| Revision as of 22:23, 1 January 2023 editHazhk (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Rollbackers43,735 edits →top: rewording← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 05:48, 23 December 2024 edit undoWatson1234567 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users633 edits →Conquest by the Neo-Assyrian Empire (732–720 BCE)Tag: Visual edit | ||
| (194 intermediate revisions by 88 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{ |
{{Short description|Israelite kingdom in the Southern Levant}} | ||
| {{About|one of the two historical Israelite kingdoms|the biblical Israelite kingdom that is described as preceding this one|Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy)|other uses|Kingdom of Israel (disambiguation){{!}}Kingdom of Israel}} | |||
| {{More citations needed|date=January 2022}} | {{More citations needed|date=January 2022}} | ||
| {{About|the historical Kingdom of Israel, that lay to the north of the Kingdom of Judah|the Biblical, unified monarchy|Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy)|other uses|Kingdom of Israel (disambiguation){{!}}Kingdom of Israel}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=February 2020}} | {{Use dmy dates|date=February 2020}} | ||
| {{Infobox country | {{Infobox country | ||
| | native_name = 𐤉𐤔𐤓𐤀𐤋<ref> | | native_name = {{lang|obm|𐤉𐤔𐤓𐤀𐤋}}<ref> | ||
| * {{cite book |last=Rollston |first=Chris A. |author-link=Christopher Rollston |title=Writing and Literacy in the World of Ancient Israel: Epigraphic Evidence from the Iron Age |year=2010 |publisher=Society of Biblical Literature |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=kx9Uke_IfloC&pg=PA52 |pages=52–54 |isbn=978- |
* {{cite book |last=Rollston |first=Chris A. |author-link=Christopher Rollston |title=Writing and Literacy in the World of Ancient Israel: Epigraphic Evidence from the Iron Age |year=2010 |publisher=Society of Biblical Literature |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=kx9Uke_IfloC&pg=PA52 |pages=52–54 |isbn=978-1-58983-107-0 }} | ||
| * {{cite book |last=Compston |first=Herbert F. B. |title=The Inscription on the Stele of Méšaʿ |year=1919 |url=http://en.wikisource.org/The_Inscription_on_the_Stele_of_M%C3%A9%C5%A1a%CA%BF }}</ref> | * {{cite book |last=Compston |first=Herbert F. B. |title=The Inscription on the Stele of Méšaʿ |year=1919 |url=http://en.wikisource.org/The_Inscription_on_the_Stele_of_M%C3%A9%C5%A1a%CA%BF }}</ref> | ||
| | conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Israel | | conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Israel | ||
| | common_name = Israel | |||
| | status = Kingdom | | status = Kingdom | ||
| | era = ] | | era = ] | ||
| Line 15: | Line 14: | ||
| | government_type = ] | | government_type = ] | ||
| | title_leader = ] | | title_leader = ] | ||
| | leader1 = ] <small>(first)</small> | |||
| | year_leader1 = 931–910 BCE | |||
| | leader2 = ] <small>(last)</small> | | leader2 = ] <small>(last)</small> | ||
| | year_leader2 = |
| year_leader2 = 732–{{Circa|720 BCE}} | ||
| | |
| p1 = Twelve Tribes of Israel | ||
| | s1 = |
| s1 = Samerina{{!}}Samerina (Assyrian province) | ||
| | |
| year_start = {{Circa|930 BCE}} | ||
| | |
| year_end = {{Circa|720 BCE}} | ||
| | |
| event_end = ] | ||
| | image_map = File:William Hughes, The Kingdoms of Judah and Israel (FL36567450 3909153).jpg | |||
| | event_end = ] | |||
| | image_map = Kingdoms of Israel and Judah map 830.svg | |||
| | image_map_alt = | | image_map_alt = | ||
| | image_map_caption = | |||
| | image_map_caption = Map of Israel and Judah in the 9th century BCE, with Israel in blue and ] in yellow. | |||
| | capital = {{unbulletedlist | |||
| | capital = {{ubl|] <small>(c. 900 BCE)</small>|] <small>(900–909)</small>|] <small>(909–880)</small>|] <small>(880–c. 720)</small>}} | |||
| | ] <small>({{circa|1000–931 BCE}})</small> | |||
| | common_languages = ], ] | |||
| | ] <small>({{circa|931–909 BCE}})</small> | |||
| | religion = {{ubl|] or ] ]|]|]|]}} | |||
| | ] <small>({{circa|909–880 BCE}})</small> | |||
| | demonym = | |||
| | ] <small>({{circa|880–720 BCE}})</small>}} | |||
| | common_languages = ] (], ]) | |||
| | religion = ], other ] | |||
| | demonym = ] | |||
| | area_rank = | | area_rank = | ||
| | today = {{ubl|]|]|]|]|]}} | | today = {{ubl|]|] (])|]|]|]}} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| The '''Kingdom of Israel''' ({{Langx|hbo|{{Script/Hebrew|מַמְלֶכֶת יִשְׂרָאֵל}}|label=]}} {{Transliteration|he|Mamleḵeṯ Yīśrāʾēl}}), also called the '''Northern Kingdom''' or the '''Kingdom of Samaria''', was an ] that existed in the ] during the ]. Its beginnings date back to the first half of the 10th century BCE.<ref>{{cite book |title=From Nomadism to Monarchy?: Revisiting the Early Iron Age Southern Levant |last=Arie |first=Eran |publisher=Penn State Press |year=2023 |isbn=978-1-64602-270-0 |editor-last=Koch |editor-first=Ido |page=120 |chapter=Canaanites in a Changing World: The Jezreel Valley during the Iron Age I |quote=he growing proto-Israelite power in the central hill country, out of which would emerge the Northern Kingdom of Israel, should be dated to the first half of the 10th century BCE. |editor-last2=Lipschits |editor-first2=Oded |editor-last3=Sergi |editor-first3=Omer |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ugDkEAAAQBAJ&pg=PA120}}</ref> It controlled the areas of ], ] and parts of ]; the former two regions underwent a period in which a large number of new settlements were established shortly after the kingdom came into existence.<ref>Killebrew, Ann E., (2014). , in: The Archaeology of the Levant, Oxford University Press, p. 733: "In the Lower Galilee during the Iron IIA, earlier Iron I settlements were deserted and appear to have been replaced by new large fortified sites Zertal's landmark survey of northern Samaria demonstrates a doubling of the number of sites from the Iron I to II Finkelstein and Lederman's survey of the territory of Ephraim revealed settlement density peaks in the later Iron II period, with over 200 sites identified "</ref> It had four capital cities in succession: ], ], ], and the ]. In the 9th century BCE, it was ruled by the ], whose political centre was the city of Samaria. | |||
| The '''Kingdom of Israel''' ({{Hebrew Name|מַמְלֶכֶת יִשְׂרָאֵל|Mamleḵet Yīsra'ēl|Mamleḵeṯ Yīśrāʼēl}}), or the '''Kingdom of Samaria''', was an ] kingdom in the ] during the ]. The kingdom controlled the areas of ], ] and parts of ] Its capital, for the most part, was ] (modern ]). A separate ] polity, named ], with its capital in ], existed to its south. | |||
| According to the ], the territory of the ] was once amalgamated under a ], which was ruled by the ] and then by the ]. However, upon the death of ], who was the son and successor of ], there was discontent over his son and successor ], whose reign was only accepted by the ] and the ]. The unpopularity of Rehoboam's reign among the rest of the ], who sought ] as their monarch, resulted in ], which led to the establishment of the Kingdom of Israel in the north (Samaria), whereas the loyalists of Judah and Benjamin kept Rehoboam as their monarch and established the ] in the south (]), ending Israelite political unity. While the existence of Israel and Judah as two independent kingdoms is not disputed, some historians and archaeologists reject the ].<ref group="Notes" name="United Monarchy debated">The debate is described in Amihai Mazar (2010), , pp. 29-30, fn. 2: "For conservative approaches defining the United Monarchy as a state 'from Dan to Beer Sheba' including 'conquered kingdoms' (Ammon, Moab, Edom) and 'spheres of influence' in Geshur and Hamath cf. e.g. Ahlström (1993), 455–542; Meyers (1998); Lemaire (1999); Masters (2001); Stager (2003); Rainey (2006), 159–168; Kitchen (1997); Millard (1997; 2008). For a total denial of the historicity of the United Monarchy cf. e.g. Davies (1992), 67–68; others suggested a 'chiefdom' comprising a small region around Jerusalem, cf. Knauf (1997), 81–85; Niemann (1997), 252–299 and Finkelstein (1999). For a 'middle of the road' approach suggesting a United Monarchy of larger territorial scope though smaller than the biblical description cf. e.g. Miller (1997); Halpern (2001), 229–262; Liverani (2005), 92–101. The latter recently suggested a state comprising the territories of Judah and Ephraim during the time of David, that was subsequently enlarged to include areas of northern Samaria and influence areas in the Galilee and Transjordan. Na'aman (1992; 1996) once accepted the basic biography of David as authentic and later rejected the United Monarchy as a state, cf. id. (2007), 401–402."</ref> | |||
| Around 720 BCE, Israel was conquered by the ].{{sfn|Hasegawa|Levin|Radner|2018|p=55}} The records of Assyrian king ] indicate that he deported 27,290 Israelites to ].<ref name="fink" /><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Younger|first=K. Lawson|date=1998|title=The Deportations of the Israelites|url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/3266980|journal=Journal of Biblical Literature|volume=117|issue=2|pages=201–227|doi=10.2307/3266980|jstor=3266980 |issn=0021-9231}}</ref> This deportation resulted in the loss of one-fifth of the kingdom's population and is known as the ], which gave rise to the notion of the ]. Some of these Israelites, however, managed to migrate to safety in neighbouring Judah,<ref name=":2">{{Cite journal|last=Finkelstein|first=Israel|date=2015-06-28|title=Migration of Israelites into Judah after 720 BCE: An Answer and an Update|url=https://doi.org/10.1515/zaw-2015-0011|journal=Zeitschrift für die alttestamentliche Wissenschaft|language=en|volume=127|issue=2|pages=188–206|doi=10.1515/zaw-2015-0011|s2cid=171178702 |issn=1613-0103}}</ref> though the ] themselves would be conquered by the ] nearly two centuries later. Those who stayed behind in Samaria following the Assyrian conquest mainly concentrated themselves around ] and eventually came to be known as the ].{{sfn|Shen|Lavi|Kivisild|Chou|2004}}<ref name=":1" /> The Assyrians, as part of ], also settled other conquered foreign populations in the territory of Israel.<ref name=":1">{{Cite book|last=Finkelstein|first=Israel|url=http://worldcat.org/oclc/949151323|title=The forgotten kingdom : the archaeology and history of Northern Israel|publisher=Society of Biblical Literature|year=2013|isbn=978-1-58983-910-6|pages=158|oclc=949151323}}</ref> | |||
| ==History== | ==History== | ||
| ] |
] in the ], which was the capital of Israel from 880 BCE to 720 BCE.]] | ||
| The existence of an Israelite state in the north is documented in 9th century inscriptions.{{sfn|Dever|2017|p=338}} The earliest mention is from the ] of c.853 BCE, when ] mentions "Ahab the Israelite", plus the denominative for "land", and his ten thousand troops.{{sfn|Davies|2015|p=72}} This kingdom will have included parts of the lowlands (the ]), the Jezreel plain, lower Galilee and parts of the Transjordan.{{sfn|Davies|2015|p=72}} Ahab's forces were part of an anti-Assyrian coalition, implying that the kingdom was ruled by an urban elite, possessed a royal and state cult with large urban temples, and had scribes, mercenaries, and an administrative apparatus.{{sfn|Davies|2015|p=72}} In all this, it was similar to other recently-founded kingdoms of the time, such as ] and ].{{sfn|Davies|2015|p=72}} | |||
| According to ], ]'s campaign in the second half of the 10th century BCE collapsed the early polity of ] in central highlands, and made possible the beginning of the Northern Kingdom, with its capital at ],<ref>Finkelstein, Israel, (2022). , " Sheshoq I campaign brought the collapse of an early Israelite polity in the central highlands and neighboring areas the Northern Kingdom in the Samaria highlands and the Jezreel Valley" (Abstract).</ref><ref>Finkelstein, Israel, (2022): "...In the central part of the country, caused the decline of an early Israelite entity , probably the one memorized in the Bible as the House of Saul, and the rise of the Northern Kingdom, which was centered around Shechem and expanded, under pharaonic auspices, to the Jezreel--Beth-shean Valley..." (Summary).</ref> around 931 BCE. Israel consolidated as a kingdom in the first half of 9th century BCE,<ref>Finkelstein, Israel, (2020). , in Joachim J. Krause, Omer Sergi, and Kristin Weingart (eds.), ''Saul, Benjamin, and the Emergence of Monarchy in Israel: Biblical and Archaeological Perspectives'', SBL Press, Atlanta, GA, p. 48, footnote 57: "...They became territorial kingdoms later, Israel in the first half of the ninth century BCE and Judah in its second half..."</ref> with its capital at ] first,{{sfn|Sergi|2023|p=77|ps=, "...almost one hundred years from the destruction of Shechem ...a new urban center emerged in the region, first and only for a short time at Tell el-Far'ah (North), identified as the biblical Tirzah (Albright 1925)..."}} and next at the city of ] since 880 BCE. The existence of this ] state in the north is documented in ] inscriptions.{{sfn|Dever|2017|p=338}} The earliest mention is from the ] of c. 853 BCE, when ] mentions "Ahab the Israelite", plus the denominative for "land", and his ten thousand troops.{{sfn|Davies|2015|p=72}} This kingdom would have included parts of the lowlands (the ]), the Jezreel plain, lower Galilee and parts of the Transjordan.{{sfn|Davies|2015|p=72}} | |||
| In later Assyrian inscriptions, the kingdom is referred to as the "House of ]".{{sfn|Davies|2015|p=72}} Shalmanesser III's "Black Obelisk" mentions ], son of Omri; and King ] of Assyria, who leaded an expedition into the Levant in 803, mentions "the Hatti-land and Amurru-land, the cities of Tyre and Sidon, Philistia, Edom, Aram, and the ''mat'' (land) of Hu-um-ri", or Omri.{{sfn|Davies|2015|p=72}} Another inscription from the same king introduces a third way of talking about the kingdom, as Samaria, in the phrase "]".{{sfn|Davies|2015|p=72-73}} The use of Omri's name to refer to the kingdom still survived, and was used by ] in the phrase "the whole house of Omri" in describing his conquest of the city of Samaria in 722 BCE.{{sfn|Davies|2015|p=73}} It is significant that the Assyrians never mention the ] until the end of the 8th century, when it was an Assyrian vassal: possibly they never had contact with it, or possibly they regarded it as a vassal of Israel/Samaria or Aram, or possibly the southern kingdom did not exist during this period.{{sfn|Davies|2015|p=3}} | |||
| Samaria is one of the most universally accepted archaeological sites from the biblical period.<ref>See Yohanan Aharoni, et al. (1993) ''The Macmillan Bible Atlas'', p. 94, Macmillan Publishing: New York; and Amihai Mazar (1992) ''The Archaeology of the Land of the Bible: 10,000 – 586 B.C.E'', p. 404, New York: Doubleday, see pp. 406-410 for discussion of archaeological significance of Shomron (]) under Omride Dynasty.</ref> At around 850 BCE, the ] records the victory of the Kingdom of ] (in today's ]), under, King ], against the Kingdom of Israel, under king ] and his son ].<ref>{{Bibleverse|2|Kings|3|HE}}</ref> | |||
| Ahab's forces were part of an anti-Assyrian coalition, implying that an urban elite ruled the kingdom, possessed a royal and state cult with large urban temples, and had scribes, mercenaries, and an administrative apparatus.{{sfn|Davies|2015|p=72}} In all this, it was similar to other recently founded kingdoms of the time, such as ] and ].{{sfn|Davies|2015|p=72}} Samaria is one of the most universally accepted archaeological sites from the biblical period.<ref>See Yohanan Aharoni, et al. (1993) ''The Macmillan Bible Atlas'', p. 94, Macmillan Publishing: New York; and Amihai Mazar (1992) ''The Archaeology of the Land of the Bible: 10,000 – 586 B.C.E'', p. 404, New York: Doubleday, see pp. 406-410 for discussion of the archaeological significance of Shomron (]) under Omride Dynasty.</ref> In around 840 BCE, the ] records the victory of ] (in today's ]), under King ], over Israel, King ] and his son ].<ref>{{Bibleverse|2|Kings|3|HE}}</ref> | |||
| Archaeological finds, ancient Near Eastern texts, and the biblical record testify that in the time of the ], the Kingdom of Israel ruled in the mountainous Galilee, at ] in the upper ], in large parts of ] between the Arnon and the ] Rivers, and in the coastal plain of the ].<ref name=":0">{{Cite book|last=Israel.|first=Finkelstein|url=http://worldcat.org/oclc/949151323|title=The forgotten kingdom : the archaeology and history of Northern Israel|isbn=978-1-58983-910-6|pages=74|oclc=949151323}}</ref> | |||
| Archaeological finds, ancient Near Eastern texts, and the biblical record testify that in the time of the ], Israel ruled in the mountainous ], at ] in the upper ], in large parts of ] between the ] and the ], and in the coastal ].<ref name=":0">{{Cite book|last=Finkelstein|first=Israel|url=http://worldcat.org/oclc/949151323|year=2013|title=The forgotten kingdom: the archaeology and history of Northern Israel|isbn=978-1-58983-910-6|pages=74|oclc=949151323}}</ref> | |||
| ==In the Bible== | |||
| ], per ] 14.]] | |||
| One tradition source for the history of the Kingdom of Israel has been the ], written by authors in ], the capital of the ]; being written by a rival kingdom, it is inspired by ideological and theological viewpoints that influence the narrative.<ref name=":0"/> Anachronisms, legends and literary forms also affect the story. Some of the events are believed to have been recorded long after the destruction of the kingdom of Israel. ] has both confirmed and challenged parts of the biblical account.<ref name=":0" /> According to the Jewish Bible, there existed a ], ruled from ] by ] and his son ], after whose death the Israel and ] separated into two kingdoms. | |||
| In Assyrian inscriptions, the Kingdom of Israel is referred to as the "House of ]".{{sfn|Davies|2015|p=72}} The ] mentions ], son of ʻOmri.{{sfn|Davies|2015|p=72}} The ] ] did an expedition into the Levant around 803 BCE mentioned in the Nimrud slab, which comments he went to "the Hatti and Amurru lands, Tyre, Sidon, the ''mat'' of Hu-um-ri "land of ʻOmri", ], ], and ] (not Judah)."{{sfn|Davies|2015|p=72}} The ] of the same king introduces a third way of talking about the kingdom, as Samaria, in the phrase "]".{{sfn|Davies|2015|p=72-73}} The use of Omri's name to refer to the kingdom still survived, and was used by ] in the phrase "the whole house of Omri" in describing his conquest of the city of Samaria in 722 BCE.{{sfn|Davies|2015|p=73}} It is significant that the Assyrians never mention the ] until the end of the 8th century, when it was an Assyrian ]: possibly they never had contact with it, or possibly they regarded it as a vassal of Israel/Samaria or Aram, or possibly the southern kingdom did not exist during this period.{{sfn|Davies|2015|p=3}} | |||
| The first mention of the name "Israel" is from an Egyptian inscription, the ], dating from the Late Bronze Age (c. 1208 BCE); this gives little solid information, but indicates that the name of the later kingdom was borrowed rather than originating with the kingdom itself.{{sfn|Davies|2015|p=71-72}} | |||
| ==In the Hebrew Bible== | |||
| ===Relations between the kingdoms of Israel and Judah=== | |||
| ], as per ].]] | |||
| ] of the people of the land of ]" ({{lang-akk|𒅀𒌑𒀀 𒈥 𒄷𒌝𒊑𒄿}}) as depicted on the ] of ], 841-840 BCE.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Kuan|first1=Jeffrey Kah-Jin|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=zMOqCwAAQBAJ&pg=PA65|title=Neo-Assyrian Historical Inscriptions and Syria-Palestine: Israelite/Judean-Tyrian-Damascene Political and Commercial Relations in the Ninth-Eighth Centuries BCE|date=2016|publisher=Wipf and Stock Publishers|isbn=978-1-4982-8143-0|pages=64–66|language=en}}</ref> This is "the only portrayal we have in ancient Near Eastern art of an Israelite or Judaean monarch".<ref name="AD">{{cite book|last1=Cohen|first1=Ada|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=uRKU0YXBWtgC&pg=PA127|title=Assyrian Reliefs from the Palace of Ashurnasirpal II: A Cultural Biography|last2=Kangas|first2=Steven E.|date=2010|publisher=UPNE|isbn=978-1-58465-817-7|page=127|language=en}}</ref>]]Still according to the Jewish Bible, for the first sixty years after the split, the kings of Judah tried to re-establish their authority over the northern kingdom, and there was perpetual war between them. For the following eighty years, there was no open war between them, and, for the most part, they were in friendly alliance, co-operating against their common enemies, especially against ].], 841-840 BCE.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Delitzsch|first1=Friedrich|url=https://archive.org/stream/babelbibl00deli/babelbibl00deli#page/78/mode/1up|title=Babel and Bible;|last2=McCormack|first2=Joseph|last3=Carruth|first3=William Herbert|last4=Robinson|first4=Lydia Gillingham|date=1906|publisher=Chicago, The Open court publishing company|page=78}}</ref>]]The conflict between Israel and Judah was temporarily settled when ], King of Judah, allied himself with the reigning house of Israel, ], through marriage. Later, Jehosophat's son and successor, ], married Ahab's daughter ], cementing the alliance. However, the sons of Ahab were slaughtered by ] following his ] around 840 BCE. | |||
| One traditional source for the history of the Kingdom of Israel has been the Hebrew Bible, especially the Books of ] and ]. These books were written by authors in ], the capital of the Kingdom of Judah. Being written in a rival kingdom, they were inspired by ideological and theological viewpoints that influence the narrative.<ref name=":0"/> Anachronisms, legends and literary forms also affect the story. Some of the recorded events are believed to have occurred long after the destruction of the kingdom of Israel. ] has both confirmed and challenged parts of the biblical account.<ref name=":0" /> According to the Hebrew Bible, there existed a United Kingdom of Israel (the ]), ruled from ] by ] and his son ], after whose death Israel and ] separated into two kingdoms. | |||
| The first mention of the name ''Israel'' is from an Egyptian inscription, the ], dating from the Late Bronze Age (c. 1208 BCE); this gives little solid information, but indicates that the name of the later kingdom was borrowed rather than originating with the kingdom itself.{{sfn|Davies|2015|p=71-72}} | |||
| ]'s delegation to ], ], 841-840 BCE.]] | |||
| === Destruction of the Kingdom, 732–720 BC === | |||
| ===Relationship with the Kingdom of Judah=== | |||
| According to the Hebrew Bible, for the first sixty years after the split, the kings of Judah tried to re-establish their authority over the northern kingdom, and there was perpetual war between them. For the following eighty years, there was no open war between them, as, for the most part, Judah had engaged in a military alliance with ], opening a northern front against Israel.{{sfn|Roberts|2016|p=203}} The conflict between Israel and Judah was temporarily settled when ], King of Judah, allied himself with the reigning house of Israel, ], through marriage. Later, Jehosophat's son and successor, ], married Ahab's daughter ], cementing the alliance.{{sfn|Roberts|2016|p=203}} However, the sons of Ahab were slaughtered by ] following his ] around 840 BCE.{{sfn|Roberts|2016|p=204}} | |||
| ===From Hazael to Jeroboam II=== | |||
| After being defeated by ], Israel began a period of progressive recovery following the campaigns against Aram-Damascus of ].{{sfn|Roberts|2016|p=206}} This ultimately led to a period of major territorial expansion under ], who extended the kingdom's possessions throughout the Northern Transjordan. Following Jeroboam II's death, the Kingdom experienced a period of decline as a result of sectional rivalries and struggles for the throne.{{sfn|Roberts|2016|p=207}} | |||
| === Conquest by the Neo-Assyrian Empire (732–720 BCE) === | |||
| {{main|Assyrian captivity}} | {{main|Assyrian captivity}} | ||
| ]'s delegation to ], ], 841–840 BCE.]] | |||
| In c. 732 BCE, king ] of Israel, while allied with ], king of ], threatened ]. ], ], appealed to ], the king of ], for help. After Ahaz paid tribute to Tiglath-Pileser,<ref>{{Bibleverse|2|Kings|16:7-9|NIV}}</ref> Tiglath-Pileser sacked Damascus and Israel, annexing Aram<ref name="Grabbe">{{cite book |author=Lester L. Grabbe |title=Ancient Israel: What Do We Know and How Do We Know It? |url=https://archive.org/details/ancientisraelwha00grab |url-access=limited |location=New York |publisher= T&T Clark |date=2007 |page= |isbn=978-05-67-11012-1}}</ref> and territory of the tribes of ], ] and ] in Gilead including the desert outposts of ], ] and ]. People from these tribes, including the Reubenite leader, were taken captive and resettled in the region of the ] system, in ], Habor, Hara and ] ({{Bibleverse|1 Chronicles|5:26}}). Tiglath-Pilesar also captured the territory of ] and the city of ] in ], and an Assyrian governor was placed over the region of Naphtali. According to {{Bibleverse|2 Kings|16:9}} and {{Bibleverse|2 Kings|15:29}}, the population of Aram and the annexed part of Israel was deported to Assyria.<ref>{{Bibleverse|2|Kings|16:9|NIV}} and {{Bibleverse-nb|2|Kings|15:29|NIV}}</ref> | |||
| In c. 732 BCE, King ] of Israel, while allied with ], king of ], threatened ]. ], ], appealed to ], the King of ], for help. After Ahaz paid tribute to Tiglath-Pileser,<ref>{{Bibleverse|2|Kings|16:7-9|NIV}}</ref> Tiglath-Pileser sacked Damascus and Israel, annexing Aram<ref name="Grabbe">{{cite book |first=Lester L. |last=Grabbe |title=Ancient Israel: What Do We Know and How Do We Know It? |url=https://archive.org/details/ancientisraelwha00grab |url-access=limited |location=New York |publisher= T&T Clark |date=2007 |page= |isbn=978-05-67-11012-1}}</ref> and the territories of the tribes of ], ] and ] in Gilead, including the desert outposts of ], ] and ]. People from these tribes, including the Reubenite leader, were taken captive and resettled in the region of the ] system, in ], Habor, Hara and ] ({{Bibleverse|1 Chronicles|5:26}}). Tiglath-Pilesar also captured the territory of ] and the city of ] in ], and an Assyrian governor was placed over the region of Naphtali. According to {{Bibleverse|2 Kings|16:9}} and {{Bibleverse|2 Kings|15:29}}, the population of Aram and the annexed part of Israel was deported to Assyria.<ref>{{Bibleverse|2|Kings|16:9|NIV}} and {{Bibleverse-nb|2|Kings|15:29|NIV}}</ref> | |||
| ] of the people of the land of ]" ({{langx|akk|𒅀𒌑𒀀 𒈥 𒄷𒌝𒊑𒄿}}), as depicted on the ] from 841 to 840 BCE.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Kuan|first1=Jeffrey Kah-Jin|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=zMOqCwAAQBAJ&pg=PA65|title=Neo-Assyrian Historical Inscriptions and Syria-Palestine: Israelite/Judean-Tyrian-Damascene Political and Commercial Relations in the Ninth-Eighth Centuries BCE|date=2016|publisher=Wipf and Stock Publishers|isbn=978-1-4982-8143-0|pages=64–66|language=en}}</ref> This is "the only portrayal we have in ] of an Israelite or Judaean monarch."<ref name="AD">{{cite book|last1=Cohen|first1=Ada|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=uRKU0YXBWtgC&pg=PA127|title=Assyrian Reliefs from the Palace of Ashurnasirpal II: A Cultural Biography|last2=Kangas|first2=Steven E.|date=2010|publisher=UPNE|isbn=978-1-58465-817-7|page=127|language=en}}</ref>]] | |||
| The remainder of the northern kingdom of Israel continued to exist within the reduced territory as an independent kingdom until around 720 BCE, when it was again invaded by ] and the rest of the population deported. During the three-year siege of ] in the territory of Ephraim by the Assyrians, ] died and was succeeded by ], who himself records the capture of that city thus: "Samaria I looked at, I captured; 27,280 men who dwelt in it I carried away" into Assyria. Thus, around 720 BCE, after two centuries, the kingdom of the ten tribes came to an end. Some of the Israelite captives were resettled in the Khabur region, and the rest in the land of the ], thus establishing Hebrew communities in ] and ]. The ] additionally records that Sargon had taken other captives from the northern kingdom to the Assyrian capital of Nineveh, in particular Tobit from the town of Thisbe in Naphtali.{{fact|date=December 2021}} | |||
| The remainder of the northern kingdom of Israel continued to exist within the reduced territory as an independent kingdom until around 720 BCE, when it was again invaded by Assyria and more of the population was deported. Not all of Israel's populace was deported by the Assyrians. During the three-year siege of ] in the territory of Ephraim by the Assyrians, ] died and was succeeded by ], who himself records the capture of that city thus: "Samaria I looked at, I captured; 27,280 men who dwelt in it I carried away" into Assyria. Thus, around 720 BCE, after two centuries, the northern kingdom came to an end. Some of the Israelite captives were resettled in the Khabur region, and the rest in the land of the ], thus establishing Hebrew communities in ] and ]. The ] additionally records that Sargon had taken other captives from the northern kingdom to the Assyrian capital of ], in particular Tobit from the town of Thisbe in Naphtali.{{citation needed|date=December 2021}} | |||
| The |
The Hebrew Bible relates that the population of the Kingdom of Israel was exiled, becoming known as the ]. To the south, the ], the ] (that was "absorbed" into Judah), the ] and the people of the ], who lived among them of the original ] nation, remained in the southern Kingdom of Judah. The Kingdom of Judah continued to exist as an independent state until 586 BCE, when it was conquered by the ]. | ||
| ====Samaritan version==== | |||
| Samaritan tradition states that much of the population of the Northern Kingdom of Israel remained in place after the Exile, including the Tribes of Naphtali, Menasseh, Benjamin and Levi – being the progenitors of the modern ]. In their book '']'', Israeli authors ] and ] estimate that only a fifth (about 40,000) of the population of the northern Kingdom of Israel were actually resettled out of the area during the two deportation periods under ] and ].<ref name=fink>Finkelstein, Israel; Silberman, Neil Asher (2002) ''The Bible Unearthed : Archaeology's New Vision of Ancient Israel and the Origin of Its Sacred Texts'', Simon & Schuster, {{ISBN|0-684-86912-8}}</ref>{{rp|221}} Many of the Northern Tribes also fled south to the ]; Jerusalem seems to have expanded in size five-fold during this period, requiring a new wall to be built, and a new source of water ] to be provided by King ].<ref name=":2" /> | |||
| ==== |
====Samaritan tradition==== | ||
| The tradition of the ] states that much of the population of the Kingdom of Israel remained in place after the ], including the Tribes of Naphtali, Manasseh, Benjamin and Levi – being the progenitors of the modern Samaritans. In their book '']'', Israeli authors ] and ] estimate that only a fifth (about 40,000) of the population of the Kingdom of Israel were actually resettled out of the area during the two deportation periods under ] and ].<ref name=fink>Finkelstein, Israel; Silberman, Neil Asher (2002) ''The Bible Unearthed : Archaeology's New Vision of Ancient Israel and the Origin of Its Sacred Texts'', Simon & Schuster, {{ISBN|978-0-684-86912-4}}</ref>{{rp|221}} Many members of these northern tribes also fled south to the Kingdom of Judah. Jerusalem seems to have expanded in size five-fold during this period, requiring a new wall to be built, and a new source of water ] to be provided by King ].<ref name=":2" /> | |||
| In medieval Rabbinic fable, the concept of the ten tribes becomes confounded with accounts of the Assyrian deportations, leading to the myth of the "]".{{fact|date=December 2021}} | |||
| ====Recorded |
====Recorded accounts==== | ||
| ], as depicted on the ] (841–840 BCE)<ref>{{cite book|last1=Delitzsch|first1=Friedrich|url=https://archive.org/stream/babelbibl00deli/babelbibl00deli#page/78/mode/1up|title=Babel and Bible;|last2=McCormack|first2=Joseph|last3=Carruth|first3=William Herbert|last4=Robinson|first4=Lydia Gillingham|date=1906|publisher=Chicago, The Open court publishing company|page=78}}</ref>]] | |||
| In their book '']'', Israeli authors ] and ] estimate that only a fifth (about 40,000) of the population of the northern Kingdom of Israel were actually resettled out of the area during the two deportation periods under ] and ].<ref name="fink" /> No known non-Biblical record exists of the Assyrians having exiled people from four of the tribes of Israel: ], ], ], ]. Descriptions of the deportation of people from ], ], ], Ephraim and Naphtali indicate that only a portion of these tribes were deported, and the places to which they were deported are known locations given in the accounts. The deported communities are mentioned as still existing at the time of the composition of the ] and ] and did not disappear by assimilation. 2 Chronicles 30:1-18 explicitly mentions northern Israelites who had been spared by the Assyrians, in particular people of Ephraim, Manasseh, Asher, Issachar and Zebulun, and how members of the latter three returned to worship at the Temple in Jerusalem during the reign of ].<ref>{{Bibleverse|2|Chronicles|30:1-18|NIV}}</ref> | |||
| In their book ''The Bible Unearthed'', Israeli authors ] and ] estimate that only a fifth (about 40,000) of the population of the northern Kingdom of Israel were actually resettled out of the area during the two deportation periods under ] and ].<ref name="fink" /> No known non-Biblical record exists of the Assyrians having exiled people from four of the tribes of Israel: ], ], ], ]. Descriptions of the deportation of people from ], ], ], Ephraim and Naphtali indicate that only a portion of these tribes were deported, and the places to which they were deported are known locations given in the accounts. The deported communities are mentioned as still existing at the time of the composition of the ] and ] and did not disappear by assimilation. 2 Chronicles 30:1–18 explicitly mentions northern Israelites who had been spared by the Assyrians, in particular people of Ephraim, Manasseh, Asher, Issachar and Zebulun, and how members of the latter three returned to worship at the ] during the reign of ].<ref>{{Bibleverse|2|Chronicles|30:1-18|NIV}}</ref> | |||
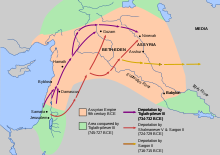
| ]]] | ], showing the routes of the deported population of Israel after the kingdom was conquered by the ] in 720 BCE.]] | ||
| ===Religion=== | ===Religion=== | ||
| The religious climate of the Kingdom of Israel appears to have followed two major trends. The first |
The ] of the Kingdom of Israel appears to have followed two major trends. The first was the worship of ]; the religion of ancient Israel is sometimes referred to by modern scholars as ].<ref name="auto"/> The ], however, states that some of the northern Israelites also adored ] (see {{Bibleverse|1 Kings|16:31}} and the ] discovered at ]).<ref name="auto">{{Cite book|last=Miller|first=Patrick D.|url=https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/44174114|title=The religion of ancient Israel|date=2000|publisher=SPCK|isbn=978-0-664-22145-4|location=London|oclc=44174114}}</ref> The reference in ] to Israel's "divided heart"<ref>{{bibleverse|Hosea|10:2|NRSV}} in the ], but some translators prefer "deceitful", as in the ].</ref> may refer to these two cultic observances, although alternatively it may refer to hesitation between looking to Assyria and Egypt for support.<ref>Jerusalem Bible (1966), Footnote b at Hosea 10:2</ref> | ||
| The Jewish Bible also states that ] allowed the cult worship of ] to become acceptable of the kingdom. His wife ] was the daughter of the ]n king of ] and a devotee to Baal worship ({{Bibleverse|1 Kings|16:31}}).<ref>{{JewishEncyclopedia|title=JEZEBEL|last=Hirsch|first=Emil G.|last2=Price|first2=Ira Maurice|url=http://www.jewishencyclopedia.com/articles/8675-jezebel}}</ref> | |||
| According to the Hebrew Bible ({{Bibleverse|1 Kings|12:29}}), ] built two places of worship, one at ] and one at far northern ], as alternatives to the ].<ref>Jonathan S. Greer (2015) </ref> He did not want the people of his kingdom to have religious ties to ], the capital city of the rival ]. He erected golden bulls at the entrance to the temples to represent the ].<ref name="teldan.wordpress.com">, Tel Dan Excavations</ref> The Hebrew Bible, written from the perspective of scribes in Jerusalem, referred to these acts as the way of Jeroboam or the errors of Jeroboam ({{Bibleverse|1 Kings|12:26-29}}).<ref name="teldan.wordpress.com" /> | |||
| ===Dynasties=== | |||
| The Jewish Bible also states that ] allowed the cult worship of ] to become acceptable of the kingdom. His wife ] was the daughter of the ] king of ] and a devotee to Baal worship ({{Bibleverse|1 Kings|16:31}}). | |||
| {{History of Israel}} | |||
| {{History of Palestine}} | |||
| {{Main|Kings of Israel and Judah}} | |||
| ===Royal houses=== | |||
| {{Full article|Kings of Israel and Judah}} | |||
| According to the Bible, the Northern Kingdom had 19 kings across 9 different dynasties throughout its 208 years of existence. | According to the Bible, the Northern Kingdom had 19 kings across 9 different dynasties throughout its 208 years of existence. | ||
| {{History of Israel}}] or ], or the newer chronologies of ] and ], all of which are shown below. All dates are ]/].]] | |||
| ] or ], or the newer chronologies of ] and ], all of which are shown below. All dates are ]/].]] | |||
| ==List of proposed Assyrian references to Kingdom of Israel (Samaria)== | |||
| {{missing information|section|Archaeological findings and/or evidence|date=August 2015}} | |||
| {{Clear}} | |||
| The table below lists all the historical references to the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria) in Assyrian records.<ref>{{citation |jstor= 3268575 |title= What's in a Name? Neo-Assyrian Designations for the Northern Kingdom and Their Implications for Israelite History and Biblical Interpretation |first= Brad |last= Kelle |journal= Journal of Biblical Literature |volume= 121 |issue= 4|year= 2002 |pages= 639–666 |doi= 10.2307/3268575 }}</ref> King ]'s name takes the Assyrian shape of "Humri", his kingdom or dynasty that of Bit Humri or alike - the "House of Humri/Omri". | |||
| ==Mentions of Israel/Samaria in Assyrian literature and inscriptions== | |||
| The table below lists all the historical references to the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria) in Assyrian records.<ref>Kelle, Brad, (2002). , Journal of Biblical Literature, 121 (4), pp. 639–666, (See table in p. 640).</ref> King ]'s name takes the Assyrian shape of "Humri", his kingdom or dynasty that of Bit Humri or alike—the "House of Humri/Omri". | |||
| {|class="wikitable" style="text-align:center;" | {|class="wikitable" style="text-align:center;" | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| Line 105: | Line 116: | ||
| | ] | | ] | ||
| | 853 BCE | | 853 BCE | ||
| | KUR sir-'i-la-a-a |
| KUR sir-'i-la-a-a | ||
| | "Israel" | | "Israel" | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| Line 111: | Line 122: | ||
| | ], Calah Fragment, Kurba'il Stone, Ashur Stone | | ], Calah Fragment, Kurba'il Stone, Ashur Stone | ||
| | 841 BCE | | 841 BCE | ||
| | mar Hu-um-ri-i |
| mar Hu-um-ri-i | ||
| | "of Omri" | | "of Omri" | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| Line 117: | Line 128: | ||
| | ] | | ] | ||
| | 803 BCE | | 803 BCE | ||
| | KUR Sa-me-ri-na-a-a |
| KUR Sa-me-ri-na-a-a | ||
| | "land of Samaria" | | "land of Samaria" | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| Line 123: | Line 134: | ||
| | ] | | ] | ||
| | 803 BCE | | 803 BCE | ||
| | KUR <Bit>-Hu-um-ri-i |
| KUR <Bit>-Hu-um-ri-i | ||
| | "the 'land of Omri" | | "the 'land of Omri" | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| Line 133: | Line 144: | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | | ] | ||
| | Iran Stela | | ] | ||
| | 739–738 BCE | | 739–738 BCE | ||
| | KUR sa-m-ri-i-na-a- |
| KUR sa-m-ri-i-na-a- | ||
| | "land of Samaria" | | "land of Samaria" | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| Line 148: | Line 159: | ||
| | 732–731 BCE | | 732–731 BCE | ||
| | URU Sa-me-ri-na | | URU Sa-me-ri-na | ||
| | "city of Samaria" |
| "city of Samaria" | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | ] | | ] | ||
| | III R 10,2 | | III R 10,2 | ||
| | 731 BCE | | 731 BCE | ||
| | KUR E Hu-um-ri-a |
| KUR E Hu-um-ri-a | ||
| | "land of the House of Omri" | | "land of the House of Omri" | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| Line 171: | Line 182: | ||
| | Nimrud Prism, Great Summary Inscription | | Nimrud Prism, Great Summary Inscription | ||
| | 720 BCE | | 720 BCE | ||
| | URU Sa-me-ri-na |
| URU Sa-me-ri-na | ||
| | "city of Samaria" | | "city of Samaria" | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| Line 181: | Line 192: | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| == See also == | |||
| * ] | |||
| ** ], the other Israelite kingdom | |||
| ** ] | |||
| * ], claimed by the Hebrew Bible as Israel's (and Judah's) predecessor state | |||
| * ], the Northern Kingdom's population that was lost after the Assyrian conquest in 720 BCE | |||
| * ], the traditional descendants of the Northern Kingdom's non-deported Israelites | |||
| == References == | == References == | ||
| === Notes === | === Notes === | ||
| {{sources|section|date=January 2022}} | |||
| {{reflist |group="Notes"}} | {{reflist |group="Notes"}} | ||
| === Citations === | === Citations === | ||
| {{Reflist}} | {{Reflist}} | ||
| === Sources === | === Sources === | ||
| * {{Cite book | * {{Cite book | ||
| |last = Davies | |last = Davies | ||
| Line 195: | Line 217: | ||
| |year = 2015 | |year = 2015 | ||
| |publisher = Bloomsbury Publishing | |publisher = Bloomsbury Publishing | ||
| |isbn = |
|isbn = 978-0-567-65582-0 | ||
| |url = https://books.google.com/books?id=xKf2CQAAQBAJ&pg=PA72 | |url = https://books.google.com/books?id=xKf2CQAAQBAJ&pg=PA72 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| Line 204: | Line 226: | ||
| |year = 2017 | |year = 2017 | ||
| |publisher = SBL Press | |publisher = SBL Press | ||
| |isbn = |
|isbn = 978-0-88414-217-1 | ||
| |url = https://books.google.com/books?id=mog6DwAAQBAJ&pg=PA338 | |url = https://books.google.com/books?id=mog6DwAAQBAJ&pg=PA338 | ||
| }} | |||
| * {{Cite book | |||
| |title=The Last Days of the Kingdom of Israel | |||
| |publisher=Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG | |||
| |year=2018 | |||
| |isbn=978-3-11-056660-4 | |||
| |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Jwh2DwAAQBAJ | |||
| |editor-last=Hasegawa | |||
| |editor-first=Shuichi | |||
| |editor-last2=Levin | |||
| |editor-first2=Christoph | |||
| |editor-last3=Radner | |||
| |editor-first3=Karen | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| * {{Cite book | * {{Cite book | ||
| Line 218: | Line 253: | ||
| |year = 2010 | |year = 2010 | ||
| |publisher = Walter de Gruyter | |publisher = Walter de Gruyter | ||
| |isbn = |
|isbn = 978-3-11-022358-3 | ||
| |chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=oCqSZdoWZMkC&pg=PA29 | |chapter-url = https://books.google.com/books?id=oCqSZdoWZMkC&pg=PA29 | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| * {{Cite book | * {{Cite book | ||
| |title=The Wiley Blackwell Companion to Ancient Israel | |||
| |last = Schipper | |||
| |last=Roberts | |||
| |first = Berndt U. | |||
| |first=J. J. M. | |||
| |title = A Concise History of Ancient Israel | |||
| |publisher=John Wiley & Sons | |||
| |year = 2020 | |||
| |year=2016 | |||
| |publisher = Penn State Press | |||
| |isbn=978-0-470-65677-8 | |||
| |url = https://books.google.com/books?id=osfhDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA31 | |||
| |pages=197–212 | |||
| |isbn = 978-0495391050 | |||
| |editor-last=Niditch | |||
| |editor-first=Susan | |||
| |chapter=The Divided Monarchy | |||
| |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=-eMACgAAQBAJ&pg=PA197 | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| * {{Cite book |title=The Two Houses of Israel: State Formation and the Origins of Pan-Israelite Identity |last=Sergi |first=Omer |publisher=SBL Press |year=2023 |isbn=978-1-62837-345-5 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=4nLMEAAAQBAJ}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal|last1=Shen|first1=Peidong|last2=Lavi|first2=Tal|last3=Kivisild|first3=Toomas|last4=Chou|first4=Vivian|last5=Sengun|first5=Deniz|last6=Gefel|first6=Dov|last7=Shpirer|first7=Issac|last8=Woolf|first8=Eilon|last9=Hillel|first9=Jossi|last10=Feldman|first10=Marcus W.|last11=Oefner|first11=Peter J.|date=2004|title=Reconstruction of patrilineages and matrilineages of Samaritans and other Israeli populations from Y-Chromosome and mitochondrial DNA sequence Variation|url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/humu.20077|journal=Human Mutation|volume=24|issue=3|pages=248–260|doi=10.1002/humu.20077|pmid=15300852 |s2cid=1571356 |issn=1059-7794}} | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{commons category}} | |||
| * | * | ||
| * . The Jewish History Resource Center |
* Project of the Dinur Center for Research in Jewish History, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem | ||
| * A synchronized chart of the kings of Israel and Judah | * A synchronized chart of the kings of Israel and Judah | ||
| Line 239: | Line 281: | ||
| {{IsraeliteKings}} | {{IsraeliteKings}} | ||
| {{Ancient states and regions of the Levant |state=collapsed}} | {{Ancient states and regions of the Levant |state=collapsed}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 05:48, 23 December 2024
Israelite kingdom in the Southern Levant This article is about one of the two historical Israelite kingdoms. For the biblical Israelite kingdom that is described as preceding this one, see Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy). For other uses, see Kingdom of Israel.| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Kingdom of Israel" Samaria – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Kingdom of Israel𐤉𐤔𐤓𐤀𐤋 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c. 930 BCE–c. 720 BCE | |||||||||
 | |||||||||
| Status | Kingdom | ||||||||
| Capital | |||||||||
| Common languages | Hebrew (Biblical, Israelian) | ||||||||
| Religion | Yahwism, other Semitic religions | ||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Israelite | ||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||
| King | |||||||||
| • 931–910 BCE | Jeroboam I (first) | ||||||||
| • 732–c. 720 BCE | Hoshea (last) | ||||||||
| Historical era | Iron Age | ||||||||
| • Established | c. 930 BCE | ||||||||
| • Assyrian conquest | c. 720 BCE | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||
The Kingdom of Israel (Hebrew: מַמְלֶכֶת יִשְׂרָאֵל Mamleḵeṯ Yīśrāʾēl), also called the Northern Kingdom or the Kingdom of Samaria, was an Israelite kingdom that existed in the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. Its beginnings date back to the first half of the 10th century BCE. It controlled the areas of Samaria, Galilee and parts of Transjordan; the former two regions underwent a period in which a large number of new settlements were established shortly after the kingdom came into existence. It had four capital cities in succession: Shiloh, Shechem, Tirzah, and the city of Samaria. In the 9th century BCE, it was ruled by the Omride dynasty, whose political centre was the city of Samaria.
According to the Hebrew Bible, the territory of the Twelve Tribes of Israel was once amalgamated under a Kingdom of Israel and Judah, which was ruled by the House of Saul and then by the House of David. However, upon the death of Solomon, who was the son and successor of David, there was discontent over his son and successor Rehoboam, whose reign was only accepted by the Tribe of Judah and the Tribe of Benjamin. The unpopularity of Rehoboam's reign among the rest of the Israelites, who sought Jeroboam as their monarch, resulted in Jeroboam's Revolt, which led to the establishment of the Kingdom of Israel in the north (Samaria), whereas the loyalists of Judah and Benjamin kept Rehoboam as their monarch and established the Kingdom of Judah in the south (Judea), ending Israelite political unity. While the existence of Israel and Judah as two independent kingdoms is not disputed, some historians and archaeologists reject the historicity of the Kingdom of Israel and Judah.
Around 720 BCE, Israel was conquered by the Neo-Assyrian Empire. The records of Assyrian king Sargon II indicate that he deported 27,290 Israelites to Mesopotamia. This deportation resulted in the loss of one-fifth of the kingdom's population and is known as the Assyrian captivity, which gave rise to the notion of the Ten Lost Tribes. Some of these Israelites, however, managed to migrate to safety in neighbouring Judah, though the Judahites themselves would be conquered by the Neo-Babylonian Empire nearly two centuries later. Those who stayed behind in Samaria following the Assyrian conquest mainly concentrated themselves around Mount Gerizim and eventually came to be known as the Samaritans. The Assyrians, as part of their historic deportation policy, also settled other conquered foreign populations in the territory of Israel.
History

According to Israel Finkelstein, Shoshenq I's campaign in the second half of the 10th century BCE collapsed the early polity of Gibeon in central highlands, and made possible the beginning of the Northern Kingdom, with its capital at Shechem, around 931 BCE. Israel consolidated as a kingdom in the first half of 9th century BCE, with its capital at Tirzah first, and next at the city of Samaria since 880 BCE. The existence of this Israelite state in the north is documented in 9th century BCE inscriptions. The earliest mention is from the Kurkh stela of c. 853 BCE, when Shalmaneser III mentions "Ahab the Israelite", plus the denominative for "land", and his ten thousand troops. This kingdom would have included parts of the lowlands (the Shephelah), the Jezreel plain, lower Galilee and parts of the Transjordan.
Ahab's forces were part of an anti-Assyrian coalition, implying that an urban elite ruled the kingdom, possessed a royal and state cult with large urban temples, and had scribes, mercenaries, and an administrative apparatus. In all this, it was similar to other recently founded kingdoms of the time, such as Ammon and Moab. Samaria is one of the most universally accepted archaeological sites from the biblical period. In around 840 BCE, the Mesha Stele records the victory of Moab (in today's Jordan), under King Mesha, over Israel, King Omri and his son Ahab.
Archaeological finds, ancient Near Eastern texts, and the biblical record testify that in the time of the Omrides, Israel ruled in the mountainous Galilee, at Hazor in the upper Jordan Valley, in large parts of Transjordan between the Wadi Mujib and the Yarmuk, and in the coastal Sharon plain.
In Assyrian inscriptions, the Kingdom of Israel is referred to as the "House of ʻOmri". The Black Obelisk of Shalmaneser III mentions Jehu, son of ʻOmri. The Neo-Assyrian emperor Adad-nirari III did an expedition into the Levant around 803 BCE mentioned in the Nimrud slab, which comments he went to "the Hatti and Amurru lands, Tyre, Sidon, the mat of Hu-um-ri "land of ʻOmri", Edom, Philistia, and Aram (not Judah)." The Tell al-Rimah stela of the same king introduces a third way of talking about the kingdom, as Samaria, in the phrase "Joash of Samaria". The use of Omri's name to refer to the kingdom still survived, and was used by Sargon II in the phrase "the whole house of Omri" in describing his conquest of the city of Samaria in 722 BCE. It is significant that the Assyrians never mention the Kingdom of Judah until the end of the 8th century, when it was an Assyrian vassal state: possibly they never had contact with it, or possibly they regarded it as a vassal of Israel/Samaria or Aram, or possibly the southern kingdom did not exist during this period.
In the Hebrew Bible

One traditional source for the history of the Kingdom of Israel has been the Hebrew Bible, especially the Books of Kings and Chronicles. These books were written by authors in Jerusalem, the capital of the Kingdom of Judah. Being written in a rival kingdom, they were inspired by ideological and theological viewpoints that influence the narrative. Anachronisms, legends and literary forms also affect the story. Some of the recorded events are believed to have occurred long after the destruction of the kingdom of Israel. Biblical archaeology has both confirmed and challenged parts of the biblical account. According to the Hebrew Bible, there existed a United Kingdom of Israel (the United Monarchy), ruled from Jerusalem by David and his son Solomon, after whose death Israel and Judah separated into two kingdoms.
The first mention of the name Israel is from an Egyptian inscription, the Merneptah Stele, dating from the Late Bronze Age (c. 1208 BCE); this gives little solid information, but indicates that the name of the later kingdom was borrowed rather than originating with the kingdom itself.
Relationship with the Kingdom of Judah
According to the Hebrew Bible, for the first sixty years after the split, the kings of Judah tried to re-establish their authority over the northern kingdom, and there was perpetual war between them. For the following eighty years, there was no open war between them, as, for the most part, Judah had engaged in a military alliance with Aram-Damascus, opening a northern front against Israel. The conflict between Israel and Judah was temporarily settled when Jehoshaphat, King of Judah, allied himself with the reigning house of Israel, Ahab, through marriage. Later, Jehosophat's son and successor, Jehoram of Judah, married Ahab's daughter Athaliah, cementing the alliance. However, the sons of Ahab were slaughtered by Jehu following his coup d'état around 840 BCE.
From Hazael to Jeroboam II
After being defeated by Hazael, Israel began a period of progressive recovery following the campaigns against Aram-Damascus of Adad-nirari III. This ultimately led to a period of major territorial expansion under Jeroboam II, who extended the kingdom's possessions throughout the Northern Transjordan. Following Jeroboam II's death, the Kingdom experienced a period of decline as a result of sectional rivalries and struggles for the throne.
Conquest by the Neo-Assyrian Empire (732–720 BCE)
Main article: Assyrian captivity
In c. 732 BCE, King Pekah of Israel, while allied with Rezin, king of Aram, threatened Jerusalem. Ahaz, King of Judah, appealed to Tiglath-Pileser III, the King of Assyria, for help. After Ahaz paid tribute to Tiglath-Pileser, Tiglath-Pileser sacked Damascus and Israel, annexing Aram and the territories of the tribes of Reuben, Gad and Manasseh in Gilead, including the desert outposts of Jetur, Naphish and Nodab. People from these tribes, including the Reubenite leader, were taken captive and resettled in the region of the Khabur River system, in Halah, Habor, Hara and Gozan (1 Chronicles 5:26). Tiglath-Pilesar also captured the territory of Naphtali and the city of Janoah in Ephraim, and an Assyrian governor was placed over the region of Naphtali. According to 2 Kings 16:9 and 2 Kings 15:29, the population of Aram and the annexed part of Israel was deported to Assyria.

The remainder of the northern kingdom of Israel continued to exist within the reduced territory as an independent kingdom until around 720 BCE, when it was again invaded by Assyria and more of the population was deported. Not all of Israel's populace was deported by the Assyrians. During the three-year siege of Samaria in the territory of Ephraim by the Assyrians, Shalmaneser V died and was succeeded by Sargon II, who himself records the capture of that city thus: "Samaria I looked at, I captured; 27,280 men who dwelt in it I carried away" into Assyria. Thus, around 720 BCE, after two centuries, the northern kingdom came to an end. Some of the Israelite captives were resettled in the Khabur region, and the rest in the land of the Medes, thus establishing Hebrew communities in Ecbatana and Rages. The Book of Tobit additionally records that Sargon had taken other captives from the northern kingdom to the Assyrian capital of Nineveh, in particular Tobit from the town of Thisbe in Naphtali.
The Hebrew Bible relates that the population of the Kingdom of Israel was exiled, becoming known as the Ten Lost Tribes. To the south, the Tribe of Judah, the Tribe of Simeon (that was "absorbed" into Judah), the Tribe of Benjamin and the people of the Tribe of Levi, who lived among them of the original Israelite nation, remained in the southern Kingdom of Judah. The Kingdom of Judah continued to exist as an independent state until 586 BCE, when it was conquered by the Neo-Babylonian Empire.
Samaritan tradition
The tradition of the Samaritan people states that much of the population of the Kingdom of Israel remained in place after the Assyrian captivity, including the Tribes of Naphtali, Manasseh, Benjamin and Levi – being the progenitors of the modern Samaritans. In their book The Bible Unearthed, Israeli authors Israel Finkelstein and Neil Asher Silberman estimate that only a fifth (about 40,000) of the population of the Kingdom of Israel were actually resettled out of the area during the two deportation periods under Tiglath-Pileser III and Sargon II. Many members of these northern tribes also fled south to the Kingdom of Judah. Jerusalem seems to have expanded in size five-fold during this period, requiring a new wall to be built, and a new source of water Siloam to be provided by King Hezekiah.
Recorded accounts

In their book The Bible Unearthed, Israeli authors Israel Finkelstein and Neil Asher Silberman estimate that only a fifth (about 40,000) of the population of the northern Kingdom of Israel were actually resettled out of the area during the two deportation periods under Tiglath-Pileser III and Sargon II. No known non-Biblical record exists of the Assyrians having exiled people from four of the tribes of Israel: Dan, Asher, Issachar, Zebulun. Descriptions of the deportation of people from Reuben, Gad, Manasseh, Ephraim and Naphtali indicate that only a portion of these tribes were deported, and the places to which they were deported are known locations given in the accounts. The deported communities are mentioned as still existing at the time of the composition of the Books of Kings and Chronicles and did not disappear by assimilation. 2 Chronicles 30:1–18 explicitly mentions northern Israelites who had been spared by the Assyrians, in particular people of Ephraim, Manasseh, Asher, Issachar and Zebulun, and how members of the latter three returned to worship at the Temple in Jerusalem during the reign of Hezekiah.
Religion
The religious climate of the Kingdom of Israel appears to have followed two major trends. The first was the worship of Yahweh; the religion of ancient Israel is sometimes referred to by modern scholars as Yahwism. The Hebrew Bible, however, states that some of the northern Israelites also adored Baal (see 1 Kings 16:31 and the Baal cycle discovered at Ugarit). The reference in Hosea 10 to Israel's "divided heart" may refer to these two cultic observances, although alternatively it may refer to hesitation between looking to Assyria and Egypt for support.
The Jewish Bible also states that Ahab allowed the cult worship of Baal to become acceptable of the kingdom. His wife Jezebel was the daughter of the Phoenician king of Tyre and a devotee to Baal worship (1 Kings 16:31).
Dynasties
| Part of a series on the | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History of Israel | ||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||
| Early historyPrehistoric Levant | ||||||||||||||
Ancient Israel and Judah
|
||||||||||||||
Second Temple period
|
||||||||||||||
Late Antiquity and Middle Ages
|
||||||||||||||
|
Modern historyModern history (1517–1948)
State of Israel (1948–present) |
||||||||||||||
| By topic | ||||||||||||||
| Related | ||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||
| Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Palestine |
 |
| Prehistory |
| Ancient history |
| Classical period |
| Islamic rule |
| Modern era |
|
|
According to the Bible, the Northern Kingdom had 19 kings across 9 different dynasties throughout its 208 years of existence.

Mentions of Israel/Samaria in Assyrian literature and inscriptions
The table below lists all the historical references to the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria) in Assyrian records. King Omri's name takes the Assyrian shape of "Humri", his kingdom or dynasty that of Bit Humri or alike—the "House of Humri/Omri".
| Assyrian King | Inscription | Year | Transliteration | Translation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shalmaneser III | Kurkh Monoliths | 853 BCE | KUR sir-'i-la-a-a | "Israel" |
| Shalmaneser III | Black Obelisk, Calah Fragment, Kurba'il Stone, Ashur Stone | 841 BCE | mar Hu-um-ri-i | "of Omri" |
| Adad-nirari III | Tell al-Rimah Stela | 803 BCE | KUR Sa-me-ri-na-a-a | "land of Samaria" |
| Adad-nirari III | Nimrud Slab | 803 BCE | KUR <Bit>-Hu-um-ri-i | "the 'land of Omri" |
| Tiglath-Pileser III | Layard 45b+ III R 9,1 | 740 BCE | ||
| Tiglath-Pileser III | Iran Stela | 739–738 BCE | KUR sa-m-ri-i-na-a- | "land of Samaria" |
| Tiglath-Pileser III | Layard 50a + 50b + 67a | 738–737 BCE | URU sa-me-ri-na-a-a | "city of Samaria" |
| Tiglath-Pileser III | Layard 66 | 732–731 BCE | URU Sa-me-ri-na | "city of Samaria" |
| Tiglath-Pileser III | III R 10,2 | 731 BCE | KUR E Hu-um-ri-a | "land of the House of Omri" |
| Tiglath-Pileser III | ND 4301 + 4305 | 730 BCE | KUR E Hu-um-ri-a | "land of the House of Omri" |
| Shalmaneser V | Babylonian Chronicle ABC1 | 725 BCE | URU Sa-ma/ba-ra-'-in | "city of Samaria" |
| Sargon II | Nimrud Prism, Great Summary Inscription | 720 BCE | URU Sa-me-ri-na | "city of Samaria" |
| Sargon II | Palace Door, Small Summary Inscription, Cylinder Inscription, Bull Inscription | 720 BCE | KUR Bit-Hu-um-ri-a | "land of Omri" |
See also
- History of ancient Israel and Judah
- Kingdom of Judah, the other Israelite kingdom
- Kings of Israel and Judah
- Kingdom of Israel and Judah, claimed by the Hebrew Bible as Israel's (and Judah's) predecessor state
- Ten Lost Tribes, the Northern Kingdom's population that was lost after the Assyrian conquest in 720 BCE
- Samaritan people, the traditional descendants of the Northern Kingdom's non-deported Israelites
References
Notes
- The debate is described in Amihai Mazar (2010), "Archaeology and the Biblical Narrative: The Case of the United Monarchy", pp. 29-30, fn. 2: "For conservative approaches defining the United Monarchy as a state 'from Dan to Beer Sheba' including 'conquered kingdoms' (Ammon, Moab, Edom) and 'spheres of influence' in Geshur and Hamath cf. e.g. Ahlström (1993), 455–542; Meyers (1998); Lemaire (1999); Masters (2001); Stager (2003); Rainey (2006), 159–168; Kitchen (1997); Millard (1997; 2008). For a total denial of the historicity of the United Monarchy cf. e.g. Davies (1992), 67–68; others suggested a 'chiefdom' comprising a small region around Jerusalem, cf. Knauf (1997), 81–85; Niemann (1997), 252–299 and Finkelstein (1999). For a 'middle of the road' approach suggesting a United Monarchy of larger territorial scope though smaller than the biblical description cf. e.g. Miller (1997); Halpern (2001), 229–262; Liverani (2005), 92–101. The latter recently suggested a state comprising the territories of Judah and Ephraim during the time of David, that was subsequently enlarged to include areas of northern Samaria and influence areas in the Galilee and Transjordan. Na'aman (1992; 1996) once accepted the basic biography of David as authentic and later rejected the United Monarchy as a state, cf. id. (2007), 401–402."
Citations
-
- Rollston, Chris A. (2010). Writing and Literacy in the World of Ancient Israel: Epigraphic Evidence from the Iron Age. Society of Biblical Literature. pp. 52–54. ISBN 978-1-58983-107-0.
- Compston, Herbert F. B. (1919). The Inscription on the Stele of Méšaʿ.
- Arie, Eran (2023). "Canaanites in a Changing World: The Jezreel Valley during the Iron Age I". In Koch, Ido; Lipschits, Oded; Sergi, Omer (eds.). From Nomadism to Monarchy?: Revisiting the Early Iron Age Southern Levant. Penn State Press. p. 120. ISBN 978-1-64602-270-0.
he growing proto-Israelite power in the central hill country, out of which would emerge the Northern Kingdom of Israel, should be dated to the first half of the 10th century BCE.
- Killebrew, Ann E., (2014). "Israel during the Iron Age II Period", in: The Archaeology of the Levant, Oxford University Press, p. 733: "In the Lower Galilee during the Iron IIA, earlier Iron I settlements were deserted and appear to have been replaced by new large fortified sites Zertal's landmark survey of northern Samaria demonstrates a doubling of the number of sites from the Iron I to II Finkelstein and Lederman's survey of the territory of Ephraim revealed settlement density peaks in the later Iron II period, with over 200 sites identified "
- Hasegawa, Levin & Radner 2018, p. 55.
- ^ Finkelstein, Israel; Silberman, Neil Asher (2002) The Bible Unearthed : Archaeology's New Vision of Ancient Israel and the Origin of Its Sacred Texts, Simon & Schuster, ISBN 978-0-684-86912-4
- Younger, K. Lawson (1998). "The Deportations of the Israelites". Journal of Biblical Literature. 117 (2): 201–227. doi:10.2307/3266980. ISSN 0021-9231. JSTOR 3266980.
- ^ Finkelstein, Israel (28 June 2015). "Migration of Israelites into Judah after 720 BCE: An Answer and an Update". Zeitschrift für die alttestamentliche Wissenschaft. 127 (2): 188–206. doi:10.1515/zaw-2015-0011. ISSN 1613-0103. S2CID 171178702.
- Shen et al. 2004.
- ^ Finkelstein, Israel (2013). The forgotten kingdom : the archaeology and history of Northern Israel. Society of Biblical Literature. p. 158. ISBN 978-1-58983-910-6. OCLC 949151323.
- Finkelstein, Israel, (2022). "The Impact of the Sheshonq I Campaign on the Territorial History of the Levant: An Update", " Sheshoq I campaign brought the collapse of an early Israelite polity in the central highlands and neighboring areas the Northern Kingdom in the Samaria highlands and the Jezreel Valley" (Abstract).
- Finkelstein, Israel, (2022): "...In the central part of the country, caused the decline of an early Israelite entity , probably the one memorized in the Bible as the House of Saul, and the rise of the Northern Kingdom, which was centered around Shechem and expanded, under pharaonic auspices, to the Jezreel--Beth-shean Valley..." (Summary).
- Finkelstein, Israel, (2020). "Saul and Highlands of Benjamin Update: The Role of Jerusalem", in Joachim J. Krause, Omer Sergi, and Kristin Weingart (eds.), Saul, Benjamin, and the Emergence of Monarchy in Israel: Biblical and Archaeological Perspectives, SBL Press, Atlanta, GA, p. 48, footnote 57: "...They became territorial kingdoms later, Israel in the first half of the ninth century BCE and Judah in its second half..."
- Sergi 2023, p. 77, "...almost one hundred years from the destruction of Shechem ...a new urban center emerged in the region, first and only for a short time at Tell el-Far'ah (North), identified as the biblical Tirzah (Albright 1925)..."
- Dever 2017, p. 338.
- ^ Davies 2015, p. 72.
- See Yohanan Aharoni, et al. (1993) The Macmillan Bible Atlas, p. 94, Macmillan Publishing: New York; and Amihai Mazar (1992) The Archaeology of the Land of the Bible: 10,000 – 586 B.C.E, p. 404, New York: Doubleday, see pp. 406-410 for discussion of the archaeological significance of Shomron (Samaria) under Omride Dynasty.
- 2 Kings 3
- ^ Finkelstein, Israel (2013). The forgotten kingdom: the archaeology and history of Northern Israel. p. 74. ISBN 978-1-58983-910-6. OCLC 949151323.
- Davies 2015, p. 72-73.
- Davies 2015, p. 73.
- Davies 2015, p. 3.
- Davies 2015, p. 71-72.
- ^ Roberts 2016, p. 203.
- Roberts 2016, p. 204.
- Roberts 2016, p. 206.
- Roberts 2016, p. 207.
- 2 Kings 16:7–9
- Grabbe, Lester L. (2007). Ancient Israel: What Do We Know and How Do We Know It?. New York: T&T Clark. p. 134. ISBN 978-05-67-11012-1.
- 2 Kings 16:9 and 15:29
- Kuan, Jeffrey Kah-Jin (2016). Neo-Assyrian Historical Inscriptions and Syria-Palestine: Israelite/Judean-Tyrian-Damascene Political and Commercial Relations in the Ninth-Eighth Centuries BCE. Wipf and Stock Publishers. pp. 64–66. ISBN 978-1-4982-8143-0.
- Cohen, Ada; Kangas, Steven E. (2010). Assyrian Reliefs from the Palace of Ashurnasirpal II: A Cultural Biography. UPNE. p. 127. ISBN 978-1-58465-817-7.
- Delitzsch, Friedrich; McCormack, Joseph; Carruth, William Herbert; Robinson, Lydia Gillingham (1906). Babel and Bible;. Chicago, The Open court publishing company. p. 78.
- 2 Chronicles 30:1–18
- ^ Miller, Patrick D. (2000). The religion of ancient Israel. London: SPCK. ISBN 978-0-664-22145-4. OCLC 44174114.
- Hosea 10:2 in the New Revised Standard Version, but some translators prefer "deceitful", as in the New International Version.
- Jerusalem Bible (1966), Footnote b at Hosea 10:2
-
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Hirsch, Emil G.; Price, Ira Maurice (1901–1906). "JEZEBEL". In Singer, Isidore; et al. (eds.). The Jewish Encyclopedia. New York: Funk & Wagnalls.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Hirsch, Emil G.; Price, Ira Maurice (1901–1906). "JEZEBEL". In Singer, Isidore; et al. (eds.). The Jewish Encyclopedia. New York: Funk & Wagnalls.
- Kelle, Brad, (2002). "What's in a Name? Neo-Assyrian Designations for the Northern Kingdom and Their Implications for Israelite History and Biblical Interpretation", Journal of Biblical Literature, 121 (4), pp. 639–666, (See table in p. 640).
Sources
- Davies, Philip (2015). The History of Ancient Israel. Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 978-0-567-65582-0.
- Dever, William (2017). Beyond the Texts: An Archaeological Portrait of Ancient Israel and Judah. SBL Press. ISBN 978-0-88414-217-1.
- Hasegawa, Shuichi; Levin, Christoph; Radner, Karen, eds. (2018). The Last Days of the Kingdom of Israel. Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG. ISBN 978-3-11-056660-4.
- Mazar, Amihai (2010). "Archaeology and the Biblical Narrative: The Case of the United Monarchy". In Kratz, Reinhard G.; Spieckermann, Hermann (eds.). One God – One Cult – One Nation: Archaeological and Biblical Perspectives. Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-11-022358-3.
- Roberts, J. J. M. (2016). "The Divided Monarchy". In Niditch, Susan (ed.). The Wiley Blackwell Companion to Ancient Israel. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 197–212. ISBN 978-0-470-65677-8.
- Sergi, Omer (2023). The Two Houses of Israel: State Formation and the Origins of Pan-Israelite Identity. SBL Press. ISBN 978-1-62837-345-5.
- Shen, Peidong; Lavi, Tal; Kivisild, Toomas; Chou, Vivian; Sengun, Deniz; Gefel, Dov; Shpirer, Issac; Woolf, Eilon; Hillel, Jossi; Feldman, Marcus W.; Oefner, Peter J. (2004). "Reconstruction of patrilineages and matrilineages of Samaritans and other Israeli populations from Y-Chromosome and mitochondrial DNA sequence Variation". Human Mutation. 24 (3): 248–260. doi:10.1002/humu.20077. ISSN 1059-7794. PMID 15300852. S2CID 1571356.
External links
- About Israel - The Information Center About Israel
- The Jewish History Resource Center Project of the Dinur Center for Research in Jewish History, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem
- Complete Bible Genealogy A synchronized chart of the kings of Israel and Judah
| The Biblical and historical Israelites | |
|---|---|
| Rulers of Israel and Judah | |
|---|---|
| Israel (united monarchy) | |
| Israel (northern kingdom) | |
| Judah (southern kingdom) | |
| Judea (Hasmonean dynasty) | |
| See also | |
| Ancient states and regions in the history of the Levant | |
|---|---|
| Copper Age | |
| Bronze Age | |
| Iron Age | |
| Classical Age | |
| Sources | |