| Revision as of 15:42, 25 November 2013 editMike Cline (talk | contribs)Administrators53,120 edits →First travelers and Indian campaigns: fixing redirect to allow better verb use← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 19:45, 11 December 2024 edit undoMissvain (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Administrators235,510 edits Filled in 0 bare reference(s) with reFill 2 | ||
| (152 intermediate revisions by 85 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Protected area}} | |||
| {{Infobox protected area | {{Infobox protected area | ||
| | name = Bozeman Trail | | name = The Bozeman Trail | ||
| | alt_name = | | alt_name = | ||
| | iucn_category = | | iucn_category = | ||
| | photo = Bozeman01.png | | photo = Bozeman01.png | ||
| | photo_alt = | | photo_alt = | ||
| | photo_caption = The Bozeman Trail (in yellow) | | photo_caption = The Bozeman Trail (in yellow). While the route was in use, it largely crossed the 1851 Crow Indian treaty-guaranteed territory west of Powder River. | ||
| | photo_width = 250 | | photo_width = 250 | ||
| | map = | | map = | ||
| Line 13: | Line 15: | ||
| | location = ], ] | | location = ], ] | ||
| | nearest_city = | | nearest_city = | ||
| | lat_d = | |||
| | lat_m = | |||
| | lat_s = | |||
| | lat_NS = | |||
| | long_d = | |||
| | long_m = | |||
| | long_s = | |||
| | long_EW = | |||
| | coords = | | coords = | ||
| | coords_ref = | | coords_ref = | ||
| Line 33: | Line 27: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| The '''Bozeman Trail''' was an overland route connecting the gold rush territory of ] to the ] |
The '''Bozeman Trail''' was an overland route in the ], connecting the ] territory of southern ] to the ] in eastern ]. Its important period was from 1863 to 1868. While the major part of the route used by Bozeman Trail travelers in 1864 was pioneered by Allen Hurlbut, it was named after ].<ref>Moulton, Candy: Susan Badger Doyle's two-volume work on the Bozeman Trail blazes some new ground. (Interview with S.B. Doyle). ''Wild West'', Vol. 14, No. 2 (Aug. 2001), p. 56, column II.</ref> Many miles of the Bozeman Trail in present Montana followed the tracks of ], opened by ] in 1864.<ref>Doyle, Susan Badger (Ed.): Journeys to the Land of Gold. Emigrant Diaries from the Bozeman Trail, 1863-1866. Helena, 2000, Vol. 2, p. 743.</ref> | ||
| The flow of pioneers and settlers through territory of ] provoked fear and anger in the local tribes; some of whom chose to respond with aggressive, and even violent action. The challengers to the route were newly arrived Lakotas and their Native allies, the Arapahoe and the Cheyenne. The United States put emphasis on a right to "establish roads, military and other posts" as described in Article 2 in the Fort Laramie Treaty of 1851. All parties in the conflict had signed that treaty. The Crow Natives held the treaty right to the contested area and had called it their homeland for decades.<ref>Kappler, Charles J.: Indian Affairs. Laws and Treaties. Washington, 1904. Vol. 2, p. 594. http://digital.library.okstate.edu/kappler/Vol2/treaties/sio0594.htm {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140812163225/http://digital.library.okstate.edu/kappler/Vol2/treaties/sio0594.htm |date=2014-08-12 }}. Utley, Robert M.: The Bozeman Trail before John Bozeman: A busy Land. ''Montana, The Magazine of Western History'', Vol. 53, No. 2 (Summer 2003), pp. 20-31.</ref> They sided with the whites. The U.S. Army undertook several military campaigns against the hostile Natives to try to control the trail. Because of its association with frontier history and conflict with American Natives, various segments of the trail are listed on the ] (NRHP). | |||
| == Establishment == | == Establishment == | ||
| In 1863 ] and |
In 1863, ] and John Jacobs scouted for a direct route from ] to central ] to connect with the ], then the major passage to the West Coast. Before this, most access to the southwestern Montana Territory was from ] via the ] to ]. Thence travelers went by the 'Benton Road,' around the ] and through the Chestnut, Hilger and Prickly Pear valleys (current site of ] and ]). | ||
| The overland Bozeman Trail followed many |
The overland Bozeman Trail followed many north–south trails the ] had used since prehistoric times to travel through ]. This route was more direct and better watered than any previous trail into Montana. Bozeman's and Jacobs's most important contribution was to improve the trail so that it was wide enough for wagons. But there was a major drawback — the trail passed directly through territory occupied by the ], ], and ] nations. | ||
| Decades before the Bozeman Trail cut through the plains of present Wyoming, the expanse "... was made busy by Crows and white trappers and traders ...".<ref name="auto">Utley, Robert M.: The Bozeman Trail before John Bozeman: A busy Land. ''Montana, The Magazine of Western History'', Vol. 53, No. 2 (Summer 2003), pp. 20-31, quote p. 20.</ref> According to the ], most of the Bozeman Trail ran across native Crow territory established by treaty.<ref>Kappler, Charles J.: Indian Affairs. Laws and Treaties. Washington, 1904. Vol. 2, p. 594. http://digital.library.okstate.edu/kappler/Vol2/treaties/sio0594.htm {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140812163225/http://digital.library.okstate.edu/kappler/Vol2/treaties/sio0594.htm |date=2014-08-12 }}.</ref> "For the Crows, the Bozeman Trail introduced them to a relationship that would profoundly affect the tribe in coming decades".<ref>Rzeczkowski, Frank: The Crow Indians and the Bozeman Trail. ''Montana, The Magazine of Western History''. Vol. 49, No. 4 (Winter 1999), pp. 30-47, quote p.47.</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | ==First travelers and |
||
| Bozeman led the first group of about 2,000 settlers on the trail in 1864. Indian raids on white settlers increased dramatically from 1864 to 1866, which prompted the U.S. government to order the Army to carry out military campaigns against the ]. ] led several of the earliest campaigns. He defeated the Shoshone at the ] and during the ] of 1865, and he defeated the ] at the ]. | |||
| To complicate the matter, the southeastern part of the 1851 Crow domain was taken over by the Arapahoe, the Cheyenne and the Lakota. They had invaded the western Powder River area during the 1850s and after "large scale battles" won this buffalo rich Native land from the original tribe around 1860.<ref>Medicine Crow, Joseph: From the Heart of the Crow Country. New York, 1992, p. 84. Serial 1308, 40th Congress, 1st Session, Vol. 1, Senate Executive Document No. 13, p. 127.</ref> The principal Bozeman Trail conflict took place along the roughly {{convert|250|mi|km}} of southern wagon wheel tracks through this particular area. Usually, the emigrants could breathe again, when they started on the last nearly {{convert|190|mi|km}} of the trail westward from the crossing of the Bighorn River to the city of Bozeman. | |||
| == The trail and travelers == | |||
| During the few years the trail was open to emigrants, 3,500 traveled it. ] killed between 40 and 50 of them. The short cut was at the time "most often called the road to Montana" and not the Bozeman Trail.<ref>Moulton, Candy: Susan Badger Doyle's two-volume work on the Bozeman Trail blazes some new ground. (Interview with S. B. Doyle). ''Wild West'', Vol. 14, No. 2 (Aug. 2001), p. 56, column I.</ref> While short in bee line, the actual road from the Oregon Trail to the mining towns was much longer due to the hilly and undulating terrain. Shorter or longer stretches of the route were altered every year to avoid the worst stages. The journey took around eight weeks. Many of the travelers had prepared themselves for the arduous trip by reading ]'s popular guidebook. Drowning and fatal accidents with firearms occurred. Some travelers came down with critical diseases such as "mountain fever" (]) and never made it to their destination. Game including elk, mountain sheep and bear was shot an occasion, also buffalo. "The men are killing them in large numbers. I feel sorry to see such destruction. They leave tons of good meat every day to be devoured by wolfs at night", lamented traveler Richard Owen in 1864. The travelers grouped in organized "trains" with chosen people holding posts such as captain, train marshal and orderly sergeant. One group, known as the ], led by Captain ] of Wisconsin, was made up of "wagons ... 150, men ... 375, women ... 36, children ... 36, oxen ... 636".<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Ryan|first=Benjamin|date=July 1864|title=Diary of Benjamin Ryan|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=5DoMf1Uq-tMC&q=benjamin+w.+ryan+diary+of+bozeman+trail+and+trip+to+montana&pg=PA213|journal=Handwritten Journal|volume=NA|pages=NA|isbn=9780917298486}}</ref> Every fifth of those crossing the plains via Bozeman Trail was a woman or a child. Each wagon paid the train pilot, maybe six dollars in 1864. Being a route used by single emigrants and small families at first, the trail transformed towards a supply route with freight wagons carrying equipment and necessities of life to the new, western towns.<ref>Doyle, Susan Badger (Ed.): ''Journeys to the Land of Gold. Emigrant Diaries from the Bozeman Trail, 1863–1866''. Helena, 2000, Vol. 1, p. 1 (total number of travelers); Vol. 1, p. 154 (casualties): Vol. 1, p. XII (altering of route); Vol. 2, p. 744 (guidebook); Vol. 2, p. 759 (mountain fever); Vol. 1, p. 293 (Richard Owen); Vol. 2, p. 767 (organization); Vol. 1, p. 224 (description of train); Vol. 2, p. 435 (ration of women and children); Vol. 1, p. 62 (rate) and Vol 2. p. 435 (freight trains).</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | ==First travelers and Native American campaigns== | ||
| Bozeman led the first wagon train on the trail in 1864. ] was captain of another very large wagon train (over 400 people and 150+ wagons) and had a battle with the ].<ref>{{Cite book|last=Michno|first=Gregory and Susan|title=Circle the Wagons!: Attacks on Wagon Trains in History and Hollywood Films|publisher=McFarland and Company, Inc.|year=1948|isbn=978-0-7864-3997-3|location=Jefferson, North Carolina|pages=96–98}}</ref> Known as the ], the attack occurred on July 7, 1864, with casualties on both sides. Native raids on white settlers increased dramatically from 1864 to 1866, which prompted the U.S. government to order the Army to carry out military campaigns against the ]. ] led several of the earliest campaigns, including the ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.lemhi-shoshone.com/bear-river-massacre.html |title=In remembrance of the Bear River Massacre |work=lemhi-shoshone.com/ |access-date=2013-11-30 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131016144408/http://lemhi-shoshone.com/bear-river-massacre.html |archive-date=2013-10-16 |url-status=dead }}</ref> and the ] of 1865. He also fought the ] at the ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.wyohistory.org/encyclopedia/connor-battlefield |title=Connor Battlefield |publisher=Wyoming State Historical Society |access-date=2013-11-30}}</ref> | |||
| The trail itself diverged from the ] and ]s to the north through the ]. Lieutenant General ] authorized construction of three forts in 1866 to guard travelers on the trail. Soldiers were harassed by the ], at that time led by ] (the United States named the war ] after the Sioux leader). Colonel ] was stationed at a halfway point between ] and the Bozeman Trail, but his well-fortified position was not attacked directly. However, when Captain ], acting against orders, led soldiers in retaliation for attacks against ]; all eighty of Fetterman's men were killed. In the aftermath of the ], the United States agreed, a part of the ], to abandon its forts along the Bozeman Trail.<ref>{{cite book|last=Hogland|first=Alison K.|title=Army Architecture in the West: Forts Laramie, Bridger and D.A. Russell, 1849-1912 |publisher=University of Oklahoma Press|page=20}}</ref> | |||
| ==Post-Civil War travel== | ==Post-Civil War travel== | ||
| In 1866, |
In 1866, after the ] ended, the number of settlers who used the trail en route to Montana gold fields increased. Around 1,200 wagons brought some 2,000 people to the city of Bozeman following the trail that year.<ref>Doyle, Susan Badger (Ed.): Journeys to the Land of Gold. Emigrant Diaries from the Bozeman Trail, 1863-1866. Helena, 2000, Vol. 2, p. 423.</ref> The U.S. Army called a council at ], which ] leader ] attended. The U.S. Army wanted to negotiate a right-of-way with the Lakota for settlers' use of the trail. As negotiations continued, ] became outraged when he discovered that a regiment of U.S. infantry was already using the route without receiving permission from the Lakota nation. Thus ] began. | ||
| ] | |||
| ⚫ | That same year<!--1866-->, ], a successful ], gold miner originally from ], used the Bozeman Trail to successfully ] about |
||
| It was impossible for the army to undertake significant negotiations about the traffic through the western Powder River area and the future use of it with Red Cloud and any other Lakota. In 1851, the United States had acknowledged the tract belonged to the ] and was obliged by that. The Lakota tribe itself had recognized the same.<ref>Kappler, Charles J.: Indian Affairs. Laws and Treaties. Washington, 1904. Vol. 2, p. 594. http://digital.library.okstate.edu/kappler/Vol2/treaties/sio0594.htm {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140812163225/http://digital.library.okstate.edu/kappler/Vol2/treaties/sio0594.htm |date=2014-08-12 }}</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | The Army established ], ] and ] along the route, staffed with troops meant to protect travelers. |
||
| ⚫ | That same year<!--1866-->, ], a successful ], gold miner originally from ], used the Bozeman Trail to successfully ] about 1,000 head of ] into Montana. The U.S. Army unsuccessfully tried to turn Story back to protect the drive from Native American attacks, but Story brought cattle through to the ] and formed one of the earliest significant herds in Montana's cattle industry.<ref name=Kennedy>{{cite book |last=Kennedy |first=Michael S. |title=Cowboys and Cattlemen-A Roundup from Montana The Magazine of Western History |year=1964 |chapter=Tall in the Saddle-First Trail Drive to Montana Territory |publisher=Hastings House Publishing |location=New York |pages=103–111}}</ref> | ||
| ⚫ | Later, by the 1868 ], the |
||
| ⚫ | The U.S. Army established ], ] and ] along the route, staffed with troops meant to protect travelers. All three military posts were built west of Powder River, consequently outside the Lakota territory as recognized by the whites in the Fort Laramie Treaty. " ... the Sioux attacked the United States anyway, claiming that the Yellowstone was now their land".<ref>Hoxie, Frederick E.: Parading Through History. The making of the Crow Nation in America, 1805-1935. Cambridge, 1995, p. 89.</ref> Native American raids along the trail and around the forts continued. When the Lakota annihilated a detachment under ] at the ] near Fort Phil Kearny on December 21, 1866, civilian travel along the trail ceased. On August 1, 1867, and August 2, 1867, U.S. forces resisted coordinated attempts by large parties of Lakota and Cheyenne to overrun ] and ] in the ] and ]. | ||
| ⚫ | ] could thus be said to be the only |
||
| The strikes and attacks on the soldiers "appeared to be a great Sioux war to protect their land. And it was - but the Sioux had only recently conquered this land from other tribes and now defending the territory both from other tribes and from the advance of white settlers".<ref>McGinnis, Anthony: Counting Coup and Cutting Horses. Intertribal Warfare on the Northern Plains, 1738-1889. Evergreen, 1990, p. 114.</ref> "In 1866, Red Cloud and his alliance of Lakotas, Cheyennes, and Arapahos fought for a territory they had dominated for only a few years".<ref name="auto"/> | |||
| The troops in Fort Phil Kearny and Fort C. F. Smith got from time to time warnings of imminent attacks from the Crow, who also brought information about the location of Lakota camps.<ref>Hebard, Grace Raymond and E.A. Brininstool: The Bozeman Trail. Glendale, 1960, p. 160. Templeton, George M.: Diaries, 1866-1868, (typescript), The Newberry Library, Chicago, pp. 55,59, 72 and 99.</ref> The Crows were all but pleased to see a part of their treaty-guaranteed land taken over by hereditary enemies, the Arapahoes, Cheyennes, and Lakotas. Despite resentment against the traffic on the Bozeman Trail, "the Crows still acted as allies of the harassed troops" in the forts.<ref>Rzeczkowski, Frank: The Crow Indians and the Bozeman Trail. ''Montana, The Magazine of Western History''. Vol. 49, No. 4 (Winter 1999), pp. 30-47. Dunlay, Thomas W.: Wolves for the Blue Soldiers. Indian Scouts and Auxiliaries with the United States Army, 1860-1890. Lincoln and London, 1982, p. 39.</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | Later, by the 1868 ], the U.S. recognized the ] as unceded hunting territory for the Lakota and allied tribes. Most was located on former Crow treaty territory, now by conquest converted into new Lakota country.<ref>Kappler, Charles J.: Indian Affairs. Laws and Treaties. Washington, 1904. Vol. 2 pp. 998-1003. {{cite web |url=http://digital.library.okstate.edu/kappler/Vol2/treaties/sio0998.htm |title=INDIAN AFFAIRS: LAWS AND TREATIES. Vol. 2, Treaties |access-date=2011-11-26 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111126131814/http://digital.library.okstate.edu/kappler/Vol2/treaties/sio0998.htm |archive-date=2011-11-26 }}. Compare the 1851 Crow treaty territory with the 1868 unceded Indian territory of the Lakotas.</ref> For a time the government used the treaty to shut down travel by European American settlers on the Bozeman Trail. President ] ordered the abandonment of forts along the trail. | ||
| ⚫ | ] could thus be said to be the only Native American war in which Native Americans achieved their goals (if only for a brief time) with a treaty settlement essentially on their terms. By 1876, however, following the ], the U.S. Army reopened the trail. The U.S. Army continued to use the trail during later military campaigns and built a ] line along it. | ||
| ==Modern route== | ==Modern route== | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| Today, a modern ] route |
Today, a modern ] route covers roughly the same general route as the historic Bozeman Trail. The route consists of ] from ] to ]; ] from Buffalo via ] to ] MT Hwy 84; and ] to ]. | ||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 63: | Line 76: | ||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{ |
{{Reflist}} | ||
| ⚫ | * , Fort Phil Kearny State Historic Site | ||
| == Bibliography == | |||
| ⚫ | * | ||
| ⚫ | * , Fort Phil Kearny State Historic Site | ||
| ⚫ | * | ||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{ |
{{Commons category-inline}} | ||
| ==National Register Listings== | ===National Register Listings=== | ||
| There are nine individual segments of the Bozeman Trail in ] listed on the ]. One segment of the trail in ] is also listed. | There are nine individual segments of the Bozeman Trail in ] listed on the ]. One segment of the trail in ] is also listed. | ||
| {| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 79: | Line 94: | ||
| !State | !State | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| |89000816 | |89000816 | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| |89000818 | |89000818 | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| Line 94: | Line 109: | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | |
|Nine Mile Segment | ||
| |89000813 | |89000813 | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| Line 104: | Line 119: | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| |89000811 | |89000811 | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| |89000812 | |89000812 | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| |89000817 | |89000817 | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| Line 124: | Line 139: | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| |- | |- | ||
| | |
|Yellowstone Crossing | ||
| |78003407 | |78003407 | ||
| |] | |] | ||
| Line 131: | Line 146: | ||
| |} | |} | ||
| {{American frontier}} | |||
| {{Registered Historic Places}} | {{Registered Historic Places}} | ||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:45, 11 December 2024
Protected area| The Bozeman Trail | |
|---|---|
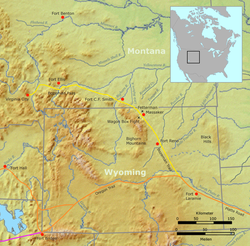 The Bozeman Trail (in yellow). While the route was in use, it largely crossed the 1851 Crow Indian treaty-guaranteed territory west of Powder River. The Bozeman Trail (in yellow). While the route was in use, it largely crossed the 1851 Crow Indian treaty-guaranteed territory west of Powder River. | |
| Location | Montana, Wyoming |
| Governing body | National Park Service |
The Bozeman Trail was an overland route in the Western United States, connecting the gold rush territory of southern Montana to the Oregon Trail in eastern Wyoming. Its important period was from 1863 to 1868. While the major part of the route used by Bozeman Trail travelers in 1864 was pioneered by Allen Hurlbut, it was named after John Bozeman. Many miles of the Bozeman Trail in present Montana followed the tracks of Bridger Trail, opened by Jim Bridger in 1864.
The flow of pioneers and settlers through territory of Native Americans provoked fear and anger in the local tribes; some of whom chose to respond with aggressive, and even violent action. The challengers to the route were newly arrived Lakotas and their Native allies, the Arapahoe and the Cheyenne. The United States put emphasis on a right to "establish roads, military and other posts" as described in Article 2 in the Fort Laramie Treaty of 1851. All parties in the conflict had signed that treaty. The Crow Natives held the treaty right to the contested area and had called it their homeland for decades. They sided with the whites. The U.S. Army undertook several military campaigns against the hostile Natives to try to control the trail. Because of its association with frontier history and conflict with American Natives, various segments of the trail are listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP).
Establishment
In 1863, John Bozeman and John Jacobs scouted for a direct route from Virginia City, Montana to central Wyoming to connect with the Oregon Trail, then the major passage to the West Coast. Before this, most access to the southwestern Montana Territory was from St. Louis via the Missouri River to Fort Benton. Thence travelers went by the 'Benton Road,' around the Great Falls and through the Chestnut, Hilger and Prickly Pear valleys (current site of Helena and Broadwater County, Montana).
The overland Bozeman Trail followed many north–south trails the American Natives had used since prehistoric times to travel through Powder River Country. This route was more direct and better watered than any previous trail into Montana. Bozeman's and Jacobs's most important contribution was to improve the trail so that it was wide enough for wagons. But there was a major drawback — the trail passed directly through territory occupied by the Shoshone, Arapaho, and Lakota nations.
Decades before the Bozeman Trail cut through the plains of present Wyoming, the expanse "... was made busy by Crows and white trappers and traders ...". According to the Fort Laramie Treaty of 1851, most of the Bozeman Trail ran across native Crow territory established by treaty. "For the Crows, the Bozeman Trail introduced them to a relationship that would profoundly affect the tribe in coming decades".
To complicate the matter, the southeastern part of the 1851 Crow domain was taken over by the Arapahoe, the Cheyenne and the Lakota. They had invaded the western Powder River area during the 1850s and after "large scale battles" won this buffalo rich Native land from the original tribe around 1860. The principal Bozeman Trail conflict took place along the roughly 250 miles (400 km) of southern wagon wheel tracks through this particular area. Usually, the emigrants could breathe again, when they started on the last nearly 190 miles (310 km) of the trail westward from the crossing of the Bighorn River to the city of Bozeman.
The trail and travelers
During the few years the trail was open to emigrants, 3,500 traveled it. Natives killed between 40 and 50 of them. The short cut was at the time "most often called the road to Montana" and not the Bozeman Trail. While short in bee line, the actual road from the Oregon Trail to the mining towns was much longer due to the hilly and undulating terrain. Shorter or longer stretches of the route were altered every year to avoid the worst stages. The journey took around eight weeks. Many of the travelers had prepared themselves for the arduous trip by reading John Lyle Campbell's popular guidebook. Drowning and fatal accidents with firearms occurred. Some travelers came down with critical diseases such as "mountain fever" (Colorado tick fever) and never made it to their destination. Game including elk, mountain sheep and bear was shot an occasion, also buffalo. "The men are killing them in large numbers. I feel sorry to see such destruction. They leave tons of good meat every day to be devoured by wolfs at night", lamented traveler Richard Owen in 1864. The travelers grouped in organized "trains" with chosen people holding posts such as captain, train marshal and orderly sergeant. One group, known as the Townsend Wagon Train, led by Captain A. A. Townsend of Wisconsin, was made up of "wagons ... 150, men ... 375, women ... 36, children ... 36, oxen ... 636". Every fifth of those crossing the plains via Bozeman Trail was a woman or a child. Each wagon paid the train pilot, maybe six dollars in 1864. Being a route used by single emigrants and small families at first, the trail transformed towards a supply route with freight wagons carrying equipment and necessities of life to the new, western towns.
First travelers and Native American campaigns
Bozeman led the first wagon train on the trail in 1864. Abasalom Austin Townsend was captain of another very large wagon train (over 400 people and 150+ wagons) and had a battle with the Natives. Known as the Townsend Wagon Train Fight, the attack occurred on July 7, 1864, with casualties on both sides. Native raids on white settlers increased dramatically from 1864 to 1866, which prompted the U.S. government to order the Army to carry out military campaigns against the Shoshone. Patrick Edward Connor led several of the earliest campaigns, including the Bear River Massacre. and the Powder River Expedition of 1865. He also fought the Arapaho at the Battle of the Tongue River.
The trail itself diverged from the Oregon and California Trails to the north through the Powder River. Lieutenant General William Tecumseh Sherman authorized construction of three forts in 1866 to guard travelers on the trail. Soldiers were harassed by the Sioux, at that time led by Red Cloud (the United States named the war Red Cloud's War after the Sioux leader). Colonel Henry B. Carrington was stationed at a halfway point between Fort Laramie and the Bozeman Trail, but his well-fortified position was not attacked directly. However, when Captain William J. Fetterman, acting against orders, led soldiers in retaliation for attacks against Fort Phil Kearny; all eighty of Fetterman's men were killed. In the aftermath of the Fetterman Fight, the United States agreed, a part of the Fort Laramie Treaty of 1868, to abandon its forts along the Bozeman Trail.
Post-Civil War travel
In 1866, after the American Civil War ended, the number of settlers who used the trail en route to Montana gold fields increased. Around 1,200 wagons brought some 2,000 people to the city of Bozeman following the trail that year. The U.S. Army called a council at Fort Laramie, which Lakota leader Red Cloud attended. The U.S. Army wanted to negotiate a right-of-way with the Lakota for settlers' use of the trail. As negotiations continued, Red Cloud became outraged when he discovered that a regiment of U.S. infantry was already using the route without receiving permission from the Lakota nation. Thus Red Cloud's War began.

It was impossible for the army to undertake significant negotiations about the traffic through the western Powder River area and the future use of it with Red Cloud and any other Lakota. In 1851, the United States had acknowledged the tract belonged to the Crow and was obliged by that. The Lakota tribe itself had recognized the same.
That same year, Nelson Story, a successful Virginia City, Montana, gold miner originally from Ohio, used the Bozeman Trail to successfully drive about 1,000 head of longhorn cattle into Montana. The U.S. Army unsuccessfully tried to turn Story back to protect the drive from Native American attacks, but Story brought cattle through to the Gallatin Valley and formed one of the earliest significant herds in Montana's cattle industry.
The U.S. Army established Fort Reno, Fort Phil Kearny and Fort C. F. Smith along the route, staffed with troops meant to protect travelers. All three military posts were built west of Powder River, consequently outside the Lakota territory as recognized by the whites in the Fort Laramie Treaty. " ... the Sioux attacked the United States anyway, claiming that the Yellowstone was now their land". Native American raids along the trail and around the forts continued. When the Lakota annihilated a detachment under William J. Fetterman at the Fetterman Fight near Fort Phil Kearny on December 21, 1866, civilian travel along the trail ceased. On August 1, 1867, and August 2, 1867, U.S. forces resisted coordinated attempts by large parties of Lakota and Cheyenne to overrun Fort C. F. Smith and Fort Phil Kearny in the Hayfield Fight and Wagon Box Fight.
The strikes and attacks on the soldiers "appeared to be a great Sioux war to protect their land. And it was - but the Sioux had only recently conquered this land from other tribes and now defending the territory both from other tribes and from the advance of white settlers". "In 1866, Red Cloud and his alliance of Lakotas, Cheyennes, and Arapahos fought for a territory they had dominated for only a few years".
The troops in Fort Phil Kearny and Fort C. F. Smith got from time to time warnings of imminent attacks from the Crow, who also brought information about the location of Lakota camps. The Crows were all but pleased to see a part of their treaty-guaranteed land taken over by hereditary enemies, the Arapahoes, Cheyennes, and Lakotas. Despite resentment against the traffic on the Bozeman Trail, "the Crows still acted as allies of the harassed troops" in the forts.
Later, by the 1868 Treaty of Fort Laramie, the U.S. recognized the Powder River Country as unceded hunting territory for the Lakota and allied tribes. Most was located on former Crow treaty territory, now by conquest converted into new Lakota country. For a time the government used the treaty to shut down travel by European American settlers on the Bozeman Trail. President Ulysses S. Grant ordered the abandonment of forts along the trail.
Red Cloud's War could thus be said to be the only Native American war in which Native Americans achieved their goals (if only for a brief time) with a treaty settlement essentially on their terms. By 1876, however, following the Black Hills War, the U.S. Army reopened the trail. The U.S. Army continued to use the trail during later military campaigns and built a telegraph line along it.
Modern route

Today, a modern highway route covers roughly the same general route as the historic Bozeman Trail. The route consists of Interstate 25 from Douglas, Wyoming to Buffalo, Wyoming; Interstate 90 from Buffalo via Sheridan, Wyoming to Bozeman, Montana MT Hwy 84; and U.S. Route 287 to Virginia City, Montana.
See also
References
- Moulton, Candy: Susan Badger Doyle's two-volume work on the Bozeman Trail blazes some new ground. (Interview with S.B. Doyle). Wild West, Vol. 14, No. 2 (Aug. 2001), p. 56, column II.
- Doyle, Susan Badger (Ed.): Journeys to the Land of Gold. Emigrant Diaries from the Bozeman Trail, 1863-1866. Helena, 2000, Vol. 2, p. 743.
- Kappler, Charles J.: Indian Affairs. Laws and Treaties. Washington, 1904. Vol. 2, p. 594. http://digital.library.okstate.edu/kappler/Vol2/treaties/sio0594.htm Archived 2014-08-12 at the Wayback Machine. Utley, Robert M.: The Bozeman Trail before John Bozeman: A busy Land. Montana, The Magazine of Western History, Vol. 53, No. 2 (Summer 2003), pp. 20-31.
- ^ Utley, Robert M.: The Bozeman Trail before John Bozeman: A busy Land. Montana, The Magazine of Western History, Vol. 53, No. 2 (Summer 2003), pp. 20-31, quote p. 20.
- Kappler, Charles J.: Indian Affairs. Laws and Treaties. Washington, 1904. Vol. 2, p. 594. http://digital.library.okstate.edu/kappler/Vol2/treaties/sio0594.htm Archived 2014-08-12 at the Wayback Machine.
- Rzeczkowski, Frank: The Crow Indians and the Bozeman Trail. Montana, The Magazine of Western History. Vol. 49, No. 4 (Winter 1999), pp. 30-47, quote p.47.
- Medicine Crow, Joseph: From the Heart of the Crow Country. New York, 1992, p. 84. Serial 1308, 40th Congress, 1st Session, Vol. 1, Senate Executive Document No. 13, p. 127.
- Moulton, Candy: Susan Badger Doyle's two-volume work on the Bozeman Trail blazes some new ground. (Interview with S. B. Doyle). Wild West, Vol. 14, No. 2 (Aug. 2001), p. 56, column I.
- Ryan, Benjamin (July 1864). "Diary of Benjamin Ryan". Handwritten Journal. NA: NA. ISBN 9780917298486.
- Doyle, Susan Badger (Ed.): Journeys to the Land of Gold. Emigrant Diaries from the Bozeman Trail, 1863–1866. Helena, 2000, Vol. 1, p. 1 (total number of travelers); Vol. 1, p. 154 (casualties): Vol. 1, p. XII (altering of route); Vol. 2, p. 744 (guidebook); Vol. 2, p. 759 (mountain fever); Vol. 1, p. 293 (Richard Owen); Vol. 2, p. 767 (organization); Vol. 1, p. 224 (description of train); Vol. 2, p. 435 (ration of women and children); Vol. 1, p. 62 (rate) and Vol 2. p. 435 (freight trains).
- Michno, Gregory and Susan (1948). Circle the Wagons!: Attacks on Wagon Trains in History and Hollywood Films. Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland and Company, Inc. pp. 96–98. ISBN 978-0-7864-3997-3.
- "In remembrance of the Bear River Massacre". lemhi-shoshone.com/. Archived from the original on 2013-10-16. Retrieved 2013-11-30.
- "Connor Battlefield". Wyoming State Historical Society. Retrieved 2013-11-30.
- Hogland, Alison K. Army Architecture in the West: Forts Laramie, Bridger and D.A. Russell, 1849-1912. University of Oklahoma Press. p. 20.
- Doyle, Susan Badger (Ed.): Journeys to the Land of Gold. Emigrant Diaries from the Bozeman Trail, 1863-1866. Helena, 2000, Vol. 2, p. 423.
- Kappler, Charles J.: Indian Affairs. Laws and Treaties. Washington, 1904. Vol. 2, p. 594. http://digital.library.okstate.edu/kappler/Vol2/treaties/sio0594.htm Archived 2014-08-12 at the Wayback Machine
- Kennedy, Michael S. (1964). "Tall in the Saddle-First Trail Drive to Montana Territory". Cowboys and Cattlemen-A Roundup from Montana The Magazine of Western History. New York: Hastings House Publishing. pp. 103–111.
- Hoxie, Frederick E.: Parading Through History. The making of the Crow Nation in America, 1805-1935. Cambridge, 1995, p. 89.
- McGinnis, Anthony: Counting Coup and Cutting Horses. Intertribal Warfare on the Northern Plains, 1738-1889. Evergreen, 1990, p. 114.
- Hebard, Grace Raymond and E.A. Brininstool: The Bozeman Trail. Glendale, 1960, p. 160. Templeton, George M.: Diaries, 1866-1868, (typescript), The Newberry Library, Chicago, pp. 55,59, 72 and 99.
- Rzeczkowski, Frank: The Crow Indians and the Bozeman Trail. Montana, The Magazine of Western History. Vol. 49, No. 4 (Winter 1999), pp. 30-47. Dunlay, Thomas W.: Wolves for the Blue Soldiers. Indian Scouts and Auxiliaries with the United States Army, 1860-1890. Lincoln and London, 1982, p. 39.
- Kappler, Charles J.: Indian Affairs. Laws and Treaties. Washington, 1904. Vol. 2 pp. 998-1003. "INDIAN AFFAIRS: LAWS AND TREATIES. Vol. 2, Treaties". Archived from the original on 2011-11-26. Retrieved 2011-11-26.. Compare the 1851 Crow treaty territory with the 1868 unceded Indian territory of the Lakotas.
Bibliography
- "Bozeman Trail History", Fort Phil Kearny State Historic Site
- Grace Raymond Hebard, et al., The Bozeman Trail: Historical Accounts of the Blazing of the Overland Routes, Volume II
External links
![]() Media related to Bozeman Trail at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Bozeman Trail at Wikimedia Commons
National Register Listings
There are nine individual segments of the Bozeman Trail in Wyoming listed on the National Register of Historic Places. One segment of the trail in Montana is also listed.
| NRHP Place | NRHP Number | County | State |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antelope Creek Crossing | 89000816 | Converse | Wyoming |
| Holdup Hollow Segment | 89000818 | Converse | Wyoming |
| Lake Desmet Segment | 89000814 | Johnson | Wyoming |
| Nine Mile Segment | 89000813 | Campbell | Wyoming |
| Powder River Station | 89000810 | Campbell | Wyoming |
| Ross Flat Segment | 89000811 | Converse | Wyoming |
| Sage Creek Station | 89000812 | Converse | Wyoming |
| Stinking Water Gulch Segment | 89000817 | Converse | Wyoming |
| Trabing Station-Crazy Woman Crossing | 89000815 | Johnson | Wyoming |
| Yellowstone Crossing | 78003407 | Sweet Grass | Montana |
| U.S. National Register of Historic Places | |
|---|---|
| Topics | |
| Lists by state |
|
| Lists by insular areas | |
| Lists by associated state | |
| Other areas | |
| Related | |