| Revision as of 05:05, 17 January 2008 view sourceArrow740 (talk | contribs)7,908 edits →Human rights violations by militants← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 07:44, 11 December 2024 view source 特磨 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users1,250 editsNo edit summaryTags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Ongoing separatist militancy in Indian-administered Jammu and Kashmir}} | |||
| {{Cleanup|date=April 2006}} | |||
| {{about |the localized insurgency in ]|the conflict between India and Pakistan over the larger region of Kashmir|Kashmir conflict}} | |||
| {{POV|date=December 2007}} | |||
| {{pp|small=yes}} | |||
| ]''''' : Shown in green is the Kashmiri region under Pakistani control. The dark-brown region represents Indian-controlled Jammu and Kashmir while the Aksai Chin is under Chinese occupation.]] | |||
| {{Use Indian English|date=July 2016}} | |||
| <!--] which shows Maharaja ]'s accession of the state of Jammu and Kashmir to ] ]]--> | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=April 2020}} | |||
| '''Violence in Kashmir''' has existed in various forms, mainly in ], the Indian-controlled side of the disputed territory. ] has been the target of a campaign of ] by all sides in the conflict. Thousands of lives have been lost since ] due to the intensified insurgency. Casualties include civilians, ], and Kashmiri and non-Kashmiri militants which are supported by Pakistan. | |||
| {{Infobox military conflict | |||
| {{seealso|History of Jammu and Kashmir}} | |||
| | conflict = Insurgency in Jammu and Kashmir | |||
| | partof = the ] | |||
| | image = Kashmir region. LOC 2003626427 - showing sub-regions administered by different countries.jpg | |||
| | image_size = 300px | |||
| | caption = CIA map of the ] | |||
| | date = 13 July 1989<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.jammu-kashmir.com/basicfacts/politics/political_history.html|title=Chronicle of Important events/date in J&K's political history|first=Not|last=Specified|website=www.jammu-kashmir.com|access-date=29 April 2018|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171012061358/http://www.jammu-kashmir.com/basicfacts/politics/political_history.html|archive-date=12 October 2017}}</ref> – present ({{Age in years, months, weeks and days|year1=1989|month1=6|day=13}}) | |||
| | place = ] | |||
| | status = ] | |||
| | combatant1 = {{flag|India}} | |||
| * {{flagicon image|Flag of the Ministry of Defence of India.svg}} ] | |||
| ** {{flagicon image|Flag of Indian Army.svg}} ] | |||
| * {{flagicon image|CRPF Flag.svg}} ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| | combatant2 = Political Parties: | |||
| *] ] | |||
| *] ] | |||
| Armed groups: | |||
| *{{flagicon image|Jammu Kashmir Liberation Front flag.svg}} ] | |||
| *{{flagicon image|Flag of Lashkar-e-Taiba.svg}} ] | |||
| *{{flagicon image|Jaishi-e-Mohammed.svg}} ] | |||
| *{{flagicon image|Flag of Jihad.svg|center|250px}} ] | |||
| *] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] ] | |||
| *{{flagicon image|Green Shahada.png}} ]<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.greaterkashmir.com/news/kashmir/story/224631.html |title= DeM cadres lead women congregations across Kashmir |work= Greater Kashmir |date= 3 August 2016 |access-date= 9 August 2016 |archive-date= 24 December 2018 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20181224181641/https://www.greaterkashmir.com/news/kashmir/story/224631.html |url-status= live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.greaterkashmir.com/news/kashmir/pro-freedom-rallies-in-pampore-bijbehara/224875.html |title= Pro-freedom rallies in Pampore, Bijbehara |first= Khalid |last= Gul |work= Greater Kashmir |date= 5 August 2016 |access-date= 9 August 2016 |archive-date= 8 August 2016 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20160808152845/http://www.greaterkashmir.com/news/kashmir/pro-freedom-rallies-in-pampore-bijbehara/224875.html |url-status= live }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url= http://kashmirreader.com/2016/08/02/dem-activists-asked-to-make-dua-e-majlis-successful/ |title= DeM activists asked to make Dua-e-Majlis successful |work= Kashmir Reader |date= 2 August 2016 |access-date= 9 August 2016 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20160803000443/http://kashmirreader.com/2016/08/02/dem-activists-asked-to-make-dua-e-majlis-successful/ |archive-date= 3 August 2016 |url-status= dead }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.greaterkashmir.com/news/kashmir/this-is-people-s-movement-be-united-dem/223425.html |title= This is people's Movement, be United: DeM |date= 22 July 2016 |access-date= 9 August 2016 |archive-date= 24 December 2018 |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20181224181639/https://www.greaterkashmir.com/news/kashmir/this-is-people-s-movement-be-united-dem/223425.html |url-status= live }}</ref> | |||
| *{{flagicon image|Flag of Harkat-ul-Mujahideen.svg}} ] | |||
| *{{flagicon image|Flag of Jihad.svg|center|250px}} ] | |||
| *{{flagicon image|Al-Badr flag.svg}} ] | |||
| *{{flagicon image|Flag of Al-Umar-Mujahideen.svg}} ] | |||
| *Other separatist Movements & ] militant groups<ref name="2011freedomhascome">{{cite book|title=Until My Freedom Has Come: The New Intifada in Kashmir|date=2011|publisher=Penguin Books India|isbn=9780143416470|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=X7YOrcv1Bz0C&q=Kashmir+intifada|access-date=12 November 2020|archive-date=20 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230420104155/https://books.google.com/books?id=X7YOrcv1Bz0C&q=Kashmir+intifada|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="margolis2004">{{cite book|last1=Margolis|first1=Eric|title=War at the Top of the World: The Struggle for Afghanistan, Kashmir and Tibet|date=2004|publisher=Routledge|isbn=9781135955595|page=81|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=FQGUAgAAQBAJ&q=Kashmiri+intifada|access-date=12 November 2020|archive-date=20 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230420104114/https://books.google.com/books?id=FQGUAgAAQBAJ&q=Kashmiri+intifada|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="bose2009">{{cite book|last1=Bose|first1=Sumantra|title=Kashmir: Roots of Conflict, Paths to Peace|date=2009|publisher=Harvard University Press|isbn=9780674028555|page=107|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=3ACMe9WBdNAC&q=Kashmir+intifada&pg=PA107|access-date=12 November 2020|archive-date=20 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230420104115/https://books.google.com/books?id=3ACMe9WBdNAC&q=Kashmir+intifada&pg=PA107|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name=websters_unabridged>{{citation|title="insurgency" (noun)|url=http://unabridged.merriam-webster.com/unabridged/insurgency|publisher=Merriam-Webster Unabridged|access-date=27 November 2019|archive-date=20 January 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200120131116/https://unabridged.merriam-webster.com/subscriber/login?redirect_to=%2Funabridged%2Finsurgency|url-status=live}} Quote: "The quality or state of being insurgent; specifically : a condition of revolt against a recognized government that does not reach the proportions of an organized revolutionary government and is not recognized as belligerency" (subscription required)</ref><ref name=oed_insurgency>{{citation|title=insurgency, n|publisher=Oxford English Dictionary|url=https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/97279?redirectedFrom=insurgency#eid|access-date=27 November 2019|archive-date=20 January 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200120131120/https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/97279?redirectedFrom=insurgency#eid|url-status=live}} Quote: "The quality or state of being insurgent; the tendency to rise in revolt; = insurgence n. = The action of rising against authority; a rising, revolt." (subscription required)</ref><ref name=britannica_insurgency>{{citation|title=Insurgency|publisher=Encyclopedia Britannica|url=https://www.britannica.com/topic/insurgency|access-date=27 November 2019|archive-date=27 November 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191127191403/https://www.britannica.com/topic/insurgency|url-status=live}} Quote: "Insurgency, term historically restricted to rebellious acts that did not reach the proportions of an organized revolution. It has subsequently been applied to any such armed uprising, typically guerrilla in character, against the recognized government of a state or country." (subscription required)"</ref> | |||
| *{{flagicon image|Flag of Jihad.svg|center|250px}} ]<ref>{{Cite web|title=Al Qaeda In the Indian Subcontinent Released Video Titled 'Kashmir is our' Al Qaeda again target india|date=12 October 2021|url=https://www.news18.com/news/india/twice-in-a-week-al-qaeda-in-indian-subcontinent-releases-new-video-named-kashmir-is-ours-4313042.html|access-date=13 October 2021|archive-date=19 November 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221119065551/https://www.news18.com/news/india/twice-in-a-week-al-qaeda-in-indian-subcontinent-releases-new-video-named-kashmir-is-ours-4313042.html|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| **{{flagicon image|Flag of Jihad.svg|center|250px}} ] | |||
| '''Supported by:''' | |||
| *{{flag|Pakistan}}<ref name="DavisAzizian2007">{{cite book|author1=Elizabeth Van Wie Davis|author2=Rouben Azizian|title=Islam, Oil, and Geopolitics: Central Asia After September 11|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=7s4jAQAAIAAJ|year=2007|publisher=Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, Incorporated|isbn=978-0-7425-4128-3|pages=281|quote=The trouble was that elements of Pakistan ' s government were involved with Islamist extremists . They had protected and supported not only the Taliban but also insurgents crossing the Line of Control into Indian - held Kashmir|access-date=13 May 2021|archive-date=20 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230420104112/https://books.google.com/books?id=7s4jAQAAIAAJ|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="Kazi_Zutshi2017"/><ref name="Kapur2017b">{{citation|last=Kapur|first=S. Paul|title=Jihad as Grand Strategy: Islamist Militancy, National Security, and the Pakistani State|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=AhYBDQAAQBAJ&pg=PA84|pages=84–|year=2017|publisher=Oxford University Press|isbn=978-0-19-976852-3|access-date=27 November 2019|archive-date=20 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230420104112/https://books.google.com/books?id=AhYBDQAAQBAJ&pg=PA84|url-status=live}}</ref><ref> | |||
| * {{cite book|title=India, Pakistan and the Secret Jihad |last1= Swami |first1=Praveen |year=2007 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-0-415-40459-4 |location= New York}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal|title=Al Qaeda thriving in Kashmir in support of Pakistani intelligence against india reports Al Qaeda camps in azad kashmir Pakistan|journal=Christian Science Monitor|date=2 July 2002|url=https://www.csmonitor.com/2002/0702/p01s02-wosc.html|access-date=12 November 2021|archive-date=12 November 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211112160316/https://www.csmonitor.com/2002/0702/p01s02-wosc.html|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| *{{flagicon image|Flag of Jihad.svg|center|250px}} ]<ref>{{Cite web|title=Al-Qaeda calls for liberation of Kashmir|website = ]|url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5skKkj2eEv0&ab_channel=WION |archive-url=https://ghostarchive.org/varchive/youtube/20211213/5skKkj2eEv0 |archive-date=2021-12-13 |url-status=live|access-date=1 August 2021}}{{cbignore}}</ref> | |||
| *{{flagicon image|C5e2f596ddahgd.png}} ]<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/Dawood-is-a-terrorist-has-strategic-alliance-with-ISI-says-US/articleshow/5418149.cms|title=Dawood is a terrorist, has 'strategic alliance' with ISI, says US|work=The Times of India|access-date=2017-06-07|archive-date=3 October 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171003232824/http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/Dawood-is-a-terrorist-has-strategic-alliance-with-ISI-says-US/articleshow/5418149.cms|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ---- | |||
| *{{flagdeco|ISIL}} ] | |||
| ** {{flagicon|Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant}} ]<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://thedefensepost.com/2019/05/15/islamic-state-pakistan-province-al-hind/|title=ISIS announces new India and Pakistan provinces, casually breaking up Khorasan|date=15 May 2019|website=The Defense Post|access-date=4 June 2019|archive-date=10 June 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200610230850/https://www.thedefensepost.com/2019/05/15/islamic-state-pakistan-province-al-hind/|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ***{{flagicon|Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant}} ]<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.indiatoday.in/india/story/islamic-state-claims-province-india-wilayah-of-hind-kashmir-1522610-2019-05-11|title=Islamic State claims it has established province in India, calls it Wilayah of Hind: Report|date=11 May 2019 |access-date=18 April 2021|archive-date=18 April 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210418175524/https://www.indiatoday.in/india/story/islamic-state-claims-province-india-wilayah-of-hind-kashmir-1522610-2019-05-11|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ***{{flagdeco|ISIL}} ]<ref name="Rediff.com">{{cite news|work=]|title=Islamic State J-K chief among 4 terrorists killed in Kashmir|date=22 June 2018|url=http://www.rediff.com/news/report/pix-encounter-breaks-out-between-security-forces-and-terrorists-in-anantnag/20180622.htm|access-date=20 April 2023|archive-date=20 December 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221220202558/https://www.rediff.com/news/report/pix-encounter-breaks-out-between-security-forces-and-terrorists-in-anantnag/20180622.htm|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| | strength1 = * ] ~ 343,000-700,000<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2019/8/4/india-imposes-kashmir-lockdown-puts-leaders-under-house-arrest|title=India imposes Kashmir lockdown, puts leaders 'under house arrest'|access-date=29 March 2022|archive-date=19 November 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221119065554/https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2019/8/4/india-imposes-kashmir-lockdown-puts-leaders-under-house-arrest|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="theprint.in">Snehesh Alex Philip, {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210902161621/https://theprint.in/defence/what-imran-khan-says-is-9-lakh-soldiers-in-kashmir-is-actually-3-43-lakh-only/319442/ |date=2 September 2021 }}, The Print, 12 November 2019.</ref><ref name="The Times"/> | |||
| <ref name=Stimson> | |||
| {{cite web |title=Kashmir |publisher=Stimson Center |url=http://www.stimson.org/southasia/?SN=SA2001112045 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060630204847/http://www.stimson.org/southasia/?SN=SA2001112045 |archive-date=30 June 2006 }}: "Some reports estimate that India deploys approximately 400,000 combined army and paramilitary forces in Kashmir, most of which are stationed in the interior, 80,000 of which are deployed along the LoC." | |||
| </ref><br /> (Nov 2019, including soldier posted at international border (LoC)) | |||
| ** ]: 168,000<ref name="theprint.in"/> | |||
| ** ]: 160,000<ref name="theprint.in"/> | |||
| ** ]: (Unknown) | |||
| | strength2 = Unknown | |||
| | commanders1 = {{flagicon|India}} ] <br />(])<br />{{flagicon|India}} ] <br />(])<br />] ]<br />(])<br />{{Flagicon image|Flag of Chief of Defence Staff (India).svg|25px}} ] ]<br />(])<br />{{flagicon image|Flag COAS.svg|size=24px}} ] <br />(])<br />{{flagicon image|Flag of the Chief of Air Staff and Air Chief Marshal of the Indian Air Force.svg|size=24px}} ] <br />(]) | |||
| | commanders2 = ] ] (until 2020) <br /> ] ] (2021–present)<ref>{{Cite web|author=News Desk|date=2021-09-07|title=Masarat Alam is new chairman of Hurriyat Conference {{!}} Free Press Kashmir|url=https://freepresskashmir.news/2021/09/07/masarat-alam-is-new-chairman-of-hurriyat-conference/|access-date=2021-10-17|website=freepresskashmir.news|language=en-GB}}</ref><br /> ] ] (until 2022)<br /> {{flagicon image|Jammu Kashmir Liberation Front flag.svg}} ] (until 2016)<br /> {{flagicon image|Flag of Lashkar-e-Taiba.svg}} ]<br /> {{flagicon image|Jaishi-e-Mohammed.svg}} ]<br />{{flagicon image|Flag of Jihad.svg|center|250px}} ]{{KIA}}<br />{{flagicon image|Flag of Jihad.svg|center|250px}} ]{{KIA}}<br />{{flagicon image|Green Shahada.png}}{{flagicon image|Flag of Jihad.svg|center|250px}} ]<br />{{flagicon image|Green Shahada.png}}{{flagicon image|Flag of Jihad.svg|center|250px}} ]{{KIA}}<br />{{flagicon image|Green Shahada.png}} ]<br /> {{flagicon image|Flag of Harkat-ul-Mujahideen.svg}} ]<br />{{flagicon image|Harakat flag.png}} Farooq Kashmiri<br /> {{flagicon image|Al-Badr flag.svg}} Arfeen Bhai<br />{{flagicon image|Al-Badr flag.svg}} Bakht Zameen<br />Yasir Ahmed {{POW}} | |||
| ---- | |||
| {{flagdeco|ISIL}} '''Islamic State-aligned''' | |||
| {{flagdeco|ISIL}} Dawood Ahmed Sofi{{KIA}}<ref name="Rediff.com" /> | |||
| | casualties1 = '''2000–2024:'''<br>3,590 Security Forces killed <ref>{{Cite news|title=Yearly Fatalities|url=https://www.satp.org/datasheet-terrorist-attack/fatalities/india-jammukashmir|access-date=2024-06-01|website=SATP}}</ref> | |||
| | casualties2 = '''2000–2024:'''<br> 13,321 militants killed<br>847 Surrendered <br>5,832 Arrested<ref>{{Cite news|title=Yearly Fatalities|url=https://www.satp.org/datasheet-terrorist-attack/fatalities/india-jammukashmir|access-date=2024-06-01|website=SATP}}</ref> | |||
| | casualties3 = 20,000+ civilian deaths<ref>{{cite web|url=http://ucdp.uu.se/#/actor/325|title=Kashmir insurgents|publisher=]|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171001172908/http://ucdp.uu.se/#/actor/325|archive-date=1 October 2017|access-date=29 March 2017}}</ref><ref name="The Express Tribune">{{Cite news|url=https://tribune.com.pk/story/228506/40000-people-killed-in-kashmir-india/|title=40,000 people killed in Kashmir: India|work=The Express Tribune|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170227232416/https://tribune.com.pk/story/228506/40000-people-killed-in-kashmir-india/|archive-date=27 February 2017}}</ref> | |||
| }} | |||
| The '''insurgency in Jammu and Kashmir''', also known as the '''Kashmir insurgency''', is an ongoing ] militant insurgency against the ] in ],<ref name="Kazi_Zutshi2017">{{citation|last=Kazi|first=Seema|editor=Chitralekha Zutshi|title=Kashmir: History, Politics, Representation|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=CPFKDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA72|year=2017|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=978-1-108-22612-7|pages=150–171, 153|chapter=Law, Gender and Governance in Kashmir|access-date=27 November 2019|archive-date=20 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230420104237/https://books.google.com/books?id=CPFKDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA72|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name=slater_wapo_march_2019>{{citation|title=From scholars into militants: Educated Kashmiri youths are joining an anti-India insurgency|url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/asia_pacific/from-scholar-to-militant-why-more-kashmiri-youth-are-joining-an-insurgency-against-india/2019/03/26/2a6e92c6-45ce-11e9-94ab-d2dda3c0df52_story.html|last=Slater|first=Joanna|date=28 March 2019|newspaper=]|access-date=27 November 2019|archive-date=27 November 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191127191410/https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/asia_pacific/from-scholar-to-militant-why-more-kashmiri-youth-are-joining-an-insurgency-against-india/2019/03/26/2a6e92c6-45ce-11e9-94ab-d2dda3c0df52_story.html|url-status=live}}</ref> a territory constituting the southwestern portion of the larger geographical region of ], which has been the subject of a ] between ] and ] since 1947.<ref name=britannica-jammu-kashmir>(a) {{citation|title=Kashmir, region Indian subcontinent|publisher=Encyclopaedia Britannica|url=https://www.britannica.com/place/Kashmir-region-Indian-subcontinent|access-date=15 August 2019|archive-date=13 August 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190813203817/https://www.britannica.com/place/Kashmir-region-Indian-subcontinent|url-status=live}} (subscription required);<br /> (b) {{citation|chapter=Kashmir|title=Encyclopedia Americana|publisher=Scholastic Library Publishing|chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=l_cWAQAAMAAJ&pg=PA328|year=2006|isbn=978-0-7172-0139-6|page=328|access-date=27 November 2019|archive-date=17 January 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230117135716/https://books.google.com/books?id=l_cWAQAAMAAJ&pg=PA328|url-status=live}} C. E Bosworth, University of Manchester</ref><ref name="Jan·Osma鈔czykOsmańczyk2003">{{citation|last1=Jan·Osma鈔czyk|first1=Edmund|last2=Osmańczyk|first2=Edmund Jan|title=Encyclopedia of the United Nations and International Agreements: G to M|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=fSIMXHMdfkkC&pg=PA1191|year=2003|publisher=Taylor & Francis|isbn=978-0-415-93922-5|pages=1191–|access-date=27 November 2019|archive-date=17 January 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230117140437/https://books.google.com/books?id=fSIMXHMdfkkC&pg=PA1191|url-status=live}} Quote: "Jammu and Kashmir: Territory in northwestern India, subject to a dispute between India and Pakistan. It has borders with Pakistan and China."</ref> | |||
| ==Militancy and military== | |||
| Though there had been instances of sporadic conflict in many regions for many years, intensified attacks occurred in the late ], when ] fighters from ] slowly infiltrated the region, allegedly with Pakistan's help, following the end of the ] in 1989.<ref name="BBC Timeline">{{cite web|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/hi/english/static/in_depth/south_asia/2002/india_pakistan/timeline/1989.stm |title=Kashmir insurgency Timeline}}</ref> Since then, violence has increased significantly in strength. Many separatists have carried out attacks on Indian civilians and Indian army installations in response to what they see as Indian army occupation.<ref name="fact">{{cite web|url=http://www.stephen-knapp.com/facts_on_the_pakistani_terrorism_against_kashmir.htm |title=Facts on Kashmiri Terrorism}}</ref> | |||
| Jammu and Kashmir, long a breeding ground of separatist ambitions,<ref name=editorial_board_nytimes_5_August_2019>{{citation|title=India Tempts Fate in Kashmir, 'The Most Dangerous Place in the World'|author=The Editorial Board|newspaper=The New York Times|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2019/08/05/opinion/kashmir-article-370.html|date=6 August 2019|access-date=27 November 2019|archive-date=19 November 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221119065550/https://www.nytimes.com/2019/08/05/opinion/kashmir-article-370.html|url-status=live}} Quote: "The Himalayan territory of Kashmir has long been the central source of friction between India and Pakistan and a hotbed of separatist aspirations."</ref> has experienced the insurgency since 1989.<ref name=guardian_ratcliffe_5_august_2019>{{citation|url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2019/aug/04/heightened-security-and-anxiety-in-kashmir-amid-fears-of-unrest|last=Ratcliffe|first=Rebecca|work=Guardian|title=Heightened security and anxiety in Kashmir amid fears of unrest|date=4 August 2019|access-date=27 November 2019|archive-date=12 December 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191212210011/https://www.theguardian.com/world/2019/aug/04/heightened-security-and-anxiety-in-kashmir-amid-fears-of-unrest|url-status=live}} Quote: "Kashmir is claimed by India and Pakistan in full and ruled in part by both. An insurgency on the Indian-administered side has been ongoing for three decades, and tens of thousands of people have been killed."</ref><ref name=slater_wapo_march_2019/> Although the failure of Indian governance and democracy lay at the root of the initial disaffection, Pakistan played an important role in converting the latter into a fully-developed armed insurgency.<ref name="Kazi_Zutshi2017"/><ref name="Kapur2017b" /> Some insurgent groups in Kashmir support complete independence, whereas others seek the region's accession to Pakistan.<ref> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171001172908/http://ucdp.uu.se/ |date=1 October 2017 }}, ], 29 May 1977, retrieved 2013-05-29,</ref><ref name="Kapur2017b"/> | |||
| India claims most of the separatist terrorist groups are based in ] and Pakistan-administered Kashmir (also known as ]). Some like the ] and the ], demand an independent Kashmir. Other terrorist groups such as ] and ] favour a Pakistani-Kashmir. These terror groups have contacts with Taliban and Bin Laden. Both the organisations no longer operate under these names after they were banned by the Indian and Pakistani government, and by other countries including the ] and ]. Of the larger militant groups, the ], a militant organisation based in Indian administered Kashmir, unlike other groups, has only kept its name.<ref name="al">{{cite web|url=http://www.armyinkashmir.org/v2/articles/art_strategy.shtml |title=Information regarding militants international links}}</ref> Despite casualties, the militants are still believed to number thousands rather than hundreds. Several new separatist organizations have also emerged. According to ] Intelligence, ] also has a main base in Pakistani Kashmir and is helping to foment terrorism in Jammu and Kashmir. | |||
| More explicitly, the roots of the insurgency are tied to a dispute over local autonomy.<ref name="ucdp.uu.se">] Conflict Encyclopedia, Conflict Summary, Conflict name: India: Kashmir, "Roots of Conflict and the emergence of Kashmir Insurgents", viewed 2013-05-29, http://www.ucdp.uu.se/gpdatabase/gpcountry.php?id=74®ionSelect=6-Central_and_Southern_Asia# {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130203162633/http://www.ucdp.uu.se/gpdatabase/gpcountry.php?id=74®ionSelect=6-Central_and_Southern_Asia |date=3 February 2013 }}</ref> Democratic development was limited in Kashmir until the late 1970s, and by 1988, many of the democratic reforms provided by the Indian government had been reversed and non-violent channels for expressing discontent were limited, which caused a dramatic increase in support for insurgents advocating violent secession from India.<ref name="ucdp.uu.se" /> In 1987, a ]<ref name="Elections in Kashmir">{{cite web|url=http://www.kashmirlibrary.org/kashmir_timeline/kashmir_chapters/kashmir-elections.shtml|title=Elections in Kashmir|publisher=Kashmirlibrary.org|access-date=2017-02-23|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170201045510/http://kashmirlibrary.org/kashmir_timeline/kashmir_chapters/kashmir-elections.shtml|archive-date=1 February 2017}}</ref> held in the erstwhile ] created a catalyst for the insurgency when it resulted in some of the ] members forming armed insurgent groups.<ref name="BBCKashmir" /><ref>{{cite web|last1=Jeelani|first1=Mushtaq A.|title=Kashmir: A History Littered With Rigged Elections|url=http://www.mediamonitors.net/jeelani4.html|website=Media Monitors Network|access-date=24 February 2017|date=25 June 2001|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304051443/http://www.mediamonitors.net/jeelani4.html|archive-date=4 March 2016}}</ref><ref name="AltafElections"/> In July 1988, a series of demonstrations, strikes, and attacks on the Indian government effectively marked the beginning of the insurgency in Jammu and Kashmir, which escalated into the most severe ] during the 1990s. | |||
| It is hard to determine the total number of casualties. According to a report by the ] in the year ], 31,000 Indian civilians had lost their lives due to the insurgency. Human rights groups and local ]s put the total figure at more than 84,000 (] figure).<ref name="Kashinfo">{{cite web|url=http://www.kashmir-information.com/Pakistan/machine.html |title=Information on the terrorist camps in Pakistan}}</ref> Militancy had reached its peak in ] when the region saw more than 6,043 incidents and has since declined. However, ] continues to remain as the most volatile region in the world with an average of 2,500 incidents every year.<ref name="incidents">{{cite web|url=http://www.thehindubusinessline.com/businessline/2001/03/08/stories/040855ks.htm |title=The surrogate war in Kashmir}}</ref> According to an ]n estimate in ] there were about 2,000 militants in the Kashmir valley alone; 1,200 of them belong to the ]. Not all Kashmiri separatists and militant organizations share the same ideology. Some fight in the name of religion, some are pro-] and some favour an independent Kashmir. | |||
| Pakistan, with whom India has fought ] over the ], has officially claimed to be giving only its "moral and diplomatic" support to the separatist movement.<ref name="bbc2015">{{cite news|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/hi/english/static/in_depth/south_asia/2002/india_pakistan/timeline/1989.stm|title=India Pakistan – Timeline|access-date=10 April 2015|work=BBC News|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170222035446/http://news.bbc.co.uk/hi/english/static/in_depth/south_asia/2002/india_pakistan/timeline/1989.stm|archive-date=22 February 2017|url-status=live}}</ref> The Pakistani ] has been accused by both India and the ] of supporting and supplying arms as well as providing training to "]" militants<ref>{{cite news|last1=Ali|first1=Mahmud|title=Pakistan's shadowy secret service|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/6033383.stm|access-date=22 February 2017|work=]|date=9 October 2006|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170221224921/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/6033383.stm|archive-date=21 February 2017}}</ref><ref name="Telegraph.co.uk">{{cite news|last1=Rashid|first1=Ahmed|title=Nato's top brass accuse Pakistan over Taliban aid|url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/1530756/Natos-top-brass-accuse-Pakistan-over-Taliban-aid.html|access-date=22 February 2017|newspaper=]|date=6 October 2006|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170222113552/http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/1530756/Natos-top-brass-accuse-Pakistan-over-Taliban-aid.html|archive-date=22 February 2017}}</ref> in Jammu and Kashmir.<ref name="Talib">{{cite news|last1=Gall|first1=Carlotta|title=At Border, Signs of Pakistani Role in Taliban Surge|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2007/01/21/world/asia/21quetta.html|access-date=21 February 2017|newspaper=]|date=21 January 2007|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161231131515/http://www.nytimes.com/2007/01/21/world/asia/21quetta.html|archive-date=31 December 2016}}</ref><ref name="Telegraph.co.uk"/><ref>{{cite news|last1=Jehl|first1=Douglas|last2=Dugger|first2=Celia W.|last3=Barringer|first3=Felicity|title=Death of Reporter Puts Focus on Pakistan Intelligence Unit|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2002/02/25/world/nation-challenged-suspects-death-reporter-puts-focus-pakistan-intelligence-unit.html|access-date=21 February 2017|newspaper=]|date=25 February 2002|archive-date=2 May 2017|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170502010653/http://www.nytimes.com/2002/02/25/world/nation-challenged-suspects-death-reporter-puts-focus-pakistan-intelligence-unit.html|url-status=live}}</ref> In 2015, a former ], ], admitted that the Pakistani state had supported and trained insurgent groups in Kashmir throughout the 1990s.<ref>{{cite news|title=Pakistan supported, trained terror groups: Pervez Musharraf|url=http://www.business-standard.com/article/international/pakistan-supported-trained-terror-groups-pervez-musharraf-115102800015_1.html|access-date=21 February 2017|agency=]|newspaper=]|date=28 October 2015|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170605051514/http://www.business-standard.com/article/international/pakistan-supported-trained-terror-groups-pervez-musharraf-115102800015_1.html|archive-date=5 June 2017}}</ref> Several new militant groups with radical ] views emerged during this time and changed the ideological emphasis of the movement from that of plain separatism to ]. This occurred partly due to the influence of a large number of Muslim ] militants who began to enter the Indian-administered ] through Pakistani-controlled territory across the ] following the end of the ] in the 1980s.<ref name="bbc2015" /> India has repeatedly called on Pakistan to end its alleged "]" in the region.<ref name="bbc2015" /> | |||
| India claims it is the presence of these numerous anti-India insurgent groups that has compelled ] to deploy massive number of troops in ''Jammu and Kashmir'' for the task of ]. New Delhi has never made an official count, but military analysts estimate that anywhere from 30,000 to nearly 33,000 security personnel are most likely involved, supported by thousands of Indian paramilitary groups such as the Rashtriya rifles, and the Romeo Force(all a part of Indian army).<ref>, , Multiple sources for the number of Indian counter-insurgency troops in the region</ref> Stimson.org notes of the Indian Armed forces in Kashmir that: | |||
| The conflict between militants and ] in Kashmir has led to a large number of casualties;<ref>] Conflict Encyclopedia, Conflict Summary, India: Kashmir (entire conflict), Fatality estimates, viewed 2013-05-29, http://www.ucdp.uu.se/gpdatabase/gpcountry.php?id=74®ionSelect=6-Central_and_Southern_Asia# {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130203162633/http://www.ucdp.uu.se/gpdatabase/gpcountry.php?id=74®ionSelect=6-Central_and_Southern_Asia |date=3 February 2013 }}</ref> many civilians have also died as a result of being targeted by various armed militant groups.<ref>] Conflict Encyclopedia, India One-sided violence, Government of India – civilians, Kashmir insurgents – civilians, Lashkar-e-Taiba – civilians, viewed on 2012-05-29, http://www.ucdp.uu.se/gpdatabase/gpcountry.php?id=74®ionSelect=6-Central_and_Southern_Asia# {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130203162633/http://www.ucdp.uu.se/gpdatabase/gpcountry.php?id=74®ionSelect=6-Central_and_Southern_Asia |date=3 February 2013 }}</ref> According to government data, around 41,000 people—consisting of 14,000 civilians, 5,000 security personnel and 22,000 militants—have died because of the insurgency {{As of|2017|March|lc=y}}, with most deaths happening in the 1990s and early 2000s.<ref name=ht2017/> Non-governmental organisations have claimed a higher death toll. The insurgency has also forced the ] of non-Muslim minority ] out of the Kashmir Valley.<ref>{{harvnb|Evans|2002|loc=p. 19: "Most Kashmiri Pandits living in the Kashmir Valley left in 1990 as militant violence engulfed the state. Some 95% of the 160,000-170,000 community left in what is often described as a case of ethnic cleansing."}}</ref> Since the ] in August 2019, the Indian military has intensified its ] in the region. | |||
| <blockquote> | |||
| Some reports estimate that India deploys approximately 400,000 combined army and paramilitary forces in Kashmir, most of which are stationed in the interior, 80,000 of which are deployed along the LoC. Pakistani forces deployed along the LoC are reported to number in the 40,000-50,000 range | |||
| </blockquote><ref>http://www.stimson.org/southasia/?SN=SA2001112045</ref> | |||
| == History == | |||
| Times Online reports that around 250,000 Indian troops are stationed in Kashmir,<ref>http://www.timesonline.co.uk/tol/news/world/article392432.ece</ref> while Pravda.RU, a widely read Russian News source notes that 350,000-600,000 troops may be deployed in Kashmir.<ref>http://newsfromrussia.com/world/2004/11/12/57097.html</ref> | |||
| {{See also|History of Kashmir|List of terrorist incidents in Jammu and Kashmir}} | |||
| === |
=== 1947–1982 === | ||
| {{See also|Partition of India|First Kashmir War}} | |||
| Over the last two years, a terrorist group, ] has split into two factions: ''Al Mansurin'' and ''Al Nasirin''. Another new group reported to have emerged is the ]. ] (formerly known as ]) and ] are believed to be operating from ], ] and ], ] respectively.{{ref|figure}} Other less well known groups are the ] and ]. A smaller group, ], has been active in Kashmir for many years and is still believed to be functioning.<ref name="name">{{cite web|url=http://www.solcomhouse.com/terrorists.htm |title=List of terrorist organisations}}</ref> ], an organisation that uses moderate means to press for the rights of the Kashmiris, is often considered as the ''mediator'' between ] and insurgent groups. | |||
| After independence from colonial rule India and Pakistan ] over the princely state of ]. At the end of the war India controlled the southern portion of the princely state.<ref name="SumantraKashmir" /> While there were sporadic periods of violence there was no organised insurgency movement.<ref name="SwamiSecret" /> | |||
| Not much is known about collaboration between the various groups, but most say they are members of an alliance known as the ] (UJC).<ref name="UJC">{{cite web|url=http://www.fas.org/irp/world/para/mjc.htm |title=Info regarding UJC and its members}}</ref> The two groups which ] says were behind the ] on the Indian parliament in ] — known then as ] and ] are believed to be members of the ''UJC''. India says that it was ] that attacked the ] in ] in October ].<ref name="parliament">{{cite web |url=http://www2.chinadaily.com.cn/en/doc/2003-08/31/content_259902.htm |title=Article on Indian Parliament Attack}}</ref> It is also known that the ] was responsible for the hijacking of ] to ], which forced the ] to release Maulana Masood Azhar, the chief of the ].<ref name="IC814">{{cite web|url=http://meaindia.nic.in/speech/2000/01/060100spc01.htm |title=IC 814 Hijacking}}</ref> | |||
| Recruits from various parts of the world have been sent to Pakistan-administered Kashmir for training and advice.<ref name="pokterror"> {{cite web |url=http://www.time.com/time/world/article/0,8599,1254773,00.html|title=Where Some British Extremists Go On Holiday}}</ref> | |||
| During this period legislative elections in the state of ] were first held in 1951 and ]'s secular party stood unopposed. He was an instrumental member in the accession of the state to India.<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://articles.economictimes.indiatimes.com/2013-12-05/news/44808338_1_omar-abdullah-jammu-and-kashmir-sheikh-abdullah|title=Omar Abdullah hails Sheikh Abdullah's decision to accede J-K to India|access-date=10 November 2016|archive-date=8 December 2013|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131208164553/http://articles.economictimes.indiatimes.com/2013-12-05/news/44808338_1_omar-abdullah-jammu-and-kashmir-sheikh-abdullah|url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://m.greaterkashmir.com/news/opinion/story/225175.html|title=Excerpts of Sheikh Abdullah's speech defending the accession|date=9 August 2016|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161110172831/http://m.greaterkashmir.com/news/opinion/story/225175.html|archive-date=10 November 2016}}</ref> | |||
| ===Involvement of Pakistan=== | |||
| A 1994 report by ] group lends support to both Indian and Pakistani charges. In support of Indian claims, it states that "<blockquote>There is compelling evidence that elements of the Pakistani government have sponsored a significant flow of arms to Kashmiri militants , as well as an extensive training program.</blockquote> While in support of Pakistani claims, its states that "''the human rights record of the Indian government in Punjab and Kashmir is appalling. Abuses in Kashmir are clearly on the rise''."<ref name="Guardian">{{cite web|url=http://www.hrw.org/campaigns/kashmir/1994/kashmir94-01.htm|title=Introduction to Kashmir conflict}}</ref> The US government has also supported the claim that anti-India terror groups exist in India.<ref> </ref> India claims that there are also other ], ]ian, ]i and ]i terrorists active in Jammu and Kashmir. The Council on Foreign Relations states that Pakistan’s military and ] (ISI) both include personnel who sympathize with—or even assist—Islamist militants adding that "ISI has provided covert but well-documented support to terrorist groups active in Kashmir, among other outfits."<ref> - ] </ref> In a recent infiltration bid, a ] officer was shot dead, with India citing that this was clear and conclusive evidence of Pakistani involvement in the insurgency.<ref></ref> The ] has also confirmed the existence of terrorist groups based in Kashmir and urged Pakistan to crack down on terrorist groups which had been operating in Kashmir and killing innocent people.<ref></ref> | |||
| However, Sheikh Abdullah would fall in and out of favour with the central government and would often be dismissed only to be re-appointed later on.<ref>{{Cite encyclopedia|title=Sheikh Muhammad Abdullah |url=https://www.britannica.com/biography/Sheikh-Muhammad-Abdullah |access-date=2024-06-09 |encyclopedia=Encyclopædia Britannica |language=en}}</ref> This was a time of political instability and power struggle in Jammu and Kashmir, and it went through several periods of ] by the ].<ref name="AltafElections" /> | |||
| Pakistan describes the separatists as "freedom fighters" and says that it supports their effort for the cause of the Kashmiris only morally and diplomatically. Pakistan however admits that there has been 'cross border infiltration of militants' across the line of controls ]. In 2002, ] Pervez Musharraf tried to clamp down on the militants operating from Pakistan. India, however, claims that ] supports these groups financially and militarily. Sources have maintained that Pakistan's intelligence organisation, ], is the main supplier of funds and arms to these groups;<ref name="FAS">{{cite web|url=http://www.fas.org/irp/world/pakistan/isi/|title="Directorate for ISI" article on FAS, Intelligence Resource Program}}</ref> a claim that ] has dismissed. According to the Indian news site Rediff.com, ] had stated in 2002 that there is a 'clear link' between Pakistan's Inter Services Intelligence and three major militant groups<ref name="ISI">{{cite web|url=http://www.rediff.com/news/2002/jun/11war4.htm |title=Information regarding links between ISI and militants}}</ref> An article in ] had uncovered evidence that Pakistani militants were openly raising funds and training new recruits and that the ISI's Kashmir Cell was instrumental in funding and controlling the militant outfits.<ref name="Guardian">{{cite web|url=http://www.guardian.co.uk/kashmir/Story/0,2763,722049,00.html |title=Dangerous game of state-sponsored terror...}}</ref> Richard Bennett, a British military and intelligence analyst states that the ISI has armed and trained generations of Islamist extremists and has directed many of their attacks both within the Kashmir and in India's major cities.<ref></ref> | |||
| === 1982–2004 === | |||
| Indian sources also allege that there are between 2,600 to 3,000 militants receiving training in camps across Pakistan and Pakistan Administered Kashmir (]. During a peace summit between Pakistani President ] and Indian former-Prime Minister ] in January ], ] assured India that it would do everything possible to curb the activities any training camps on its territory. However, violence has continued in Kashmir despite a 3 year long peace process between India and Pakistan. There were as many as 166 incidents in ] alone in which some 201 people have died.<ref name="HT">{{cite web|url=http://www.hindustantimes.com |title=July 22, 2005 edition of the Hindustan Times newspaper - report by journalist Nilova Roy Chaudhury}}</ref> | |||
| {{webarchive|url=http://archive.wikiwix.com/cache/20110715154921/http://www.satp.org/satporgtp/countries/india/database/index.html |date=15 July 2011 }}, South Asian Terrorism, SATP (2014)</ref>]] | |||
| After ]'s death, his son ] took over as ]. Farooq Abdullah eventually fell out of favour with the Central Government and the Prime Minister ], who had his government toppled with the help of his brother-in-law ]. GM Shah was the chief minister during the ] until he was removed and replaced by Farooq Abdullah.<ref name="Tikoo">{{cite book|author=Tikoo|first=Colonel Tej K|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=iuURFTHTU0EC&pg=PT397|title=Kashmir: Its Aborigines and Their Exodus|publisher=Lancer Publishers LLC|year=2013|isbn=978-1-935501-58-9|pages=397–}}</ref> A year later, Abdullah reached an accord with the new Prime Minister ] and announced an alliance with the ] for the elections of 1987. The elections were allegedly rigged in favour of Abdullah.<ref name="BBCKashmir" /><ref name="AltafElections" /> | |||
| Most commentators state that this led to the rise of an armed insurgency movement composed, in part, of those who unfairly lost the elections. Pakistan supplied these groups with logistical support, arms, recruits and training.<ref name="HasanPakistan" /><ref name="BBCKashmir" /><ref name="AltafElections" /><ref name="ArifShadow" /><ref name="KhanMilitants" /> | |||
| -] July 2005</ref>]] | |||
| According to Indian sources there are about 37 training camps in ], 49 in ] and 22 in ].{{ref|Kashinfo}} The ] also has produced images of camps operating in Pakistan.<ref></ref> India claims that every year thousands of armed insurgents infiltrate into ] and carry out attacks against ] and Kashmiri civilians. In June ], the Indian Army had foiled at least 72 infiltration attempts along the ] in ].{{ref|HT}} ] alleges that despite the commitments made by ], ] has done little to stop the training camps on its soil. According to India, most of the militants in Kashmir come from Pakistan, ], ], ] and ]. Not all Kashmiri separatists and militant organizations share the same ideology. Some fight in the name of religion, some are pro-] and some favour an independent Kashmir. While the vast majority of militants are Muslims, one report indicated a minority of fighter (40 to 50) are Hindu militants who have either taken up arms or provided safe cover for militants.<ref name="Sify">{{cite web|url=http://headlines.sify.com/news/fullstory.php?id=13943651 |title=Kashmir’s new headache: Hindu militants}}</ref> | |||
| In the second half of 1989 the alleged assassinations of the Indian spies and political collaborators by the ] was intensified. Over six months more than a hundred officials were killed to paralyse government's administrative and intelligence apparatus. The daughter of then interior affairs minister, Mufti Mohammad Sayeed was kidnapped in December and four militants had to be released for her release. This event led to mass celebrations all over the valley. Farooq Abdullah resigned in January after the appointment of Jagmohan Malhotra as the Governor of Jammu and Kashmir. Subsequently, J&K was placed under Governor's Rule under Article 92 of ].<ref>{{Cite book|title=Kashmir Demysitified|last=Behera|first=Navnita Chadha|publisher=Brookings Institution Press|year=2006|location=Washington}}</ref> | |||
| ===Human rights violations by India=== | |||
| A 1996 ] report accuses the Indian military and Indian-government backed paramilitaries of "committ serious and widespread human rights violations in Kashmir."<ref>http://www.hrw.org/campaigns/kashmir/1996/India-07.htm</ref> In a 1999 follow-up report which implicated both the government and the militants for human rights violations, HRW alleged that Indian forces "have retaliated against local Muslims whom they accuse of supporting the militants" employing widespread tactics including "summary executions, 'disappearances,' torture and rape." <ref name="HRW">http://hrw.org/english/docs/1999/07/16/india954.htm</ref> | |||
| One such alleged massacre occurred on ], ] in the town of ]. ] described the incident as such: "In retaliation for the killing of one soldier, paramilitary forces rampaged through Sopore's market setting buildings ablaze and shooting bystanders. The Indian government pronounced the event 'unfortunate' and claimed that an ammunition dump had been hit by gunfire, setting off fires that killed most of the victims." <ref>http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,977469,00.html</ref> In addition to this, there have been claims of disappearances and fake encounters by the police or the army in Kashmir by several human rights organizations. <ref>http://www.state.gov/g/drl/rls/hrrpt/2006/78871.htm</ref><ref>http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/south_asia/6367917.stm</ref> | |||
| Under JKLF's leadership on 21–23 January large scale protests were organised in the Kashmir Valley. As a response to this largely explosive situation paramilitary units of BSF and CRPF were called. These units were used by the government to combat Maoist insurgency and the North-Eastern insurgency. The challenge to them in this situation was not posed by armed insurgents but by the stone pelters. Their inexperience caused at least 50 casualties in Gawkadal massacre. In this incident the underground militant movement was transformed into a mass struggle. To curb the situation AFSPA (Armed Forces Special Powers Act) was imposed on Kashmir in September 1990 to suppress the insurgency by giving armed forces the powers to kill and arrest without warrant to maintain public order. During this time the dominant tactic involved killing of a prominent figure in a public gathering, such as ] in 1994, to push forces into action and the public prevented them from capturing these insurgents. This sprouting of sympathisers in Kashmir led to the hard-line approach of Indian army.<ref>{{Cite book|title=Kashmir Demystified|last=Behera|first=Navnita Chadha|publisher=Brookings Institution Press|year=2006|location=Washington D.C.}}</ref> | |||
| ===Human rights violations by militants=== | |||
| Islamic terrorists are accused of following a policy of ] against the Kashmir populace.<ref>http://www.satp.org/satporgtp/kpsgill/2003/chapter9.htm</ref> Thousands of civilian Kashmiri Hindus have been killed in Kashmir over the past 10 years by Islamic militants organizations or Muslim mobs.<ref name="HRW"/> Human rights organisations put the figure of the number killed since the late 80's at 11,000.<ref name="incidents"/> Tens of thousands of Kashmiri Pandits have emigrated as a result of the violence. | |||
| With JKLF at forefront large number of militant groups like Allah Tigers, People's League and Hizb-i-Islamia sprung up. Weapons were smuggled on a large scale from Pakistan. In Kashmir JKLF operated under the leadership of Ashfaq Majid Wani, Yasin Bhat, Hamid Shiekh and Javed Mir. To counter this growing pro-Pakistani sentiment in Kashmir, Indian media associated it exclusively with Pakistan.<ref>{{Cite book|title=Kashmir Roots of Conflict Paths to Peace|url=https://archive.org/details/kashmirrootsconf00bose|url-access=limited|last=Bose|first=Sumantra|publisher=Harvard University Press|year=2003|location=Cambridge|pages=}}</ref> | |||
| Estimates of the displaced varies from 170,000 to 700,000.<ref name="kps">Alexander Evans, A departure from history: Kashmiri Pandits, 1990–2001, Contemporary South Asia (Volume 11, Number 1, 1 March 2002, pp. 19-37)</ref> The ''Jammu and Kashmir'' provincial government stated in ], that a total of 3,744 people had 'disappeared' since ]. However, human rights activists put the total figure at more than 8,000.{{fact}} | |||
| JKLF used distinctly Islamic themes to mobilise crowds and justify their use of violence. They sought to establish an Islamic democratic state where the rights of minorities would be protected according to Quran and Sunna and economy would be organised on the principles of Islamic socialism.<ref>{{Cite book|title=Demystifying Kashmir|last=Behra|first=Navnita Chadha|publisher=Brookings Institution Press|year=2006|location=Washington D.C.|pages=150}}</ref> | |||
| More than 120 local politicians have lost their lives, 15 of whom were members of Kashmir ].{{fact}} | |||
| The Indian army has conducted various operations to control and eliminate insurgency in the region such as ],<ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.thehindu.com/2003/07/31/stories/2003073102911200.htm|title=Fernandes reveals 'Sarp Vinash' toll|date=31 July 2003|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20051105210943/http://www.thehindu.com/2003/07/31/stories/2003073102911200.htm|newspaper=]|archive-date=5 November 2005}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.satp.org/satporgtp/sair/Archives/1_46.htm|title=A Militia Against Terror {{!}} J&K: Operation Sarp Vinash - The Army Strikes Hard {{!}} South Asia Intelligence Review (SAIR), Vol. No. 1.46|website=www.satp.org|access-date=2018-03-07|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160925235718/http://www.satp.org/satporgtp/sair/Archives/1_46.htm|archive-date=25 September 2016}}</ref> in which a multi-battalion offensive was launched against militants from groups like ], ], ] and ] who had been constructing shelters in the ] region of Jammu and Kashmir over several years.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/operation-sarp-vinash-army-clears-hill-kaka/articleshow/47305413.cms?from=mdr|title=Operation Sarp Vinash: Army clears Hill Kaka|last=Kumar|first=Devesh|date=2003-05-24|work=The Economic Times|access-date=2018-03-07|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180308044308/https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/operation-sarp-vinash-army-clears-hill-kaka/articleshow/47305413.cms?from=mdr|archive-date=8 March 2018}}</ref> The subsequent operations led to the death of over 60 militants<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.rediff.com/news/2003/may/23josy1.htm|title=Operation 'Sarp Vinash': Over 60 terrorists killed|website=www.rediff.com|access-date=2018-03-07|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170613172236/http://www.rediff.com/news/2003/may/23josy1.htm|archive-date=13 June 2017}}</ref> and uncovered the largest network of militant hideouts in the history of insurgency in Jammu and Kashmir covering almost 100 square kilometers.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Majid |first=Zulfikar |title='Sarp Vinash type of operation needed to eradicate militancy in Rajuri-Poonch' |url=https://www.deccanherald.com/india/sarp-vinash-type-of-operation-needed-to-eradicate-militancy-in-rajuri-poonch-1217460.html |access-date=2024-06-09 |website=Deccan Herald |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Joseph |first=Josy |title=Operation Sarp Vinash chief pulled up |url=https://www.rediff.com/news/2003/may/28josy.htm |access-date=2024-06-09 |website=Rediff |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| In addition, it is also alleged that Islamic terrorists have on numerous occasions committed murder and rape in an attempt to implicate Indian security forces.{{fact}} | |||
| == |
===Cultural changes=== | ||
| Cinema houses were banned by some militant groups.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.indiatoday.in/movies/bollywood/story/cinema-halls-are-first-fatality-of-militancy-in-kashmir-1378048-2018-10-29|title=Cinema halls are first fatality of militancy in Kashmir|date=29 October 2018 |access-date=29 April 2021|archive-date=29 April 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210429074807/https://www.indiatoday.in/movies/bollywood/story/cinema-halls-are-first-fatality-of-militancy-in-kashmir-1378048-2018-10-29|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.firstpost.com/long-reads/kashmirs-ghost-theatres-4393023.html|title=Kashmir's ghost theatres|date=16 March 2018 |access-date=29 April 2021|archive-date=29 April 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210429074807/https://www.firstpost.com/long-reads/kashmirs-ghost-theatres-4393023.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=https://scroll.in/reel/824328/kashmir-has-lost-its-cinema-halls-but-not-its-love-for-the-movies|title=Kashmir has lost its cinema halls but not its love for the movies|date=19 December 2016 |access-date=29 April 2021|archive-date=29 April 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210429074810/https://scroll.in/reel/824328/kashmir-has-lost-its-cinema-halls-but-not-its-love-for-the-movies|url-status=live}}</ref> Many militant organisations like ''Al baqr, People's league, Wahdat-e-Islam and Allah Tigers'' imposed restrictions like banning cigarettes, restrictions on Kashmiri girls.<ref>{{Cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=CUB4DgAAQBAJ&pg=PA47 |title=What Is Moderate Islam? |last=Benkin |first=Richard L. |date=2017-04-12 |publisher=Lexington Books |isbn=9781498537421 |page=47 |language=en |access-date=12 November 2020 |archive-date=20 April 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230420104113/https://books.google.com/books?id=CUB4DgAAQBAJ&pg=PA47 |url-status=live }}</ref>{{Tone inline|date=March 2022}} | |||
| *] daughter of them Home Minister of India Mufti Sayeed. | |||
| *] six forien trekkers from Anantnag district were kidnapped by Al Faran, One was beheaded later, one escaped and other four remain untraced presumable killed. | |||
| * ] - In January ], 24 ] living in the city ] were massacred by Pakistani Militants. According to the testimony of one of the survivors, the militants dressed themselves as officers of the ], entered their houses and then started firing blindly. The incident was significant because it coincided with former US president ]'s visit to ] and ] used the massacre to present a case against the alleged Pakistan-supported terrorism in Kashmir.<ref name="Wandhama">{{cite web|url=http://www.subcontinent.com/sapra/terrorism/tr_1998_01_002_s.html |title=Wandhama Massacre report}}</ref> | |||
| * Sangrampora Killings - On ] ], 7 Kashmiri Pandits were killed in ] village in the ] district.<ref name="Sangrampora ">{{cite web|url=http://www.kashmiri-pandit.org/atrocities/sangrampura.html |title=Sangrampora killings}}</ref> | |||
| *] On ], ], a bombing at the Legislative Assembly in ] killed 38.<ref name="Dugger">{{cite news|title=Pakistan Asks India to Revive Talks Aimed at Bringing Peace to Kashmir |publisher=The New York Times |author=Dugger, Celia |date=2001, October 9}}</ref> | |||
| * Qasim Nagar Attack - On ], ], armed militants believed to be a part of the ] threw hand grenades at the Qasim Nagar market in ] and then fired on civilians standing nearby killing twenty-seven and injuring many more.<ref name="hrw">{{cite web|url=http://www.hrw.org/wr2k3/asia6.html |title=Human Rights Watch World Report 2003: India}}</ref> | |||
| * Assassination of Abdul Ghani Lone - Abdul Ghani Lone, a prominent All Party Hurriyat Conference leader, was assassinated by unidentified gunmen during a memorial rally in ]. The assassination resulted in wide-scale demonstrations against the Indian forces for failing to provide enough security cover for Mr. Lone.<ref name="hrw"/> | |||
| * ] ] ] Bombing - A car bomb exploded near an armoured ] vehicle in the famous Church Lane area in ] killing 4 ] personnel, one civilian and the suicide bomber. Militant group ], claimed responsibility for the attack.<ref name="church">{{cite web|url=http://www.ndtv.com/template/template.asp?template=Ceasefire&slug=Car+bomb+attack+in+Srinagar%2C+6+killed&id=17351&callid=0&amp;category=National |title=20 July 2005 Srinagar attack}}</ref> | |||
| * ] - A militant attack on ], ] at ]'s city centre, Budshah Chowk, killed 2 and left more than 17 people injured. Most of those injured were media journalists.<ref name="Bud">{{cite web|url=http://www.hindustantimes.com/news/181_1445705,000900010002.htm |title=July 29 attack in Srinagar}}</ref> | |||
| * Murder of Ghulam Nabi Lone - On October 18, 2005 suspected Kashmiri militants killed Jammu and Kashmir's then education minister Ghulam Nabi Lone. Militant group called Al Mansurin claimed responsibility for the attack.<ref name="Nabi">{{cite web|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/4351950.stm |title=Nabi Lone's assassination}}</ref> | |||
| * On ] ] militants massacred 35 Hindus in ] and ] districts in Jammu and Kashmir.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.tribuneindia.com/2006/20060504/jal.htm#4 |title=Massacre of 35 Hindus in Doda and Udhampur districts of Jammu}}</ref> | |||
| *On ] ] one person was killed and 31 were wounded when terrorists hurled three grenades on Vaishnodevi shrine-bound buses at the general bus stand here this morning.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.tribuneindia.com/2006/20060613/main1.htm|title=Terror in Jammu, Anantnag}}</ref> | |||
| * On ], ], over 190 people were killed and over 700 injured from bombs planted on 7 commuter trains in Mumbai by Lashkar-e-Toiba terrorists. | |||
| == |
=== 2004–11 === | ||
| {{main|2010 Kashmir unrest}} | |||
| {{update}} | |||
| Beginning in 2004 Pakistan began to end its support for insurgents in Kashmir.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Tucker|first1=Spencer C.|title=Encyclopedia of Insurgency and Counterinsurgency A New Era of Modern Warfare|date=2013|publisher=ABC-CLIO, LLC|location=Santa Barbara, California|isbn=978-1-61069-279-3}}</ref> This happened because militant groups linked to Kashmir twice tried to assassinate ] General ].<ref name="KhanMilitants" /> His successor, ] has continued the policy, calling insurgents in Kashmir "terrorists",<ref name="StephensJob" /> although it is unclear if Pakistan's intelligence agency, the ], thought to be the agency aiding and controlling the insurgency<ref name="StephensJob" /><ref name="ColeObama" /><ref name="RediffKashmir" /> is following Pakistan's commitment to end support for the insurgency in Kashmir.<ref name="StephensJob" /> Despite the change in the nature of the insurgency from a phenomenon supported by external forces to a primarily domestic-driven movement<ref name="SumantraKashmir" /><ref name="StephensJob" /><ref name="EconomistStony" /><ref name="EconomistPlace" /><ref name="EconomistGrim" /> the Indian government has continued to send large numbers of troops to the Indian border.<ref name="EconomistStony" /><ref name="EconomistGrim" /><ref name="BBCKillings" /> There have been widespread protests against the Indian army presence in Kashmir.<ref name="EconomistStony" /> | |||
| The following statistics were compiled by Indian Army, the US State Department Patterns of Global Terrorism and News Sources:<ref name="fact"/> | |||
| *Number of Islamic Terrorists camps in ]: 49 | |||
| Once the most formidable face of Kashmir militancy, ] is slowly fading away as its remaining commanders and cadres are being taken out on a regular interval by security forces.<ref>{{cite news| url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/Hizbul-Mujahideen-almost-wiped-out-in-Kashmir/articleshow/10408682.cms | archive-url=https://archive.today/20120729010520/http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2011-10-19/india/30296919_1_kashmir-valley-security-forces-mohammad-shafi | url-status=live | archive-date=29 July 2012 | work=The Times of India | title=Hizbul Mujahideen almost wiped out in Kashmir | date=19 October 2011}}</ref> Some minor incidents of grenade throwing and sniper firing at security forces notwithstanding, the situation is under control and more or less peaceful. A record number of tourists including Amarnath pilgrims visited Kashmir during 2012. On 3 August 2012, a top ] militant commander, Abu Hanzulah involved in various attacks on civilians and security forces was killed in an encounter with security forces in a village in Kupwara district of north Kashmir.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.hindustantimes.com/India-news/Srinagar/J-amp-K-Top-LeT-commander-killed-in-encounter/Article1-907473.aspx |title=J&K: Top LeT commander killed in encounter |date=3 August 2012 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120803100038/http://www.hindustantimes.com/India-news/Srinagar/J-amp-K-Top-LeT-commander-killed-in-encounter/Article1-907473.aspx |archive-date=3 August 2012}}</ref> | |||
| *Total number of Islamic Terrorists camps in ]: 37 | |||
| *Number of Kashmiri Terrorists camps in ]: 22 (During Taliban rule) | |||
| ===2012–present=== | |||
| *Number of Terrorists* operating in Jammu and Kashmir: 3200 (1996 estimate<ref name=HRW-VII-VIOLATION-Terrorists-ORGANIZATIONS>{{cite web | |||
| {{main|2013 India–Pakistan border skirmishes|2014–15 India–Pakistan border skirmishes|2016–17 Kashmir unrest}} | |||
| |title=VII. Violations by Terrorists Organizations | |||
| According to ] data quoted by ], at least 70 young Kashmiris joined the insurgency in 2014, army records showed, with most joining the terrorist organization ], which was responsible for carrying out the ].<ref>{{Cite web |date=2016-01-10 |title=NIA :: Banned Terrorist Organisations |url=http://www.nia.gov.in/banned_org.aspx |access-date=2022-04-20 |website= |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160110115355/http://www.nia.gov.in/banned_org.aspx |archive-date=10 January 2016 |url-status=dead}}</ref> Two of the new recruits have doctorates and eight were post graduates, the army data showed.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://tribune.com.pk/story/843452/kashmiris-join-insurgency-against-india-at-highest-rate-in-two-decades/|title=Kashmiris join insurgency against India at highest rate in two decades|work=The Express Tribune|date=24 February 2015|access-date=25 June 2015|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150626104329/http://tribune.com.pk/story/843452/kashmiris-join-insurgency-against-india-at-highest-rate-in-two-decades/|archive-date=26 June 2015}}</ref> According to ], despite a Pakistani ban on militant activity in Kashmir in 2006, its militants continue to attempt infiltration into Indian-administered Kashmir. These attempts were curtailed however when people living along the ] which divides Indian and Pakistani Kashmir started to hold public protests against the activities of the insurgent groups.<ref>{{cite news|title=Who are the Kashmir militants?|url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-18738906|access-date=21 February 2017|work=]|date=1 August 2012|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170220135306/http://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-18738906|archive-date=20 February 2017}}</ref> | |||
| |url=http://www.gharib.demon.co.uk/reports/milvio.htm | |||
| |date=] | |||
| In 2016, ] erupted in the aftermath of the killing of ] militant ] by security forces. Since then, militants belonging to the ] group carried out the ] and the ]. In February 2019, the ] occurred, in which 40 ] personnel were killed by a Jaish-e-Mohammed suicide bomber. | |||
| |work=Human Rights Watch/Asia: India: India's Secret Army in Kashmir, New Patterns of Abuse Emerge in the Conflict | |||
| |publisher=] | |||
| In August 2019, the special status of Jammu and Kashmir was ], following which the Indian Army intensified its counter-insurgency operations. In June 2020, ] was declared militancy free while ] was declared free from Hizbul Mujahideen militants.<ref>{{Cite web|date=2020-06-29|title=Jammu's Doda is militancy free, say cops after Hizbul terrorist Masood killed in encounter|url=https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/jammu-s-doda-is-militancy-free-say-cops-after-hizbul-terrorist-masood-killed-in-encounter/story-dZsjrZuPZISqGz4mwlnzEL.html|access-date=2020-06-29|website=Hindustan Times|language=en|archive-date=29 June 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200629073031/https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/jammu-s-doda-is-militancy-free-say-cops-after-hizbul-terrorist-masood-killed-in-encounter/story-dZsjrZuPZISqGz4mwlnzEL.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|date=26 June 2020|agency=PTI|title=No Hizbul militant in south Kashmir's Tral now, first time since 1989: Police|url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/no-hizbul-militant-in-south-kashmirs-tral-now-first-time-since-1989-police/articleshow/76649954.cms|access-date=2020-06-29|website=The Times of India|language=en|archive-date=28 September 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200928030927/https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/no-hizbul-militant-in-south-kashmirs-tral-now-first-time-since-1989-police/articleshow/76649954.cms|url-status=live}}</ref> In July, a Kashmir police tweet from an official twitter handle said "no resident of #] in terrorist ranks now".<ref>{{Cite web|date=2020-07-26|title=No resident of Srinagar in terrorist ranks after killing of top LeT commander: Kashmir IGP|url=https://indianexpress.com/article/india/no-resident-of-srinagar-in-terrorist-ranks-after-killing-of-top-let-commander-kashmir-igp-6524514/|access-date=2020-07-27|website=The Indian Express|language=en|archive-date=27 July 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200727110035/https://indianexpress.com/article/india/no-resident-of-srinagar-in-terrorist-ranks-after-killing-of-top-let-commander-kashmir-igp-6524514/|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|last=Hussain|first=Ashiq|date=2020-07-26|title=After killing of LeT man, no resident of Srinagar is in terrorist ranks: IGP|url=https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/after-killing-of-let-man-no-resident-of-srinagar-is-in-terrorist-ranks-igp/story-J6Wr5jJwe3ukfvhBqcrGAO.html|access-date=2020-07-27|website=Hindustan Times|language=en|archive-date=27 July 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200727105556/https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/after-killing-of-let-man-no-resident-of-srinagar-is-in-terrorist-ranks-igp/story-J6Wr5jJwe3ukfvhBqcrGAO.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|last=Pandit|first=M. Saleem|date=26 July 2020|title=Srinagar district is now terror-free: Police|url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/srinagar-district-is-now-terror-free-police/articleshow/77186638.cms|access-date=2020-07-27|website=The Times of India|language=en|archive-date=27 July 2020|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200727110353/https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/srinagar-district-is-now-terror-free-police/articleshow/77186638.cms|url-status=live}}</ref> On 27 June 2021, a day after the successful completion of discussions between the Indian Prime Minister and Jammu and Kashmir political leaders, a drone based attack was reported at the technical area of ] which is under the control of the IAF.<ref>{{Cite web|title=NC terms drone attack inside Jammu airport as terrorism by rogue state Pakistan|url=https://english.mathrubhumi.com/news/india/nc-terms-drone-attack-inside-jammu-airport-as-terrorism-by-rogue-state-pakistan-1.5786856|access-date=2021-06-28|website=Mathrubhumi|date=28 June 2021 |language=en|archive-date=28 June 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210628074547/https://english.mathrubhumi.com/news/india/nc-terms-drone-attack-inside-jammu-airport-as-terrorism-by-rogue-state-pakistan-1.5786856|url-status=live}}</ref> In the first three months of 2022, there was a 100% increase in the number of Indian soldiers killed by Kashmiri militants compared to the same period in 2021.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2022-04-22 |title=10 Jawans Killed This Year in J&K as Terrorists Ramp Up Grenade, Hit-&-Run Attacks on Security Forces |url=https://www.news18.com/news/india/jammu-kashmir-100-more-jawans-killed-in-encounters-58-more-injured-in-2022-5030965.html |access-date=2022-04-22 |website=News18 |language=en |archive-date=22 April 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220422130341/https://www.news18.com/news/india/jammu-kashmir-100-more-jawans-killed-in-encounters-58-more-injured-in-2022-5030965.html |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| |accessdate=2007-02-09 }}</ref>) | |||
| *Number of Kashmiri Terrorists in Indian jails: 125 | |||
| == Motivations behind the insurgency == | |||
| *Number of Indian civilians killed by Kashmiri Terrorists* since 1988: over 29,000 | |||
| *Number of explosions carried out by the Terrorists* in India: 4,730 | |||
| === Rigging of 1987 Assembly elections === | |||
| *Total number of Kashmiri Pandits displaced from the state: over 300,000 | |||
| {{Further|1987 Jammu and Kashmir Legislative Assembly election}} | |||
| *Amount of explosives recovered from Kashmiri Terrorists* in India: 60 tons or 30,000 kg (estimate) | |||
| *Major Islamic Terrorists training camps:<ref name="HT"/> | |||
| Following the rise of Islamisation in the Kashmir valley, during the 1987 state elections, various Islamic anti-establishment groups including ] were organised under a single banner named ] (MUF), that is largely current ]. MUF's election manifesto stressed the need for a solution to all outstanding issues according to ], work for Islamic unity and against political interference from the centre. Their slogan was wanting the law of the Quran in the Assembly.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Schofield |first=Victoria |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=rkTetMfI6QkC&pg=PA137 |title=Kashmir in Conflict: India, Pakistan and the Unending War |date=2000 |publisher=I.B.Tauris |isbn=9781860648984 |pages=137 |language=en}}</ref> But the MUF won only four seats, even though it had polled 31% votes in the election. However, the elections were widely believed to be rigged, changing the course of politics in the state. The insurgency was sparked by the apparent rigging of ].<ref name="BBCKashmir" /><ref name="AltafElections" /><ref>{{Cite news |date=2016-03-22 |title=How Mufti Mohammad Sayeed Shaped the 1987 Elections in Kashmir |language=en-US |work=The Caravan |url=http://www.caravanmagazine.in/vantage/mufti-mohammad-sayeed-shaped-1987-kashmir-elections |url-status=live |access-date=2017-05-04 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170428235753/http://www.caravanmagazine.in/vantage/mufti-mohammad-sayeed-shaped-1987-kashmir-elections |archive-date=28 April 2017}}</ref> | |||
| {| align="center" border=1 style="border-collapse: collapse;" | |||
| | bgcolor="#ff2222 align="center" colspan="2" | '''Location of major Terrorists* camps''' | |||
| === Human rights abuses === | |||
| {{Main|Human rights abuses in Jammu and Kashmir}} | |||
| Indian troops entered the valley to quell the insurgency after it began.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Hashim |first1=Asad |date=27 May 2014 |title=Timeline: India-Pakistan relations |publisher=] |url=http://www.aljazeera.com/indepth/spotlight/kashmirtheforgottenconflict/2011/06/2011615113058224115.html |url-status=live |access-date=23 February 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170301040548/http://www.aljazeera.com/indepth/spotlight/kashmirtheforgottenconflict/2011/06/2011615113058224115.html |archive-date=1 March 2017}}</ref> Some analysts have suggested that the number of Indian troops in Jammu and Kashmir is close to 600,000 although estimates vary and the government refuses to release official figures.<ref name="The Times" /> The troops have been accused and held accountable for several humanitarian abuses<ref name="EconomistGrim" /> and have engaged in ], ].<ref name="BBCKillings" /> | |||
| Indian security forces have been implicated in many reports for ] of thousands of Kashmiris whereas the security forces deny having their information and/or custody. This is often in association with torture or ]. Human right activists estimate the number of disappeared to be over eight thousand, last seen in government detention.<ref name="hrw.org">{{cite web |author=Brad Adams, Asia director at Human Rights Watch |date=16 February 2007 |title=India: Investigate All 'Disappearances' in Kashmir | Human Rights Watch |url=https://www.hrw.org/news/2007/02/14/india-investigate-all-disappearances-kashmir |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120805163849/http://www.hrw.org/news/2007/02/14/india-investigate-all-disappearances-kashmir |archive-date=5 August 2012 |access-date=2012-10-01 |publisher=Hrw.org}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |author=Human Rights Watch |date=11 September 2006 |title=Everyone Lives in Fear |url=https://www.hrw.org/print/reports/2006/09/11/everyone-lives-fear-0 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://archive.today/20130415014414/http://www.hrw.org/print/reports/2006/09/11/everyone-lives-fear-0 |archive-date=15 April 2013 |access-date=2012-10-01 |publisher=Hrw.org}}</ref> The disappeared are believed to be dumped in thousands of mass graves across Kashmir.<ref>{{cite book |url=https://www.hrw.org/world-report/2009/india |title=India | Human Rights Watch |date=14 January 2009 |publisher=Hrw.org |chapter=India: Events of 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120903082652/http://www.hrw.org/world-report/2009/india |archive-date=3 September 2012 |url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |last=Bukhari |first=Shujaat |title=Mass graves found in North Kashmir containing 2,900 unmarked bodies |language=en |work=The Hindu |url=http://www.thehindu.com/news/national/Mass-graves-found-in-North-Kashmir-containing-2900-unmarked-bodies/article16851202.ece |url-status=live |access-date=2017-04-22 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180429233249/http://www.thehindu.com/news/national/Mass-graves-found-in-North-Kashmir-containing-2900-unmarked-bodies/article16851202.ece |archive-date=29 April 2018}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |date=2011-08-25 |title=Kashmir graves: Human Rights Watch calls for inquiry |language=en-GB |work=BBC News |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-south-asia-14660253 |url-status=live |access-date=2017-04-22 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170423001359/http://www.bbc.com/news/world-south-asia-14660253 |archive-date=23 April 2017}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |date=2008-08-30 |title=India must investigate unidentified graves, News, Amnesty International Australia |url=https://www.amnesty.org.au/news/comments/11808/ |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080830095509/http://www.amnesty.org.au/news/comments/11808/ |archive-date=2008-08-30 |access-date=2017-04-22}}</ref><ref> {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111017070644/http://www.kashmirprocess.org/reports/graves/BuriedEvidenceKashmir.pdf|date=17 October 2011}} A preliminary report; '']''</ref> A ] inquiry in 2011, has confirmed there are thousands of bullet-ridden bodies buried in unmarked graves in Jammu and Kashmir. Of the 2730 bodies uncovered in 4 of the 14 districts, 574 bodies were identified as missing locals in contrast to the Indian governments insistence that all the graves belong to foreign militants.<ref name="ReferenceC">{{cite web |date=24 August 2011 |title=India: Investigate Unmarked Graves in Jammu and Kashmir | Human Rights Watch |url=https://www.hrw.org/news/2011/08/24/india-investigate-unmarked-graves-jammu-and-kashmir |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120904202829/http://www.hrw.org/news/2011/08/24/india-investigate-unmarked-graves-jammu-and-kashmir |archive-date=4 September 2012 |access-date=2012-10-01 |publisher=Hrw.org}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |last=LYDIA POLGREEN |date=22 August 2011 |title=Mass Graves Hold Thousands, Kashmir Inquiry Finds |newspaper=NYTimes |url=https://www.nytimes.com/2011/08/23/world/asia/23kashmir.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160502195234/http://www.nytimes.com/2011/08/23/world/asia/23kashmir.html |archive-date=2 May 2016}}</ref> | |||
| Military forces in Jammu and Kashmir operate under impunity and emergency powers granted to them by the central government. These powers allow the military to curtail civil liberties, creating further support for the insurgency.<ref name="YardleyPower" /><ref name="AI Press Release Feb 2012">{{cite web |date=7 February 2012 |title=India: Security forces cannot claim immunity under AFSPA, must face trial for violations |url=https://www.amnesty.org/en/latest/news/2012/02/india-security-forces-cannot-claim-immunity-under-afspa-must-face-trial-violations/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170423062142/https://www.amnesty.org/en/latest/news/2012/02/india-security-forces-cannot-claim-immunity-under-afspa-must-face-trial-violations/ |archive-date=23 April 2017 |access-date=7 March 2012 |publisher=Amnesty International}}</ref> | |||
| The insurgents have also abused human rights, ] ] from the Kashmir Valley, an action that has been called ]<ref name="PalloneEthnic" /> The government's inability to protect the people from both its own troops and the insurgency has further eroded support for the government.<ref name="HRW99">{{cite web |date=16 July 1999 |title=Rights Abuses Behind Kashmir Fighting – Human Rights Watch |url=http://hrw.org/english/docs/1999/07/16/india954.htm |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081019175125/http://hrw.org/english/docs/1999/07/16/india954.htm |archive-date=19 October 2008 |access-date=25 June 2015 |work=hrw.org}}</ref> | |||
| ] accused security forces of exploiting the ] (AFSPA) that enables them to "hold prisoners without trial". The group argues that the law, which allows security to detain individuals for as many as two years "without presenting charges, violating prisoners' human rights".<ref>{{cite web |last=Huey |first=Caitlin |date=28 March 2011 |title=Amnesty International Cites Human Rights Abuse in Kashmir |url=https://www.usnews.com/news/articles/2011/03/28/amnesty-international-cites-human-rights-abuse-in-kashmir |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130430022351/http://www.usnews.com/news/articles/2011/03/28/amnesty-international-cites-human-rights-abuse-in-kashmir |archive-date=30 April 2013 |access-date=2012-10-01 |publisher=Usnews.com}}</ref> The Army sources maintain that "any move to revoke AFSPA in Jammu and Kashmir would be detrimental to the security of the Valley and would provide a boost to the terrorists."<ref>{{Cite news |title=Army opposes Omar's plans to revoke AFSPA: Report |work=The Times of India |url=http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/Army-opposes-Omars-plans-to-revoke-AFSPA-Report/articleshow/4197012.cms |url-status=live |access-date=2017-05-06 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171012072106/https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/Army-opposes-Omars-plans-to-revoke-AFSPA-Report/articleshow/4197012.cms |archive-date=12 October 2017}}</ref> | |||
| Former ] ] rejected the accusations that the action was not taken in the cases of human rights violations by Army personnel. On 24 October 2010, he has said that 104 Army personnel had been punished in Jammu and Kashmir in this regard, including 39 officers. He also said that 95% of the allegations of human rights abuses against Indian Army were proved to be false, of which he remarked, had apparently been made with the "ulterior motive of maligning the armed forces".<ref>{{Cite news |date=2010-10-24 |title=104 armymen punished for human rights violations in JK: Gen VK Singh {{!}} Latest News & Updates at Daily News & Analysis |language=en-US |work=dna |url=http://www.dnaindia.com/india/report-104-armymen-punished-for-human-rights-violations-in-jk-gen-vk-singh-1457257 |url-status=live |access-date=2017-04-24 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170425121321/http://www.dnaindia.com/india/report-104-armymen-punished-for-human-rights-violations-in-jk-gen-vk-singh-1457257 |archive-date=25 April 2017}}</ref> However, according to Human Rights Watch, the military courts in India, in general, were proved to be incompetent to deal with cases of serious human rights abuses and were responsible in covering up evidence and protecting the involved officers.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Rape by Security Forces: The Pattern of Impunity |url=https://www.hrw.org/legacy/about/projects/womrep/General-42.htm |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171012104533/https://www.hrw.org/legacy/about/projects/womrep/General-42.htm |archive-date=12 October 2017 |access-date=2017-05-01 |website=www.hrw.org}}</ref> Amnesty International in its report in 2015, titled ''"Denied"-Failures in Accountability in Jammu and Kashmir'', says, "...with respect to investigations, an inquiry that is conducted by the same authority accused of the crime raises serious questions about the independence and impartiality of those proceedings", adding that according to the international law, an independent authority that is not involved in the alleged violations has to investigate such crimes.<ref>{{Cite web |author=<!--Staff writer(s); no by-line.--> |date=2016-09-03 |title=96% complaints against army rejected by GoI under 'colonial' AFSPA: Amnesty |url=http://kashmirreader.com/2016/09/03/96-complaints-against-army-rejected-by-goi-under-colonial-afspa-amnesty/ |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170804103846/http://kashmirreader.com/2016/09/03/96-complaints-against-army-rejected-by-goi-under-colonial-afspa-amnesty/ |archive-date=4 August 2017 |access-date=2017-05-01 |website=Kashmir Reader}}</ref> | |||
| These human rights violations are said to have contributed to the rise of resistance in Kashmir.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Kashmir's disturbing new reality {{!}} the young militants of Kashmir |url=http://www.hindustantimes.com/static/the-young-militants-of-kashmir/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170530162002/http://www.hindustantimes.com/static/the-young-militants-of-kashmir/ |archive-date=30 May 2017 |access-date=2017-05-24 |website=Hindustantimes.com |quote=Then, youngsters used to take to the streets and pelt stones to protest human right violations...}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |last=Parthasarathy |first=Malini |title=Understanding Kashmir's stone pelters |language=en |work=The Hindu |url=http://www.thehindu.com/opinion/lead/Understanding-Kashmirs-stone-pelters/article16120870.ece |url-status=live |access-date=2017-05-24 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180429233249/http://www.thehindu.com/opinion/lead/Understanding-Kashmirs-stone-pelters/article16120870.ece |archive-date=29 April 2018 |quote=Today's protesters might shout anti-India slogans such as ''azadi'', but their anger is specifically directed at the security forces in the context of the brutal killings of innocent boys...}}</ref> | |||
| === ISI's role === | |||
| The Pakistani ] has encouraged and aided the Kashmir independence movement through an insurgency<ref name="StephensJob" /><ref name="ColeObama" /><ref name="RediffKashmir" /> due to its dispute on the legitimacy of Indian rule in Kashmir, with the insurgency as an easy way to keep Indian troops distracted and cause international condemnation of India.<ref name="SumantraKashmir" /> Former ] General ] in Oct 2014 said during TV interview, "We have source (in Kashmir) besides the (Pakistan) army...People in Kashmir are fighting against (India). We just need to incite them."<ref>{{cite magazine |date=16 October 2014 |title=Pakistan needs to incite those fighting in Kashmir: Musharraf |url=http://indiatoday.intoday.in/story/musharraf-pakistan-kashmir-kargil-conflict-militants/1/396106.html |url-status=live |magazine=] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171012065029/http://indiatoday.intoday.in/story/musharraf-pakistan-kashmir-kargil-conflict-militants/1/396106.html |archive-date=12 October 2017 |access-date=22 February 2017}}</ref> | |||
| The ], in their first ever open acknowledgement in 2011 in US Court, said that the ] sponsors and oversees separatist militant groups in Kashmir.<ref name="firstpost1">{{cite web |date=21 July 2011 |title=ISI sponsors terror activities in Kashmir, FBI tells US court |url=http://www.firstpost.com/politics/isi-sponsors-terror-activities-in-kashmir-fbi-tells-us-court-46038.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150924145916/http://www.firstpost.com/politics/isi-sponsors-terror-activities-in-kashmir-fbi-tells-us-court-46038.html |archive-date=24 September 2015 |access-date=1 April 2015 |work=Firstpost}}</ref><ref name="indiatimes.com1">{{cite news |last1=Rajghatta |first1=Chidanand |date=20 July 2011 |title=US exposes ISI subversion of Kashmir issue; FBI arrests US-based lobbyist |newspaper=] |url=http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/world/us/US-exposes-ISI-subversion-of-Kashmir-issue-FBI-arrests-US-based-lobbyist/articleshow/9294830.cms |url-status=live |access-date=22 February 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170812140040/http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/world/us/US-exposes-ISI-subversion-of-Kashmir-issue-FBI-arrests-US-based-lobbyist/articleshow/9294830.cms |archive-date=12 August 2017}}</ref><ref name="rediff1">{{cite news |last1=Kumar |first1=Himani |date=7 June 2011 |title=ISI gives arms to Kashmir terrorists: Rana to FBI |work=] |url=http://www.rediff.com/news/slide-show/slide-show-1-isi-gives-arms-to-kashmiri-terrorists-rana-to-fbi/20110607.htm |url-status=live |access-date=22 February 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170805015010/http://www.rediff.com/news/slide-show/slide-show-1-isi-gives-arms-to-kashmiri-terrorists-rana-to-fbi/20110607.htm |archive-date=5 August 2017}}</ref><ref name="indianexpress1">{{cite news |last1=Agencies |date=20 July 2011 |title=ISI funneled millions to influence US policy on Kashmir: FBI |newspaper=] |url=http://archive.indianexpress.com/news/isi-funneled-millions-to-influence-us-policy-on-kashmir-fbi/819859/ |url-status=live |access-date=22 February 2017 |archive-url=http://archive.wikiwix.com/cache/20170224070053/http://archive.indianexpress.com/news/isi-funneled-millions-to-influence-us-policy-on-kashmir-fbi/819859/ |archive-date=24 February 2017}}</ref> | |||
| In 2019, ] ] publicly discouraged Pakistani people from going to Kashmir to do a '']''. People who went to Kashmir will do an "injustice to the Kashmiri people".<ref name="DawnSept2019">{{cite news |date=18 September 2019 |title='Historic day': PM Imran inaugurates 24/7 border crossing at Torkham |language=en |work=DAWN.COM |url=https://www.dawn.com/news/1505914 |access-date=27 November 2019 |archive-date=23 May 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220523151227/https://www.dawn.com/news/1505914 |url-status=live }}</ref><ref name="Puri">{{cite news |last1=Puri |first1=Luv |date=27 November 2019 |title=The many faces of Pakistani Punjab's militancy |language=en-IN |work=The Hindu |url=https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/op-ed/the-many-faces-of-pakistani-punjabs-militancy/article30090521.ece |access-date=27 November 2019 |archive-date=19 November 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211119102300/https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/op-ed/the-many-faces-of-pakistani-punjabs-militancy/article30090521.ece |url-status=live }}</ref> Most of the Pakistani militants who had crossed the border over the years and were caught by the Indian security forces were found to belong to the ] of Pakistan.<ref name="Puri" /> | |||
| === Mujahideen influence === | |||
| After the ] victory in the ], Mujahideen militants, under the ] with the aid of ], slowly infiltrated ] with the goal of spreading a radical ] to wage ] against India in the region.<ref name="BBCKashmir" /> | |||
| === Religion === | |||
| The majority of the people of Jammu and Kashmir practise ]. Indian-American journalist ] states that while India itself is a secular state, Muslims are politically, culturally and economically marginalised when compared to Hindus in India as a whole.<ref name="NomaniMuslims" /> The government's ] to transfer 99 acres of forest land near the ] in Kashmir division to a Hindu organisation (for setting up temporary shelters and facilities for Hindu pilgrims) solidified this feeling and led to one of the largest protest rallies in Jammu and Kashmir.<ref name="ThottamValley" /> | |||
| <ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.dailyo.in/politics/jammu-and-kashmir-afspa-hizbul-mujahideen-lashkar-e-taiba-pakistan-ghar-wapsi-jihad-hindutva/story/1/5698.html|title=Five reasons behind radicalisation in Kashmir|last=Gowhar Geelani|website=www.dailyo.in|access-date=2017-05-24|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170309014546/http://www.dailyo.in/politics/jammu-and-kashmir-afspa-hizbul-mujahideen-lashkar-e-taiba-pakistan-ghar-wapsi-jihad-hindutva/story/1/5698.html|archive-date=9 March 2017}}</ref> | |||
| === Other motivations === | |||
| ==== Psychological ==== | |||
| Psychologist Waheeda Khan, explaining the rebellious nature of the Kashmiris, says that because of the tense situations in the valley from the 1990s, the generation gap between parents and young generations has increased. Young generations tend to blame their parents for failing to do anything about the political situation. So they start experimenting with their own aggressive ways to show their curbed feelings and would go against any authority. A prominent psychiatrist of the valley, Margoob, described that children/teenagers are much more vulnerable to passionate actions and reactions, since the young minds are yet to completely develop psychological mechanisms. When they assume that they are "pushed against the wall", they get controlled by the emotions without bothering about the consequences. Also young people easily identify themselves with the "group" rather than with their individual identities. It leads to psychological distress which causes antisocial behaviour and aggressive attitude. Often, this situation gets worsened by the availability of weapons and people becoming familiar to violence after having exposed to conflict for so long. Waheeda Khan remarks, the major concern is that generations of children who are experiencing long-term violence in their lives, may reach adulthood perceiving that violence is a fair means of solving ethnic, religious, or political differences.{{sfn|Waheeda Khan, Conflict in Kashmir|2015|p=90, 91}} | |||
| ====Economic==== | |||
| High unemployment and lack of economic opportunities in Kashmir are also said to have intensified the struggle.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-india-40008876|title=Indian award for Kashmir 'human shield' officer|date=2017-05-23|work=BBC News|access-date=2017-05-23|language=en-GB|quote=High unemployment and complaints of heavy-handed tactics by security forces battling street protesters and fighting insurgents have aggravated the problem.|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170523075335/http://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-india-40008876|archive-date=23 May 2017}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/unemployment-a-reason-for-surge-in-jk-violence/articleshow/51849148.cms|title=Unemployment a reason for surge in J&K violence? |work=The Times of India|access-date=2017-05-24|archive-date=20 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230420104114/https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/unemployment-a-reason-for-surge-in-jk-violence/articleshow/51849148.cms|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=http://www.thehindu.com/opinion/lead/Understanding-Kashmirs-stone-pelters/article16120870.ece|title=Understanding Kashmir's stone pelters|last=Parthasarathy|first=Malini|work=The Hindu|access-date=2017-05-24|language=en|quote=The protesters on the streets...(are) frustrated at the lack of employment and economic opportunities. It is not hard to see where the frustration of the educated Kashmiri youth comes from. On the one hand, they are told that they are Indian citizens but they are shut out of the narrative of India as an emerging economic power. With mobile phones and internet communication being restricted, their sense of participation in the larger Indian discourse is sharply reduced.|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180429233249/http://www.thehindu.com/opinion/lead/Understanding-Kashmirs-stone-pelters/article16120870.ece|archive-date=29 April 2018}}</ref> | |||
| == Stone pelting == | |||
| {{Main|Stone Pelting in Kashmir}} | |||
| Following the ] and ], the turmoil took on a new dimension when people, particularly young people of the Kashmir valley began pelting stones on security forces to express their aggression and protest for the loss of freedom. In turn they get attacked by the armed personnel with pellets, rubber bullets, sling shots and tear gas shells. This leads to eye-injuries and several other kind of injuries to many people. Security forces also face injuries, and sometimes get beaten up during these events. According to Waheeda Khan, most of the 'stone-pelters' are school and college going students. Large number of these people get arrested during these events for allegedly resorting to stone pelting, after which some of them are also tortured. According to political activist Mannan Bukhari, Kashmiris made stone, an easily accessible and defenseless weapon, their weapon of choice for protest.<ref name=":0A">{{harvnb|Waheeda Khan, Conflict in Kashmir|2015|p=88}}</ref><ref name="Bukhari-2015">{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=43ZJCgAAQBAJ&q=kashmir+stone+pelting&pg=PT44|title=Kashmir - Scars of Pellet Gun: The Brutal Face of Suppression|last=Bukhari|first=Mannan|date=2015-07-28|publisher=Partridge Publishing|isbn=9781482850062|pages=44|language=en|access-date=12 November 2020|archive-date=20 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230420104718/https://books.google.com/books?id=43ZJCgAAQBAJ&q=kashmir+stone+pelting&pg=PT44|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Kashmiri senior journalist Parvaiz Bukhari remarked:<ref name="Bukhari-2015" /><ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.kashmirlife.net/summers-of-unrest-challenging-india-1089/|title=Summers of Unrest Challenging India|website=www.kashmirlife.net|language=en-GB|date=20 December 2010|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171012061809/http://kashmirlife.net/summers-of-unrest-challenging-india-1089/|archive-date=12 October 2017}}</ref><blockquote>The summer of 2010 witnessed a convulsion in the world's most militarized zone, the Indian-controlled part of Kashmir, an unprecedented and deadly civil unrest that is beginning to change a few things on the ground. Little known and relatively anonymous resistance activists emerged, organizing an unarmed agitation more fierce than the armed rebellion against Indian rule two decades earlier. And apparently aware of the post 9/11 world, young Kashmiris, children of the conflict, made stones and rocks a weapon of choice against government armed forces, side-stepping the tag of a terrorist movement linked with Pakistan. The unrest represents a conscious transition to an unarmed mass movement, one that poses a moral challenge to New Delhi's military domination over the region.</blockquote> | |||
| == Human rights abuses by militants and army == | |||
| {{further|Human rights abuses in Jammu and Kashmir|Rape in Kashmir conflict#Rape by militants}} | |||
| {{See also|Ethnic cleansing of Kashmiri Hindus}} | |||
| Islamic separatist militants are accused of violence against the Kashmir populace.<ref>{{cite news|title=Four killed in Kashmir bomb blast|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/4698705.stm|access-date=22 February 2017|work=]|date=20 July 2005|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160825041916/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/4698705.stm|archive-date=25 August 2016}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|last1=Mushtaq|first1=Sheikh|title=Ten Killed in Kashmir Car Bomb Blast|url=https://abcnews.go.com/International/story?id=82930|access-date=24 February 2017|publisher=]|archive-date=29 April 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180429233249/http://abcnews.go.com/International/story?id=82930|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.satp.org/satporgtp/kpsgill/2003/chapter9.htm |title=K P S Gill: The Kashmiri Pandits: An Ethnic Cleansing the World Forgot – Islamist Extremism & Terrorism in South Asia |work=satp.org |access-date=25 June 2015 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090309001010/http://www.satp.org/satporgtp/kpsgill/2003/chapter9.htm |archive-date=9 March 2009}}</ref> On the other hand, the Indian army has also allegedly committed serious crimes like using pellet guns, torture, murder and rape, though many such incidents were subject to legal proceedings. The militants have kidnapped and killed many civil servants and suspected informers. Tens of thousands of Kashmiri Pandits have been forced to emigrate as a result of continued violence by the majority. Estimates of the displaced vary from 170,000 to 700,000. Thousands of Kashmiri Pandits had to move to ] because of targeted attacks by Islamic radical organizations.<ref name="kps">Alexander Evans, A departure from history: Kashmiri Pandits, 1990–2001, Contemporary South Asia (Volume 11, Number 1, 1 March 2002, pp. 19–37)</ref> | |||
| === Notable insurgencies === | |||
| * ] | |||
| * July and August 1989 – Three CRPF personnel and politician Mohd. Yusuf Halwai of NC/F were killed.<ref name="ReferenceB">{{cite web|url=http://www.jammu-kashmir.com/basicfacts/politics/political_history.html|title=Chronicle of Important events/date in J&K's political history|work=jammu-kashmir.com|access-date=25 June 2015|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150614030618/http://www.jammu-kashmir.com/basicfacts/politics/political_history.html|archive-date=14 June 2015}}</ref> | |||
| * ] daughter of the then Home Minister of India Mufti Sayeed. | |||
| * ]- ] opened fire on a group of Kashmiri protestors, killing 50.<ref>{{Cite web|date=2005-05-01|title=Kashmir's first blood|url=https://indianexpress.com/article/news-archive/kashmirs-first-blood/|access-date=2021-09-09|website=The Indian Express|language=en|archive-date=9 September 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210909115900/https://indianexpress.com/article/news-archive/kashmirs-first-blood/|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| * ]- Killing of 55 Kashmiri civilians by Border security force(]) | |||
| * ]- Massacre of 51 protestors by BSF. | |||
| * ] – Six foreign trekkers from Anantnag district were kidnapped by Al Faran. One was beheaded later, one escaped, and the other four remain missing, presumably killed. | |||
| * ] – On 22 March 1997, seven Kashmiri Pandits were killed in Sangrampora village in the ] district.<ref name="Sangrampora">{{cite web|url=http://www.kashmiri-pandit.org/atrocities/sangrampura.html |title=Sangrampora killings |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20050415043415/http://www.kashmiri-pandit.org/atrocities/sangrampura.html |archive-date=15 April 2005 }}</ref> | |||
| * ] – In January 1998, 24 ] living in the village of Wandhama were massacred by Pakistani militants. According to the testimony of one of the survivors, the militants dressed themselves as officers of the ], entered their houses and then started firing blindly. The incident was significant because it coincided with former US president ]'s visit to ] and ] highlighted the massacre to prove Pakistan-supported militancy in Kashmir .<ref name="Wandhama">{{cite web |url=http://www.subcontinent.com/sapra/terrorism/tr_1998_01_002_s.html |title=Wandhama Massacre report |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://archive.today/19991009122607/http://www.subcontinent.com/sapra/terrorism/tr_1998_01_002_s.html |archive-date=9 October 1999 |access-date=29 May 2005 }}</ref> | |||
| * ] – 26 Hindu villagers of Udhampur district were killed by militants. | |||
| * ] – 25 Hindu villagers killed on 19 June 1998 by Islamic militants. | |||
| * ] – 30 Hindu pilgrims massacred by militants. | |||
| * ] – 36 Sikhs massacred by LeT militants though some allegations on Indian security forces exist too. (unclear) | |||
| * ] – On 1 October 2001, a bombing at the Legislative Assembly in ] killed 38.<ref name="Dugger">{{cite news|last1=Dugger|first1=Celia W.|title=Pakistan Asks India to Revive Talks Aimed at Bringing Peace to Kashmir|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2001/10/09/world/pakistan-asks-india-to-revive-talks-aimed-at-bringing-peace-to-kashmir.html|access-date=23 February 2017|newspaper=]|date=9 October 2001|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170223131222/http://www.nytimes.com/2001/10/09/world/pakistan-asks-india-to-revive-talks-aimed-at-bringing-peace-to-kashmir.html|archive-date=23 February 2017}}</ref> | |||
| * ] – An attack occurred on 30 March 2002 when two suicide bombers attacked the temple. Eleven persons including three security forces personnel were killed and 20 were injured. In second attack, the fidayeen suicide squad attacked the temple second time on 24 November 2002 when two suicide bombers stormed the temple and killed fourteen devotees and injured 45 others. | |||
| * ] – On 13 July 2002, armed militants believed to be a part of the ] threw hand grenades at the Qasim Nagar market in ] and then fired on civilians standing nearby killing 27 and injuring many more.<ref name="hrw03">{{cite web |url=https://www.hrw.org/wr2k3/asia6.html |title=Human Rights Watch World Report 2003: India |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101006054544/http://www.hrw.org/wr2k3/asia6.html |archive-date=6 October 2010}}</ref> | |||
| * ] – 24 Hindus killed in Nadimarg, Kashmir on 23 March 2003 by ] militants. | |||
| * 20 July 2005 ] bombing – A car bomb exploded near an armoured ] vehicle in the famous Church Lane area in ] killing 4 ] personnel, one civilian and the suicide bomber. Militant group ], claimed responsibility for the attack.<ref name="church">{{cite web |url=http://www.ndtv.com/template/template.asp?template=Ceasefire&slug=Car+bomb+attack+in+Srinagar%2C+6+killed&id=17351&callid=0&amp;category=National |title=20 July 2005 Srinagar attack |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20051118091346/http://www.ndtv.com/template/template.asp?template=ceasefire |archive-date=18 November 2005}}</ref> | |||
| * Budshah Chowk attack – A militant attack on 29 July 2005 at ]'s city centre, Budshah Chowk, killed 2 and left more than 17 people injured. Most of those injured were media journalists.<ref name="Bud">{{cite web|url=http://www.hindustantimes.com/news/181_1445705,000900010002.htm |title=July 29 attack in Srinagar |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070303044412/http://www.hindustantimes.com/news/181_1445705%2C000900010002.htm |archive-date=3 March 2007}}</ref> | |||
| * Assassination of Ghulam Nabi Lone – On 18 October 2005, suspected Kashmiri militants killed Jammu and Kashmir's then education minister Ghulam Nabi Lone. Militant group called Al Mansurin claimed responsibility for the attack.<ref name="Nabi">{{cite news|title=Kashmir minister killed in attack|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/4351950.stm|access-date=22 February 2017|work=]|date=18 October 2005|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170222122343/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/4351950.stm|archive-date=22 February 2017}}</ref> Abdul Ghani Lone, a prominent All Party Hurriyat Conference leader, was assassinated by unidentified gunmen during a memorial rally in ]. The assassination resulted in wide-scale demonstrations against the Indian forces for failing to provide enough security cover for Lone.<ref name="hrw03" /> | |||
| * ] – On 3 May 2006, militants massacred 35 Hindus in ] and ] districts in Jammu and Kashmir.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Tribune News Service|title=Phagwara observes bandh over J&K massacre|url=http://www.tribuneindia.com/2006/20060504/jal.htm#4|access-date=22 February 2017|newspaper=]|date=4 May 2006|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171012070828/http://www.tribuneindia.com/2006/20060504/jal.htm#4|archive-date=12 October 2017}}</ref> | |||
| * On 12 June 2006, one person was killed and 31 were wounded when militants hurled three grenades on Vaishnodevi shrine-bound buses at the general bus stand.<ref>{{cite news|last1=Sharma|first1=S.P.|title=Terror in Jammu, Anantnag|url=http://www.tribuneindia.com/2006/20060613/main1.htm|access-date=22 February 2017|newspaper=]|date=13 June 2006|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171001103659/http://www.tribuneindia.com/2006/20060613/main1.htm|archive-date=1 October 2017}}</ref> | |||
| * ] – There were four attacks on 5 December 2014 on army, police and civilians resulted in 21 deaths and several injured. Their motive was to disrupt the ].<ref name="The Hindu14">{{cite web|title=Multiple attacks rock Kashmir Valley|website=The Hindu: Mobile Edition|date=5 December 2014|url=http://m.thehindu.com/news/national/militants-attack-army-camp-at-mohra-near-uri-border-town-in-kashmir/article6664357.ece/|archive-url=https://archive.today/20141224205414/http://m.thehindu.com/news/national/militants-attack-army-camp-at-mohra-near-uri-border-town-in-kashmir/article6664357.ece/|url-status=dead|archive-date=24 December 2014|access-date=24 December 2014}}</ref> | |||
| * ] – Four armed militants sneaked into an army camp and lobbed grenades onto tents causing massive fire culminating in the death of 19 military personnel. | |||
| * ] - On 10 February 2018, Jaish-e-Mohammad militants attacked Sunjuwan Army Camp in Jammu and Kashmir. 6 Indian army soldiers, 4 militants, 1 civilian died and 11 were injured. | |||
| * ] - On 14 February 2019, Jaish-e-Mohammad militants attacked a convoy of CRPF men, killing 46 personnel and injuring 20. | |||
| == Tactics == | |||
| === India === | |||
| The Indian government has increasingly relied on military presence to control the insurgency.<ref name="EconomistGrim" /> The military has allegedly committed human rights violations.<ref name="HRW96" /> The government would often dissolve assemblies, arrest elected politicians and impose president's rule. The government also rigged elections in 1987.<ref name="AltafElections" /> In recent times there have been signs that the government is taking local elections more seriously.<ref name="RamaDilemma" /> The government has also funneled development aid to Kashmir and Kashmir has now become the biggest per capita receiver of Federal aid.<ref name="SangThink" /> | |||
| === Pakistan === | |||
| The Pakistani central government originally supported, trained and armed the insurgency in Kashmir,<ref name="firstpost1"/><ref name="indiatimes.com1"/><ref name="rediff1"/><ref name="indianexpress1"/><ref>{{cite news|title=Afzal Guru's confession: I helped them, took training in Pak|url=http://daily.bhaskar.com/article/WOR-TOP-afzal-guru---s-confession-i-helped-them-took-training-in-pak-4175799-NOR.html|access-date=19 April 2015|publisher=DAILY BHASKAR|date=10 February 2013|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150402124224/http://daily.bhaskar.com/article/WOR-TOP-afzal-guru---s-confession-i-helped-them-took-training-in-pak-4175799-NOR.html|archive-date=2 April 2015}}</ref> sometimes known as "ultras" (extremists),<ref name="indianexpress2">{{cite news|author=Agencies |date=6 April 2012 |title=Attempts will be made to push ultras across LoC: Army |newspaper=Indian Express |url=http://www.indianexpress.com/news/attempts-will-be-made-to-push-ultras-across-loc-army/933432/ |archive-url=https://archive.today/20140107184502/http://www.indianexpress.com/news/attempts-will-be-made-to-push-ultras-across-loc-army/933432/ |archive-date=7 January 2014 |url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="indiatimes1">{{cite news|author=] |date=7 January 2014 |title=Militants, Army troopers exchange fire in Pulwama, none hurt |newspaper=The Times of India|url=http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/Militants-Army-troopers-exchange-fire-in-Pulwama-none-hurt/articleshow/28522668.cms |archive-url=https://archive.today/20140107184652/http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/Militants-Army-troopers-exchange-fire-in-Pulwama-none-hurt/articleshow/28522668.cms |archive-date=7 January 2014 |url-status=live}}</ref> however after groups linked to the Kashmiri insurgency twice attempted to assassinate president Pervez Musharraf, Musharraf decided to end support for such groups.<ref name="KhanMilitants" /> His successor, ] has continued the policy, calling insurgents in Kashmir "terrorists".<ref name="StephensJob" /> | |||
| But the Pakistani ] hasn't followed the lead of the government and has continued its support for insurgent groups in Kashmir<ref name="StephensJob" /><ref name="ColeObama" /><ref name="RediffKashmir" /> In 2008, 541 people died due to insurgency, ''The Economist'' called it the lowest in two decades. The report cited a reduction in the support for militants by Pakistan and war fatigue among the Kashmiris as the reasons for the reduction in casualty figures.<ref name="EconomistGrim" /> | |||
| === Insurgents === | |||
| After around 2000, the insurgency became far less violent and has instead taken on the form of protests and marches.<ref name="ThottamValley" /> Certain groups have also chosen to lay down their arms and look for a peaceful resolution to the conflict.<ref name="GuptaKashmir" /> | |||
| === Groups === | |||
| The different insurgent groups have different aims in Kashmir. Some want complete independence from both India and Pakistan, others want unification with Pakistan and still others just want greater autonomy from the Indian government.<ref name="BBCFuture" /> | |||
| A 2010 survey found that 43% of the people in J&K and 44% of the people in ] would favour complete independence from both India and Pakistan, with support for the independence movement unevenly distributed across the region.<ref name="CHSurvey" /><ref>{{cite news|url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/Just-2-of-people-in-JK-want-to-join-Pak-Survey/articleshow/5982710.cms|archive-url=https://archive.today/20140114082544/http://articles.timesofindia.indiatimes.com/2010-05-28/india/28318260_1_favoured-budgam-plebiscite|url-status=live|archive-date=14 January 2014|title=Just 2% of people in J&K want to join Pak: Survey|work=The Times of India|date=28 May 2010 |access-date=25 June 2015}}</ref> | |||
| == Militant groups== | |||
| Over the last two years, the militant group, ] has split into two factions: ''Al Mansurin'' and ''Al Nasirin''. Another new group reported to have emerged is the "Save Kashmir Movement". ] (formerly known as ]) and ] are believed to be operating from ], and ], Pakistan respectively. <ref>{{Cite news |date=2024-04-16 |title=Shocked by Amir Sarfaraz's killing, LeT calls emergency meet |url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/world/pakistan/shocked-by-elimination-let-calls-emergency-meet/articleshow/109323995.cms |access-date=2024-06-09 |work=The Times of India |issn=0971-8257}}</ref> | |||
| Other less well known groups are the Freedom Force and Farzandan-e-Milat. A smaller group, ], has been active in Kashmir for many years and is still believed to be functioning. ], an organisation that uses moderate means to press for the rights of the Kashmiris, is often considered as the ''mediator'' between New Delhi and insurgent groups. <ref>{{Cite web |date=2015-08-31 |title=Hurriyat: Its History, Role and Relevance |url=https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/hurriyat-its-history-role-and-relevance/ |access-date=2024-06-09 |website=The Indian Express |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| === Al-Qaeda === | |||
| It is unclear if ] has a presence in Jammu and Kashmir. ] suggested that they were active<ref name="AbbasQaeda" /> and in 2002 the ] hunted for ] in Jammu and Kashmir.<ref name="SmithSAS" /> Al Qaeda claims that it has established a base in Jammu and Kashmir.<ref name="IHTKashmir" /> However, there has been no evidence for any of these assertions.<ref name="AbbasQaeda" /><ref name="SmithSAS" /><ref name="IHTKashmir" /> The Indian army also claims that there is no evidence of Al Qaeda presence in Jammu and Kashmir.<ref name="HinduQaeda" /> Al Qaeda has established bases in Pakistani administered Kashmir and some, including ] have suggested that they have helped to plan attacks in India.<ref name="HinduQaeda" /><ref name="DawnQaeda" /><ref name="SmuckerQaeda" /> | |||
| == Casualties == | |||
| According to government data, around 41,000 people—consisting of 14,000 civilians, 5,000 security personnel and 22,000 militants—have died because of the insurgency {{As of|2017|March|lc=y}} in both ] and ]. The overwhelming majority of these deaths happened in the 1990s and early 2000s, and there has been a steady decline in violence and sharp drop in the number of deaths 2004 onwards.<ref name=ht2017>{{Cite news|url= https://www.hindustantimes.com/india-news/the-anatomy-of-kashmir-militancy-in-numbers/story-UncrzPTGhN22Uf1HHe64JJ_amp.html |title= 41,000 deaths in 27 years: The anatomy of Kashmir militancy in numbers | |||
| |author1=Jayanth Jacob |author2=Aurangzeb Naqshbandi |work=] |access-date=18 May 2023 |language=en-IN}}</ref> A 2006 report by ] claimed that at least 20,000 civilians had died in the conflict by then.<ref>{{cite report| url= https://www.hrw.org/sites/default/files/reports/india0906web.pdf |title= Everyone Lives in Fear: Patterns of Impunity in Jammu and Kashmir |publisher=] |date=September 2006 |page=1}}</ref> The territory witnessed about 69,820 militancy-related incidents till March 2017.<ref name=ht2017/> Among the militants killed between 1989 and 2002, about 3,000 were from outside Jammu and Kashmir (mostly from Pakistan and some Afghans). Indian forces engaged in counter insurgency operations captured around 40,000 firearms, 150,000 explosive devices, and over 6 million rounds of assorted ammunition during this period.<ref name="sbose">{{cite book | last = Bose | first = Sumantra | title = Kashmir: Roots of Conflict, Paths to Peace | publisher = ] | url = https://www.questia.com/read/118148594/kashmir-roots-of-conflict-paths-to-peace | date = 2003 | page = 3 | url-status = live | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20171012061143/https://www.questia.com/read/118148594/kashmir-roots-of-conflict-paths-to-peace | archive-date = 12 October 2017}}</ref> Jammu and Kashmir Coalition of Civil Society posits a figure of 70,000 deaths, most of them civilians.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://kashmirobserver.net/2016/local-news/karadzic-prosecute-all-accused-hr-violations-kashmir-jkccs-4777|title=Like Karadzic, Prosecute All Accused of HR Violations in Kashmir: JKCCS|work=Kashmir Observer|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171016071013/https://kashmirobserver.net/2016/local-news/karadzic-prosecute-all-accused-hr-violations-kashmir-jkccs-4777|archive-date=16 October 2017|access-date=19 October 2017}}</ref> The pro-Pakistan ] has claimed a higher death toll of 80,000 including civilians, security forces and militants.<ref>{{citation |author=] |title=Kashmir : roots of conflict, paths to peace |year=2003 |publisher=Harvard University Press |isbn=0-674-01173-2 |page=4}}</ref> The districts with the most incidents of killing were ], ], ], ], ] and ].<ref name="satp2022">{{Cite web|title=datasheet-terrorist-attack-fatalities|url=https://www.satp.org/datasheet-terrorist-attack/fatalities/india-jammukashmir|access-date=2022-02-12|website=www.satp.org|archive-date=31 January 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220131101210/https://www.satp.org/datasheet-terrorist-attack/fatalities/india-jammukashmir|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| {| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
| |+Casualties every year in the Jammu and Kahmir insurgency (since 2007)<ref name="satp2022" /> | |||
| !Year | |||
| !Incidents of Killing | |||
| !Civilians | |||
| !Security Forces | |||
| !Militants | |||
| !Total | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''2007''' | |||
| | ] (near ]) | |||
| |427 | |||
| | ] | |||
| |127 | |||
| |119 | |||
| |498 | |||
| |744 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''2008''' | |||
| | Kotli | |||
| |261 | |||
| | ] | |||
| | |
|71 | ||
| |85 | |||
| | ] | |||
| |382 | |||
| | ] | |||
| |538 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''2009''' | |||
| | ] | |||
| |208 | |||
| | ] | |||
| | |
|53 | ||
| |73 | |||
| | Gultari | |||
| |247 | |||
| | ] | |||
| |373 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''2010''' | |||
| | Tarkuti | |||
| |189 | |||
| | ] | |||
| |34 | |||
| |69 | |||
| |258 | |||
| |361 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''2011''' | |||
| | Batrasi | |||
| |119 | |||
| | ], ] | |||
| |33 | |||
| |31 | |||
| |117 | |||
| |181 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''2012''' | |||
| | Sufaida | |||
| |70 | |||
| | ], ] | |||
| |19 | |||
| |18 | |||
| |84 | |||
| |121 | |||
| |- | |- | ||
| |'''2013''' | |||
| |Tanda Allabyar | |||
| |84 | |||
| | ], ] | |||
| |19 | |||
| |53 | |||
| |100 | |||
| |172 | |||
| |- | |||
| |'''2014''' | |||
| |91 | |||
| |28 | |||
| |47 | |||
| |114 | |||
| |189 | |||
| |- | |||
| |'''2015''' | |||
| |86 | |||
| |19 | |||
| |41 | |||
| |115 | |||
| |175 | |||
| |- | |||
| |'''2016''' | |||
| |112 | |||
| |14 | |||
| |88 | |||
| |165 | |||
| |267 | |||
| |- | |||
| |'''2017''' | |||
| |163 | |||
| |54 | |||
| |83 | |||
| |220 | |||
| |357 | |||
| |- | |||
| |'''2018''' | |||
| |206 | |||
| |86 | |||
| |95 | |||
| |271 | |||
| |452 | |||
| |- | |||
| |'''2019''' | |||
| |135 | |||
| |42 | |||
| |78 | |||
| |163 | |||
| |283 | |||
| |- | |||
| |'''2020''' | |||
| |140 | |||
| |33 | |||
| |56 | |||
| |232 | |||
| |321 | |||
| |- | |||
| |'''2021''' | |||
| |153 | |||
| |36 | |||
| |45 | |||
| |193 | |||
| |274 | |||
| |- | |||
| |'''2022''' | |||
| |151 | |||
| |30 | |||
| |30 | |||
| |193 | |||
| |253 | |||
| |} | |} | ||
| == Surrender and rehabilitation policy == | |||
| ==Recent developments== | |||
| Surrendering in ] has been institutionalized over the years.<ref name="Kakar-2017">{{Cite web|last=Kakar|first=Harsha|date=24 November 2017|title=Why Kashmir needs much more than surrender appeals|url=https://www.orfonline.org/expert-speak/kashmir-needs-more-than-surrender-appeals/|access-date=2021-10-16|website=ORF|archive-date=20 October 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211020015417/https://www.orfonline.org/expert-speak/kashmir-needs-more-than-surrender-appeals/|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="Malik-2020">{{Cite web|last=Malik|first=Irfan Amin|date=2020-11-25|title=Will Army's Draft 'Surrender Policy' In J&K Help Combat Militancy?|url=https://www.thequint.com/voices/opinion/kashmir-valley-militants-indian-army-security-forces-draft-surrender-policy-jammu-kashmir-police-shopian-fake-encounter|access-date=2021-10-16|website=TheQuint|language=en|archive-date=20 October 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211020031915/https://www.thequint.com/voices/opinion/kashmir-valley-militants-indian-army-security-forces-draft-surrender-policy-jammu-kashmir-police-shopian-fake-encounter|url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|last=Yasir|first=Sameer|date=2017-10-16|title=Jammu and Kashmir security forces' new appeal to militants: Surrender, come home and rejoin society|url=https://www.firstpost.com/india/jammu-and-kashmir-security-forces-new-appeal-to-militants-surrender-come-home-and-rejoin-society-4148277.html|access-date=2021-10-16|website=Firstpost|language=en|archive-date=20 October 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211020044257/https://www.firstpost.com/india/jammu-and-kashmir-security-forces-new-appeal-to-militants-surrender-come-home-and-rejoin-society-4148277.html|url-status=live}}</ref> The 1990s saw some surrender policies, while in the 2000s, there was a policy for militants belonging to Indian administered Jammu and Kashmir and another for Pakistan administered territory.<ref name="Kakar-2017" /><ref name="Malik-2020" /> The first surrender policy for militants in Kashmir was launched on 15 August 1995. It was a copy of the policies already there for ].<ref>{{Cite web|last=Kartha|first=Tara|date=5 June 2018|title=New Age Militancy – Kashmir Youth Need Policies Encouraging Change, Not Surrender|url=https://thewire.in/rights/kashmir-militancy-surrender-policy|access-date=2021-10-20|website=The Wire|archive-date=20 April 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230420105454/https://thewire.in/rights/kashmir-militancy-surrender-policy|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| Violent activities in the region declined in ]. There are two main reasons for this: warming of relations between ] and ] which consequently lead to a ] between the two countries in 2003 and the fencing of the ] being carried out by the ]. Moreover, coming under intense international pressure, ] was compelled to take actions against the militants' training camps on its territory. In 2004, the two countries also agreed upon decreasing the number of troops present in the region. | |||
| === Appeals to surrender === | |||
| Under pressure, Kashmiri militant organisations have made an offer for talks and negotiations with ], which was accepted by India. India's ] blamed the ]i military for providing cover-fire for the militants whenever they infiltrated into ]n territory from ]. However, ever since the ] has come into action, the militants have received no back-up from ], which has contributed significantly to the decline in ''cross-border terrorism''<ref> ] - June 14, 2003</ref> in the state. | |||
| Appeals to surrender are made by security forces to militants at encounter sites as well.<ref name="Ashiq-2021">{{Cite news|last=Ashiq|first=Peerzada|date=2021-01-30|title=Two Hizb militants 'motivated' to surrender|language=en-IN|work=The Hindu|url=https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/2-trapped-militants-surrender-one-injured-shifted-at-pulwama-encounter-site/article33701358.ece|access-date=2021-10-16|issn=0971-751X|archive-date=19 October 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211019144747/https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/2-trapped-militants-surrender-one-injured-shifted-at-pulwama-encounter-site/article33701358.ece|url-status=live}}</ref> Some attempts are successful,<ref name="Ashiq-2021" /><ref>{{Cite news|last=IANS|date=2020-12-22|title=Two terrorists surrender during encounter with security forces in Kashmir|work=Business Standard India|url=https://www.business-standard.com/article/current-affairs/two-terrorists-surrender-during-encounter-with-security-forces-in-kashmir-120122200169_1.html|access-date=2021-10-16|archive-date=19 October 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211019111539/https://www.business-standard.com/article/current-affairs/two-terrorists-surrender-during-encounter-with-security-forces-in-kashmir-120122200169_1.html|url-status=live}}</ref> while others are not.<ref>{{Cite web|date=6 May 2021|title=J-K: Surrendered militant urged companions to surrender, they refused and get killed in encounter|url=https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/defence/j-k-surrendered-militant-urged-companions-to-surrender-they-refused-and-killed/videoshow/82429458.cms|access-date=2021-10-16|website=The Economic Times|archive-date=16 October 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211016142911/https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/defence/j-k-surrendered-militant-urged-companions-to-surrender-they-refused-and-killed/videoshow/82429458.cms|url-status=live}}</ref> Mothers and other family members have made videos urging their child turned militant to surrender to the security forces. Sometimes the family member is brought to the encounter site and urged to talk to their children through loudspeakers to surrender.<ref>{{Cite web|last=Islah|first=Mufti|date=2021-03-22|title='Missing You': A Kashmiri Child's Plea to Holed up Militant Father Fails, Body Found after Encounter|url=https://www.news18.com/news/india/kashmir-shopian-encounter-child-appeal-surrender-militant-holed-up-death-3562604.html|access-date=2021-10-16|website=News18|language=en|archive-date=19 October 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211019193812/https://www.news18.com/news/india/kashmir-shopian-encounter-child-appeal-surrender-militant-holed-up-death-3562604.html|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="Kakar-2017" /><ref>{{Cite web|last=Masood|first=Bashaarat|date=2021-03-23|title=Four militants killed; ignored pleas from family: police|url=https://indianexpress.com/article/india/four-let-militants-killed-in-encounter-with-security-forces-in-j-ks-shopian-7240080/|access-date=2021-10-16|website=The Indian Express|language=en|archive-date=19 October 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211019160245/https://indianexpress.com/article/india/four-let-militants-killed-in-encounter-with-security-forces-in-j-ks-shopian-7240080/|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| == |
== See also == | ||
| * ] | |||
| The insurgents who initially started their movement as a pro-Kashmiri ] movement, have gone through a lot of change in their ideology. Most of the insurgents portray their struggle as a religious one. | |||
| * ] | |||
| Indian analysts allege that by supporting these insurgents, Pakistan is trying to wage a ] against India while Pakistan claims that it regards most of these ] groups as "freedom fighters" rather than militants. | |||
| Internationally known to be the most deadly theatre of conflict, nearly 10 million people, including ], ], and ] have been fighting a daily battle for survival. The ''cross-border firing'' between ] and ], and the terrorist attacks combined have mostly taken its toll on the muslim Kashmiris, who have suffered poor living standards and an erosion of human rights. | |||
| ==Films and Books== | |||
| * '''' — A love story of an idealistic Indian army soldier and a local Kashmiri girl. | |||
| '''Books''' | |||
| * '''' — by Sumit Ganguly | |||
| * '''' — by Oddny Wiggen and Ramesh Chandra Thakur | |||
| * Kashmir: Beyond the vale -- by M J Akbar | |||
| ==References== | |||
| <references/> | |||
| ], ''Lost Rebellion: Kashmir in the Nineties'' (New Delhi, Penguin Books, 1999) | |||
| ==Bibliography== | |||
| #{{note|BBC}} | |||
| #{{note|jihad}} | |||
| #{{note|target}} | |||
| #{{note|Nadimarg}} | |||
| #{{note|Amarnath}} | |||
| #{{note|Ethnic}} | |||
| #{{note|Schofield}} ] ])] Retrieved ] ] | |||
| #{{note|pandits}} | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| ;Related articles | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] or the Indo-Pakistani War of 1999 | |||
| * '']'', a 2003 ] ] based on "]" or the "Indo-Pakistani War of 1999", directed by ] | |||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| == References == | |||
| ;Militant groups | |||
| {{Reflist|30em|refs= | |||
| * ] | |||
| <ref name="SumantraKashmir">Bose, Sumantra. ''Kashmir: Roots of Conflict, Paths to Peace''. Harvard, 2005.</ref> | |||
| * ] | |||
| <ref name="SwamiSecret">Swami, Praveen.''India, Pakistan and the Secret Jihad''. 2006.</ref> | |||
| * ] | |||
| <ref name="AltafElections">{{cite news|last1=Hussain|first1=Altaf|title=Kashmir's flawed elections|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/2223364.stm|access-date=22 February 2017|work=]|date=14 September 2002|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170226225810/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/2223364.stm|archive-date=26 February 2017}}</ref> | |||
| * ] | |||
| <ref name="BBCKashmir">{{cite news|title=Kashmir insurgency|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/hi/english/static/in_depth/south_asia/2002/india_pakistan/timeline/1989.stm|access-date=21 February 2017|work=]|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170222035446/http://news.bbc.co.uk/hi/english/static/in_depth/south_asia/2002/india_pakistan/timeline/1989.stm|archive-date=22 February 2017}}</ref> | |||
| * ] | |||
| <ref name="ArifShadow">Jamar, Arif. ''The untold story of Jihad in Kashmir''. 2009.</ref> | |||
| <ref name="HasanPakistan">{{cite news|last1=Hasan|first1=Syed Shoaib|title=Why Pakistan is 'boosting Kashmir militants'|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/4416771.stm|access-date=22 February 2017|work=]|date=3 March 2010|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170228011213/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/4416771.stm|archive-date=28 February 2017}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="KhanMilitants">{{cite news|last1=Khan|first1=Aamer Ahmed|title=Pakistan: Where have the militants gone?|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/4415823.stm|access-date=22 February 2017|work=]|date=6 April 2005|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170222121728/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/4415823.stm|archive-date=22 February 2017}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="StephensJob">{{cite news|last1=Stephens|first1=Bret|title=The Most Difficult Job in the World|url=https://www.wsj.com/articles/SB122307507392703831|access-date=22 February 2017|newspaper=]|date=4 October 2008|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170222112027/https://www.wsj.com/articles/SB122307507392703831|archive-date=22 February 2017}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="ColeObama">{{cite news|last1=Cole|first1=Juan|title=Does Obama understand his biggest foreign-policy challenge?|url=http://www.salon.com/2008/12/12/pakistan_7/|access-date=22 February 2017|work=]|date=12 December 2008|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170323103257/http://www.salon.com/2008/12/12/pakistan_7/|archive-date=23 March 2017}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="RediffKashmir">{{cite news|title=Links between ISI, militant groups: Straw|url=http://www.rediff.com/news/2002/jun/11war4.htm|access-date=24 February 2017|work=]|date=11 June 2002|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170324080707/http://www.rediff.com/news/2002/jun/11war4.htm|archive-date=24 March 2017}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="EconomistStony">{{cite news|title=Stony ground|url=http://www.economist.com/node/16542619|access-date=22 February 2017|newspaper=]|date=8 July 2010|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161223073757/http://www.economist.com/node/16542619|archive-date=23 December 2016}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="EconomistGrim">{{cite news|title=Grim up north|url=http://www.economist.com/node/13927142|access-date=22 February 2017|newspaper=]|date=25 June 2009|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170429113754/http://www.economist.com/node/13927142|archive-date=29 April 2017}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="EconomistPlace">{{cite news|title=Your place or mine?|url=http://www.economist.com/node/2423976|access-date=22 February 2017|newspaper=]|date=12 February 2004|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170222194246/http://www.economist.com/node/2423976|archive-date=22 February 2017}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="BBCKillings">{{cite news|title=Kashmir's extra-judicial killings|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/6367917.stm|access-date=22 February 2017|work=]|date=8 March 2007|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170614185945/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/6367917.stm|archive-date=14 June 2017}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="The Times">{{citation |title=India's leader makes peace overtures in Kashmir |newspaper=The Times |date=18 November 2004 |url=http://www.timesonline.co.uk/tol/news/world/article392432.ece |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110523122550/http://www.timesonline.co.uk/tol/news/world/article392432.ece |archive-date=23 May 2011}}: "Military experts estimate that India has about 250,000 troops in the region."</ref><ref name="HRW96">Human Rights Watch, Patricia Gossman. "India's secret army in Kashmir : new patterns of abuse emerge in the conflict ", 1996</ref> | |||
| <ref name="YardleyPower">{{cite news|last1=Yardley|first1=Jim|title=India Reopens Kashmir's Schools, but Many Stay Away|url=https://www.nytimes.com/2010/09/28/world/asia/28kashmir.html|access-date=22 February 2017|newspaper=]|date=27 September 2010|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170222113514/http://www.nytimes.com/2010/09/28/world/asia/28kashmir.html|archive-date=22 February 2017}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="PalloneEthnic">{{citation |last=Pallone |first=Frank |title=Resolution condemning Human Rights Violations against Kashmiri Pandits |url=http://www.house.gov/list/press/nj06_pallone/pr_feb15_kashmir.html |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090810032903/http://www.house.gov/list/press/nj06_pallone/pr_feb15_kashmir.html |archive-date=10 August 2009 |publisher=US House of Representatives |date=15 February 2006 }}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="RamaDilemma">{{cite news|last1=Ramaseshan|first1=Radhika|title=Cong dilemma: young Omar or PDP|url=https://www.telegraphindia.com/1081230/jsp/nation/story_10319531.jsp|access-date=23 February 2017|newspaper=]|date=30 December 2008|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170223212047/https://www.telegraphindia.com/1081230/jsp/nation/story_10319531.jsp|archive-date=23 February 2017}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="NomaniMuslims">{{cite news|last1=Nomani|first1=Asra Q.|title=Muslims -- India's new 'untouchables'|url=https://www.latimes.com/la-oe-nomani1-2008dec01-story.html|access-date=22 February 2017|newspaper=]|date=1 December 2008|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170222111942/http://www.latimes.com/la-oe-nomani1-2008dec01-story.html|archive-date=22 February 2017}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="SangThink">Sanghvi, Vir {{cite web|url=http://www.hindustantimes.com/Think-the-Unthinkable/Article1-331689.aspx |title=Think the Unthinkable - Hindustan Times |access-date=2010-12-23 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110208001159/http://www.hindustantimes.com/Think-the-Unthinkable/Article1-331689.aspx |archive-date=8 February 2011}} "Think the unthinkable" ''Hindustan Times'', August 2008</ref> | |||
| <ref name="ThottamValley">{{cite magazine|last1=Thottam|first1=Jyoti|title=Valley of Tears|url=http://content.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,1838586,00.html|access-date=22 February 2017|magazine=]|date=4 September 2008|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170124194816/http://content.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,1838586,00.html|archive-date=24 January 2017}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="BBCFuture">{{cite news|title=The Future of Kashmir?|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/shared/spl/hi/south_asia/03/kashmir_future/html/|access-date=22 February 2017|work=]|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170319084333/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/shared/spl/hi/south_asia/03/kashmir_future/html/|archive-date=19 March 2017}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="CHSurvey">Bradnock, Robert "Kashmir: Paths to Peace" Chatham House, London, 2008</ref> | |||
| <ref name="AbbasQaeda">{{cite news|last1=Abbas|first1=Zaffar|title=Analysis: Is al-Qaeda in Kashmir?|url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/2043800.stm|access-date=22 February 2017|work=]|date=13 June 2002|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161229210916/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/2043800.stm|archive-date=29 December 2016}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="SmithSAS">{{cite news|last1=Smith|first1=Michael|title=SAS joins Kashmir hunt for bin Laden|url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/asia/india/1385795/SAS-joins-Kashmir-hunt-for-bin-Laden.html|access-date=21 February 2017|newspaper=]|date=23 February 2002|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170315031644/http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/asia/india/1385795/SAS-joins-Kashmir-hunt-for-bin-Laden.html|archive-date=15 March 2017}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="IHTKashmir">International Herald Tribune. "Al Qaeda Claim of Kashmiri Link Worries India"</ref> | |||
| <ref name="HinduQaeda">''The Hindu''.{{cite news |url=http://www.hindu.com/2007/06/18/stories/2007061801191400.htm |title=No al Qaeda presence in Kashmir: Army |date=18 June 2007 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100411003850/http://www.hindu.com/2007/06/18/stories/2007061801191400.htm |newspaper=] |archive-date=11 April 2010}} "No Al Qaeda presence in Kashmir: Army"</ref> | |||
| <ref name="SmuckerQaeda">{{cite news|last1=Smucker|first1=Phillip|title=Al Qaeda thriving in Pakistani Kashmir|url=http://www.csmonitor.com/2002/0702/p01s02-wosc.html|access-date=21 February 2017|newspaper=]|date=2 July 2002|url-status=live|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170111054702/http://www.csmonitor.com/2002/0702/p01s02-wosc.html|archive-date=11 January 2017}}</ref> | |||
| <ref name="DawnQaeda">''Dawn''. , January 20, 2010</ref> | |||
| <ref name="GuptaKashmir">Gupta, Amit; Leather, Kaia. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170330001714/https://docs.google.com/viewer?a=v&q=cache%3Alnhk5esbgrkJ%3Afpc.state.gov%2Fdocuments%2Forganization%2F13390.pdf%20kashmir%20insurgents%20lay%20down%20arms&hl=en&gl=de&pid=bl&srcid=ADGEEShAKwH9pVW16YC2-dyX6RP_KYtdoG3X7iD1GKwTxaO0O1l4JdLMf_wKYEJVQ_LinyIgx2I0TWSQAxl2oc8OSyUWAIBHSyTHuVs8XTVkGhMaBsvXUMUfvxddyygReETuQKp4mTjA&sig=AHIEtbQWdbVbaShVvuAURLFsmBS-IR4gog |date=30 March 2017 }} "Kashmir: Recent Developments and US Concerns", June 2002</ref> | |||
| }} | |||
| == |
==Bibliography== | ||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Evans |first1=Alexander |title=A departure from history: Kashmiri Pandits, 1990–2001 |journal=Contemporary South Asia |volume=11 |issue=1 |year=2002 |pages=19–37 |issn=0958-4935 |doi=10.1080/0958493022000000341 |s2cid=145573161}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{citation |last=Khan |first=Waheeda |chapter=Conflict in Kashmir: Psychosocial Consequences on Children |editor=Sibnath Deb |title=Child Safety, Welfare and Well-being: Issues and Challenges |chapter-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=BvpUCgAAQBAJ&pg=PA83 |date=2015 |publisher=Springer |isbn=978-81-322-2425-9 |pages=83–93 |ref={{sfnref|Waheeda Khan, Conflict in Kashmir|2015}}}} | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * - Public Affairs Magazine | |||
| * | |||
| * ] Library Bibliographies and Web-Bibliographies list] | |||
| {{Jammu and Kashmir freedom movement}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Indo-Pakistani relations}} | |||
| {{Military of India}} | |||
| {{Post-Cold War Asian conflicts}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 07:44, 11 December 2024
Ongoing separatist militancy in Indian-administered Jammu and Kashmir This article is about the localized insurgency in Indian-administered Jammu and Kashmir. For the conflict between India and Pakistan over the larger region of Kashmir, see Kashmir conflict.
| Insurgency in Jammu and Kashmir | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Kashmir conflict | |||||||
 CIA map of the Kashmir region | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
Political Parties: Armed groups:
Supported by: | |||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
| Unknown | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
2000–2024: 3,590 Security Forces killed |
2000–2024: 13,321 militants killed 847 Surrendered 5,832 Arrested | ||||||
| 20,000+ civilian deaths | |||||||
The insurgency in Jammu and Kashmir, also known as the Kashmir insurgency, is an ongoing separatist militant insurgency against the Indian administration in Jammu and Kashmir, a territory constituting the southwestern portion of the larger geographical region of Kashmir, which has been the subject of a territorial dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947.
Jammu and Kashmir, long a breeding ground of separatist ambitions, has experienced the insurgency since 1989. Although the failure of Indian governance and democracy lay at the root of the initial disaffection, Pakistan played an important role in converting the latter into a fully-developed armed insurgency. Some insurgent groups in Kashmir support complete independence, whereas others seek the region's accession to Pakistan.
More explicitly, the roots of the insurgency are tied to a dispute over local autonomy. Democratic development was limited in Kashmir until the late 1970s, and by 1988, many of the democratic reforms provided by the Indian government had been reversed and non-violent channels for expressing discontent were limited, which caused a dramatic increase in support for insurgents advocating violent secession from India. In 1987, a disputed election held in the erstwhile state of Jammu and Kashmir created a catalyst for the insurgency when it resulted in some of the state's legislative assembly members forming armed insurgent groups. In July 1988, a series of demonstrations, strikes, and attacks on the Indian government effectively marked the beginning of the insurgency in Jammu and Kashmir, which escalated into the most severe security issue in India during the 1990s.
Pakistan, with whom India has fought three major wars over the Muslim-majority region, has officially claimed to be giving only its "moral and diplomatic" support to the separatist movement. The Pakistani Inter-Services Intelligence has been accused by both India and the international community of supporting and supplying arms as well as providing training to "mujahideen" militants in Jammu and Kashmir. In 2015, a former President of Pakistan, Pervez Musharraf, admitted that the Pakistani state had supported and trained insurgent groups in Kashmir throughout the 1990s. Several new militant groups with radical Islamist views emerged during this time and changed the ideological emphasis of the movement from that of plain separatism to Islamic fundamentalism. This occurred partly due to the influence of a large number of Muslim jihadist militants who began to enter the Indian-administered Kashmir Valley through Pakistani-controlled territory across the Line of Control following the end of the Soviet–Afghan War in the 1980s. India has repeatedly called on Pakistan to end its alleged "cross-border terrorism" in the region.
The conflict between militants and Indian security forces in Kashmir has led to a large number of casualties; many civilians have also died as a result of being targeted by various armed militant groups. According to government data, around 41,000 people—consisting of 14,000 civilians, 5,000 security personnel and 22,000 militants—have died because of the insurgency as of March 2017, with most deaths happening in the 1990s and early 2000s. Non-governmental organisations have claimed a higher death toll. The insurgency has also forced the large-scale migration of non-Muslim minority Kashmiri Hindus out of the Kashmir Valley. Since the revocation of the special status of Jammu and Kashmir in August 2019, the Indian military has intensified its counter-insurgency operations in the region.
History
See also: History of Kashmir and List of terrorist incidents in Jammu and Kashmir1947–1982
See also: Partition of India and First Kashmir WarAfter independence from colonial rule India and Pakistan were engaged in a war over the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir. At the end of the war India controlled the southern portion of the princely state. While there were sporadic periods of violence there was no organised insurgency movement.
During this period legislative elections in the state of Jammu and Kashmir were first held in 1951 and Sheikh Abdullah's secular party stood unopposed. He was an instrumental member in the accession of the state to India.
However, Sheikh Abdullah would fall in and out of favour with the central government and would often be dismissed only to be re-appointed later on. This was a time of political instability and power struggle in Jammu and Kashmir, and it went through several periods of president's rule by the Federal Government.
1982–2004
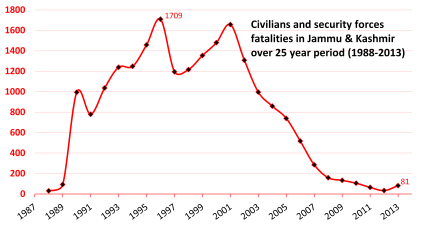
After Sheikh Abdullah's death, his son Farooq Abdullah took over as Chief Minister of Jammu and Kashmir. Farooq Abdullah eventually fell out of favour with the Central Government and the Prime Minister Indira Gandhi, who had his government toppled with the help of his brother-in-law G. M. Shah. GM Shah was the chief minister during the 1986 Anantnag Riots until he was removed and replaced by Farooq Abdullah. A year later, Abdullah reached an accord with the new Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi and announced an alliance with the Indian National Congress for the elections of 1987. The elections were allegedly rigged in favour of Abdullah.
Most commentators state that this led to the rise of an armed insurgency movement composed, in part, of those who unfairly lost the elections. Pakistan supplied these groups with logistical support, arms, recruits and training.
In the second half of 1989 the alleged assassinations of the Indian spies and political collaborators by the Jammu Kashmir Liberation Front was intensified. Over six months more than a hundred officials were killed to paralyse government's administrative and intelligence apparatus. The daughter of then interior affairs minister, Mufti Mohammad Sayeed was kidnapped in December and four militants had to be released for her release. This event led to mass celebrations all over the valley. Farooq Abdullah resigned in January after the appointment of Jagmohan Malhotra as the Governor of Jammu and Kashmir. Subsequently, J&K was placed under Governor's Rule under Article 92 of state constitution.
Under JKLF's leadership on 21–23 January large scale protests were organised in the Kashmir Valley. As a response to this largely explosive situation paramilitary units of BSF and CRPF were called. These units were used by the government to combat Maoist insurgency and the North-Eastern insurgency. The challenge to them in this situation was not posed by armed insurgents but by the stone pelters. Their inexperience caused at least 50 casualties in Gawkadal massacre. In this incident the underground militant movement was transformed into a mass struggle. To curb the situation AFSPA (Armed Forces Special Powers Act) was imposed on Kashmir in September 1990 to suppress the insurgency by giving armed forces the powers to kill and arrest without warrant to maintain public order. During this time the dominant tactic involved killing of a prominent figure in a public gathering, such as Wali Mohammad Itoo in 1994, to push forces into action and the public prevented them from capturing these insurgents. This sprouting of sympathisers in Kashmir led to the hard-line approach of Indian army.
With JKLF at forefront large number of militant groups like Allah Tigers, People's League and Hizb-i-Islamia sprung up. Weapons were smuggled on a large scale from Pakistan. In Kashmir JKLF operated under the leadership of Ashfaq Majid Wani, Yasin Bhat, Hamid Shiekh and Javed Mir. To counter this growing pro-Pakistani sentiment in Kashmir, Indian media associated it exclusively with Pakistan.
JKLF used distinctly Islamic themes to mobilise crowds and justify their use of violence. They sought to establish an Islamic democratic state where the rights of minorities would be protected according to Quran and Sunna and economy would be organised on the principles of Islamic socialism.
The Indian army has conducted various operations to control and eliminate insurgency in the region such as Operation Sarp Vinash, in which a multi-battalion offensive was launched against militants from groups like Lashkar-e-Taiba, Harkat-ul-Jihad-e-Islami, al-Badr and Jaish-e-Mohammed who had been constructing shelters in the Pir Panjal region of Jammu and Kashmir over several years. The subsequent operations led to the death of over 60 militants and uncovered the largest network of militant hideouts in the history of insurgency in Jammu and Kashmir covering almost 100 square kilometers.
Cultural changes
Cinema houses were banned by some militant groups. Many militant organisations like Al baqr, People's league, Wahdat-e-Islam and Allah Tigers imposed restrictions like banning cigarettes, restrictions on Kashmiri girls.
2004–11
Main article: 2010 Kashmir unrestBeginning in 2004 Pakistan began to end its support for insurgents in Kashmir. This happened because militant groups linked to Kashmir twice tried to assassinate Pakistani President General Pervez Musharraf. His successor, Asif Ali Zardari has continued the policy, calling insurgents in Kashmir "terrorists", although it is unclear if Pakistan's intelligence agency, the Inter-Services Intelligence, thought to be the agency aiding and controlling the insurgency is following Pakistan's commitment to end support for the insurgency in Kashmir. Despite the change in the nature of the insurgency from a phenomenon supported by external forces to a primarily domestic-driven movement the Indian government has continued to send large numbers of troops to the Indian border. There have been widespread protests against the Indian army presence in Kashmir.
Once the most formidable face of Kashmir militancy, Hizbul Mujahideen is slowly fading away as its remaining commanders and cadres are being taken out on a regular interval by security forces. Some minor incidents of grenade throwing and sniper firing at security forces notwithstanding, the situation is under control and more or less peaceful. A record number of tourists including Amarnath pilgrims visited Kashmir during 2012. On 3 August 2012, a top Lashkar-e-Taiba militant commander, Abu Hanzulah involved in various attacks on civilians and security forces was killed in an encounter with security forces in a village in Kupwara district of north Kashmir.
2012–present
Main articles: 2013 India–Pakistan border skirmishes, 2014–15 India–Pakistan border skirmishes, and 2016–17 Kashmir unrestAccording to Indian Army data quoted by Reuters, at least 70 young Kashmiris joined the insurgency in 2014, army records showed, with most joining the terrorist organization Lashkar-e-Taiba, which was responsible for carrying out the 2008 Mumbai attacks. Two of the new recruits have doctorates and eight were post graduates, the army data showed. According to BBC, despite a Pakistani ban on militant activity in Kashmir in 2006, its militants continue to attempt infiltration into Indian-administered Kashmir. These attempts were curtailed however when people living along the Line of Control which divides Indian and Pakistani Kashmir started to hold public protests against the activities of the insurgent groups.
In 2016, violence erupted in the aftermath of the killing of Hizbul Mujahideen militant Burhan Wani by security forces. Since then, militants belonging to the Jaish-e-Mohammed group carried out the 2016 Uri attack and the 2018 Sunjuwan attack. In February 2019, the Pulwama attack occurred, in which 40 CRPF personnel were killed by a Jaish-e-Mohammed suicide bomber.
In August 2019, the special status of Jammu and Kashmir was revoked, following which the Indian Army intensified its counter-insurgency operations. In June 2020, Doda district was declared militancy free while Tral was declared free from Hizbul Mujahideen militants. In July, a Kashmir police tweet from an official twitter handle said "no resident of #Srinagar district in terrorist ranks now". On 27 June 2021, a day after the successful completion of discussions between the Indian Prime Minister and Jammu and Kashmir political leaders, a drone based attack was reported at the technical area of Jammu Airport which is under the control of the IAF. In the first three months of 2022, there was a 100% increase in the number of Indian soldiers killed by Kashmiri militants compared to the same period in 2021.
Motivations behind the insurgency
Rigging of 1987 Assembly elections
Further information: 1987 Jammu and Kashmir Legislative Assembly electionFollowing the rise of Islamisation in the Kashmir valley, during the 1987 state elections, various Islamic anti-establishment groups including Jamaat-e-Islami Kashmir were organised under a single banner named Muslim United Front (MUF), that is largely current Hurriyat. MUF's election manifesto stressed the need for a solution to all outstanding issues according to Simla Agreement, work for Islamic unity and against political interference from the centre. Their slogan was wanting the law of the Quran in the Assembly. But the MUF won only four seats, even though it had polled 31% votes in the election. However, the elections were widely believed to be rigged, changing the course of politics in the state. The insurgency was sparked by the apparent rigging of state elections in 1987.
Human rights abuses
Main article: Human rights abuses in Jammu and KashmirIndian troops entered the valley to quell the insurgency after it began. Some analysts have suggested that the number of Indian troops in Jammu and Kashmir is close to 600,000 although estimates vary and the government refuses to release official figures. The troops have been accused and held accountable for several humanitarian abuses and have engaged in mass extrajudicial killings, torture, rape and sexual abuse.
Indian security forces have been implicated in many reports for enforced disappearances of thousands of Kashmiris whereas the security forces deny having their information and/or custody. This is often in association with torture or extrajudicial killing. Human right activists estimate the number of disappeared to be over eight thousand, last seen in government detention. The disappeared are believed to be dumped in thousands of mass graves across Kashmir. A State Human Rights Commission inquiry in 2011, has confirmed there are thousands of bullet-ridden bodies buried in unmarked graves in Jammu and Kashmir. Of the 2730 bodies uncovered in 4 of the 14 districts, 574 bodies were identified as missing locals in contrast to the Indian governments insistence that all the graves belong to foreign militants.
Military forces in Jammu and Kashmir operate under impunity and emergency powers granted to them by the central government. These powers allow the military to curtail civil liberties, creating further support for the insurgency.
The insurgents have also abused human rights, driving away Kashmiri Pandits from the Kashmir Valley, an action that has been called ethnic cleansing The government's inability to protect the people from both its own troops and the insurgency has further eroded support for the government.
Amnesty International accused security forces of exploiting the Armed Forces Special Powers Act (AFSPA) that enables them to "hold prisoners without trial". The group argues that the law, which allows security to detain individuals for as many as two years "without presenting charges, violating prisoners' human rights". The Army sources maintain that "any move to revoke AFSPA in Jammu and Kashmir would be detrimental to the security of the Valley and would provide a boost to the terrorists."
Former Indian Army Chief General V. K. Singh rejected the accusations that the action was not taken in the cases of human rights violations by Army personnel. On 24 October 2010, he has said that 104 Army personnel had been punished in Jammu and Kashmir in this regard, including 39 officers. He also said that 95% of the allegations of human rights abuses against Indian Army were proved to be false, of which he remarked, had apparently been made with the "ulterior motive of maligning the armed forces". However, according to Human Rights Watch, the military courts in India, in general, were proved to be incompetent to deal with cases of serious human rights abuses and were responsible in covering up evidence and protecting the involved officers. Amnesty International in its report in 2015, titled "Denied"-Failures in Accountability in Jammu and Kashmir, says, "...with respect to investigations, an inquiry that is conducted by the same authority accused of the crime raises serious questions about the independence and impartiality of those proceedings", adding that according to the international law, an independent authority that is not involved in the alleged violations has to investigate such crimes.
These human rights violations are said to have contributed to the rise of resistance in Kashmir.
ISI's role
The Pakistani Inter-Services Intelligence has encouraged and aided the Kashmir independence movement through an insurgency due to its dispute on the legitimacy of Indian rule in Kashmir, with the insurgency as an easy way to keep Indian troops distracted and cause international condemnation of India. Former Pakistan President General Pervez Musharraf in Oct 2014 said during TV interview, "We have source (in Kashmir) besides the (Pakistan) army...People in Kashmir are fighting against (India). We just need to incite them."
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), in their first ever open acknowledgement in 2011 in US Court, said that the Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI) sponsors and oversees separatist militant groups in Kashmir.
In 2019, Prime Minister of Pakistan Imran Khan publicly discouraged Pakistani people from going to Kashmir to do a jihad. People who went to Kashmir will do an "injustice to the Kashmiri people". Most of the Pakistani militants who had crossed the border over the years and were caught by the Indian security forces were found to belong to the Punjab province of Pakistan.
Mujahideen influence
After the Mujahideen victory in the Soviet–Afghan War, Mujahideen militants, under the Operation Tupac with the aid of Pakistan, slowly infiltrated Kashmir with the goal of spreading a radical Islamist ideology to wage Jihad against India in the region.
Religion
The majority of the people of Jammu and Kashmir practise Islam. Indian-American journalist Asra Nomani states that while India itself is a secular state, Muslims are politically, culturally and economically marginalised when compared to Hindus in India as a whole. The government's decision to transfer 99 acres of forest land near the Amarnath Temple in Kashmir division to a Hindu organisation (for setting up temporary shelters and facilities for Hindu pilgrims) solidified this feeling and led to one of the largest protest rallies in Jammu and Kashmir.
Other motivations
Psychological
Psychologist Waheeda Khan, explaining the rebellious nature of the Kashmiris, says that because of the tense situations in the valley from the 1990s, the generation gap between parents and young generations has increased. Young generations tend to blame their parents for failing to do anything about the political situation. So they start experimenting with their own aggressive ways to show their curbed feelings and would go against any authority. A prominent psychiatrist of the valley, Margoob, described that children/teenagers are much more vulnerable to passionate actions and reactions, since the young minds are yet to completely develop psychological mechanisms. When they assume that they are "pushed against the wall", they get controlled by the emotions without bothering about the consequences. Also young people easily identify themselves with the "group" rather than with their individual identities. It leads to psychological distress which causes antisocial behaviour and aggressive attitude. Often, this situation gets worsened by the availability of weapons and people becoming familiar to violence after having exposed to conflict for so long. Waheeda Khan remarks, the major concern is that generations of children who are experiencing long-term violence in their lives, may reach adulthood perceiving that violence is a fair means of solving ethnic, religious, or political differences.
Economic
High unemployment and lack of economic opportunities in Kashmir are also said to have intensified the struggle.
Stone pelting
Main article: Stone Pelting in KashmirFollowing the 2008 protests and 2010 unrest, the turmoil took on a new dimension when people, particularly young people of the Kashmir valley began pelting stones on security forces to express their aggression and protest for the loss of freedom. In turn they get attacked by the armed personnel with pellets, rubber bullets, sling shots and tear gas shells. This leads to eye-injuries and several other kind of injuries to many people. Security forces also face injuries, and sometimes get beaten up during these events. According to Waheeda Khan, most of the 'stone-pelters' are school and college going students. Large number of these people get arrested during these events for allegedly resorting to stone pelting, after which some of them are also tortured. According to political activist Mannan Bukhari, Kashmiris made stone, an easily accessible and defenseless weapon, their weapon of choice for protest.
Kashmiri senior journalist Parvaiz Bukhari remarked:
The summer of 2010 witnessed a convulsion in the world's most militarized zone, the Indian-controlled part of Kashmir, an unprecedented and deadly civil unrest that is beginning to change a few things on the ground. Little known and relatively anonymous resistance activists emerged, organizing an unarmed agitation more fierce than the armed rebellion against Indian rule two decades earlier. And apparently aware of the post 9/11 world, young Kashmiris, children of the conflict, made stones and rocks a weapon of choice against government armed forces, side-stepping the tag of a terrorist movement linked with Pakistan. The unrest represents a conscious transition to an unarmed mass movement, one that poses a moral challenge to New Delhi's military domination over the region.
Human rights abuses by militants and army
Further information: Human rights abuses in Jammu and Kashmir and Rape in Kashmir conflict § Rape by militants See also: Ethnic cleansing of Kashmiri HindusIslamic separatist militants are accused of violence against the Kashmir populace. On the other hand, the Indian army has also allegedly committed serious crimes like using pellet guns, torture, murder and rape, though many such incidents were subject to legal proceedings. The militants have kidnapped and killed many civil servants and suspected informers. Tens of thousands of Kashmiri Pandits have been forced to emigrate as a result of continued violence by the majority. Estimates of the displaced vary from 170,000 to 700,000. Thousands of Kashmiri Pandits had to move to Jammu because of targeted attacks by Islamic radical organizations.
Notable insurgencies
- Exodus of Kashmiri Hindus
- July and August 1989 – Three CRPF personnel and politician Mohd. Yusuf Halwai of NC/F were killed.
- 1989 kidnapping of Rubaiya Sayeed daughter of the then Home Minister of India Mufti Sayeed.
- Gawkadal massacre- Central Reserve Police Force opened fire on a group of Kashmiri protestors, killing 50.
- Sopore massacre- Killing of 55 Kashmiri civilians by Border security force(BSF)
- Bijbehara massacre- Massacre of 51 protestors by BSF.
- 1995 kidnapping of western tourists in Jammu and Kashmir – Six foreign trekkers from Anantnag district were kidnapped by Al Faran. One was beheaded later, one escaped, and the other four remain missing, presumably killed.
- 1997 Sangrampora massacre – On 22 March 1997, seven Kashmiri Pandits were killed in Sangrampora village in the Budgam district.
- Wandhama massacre – In January 1998, 24 Kashmiri Pandits living in the village of Wandhama were massacred by Pakistani militants. According to the testimony of one of the survivors, the militants dressed themselves as officers of the Indian Army, entered their houses and then started firing blindly. The incident was significant because it coincided with former US president Bill Clinton's visit to India and New Delhi highlighted the massacre to prove Pakistan-supported militancy in Kashmir .
- 1998 Prankote massacre – 26 Hindu villagers of Udhampur district were killed by militants.
- 1998 Champanari massacre – 25 Hindu villagers killed on 19 June 1998 by Islamic militants.
- 2000 Amarnath pilgrimage massacre – 30 Hindu pilgrims massacred by militants.
- Chittisinghpura massacre – 36 Sikhs massacred by LeT militants though some allegations on Indian security forces exist too. (unclear)
- 2001 Jammu and Kashmir legislative assembly bombing – On 1 October 2001, a bombing at the Legislative Assembly in Srinagar killed 38.
- 2002 Raghunath temple attacks – An attack occurred on 30 March 2002 when two suicide bombers attacked the temple. Eleven persons including three security forces personnel were killed and 20 were injured. In second attack, the fidayeen suicide squad attacked the temple second time on 24 November 2002 when two suicide bombers stormed the temple and killed fourteen devotees and injured 45 others.
- 2002 Qasim Nagar massacre – On 13 July 2002, armed militants believed to be a part of the Lashkar-e-Toiba threw hand grenades at the Qasim Nagar market in Srinagar and then fired on civilians standing nearby killing 27 and injuring many more.
- 2003 Nadimarg Massacre – 24 Hindus killed in Nadimarg, Kashmir on 23 March 2003 by Lashkar-e-Taiba militants.
- 20 July 2005 Srinagar bombing – A car bomb exploded near an armoured Indian Army vehicle in the famous Church Lane area in Srinagar killing 4 Indian Army personnel, one civilian and the suicide bomber. Militant group Hizbul Mujahideen, claimed responsibility for the attack.
- Budshah Chowk attack – A militant attack on 29 July 2005 at Srinigar's city centre, Budshah Chowk, killed 2 and left more than 17 people injured. Most of those injured were media journalists.
- Assassination of Ghulam Nabi Lone – On 18 October 2005, suspected Kashmiri militants killed Jammu and Kashmir's then education minister Ghulam Nabi Lone. Militant group called Al Mansurin claimed responsibility for the attack. Abdul Ghani Lone, a prominent All Party Hurriyat Conference leader, was assassinated by unidentified gunmen during a memorial rally in Srinagar. The assassination resulted in wide-scale demonstrations against the Indian forces for failing to provide enough security cover for Lone.
- 2006 Doda massacre – On 3 May 2006, militants massacred 35 Hindus in Doda and Udhampur districts in Jammu and Kashmir.
- On 12 June 2006, one person was killed and 31 were wounded when militants hurled three grenades on Vaishnodevi shrine-bound buses at the general bus stand.
- 2014 Kashmir Valley attacks – There were four attacks on 5 December 2014 on army, police and civilians resulted in 21 deaths and several injured. Their motive was to disrupt the ongoing assembly elections.
- 2016 Uri attack – Four armed militants sneaked into an army camp and lobbed grenades onto tents causing massive fire culminating in the death of 19 military personnel.
- 2018 Sunjuwan attack - On 10 February 2018, Jaish-e-Mohammad militants attacked Sunjuwan Army Camp in Jammu and Kashmir. 6 Indian army soldiers, 4 militants, 1 civilian died and 11 were injured.
- 2019 Pulwama attack - On 14 February 2019, Jaish-e-Mohammad militants attacked a convoy of CRPF men, killing 46 personnel and injuring 20.
Tactics
India
The Indian government has increasingly relied on military presence to control the insurgency. The military has allegedly committed human rights violations. The government would often dissolve assemblies, arrest elected politicians and impose president's rule. The government also rigged elections in 1987. In recent times there have been signs that the government is taking local elections more seriously. The government has also funneled development aid to Kashmir and Kashmir has now become the biggest per capita receiver of Federal aid.
Pakistan
The Pakistani central government originally supported, trained and armed the insurgency in Kashmir, sometimes known as "ultras" (extremists), however after groups linked to the Kashmiri insurgency twice attempted to assassinate president Pervez Musharraf, Musharraf decided to end support for such groups. His successor, Asif Ali Zardari has continued the policy, calling insurgents in Kashmir "terrorists".
But the Pakistani Inter-Services Intelligence hasn't followed the lead of the government and has continued its support for insurgent groups in Kashmir In 2008, 541 people died due to insurgency, The Economist called it the lowest in two decades. The report cited a reduction in the support for militants by Pakistan and war fatigue among the Kashmiris as the reasons for the reduction in casualty figures.
Insurgents
After around 2000, the insurgency became far less violent and has instead taken on the form of protests and marches. Certain groups have also chosen to lay down their arms and look for a peaceful resolution to the conflict.
Groups
The different insurgent groups have different aims in Kashmir. Some want complete independence from both India and Pakistan, others want unification with Pakistan and still others just want greater autonomy from the Indian government.
A 2010 survey found that 43% of the people in J&K and 44% of the people in AJK would favour complete independence from both India and Pakistan, with support for the independence movement unevenly distributed across the region.
Militant groups
Over the last two years, the militant group, Lashkar-e-Toiba has split into two factions: Al Mansurin and Al Nasirin. Another new group reported to have emerged is the "Save Kashmir Movement". Harkat-ul-Mujahideen (formerly known as Harkat-ul-Ansar) and Lashkar-e-Toiba are believed to be operating from Muzaffarabad, and Muridke, Pakistan respectively.
Other less well known groups are the Freedom Force and Farzandan-e-Milat. A smaller group, Al-Badr, has been active in Kashmir for many years and is still believed to be functioning. All Parties Hurriyat Conference, an organisation that uses moderate means to press for the rights of the Kashmiris, is often considered as the mediator between New Delhi and insurgent groups.
Al-Qaeda
It is unclear if Al Qaeda has a presence in Jammu and Kashmir. Donald Rumsfeld suggested that they were active and in 2002 the SAS hunted for Osama bin Laden in Jammu and Kashmir. Al Qaeda claims that it has established a base in Jammu and Kashmir. However, there has been no evidence for any of these assertions. The Indian army also claims that there is no evidence of Al Qaeda presence in Jammu and Kashmir. Al Qaeda has established bases in Pakistani administered Kashmir and some, including Robert Gates have suggested that they have helped to plan attacks in India.
Casualties
According to government data, around 41,000 people—consisting of 14,000 civilians, 5,000 security personnel and 22,000 militants—have died because of the insurgency as of March 2017 in both Kashmir Valley and Jammu region. The overwhelming majority of these deaths happened in the 1990s and early 2000s, and there has been a steady decline in violence and sharp drop in the number of deaths 2004 onwards. A 2006 report by Human Rights Watch claimed that at least 20,000 civilians had died in the conflict by then. The territory witnessed about 69,820 militancy-related incidents till March 2017. Among the militants killed between 1989 and 2002, about 3,000 were from outside Jammu and Kashmir (mostly from Pakistan and some Afghans). Indian forces engaged in counter insurgency operations captured around 40,000 firearms, 150,000 explosive devices, and over 6 million rounds of assorted ammunition during this period. Jammu and Kashmir Coalition of Civil Society posits a figure of 70,000 deaths, most of them civilians. The pro-Pakistan Huriyat group has claimed a higher death toll of 80,000 including civilians, security forces and militants. The districts with the most incidents of killing were Kupwara, Baramulla, Poonch, Doda, Anantnag and Pulwama.
| Year | Incidents of Killing | Civilians | Security Forces | Militants | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | 427 | 127 | 119 | 498 | 744 |
| 2008 | 261 | 71 | 85 | 382 | 538 |
| 2009 | 208 | 53 | 73 | 247 | 373 |
| 2010 | 189 | 34 | 69 | 258 | 361 |
| 2011 | 119 | 33 | 31 | 117 | 181 |
| 2012 | 70 | 19 | 18 | 84 | 121 |
| 2013 | 84 | 19 | 53 | 100 | 172 |
| 2014 | 91 | 28 | 47 | 114 | 189 |
| 2015 | 86 | 19 | 41 | 115 | 175 |
| 2016 | 112 | 14 | 88 | 165 | 267 |
| 2017 | 163 | 54 | 83 | 220 | 357 |
| 2018 | 206 | 86 | 95 | 271 | 452 |
| 2019 | 135 | 42 | 78 | 163 | 283 |
| 2020 | 140 | 33 | 56 | 232 | 321 |
| 2021 | 153 | 36 | 45 | 193 | 274 |
| 2022 | 151 | 30 | 30 | 193 | 253 |
Surrender and rehabilitation policy
Surrendering in Jammu and Kashmir has been institutionalized over the years. The 1990s saw some surrender policies, while in the 2000s, there was a policy for militants belonging to Indian administered Jammu and Kashmir and another for Pakistan administered territory. The first surrender policy for militants in Kashmir was launched on 15 August 1995. It was a copy of the policies already there for Naxalites.
Appeals to surrender
Appeals to surrender are made by security forces to militants at encounter sites as well. Some attempts are successful, while others are not. Mothers and other family members have made videos urging their child turned militant to surrender to the security forces. Sometimes the family member is brought to the encounter site and urged to talk to their children through loudspeakers to surrender.
See also
- 2018 Sunjuwan attack
- List of massacres in Jammu and Kashmir
- All Parties Hurriyat Conference
- Pakistan and state-sponsored terrorism
- Partition of India
- Ikhwan (Kashmir)
References
- "DeM cadres lead women congregations across Kashmir". Greater Kashmir. 3 August 2016. Archived from the original on 24 December 2018. Retrieved 9 August 2016.
- Gul, Khalid (5 August 2016). "Pro-freedom rallies in Pampore, Bijbehara". Greater Kashmir. Archived from the original on 8 August 2016. Retrieved 9 August 2016.
- "DeM activists asked to make Dua-e-Majlis successful". Kashmir Reader. 2 August 2016. Archived from the original on 3 August 2016. Retrieved 9 August 2016.
- "This is people's Movement, be United: DeM". 22 July 2016. Archived from the original on 24 December 2018. Retrieved 9 August 2016.
- Until My Freedom Has Come: The New Intifada in Kashmir. Penguin Books India. 2011. ISBN 9780143416470. Archived from the original on 20 April 2023. Retrieved 12 November 2020.
- Margolis, Eric (2004). War at the Top of the World: The Struggle for Afghanistan, Kashmir and Tibet. Routledge. p. 81. ISBN 9781135955595. Archived from the original on 20 April 2023. Retrieved 12 November 2020.
- Bose, Sumantra (2009). Kashmir: Roots of Conflict, Paths to Peace. Harvard University Press. p. 107. ISBN 9780674028555. Archived from the original on 20 April 2023. Retrieved 12 November 2020.
- "insurgency" (noun), Merriam-Webster Unabridged, archived from the original on 20 January 2020, retrieved 27 November 2019 Quote: "The quality or state of being insurgent; specifically : a condition of revolt against a recognized government that does not reach the proportions of an organized revolutionary government and is not recognized as belligerency" (subscription required)
- insurgency, n, Oxford English Dictionary, archived from the original on 20 January 2020, retrieved 27 November 2019 Quote: "The quality or state of being insurgent; the tendency to rise in revolt; = insurgence n. = The action of rising against authority; a rising, revolt." (subscription required)
- Insurgency, Encyclopedia Britannica, archived from the original on 27 November 2019, retrieved 27 November 2019 Quote: "Insurgency, term historically restricted to rebellious acts that did not reach the proportions of an organized revolution. It has subsequently been applied to any such armed uprising, typically guerrilla in character, against the recognized government of a state or country." (subscription required)"
- "Al Qaeda In the Indian Subcontinent Released Video Titled 'Kashmir is our' Al Qaeda again target india". 12 October 2021. Archived from the original on 19 November 2022. Retrieved 13 October 2021.
- Elizabeth Van Wie Davis; Rouben Azizian (2007). Islam, Oil, and Geopolitics: Central Asia After September 11. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, Incorporated. p. 281. ISBN 978-0-7425-4128-3. Archived from the original on 20 April 2023. Retrieved 13 May 2021.
The trouble was that elements of Pakistan ' s government were involved with Islamist extremists . They had protected and supported not only the Taliban but also insurgents crossing the Line of Control into Indian - held Kashmir
- ^ Kazi, Seema (2017), "Law, Gender and Governance in Kashmir", in Chitralekha Zutshi (ed.), Kashmir: History, Politics, Representation, Cambridge University Press, pp. 150–171, 153, ISBN 978-1-108-22612-7, archived from the original on 20 April 2023, retrieved 27 November 2019
- ^ Kapur, S. Paul (2017), Jihad as Grand Strategy: Islamist Militancy, National Security, and the Pakistani State, Oxford University Press, pp. 84–, ISBN 978-0-19-976852-3, archived from the original on 20 April 2023, retrieved 27 November 2019
-
- Swami, Praveen (2007). India, Pakistan and the Secret Jihad. New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-40459-4.
- "Al Qaeda thriving in Kashmir in support of Pakistani intelligence against india reports Al Qaeda camps in azad kashmir Pakistan". Christian Science Monitor. 2 July 2002. Archived from the original on 12 November 2021. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- "Al-Qaeda calls for liberation of Kashmir". YouTube. Archived from the original on 13 December 2021. Retrieved 1 August 2021.
- "Dawood is a terrorist, has 'strategic alliance' with ISI, says US". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 3 October 2017. Retrieved 7 June 2017.
- "ISIS announces new India and Pakistan provinces, casually breaking up Khorasan". The Defense Post. 15 May 2019. Archived from the original on 10 June 2020. Retrieved 4 June 2019.
- "Islamic State claims it has established province in India, calls it Wilayah of Hind: Report". 11 May 2019. Archived from the original on 18 April 2021. Retrieved 18 April 2021.
- "Islamic State J-K chief among 4 terrorists killed in Kashmir". Rediff.com. 22 June 2018. Archived from the original on 20 December 2022. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- Specified, Not. "Chronicle of Important events/date in J&K's political history". www.jammu-kashmir.com. Archived from the original on 12 October 2017. Retrieved 29 April 2018.
- "India imposes Kashmir lockdown, puts leaders 'under house arrest'". Archived from the original on 19 November 2022. Retrieved 29 March 2022.
- ^ Snehesh Alex Philip, What Imran Khan says is 9 lakh soldiers in Kashmir is actually 3.43 lakh only Archived 2 September 2021 at the Wayback Machine, The Print, 12 November 2019.
- ^ "India's leader makes peace overtures in Kashmir", The Times, 18 November 2004, archived from the original on 23 May 2011: "Military experts estimate that India has about 250,000 troops in the region."
- "Kashmir". Stimson Center. Archived from the original on 30 June 2006.: "Some reports estimate that India deploys approximately 400,000 combined army and paramilitary forces in Kashmir, most of which are stationed in the interior, 80,000 of which are deployed along the LoC."
- "Yearly Fatalities". SATP. Retrieved 1 June 2024.
- "Yearly Fatalities". SATP. Retrieved 1 June 2024.
- "Kashmir insurgents". Uppsala Conflict Data Program. Archived from the original on 1 October 2017. Retrieved 29 March 2017.
- "40,000 people killed in Kashmir: India". The Express Tribune. Archived from the original on 27 February 2017.
- ^ Slater, Joanna (28 March 2019), "From scholars into militants: Educated Kashmiri youths are joining an anti-India insurgency", The Washington Post, archived from the original on 27 November 2019, retrieved 27 November 2019
- (a) Kashmir, region Indian subcontinent, Encyclopaedia Britannica, archived from the original on 13 August 2019, retrieved 15 August 2019 (subscription required);
(b) "Kashmir", Encyclopedia Americana, Scholastic Library Publishing, 2006, p. 328, ISBN 978-0-7172-0139-6, archived from the original on 17 January 2023, retrieved 27 November 2019 C. E Bosworth, University of Manchester - Jan·Osma鈔czyk, Edmund; Osmańczyk, Edmund Jan (2003), Encyclopedia of the United Nations and International Agreements: G to M, Taylor & Francis, pp. 1191–, ISBN 978-0-415-93922-5, archived from the original on 17 January 2023, retrieved 27 November 2019 Quote: "Jammu and Kashmir: Territory in northwestern India, subject to a dispute between India and Pakistan. It has borders with Pakistan and China."
- The Editorial Board (6 August 2019), "India Tempts Fate in Kashmir, 'The Most Dangerous Place in the World'", The New York Times, archived from the original on 19 November 2022, retrieved 27 November 2019 Quote: "The Himalayan territory of Kashmir has long been the central source of friction between India and Pakistan and a hotbed of separatist aspirations."
- Ratcliffe, Rebecca (4 August 2019), "Heightened security and anxiety in Kashmir amid fears of unrest", Guardian, archived from the original on 12 December 2019, retrieved 27 November 2019 Quote: "Kashmir is claimed by India and Pakistan in full and ruled in part by both. An insurgency on the Indian-administered side has been ongoing for three decades, and tens of thousands of people have been killed."
- Conflict Encyclopedia – India: Kashmir Archived 1 October 2017 at the Wayback Machine, Uppsala Conflict Data Program, 29 May 1977, retrieved 2013-05-29,
- ^ Uppsala Conflict Data Program Conflict Encyclopedia, Conflict Summary, Conflict name: India: Kashmir, "Roots of Conflict and the emergence of Kashmir Insurgents", viewed 2013-05-29, http://www.ucdp.uu.se/gpdatabase/gpcountry.php?id=74®ionSelect=6-Central_and_Southern_Asia# Archived 3 February 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- "Elections in Kashmir". Kashmirlibrary.org. Archived from the original on 1 February 2017. Retrieved 23 February 2017.
- ^ "Kashmir insurgency". BBC News. Archived from the original on 22 February 2017. Retrieved 21 February 2017.
- Jeelani, Mushtaq A. (25 June 2001). "Kashmir: A History Littered With Rigged Elections". Media Monitors Network. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 24 February 2017.
- ^ Hussain, Altaf (14 September 2002). "Kashmir's flawed elections". BBC News. Archived from the original on 26 February 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- ^ "India Pakistan – Timeline". BBC News. Archived from the original on 22 February 2017. Retrieved 10 April 2015.
- Ali, Mahmud (9 October 2006). "Pakistan's shadowy secret service". BBC News. Archived from the original on 21 February 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- ^ Rashid, Ahmed (6 October 2006). "Nato's top brass accuse Pakistan over Taliban aid". The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on 22 February 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- Gall, Carlotta (21 January 2007). "At Border, Signs of Pakistani Role in Taliban Surge". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 31 December 2016. Retrieved 21 February 2017.
- Jehl, Douglas; Dugger, Celia W.; Barringer, Felicity (25 February 2002). "Death of Reporter Puts Focus on Pakistan Intelligence Unit". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2 May 2017. Retrieved 21 February 2017.
- "Pakistan supported, trained terror groups: Pervez Musharraf". Business Standard. Press Trust of India. 28 October 2015. Archived from the original on 5 June 2017. Retrieved 21 February 2017.
- Uppsala Conflict Data Program Conflict Encyclopedia, Conflict Summary, India: Kashmir (entire conflict), Fatality estimates, viewed 2013-05-29, http://www.ucdp.uu.se/gpdatabase/gpcountry.php?id=74®ionSelect=6-Central_and_Southern_Asia# Archived 3 February 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- Uppsala Conflict Data Program Conflict Encyclopedia, India One-sided violence, Government of India – civilians, Kashmir insurgents – civilians, Lashkar-e-Taiba – civilians, viewed on 2012-05-29, http://www.ucdp.uu.se/gpdatabase/gpcountry.php?id=74®ionSelect=6-Central_and_Southern_Asia# Archived 3 February 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Jayanth Jacob; Aurangzeb Naqshbandi. "41,000 deaths in 27 years: The anatomy of Kashmir militancy in numbers". Hindustan Times. Retrieved 18 May 2023.
- Evans 2002, p. 19: "Most Kashmiri Pandits living in the Kashmir Valley left in 1990 as militant violence engulfed the state. Some 95% of the 160,000-170,000 community left in what is often described as a case of ethnic cleansing."
- ^ Bose, Sumantra. Kashmir: Roots of Conflict, Paths to Peace. Harvard, 2005.
- Swami, Praveen.India, Pakistan and the Secret Jihad. 2006.
- "Omar Abdullah hails Sheikh Abdullah's decision to accede J-K to India". Archived from the original on 8 December 2013. Retrieved 10 November 2016.
- "Excerpts of Sheikh Abdullah's speech defending the accession". 9 August 2016. Archived from the original on 10 November 2016.
- "Sheikh Muhammad Abdullah". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 9 June 2024.
- Fatalities in Terrorist Violence 1988–2014 in Jammu & Kashmir Archived 15 July 2011 at Wikiwix, South Asian Terrorism, SATP (2014)
- Tikoo, Colonel Tej K (2013). Kashmir: Its Aborigines and Their Exodus. Lancer Publishers LLC. pp. 397–. ISBN 978-1-935501-58-9.
- Hasan, Syed Shoaib (3 March 2010). "Why Pakistan is 'boosting Kashmir militants'". BBC News. Archived from the original on 28 February 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- Jamar, Arif. The untold story of Jihad in Kashmir. 2009.
- ^ Khan, Aamer Ahmed (6 April 2005). "Pakistan: Where have the militants gone?". BBC News. Archived from the original on 22 February 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- Behera, Navnita Chadha (2006). Kashmir Demysitified. Washington: Brookings Institution Press.
- Behera, Navnita Chadha (2006). Kashmir Demystified. Washington D.C.: Brookings Institution Press.
- Bose, Sumantra (2003). Kashmir Roots of Conflict Paths to Peace. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. pp. 146.
- Behra, Navnita Chadha (2006). Demystifying Kashmir. Washington D.C.: Brookings Institution Press. p. 150.
- "Fernandes reveals 'Sarp Vinash' toll". The Hindu. 31 July 2003. Archived from the original on 5 November 2005.
- "A Militia Against Terror | J&K: Operation Sarp Vinash - The Army Strikes Hard | South Asia Intelligence Review (SAIR), Vol. No. 1.46". www.satp.org. Archived from the original on 25 September 2016. Retrieved 7 March 2018.
- Kumar, Devesh (24 May 2003). "Operation Sarp Vinash: Army clears Hill Kaka". The Economic Times. Archived from the original on 8 March 2018. Retrieved 7 March 2018.
- "Operation 'Sarp Vinash': Over 60 terrorists killed". www.rediff.com. Archived from the original on 13 June 2017. Retrieved 7 March 2018.
- Majid, Zulfikar. "'Sarp Vinash type of operation needed to eradicate militancy in Rajuri-Poonch'". Deccan Herald. Retrieved 9 June 2024.
- Joseph, Josy. "Operation Sarp Vinash chief pulled up". Rediff. Retrieved 9 June 2024.
- "Cinema halls are first fatality of militancy in Kashmir". 29 October 2018. Archived from the original on 29 April 2021. Retrieved 29 April 2021.
- "Kashmir's ghost theatres". 16 March 2018. Archived from the original on 29 April 2021. Retrieved 29 April 2021.
- "Kashmir has lost its cinema halls but not its love for the movies". 19 December 2016. Archived from the original on 29 April 2021. Retrieved 29 April 2021.
- Benkin, Richard L. (12 April 2017). What Is Moderate Islam?. Lexington Books. p. 47. ISBN 9781498537421. Archived from the original on 20 April 2023. Retrieved 12 November 2020.
- Tucker, Spencer C. (2013). Encyclopedia of Insurgency and Counterinsurgency A New Era of Modern Warfare. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO, LLC. ISBN 978-1-61069-279-3.
- ^ Stephens, Bret (4 October 2008). "The Most Difficult Job in the World". The Wall Street Journal. Archived from the original on 22 February 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- ^ Cole, Juan (12 December 2008). "Does Obama understand his biggest foreign-policy challenge?". Salon. Archived from the original on 23 March 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- ^ "Links between ISI, militant groups: Straw". Rediff.com. 11 June 2002. Archived from the original on 24 March 2017. Retrieved 24 February 2017.
- ^ "Stony ground". The Economist. 8 July 2010. Archived from the original on 23 December 2016. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- "Your place or mine?". The Economist. 12 February 2004. Archived from the original on 22 February 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- ^ "Grim up north". The Economist. 25 June 2009. Archived from the original on 29 April 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- ^ "Kashmir's extra-judicial killings". BBC News. 8 March 2007. Archived from the original on 14 June 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- "Hizbul Mujahideen almost wiped out in Kashmir". The Times of India. 19 October 2011. Archived from the original on 29 July 2012.
- "J&K: Top LeT commander killed in encounter". 3 August 2012. Archived from the original on 3 August 2012.
- "NIA :: Banned Terrorist Organisations". 10 January 2016. Archived from the original on 10 January 2016. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- "Kashmiris join insurgency against India at highest rate in two decades". The Express Tribune. 24 February 2015. Archived from the original on 26 June 2015. Retrieved 25 June 2015.
- "Who are the Kashmir militants?". BBC News. 1 August 2012. Archived from the original on 20 February 2017. Retrieved 21 February 2017.
- "Jammu's Doda is militancy free, say cops after Hizbul terrorist Masood killed in encounter". Hindustan Times. 29 June 2020. Archived from the original on 29 June 2020. Retrieved 29 June 2020.
- "No Hizbul militant in south Kashmir's Tral now, first time since 1989: Police". The Times of India. PTI. 26 June 2020. Archived from the original on 28 September 2020. Retrieved 29 June 2020.
- "No resident of Srinagar in terrorist ranks after killing of top LeT commander: Kashmir IGP". The Indian Express. 26 July 2020. Archived from the original on 27 July 2020. Retrieved 27 July 2020.
- Hussain, Ashiq (26 July 2020). "After killing of LeT man, no resident of Srinagar is in terrorist ranks: IGP". Hindustan Times. Archived from the original on 27 July 2020. Retrieved 27 July 2020.
- Pandit, M. Saleem (26 July 2020). "Srinagar district is now terror-free: Police". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 27 July 2020. Retrieved 27 July 2020.
- "NC terms drone attack inside Jammu airport as terrorism by rogue state Pakistan". Mathrubhumi. 28 June 2021. Archived from the original on 28 June 2021. Retrieved 28 June 2021.
- "10 Jawans Killed This Year in J&K as Terrorists Ramp Up Grenade, Hit-&-Run Attacks on Security Forces". News18. 22 April 2022. Archived from the original on 22 April 2022. Retrieved 22 April 2022.
- Schofield, Victoria (2000). Kashmir in Conflict: India, Pakistan and the Unending War. I.B.Tauris. p. 137. ISBN 9781860648984.
- "How Mufti Mohammad Sayeed Shaped the 1987 Elections in Kashmir". The Caravan. 22 March 2016. Archived from the original on 28 April 2017. Retrieved 4 May 2017.
- Hashim, Asad (27 May 2014). "Timeline: India-Pakistan relations". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 1 March 2017. Retrieved 23 February 2017.
- Brad Adams, Asia director at Human Rights Watch (16 February 2007). "India: Investigate All 'Disappearances' in Kashmir | Human Rights Watch". Hrw.org. Archived from the original on 5 August 2012. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- Human Rights Watch (11 September 2006). "Everyone Lives in Fear". Hrw.org. Archived from the original on 15 April 2013. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- "India: Events of 2008". India | Human Rights Watch. Hrw.org. 14 January 2009. Archived from the original on 3 September 2012.
- Bukhari, Shujaat. "Mass graves found in North Kashmir containing 2,900 unmarked bodies". The Hindu. Archived from the original on 29 April 2018. Retrieved 22 April 2017.
- "Kashmir graves: Human Rights Watch calls for inquiry". BBC News. 25 August 2011. Archived from the original on 23 April 2017. Retrieved 22 April 2017.
- "India must investigate unidentified graves, News, Amnesty International Australia". 30 August 2008. Archived from the original on 30 August 2008. Retrieved 22 April 2017.
- Buried Evidence: Unknown, Unmarked, and Mass Graves in Indian-Administered Kashmir Archived 17 October 2011 at the Wayback Machine A preliminary report; International People's Tribunal on Human Rights and Justice in Kashmir
- "India: Investigate Unmarked Graves in Jammu and Kashmir | Human Rights Watch". Hrw.org. 24 August 2011. Archived from the original on 4 September 2012. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- LYDIA POLGREEN (22 August 2011). "Mass Graves Hold Thousands, Kashmir Inquiry Finds". NYTimes. Archived from the original on 2 May 2016.
- Yardley, Jim (27 September 2010). "India Reopens Kashmir's Schools, but Many Stay Away". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 22 February 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- "India: Security forces cannot claim immunity under AFSPA, must face trial for violations". Amnesty International. 7 February 2012. Archived from the original on 23 April 2017. Retrieved 7 March 2012.
- Pallone, Frank (15 February 2006), Resolution condemning Human Rights Violations against Kashmiri Pandits, US House of Representatives, archived from the original on 10 August 2009
- "Rights Abuses Behind Kashmir Fighting – Human Rights Watch". hrw.org. 16 July 1999. Archived from the original on 19 October 2008. Retrieved 25 June 2015.
- Huey, Caitlin (28 March 2011). "Amnesty International Cites Human Rights Abuse in Kashmir". Usnews.com. Archived from the original on 30 April 2013. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- "Army opposes Omar's plans to revoke AFSPA: Report". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 12 October 2017. Retrieved 6 May 2017.
- "104 armymen punished for human rights violations in JK: Gen VK Singh | Latest News & Updates at Daily News & Analysis". dna. 24 October 2010. Archived from the original on 25 April 2017. Retrieved 24 April 2017.
- "Rape by Security Forces: The Pattern of Impunity". www.hrw.org. Archived from the original on 12 October 2017. Retrieved 1 May 2017.
- "96% complaints against army rejected by GoI under 'colonial' AFSPA: Amnesty". Kashmir Reader. 3 September 2016. Archived from the original on 4 August 2017. Retrieved 1 May 2017.
- "Kashmir's disturbing new reality | the young militants of Kashmir". Hindustantimes.com. Archived from the original on 30 May 2017. Retrieved 24 May 2017.
Then, youngsters used to take to the streets and pelt stones to protest human right violations...
- Parthasarathy, Malini. "Understanding Kashmir's stone pelters". The Hindu. Archived from the original on 29 April 2018. Retrieved 24 May 2017.
Today's protesters might shout anti-India slogans such as azadi, but their anger is specifically directed at the security forces in the context of the brutal killings of innocent boys...
- "Pakistan needs to incite those fighting in Kashmir: Musharraf". India Today. 16 October 2014. Archived from the original on 12 October 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- ^ "ISI sponsors terror activities in Kashmir, FBI tells US court". Firstpost. 21 July 2011. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- ^ Rajghatta, Chidanand (20 July 2011). "US exposes ISI subversion of Kashmir issue; FBI arrests US-based lobbyist". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 12 August 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- ^ Kumar, Himani (7 June 2011). "ISI gives arms to Kashmir terrorists: Rana to FBI". Rediff.com. Archived from the original on 5 August 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- ^ Agencies (20 July 2011). "ISI funneled millions to influence US policy on Kashmir: FBI". The Indian Express. Archived from the original on 24 February 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- "'Historic day': PM Imran inaugurates 24/7 border crossing at Torkham". DAWN.COM. 18 September 2019. Archived from the original on 23 May 2022. Retrieved 27 November 2019.
- ^ Puri, Luv (27 November 2019). "The many faces of Pakistani Punjab's militancy". The Hindu. Archived from the original on 19 November 2021. Retrieved 27 November 2019.
- Nomani, Asra Q. (1 December 2008). "Muslims -- India's new 'untouchables'". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on 22 February 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- ^ Thottam, Jyoti (4 September 2008). "Valley of Tears". Time. Archived from the original on 24 January 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- Gowhar Geelani. "Five reasons behind radicalisation in Kashmir". www.dailyo.in. Archived from the original on 9 March 2017. Retrieved 24 May 2017.
- Waheeda Khan, Conflict in Kashmir 2015, p. 90, 91.
- "Indian award for Kashmir 'human shield' officer". BBC News. 23 May 2017. Archived from the original on 23 May 2017. Retrieved 23 May 2017.
High unemployment and complaints of heavy-handed tactics by security forces battling street protesters and fighting insurgents have aggravated the problem.
- "Unemployment a reason for surge in J&K violence?". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 20 April 2023. Retrieved 24 May 2017.
- Parthasarathy, Malini. "Understanding Kashmir's stone pelters". The Hindu. Archived from the original on 29 April 2018. Retrieved 24 May 2017.
The protesters on the streets...(are) frustrated at the lack of employment and economic opportunities. It is not hard to see where the frustration of the educated Kashmiri youth comes from. On the one hand, they are told that they are Indian citizens but they are shut out of the narrative of India as an emerging economic power. With mobile phones and internet communication being restricted, their sense of participation in the larger Indian discourse is sharply reduced.
- Waheeda Khan, Conflict in Kashmir 2015, p. 88
- ^ Bukhari, Mannan (28 July 2015). Kashmir - Scars of Pellet Gun: The Brutal Face of Suppression. Partridge Publishing. p. 44. ISBN 9781482850062. Archived from the original on 20 April 2023. Retrieved 12 November 2020.
- "Summers of Unrest Challenging India". www.kashmirlife.net. 20 December 2010. Archived from the original on 12 October 2017.
- "Four killed in Kashmir bomb blast". BBC News. 20 July 2005. Archived from the original on 25 August 2016. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- Mushtaq, Sheikh. "Ten Killed in Kashmir Car Bomb Blast". ABC News. Archived from the original on 29 April 2018. Retrieved 24 February 2017.
- "K P S Gill: The Kashmiri Pandits: An Ethnic Cleansing the World Forgot – Islamist Extremism & Terrorism in South Asia". satp.org. Archived from the original on 9 March 2009. Retrieved 25 June 2015.
- Alexander Evans, A departure from history: Kashmiri Pandits, 1990–2001, Contemporary South Asia (Volume 11, Number 1, 1 March 2002, pp. 19–37)
- "Chronicle of Important events/date in J&K's political history". jammu-kashmir.com. Archived from the original on 14 June 2015. Retrieved 25 June 2015.
- "Kashmir's first blood". The Indian Express. 1 May 2005. Archived from the original on 9 September 2021. Retrieved 9 September 2021.
- "Sangrampora killings". Archived from the original on 15 April 2005.
- "Wandhama Massacre report". Archived from the original on 9 October 1999. Retrieved 29 May 2005.
- Dugger, Celia W. (9 October 2001). "Pakistan Asks India to Revive Talks Aimed at Bringing Peace to Kashmir". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 23 February 2017. Retrieved 23 February 2017.
- ^ "Human Rights Watch World Report 2003: India". Archived from the original on 6 October 2010.
- "20 July 2005 Srinagar attack". Archived from the original on 18 November 2005.
- "July 29 attack in Srinagar". Archived from the original on 3 March 2007.
- "Kashmir minister killed in attack". BBC News. 18 October 2005. Archived from the original on 22 February 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- Tribune News Service (4 May 2006). "Phagwara observes bandh over J&K massacre". The Tribune. Archived from the original on 12 October 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- Sharma, S.P. (13 June 2006). "Terror in Jammu, Anantnag". The Tribune. Archived from the original on 1 October 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- "Multiple attacks rock Kashmir Valley". The Hindu: Mobile Edition. 5 December 2014. Archived from the original on 24 December 2014. Retrieved 24 December 2014.
- Human Rights Watch, Patricia Gossman. "India's secret army in Kashmir : new patterns of abuse emerge in the conflict ", 1996
- Ramaseshan, Radhika (30 December 2008). "Cong dilemma: young Omar or PDP". The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 23 February 2017. Retrieved 23 February 2017.
- Sanghvi, Vir "Think the Unthinkable - Hindustan Times". Archived from the original on 8 February 2011. Retrieved 23 December 2010. "Think the unthinkable" Hindustan Times, August 2008
- "Afzal Guru's confession: I helped them, took training in Pak". DAILY BHASKAR. 10 February 2013. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 19 April 2015.
- Agencies (6 April 2012). "Attempts will be made to push ultras across LoC: Army". Indian Express. Archived from the original on 7 January 2014.
- Press Trust of India (7 January 2014). "Militants, Army troopers exchange fire in Pulwama, none hurt". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 7 January 2014.
- Gupta, Amit; Leather, Kaia. Archived 30 March 2017 at the Wayback Machine "Kashmir: Recent Developments and US Concerns", June 2002
- "The Future of Kashmir?". BBC News. Archived from the original on 19 March 2017. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- Bradnock, Robert "Kashmir: Paths to Peace" Chatham House, London, 2008
- "Just 2% of people in J&K want to join Pak: Survey". The Times of India. 28 May 2010. Archived from the original on 14 January 2014. Retrieved 25 June 2015.
- "Shocked by Amir Sarfaraz's killing, LeT calls emergency meet". The Times of India. 16 April 2024. ISSN 0971-8257. Retrieved 9 June 2024.
- "Hurriyat: Its History, Role and Relevance". The Indian Express. 31 August 2015. Retrieved 9 June 2024.
- ^ Abbas, Zaffar (13 June 2002). "Analysis: Is al-Qaeda in Kashmir?". BBC News. Archived from the original on 29 December 2016. Retrieved 22 February 2017.
- ^ Smith, Michael (23 February 2002). "SAS joins Kashmir hunt for bin Laden". The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on 15 March 2017. Retrieved 21 February 2017.
- ^ International Herald Tribune. "Al Qaeda Claim of Kashmiri Link Worries India"
- ^ The Hindu."No al Qaeda presence in Kashmir: Army". The Hindu. 18 June 2007. Archived from the original on 11 April 2010. "No Al Qaeda presence in Kashmir: Army"
- Dawn. "Al Qaeda could provoke new India-Pakistan war: Gates", January 20, 2010
- Smucker, Phillip (2 July 2002). "Al Qaeda thriving in Pakistani Kashmir". The Christian Science Monitor. Archived from the original on 11 January 2017. Retrieved 21 February 2017.
- Everyone Lives in Fear: Patterns of Impunity in Jammu and Kashmir (PDF) (Report). Human Rights Watch. September 2006. p. 1.
- Bose, Sumantra (2003). Kashmir: Roots of Conflict, Paths to Peace. Harvard University Press. p. 3. Archived from the original on 12 October 2017.
- "Like Karadzic, Prosecute All Accused of HR Violations in Kashmir: JKCCS". Kashmir Observer. Archived from the original on 16 October 2017. Retrieved 19 October 2017.
- Sumantra Bose (2003), Kashmir : roots of conflict, paths to peace, Harvard University Press, p. 4, ISBN 0-674-01173-2
- ^ "datasheet-terrorist-attack-fatalities". www.satp.org. Archived from the original on 31 January 2022. Retrieved 12 February 2022.
- ^ Kakar, Harsha (24 November 2017). "Why Kashmir needs much more than surrender appeals". ORF. Archived from the original on 20 October 2021. Retrieved 16 October 2021.
- ^ Malik, Irfan Amin (25 November 2020). "Will Army's Draft 'Surrender Policy' In J&K Help Combat Militancy?". TheQuint. Archived from the original on 20 October 2021. Retrieved 16 October 2021.
- Yasir, Sameer (16 October 2017). "Jammu and Kashmir security forces' new appeal to militants: Surrender, come home and rejoin society". Firstpost. Archived from the original on 20 October 2021. Retrieved 16 October 2021.
- Kartha, Tara (5 June 2018). "New Age Militancy – Kashmir Youth Need Policies Encouraging Change, Not Surrender". The Wire. Archived from the original on 20 April 2023. Retrieved 20 October 2021.
- ^ Ashiq, Peerzada (30 January 2021). "Two Hizb militants 'motivated' to surrender". The Hindu. ISSN 0971-751X. Archived from the original on 19 October 2021. Retrieved 16 October 2021.
- IANS (22 December 2020). "Two terrorists surrender during encounter with security forces in Kashmir". Business Standard India. Archived from the original on 19 October 2021. Retrieved 16 October 2021.
- "J-K: Surrendered militant urged companions to surrender, they refused and get killed in encounter". The Economic Times. 6 May 2021. Archived from the original on 16 October 2021. Retrieved 16 October 2021.
- Islah, Mufti (22 March 2021). "'Missing You': A Kashmiri Child's Plea to Holed up Militant Father Fails, Body Found after Encounter". News18. Archived from the original on 19 October 2021. Retrieved 16 October 2021.
- Masood, Bashaarat (23 March 2021). "Four militants killed; ignored pleas from family: police". The Indian Express. Archived from the original on 19 October 2021. Retrieved 16 October 2021.
Bibliography
- Evans, Alexander (2002). "A departure from history: Kashmiri Pandits, 1990–2001". Contemporary South Asia. 11 (1): 19–37. doi:10.1080/0958493022000000341. ISSN 0958-4935. S2CID 145573161.
- Khan, Waheeda (2015), "Conflict in Kashmir: Psychosocial Consequences on Children", in Sibnath Deb (ed.), Child Safety, Welfare and Well-being: Issues and Challenges, Springer, pp. 83–93, ISBN 978-81-322-2425-9
| Kashmir separatist movement | |
|---|---|
| Political parties | |
| Militant organisations | |
| Separatists |
|
| History | |
| Nationalism | |
| Related | |
| Post–Cold War conflicts in Asia | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| South Asia |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| East Asia |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Southeast Asia |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Central Asia |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Western Asia |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inter-continental conflict | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Related topics | |||||||||||||||||||||||