| Revision as of 19:29, 7 August 2011 editBeetstra (talk | contribs)Edit filter managers, Administrators172,031 edits Script assisted update of identifiers for the Chem/Drugbox validation project (updated: 'ChEBI').← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 14:32, 25 November 2024 edit undoM97uzivatel (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users6,573 edits added Category:Thioethers using HotCat | ||
| (22 intermediate revisions by 19 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{chembox | {{chembox | ||
| | Verifiedfields = changed | |||
| ⚫ | | verifiedrevid = |
||
| | Watchedfields = changed | |||
| ⚫ | | verifiedrevid = 443553935 | ||
| | ImageFile_Ref = {{chemboximage|correct|??}} | | ImageFile_Ref = {{chemboximage|correct|??}} | ||
| | ImageFile= |
| ImageFile = Cystathionin.svg | ||
| | ImageSize = 220 | |||
| |ImageName=Skeletal formula | |||
| | ImageAlt = Skeletal formula of cystathionine | |||
| |ImageFile1=Cystathionine |
| ImageFile1 = Cystathionine zwitterion 3D ball.png | ||
| |ImageSize1= |
| ImageSize1 = 240px | ||
| |ImageName1=Ball-and-stick model | |||
| | ImageAlt1=Ball-and-stick model of the cystathionine molecule as a zwitterion | |||
| |IUPACName=2-amino-4-(2-amino-2-carboxy-ethyl) thio-butanoic acid | |||
| |OtherNames=<small>L</small>-Cystathionine; ''S''--<small>L</small>-homocysteine | | IUPACName=S-((R)-2-amino-2-carboxyethyl)-L-homocysteine | ||
| | OtherNames=<small>L</small>-Cystathionine; ''S''--<small>L</small>-homocysteine | |||
| |Section1= |
|Section1={{Chembox Identifiers | ||
| | |
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} | ||
| | KEGG = C00542 | | KEGG = C00542 | ||
| | InChI = 1/C7H14N2O4S/c8-4(6(10)11)1-2-14-3-5(9)7(12)13/h4-5H,1-3,8-9H2,(H,10,11)(H,12,13) | | InChI = 1/C7H14N2O4S/c8-4(6(10)11)1-2-14-3-5(9)7(12)13/h4-5H,1-3,8-9H2,(H,10,11)(H,12,13) | ||
| Line 16: | Line 19: | ||
| | ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | | ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | ||
| | ChEMBL = 209241 | | ChEMBL = 209241 | ||
| | StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite| |
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|changed|chemspider}} | ||
| | StdInChI = 1S/C7H14N2O4S/c8-4(6(10)11)1-2-14-3-5(9)7(12)13/h4-5H,1-3,8-9H2,(H,10,11)(H,12,13) | | StdInChI = 1S/C7H14N2O4S/c8-4(6(10)11)1-2-14-3-5(9)7(12)13/h4-5H,1-3,8-9H2,(H,10,11)(H,12,13)/t4-,5-/m0/s1 | ||
| | StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite| |
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|changed|chemspider}} | ||
| | StdInChIKey = ILRYLPWNYFXEMH- |
| StdInChIKey = ILRYLPWNYFXEMH-WHFBIAKZSA-N | ||
| | CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | | CASNo_Ref = {{cascite|correct|CAS}} | ||
| | CASNo=56-88-2 | | CASNo=56-88-2 | ||
| | UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| | UNII = 375YFJ481O | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | PubChem=439258 | ||
| ⚫ | | ChemSpiderID = |
||
| ⚫ | | ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|changed|chemspider}} | ||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | ChemSpiderID = 388392 | ||
| ⚫ | | SMILES = |
||
| | ChEBI_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| ⚫ | | |
||
| ⚫ | | ChEBI = 17755 | ||
| ⚫ | | SMILES = C(CSC(C(=O)O)N)(C(=O)O)N | ||
| ⚫ | | MeSHName=Cystathionine | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| |Section2= |
|Section2={{Chembox Properties | ||
| | C=7|H=14|N=2|O=4|S=1 | |||
| | Formula=C<sub>7</sub>H<sub>14</sub>N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>S | |||
| | Appearance= | |||
| | MolarMass=222.263 g/mol | |||
| | |
| Density= | ||
| | |
| MeltingPt= | ||
| | |
| BoilingPt= | ||
| | |
| Solubility= | ||
| | Solubility= | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| |Section3= |
|Section3={{Chembox Hazards | ||
| | |
| MainHazards= | ||
| | |
| FlashPt= | ||
| | AutoignitionPt = | |||
| | Autoignition= | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Cystathionine''' is an intermediate in the synthesis of ]. | |||
| '''Cystathionine''' is an intermediate in the synthesis of ] from ]. It is produced by the ] and is converted into cysteine by ] (CTH). | |||
| It is cleaved into ] and ] by ]. | Biosynthetically, cystathionine is generated from ] and ] by ] (upper reaction in the diagram below). It is then cleaved into ] and ] by ] (lower reaction). | ||
| An excess in the urine is called ]. | An excess of cystathionine in the urine is called ]. | ||
| ] catalyzes the upper reaction and ] catalyzes the lower reaction.]] | ] catalyzes the upper reaction and ] catalyzes the lower reaction.]]{{clear-left}} | ||
| ] (CDO), and ] can turn cysteine into ] and then ].<ref>{{ Cite journal | author = Harris Ripps, Wen Shen |date = 2012 | title = Review: Taurine: A "very essential" amino acid | journal = Molecular Vision |volume = 18 | pages = 2673–2686 | pmid=23170060 | pmc=3501277}}</ref> Alternately, the cysteine from the cystathionine gamma-lyase can be used by the enzymes ] (GCL) and ] (GSS) to produce ]. | |||
| ⚫ | {{Amino acid metabolism intermediates}} | ||
| ==References== | |||
| {{Reflist}} | |||
| ⚫ | {{Amino acid metabolism intermediates}} | ||
| ] | |||
| {{biochem-stub}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 14:32, 25 November 2024
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
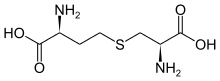
| IUPAC name S-((R)-2-amino-2-carboxyethyl)-L-homocysteine | |
| Other names L-Cystathionine; S--L-homocysteine | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.269 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Cystathionine |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C7H14N2O4S |
| Molar mass | 222.26 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Cystathionine is an intermediate in the synthesis of cysteine from homocysteine. It is produced by the transsulfuration pathway and is converted into cysteine by cystathionine gamma-lyase (CTH).
Biosynthetically, cystathionine is generated from homocysteine and serine by cystathionine beta synthase (upper reaction in the diagram below). It is then cleaved into cysteine and α-ketobutyrate by cystathionine gamma-lyase (lower reaction).
An excess of cystathionine in the urine is called cystathioninuria.
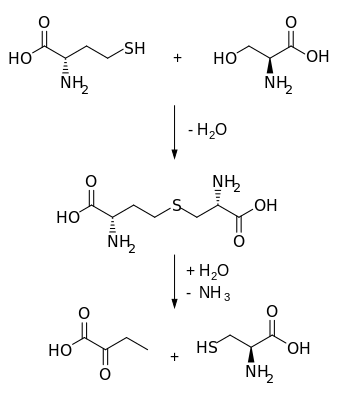
Cysteine dioxygenase (CDO), and sulfinoalanine decarboxylase can turn cysteine into hypotaurine and then taurine. Alternately, the cysteine from the cystathionine gamma-lyase can be used by the enzymes glutamate–cysteine ligase (GCL) and glutathione synthetase (GSS) to produce glutathione.
References
- Harris Ripps, Wen Shen (2012). "Review: Taurine: A "very essential" amino acid". Molecular Vision. 18: 2673–2686. PMC 3501277. PMID 23170060.