livia Pontes; Wallin, Matthew (August 1, 2013). Reaching for an Audience: U.S. Public Diplomacy Towards Iran (Report). American Security Project. JSTOR resrep06070.
- Oliver, Alex; Graham, Euan (December 19, 2017). "Which are the countries still talking to North Korea?". BBC News. London. Retrieved July 15, 2022.
- Ferraro, Matthew F. (December 22, 2014). "The Case for Stronger Bhutanese-American Ties". The Diplomat. Retrieved July 15, 2022.
- "US will continue to strengthen 'unofficial ties' with Taiwan, says Harris". South China Morning Post. September 28, 2022. Retrieved September 28, 2022.
- Ruwitch, John (September 22, 2020). "Formal Ties With U.S.? Not For Now, Says Taiwan Foreign Minister". NPR. Retrieved July 15, 2022.
- Kobara, Junnosuke; Moriyasu, Ken (March 27, 2021). "Japan will turn to Quad in 'nealsow Cold War': Defense Ministry think tank". Nikkei Asia. Retrieved April 13, 2021.
- Dumbrell, John; Schäfer, Axel (2009). America's 'Special Relationships': Foreign and Domestic Aspects of the Politics of Alliance. Taylor & Francis. p. 45. ISBN 978-0-203-87270-3. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- Ek, Carl & Fergusson, Ian F. (September 3, 2010). "Canada–U.S. Relations" (PDF). Congressional Research Service. Retrieved August 28, 2011.
- Vaughn, Bruce (August 8, 2008). Australia: Background and U.S. Relations. Congressional Research Service. OCLC 70208969.
- Vaughn, Bruce (May 27, 2011). "New Zealand: Background and Bilateral Relations with the United States" (PDF). Congressional Research Service. Retrieved August 28, 2011.
- Lum, Thomas (January 3, 2011). "The Republic of the Philippines and U.S. Interests" (PDF). Congressional Research Service. Retrieved August 3, 2011.
- Chanlett-Avery, Emma; et al. (June 8, 2011). "Japan-U.S. Relations: Issues for Congress" (PDF). Congressional Research Service. Retrieved August 28, 2011.
- Manyin, Mark E.; Chanlett-Avery, Emma; Nikitin, Mary Beth (July 8, 2011). "U.S.–South Korea Relations: Issues for Congress" (PDF). Congressional Research Service. Retrieved August 28, 2011.
- Zanotti, Jim (July 31, 2014). "Israel: Background and U.S. Relations" (PDF). Congressional Research Service. Retrieved September 12, 2014.
- "U.S. Relations With Poland". State.gov. January 20, 2021. Retrieved June 19, 2023.
- Kimer, James (September 26, 2019). "The Untapped Potential of the US-Colombia Partnership". Atlantic Council. Retrieved May 30, 2020.
- "INDO- PACIFIC STRATEGY OF THE UNITED STATES" (PDF). White House. Retrieved February 3, 2022.
- Meidan, Michal (July 1, 2019). US-China: The Great Decoupling (Report). Oxford Institute for Energy Studies. JSTOR resrep33982.
- Bala, Sumathi (March 28, 2023). "U.S.-China relations are going downhill with 'no trust' on either side, Stephen Roach says". CNBC. Retrieved May 7, 2023.
- Rumer, Eugene; Sokolsky, Richard (June 20, 2019). "Thirty Years of U.S. Policy Toward Russia: Can the Vicious Circle Be Broken?". Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. Washington, D.C. Retrieved July 14, 2022.
- Macias, Amanda (June 17, 2022). "Here's a look at the $5.6 billion in firepower the U.S. has committed to Ukraine in its fight against Russia". CNBC. Retrieved September 28, 2022.
- "Our Forces". United States Department of Defense. Retrieved July 12, 2024.
- Lindsay, James M. (August 4, 2021). "Happy 231st Birthday to the United States Coast Guard!". New York City: Council on Foreign Relations. Retrieved July 16, 2022.
During peacetime it is part of the Department of Homeland Security. During wartime, or when the president or Congress so direct, it becomes part of the Department of Defense and is included in the Department of the Navy.
- "Trends in Military Expenditure 2023" (PDF). Stockholm International Peace Research Institute. April 2024. Retrieved April 22, 2024.
- "Data for all countries from 1988–2020 in constant (2019) USD (pdf)" (PDF). SIPRI. Archived (PDF) from the original on April 28, 2021. Retrieved April 28, 2021.
- "Role of nuclear weapons grows as geopolitical relations deteriorate—new SIPRI Yearbook out now | SIPRI". Stockholm International Peace Research Institute. June 17, 2024. Retrieved June 18, 2024.
- Hackett, James (2023). The military balance. 2023. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-1032508955.
- Harris, Johnny (May 18, 2015). "Why does the US have 800 military bases around the world?". Vox. Archived from the original on September 24, 2020. Retrieved September 23, 2020.
- "Active Duty Military Personnel Strengths by Regional Area and by Country (309A)" (PDF). Department of Defense. March 31, 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 24, 2013. Retrieved October 7, 2010.
- "StateDefenseForce.com". StateDefenseForce.com. September 17, 2024.
- "State Guard Association of the United States – Supporting the State Defense Forces of the United States". sgaus.org.
- "32 U.S. Code § 109 – Maintenance of other troops".
- "Legal Basis of the National Guard". Army National Guard. 2013. Archived from the original on May 21, 2013. Retrieved May 17, 2013.
- Banks, Duren; Hendrix, Joshua; Hickman, Mathhew (October 4, 2016). "National Sources of Law Enforcement Employment Data" (PDF). U.S. Department of Justice: 1.
- "U.S. Federal Law Enforcement Agencies, Who Governs & What They Do". Chiff.com. Archived from the original on February 10, 2014. Retrieved November 10, 2021.
- Manweller, Mathew (2006). "Chapter 2, The Roles, Functions, and Powers of State Courts". In Hogan, Sean O. (ed.). The Judicial Branch of State Government: People, Process, and Politics. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-Clio. pp. 37–96. ISBN 978-1-85109-751-7. Retrieved October 5, 2020.
- "Introduction To The Federal Court System". United States Attorney. Washington, D.C.: United States Department of Justice. November 7, 2014. Retrieved July 14, 2022.
- ^ Sawyer, Wendy; Wagner, Peter (July 6, 2023). "Mass Incarceration: The Whole Pie 2023". Prison Policy Initiative. Retrieved August 23, 2024.
- ^ The Growth of Incarceration in the United States: Exploring Causes and Consequences. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press. April 24, 2014. doi:10.17226/18613. ISBN 978-0-309-29801-8.
- Foundation, The Annie E. Casey (November 14, 2020). "Juvenile Detention Explained". The Annie E. Casey Foundation. Retrieved July 6, 2023.
- United States of America. World Prison Brief.
- Highest to Lowest. World Prison Brief (WPB). Use the dropdown menu to choose lists of countries by region or the whole world. Use the menu to select highest-to-lowest lists of prison population totals, prison population rates, percentage of pre-trial detainees/remand prisoners, percentage of female prisoners, percentage of foreign prisoners, and occupancy rate. Column headings in WPB tables can be clicked to reorder columns lowest to highest, or alphabetically. For detailed information for each country click on any country name in lists. See the WPB main data page and click on the map links or the sidebar links to get to the region and country desired.
- Grinshteyn, Erin; Hemenway, David (March 2016). "Violent Death Rates: The US Compared with Other High-income OECD Countries, 2010". The American Journal of Medicine. 129 (3): 226–273. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2015.10.025. PMID 26551975. Retrieved June 18, 2017.
- ^ "The Implementation of Monetary Policy – The Federal Reserve in the International Sphere" (PDF). Retrieved August 24, 2010.
- Fordham, Benjamin (October 2017). "Protectionist Empire: Trade, Tariffs, and United States Foreign Policy, 1890–1914". Studies in American Political Development. 31 (2): 170–192. doi:10.1017/s0898588x17000116. ISSN 0898-588X. S2CID 148917255.
- "Report for Selected Countries and Subjects". Imf.org.
- Hagopian, Kip; Ohanian, Lee (August 1, 2012). "The Mismeasure of Inequality". Policy Review (174). Archived from the original on December 3, 2013. Retrieved January 23, 2020.
- "Gross Domestic Product, Fourth Quarter and Year 2022 (Third Estimate), GDP by Industry, and Corporate Profits". U.S. Department of Commerce.
- "Household disposable income". OECD Data.
- Fox, Michelle (March 1, 2024). "The U.S. national debt is rising by $1 trillion about every 100 days". CNBC.
- "Microsoft back as most valuable listed company as Nvidia slips". BBC. June 21, 2024. Retrieved August 6, 2024.
- "Global 500". Fortune Global 500. Retrieved August 3, 2023.
- Hyam, Benji (November 29, 2023). "Most Profitable Companies: U.S. vs. Rest of the World, 2023". www.growandconvert.com. Retrieved July 16, 2024.
- Benjamin J. Cohen, The Future of Money, Princeton University Press, 2006, ISBN 0691116660; cf. "the dollar is the de facto currency in Cambodia", Charles Agar, Frommer's Vietnam, 2006, ISBN 0471798169, p. 17.
- "US GDP Growth Rate by Year". multpl.com. US Bureau of Economic Analysis. March 31, 2014. Retrieved June 18, 2014.
- "United States free trade agreements". Office of the United States Trade Representative. Retrieved May 31, 2019.
- "Rankings: Global Competitiveness Report 2013–2014" (PDF). World Economic Forum. Retrieved June 1, 2014.
- ^ Collins, Michael (August 11, 2023). "The Post-Industrial Service Economy Isn't Working for the Middle Class". IndustryWeek. Retrieved August 10, 2024.
- "USA Economy in Brief". U.S. Dept. of State, International Information Programs. Archived from the original on March 12, 2008.
- "The State of Manufacturing in the United States". International Trade Administration. July 2010. Archived from the original on February 26, 2013. Retrieved March 10, 2013.
- "Manufacturing, Value Added (Current US$)". World Bank. Archived from the original on January 7, 2020. Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- Kat Tretina and Benjamin Curry (April 9, 2021). "NYSE: What Is The New York Stock Exchange". Forbes. Retrieved July 24, 2022.
- Jones, Huw (March 24, 2022). "New York widens lead over London in top finance centres index". Reuters. Retrieved July 29, 2022.
- "The Global Financial Centres Index 35". Long Finance. March 21, 2024. Retrieved May 1, 2024.
- Ghosh, Iman (September 24, 2020). "This 3D map shows the U.S. cities with the highest economic output". World Economic Forum. Retrieved March 5, 2023.
The New York metro area dwarfs all other cities for economic output by a large margin.
- "Monthly Reports – World Federation of Exchanges". WFE.
- Table A – Market Capitalization of the World's Top Stock Exchanges (As at end of June 2012). Securities and Exchange Commission (China).
- WIPO (2022). Global Innovation Index 2022, 15th Edition. World Intellectual Property Organization. doi:10.34667/tind.46596. ISBN 9789280534320. Retrieved February 25, 2023.
- Wright, Gavin, and Jesse Czelusta, "Resource-Based Growth Past and Present", in Natural Resources: Neither Curse Nor Destiny, ed. Daniel Lederman and William Maloney (World Bank, 2007), p. 185. ISBN 0821365452.
- "Top Trading Partners – October 2022". U.S. Census Bureau. October 2022. Retrieved May 12, 2023.
- "World Trade Statistical Review 2019" (PDF). World Trade Organization. p. 100. Retrieved May 31, 2019.
- "Exports of goods, services and primary income (BoP, current US$)". data.worldbank.org. Retrieved May 24, 2024.
- "Service exports (BoP, current US$)". World Bank. Retrieved August 4, 2023.
- "Income". Better Life Index. OECD. Retrieved September 28, 2019.
In the United States, the average household net adjusted disposable income per capita is USD 45 284 a year, much higher than the OECD average of USD 33 604 and the highest figure in the OECD.
- "Median Income by Country 2023". Wisevoter. Retrieved July 28, 2023.
- "Society at a Glance 2014". Society at a Glance 2014: OECD Social Indicators. OECD Publishing. March 18, 2014. doi:10.1787/soc_glance-2014-en. ISBN 9789264200722. Retrieved May 29, 2014.
- "Personal Consumption Expenditures". fred.stlouisfed.org. March 28, 2024. Retrieved July 24, 2024.
- Rocha, Laura (August 18, 2023). "Playing To Win In The U.S. Market". Forbes. Retrieved July 24, 2024.
- Piketty, Thomas (2014). Capital in the Twenty-First Century. Belknap Press. p. 257. ISBN 978-0-674-43000-6
- "Income inequality in America is the highest it's been since Census Bureau started tracking it, data shows". The Washington Post. Retrieved July 27, 2020.
- Long, Heather (September 12, 2017). "U.S. middle-class incomes reached highest-ever level in 2016, Census Bureau says". The Washington Post. Retrieved November 11, 2019.
- Smeeding, T. M. (2005). "Public Policy: Economic Inequality and Poverty: The United States in Comparative Perspective". Social Science Quarterly. 86: 955–983. doi:10.1111/j.0038-4941.2005.00331.x. S2CID 154642286.
- Hopkin, Jonathan (2020). "American Nightmare: How Neoliberalism Broke US Democracy". Anti-System Politics: The Crisis of Market Liberalism in Rich Democracies. Oxford University Press. pp. 87–88. doi:10.1093/oso/9780190699765.003.0004. ISBN 978-0190699765.
- "Here's How Many Billionaires And Millionaires Live In The U.S. – Forbes Advisor". Forbes. October 20, 2023. Retrieved November 20, 2023.
- "The 2022 Annual Homelessness Assessment Report (AHAR) to Congress" (PDF). The U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development. December 2022. Retrieved June 16, 2023.
- "USDA ERS – Key Statistics & Graphics". ers.usda.gov. Retrieved December 4, 2019.
- "Facts About Child Hunger in America | Feeding America". feedingamerica.org. Retrieved December 4, 2019.
- "National Poverty in America Awareness Month: January 2023". Census.gov.
- Joumard, Isabelle; Pisu, Mauro; Bloch, Debbie (2012). "Tackling income inequality The role of taxes and transfers" (PDF). OECD. Retrieved May 21, 2015.
- Rank, Mark Robert (2023). The Poverty Paradox: Understanding Economic Hardship Amid American Prosperity. Oxford University Press. pp. 116–117. ISBN 978-0190212636.
- Min, Sarah (May 24, 2019). "1 in 4 workers in U.S. don't get any paid vacation time or holidays". CBS News. Retrieved July 15, 2022.
The United States is the only advanced economy that does not federally mandate any paid vacation days or holidays.
- Bernard, Tara Siegel (February 22, 2013). "In Paid Family Leave, U.S. Trails Most of the Globe". The New York Times. Retrieved August 27, 2013.
- Van Dam, Andrew (July 4, 2018). "Is it great to be a worker in the U.S.? Not compared with the rest of the developed world". The Washington Post. Retrieved July 12, 2018.
- Mowery, David. "Technological Change and the Evolution of the U.S. "National Innovation System", 1880-1990". OpenMind. Retrieved July 10, 2024.
- Goodfriend, Marvin; McDermott, John (February 24, 2021). "The American System of economic growth". Journal of Economic Growth. 26 (1): 31–75. doi:10.1007/s10887-021-09186-x. ISSN 1573-7020. PMC 7902180. PMID 33642936.
- Hounshell, David A. (1984), From the American System to Mass Production, 1800–1932: The Development of Manufacturing Technology in the United States, Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press, ISBN 978-0-8018-2975-8, LCCN 83016269, OCLC 1104810110
- "Measuring trends in AI". Artificial Intelligence Index. Stanford University. 2021.
- Espinel, Victoria. "America leads the world in AI–but we could fall behind on AI regulation by the end of 2023". Fortune Europe. Retrieved July 30, 2024.
- Radu, Sintia (August 19, 2019). "Despite Chinese Efforts, the U.S. Still Leads in AI". U.S. News & World Report. Retrieved July 30, 2024.
- "SJR – International Science Ranking". Scimagojr.com. Retrieved February 5, 2022.
- World Intellectual Property Organization. (2021). World Intellectual Property Indicators 2021. World IP Indicators (WIPI). World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO). doi:10.34667/tind.44461. ISBN 9789280533293. Retrieved April 27, 2022.
- "Global Innovation Index 2024 : Unlocking the Promise of Social Entrepreneurship". www.wipo.int. Retrieved November 29, 2024.
- WIPO (December 28, 2023). Global Innovation Index 2023, 15th Edition. World Intellectual Property Organization. doi:10.34667/tind.46596. ISBN 9789280534320. Retrieved October 17, 2023.
- Desjardins, Jeff (December 18, 2018). "Innovators wanted: these countries spend the most on R&D". www.weforum.org. Retrieved May 22, 2024.
- Fleming, Sean (November 16, 2020). "These countries spend the most on research and development". www.weforum.org. Retrieved May 22, 2024.
- Getzoff, Marc (December 1, 2023). "Most Technologically Advanced Countries In The World 2023". Global Finance Magazine. Retrieved July 29, 2024.
- "65 Years Ago: The National Aeronautics and Space Act of 1958 Creates NASA – NASA". July 26, 2023. Retrieved September 6, 2024.
- "National Aeronautics and Space Administration | US Space Agency & Exploration Achievements | Britannica". www.britannica.com. September 4, 2024. Retrieved September 5, 2024.
- "Apollo | History, Missions, Significance, & Facts | Britannica". www.britannica.com. August 29, 2024. Retrieved September 5, 2024.
- "The Apollo Missions". The Apollo Missions. July 4, 2019. Retrieved September 5, 2024.
- "Space Shuttle – NASA". Retrieved September 5, 2024.
- "Quick Facts". HubbleSite. Retrieved September 5, 2024.
- "Quick Facts". Webb. Retrieved September 5, 2024.
- "Mars Exploration – NASA Science". science.nasa.gov. Retrieved September 5, 2024.
- "International Space Station Facts and Figures – NASA". Retrieved September 5, 2024.
- Howell, Elizabeth (August 24, 2022). "International Space Station: Facts, History & Tracking". Space.com (updated, last ed.). Retrieved September 5, 2024.
- "Analysis | Companies are commercializing outer space. Do government programs still matter?". Washington Post. January 11, 2022. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved September 5, 2024.
- "Commercial Space – NASA". Retrieved September 5, 2024.
- "U.S. energy facts explained – consumption and production – U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)". eia.gov. Retrieved November 21, 2023.
- "Energy Flow Charts: Charting the Complex Relationships among Energy, Water, and Carbon". Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. March 2022. Retrieved May 16, 2023.
- "What is the United States' share of world energy consumption?". U.S. Energy Information Administration. November 5, 2021.
- US Environmental Protection Agency, OAR (February 8, 2017). "Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks". US EPA. Retrieved December 3, 2020.
- Hunter, Marnie (April 11, 2022). "This US airport has reclaimed its title as the world's busiest". CNN.
- "Waterways – The World Factbook". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved July 14, 2022.
- Edwards, Chris (July 12, 2020). "Privatization". Downsizing the Federal Government. Cato Institute. Retrieved January 23, 2021.
- "Scheduled Passengers Carried". International Air Transport Association (IATA). 2011. Archived from the original on January 2, 2015. Retrieved February 17, 2012.
- "2021 Airport Traffic Report" (PDF). Port Authority of New York and New Jersey. April 2022. p. 32.
- "Preliminary World Airport Traffic and Rankings 2013—High Growth Dubai Moves Up to 7th Busiest Airport". March 31, 2014. Archived from the original on April 1, 2014. Retrieved May 17, 2014.
- "Number of U.S. Airports". Bureau of Transportation Statistics. Retrieved December 15, 2023.
- Black, Alan (1995). Urban mass transportation planning. New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0070055575. OCLC 31045097.
- "Cars still dominate the American commute". World Economic Forum. May 19, 2022. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- Humes, Edward (April 12, 2016). "The Absurd Primacy of the Automobile in American Life". The Atlantic. Retrieved July 12, 2023.
- "Roadways – The World Factbook". Cia.gov. Archived from the original on July 12, 2021. Retrieved July 15, 2021.
- "Public Road and Street Mileage in the United States by Type of Surface". United States Department of Transportation. Archived from the original on January 2, 2015. Retrieved January 13, 2015.
- "Railways – The World Factbook". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved July 14, 2022.
- "Seasonally Adjusted Transportation Data". Washington, D.C.: Bureau of Transportation Statistics. 2021. Archived from the original on April 22, 2021. Retrieved February 16, 2021.
- Fitzsimmons, Emma G. (April 24, 2017). "Amtrak at a Junction: Invest in Improvements, or Risk Worsening Problems". The New York Times. Retrieved April 16, 2023.
- "The Top 50 Container Ports". World Shipping Council. Washington, D.C. Retrieved July 14, 2022.
- "SOME MILESTONES OF THE AUTO AGE". The New York Times. January 26, 1986. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved June 1, 2023.
- "1926 Ford Model T Sports Touring Car". The Washington Post. September 1, 2002. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved June 1, 2023.
- "2023 production statistics". International Organization of Motor Vehicle Manufacturers. Retrieved July 1, 2024.
- Klebnikov, Sergei. "Tesla Is Now The World's Most Valuable Car Company With A $208 Billion Valuation". Forbes. Retrieved April 14, 2023.
- Bunkley, Nick (January 21, 2009). "Toyota Ahead of G.M. in 2008 Sales". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved April 14, 2023.
- "China overtakes US in car sales". The Guardian. London. January 8, 2010. Retrieved July 10, 2011.
- "Fact #962: Vehicles per Capita: Other Regions/Countries Compared to the United States". Energy.gov. January 30, 2017. Retrieved January 23, 2021.
- "Vehicle Statistics: Cars Per Capita". Capitol Tires. August 2017.
- "Cars". The Observatory of Economic Complexity. Retrieved July 27, 2024.
- "Annual and cumulative estimates of residential population change for the United States, regions, states, District of Columbia, Puerto Rico". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved December 20, 2024.
- "Census Bureau's 2020 Population Count". United States Census. Retrieved April 26, 2021.
- "National Population Totals and Components of Change: 2020-2024".
- "Population Clock". Census.gov.
- "Table MS-1. Marital Status of the Population 15 Years Old and Over, by Sex, Race and Hispanic Origin: 1950 to Present". Historical Marital Status Tables. U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved September 11, 2019.
- Saric, Ivana (April 25, 2024). "Births dropped in 2023, ending pandemic baby boom". Axios. Retrieved July 1, 2024.
- "U.S. has world's highest rate of children living in single-parent households". Pew Research Center. December 12, 2019. Retrieved March 17, 2020.
- ^ "Ancestry 2000" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. June 2004. Archived (PDF) from the original on December 4, 2004. Retrieved December 2, 2016.
- "The Chance That Two People Chosen at Random Are of Different Race or Ethnicity Groups Has Increased Since 2010".
- "Table 52. Population by Selected Ancestry Group and Region: 2009" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 25, 2012. Retrieved February 11, 2017.
- "Federally recognized American Indian tribes and Alaska Native entities | USAGov". www.usa.gov. Retrieved April 5, 2024.
- "America Is Getting Older". Census.gov. June 22, 2023. Retrieved June 30, 2024.
- Kaur, Harmeet (May 20, 2018). "FYI: English isn't the official language of the United States". CNN. Retrieved May 11, 2023.
- "States Where English Is the Official Language". The Washington Post. August 12, 2014. Retrieved September 12, 2020.
- "The Constitution of the State of Hawaii, Article XV, Section 4". Hawaii Legislative Reference Bureau. November 7, 1978. Archived from the original on July 24, 2013. Retrieved June 19, 2007.
- Chapel, Bill (April 21, 2014). "Alaska OKs Bill Making Native Languages Official". NPR.
- "South Dakota recognizes official indigenous language". Argus Leader. Retrieved March 26, 2019.
- Siebens, Julie; Julian, Tiffany (December 2011). "Native North American Languages Spoken at Home in the United States and Puerto Rico: 2006–2010" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved April 5, 2024.
- "Translation in Puerto Rico". Puerto Rico Channel. Archived from the original on December 30, 2013. Retrieved December 29, 2013.
- "ACS B16001". ACS B16001. U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved December 26, 2022.
- "American FactFinder—Results". Archived from the original on February 12, 2020. Retrieved May 29, 2017.
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (August 2019). "International Migrant Stock 2019 Documentation" (PDF). United Nations. Retrieved June 19, 2023.
- "UN Migrant Stock Total 2019". United Nations. Retrieved June 19, 2023.
- "Frequently Requested Statistics on Immigrants and Immigration in the United States". Migration Policy Institute. March 14, 2019.
- "Key findings about U.S. immigrants". Pew Research Center. June 17, 2019.
- "Immigrants in the United States" (PDF). americanimmigrationcouncil.org. September 21, 2021. Retrieved August 18, 2023.
- "Who Are America's Immigrants?". Population Reference Bureau. May 22, 2024.
- Krogstad, Jens Manuel (October 7, 2019). "Key facts about refugees to the U.S." Pew Research Center.
- Donadio, Rachel (November 22, 2021). "Why Is France So Afraid of God?". The Atlantic. Retrieved March 25, 2023.
- "First Amendment". Constitution Annotated. United States Congress.
- Alesina, Alberto; et al. (2003). "Fractionalization" (PDF). Journal of Economic Growth. 8 (2): 155–194. doi:10.1023/a:1024471506938. S2CID 260685524. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 31, 2012. Retrieved September 13, 2012.
- Fahmy, Dalia (July 31, 2018). "Americans are far more religious than adults in other wealthy nations". Pew Research Center. Archived from the original on January 9, 2020. Retrieved January 23, 2020.
- ANALYSIS (December 19, 2011). "Global Christianity". Pewforum.org. Archived from the original on July 30, 2013. Retrieved August 17, 2012.
- Sewell, Elizabeth (2010). "Religious Liberty and Religious Minorities in the United States". In Davis, Derek (ed.). The Oxford Handbook of Church and State in the United States. University of Oxford. pp. 249–275. ISBN 9780199892228.
- ^ Williams, Daniel (March 1, 2023). "'Christian America' Isn't Dying. It's Dividing". Christianity Today. Retrieved March 25, 2023.
- Merriam, Jesse; Lupu, Ira; Elwood, F; Davis, Eleanor (August 28, 2008). "On Ceremonial Occasions, May the Government Invoke a Deity?". Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project. Retrieved March 31, 2023.
- Kallo, Becka; et al. (December 7, 2023). "Spirituality Among Americans". Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project. Retrieved December 8, 2023.
- Froese, Paul; Uecker, Jeremy E. (September 2022). "Prayer in America: A Detailed Analysis of the Various Dimensions of Prayer". Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion. 61 (3–4): 663–689. doi:10.1111/jssr.12810. ISSN 0021-8294. S2CID 253439298.
- Howe 2008, pp. 727–728.
- "Mormon Population by State". World Population Review. June 2023.
- "United States—Urban/Rural and Inside/Outside Metropolitan Area". U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on April 3, 2009. Retrieved September 23, 2008.
- "City and Town Population Totals: 2020-2022". Census.gov. Retrieved November 26, 2023.
- "Counties in South and West Lead Nation in Population Growth". The United States Census Bureau. April 18, 2019. Retrieved August 29, 2020.
- "Metropolitan and Micropolitan Statistical Areas Population Totals: 2020–2023". United States Census Bureau. May 2023. Retrieved February 14, 2024.
- "About Us".
- "Texas Medical Center, largest medical complex in the world, reaches 98 percent ICU capacity". Newsweek. August 19, 2020.
- "TMC Facts & Figures" (PDF).
- Mayes-Osterman, Cybele (November 30, 2023). "Americans are living longer but there's a catch: CDC report on life expectancy". USA Today. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- McPhillips, Deidre (November 29, 2023). "US life expectancy rebounded in 2022 but not back to pre-pandemic levels". CNN. Retrieved February 12, 2024.
- Achenbach, Joel (November 26, 2019). "'There's something terribly wrong': Americans are dying young at alarming rates". The Washington Post. Retrieved December 19, 2019.
- "New International Report on Health Care: U.S. Suicide Rate Highest Among Wealthy Nations | Commonwealth Fund". Commonwealthfund.org. January 30, 2020. Retrieved March 17, 2020.
- "Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity Among Adults: United States, 2003–2004". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. Retrieved June 5, 2007.
- "The U.S. Healthcare System: The Best in the World or Just the Most Expensive?" (PDF). University of Maine. 2001. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 9, 2007. Retrieved November 29, 2006.
- Vladeck, Bruce (January 2003). "Universal Health Insurance in the United States: Reflections on the Past, the Present, and the Future". American Journal of Public Health. 93 (1): 16–19. doi:10.2105/ajph.93.1.16. PMC 1447684. PMID 12511377.
- Oberlander, Jonathan (June 1, 2010). "Long Time Coming: Why Health Reform Finally Passed". Health Affairs. 29 (6): 1112–1116. doi:10.1377/hlthaff.2010.0447. ISSN 0278-2715. PMID 20530339.
- Glenza, Jessica; Noor, Poppy. "Tracking abortion laws across the United States". The Guardian. Retrieved August 14, 2024.
- National Center for Education Statistics. "U.S. Undergraduate Enrollment". Accessed July 29, 2024.
- "Ages for Compulsory School Attendance ..." U.S. Dept. of Education, National Center for Education Statistics. Retrieved June 10, 2007.
- Rushe, Dominic (September 7, 2018). "The US spends more on education than other countries. Why is it falling behind?". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved August 29, 2020.
- "Fast Facts: Expenditures". nces.ed.gov. April 2020. Retrieved August 29, 2020.
- "Educational Attainment in the United States: 2022". U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved July 20, 2024.
- For more detail on U.S. literacy, see A First Look at the Literacy of America's Adults in the 21st century, U.S. Department of Education (2003).
- "All Nobel Prizes". Nobel Foundation.
- "2022–2023 Best Global Universities Rankings". U.S. News & World Report. Retrieved April 27, 2023.
- Fink, Jenni (October 22, 2019). "U.S. Schools Take 8 of 10 Top Spots on U.S. News' Best Global Universities". Newsweek. Retrieved April 18, 2023.
- "Best Countries for Education: North American and European countries are seen as offering the best opportunities for education". U.S. News & World Report. April 19, 2023.
- Pannoni, Alexandra; Kerr, Emma (July 14, 2020). "Everything You Need to Know About Community Colleges: FAQ". U.S. News & World Report. Retrieved July 9, 2022.
- "U.S. education spending tops global list, study shows". CBS. Associated Press. June 25, 2013. Archived from the original on July 26, 2013. Retrieved October 5, 2013.
- "The Biden administration cancelled $9.5B in student loan debt. Here's who it affects". USAFacts. Retrieved July 15, 2022.
- Hess, Abigail Johnson (December 22, 2020). "U.S. student debt has increased by more than 100% over the past 10 years". CNBC. Retrieved January 8, 2022.
- Dickler, Jessica; Nova, Annie (May 6, 2022). "This is how student loan debt became a $1.7 trillion crisis". CNBC. Retrieved July 8, 2022.
- "Statue of Liberty". World Heritage. UNESCO. Retrieved January 4, 2022.
- Huntington, Samuel P. (2004). "Chapters 2–4". Who are We?: The Challenges to America's National Identity. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-0-684-87053-3. Retrieved October 25, 2015.: see American Creed, written by William Tyler Page and adopted by Congress in 1918.
- Hoeveler, J. David, Creating the American Mind: Intellect and Politics in the Colonial Colleges, Rowman & Littlefield, ISBN 978-0742548398, 2007, p. xi
- Grabb, Edward; Baer, Douglas; Curtis, James (1999). "The Origins of American Individualism: Reconsidering the Historical Evidence". Canadian Journal of Sociology. 24 (4). University of Alberta: 511–533. doi:10.2307/3341789. ISSN 0318-6431. JSTOR 3341789.
- Marsh, Abigail (May 26, 2021). "Everyone Thinks Americans Are Selfish. They're Wrong". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved July 16, 2023.
- Porter, Gayle (November 2010). "Work Ethic and Ethical Work: Distortions in the American Dream". Journal of Business Ethics. 96 (4). Springer: 535–550. doi:10.1007/s10551-010-0481-6. JSTOR 29789736. S2CID 143991044.
- Stephens, R. H. (September 1952). "The Role Of Competition In American Life". The Australian Quarterly. 24 (3). Australian Institute of Policy and Science: 9–14. JSTOR 41317686.
- "World Giving Index 2022" (PDF). Charities Aid Foundation. September 9, 2022. Retrieved April 27, 2023.
- "Country-level estimates of altruism". Our World in Data. Retrieved March 14, 2023.
- Marsh, Abigail (February 5, 2018). "Could A More Individualistic World Also Be A More Altruistic One?". NPR. Retrieved March 14, 2023.
- "GROSS DOMESTIC PHILANTHROPY: An international analysis of GDP, tax and giving" (PDF). Charities Aid Foundation. January 2016. Retrieved July 18, 2022.
- Volokh, Eugene (January 17, 2015). "The American tradition of multiculturalism". The Washington Post. Retrieved July 30, 2024.
- Jackson, Lucas (August 22, 2014). "America's Tipping Point: Most Of U.S. Now Multicultural, Says Group". NBC News. Retrieved July 30, 2024.
- Berghahn, Volker R. (February 1, 2010). "The debate on 'Americanization' among economic and cultural historians". Cold War History. 10 (1): 107–130. doi:10.1080/14682740903388566. ISSN 1468-2745. S2CID 144459911.
- Fergie, Dexter (March 24, 2022). "How American Culture Ate the World". The New Republic. ISSN 0028-6583. Retrieved July 3, 2022.
- Fiorina, Morris P.; Peterson, Paul E. (2010). The New American democracy (7th ed.). London: Longman. p. 97. ISBN 978-0-205-78016-7.
-
- Holloway, Joseph E. (2005). Africanisms in American culture (2nd ed.). Bloomington: Indiana University Press. pp. 18–38. ISBN 978-0-253-21749-3.
- Johnson, Fern L. (2000). Speaking culturally : language diversity in the United States. Sage Publications. p. 116. ISBN 978-0-8039-5912-5.
- Clifton, Jon (March 21, 2013). "More Than 100 Million Worldwide Dream of a Life in the U.S. More than 25% in Liberia, Sierra Leone, Dominican Republic want to move to the U.S." Gallup. Retrieved January 10, 2014.
- Kulkarni, Jay (January 12, 2022). "Attracting Immigrant Talent With A New American Dream". Forbes. Retrieved July 24, 2024.
- "A Family Affair: Intergenerational Social Mobility across OECD Countries" (PDF). Economic Policy Reforms: Going for Growth. OECD. 2010. Retrieved September 20, 2010.
- "Understanding Mobility in America". Center for American Progress. April 26, 2006.
- Gould, Elise (October 10, 2012). "U.S. lags behind peer countries in mobility". Economic Policy Institute. Retrieved July 15, 2013.
- Gutfeld, Amon (2002). American Exceptionalism: The Effects of Plenty on the American Experience. Brighton and Portland: Sussex Academic Press. p. 65. ISBN 978-1-903900-08-6.
- Zweig, Michael (2004). What's Class Got To Do With It, American Society in the Twenty-First Century. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press. ISBN 978-0-8014-8899-3.
- Hoff-Ginsberg, Erika (April 1989). Effects of Social Class and Interactive Setting on Maternal Speech (Report). Bethesda, MD: National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NIH) – via Education Resource Information Center. Republished with revisions as Hoff-Ginsberg, Erika (1991). "Mother-Child Conversation in Different Social Classes and Communicative Settings". Child Development. 62 (4): 782–796. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8624.1991.tb01569.x. ISSN 0009-3920. PMID 1935343.
- O'Keefe, Kevin (2005). The Average American. New York: PublicAffairs. ISBN 978-1-58648-270-1.
- "National Foundation on the Arts and the Humanities". Federal Register. Retrieved October 1, 2022.
- ^ Coleman, Gabriella (2013). Coding Freedom. Princeton University Press. pp. 10, 201. ISBN 978-0-691-14461-0.
- "Held Dear In U.S., Free Speech Perplexing Abroad". NPR. September 19, 2012. Retrieved March 4, 2023.
- Liptak, Adam (June 11, 2008). "Hate speech or free speech? What much of West bans is protected in U.S.". The New York Times. Retrieved February 21, 2023.
- Durkee, Alison (April 25, 2018). "What if we didn't... have the First Amendment?". Mic. Retrieved February 6, 2023.
- Wike, Richard (October 12, 2016). "Americans more tolerant of offensive speech than others in the world". Pew Research Center. Retrieved February 6, 2023.
- Gray, Alex (November 8, 2016). "Freedom of speech: which country has the most?". World Economic Forum. Retrieved February 6, 2023.
- Norris, Pippa (February 2023). "Cancel Culture: Myth or Reality?". Political Studies. 71 (1): 145–174. doi:10.1177/00323217211037023. ISSN 0032-3217. S2CID 238647612.
As predicted, in post-industrial societies, characterized by predominately liberal social cultures, like the US, Sweden, and UK...
- ^ Derks, Marco; van den Berg, Mariecke (2020). Public Discourses About Homosexuality and Religion in Europe and Beyond. Springer International Publishing. p. 338. ISBN 978-3-030-56326-4.
...(the United States and Europe) as "already in crisis" for their permissive attitudes toward nonnormative sexualities...
- Leveille, Dan (December 4, 2009). "LGBT Equality Index: The most LGBT-friendly countries in the world". Equaldex. Retrieved January 26, 2023.
13.) United States
- Garretson, Jeremiah (2018). "A Transformed Society: LGBT Rights in the United States". The Path to Gay Rights: How Activism and Coming Out Changed Public Opinion. New York University Press. ISBN 978-1-4798-5007-5.
In the late 1980s and early 1990s, a dramatic wave began to form in the waters of public opinion: American attitudes involving homosexuality began to change... The transformation of America's response to homosexuality has been — and continues to be — one of the most rapid and sustained shifts in mass attitudes since the start of public polling.
- Jelliffe, Robert A. (1956). Faulkner at Nagano. Tokyo: Kenkyusha, Ltd.
- Baym & Levine 2013, pp. 157–159.
- Lauter 1994a, pp. 503–509.
- Baym & Levine 2013, p. 163.
- Mulford, Carla. "Enlightenment Voices, Revolutionary Visions." In Lauter 1994a, pp. 705–707.
- Lease, Benjamin (1972). That Wild Fellow John Neal and the American Literary Revolution. Chicago, Illinois: University of Chicago Press. p. 80. ISBN 0-226-46969-7.
- Finseth, Ian Frederick. "The Emergence of Transcendentalism". American Studies @ The University of Virginia. The University of Virginia. Archived from the original on July 18, 2023. Retrieved November 9, 2014.
- Coviello, Peter (2005). "Transcendentalism". The Oxford Encyclopedia of American Literature. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780195307726. Retrieved October 23, 2011 – via Oxford Reference Online.
- Baym & Levine 2013, pp. 444–447.
- Lauter 1994a, pp. 1228, 1233, 1260.
- Baym & Levine 2013, pp. 1269–1270.
- Lauter 1994b, pp. 8–10.
- Baym & Levine 2013, pp. 1271–1273.
- Lauter 1994b, p. 12.
- Baym & Levine 2013, pp. 1850–1851.
- Spillers, Hortense. "The New Negro Renaissance." In Lauter 1994b, pp. 1579–1585.
- Philipson, Robert (2006). "The Harlem Renaissance as Postcolonial Phenomenon". African American Review. 40 (1): 145–160. JSTOR 40027037.
- Baym & Levine 2013, pp. 2260–2261.
- Baym & Levine 2013, p. 2262.
- Lauter 1994b, pp. 1975–1977. "Literature of the Cold War".
- Baym & Levine 2013, pp. 2266–2267.
- "All Nobel Prizes in Literature". The Nobel Prize. Nobel Prize Outreach AB 2024. Retrieved August 6, 2024.
- "Streaming TV Services: What They Cost, What You Get". The New York Times. Associated Press. October 12, 2015. Archived from the original on October 15, 2015. Retrieved October 12, 2015.
- "Audio and Podcasting Fact Sheet". Washington, D.C.: Pew Research Center. June 29, 2021. Retrieved July 3, 2022.
- "BROADCAST STATION TOTALS AS OF SEPTEMBER 30, 2020" (PDF).
- "History: NPR". NPR. June 20, 2013. Retrieved May 5, 2021.
- Shaffer, Brenda (2006). The Limits of Culture: Islam and Foreign Policy. MIT Press. p. 116. ISBN 978-0-262-19529-4.
- "Spanish Newspapers in United States". W3newspapers. Retrieved August 5, 2014.
- "Spanish Language Newspapers in the USA : Hispanic Newspapers : Periódiscos en Español en los EE.UU". Onlinenewspapers.com. Archived from the original on June 26, 2014. Retrieved August 5, 2014.
- "Top Sites in United States". Alexa. 2021. Archived from the original on June 21, 2020. Retrieved October 6, 2021.
- "Top countries and markets by video game revenues". Newzoo. Archived from the original on March 26, 2023. Retrieved October 6, 2023.
- "California (CA)". ESA Impact Map. July 20, 2017. Retrieved December 14, 2022.
- Saxon, Theresa (October 11, 2011). American Theatre: History, Context, Form. Edinburgh University Press. pp. 7–. ISBN 978-0-7486-3127-8. OCLC 1162047055.
- Meserve, Walter J. An Outline History of American Drama, New York: Feedback/Prospero, 1994.
- Londré, Felicia Hardison; Watermeier, Daniel J. (1998). The History of North American Theater: From Pre-Columbian Times to the Present. Continuum. ISBN 978-0-8264-1079-5. OCLC 1024855967.
- Stephen Watt, and Gary A. Richardson, American Drama: Colonial to Contemporary (1994).
- Staff (undated). "Who's Who". Archived December 23, 2016, at the Wayback Machine. tonyawards.com. Retrieved September 13, 2013.
- Güner, Fisun (February 8, 2017). "How American Gothic became an icon". BBC. Retrieved March 2, 2017.
- American folk art the art of the common man in America, 1750-1900. New York, N.Y.: The Museum of Modern Art. 1932.
- Brown, Milton W. (1963). The Story of the Armory Show (2nd ed.). New York: Abbeville Press. ISBN 978-0-89659-795-2.
- Davenport, Alma (1991). The History of Photography: An Overview. UNM Press. p. 67. ISBN 978-0-8263-2076-6.
- Janson, Horst Woldemar; Janson, Anthony F. (2003). History of Art: The Western Tradition. Prentice Hall Professional. p. 955. ISBN 978-0-13-182895-7.
- Lester, Alfred (December 6, 1993). "Letter: The Louvre: tourism on the grand scale". The Independent. Retrieved December 2, 2023.
- "Folk Music and Song: American Folklife Center: An Illustrated Guide (Library of Congress)". Loc.gov.
- "Musical Crossroads: African American Influence on American Music". Smithsonian. September 22, 2016. Retrieved April 14, 2023.
- Winans, Robert B. (1976). "The Folk, the Stage, and the Five-String Banjo in the Nineteenth Century". The Journal of American Folklore. 89 (354). American Folklore Society: 407–437. doi:10.2307/539294. JSTOR 539294.
- Shi 2016, p. 378.
- ^ "The Invention of the Electric Guitar". Lemelson Center Studies in Invention and Innovation. Smithsonian Institution. April 18, 2014.
- ^ Biddle, Julian (2001). What Was Hot!: Five Decades of Pop Culture in America. New York: Citadel. p. ix. ISBN 978-0-8065-2311-8.
- Stoia, Nicholas (October 21, 2014). "Early blues and country music". OUP blog. Oxford University Press.
- "Bluegrass music". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved June 19, 2020.
- OpenStax 2014, § 28.4.
- "No. 1 Bob Dylan". Rolling Stone. April 10, 2020. Retrieved January 29, 2021.
- Funk, Clayton (August 16, 2016). "9. Neo-Expressionism, Punk, and Hip Hop Emerge". A Quick and Dirty Guide to Art, Music, and Culture. The Ohio State University.
- "2022 Year-End Music Industry Revenue Report". Record Industry Association of America. Retrieved November 26, 2023.
- Hennessy, Eoin (March 27, 2014). "How American Music Took Over the World". The University Times. Retrieved April 28, 2023.
- "10 ways that Frank Sinatra changed the world". USA Today. December 8, 2015. Retrieved June 24, 2021.
- "Universal Music can't help falling for Elvis Presley, to manage song catalog". Reuters. April 12, 2022. Retrieved April 12, 2022.
- "Michael Jackson's 'Thriller' First Ever 30X Multi-Platinum RIAA Certification". Recording Industry Association of America. December 16, 2015. Retrieved December 17, 2021.
- Marcos, Carlos (August 17, 2022). "Madonna has been scandalizing people for 40 years, and nobody's going to stop her". El País. Retrieved August 17, 2022.
- "The 200 Greatest Singers of All Time". Rolling Stone. January 1, 2023. Retrieved January 2, 2023.
- "Prince Tribute: The Greatest Musical Talent of His Generation". Billboard. April 28, 2016. Retrieved March 17, 2020.
- "Taylor Swift and Beyoncé reporters wanted by biggest newspaper chain in US". Sky News. September 14, 2023. Archived from the original on November 9, 2023. Retrieved November 8, 2023.
- "Global Apparel Industry Statistics (2024)". uniformmarket.com. June 19, 2024. Retrieved August 25, 2024.
- "American Classics How seven everyday clothing items became American style staples". CNN. Retrieved December 4, 2023.
- Caplin, John (September 1, 2021). "Made In New York: The Future Of New York City's Historic Garment District". Forbes. Retrieved December 5, 2023.
Spanning just about 20 square blocks between Times Square and Penn Station along Seventh Avenue (also known as "Fashion Avenue"), the vibrant and always-busy neighborhood has a long and rich history that has become synonymous with American fashion since its inception more than a century ago.
- Juarez, Diana (October 4, 2023). "The Economic Impact of New York Fashion Week". The Fordham Ram. Retrieved December 5, 2023.
- Bauman, Ali (May 1, 2023). "Met Gala 2023: Fashion's biggest night honors Karl Lagerfeld". CBS News. Retrieved April 30, 2024.
- "Met Gala 2024: How to Watch Fashion's Biggest Night". Glamour. April 29, 2024. Retrieved April 30, 2024.
- Annual Report of the Controller of the City of Los Angeles, California. ByOffice of Controller Los Angeles, CA (1914). 1914. Retrieved February 22, 2014.
- Report of the Auditor of the City of Los Angeles California of the Financial Affairs of the Corporation in Its Capacity as a City for the Fiscal Year. By Auditor's Office of Los Angeles, CA (1913). 1913. Retrieved February 22, 2014.
- "Nigeria surpasses Hollywood as world's second-largest film producer" (Press release). United Nations. May 5, 2009. Retrieved February 17, 2013.
- Kerrigan, Finola (2010). Film Marketing. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 18. ISBN 978-0-7506-8683-9. Retrieved February 4, 2022.
- Davis, Glyn; Dickinson, Kay; Patti, Lisa; Villarejo, Amy (2015). Film Studies: A Global Introduction. Abingdon: Routledge. p. 299. ISBN 978-1-317-62338-0. Retrieved August 24, 2020.
- "John Landis Rails Against Studios: 'They're Not in the Movie Business Anymore'". The Hollywood Reporter. Retrieved January 24, 2015.
- Drowne, Kathleen Morgan; Huber, Patrick (2004). The 1920s. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 236. ISBN 978-0-313-32013-2.
- Kroon, Richard W. (2014). A/V A to Z: An Encyclopedic Dictionary of Media, Entertainment and Other Audiovisual Terms. McFarland. p. 338. ISBN 978-0-7864-5740-3.
- Matthews, Charles (June 3, 2011). "Book explores Hollywood 'Golden Age' of the 1960s-'70s". The Washington Post. Retrieved August 6, 2015.
- Banner, Lois (August 5, 2012). "Marilyn Monroe, the eternal shape shifter". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved August 6, 2015.
- Rick, Jewell (August 8, 2008). "John Wayne, an American Icon". University of Southern California. Archived from the original on August 22, 2008. Retrieved August 6, 2015.
- Greven, David (2013). Psycho-Sexual: Male Desire in Hitchcock, De Palma, Scorsese, and Friedkin. University of Texas Press. p. 23. ISBN 978-0-292-74204-8.
- Morrison, James (1998). Passport to Hollywood: Hollywood Films, European Directors. SUNY Press. p. 11. ISBN 978-0-7914-3938-8.
- Seitz, Matt Zoller (April 29, 2019). "What's Next: Avengers, MCU, Game of Thrones, and the Content Endgame". RogerEbert.com. Ebert Digital LLC. Retrieved July 21, 2021.
- Avery, Hannah (January 18, 2023). "US streaming market growth continues, despite changes in the industry". Kantar Group. Retrieved April 29, 2023.
- "Wheat Info". Wheatworld.org. Archived from the original on October 11, 2009. Retrieved January 15, 2015.
- "Traditional Indigenous Recipes". American Indian Health and Diet Project. Retrieved September 15, 2014.
- Akenuwa, Ambrose (July 1, 2015). Is the United States Still the Land of the Free and Home to the Brave?. Lulu Press. pp. 92–94. ISBN 978-1-329-26112-9. Retrieved November 20, 2020.
- Mintz, Sidney Wilfred (1996). Tasting Food, Tasting Freedom: Excursions Into Eating, Culture, and the Past. Beacon Press. pp. 134–. ISBN 978-0-8070-4629-6. Retrieved October 25, 2015.
- Diner, Hasia (2001). Hungering for America: Italian, Irish, and Jewish Foodways in the Age of Migration. Cmabridge: Harvard University Press. p. 1.
- Poe, Tracy N. (February 1999). "The Origins of Soul Food in Black Urban Identity: Chicago, 1915–1947". American Studies International. 37 (1): 5.
- Cawthon, Haley (December 31, 2020). "KFC is America's favorite fried chicken, data suggests". The Business Journals. Retrieved May 8, 2021.
- Russell, Joan (May 23, 2016). "How Pizza Became America's Favorite Food". Paste. Retrieved May 8, 2021.
- Klapthor, James N. (August 23, 2003). "What, When, and Where Americans Eat in 2003". Newswise/Institute of Food Technologists. Retrieved June 19, 2007.
- "Our Story: CIA History | Culinary Institute of America". ciachef.edu. Retrieved October 11, 2022.
- Averbuch, Bonnie (September 2015). "Attention Food Entrepreneurs: School's Back in Business". Food Tank. Retrieved June 19, 2017.
- ^ Brownfield, Andy (March 20, 2020). "Cincinnati restaurants ask feds for coronavirus bailout". login.research.cincinnatilibrary.org. Retrieved March 22, 2020.
- Ramirez, Elva. "The Restaurant Industry Needs A Coronavirus Bailout. Will They Get It?". Forbes. Retrieved March 22, 2020.
- Noguchi, Yuki (March 22, 2020). "Closed All At Once: Restaurant Industry Faces Collapse". NPR. Retrieved March 22, 2020.
- "Restaurant industry reeling from coronavirus". MSNBC. Retrieved March 22, 2020.
- "Restaurants". Michelin Guide. Retrieved August 30, 2023.
- United States Department of Agriculture "Global Wine Report August 2006 Archived April 8, 2008, at the Wayback Machine", pp. 7-9.
- Birchell, D.B.; Steel, G. (2013). New Mexico Wine: An Enchanting History. American Palate Series (in Italian). American Palate. ISBN 978-1-60949-643-2. Retrieved November 15, 2019.
- New Mexico. Office of Cultural Affairs (1995). Enchanted Lifeways: The History, Museums, Arts & Festivals of New Mexico. New Mexico Magazine. ISBN 978-0-937206-39-3. Retrieved November 15, 2019.
- T. Stevenson, The Sotheby's Wine Encyclopedia Fourth Edition, p. 462, Dorling Kindersly, 2005, ISBN 0-7566-1324-8.
- J. Robinson, ed. The Oxford Companion to Wine, Third Edition, p. 719; Oxford University Press, 2006, ISBN 0-19-860990-6.
- "America's Love Of Drive-thrus". NPR. December 11, 2023. Retrieved May 4, 2024.
- "When Was the First Drive-Thru Restaurant Created?". Wisegeek.org. Retrieved January 15, 2015.
- Sheldon, Andrew (July 23, 2020). "The History of the Drive-Thru in America". Your AAA Network.
- Pavlova, Rada (April 8, 2019). "Globalization of American Fast-Food Chains: the Pinnacle of Effective Management and Adaptability – The Yale Globalist". The Yale Globalist. Retrieved May 4, 2024.
- "Sports". Gallup, Incorporated. September 25, 2007. Retrieved April 16, 2023.
- Krasnoff, Lindsay Sarah (December 26, 2017). "How the NBA went global". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. OCLC 2269358. Archived from the original on December 26, 2017. Retrieved September 14, 2023.
- Liss, Howard. Lacrosse (Funk & Wagnalls, 1970), p. 13.
- "Global sports market to hit $141 billion in 2012". Reuters. June 18, 2008. Retrieved July 24, 2013.
- Krane, David K. (October 30, 2002). "Professional Football Widens Its Lead Over Baseball as Nation's Favorite Sport". Harris Interactive. Archived from the original on July 9, 2010. Retrieved September 14, 2007. MacCambridge, Michael (2004). America's Game: The Epic Story of How Pro Football Captured a Nation. New York: Random House. ISBN 978-0-375-50454-9.
- Guliza, Anthony (August 14, 2019). "How the NFL took over America in 100 years". ESPN. Retrieved May 8, 2021.
- "As American as Mom, Apple Pie and Football? Football continues to trump baseball as America's Favorite Sport" (PDF). Harris Interactive. January 16, 2014. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 9, 2014. Retrieved July 2, 2014.
- Cowen, Tyler; Grier, Kevin (February 9, 2012). "What Would the End of Football Look Like?". Grantland/ESPN. Retrieved February 12, 2012.
- "Sports Illustrated: NCAA Reports $1.1 Billion in Revenues". Sports Illustrated. March 7, 2018.
- "Passion for College Football Remains Robust". National Football Foundation. March 19, 2013. Archived from the original on April 7, 2014. Retrieved April 1, 2014.
- Rosandich, Thomas (2002). "Collegiate Sports Programs: A Comparative Analysis". Education. 122 (3). Project Innovation Austin LLC.: 471.
- Schaus, Gerald P.; Wenn, Stephen R. (February 9, 2007). Onward to the Olympics: Historical Perspectives on the Olympic Games. Wilfrid Laurier University Press. p. 224. ISBN 978-0-88920-505-5.
- "Greatest Sporting Nation". greatestsportingnation.com.
- "1,000 times gold – The thousand medals of Team USA – Washington Post". The Washington Post.
- Chase, Chris (February 7, 2014). "The 10 most fascinating facts about the all-time Winter Olympics medal standings". USA Today. Retrieved February 28, 2014. Loumena, Dan (February 6, 2014). "With Sochi Olympics approaching, a history of Winter Olympic medals". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved February 28, 2014.
- Carlisle, Jeff (April 6, 2020). "MLS Year One, 25 seasons ago: The Wild West of training, travel, hockey shootouts and American soccer". ESPN. Retrieved May 5, 2021.
- Wamsley, Laurel (June 16, 2022). "The U.S. cities hosting the 2026 World Cup are announced". NPR. Retrieved April 16, 2023.
- Gerson, Aria (July 10, 2020). "Impact of 1999 Women's World Cup went far beyond Brandi Chastain's iconic goal". USA Today. Retrieved February 14, 2024.
Sources
- Baym, Nina; Levine, Robert S., eds. (2013). The Norton Anthology of American Literature (Shorter eighth ed.). New York, New York: W.W. Norton. ISBN 978-0-393-91885-4.
- Bianchine, Peter J.; Russo, Thomas A. (1992). "The Role of Epidemic Infectious Diseases in the Discovery of America". Allergy and Asthma Proceedings. 13 (5): 225–232. doi:10.2500/108854192778817040. PMID 1483570.
- Blackhawk, Ned (2023). "'The Centrality of Dispossession': Native American Genocide and Settler Colonialism". In Blackhawk, Ned; Kiernan, Ben; Madley, Benjamin; Taylor, Rebe (eds.). The Cambridge World History of Genocide. Vol. 2: Genocide in the Indigenous, Early Modern and Imperial Worlds, from c.1535 to World War One. Cambridge University Press. pp. 23–45. doi:10.1017/9781108765480.002.
- Blakeley, Ruth (2009). State Terrorism and Neoliberalism: The North in the South. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-68617-4.
- Boyer, Paul S.; Clark Jr., Clifford E.; Kett, Joseph F.; Salisbury, Neal; Sitkoff, Harvard; Woloch, Nancy (2007). The Enduring Vision: A History of the American People. Vol. 1. Cengage Learning. p. 588. ISBN 978-0-618-80161-9.
- Calloway, Colin G. (1998). New Worlds for All: Indians, Europeans, and the Remaking of Early America. JHU Press. p. 229. ISBN 978-0-8018-5959-5.
- Cohen, Eliot A. (July–August 2004). "History and the Hyperpower". Foreign Affairs. Washington, D.C. Retrieved July 14, 2006.
- Corbett, P. Scott; Janssen, Volker; Lund, John M.; Pfannestiel, Todd; Waskiewicz, Sylvie; Vickery, Paul (2014). U.S. History. Houston, Texas: OpenStax at Rice University.
- "Country Profile: United States of America". BBC News. London. April 22, 2008. Retrieved May 18, 2008.
- Davis, Kenneth C. (1996). Don't know much about the Civil War. New York: William Marrow and Company. p. 518. ISBN 978-0-688-11814-3.
- Daynes, Byron W.; Sussman, Glen (2010). White House Politics and the Environment: Franklin D. Roosevelt to George W. Bush. Texas A&M University Press. p. 320. ISBN 978-1-60344-254-1. OCLC 670419432.
Presidential environmental policies, 1933–2009
- Foner, Eric (2020). Give Me Liberty: An American History. Vol. 1 (6th ed.). New York, New York; London, England: W.W. Norton. ISBN 978-0-393-44123-9. Ebook.
- Erlandson, Jon M.; Rick, Torben C.; Vellanoweth, Rene L. (2008). A Canyon Through Time: Archaeology, History, and Ecology of the Tecolote Canyon Area, Santa Barbara County. California: University of Utah Press. ISBN 978-0-87480-879-7.
- Feldstein, Sylvan G.; Fabozzi, Frank J. (2011). The Handbook of Municipal Bonds. John Wiley & Sons. p. 1376. ISBN 978-1-118-04494-0.
- Flannery, Tim (2015). The Eternal Frontier: An Ecological History of North America and Its Peoples. Open Road + Grove/Atlantic. ISBN 978-0-8021-9109-0.
- Fraser, Steve; Gerstle, Gary (1989). The Rise and Fall of the New Deal Order: 1930–1980. American History: Political science. Princeton University Press. p. 311. ISBN 978-0-691-00607-9.
- Gaddis, John Lewis (1972). The United States and the Origins of the Cold War, 1941–1947. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-12239-9.
- Gordon, John Steele (2004). An Empire of Wealth: The Epic History of American Economic Power. HarperCollins. ISBN 978-0-06-009362-4.
- Haines, Michael Robert; Haines, Michael R.; Steckel, Richard H. (2000). A Population History of North America. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-49666-7.
- Hayes, Nick (November 6, 2009). "Looking back 20 years: Who deserves credit for ending the Cold War?". MinnPost. Retrieved March 11, 2013.
- Hoopes, Townsend; Brinkley, Douglas (1997). FDR and the Creation of the U.N. Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-08553-2.
- Howe, Daniel Walker (2008). What Hath God Wrought: The Transformation of America, 1815–1848. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0195078947.
- Johnson, Paul (1997). A History of the American People. HarperCollins. ISBN 978-0-06-195213-5.
- Joseph, Paul (2016). The Sage Encyclopedia of War: Social Science Perspectives. Sage Publications. ISBN 978-1-4833-5988-5.
- Lauter, Paul, ed. (1994a). The Heath Anthology of American Literature. Vol. 1 (2nd ed.). Lexington, Massachusetts: D.C. Heath and Company. ISBN 0-669-32972-X.
- Lauter, Paul, ed. (1994b). The Heath Anthology of American Literature. Vol. 2 (2nd ed.). Lexington, Massachusetts: D.C. Heath and Company. ISBN 0-669-32973-8.
- Lockard, Craig (2010). Societies, Networks, and Transitions, Volume B: From 600 to 1750. Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-1-111-79083-7.
- Lien, Arnold Johnson (1913). Studies in History, Economics, and Public Law. Vol. 54. New York: Columbia University. p. 604.
- Meyer, M.; Snow, D.; Snow, D.; Cohen, C.; Meyer, M.; Thornton, R.; Grinde, D.; Dilworth, L. (2001). "Indian History and Culture". In Boyer, Paul S. (ed.). The Oxford Companion to United States History. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/acref/9780195082098.001.0001. ISBN 978-0-19-508209-8.
- Mostert, Mary (2005). The Threat of Anarchy Leads to the Constitution of the United States. CTR Publishing, Inc. ISBN 978-0-9753851-4-2.
- Onuf, Peter S. (2010). The Origins of the Federal Republic: Jurisdictional Controversies in the United States, 1775–1787. University of Pennsylvania Press. ISBN 978-0-8122-0038-6.
- Perdue, Theda; Green, Michael D. (2005). The Columbia Guide to American Indians of the Southeast. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-50602-1.
- Quirk, Joel (2011). The Anti-Slavery Project: From the Slave Trade to Human Trafficking. University of Pennsylvania Press. p. 344. ISBN 978-0-8122-4333-8.
- Remini, Robert V. (2007). The House: The History of the House of Representatives. HarperCollins. ISBN 978-0-06-134111-3.
- Ripper, Jason (2008). American Stories: To 1877. M.E. Sharpe. p. 299. ISBN 978-0-7656-2903-6.
- Rodriguez, Junius (2015). Encyclopedia of Emancipation and Abolition in the Transatlantic World (Illustrated ed.). Routledge (Taylor & Francis). ISBN 978-1-317-47180-6.
- Safire, William (2003). No Uncertain Terms: More Writing from the Popular "On Language" Column in The New York Times Magazine. Simon and Schuster. p. 199. ISBN 978-0-7432-4955-3.
- Savage, Candace (2011). Prairie: A Natural History. Greystone Books. ISBN 978-1-55365-899-3.
- Schultz, David Andrew (2009). Encyclopedia of the United States Constitution. Infobase Publishing. p. 904. ISBN 978-1-4381-2677-7.
- Shi, David Emory (2016). America: A Narrative History. Vol. 1 (Brief 10th ed.). New York: W.W. Norton. ISBN 978-0393265941.
- Smithers, Gregory D. (2012). "Rethinking Genocide in North America". In Bloxham, Donald; Moses, A. Dirk (eds.). The Oxford Handbook of Genocide Studies. Oxford University Press. pp. 322–342. doi:10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199232116.013.0017.
- Soss, Joe (2010). Hacker, Jacob S.; Mettler, Suzanne (eds.). Remaking America: Democracy and Public Policy in an Age of Inequality. Russell Sage Foundation. ISBN 978-1-61044-694-5.
- Stannard, David E. (1993). American Holocaust: The Conquest of the New World. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-508557-0.
- The New York Times Guide to Essential Knowledge: A Desk Reference for the Curious Mind (2nd ed.). St. Martin's Press. 2007. ISBN 978-0-312-37659-8.
- Thornton, Russell (1998). Studying Native America: Problems and Prospects. Univ of Wisconsin Press. ISBN 978-0-299-16064-7.
- Walker Howe, Daniel (2007). What Hath God Wrought: The Transformation of America, 1815–1848. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-972657-8.
- Walton, Gary M.; Rockoff, Hugh (2009). History of the American Economy. Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-0-324-78662-0.
- Waters, M. R.; Stafford, T. W. (2007). "Redefining the Age of Clovis: Implications for the Peopling of the Americas". Science. 315 (5815): 1122–1126. Bibcode:2007Sci...315.1122W. doi:10.1126/science.1137166. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 17322060. S2CID 23205379.
- Winchester, Simon (2013). The men who United the States. Harper Collins. pp. 198, 216, 251, 253. ISBN 978-0-06-207960-2.
- Wright, Gavin (2022). "Slavery and the Rise of the Nineteenth-Century American Economy". Journal of Economic Perspectives. 36 (2): 123–148. doi:10.1257/jep.36.2.123. S2CID 248716718.
- Zinn, Howard (2005). A People's History of the United States. Harper Perennial Modern Classics. ISBN 978-0-06-083865-2.
- McPherson, James M. (1988). Battle Cry of Freedom: The Civil War Era. Oxford, England; New York, New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-503863-7.
 This article incorporates text from a free content work. Licensed under CC BY-SA IGO 3.0 (license statement/permission). Text taken from World Food and Agriculture – Statistical Yearbook 2023, FAO, FAO.
This article incorporates text from a free content work. Licensed under CC BY-SA IGO 3.0 (license statement/permission). Text taken from World Food and Agriculture – Statistical Yearbook 2023, FAO, FAO.
External links
Library resources aboutUnited States
Government
- Official U.S. Government web portal – gateway to government sites
- House – official website of the United States House of Representatives
- Senate – official website of the United States Senate
- White House – official website of the president of the United States
- Supreme Court – official website of the Supreme Court of the United States
History
- "Historical Documents" – website from the National Center for Public Policy Research
- "U.S. National Mottos: History and Constitutionality". Religious Tolerance. Analysis by the Ontario Consultants on Religious Tolerance.
- "Historical Statistics" – links to U.S. historical data
Maps
- "National Atlas of the United States" – official maps from the U.S. Department of the Interior
 Wikimedia Atlas of the United States
Wikimedia Atlas of the United States Geographic data related to United States at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to United States at OpenStreetMap- "Measure of America" – a variety of mapped information relating to health, education, income, safety and demographics in the United States
| Political divisions of the United States | |
|---|---|
| List of states and territories | |
| States |
|
| Federal district | Washington, D.C. |
| Territories | |
| Outlying islands | |
| Indian reservations | |
| International concessions | |
| North America | |
|---|---|
| Sovereign states | |
| Dependencies and other territories | |
 Media from Commons
Media from Commons News from Wikinews
News from Wikinews Quotations from Wikiquote
Quotations from Wikiquote Resources from Wikiversity
Resources from Wikiversity Travel guides from Wikivoyage
Travel guides from Wikivoyage
40°N 100°W / 40°N 100°W / 40; -100 (United States of America)
Categories:- United States
- Countries in North America
- English-speaking countries and territories
- Federal constitutional republics
- Former British colonies and protectorates in the Americas
- Former confederations
- G20 members
- Member states of NATO
- Member states of the United Nations
- States and territories established in 1776