| Revision as of 17:30, 15 February 2015 view sourceRacerx11 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers40,155 editsm Reverted edits by 193.83.59.144 (talk) to last version by Jeppiz← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 15:20, 18 December 2024 view source Quindraco (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users2,967 editsNo edit summaryTags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Island country in South Asia}} | |||
| {{Use British English|date=February 2012}} | |||
| {{Redirect|Maldive Islands||Maldives (disambiguation)}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=January 2014}} | |||
| {{Pp|small=yes}} | |||
| {{Pp-move|small=yes}} | |||
| {{Use British English|date=June 2024}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=June 2024}} | |||
| {{Infobox country | {{Infobox country | ||
| |conventional_long_name = Republic of |
| conventional_long_name = Republic of Maldives | ||
| | common_name = Maldives | |||
| |native_name = {{raise|0.2em|{{lang|dv|ދިވެހިރާއްޖޭގެ ޖުމްހޫރިއްޔާ}}}}<br/>''Dhivehi Raajjeyge Jumhooriyya'' | |||
| | native_name = {{unbulleted list|{{native name|dv|ދިވެހިރާއްޖޭގެ ޖުމްހޫރިއްޔާ|italics=no}}<br />{{transliteration|dv|''Dhivehi Raajjeyge Jumhooriyyaa''}}<br />}} | |||
| |common_name = Maldives | |||
| | |
| image_coat = Emblem of Maldives.svg | ||
| | |
| image_flag = Flag of the Maldives.svg | ||
| | flag_type_article = Flag of the Maldives | |||
| |symbol_type = Emblem | |||
| | symbol_type = Emblem | |||
| |image_map = Maldives (orthographic projection).svg | |||
| | symbol_type_article = Emblem of the Maldives | |||
| |map_caption = Location of Maldives in the ]. | |||
| | national_motto = {{native phrase|ar|الدولة المحلديبية}}<br/>{{transliteration|dv|]}}<br />"State of the Mahal Dibiyat"<ref name = "MVEmblems">{{cite web |url=http://www.un.int/maldives/emble.htm |title=National Emblems of the Maldives |access-date=29 October 2010|url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110606135502/http://www.un.int/maldives/emble.htm |archive-date=6 June 2011 |website=Maldives Mission to the United Nations}}</ref> | |||
| |national_anthem = '']''<br/>{{small|''National Salute''}}<br/><center>]</center> | |||
| | national_anthem = {{native phrase|dv|ޤައުމީ ސަލާމް}}<br/>{{transliteration|dv|]}}<br />"National Salute"{{parabr}}{{center|]}} | |||
| |official_languages = ] | |||
| | image_map = {{Switcher|]|Show globe|]|Show map of Maldives|default=1}} | |||
| |religion = ] | |||
| | capital = ] | |||
| |official_religion = ] | |||
| | coordinates = {{coord|4|10|31|N|73|30|32|E|}} | |||
| |demonym = Maldivian | |||
| | largest_city = Malé | |||
| |ethnic_groups = ≈100% ]<sup>a</sup><ref>{{cite book |url=http://books.google.mv/books?id=uwi-rv3VV6cC&q=maldives |title=Ethnic groups worldwide: a ready reference handbook |author=Levinson, David |year=1947 |publisher=Oryx Publishers |isbn=978-1-57356-019-1}}</ref><ref name="Maloney, Clarence"/><ref name=r1/> | |||
| | languages_type = Official language<br/> {{Nobold|and national language}} | |||
| |ethnic_groups_year = 2011 | |||
| | languages = ] | |||
| |capital = ] | |||
| | languages2_type = Common languages | |||
| |religion = ] | |||
| | languages2 = ] | |||
| |latd=4 |latm=10 |lats=27.11 |latNS=N |longd=73 |longm=30 |longs=38.29 |longEW=E | |||
| | religion = {{Tree list}} | |||
| |largest_city = ] | |||
| * 98.7% ] | |||
| |government_type = ] ] ] | |||
| ** 98.58% ] (]) | |||
| |leader_title1 = ] | |||
| ** 0.10% ] | |||
| |leader_name1 = ] | |||
| * 1.3% ] | |||
| |leader_title2 = ] | |||
| ** 0.05% ] | |||
| |leader_name2 = ] | |||
| ** 0.29% ] | |||
| |leader_title3 = ] | |||
| {{Tree list/end}} | |||
| |leader_name3 = ]<ref>{{cite web|title=Speaker of People's Majlis|url=http://www.majlis.gov.mv/en/2014/05/28/eighteenth-peoples-majlis-elects-speaker-and-deputy-speaker/|website=http://www.majlis.gov.mv/|publisher=People’s Majlis|accessdate=18 June 2014|ref=http://www.majlis.gov.mv/en/2014/05/28/eighteenth-peoples-majlis-elects-speaker-and-deputy-speaker/}}</ref> | |||
| | religion_ref = <ref name="religion">{{cite web |title=Regional Profiles: Maldives |url=https://www.thearda.com/world-religion/national-profiles?u=140c |website=The Association of Religion Data Archives |publisher=World Religion Database |access-date=18 May 2024 |archive-date=6 May 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240506192929/https://thearda.com/world-religion/national-profiles?u=140c |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| |leader_title4 = ] | |||
| | demonym = Maldivian | |||
| |leader_name4 = </ref>]] | |||
| | government_type = Unitary ] | |||
| |legislature = ] | |||
| | leader_title1 = ] | |||
| |area_rank = 206th | |||
| | leader_name1 = ] | |||
| |area_magnitude = 1 E6 | |||
| | leader_title2 = ] | |||
| |area_km2 = 298 | |||
| | leader_name2 = ] | |||
| |area_sq_mi = 115 <!--Do not remove per ]--> | |||
| | leader_title3 = ] | |||
| |percent_water = ≈99 | |||
| | leader_name3 = ] | |||
| |population_estimate = 393,500<ref>{{cite web |title=Maldives|work=CIA World Factbook |url=https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/mv.html}}</ref> | |||
| | leader_title4 = ] | |||
| |population_estimate_rank = 175th | |||
| | leader_name4 = ] | |||
| |population_estimate_year = July 2013 | |||
| | leader_title5 = | |||
| |population_density_km2 = 1,102.5 | |||
| | leader_name5 = | |||
| |population_density_sq_mi = 2,855.4 <!--Do not remove per ]--> | |||
| | legislature = ] | |||
| |population_density_rank = 11th | |||
| | sovereignty_type = ] | |||
| |GDP_PPP = $2.841 billion<ref name=imf2>{{cite web |url=http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/weorept.aspx?pr.x=44&pr.y=4&sy=2009&ey=2012&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=556&s=NGDPD%2CNGDPDPC%2CPPPGDP%2CPPPPC%2CLP&grp=0&a= |title=Maldives |publisher=International Monetary Fund |accessdate=19 April 2012}}</ref> | |||
| | sovereignty_note = from the ] | |||
| |GDP_PPP_rank = 162nd | |||
| | established_event1 = ] | |||
| |GDP_PPP_year = 2011 | |||
| | established_date1 = 26 July 1965 | |||
| |GDP_PPP_per_capita = $8,731<ref name=imf2/> <!--Do not edit!--> | |||
| | established_event2 = First Republic | |||
| |GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 89th | |||
| | established_date2 = 1 January 1953 | |||
| |GDP_nominal = $1.944 billion<ref name=imf2/> | |||
| | established_event3 = Second Republic | |||
| |GDP_nominal_year = 2011 | |||
| | established_date3 = 11 November 1968 | |||
| |GDP_nominal_per_capita = $5,973<ref name=imf2/> | |||
| | established_event4 = {{nowrap|]}} | |||
| |sovereignty_type = ] | |||
| | established_date4 = 7 August 2008 | |||
| |established_event1 = from the ] | |||
| | area_km2 = 298 | |||
| |established_date1 = 26 July 1965 | |||
| | area_sq_mi = 115 <!--Do not remove per ]--> | |||
| |established_event2 = {{nowrap|]}} | |||
| | area_footnote = {{efn|The total area, including its ] territory is approximately 89,999 square kilometers, behind ] (89,342 square kilometers) and ahead of Portugal (92,220 square kilometers). With the EEZ, the Maldives would be the ].<ref>{{cite web |title=Economic Profile |url=https://maldivesmission.ch/index.php/economy-trade/economic-profile |website=Embassy of the Republic of Maldives |access-date=13 August 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220813150531/https://maldivesmission.ch/index.php/economy-trade/economic-profile |archive-date=13 August 2022 |url-status=live}}</ref>}}<ref name="CIA World Factbook">{{Cite web|title=Maldives|url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/maldives/#geography|access-date=30 November 2023|website=]|publisher=]|archive-date=29 July 2022|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220729125757/https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/maldives/#geography|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| |established_date2 = 7 August 2008 | |||
| | area_rank = 187th <!-- Should match ] --> | |||
| |Gini_year = 1998 | |||
| | population_census = 515,132<ref>{{Cite web|title=Census Results Summary|url=https://census.gov.mv/2022/census-results-summary/|access-date=2023-11-30|website=Maldives Population and Housing Census|publisher=National Bureau of Statistics|language=en|archive-date=1 September 2023|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230901163925/https://census.gov.mv/2022/census-results-summary/|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| |Gini_change = <!--increase/decrease/steady--> | |||
| | population_census_rank = 167th | |||
| |Gini = 62.7 <!--number only--> | |||
| | population_census_year = 2022 | |||
| |Gini_ref = <ref name=gini-index>{{cite web|title=GINI index|url=http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.GINI?order=wbapi_data_value_2002+wbapi_data_value+wbapi_data_value-last&sort=asc&page=2|publisher=World Bank|accessdate=26 July 2013}}</ref> | |||
| | population_density_km2 = 1,728.63 | |||
| |Gini_rank = | |||
| | population_density_sq_mi = 4,479.41 <!--Do not remove per ]--> | |||
| |HDI_year = 2013 <!--Please use the year to which the HDI data refers, not the publication year--> | |||
| | population_density_rank = 7th <!--should match ]--> | |||
| |HDI_change = steady<!--increase/decrease/steady--> | |||
| | GDP_PPP = {{increase}} $15.827 billion<ref name="IMFWEO.MV">{{cite web |url=https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2023/October/weo-report?c=556,&s=NGDPD,PPPGDP,NGDPDPC,PPPPC,&sy=2020&ey=2028&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1 |title=World Economic Outlook Database, October 2023 Edition. (Maldives) |website=] |date=10 October 2023 |access-date=19 October 2023 |archive-date=29 October 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231029142054/https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2023/October/weo-report?c=556,&s=NGDPD,PPPGDP,NGDPDPC,PPPPC,&sy=2020&ey=2028&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| |HDI = 0.698 <!--number only--> | |||
| | GDP_PPP_year = 2024 | |||
| |HDI_ref = <ref name="HDI">{{cite web |url=http://hdr.undp.org/sites/default/files/hdr14-summary-en.pdf |title=2014 Human Development Report Summary |date=2014 |accessdate=27 July 2014 |publisher=United Nations Development Programme | pages=21–25}}</ref> | |||
| | GDP_PPP_rank = 157th | |||
| |HDI_rank = 103rd | |||
| | GDP_PPP_per_capita = {{increase}} $39,173<ref name="IMFWEO.MV" /><!--Do not edit!--> | |||
| |currency = ] | |||
| | GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 54th | |||
| |currency_code = MVR | |||
| | GDP_nominal = {{increase}} $7.502 billion<ref name="IMFWEO.MV" /> | |||
| |country_code = | |||
| | GDP_nominal_year = 2024 | |||
| |time_zone = MVT | |||
| | GDP_nominal_rank = 161st | |||
| |utc_offset = +5 | |||
| | GDP_nominal_per_capita = {{increase}} $18,568<ref name="IMFWEO.MV" /> | |||
| |time_zone_DST = |utc_offset_DST = | |||
| | GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = 58th | |||
| |drives_on = ] | |||
| | Gini = 31.3 <!--number only--> | |||
| |date_format = dd/mm/yy | |||
| | Gini_year = 2024 | |||
| |calling_code = ] | |||
| | Gini_change = decrease<!--increase/decrease/steady--> | |||
| |cctld = ] | |||
| | Gini_ref = <ref name="wb-gini">{{Cite web |title=Gini Index coefficient |url=https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/field/gini-index-coefficient-distribution-of-family-income/country-comparison/ |access-date=16 July 2021 |publisher=] |website=] |archive-date=17 July 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210717071854/https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/field/gini-index-coefficient-distribution-of-family-income/country-comparison |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| |footnote_a = Excluding foreign nationals. | |||
| | Gini_rank = | |||
| | HDI = 0.762 | |||
| | HDI_year = 2022<!--Please use the year to which the HDI data refers, not the publication year--> | |||
| | HDI_change = increase<!--increase/decrease/steady--> | |||
| | HDI_ref = <ref name="UNHDR">{{cite web |url=https://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2023-24reporten.pdf |title=Human Development Report 2023/24 |language=en |website=] |date=13 March 2024 |access-date=13 March 2024 |archive-date=13 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240313164319/https://hdr.undp.org/system/files/documents/global-report-document/hdr2023-24reporten.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| | HDI_rank = 87th | |||
| | currency = ] (]){{Efn| | |||
| The Maldives predominantly utilizes the Maldivian Rufiyaa (MVR) as its official currency. However, ] are commonly accepted in tourist establishments due to the high number of visitors from USD-based countries.}} | |||
| | time_zone = ] | |||
| | utc_offset = +5 | |||
| | utc_offset_DST = | |||
| | time_zone_DST = | |||
| | calling_code = ] | |||
| | cctld = ] | |||
| | footnote_a = | |||
| | country_code = | |||
| | today = | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Maldives''',{{ |
The '''Maldives''',{{Efn|{{IPAc-en|ˈ|m|ɔː|l|d|i|v|z|audio=British English Maldives pronunciation.ogg}} {{respell|MAWL|deevz}}; {{langx|dv|ދިވެހިރާއްޖެ|translit=Dhivehi Raajje}}, {{IPA|dv|diʋehi ɾaːd͡ʒːe|pron}}.}} officially the '''Republic of Maldives''',{{Efn|{{langx|dv|ދިވެހިރާއްޖޭގެ ޖުމްހޫރިއްޔާ|translit=Dhivehi Raajjeyge Jumhooriyyaa|label=none}}, {{IPA|dv|diʋehi ɾaːd͡ʒːeːge d͡ʒumhuːɾijjaː|pron}}.}} and historically known as the '''Maldive Islands''', is a country and ] in ] in the ]. The Maldives is southwest of ] and ], about {{convert|750|km|mi nmi|abbr=off}} from the Asian continent's mainland. The Maldives' chain of ] stretches across the equator from ] in the north to ] in the south. | ||
| The Maldives is the smallest ]. Including the sea, the territory spans roughly {{convert|90,000|km2}}, with a land area of {{convert|298|km2}}. The Maldives is one of the world's most geographically dispersed sovereign states. With a population of 515,132 in the 2022 census, it is the second ] and the ], but also one of the ]. The Maldives has an average ground-level elevation of {{convert|1.5|m}} above sea level,<ref name="guardian.co.uk">{{Cite news |last=Henley |first=Jon |date=11 November 2008 |title=The last days of paradise |work=] |location=] |url=https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2008/nov/11/climatechange-endangered-habitats-maldives |url-status=live |access-date=12 May 2010 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130904050657/http://www.theguardian.com/environment/2008/nov/11/climatechange-endangered-habitats-maldives |archive-date=4 September 2013 |quote= holds the record for the country with the lowest high point on earth: nowhere on any of the islands on Maldives does the natural ground level exceed 5.1m. Most of land mass, which totals roughly one-fifth of Greater London, is a great deal lower , averaging around 1.5m.}}</ref> and a ] of only {{convert|2.4|m}}, making it the world's lowest-lying country. Some sources state the highest point, ], as {{convert|5.1|m|disp=or}}.<ref name="guardian.co.uk" /> | |||
| Maldives has been an independent ] for the majority of its history, except for three periods in which it was ruled by outside forces. In the mid-16th century, for fifteen years, the Maldives was dominated by the ]. In the mid-17th century, the ] (]) dominated Maldives for four months. Finally, in the late 19th century, on the brink of war, the Maldives became a ] protectorate from 1887 until 1965. The Dutch referred to the islands as the "Maldivische Eilanden" ({{IPA-nl|mɑlˈdivisə ˈɛi̯lɑndə(n)|pron}}), while the British ] the local name for the islands first to the "Maldive Islands" and later to the "Maldives". The islands gained ] from the ] in 1965, and in 1968 became a republic ruled by a ] and an ] government. | |||
| ] is the capital and the most populated city, traditionally called the "King's Island", where the ancient ] ruled from its central location.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Male | Geography, Facts, & Points of Interest |url=https://www.britannica.com/place/Male-island-Maldives |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164340/https://www.britannica.com/place/Male-island-Maldives |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=11 June 2020 |website=]}}</ref> The Maldives has been inhabited for over 2,500 years. Documented contact with the outside world began around 947 AD when ] travelers began visiting the islands. In the 12th century, partly due to the importance of the Arabs and ] as traders in the Indian Ocean, Islam reached the Maldivian Archipelago.<ref>{{cite web |title=Home |url=http://www.maldivesmission.com/history |access-date=15 May 2024 |website=Permanent Mission of the Republic of the Maldives to the United Nations |archive-date=15 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240315215145/http://maldivesmission.com/history |url-status=live }}</ref> The Maldives was soon consolidated as a ], developing strong commercial and cultural ties with ] and ]. From the mid-16th century, the region came under the increasing influence of European ], with the Maldives becoming a British ] in 1887. ] came in 1965, and a ] was established in 1968 with an elected People's Majlis. The ensuing decades have seen political instability, efforts at democratic reform,<ref>{{Cite web |date=21 January 2015 |title=Maldives – Country report – Freedom in the World – 2015 |url=https://freedomhouse.org/report/freedom-world/2015/maldives |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160814024354/https://freedomhouse.org/report/freedom-world/2015/maldives |archive-date=14 August 2016 |access-date=19 June 2016 |website=]}}</ref> and environmental challenges posed by ].<ref>{{Cite report |url=https://unfccc.int/resource/docs/napa/mdv01.pdf |title=National Adaptation Program of Action: Republic of Maldives |date=2007 |access-date=24 February 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164316/https://unfccc.int/resource/docs/napa/mdv01.pdf |archive-date=14 January 2021 |url-status=live |institution=Ministry of Environment, Energy and Water}}</ref> The Maldives became a founding member of the ] (SAARC). | |||
| The Maldives archipelago is located atop the ], a vast submarine mountain range in the Indian Ocean. Maldives also form a ] together with the Chagos and the Lakshadweep.<ref>{{NatGeo ecoregion |id=im0125 |name=Maldives-Lakshadweep-Chagos Archipelago tropical moist forests |accessdate=30 December 2010}}</ref> The Maldives atolls encompass a ] spread over roughly {{convert|90000|km2}}, making the country one of the world's most geographically dispersed. Its population of 328,536 (2012) inhabits 192 of its 1,192 islands.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.smartmaldives.com/maldives-island.html |title=Lets learn more about Maldives Island |publisher=Smartmaldives.com |accessdate=30 June 2010}}</ref> In 2006, Maldives' capital and largest city ], located at the southern edge of ], had a population of 103,693.<ref>{{cite web|author=Ministry of Health and Family (MoHF) |url=http://data.worldbank.org/country/maldives |title=Maldives |publisher=The World Bank |date=28 February 2013 |accessdate=2 April 2013}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Table 3.3 Population by Atoll |url=http://planning.gov.mv/yearbook 2009/Populations/3.3. htm |publisher=Department of National Planning |accessdate=1 September 2011}}</ref> Malé is one of ] and, traditionally, it was the "King's Island" where the ancient Maldives royal dynasties were enthroned. | |||
| The Maldives is a member of the ], the ], the ], and the ]. The World Bank classifies the Maldives as having an upper-] economy.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Data for Upper middle income, Maldives |url=https://data.worldbank.org/?locations=XT-MV |access-date=15 May 2024 |website=] |archive-date=15 May 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240515151057/https://data.worldbank.org/?locations=XT-MV |url-status=live }}</ref> The Maldives is a Dialogue Partner of the ].<ref>{{Cite news |date=1 August 2022 |title=Nepal, Maldives To Join Shanghai Cooperation Organisation.As Observer |url=https://www.spotlightnepal.com/2022/08/01/nepal-maldives-join-shanghai-cooperation-organisation-observer/ |work=Spotlight |agency=Xinhua News Agency |access-date=18 May 2024 |archive-date=15 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240315172504/https://www.spotlightnepal.com/2022/08/01/nepal-maldives-join-shanghai-cooperation-organisation-observer/ |url-status=live }}</ref> ] has historically been the dominant economic activity, and remains the largest sector by far, followed by the rapidly growing ] industry. The Maldives rates "high" on the ],<ref name="HDI">{{Cite book |url=http://hdr.undp.org/sites/default/files/hdr2020.pdf |title=Human Development Report 2020 The Next Frontier: Human Development and the Anthropocene |date=15 December 2020 |publisher=United Nations Development Programme |isbn=978-92-1-126442-5 |pages=343–346 |access-date=16 December 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210102202739/http://hdr.undp.org/sites/default/files/hdr2020.pdf |archive-date=2 January 2021 |url-status=dead}}</ref> with '']'' income significantly higher than other SAARC nations.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2016 |title=2016 Human Development Report Statistical Annex |url=http://hdr.undp.org/sites/default/files/hdr_2016_statistical_annex.pdf |access-date=4 May 2019 |publisher=United Nations Development Programme |page=13 |archive-date=25 December 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181225065941/http://hdr.undp.org/en/sites/default/files/hdr_2016_statistical_annex.pdf%20 |url-status=live }}</ref> The Maldives was a member of the Commonwealth of Nations from July 1982 until withdrawing from the organisation in October 2016 in protest of allegations of its ] abuses and failing democracy.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Safi |first=Michael |date=2016-10-13 |title=Maldives quits Commonwealth over alleged rights abuses |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2016/oct/13/maldives-quits-commonwealth-over-alleged-rights-abuses |access-date=2024-05-15 |work=The Guardian |language=en-GB |issn=0261-3077 |archive-date=13 October 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161013143856/https://www.theguardian.com/world/2016/oct/13/maldives-quits-commonwealth-over-alleged-rights-abuses |url-status=live }}</ref> The Maldives rejoined the Commonwealth on 1 February 2020 after showing evidence of functioning democratic processes and popular support.<ref>{{Cite web |date=1 February 2020 |title=Maldives rejoins Commonwealth after evidence of reforms |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/feb/01/maldives-rejoins-commonwealth-after-evidence-of-reforms |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200418002056/https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/feb/01/maldives-rejoins-commonwealth-after-evidence-of-reforms |archive-date=18 April 2020 |access-date=4 February 2020 |website=The Guardian}}</ref> | |||
| The Maldives is the smallest ] in both population and land area. With an average ground level elevation of {{convert|1.5|m}} above sea level, it is the planet's lowest country.<ref name="guardian.co.uk">{{cite news| url=http://www.guardian.co.uk/environment/2008/nov/11/climatechange-endangered-habitats-maldives |work=The Guardian |location=London |title=The last days of paradise |first=Jon |last=Henley |date=11 November 2008 |accessdate=12 May 2010}}</ref> It is also the country with the ] in the world, at {{convert|2.4|m}}.<ref name="guardian.co.uk"/> Future inundation of the Maldives due to ] is of great concern to its people, motivating the government to have pledged to become a ] country by 2019.<ref name="copenhagen_accord">{{cite news|url=http://graphics8.nytimes.com/packages/pdf/science/earth/20091218_CLIMATE_TEXT.pdf|title=Copenhagen Accord|publisher=New York Times|date=18 December 2009|accessdate= 2 July 2013}}</ref> | |||
| ==Etymology== | ==Etymology== | ||
| {{See also|Names of the Maldives}} | |||
| <!--linked--><!--from where?--> | |||
| {{see also|Names of Maldives}} | |||
| According to legends, the first settlers of the Maldives were people known as Dheyvis.<ref name=":12" /> The first Kingdom of the Maldives was known as {{Ill|Kingdom of Dheeva Maari|bn|দীবামাড়ি রাজ্য}}.<ref>{{cite journal |title=The Long Road From Islam to Islamism: A Short History |url=https://www.dhivehisitee.com/religion/islamism-maldives/ |journal=Dhivehi Sitee |date=30 May 2014 |access-date=30 May 2014 |language=en |archive-date=29 August 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140829000253/http://www.dhivehisitee.com/religion/islamism-maldives/ |url-status=live }}</ref> During the 3rd century BCE visit of emissaries, it was noted that the Maldives was known as Dheeva Mahal.<ref name=":12">{{Cite journal |last=Mohamed |first=Naseema |title=First Settlers |url=https://www.persee.fr/doc/arch_0044-8613_2005_num_70_1_3970 |url-status=live |journal=Note on the Early History of the Maldives |date=2005 |volume=70 |issue=1 |pages=7–14 |doi=10.3406/arch.2005.3970 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164417/https://www.persee.fr/doc/arch_0044-8613_2005_num_70_1_3970 |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=28 November 2019 | issn=0044-8613}}</ref> | |||
| The name ''Maldives'' may derive from ] ''mālā'' (garland) and ''dvīpa'' (island),<ref name="Hogendorn" /> or <span dir="ltr" lang="si">මාල දිවයින</span> ''Maala Divaina'' ("Necklace Islands") in ].<ref name="ParanavitanaPrematilleka1978">{{cite book|author1= P. E. P Deraniyagala in Senarat Paranavitana|author2=Leelananda Prematilleka|author3=Johanna Engelberta van Lohuizen-De Leeuw|title=Senarat Paranavitana Commemoration Volume|url=http://books.google.com/?id=OIceAAAAIAAJ&pg=PA52&dq=maldives+necklace+intitle:Senarat+intitle:Paranavitana+intitle:Commemoration+intitle:Volume#v=onepage&q=maldives%20necklace%20intitle%3ASenarat%20intitle%3AParanavitana%20intitle%3ACommemoration%20intitle%3AVolume&f=false|accessdate=1 August 2013|year=1978|publisher=BRILL|isbn=978-90-04-05455-4|pages=52–}}</ref> The Maldivian people were called ''Dhivehin''. The word ''Dheeb/Deeb'' (archaic ''Dhivehi'', related to ] <span dir="ltr" lang="sa">द्वीप</span> ''dvīpa'') means "island", and ''Dhives'' (''Dhivehin'') means "islanders" (i.e., Maldivians).{{Citation needed|date=October 2009}} | |||
| During {{circa|1100}} – 1166, the Maldives was also referred to as Diva Kudha and the Laccadive archipelago which was a part of the Maldives was then referred to as Diva Kanbar by the scholar and polymath ].<ref>{{Cite book |last=Hogendorn |first=Jan |title=The Shell Money of the Slave Trade |pages=23–24}}</ref> | |||
| The ancient ]n chronicle '']'' refers to an island called ''Mahiladiva'' ("Island of Women", महिलादिभ) in ], which is probably a mistranslation of the same Sanskrit word meaning "]". | |||
| The name ] may also derive from ] {{lang|sa|माला}} {{lang|sa-Latn|mālā}} (]) and {{lang|sa|द्वीप}} {{lang|sa-Latn|dvīpa}} (island),<ref name="Hogendorn" /> or {{lang|si|මාල දිවයින}} ''Maala Divaina'' ("Necklace Islands") in ].<ref name="ParanavitanaPrematilleka1978">{{Cite book |last1=P.E.P Deraniyagala in Senarat Paranavitana |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=OIceAAAAIAAJ&pg=PA52 |title=Senarat Paranavitana Commemoration Volume |last2=Leelananda Prematilleka |last3=Johanna Engelberta van Lohuizen-De Leeuw |publisher=Brill |year=1978 |isbn=978-90-04-05455-4 |pages=52– |access-date=1 August 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164345/https://books.google.com/books?id=OIceAAAAIAAJ&pg=PA52 |archive-date=14 January 2021 |url-status=live}}</ref> The Maldivian people are called ''Dhivehin''. The word ''Dheeb/Deeb'' (archaic ''Dhivehi'', related to ] {{lang|sa|द्वीप}}, {{lang|sa-latn|dvīpa}}) means "island", and ''Dhives'' (''Dhivehin'') means "islanders" (i.e., Maldivians).<ref>Wilhelm Geiger, trans. Mrs. J. C. Willis, ''Máldivian Linguistic Studies'', ''Journal of the Ceylon Branch of the Royal Asiatic Society'' 27 (Colombo: 1911), 149–52. {{ISBN|8120612019}}</ref> In Tamil, "Garland of Islands" can be translated as {{lang|ta-Latn|Mālaitīvu}} ({{lang|ta|மாலைத்தீவு}}).<ref>{{Cite web |title=Altername Names for Republic of Maldives |url=http://www.geonames.org/MV/other-names-for-maldives.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164417/http://www.geonames.org/MV/other-names-for-maldives.html |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=23 September 2013 |website=GeoNames}}</ref> | |||
| Hogendorn theorises that the name ''Maldives'' derives from the Sanskrit ''mālādvīpa'' (<span dir="ltr" lang="sa">मालाद्वीप</span>), meaning "garland of islands".<ref name="Hogendorn">Hogendorn, Jan and Johnson Marion (1986). ''The Shell Money of the Slave Trade''. African Studies Series 49, ], ] ISBN 0521541107, pp. 20–22</ref> In Tamil, "Garland of Islands" can be translated as ''MalaiTheevu'' (<span dir="ltr" lang="ta">மாலைத்தீவு</span>).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.geonames.org/MV/other-names-for-maldives.html |title=Altername Names for Republic of Maldives |publisher=Geonames.org |accessdate=23 September 2013}}</ref> In Malayalam, "Garland of Islands" can be translated as ''Maladweepu'' (<span dir="ltr" lang="ml">മാലദ്വീപ്</span>). In Kannada, "Garland of Islands" can be translated as ''Maaledweepa'' (<span dir="ltr" lang="kn">ಮಾಲೆದ್ವೀಪ</span>). None of these names is mentioned in any literature, but classical Sanskrit texts dating back to the ] mention the "Hundred Thousand Islands" ('']''), a generic name which would include not only the Maldives, but also the ], ] Islands, ] and the ] groups.<ref>Apte, Vaman Shivram (1985). ''Sanskrit-English Dictionary''. Motilal Banarsidass, New Delhi, 1985.</ref> | |||
| The venerable ]n chronicle Mahavamsa mentions an island designated as Mahiladiva ("Island of Women", महिलादिभ) in Pali, likely arising from an erroneous translation of the Sanskrit term, signifying "garland". | |||
| Some medieval travellers such as ] called the islands ''Mahal Dibiyat'' (<span dir="rtl" lang="ar">محل دبيأت</span>) from the ] word ''Mahal'' ("palace"), which must be how the ] traveller interpreted the local name, having been through Muslim North India, where ] words were introduced into the local vocabulary.<ref>Ibn Batuta ''Travels in Asia and Africa''. translated by A. R. Gibb.</ref> This is the name currently inscribed on the scroll in the ]. The classical Persian/Arabic name for Maldives is ''Dibajat''.<ref>Akhbar al-Sin wa 'l-Hind (Notes on China and India), which dates from 851.</ref><ref>{{cite journal|url=http://www.saudiaramcoworld.com/issue/200504/the.seas.of.sindbad.htm |title=The Seas of Sinbad|volume=56|issue= 4 |year=2005 |journal=Saudi Aramco World}}</ref> | |||
| Jan Hogendorn, professor of economics at ], theorised that the name Maldives derives from the Sanskrit {{lang|sa-Latn|mālādvīpa}} ({{lang|sa|मालाद्वीप}}), meaning "garland of islands".<ref name="Hogendorn">Hogendorn, Jan and Johnson Marion (1986). ''The Shell Money of the Slave Trade''. African Studies Series 49, ], ] {{ISBN|0521541107}}, pp. 20–22</ref> In ], "Garland of Islands" can be translated as {{lang|ml-Latn|Maladweepu}} ({{lang|ml|മാലദ്വീപ്}}).<ref>{{cite web |last1=Melton |first1=Gregory |date=16 April 2024 |title=How did Maldives get its name? |url=https://www.ncesc.com/geographic-faq/how-did-maldives-get-its-name/ |access-date=15 May 2024 |website=Geographic FAQ Hub |archive-date=16 April 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240416192409/https://www.ncesc.com/geographic-faq/how-did-maldives-get-its-name/ |url-status=live }}</ref> In Kannada, "Garland of Islands" can be translated as {{lang|kn-Latn|Maaledweepa}} ({{lang|kn|ಮಾಲೆದ್ವೀಪ}}).<ref>{{cite web |title=Maldives - Summary |url=https://www.studocu.com/en-au/document/university-of-sydney/introduction-to-international-relations/maldives-summary/46348887 |access-date=15 May 2024 |website=Studocu |publisher=]}}</ref> None of these names are mentioned in any literature, however, classical Sanskrit texts dating back to the ] mention the "Hundred Thousand Islands" ({{lang|sa-Latn|]a}}), a generic name which would include not only the Maldives, but also the ], ] Islands, ], and the ] groups.<ref>Apte, Vaman Shivram (1985). ''Sanskrit–English Dictionary''. Motilal Banarsidass, New Delhi.{{full citation needed|date=September 2019}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Minicoy in English dictionary |url=https://glosbe.com/en/en/Minicoy |website=Glosbe |access-date=18 May 2024 |archive-date=16 April 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240416192412/https://glosbe.com/en/en/Minicoy |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Medieval Muslim travellers such as ] called the islands ''{{transliteration|ar|Maḥal Dībīyāt}}'' ({{lang|ar|محل ديبية}}) from the ] word ''{{transliteration|ar|maḥal}}'' ("palace"), which must be how the ] traveller interpreted the name of Malé, having been through Muslim North India, where ] words were introduced to the local vocabulary.<ref>Battuta, Ibn (1929) ''Travels in Asia and Africa 1325–1354'', translated by A. R. Gibb. London: Routledge and Keegan Paul.{{page needed|date=April 2024}}</ref> This is the name currently inscribed on the scroll in the ].<ref name="MVEmblems" /> The classical Persian/Arabic name for the Maldives is {{lang|ar-Latn|Dibajat}}.<ref>Akhbar al-Sin wa 'l-Hind (Notes on China and India), which dates from 851.{{full citation needed|date=September 2019}}</ref><ref>{{Cite magazine |date=July–August 2005 |volume=56 |number=4 |title=The Seas of Sinbad |pages=20–29 |author-link=Paul Lunde|first=Paul |last=Lunde|url=http://www.saudiaramcoworld.com/issue/200504/the.seas.of.sindbad.htm |url-status=dead |magazine=] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070208223341/http://www.saudiaramcoworld.com/issue/200504/the.seas.of.sindbad.htm |archive-date=8 February 2007 |access-date=24 September 2008}}</ref> The Dutch referred to the islands as the {{lang|nl|Maldivische Eilanden}} ({{IPA|nl|mɑlˈdivisə ˈʔɛilɑndə(n)|pron}}),<ref name="WWW.IBPUS.COM 69">{{Cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=uJ2rDwAAQBAJ&q=British+%22Maldive+Islands%22+and+later+to+%22Maldives%22&pg=PA69 |title=Pacific Islands Business Law Handbook Volume 1 Strategic Information, Regulations, Contact |date=June 2015 |publisher=Global Pro Info USA |isbn=978-1-5145-0229-7 |pages=69 |language=en |quote=IBPUS.com |access-date=16 November 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164432/https://books.google.com/books?id=uJ2rDwAAQBAJ&q=British+%22Maldive+Islands%22+and+later+to+%22Maldives%22&pg=PA69 |archive-date=14 January 2021 |url-status=live}}</ref> while the British ] the local name for the islands first to the "Maldive Islands" and later to "Maldives".<ref name="WWW.IBPUS.COM 69" /> | |||
| In a conversational book published in 1563, ] writes: "I must tell you that I have heard it said that the natives do not call it Maldiva but Nalediva. In the Malabar language, ''nale'' means four and ''diva'' island. So that in that language, the word signifies 'four islands', while we, corrupting the name, call it Maldiva."<ref>{{Cite book |last=Orta |first=Garcia |title=Colloquies on the Simple and Drugs of India |publisher=Sri Satguru Publications |year=2016 |isbn=978-81-7030-117-2 |location=India |pages=22}}</ref> | |||
| The local name for Maldives by the Maldivian people in ] language is "Dhivehi Raajje", ({{langx|dv|ދިވެހިރާއްޖެ}}).<ref>{{cite journal |author1=Dhivehi Bahaai Thareekhah Khidhumaikuraa Qaumee Marukazu |date=1 August 1990 |title=Dhivehiraajje |url=http://saruna.mnu.edu.mv/jspui/handle/123456789/4398 |publisher=Dhivehi Bahaai Thareekhah Khidhumaikuraa Qaumee Marukazu |via=Saruna |website=Digital Repository of the ] |access-date=18 May 2024 |archive-date=16 April 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240416192639/http://saruna.mnu.edu.mv/jspui/handle/123456789/4398 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ==History== | ==History== | ||
| Line 102: | Line 130: | ||
| ===Ancient history and settlement=== | ===Ancient history and settlement=== | ||
| {{main|History of the Maldives#Early Age}} | |||
| Comparative studies of Maldivian oral, linguistic and cultural traditions and customs indicate that the first settlers were ]<ref name="autogenerated2">], ''The Maldive Islanders, A Study of the Popular Culture of an Ancient Ocean Kingdom''. Barcelona 1999, ISBN 84-7254-801-5.</ref> from ] in the ] (300 BC–AD 300), most probably fishermen from the ] of what is now the south of the ] and the western shores of ]. One such community is the ] descended from ancient ]. They are mentioned in ancient legends and local folklore about the establishment of the capital and kingly rule in ]. | |||
| In the 6th–5th century BCE, the Maldives already had their kingdoms.<ref name=":12" /> The country has an established history of over 2,500 years according to historical evidence and legends.<ref>{{Cite book |title=ދިވެހީންގެ އަސްލު |publisher=ދިވެހިތާރީޚަށް ޚިދުމަތްކުރާ ޤައުމީ މަރުކަޒު |year=1998 |location=Maldives |pages=3 |language=dv}}</ref> | |||
| A strong underlying layer of Dravidian population and culture survives in Maldivian society, with a clear Dravidian-Malayalam substratum in the language, which also appears in place names, kinship terms, poetry, dance, and religious beliefs. Malabari seafaring culture led to ] settling of the ], and the Maldives were evidently viewed as an extension of that archipelago. Some argue (from the presence of Jat, Gujjar Titles and Gotra names) that ] also accounted for an early layer of migration. Seafaring from ] began during the ]. The ]s and ] show abundant evidence of this maritime trade; the use of similar traditional boat building techniques in Northwestern South Asia and the Maldives, and the presence of silver punch mark coins from both regions, gives additional weight to this. There are minor signs of Southeast Asian settlers, probably some adrift from the main group of ] reed boat migrants that settled ].<ref name="Maloney, Clarence">{{cite web|title=Maldives People |author=Maloney, Clarence |url=http://www.iias.nl/iiasn/iiasn5/insouasi/maloney.html|work=International Institute for Asian Studies |accessdate=22 June 2008}}</ref> | |||
| The '']'' (300 BCE) has records of people from Sri Lanka emigrating to the Maldives.<ref name=":12" /> Assuming that cowrie shells come from the Maldives, historians believe that there may have been people living in the Maldives during the ] (3300{{ndash}}1300 BCE).<ref>{{Cite book |title=ދިވެހީންގެ އަސްލު |publisher=ދިވެހިތާރީޚަށް ޚިދުމަތްކުރާ ޤައުމީ މަރުކަޒު |language=dv}}</ref> A number of artefacts show the presence of ] in the country before the Islamic period.<ref name=":12" /> | |||
| The earliest written history of the Maldives is marked by the arrival of ] people, who were descended from the exiled ] Prince ] from the ancient city known as ]. He and his party of several hundred landed in Sri Lanka, and some in the Maldives circa 543 to 483 BC. According to the '']'', one of the ships that sailed with Prince Vijaya, who went to Sri Lanka around 500 BC, went adrift and arrived at an island called ''Mahiladvipika'', which is the Maldives. It is also said that at that time, the people from Mahiladvipika used to travel to Sri Lanka. Their settlement in Sri Lanka and the Maldives marks a significant change in demographics and the development of the ] ], which is most similar in grammar, phonology, and structure to ], and especially to the more ancient ], which has less ]. | |||
| According to the book {{transliteration|ar|Kitāb fi āthār Mīdhu al-qādimah}} ({{lang|ar|كتاب في آثار ميذو القديمة}}) (''On the Ancient Ruins of ]''), written in the 17th century in Arabic by Allama Ahmed Shihabuddine (Allama Shihab al-Din) of ] in Addu Atoll, the first settlers of the Maldives were people known as Dheyvis.<ref name=":12" /> They came from the ] in India.<ref name=":12" /> The time of their arrival is unknown but it was before Emperor ]'s kingdom in 269–232 BCE. Shihabuddin's story tallies remarkably well with the recorded history of South Asia and that of the copperplate document of the Maldives known as ].<ref name=":12" /> | |||
| Alternatively, it is believed that ''Vijaya'' and his clan came from western India – a claim supported by linguistic and cultural features, and specific descriptions in the epics themselves, e.g. that ''Vijaya'' visited ''Bharukaccha'' (] in Gujarat) in his ship on the voyage down south.<ref name="Maloney, Clarence"/> | |||
| The ancient history of the Maldives is told in copperplates, ancient scripts carved on coral artefacts, traditions, language and different ethnicities of Maldivians.<ref name=":12" /> The ''Maapanansa'',<ref name=":12" /> the copper plates on which recorded the history of the first ] from the Solar Dynasty, were lost quite early on. | |||
| ], a Greek historian of Late Antiquity, wrote of a hostage among the Romans, from the island called ''Diva'', which is presumed to be the Maldives, who was baptised Theophilus. Theophilus was sent in the 350s to convert the ] to Christianity, and went to his homeland from Arabia; he returned to Arabia, visited ], and settled in ].<ref>Philostorgius, ''Church History'', tr. Amidon, pp.41–44; Philostorgius' history survives in fragments, and he wrote some 75 years later than these events.</ref> | |||
| A 4th-century notice written by ] (362 CE) speaks of gifts sent to the Roman emperor ] by a deputation from the nation of Divi. The name Divi is very similar to Dheyvi who were the first settlers of Maldives.<ref name=":12" /> | |||
| ===Buddhist period=== | |||
| The first Maldivians did not leave any archaeological artefacts. Their buildings were probably built of wood, palm fronds, and other perishable materials, which would have quickly decayed in the salt and wind of the tropical climate. Moreover, chiefs or headmen did not reside in elaborate stone palaces, nor did their religion require the construction of large temples or compounds.<ref>Kalpana Ram (1993). ''Mukkuvar Women''. Macquarie University.</ref> | |||
| ].]] | |||
| Buddhism came to the Maldives at the time of Emperor ]'s expansion, and became the dominant religion of the people of the Maldives until the 12th century AD. The ancient Maldivian Kings promoted ], and the first Maldive writings and artistic achievements, in the form of highly developed sculpture and architecture, are from that period. Before embracing Buddhism as their way of life, Maldivians had practised an ancient form of ], ]istic traditions known as ''Śrauta'', in the form of venerating the '']'' (the ancient ruling caste were of ''Aadheetta'' or ''Suryavanshi'' origins). | |||
| Comparative studies of Maldivian oral, linguistic, and cultural traditions confirm that the first settlers were people from the southern shores of the neighbouring ],<ref name="autogenerated2">Xavier Romero-Frias, ''The Maldive Islanders, A Study of the Popular Culture of an Ancient Ocean Kingdom''</ref> including the ], mentioned in ancient legends and local folklore about the establishment of the capital and kingly rule in Malé.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Ellis |first=Royston |author-link=Royston Ellis |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=zSjhruMm748C&q=Giraavaru+people&pg=PA36 |title=Maldives |publisher=Bradt Travel Guides |year=2008 |isbn=9781841622668 |access-date=16 November 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164457/https://books.google.com/books?id=zSjhruMm748C&q=Giraavaru+people&pg=PA36 |archive-date=14 January 2021 |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The first archaeological study of the remains of early cultures in the Maldives began with the work of ], a ] commissioner of the ]. Bell was first ordered to the islands in late 1879<ref>This was in order to care for a shipwrecked British steamer's load. Bell moreover had the chance to spend two or three in Malé, on same occasion. See: Bethia Nancy Bell, Heather M. Bell: ''H.C.P. Bell: Archaeologist of Ceylon and the Maldives,'' </ref> he returned twice to the Maldives to investigate ancient ruins. He studied the ancient mounds, called ''havitta'' or ''ustubu'' (these names are derived from ] and ]) ({{lang-dv| ހަވިއްތަ}}) by the Maldivians, which are found on many of the atolls. Although Bell asserted that the ancient Maldivians had followed ], many local Buddhist archaeological remains now in the ] Museum in fact also display elements of ] and ] iconography. | |||
| A strong underlying layer of ] and ] cultures survives in Maldivian society, with a clear ] substratum in the language, which also appears in place names, kinship terms, poetry, dance, and religious beliefs.<ref name="Maloney, Clarence">{{Cite web |last=Maloney |first=Clarence |title=Where Did the Maldives People Come From? |url=http://www.iias.nl/iiasn/iiasn5/insouasi/maloney.html |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20020129221500/http://www.iias.nl/iiasn/iiasn5/insouasi/maloney.html |archive-date=29 January 2002 |access-date=22 June 2008 |website=]}}</ref> The North Indian system was brought by the original ] from ]. ] and ] seafaring culture led to the settlement of the Islands by ] and ] seafarers.<ref name="Maloney, Clarence" /> | |||
| ] Lōmāfānu is the oldest ] book to have been discovered in the Maldives to date. The book was written in AD 1194 (590 AH) in the Evēla form of the ], during the reign of ]. | |||
| ]] | |||
| ===Buddhist period=== | |||
| In the early 11th century, the ] and Thiladhunmathi, and possibly other northern Atolls, were conquered by the ] Tamil emperor ], thus becoming a part of the ]. | |||
| {{main|History of the Maldives#Buddhist period|Buddhism in the Maldives}} | |||
| ] Lōmāfānu is the oldest ] book to have been discovered in the Maldives to date. The book was written in 1194 CE (590 AH) in the Evēla form of the ], during the reign of ].]] | |||
| According to a legend from ], in the early 12th century AD, a medieval prince named ], a nobleman of the Lion Race from Sri Lanka, sailed to Rasgetheemu island (literally "Town of the Royal House", or figuratively "King's Town") in the North Maalhosmadulu Atoll, and from there to Malé, and established a kingdom. By then, the ''Aadeetta'' (Sun) Dynasty (the ] ruling cast) had for some time ceased to rule in Malé, possibly because of invasions by the Cholas of Southern India in the 10th century. Koimala Kalou (Lord Koimala), who reigned as King Maanaabarana, was a king of the ''Homa'' (Lunar) Dynasty (the ] ruling cast), which some historians call the ]. The ''Homa'' (Lunar) dynasty sovereigns intermarried with the ''Aaditta'' (Sun) Dynasty. This is why the formal titles of Maldive kings until 1968 contained references to "''kula sudha ira''", which means "descended from the Moon and the Sun". No official record exists of the Aadeetta dynasty's reign. Since Koimala's reign, the Maldive throne was also known as the ''Singaasana'' (Lion Throne).<ref>{{cite web|title=The Lion Throne Coronation Proclamation of King Siri Kula Sudha Ira Siyaaka Saathura Audha Keerithi Katthiri Bovana|date=21 July 1938|work=Maldives Royal Family |url=http://www.maldivesroyalfamily.com/maldives_proclamation_sultan.shtml}}</ref> Before then, and in some situations since, it was also known as the ''Saridhaaleys'' (Ivory Throne).<ref name="koimala">{{cite web |title=Legend of Koimala Kalou|work=Maldives Royal Family |url=http://www.maldivesroyalfamily.com/maldives_koimala.shtml}}</ref> Some historians credit Koimala with freeing the Maldives from ] rule. | |||
| Despite being just mentioned briefly in most history books, the 1,400 year-long Buddhist period has a foundational importance in the history of the Maldives. It was during this period that the culture of the Maldives both developed and flourished, a culture that survives today. The Maldivian ], early Maldive scripts, architecture, ruling institutions, customs, and manners of the Maldivians originated at the time when the Maldives were a Buddhist kingdom.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Maloney |first=Clarence |title=People of the Maldive Islands |publisher=Orient Longman}}</ref> | |||
| Several foreign travellers, mainly Arabs, had written about a kingdom of the Maldives ruled over by a queen. This kingdom pre-dated Koimala's reign. ], referring to earlier writers, mentions the name of one of the queens, Damahaar, who was a member of the ''Aadeetta'' (Sun) dynasty. | |||
| Buddhism probably spread to the Maldives in the 3rd century BCE at the time of Emperor ]'s expansion and became the dominant religion of the people of the Maldives until the 12th century. The ancient Maldivian Kings promoted ], and the first Maldive writings and artistic achievements, in the form of highly developed sculpture and architecture, originate from that period. Nearly all archaeological remains in the Maldives are from Buddhist ]s and monasteries, and all artefacts found to date display characteristic Buddhist iconography.{{cn|date=December 2024}} | |||
| ===Islamic Period=== | |||
| ===Islamic period=== | |||
| ]'s name is written. Yusuf Tabrizi was an Iranian who is said to have converted Maldives in 12th century AD to ].]] | |||
| {{See also|History of the Maldives#Islamic Period|Islam in Maldives|List of Maldivian monarchs|Sultanate of Maldives}} | |||
| The importance of the Arabs as traders in the Indian Ocean by the 12th century may partly explain why the last Buddhist king of the Maldives, ], converted to Islam in the year 1153 (or 1193). Adopting the Muslim title of Sultan Muhammad al-Adil, he initiated a series of six Islamic dynasties that lasted until 1932 when the ] became elective. The formal title of the sultan up to 1965 was, ''Sultan of Land and Sea, Lord of the twelve-thousand islands and Sultan of the Maldives'' which came with the style '']''. | |||
| A Moroccan traveller named Abu al-Barakat Yusuf al-Barbari is traditionally cited for this conversion.<ref name=":2" /> According to the story told to ], a mosque was built with the inscription: 'The Sultan Ahmad Shanurazah accepted Islam at the hand of Abu al-Barakat Yusuf al-Barbari.'<ref name=":2">{{Cite book |last=Battutah |first=Ibn |title=The Travels of Ibn Battutah |date=2002 |publisher=Picador |isbn=9780330418799 |location=London |pages=235–236, 320}}</ref><ref>'' {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160412233846/https://books.google.com/books?id=ZF2spo9BKacC |date=12 April 2016 }}''</ref> Some scholars have suggested the possibility of Ibn Battuta misreading Maldive texts, and having a bias towards the North African, Maghrebi narrative of this Shaykh, instead of the Persian origins account that was known as well at the time.<ref>{{Citation |last=Honchell |first=Stephanie |title=Sufis, Sea Monsters, and Miraculous Circumcisions: Comparative Conversion Narratives and Popular Memories of Islamization |page=5 |year=2018 |url=https://humanities.uct.ac.za/sites/default/files/content_migration/humanities_uct_ac_za/309/files/Paper%2520-%2520Sufis%2520Sea%2520Monsters%2520and%2520Miraculous%2520Circumcisions.pdf |publisher=] and the ] |quote=In reference to Ibn Batuta's Moroccan theory of this figure, citation 8 of this text mentions, that other accounts identify Yusuf Al Barbari as East African or Persian. But as a fellow Maghribi, Ibn Battuta likely felt partial to the Moroccan version. |access-date=16 May 2024 |archive-date=16 May 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240516185324/https://humanities.uct.ac.za/sites/default/files/content_migration/humanities_uct_ac_za/309/files/Paper%2520-%2520Sufis%2520Sea%2520Monsters%2520and%2520Miraculous%2520Circumcisions.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| The conversion to Islam is mentioned in the edicts written in copper plates from the end of the 12th century AD. | |||
| Others have it that he may have been from the Persian town of ].<ref name="auto">{{Cite book |last=Paul, Ludwig |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=DuKN47W68SkC&pg=PA31 |title=Persian Origins: Early Judaeo-Persian and the Emergence of New Persian : Collected Papers of the Symposium, Göttingen 1999 |publisher=Otto Harrassowitz Verlag |year=2003 |isbn=978-3-447-04731-9 |page=31 |access-date=20 June 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150915151831/https://books.google.com/books?id=DuKN47W68SkC&pg=PA31 |archive-date=15 September 2015 |url-status=live}}</ref> This interpretation, held by the more reliable local historical chronicles, Raadavalhi and Taarikh,<ref name="Visweswaran2011">{{cite book|author=Kamala Visweswaran|title=Perspectives on Modern South Asia: A Reader in Culture, History, and Representation|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=m-EYXNnvMugC&q=candles+ships+jinn&pg=PA164|date=6 May 2011|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|isbn=978-1-4051-0062-5|pages=164–|access-date=2 October 2020|archive-date=3 May 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210503032121/https://books.google.com/books?id=m-EYXNnvMugC&q=candles+ships+jinn&pg=PA164|url-status=live}}</ref><ref name="sw">{{cite book|author=Ishtiaq Ahmed|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Jt8rBgAAQBAJ&q=islam+outside+the+arab+world+maldives&pg=PA250|title=Islam Outside the Arab World|year=2002|isbn=9780253022608|editor=Ingvar Svanberg|page=250| publisher=Routledge |editor2=David Westerlund|access-date=2 October 2020|archive-date=3 May 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210503032057/https://books.google.com/books?id=Jt8rBgAAQBAJ&q=islam+outside+the+arab+world+maldives&pg=PA250|url-status=live}}</ref> is that Abu al-Barakat Yusuf al-Barbari was Abdul Barakat Yusuf Shams ud-Dīn at-Tabrīzī, also locally known as Tabrīzugefānu.<ref>], ''The Máldive Islands. Monograph on the History, Archæology, and Epigraphy'' with W. L. De Silva, Colombo 1940</ref> In the Arabic script the words al-Barbari and al-Tabrizi are very much alike, since at the time, Arabic had several consonants that looked identical and could only be differentiated by overall context (this has since changed by addition of dots above or below letters to clarify pronunciation – For example, the letter "B" in modern Arabic has a dot below, whereas the letter "T" looks identical except there are two dots above it). "ٮوسڡ الٮٮرٮرى" could be read as "Yusuf at-Tabrizi" or "Yusuf al-Barbari".<ref>{{cite book|last=Paul |first= Ludwig|title=Persian Origins--: Early Judaeo-Persian and the Emergence of New Persian: Collected Papers of the Symposium, Göttingen 1999|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=DuKN47W68SkC&pg=PA31|year=2003|publisher=Otto Harrassowitz Verlag|isbn=978-3-447-04731-9|page=31|access-date=30 April 2017|archive-date=15 September 2015|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150915151831/https://books.google.com/books?id=DuKN47W68SkC&pg=PA31|url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The famous Moroccan traveller ], who visited the Maldives in the 14th century, wrote how a Moroccan, one ''Abu Barakat the Berber'', was believed to have been responsible for spreading Islam in the islands. Even though this report has been contested in later sources, it does explain some crucial aspects of Maldivian culture. For instance, historically Arabic has been the prime language of administration there, instead of the Persian and Urdu languages used in the nearby Muslim states. Another link to North Africa was the ] school of jurisprudence, used throughout most of North-Africa, which was the official one in the Maldives until the 17th century.<ref>''''</ref> | |||
| The venerated tomb of the scholar now stands on the grounds of ], across the street from the Friday Mosque, or ], in Malé. Originally built in 1153 and re-built in 1658,<ref>{{Cite web |last=Yoosuf |first=Muawwaz |date=2020-02-28 |title=Malé Friday Mosque |url=https://coralstonemosques.com/male-friday-mosque/ |access-date=2024-10-25 |website=Coral Stone Mosques of Maldives |language=en-US}}</ref> this is one of the oldest surviving mosques in the Maldives. Following the Islamic concept that before Islam there was the time of ] (ignorance), in the history books used by Maldivians the ] at the end of the 12th century is considered the cornerstone of the country's history. Nonetheless, the cultural influence of Buddhism remains, a reality directly experienced by Ibn Battuta during his nine months there sometime between 1341 and 1345, serving as a chief judge and marrying into the royal family of ].<ref>{{Cite news |last=Buchan |first=James |date=21 December 2002 |editor-last=Mackintosh-Smith |editor-first=Tim |title=The Travels of Ibn Battutah |url=https://www.theguardian.com/books/2002/dec/21/featuresreviews.guardianreview2 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171207085518/https://www.theguardian.com/books/2002/dec/21/featuresreviews.guardianreview2 |archive-date=7 December 2017 |access-date=6 December 2017 |work=] |issn=0261-3077}}</ref> For he became embroiled in local politics and left when his strict judgments in the laissez-faire island kingdom began to chafe with its rulers. In particular, he was angered at the local women going about with no clothing above the waist— a cultural epithet of the region at the time- was seen as a violation of Middle Eastern Islamic rules of modesty—and the locals taking no notice when he complained.<ref>Jerry Bently, ''Old World Encounters Cross-Cultural Contacts and Exchanges in Pre-Modern Times (New York: Oxford University Press, 1993), 126''.</ref> | |||
| Some scholars have suggested the possibility of Ibn Battuta misreading Maldive texts, and have posited another scenario where this Abu Barakat might have been a native of ], a significant trading port on the north western coast of ].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=K_G5Qpc2dBI |title=Richard Bulliet – History of the World to 1500 CE (Session 22) – Tropical Africa and Asia |publisher=Youtube.com |date=23 November 2010 |accessdate=23 September 2013}}</ref> This scenario would also help explain the usage of the Arabic language and the predominance of the Maliki school on the islands. | |||
| Compared to the other areas of South Asia, the conversion of the Maldives to Islam happened relatively late. The Maldives remained a Buddhist kingdom for another 500 years. Arabic became the prime language of administration (instead of Persian and Urdu), and the ] school of jurisprudence was introduced, both hinting at direct contact with the core of the Arab world.{{citation needed|date=July 2022}} | |||
| Another interpretation, held by some of the islanders, is that Abu Barakat was an Iranian from Tabriz. In the Arabic script the words al-Barbari and al-Tabrizi are very much alike, owing to the fact that Arabic has no letters to represent vowels. The first reference to an Iranian origin dates to an 18th-century Persian text.<ref>{{cite book|author=Paul, Ludwig |title=Persian Origins--: Early Judaeo-Persian and the Emergence of New Persian : Collected Papers of the Symposium, Göttingen 1999|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=DuKN47W68SkC&pg=PA31|year=2003|publisher=Otto Harrassowitz Verlag|isbn=978-3-447-04731-9|page=31}}</ref> | |||
| Middle Eastern seafarers had just begun to take over the Indian Ocean trade routes in the 10th century and found the Maldives to be an important link in those routes as the first landfall for traders from ] sailing to Southeast Asia. Trade involved mainly ]—widely used as a form of currency throughout Asia and parts of the ]n coast—and coir fibre. The ], where cowrie shells were used as legal tender, was one of the principal trading partners of the Maldives. The Bengal–Maldives cowry shell trade was the largest shell currency trade network in history.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Boomgaard |first=P. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=TXphAAAAQBAJ |title=Linking Destinies: Trade, Towns and Kin in Asian History |date=1 January 2008 |publisher=BRILL |isbn=9789004253995 |access-date=23 August 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170106131821/https://books.google.com/books?id=TXphAAAAQBAJ |archive-date=6 January 2017 |url-status=live |via=Google Books}}</ref> | |||
| The Maldives was the first landfall for traders from ], sailing to ] or Southeast Asia. In the Maldives, ships could take on fresh water, fruit and the delicious, basket-smoked red flesh of the black '']'', a delicacy exported to ], China and ]. The people of the archipelago were described as gentle, civilised and hospitable. They produced ] utensils as well as fine cotton textiles, exported in the form of sarongs and turban lengths. These local industries must have depended on imported raw materials. | |||
| The other essential product of the Maldives was |
The other essential product of the Maldives was ], the fibre of the dried ] ], resistant to saltwater. It stitched together and rigged the ]s that plied the Indian Ocean. Maldivian coir was exported to ], ], ], and the ]. | ||
| ===Protectorate period=== | |||
| "It is stronger than ]", wrote ], "and is used to sew together the planks of Sindhi and Yemeni dhows, for this sea abounds in reefs, and if the planks were fastened with iron nails, they would break into pieces when the vessel hit a rock. The coir gives the boat greater elasticity, so that it doesn't break up." | |||
| ] in the Maldives was established in 1558, by order of ], Viceroy of ].]] | |||
| ], depicting workers]] | |||
| ] from the ], depicting with detail the islands of the Maldives]] | |||
| In 1558, the Portuguese established a small garrison with a {{lang|pt|Viador}} ({{transliteration|dv|Viyazoaru}}), or overseer of a ] in the Maldives, which they administered from their main colony in ]. Their attempts to forcefully impose Christianity with the threat of death provoked a local revolt led by ], his two brothers and ] Dhandahele, who fifteen years later drove the Portuguese out of the Maldives. This event is now commemorated as National Day which is known as ] (literally meaning "National" and "Day"). It is celebrated on 1st of ], the third month of ] (Islamic) calendar. | |||
| In the mid-17th century, the Dutch, who had replaced the Portuguese as the dominant power in ], established hegemony over Maldivian affairs without involving themselves directly in local matters, which were governed according to centuries-old Islamic customs. | |||
| ===British protectorate, 1887–1965=== | |||
| The British expelled the Dutch from Ceylon in 1796 and included the Maldives as a ]. The status of the Maldives as a British protectorate was officially recorded in an 1887 agreement in which the sultan ] accepted British influence over Maldivian external relations and defence while retaining home rule, which continued to be regulated by ] traditional institutions in exchange for an ]. The status of the islands was akin to other British protectorates in the Indian Ocean region, including ] and the ]. | |||
| ] ] moored in the lagoon at Addu Atoll, during WWII]] | |||
| |url=http://purl.pt/27184/3/#/1 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164421/https://purl.pt/27184/3/#/1 |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=20 June 2020}}</ref>]] | |||
| In 1953, there was an abortive attempt to form a republic, but the sultanate survived. In 1957 the British established an air base in the strategic southernmost atoll of Addu, paying £2000 a year, employing hundreds of locals. Nineteen years later, the British government (Labour's Harold Wilson) gave up the base, as it was too expensive to maintain.<ref name="gan.philliptsmall.me.uk">{{cite web|url=http://gan.philliptsmall.me.uk/00%20-%20Articles/PeterGeary%20%5BBritish%20Empire%5D.htm |title=The Sun never sets on the British Empire |publisher=Gan.philliptsmall.me.uk |date=17 May 1971 |accessdate=2 April 2013}}</ref> | |||
| In the British period, the Sultan's powers were taken over by the Chief Minister, much to the chagrin of the British Governor-General who continued to deal with the ineffectual Sultan. Consequently, Britain encouraged the development of a ], and the first Constitution was proclaimed in 1932. However, the new arrangements favoured neither the Sultan nor the Chief Minister, but rather a young crop of British-educated reformists. As a result, angry mobs were instigated against the Constitution which was publicly torn up. | |||
| In 1959, objecting to ]'s centralism, the inhabitants of the three southernmost atolls protested against the government. They formed the ] and elected ] as president and chose ] as capital of this republic.<ref name="gan.philliptsmall.me.uk"/ | |||
| The Maldives remained a British crown protectorate until 1953 when the sultanate was suspended and the First Republic was declared under the short-lived presidency of ]. While serving as prime minister during the 1940s, Didi nationalised the fish export industry. As president, he is remembered as a reformer of the education system and an advocate of ]. Conservatives in Malé ousted his government, and during a riot over food shortages, Didi was beaten by a mob and died on a nearby island. | |||
| ===Independence and Republic=== | |||
| ] ] moored in the lagoon at Addu Atoll, during WWII]] | |||
| ] served as the first president of the Maldives for most of 1953 and was deposed for his unpopular policies.]] | |||
| During the 1950s and 1960s, the British presence east of ] was in steep decline. On 26 July 1965 an agreement was signed on behalf of His Majesty the Sultan by Ibrahim Nasir Rannabandeyri Kilegefan, Prime Minister, and on behalf of ] by Sir Michael Walker, British Ambassador designate to the Maldive Islands, which ended the British responsibility for the defence and external affairs of the Maldives. The islands thus achieved full political independence, with the ceremony taking place at the British High Commissioner's Residence in Colombo. After this, the sultanate continued for another three years under ], who declared himself King rather than Sultan. | |||
| Beginning in the 1950s, the political history in the Maldives was largely influenced by the British military presence on the islands. In 1954, the restoration of the sultanate perpetuated the rule of the past. Two years later, the United Kingdom obtained permission to reestablish its wartime ] airfield in the southernmost Addu Atoll, employing hundreds of locals. In 1957, however, the new ], ], called for a review of the agreement. Nasir was challenged in 1959 by a local secessionist movement in the three southernmost atolls that benefited economically from the British presence on ]. This group cut ties with the Maldives government and formed an independent state, the ] with ] as president and ] as its capital. One year later the Suvadive republic was scrapped after Nasir sent gunboats from Malé with government police, and Abdullah Afeef went into exile. Meanwhile, in 1960 the Maldives allowed the United Kingdom to continue to use both the ] and the Hithadhoo facilities for thirty years, with the payment of £750,000 from 1960 to 1965 for the Maldives' economic development. The base was closed in 1976 as part of the larger British withdrawal of permanently-stationed forces ']'.<ref name="gan.philliptsmall.me.uk">{{Cite web |last=Geary |first=Peter |date=17 May 1971 |title=The Sun never sets on the British Empire |url=http://gan.philliptsmall.me.uk/00%20-%20Articles/PeterGeary%20%5BBritish%20Empire%5D.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130919212227/http://gan.philliptsmall.me.uk/00%20-%20Articles/PeterGeary%20%5BBritish%20Empire%5D.htm |archive-date=19 September 2013 |access-date=2 April 2013 |website=gan.philliptsmall.me.uk}}</ref> | |||
| On 15 November 1967, a vote was taken in parliament to decide whether the Maldives should continue as a ] or become a republic. Of the 44 members of parliament, forty voted in favour of a republic. On 15 March 1968, a national referendum was held on the question, and 93.34% of those taking part voted in favour of establishing a republic. The republic was declared on 11 November 1968, thus ending the 853-year-old monarchy, which was replaced by a republic under the presidency of ]. As the King had held little real power, this was seen as a cosmetic change and required few alterations in the structures of government. | |||
| ===Independence and republic=== | |||
| ] began to be developed on the ] by the beginning of the 1970s. The first resort in the Maldives was Kurumba Maldives which welcomed the first guests on 3 October 1972. The first accurate census was held in December 1977 and showed 142,832 persons residing in Maldives.<ref>"</ref> | |||
| {{Main|Independence of the Maldives}} | |||
| However, political infighting during the '70s between Nasir's faction and other political figures led to the 1975 arrest and exile of elected prime minister ] to a remote ]. Economic decline followed the closure of the ] and the collapse of the market for dried fish, an important export. With support for his administration faltering, Nasir fled to ] in 1978, with millions of dollars from the treasury. | |||
| ]]] | |||
| ] on July 26, 1965.'']] | |||
| When the British became increasingly unable to continue their colonial hold on Asia and were losing their colonies to the indigenous populations who wanted freedom, on 26 July 1965 an agreement was signed on behalf of the Sultan by Ibrahim Nasir Rannabandeyri Kilegefan, Prime Minister, and on behalf of the British government by ], British Ambassador-designate to the Maldive Islands, which formally ended the British authority on the defence and external affairs of the Maldives.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Davies |first1=Laura |title=Maldives at Fifty: penning a chapter in history |url=https://blogs.fcdo.gov.uk/lauradavies/2015/07/26/maldives-at-fifty-penning-a-chapter-in-history/ |website=Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office |date=26 July 2015 |access-date=26 July 2015 |archive-date=25 April 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210425135723/https://blogs.fcdo.gov.uk/lauradavies/2015/07/26/maldives-at-fifty-penning-a-chapter-in-history/ |url-status=live }}</ref> The islands thus achieved independence, with the ceremony taking place at the British High Commissioner's Residence in ]. After this, the sultanate continued for another three years under ], who declared himself King upon independence.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Hadi |first1=Ahmedulla Abdul |date=26 July 2019 |title=The independence gained by the unyielding determination of Nasir |url=https://en.sun.mv/54575 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230923210604/https://en.sun.mv/54575 |archive-date=23 September 2023 |access-date=26 July 2019 |agency=Sun News}}</ref> | |||
| ] began his 30-year role as President in 1978, winning six consecutive elections without opposition. His election was seen as ushering in a period of political stability and economic development in view of Gayoom's priority to develop the poorer islands. Tourism flourished and increased foreign contact spurred development. However, Gayoom's rule was controversial, with some critics saying Gayoom was an autocrat who quelled dissent by limiting freedoms and political favouritism.<ref name="cnn_sinking">{{cite news |title=Sinking island nation seeks new home |author=CNN |url=http://edition.cnn.com/2008/WORLD/asiapcf/11/11/maldives.president/index.html |accessdate=12 November 2008|date=11 November 2008}}BAT</ref> | |||
| On 15 November 1967, a vote was taken in parliament to decide whether the Maldives should continue as a constitutional monarchy or become a republic.<ref>People's Majlis Archive | |||
| A series of coup attempts (in 1980, 1983, and 1988) by Nasir supporters and business interests tried to topple the government without success. While the first two attempts met with little success, the 1988 coup attempt involved a roughly 80-person mercenary force of the ] who seized the airport and caused Gayoom to flee from house to house until the intervention of 1600 ] airlifted into ] restored order. The November 1988 coup was headed by Muhammadu Ibrahim Lutfee, a small-businessman. On the night of 3 November 1988, the ] airlifted a parachute battalion group from ] and flew them over {{convert|2000|km|mi}} to the Maldives. The Indian ] landed at ] and secured the airfield and restored the government rule at Malé within hours. The brief, bloodless operation, labelled '']'', also involved the ]. <!-- the rest of this, about the tsunami and 2008 elections, needs to get updated in the History of the Maldives article --> | |||
| </ref> Of the 44 members of parliament, 40 voted in favour of a republic. On 15 March 1968, a ] was held on the question, and 93.34% of those taking part voted in favour of establishing a republic.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Riyaz |first1=Ahmed |date=11 November 2012 |title=ރާއްޖޭގެ ވެރިކަން ޖުމުހުރީ ވެރިކަމަކަށް ބަދަލުވުން |trans-title=Maldives Becomes a republic |url=http://utheemu.com/web/republic-day-maldives.html |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140811034839/http://utheemu.com/web/republic-day-maldives.html |archive-date=11 August 2014 |access-date=11 November 2012 |work=Utheemu |language=dv}}</ref> The republic was declared on 11 November 1968, thus ending the 853-year-old monarchy, which was replaced by a republic under the presidency of Ibrahim Nasir.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Walker |first1=James |date=26 July 2023 |title=How Maldives gained independence from the British empire |url=https://www.thenational.scot/news/23679687.maldives-gained-independence-british-empire/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230730063751/https://www.thenational.scot/news/23679687.maldives-gained-independence-british-empire/ |archive-date=30 July 2023 |access-date=26 July 2023 |work=The National}}</ref> As the King had held little real power, this was seen as a cosmetic change and required few alterations in the structures of government. | |||
| ] began to be developed on the ] by the beginning of the 1970s.<ref>{{cite news |last=Kachroo-Levine |first=Maya |date=25 May 2021 |title=How the Maldives Transformed From a Fishing Archipelago to a Tropical Hot Spot in 50 Years |url=https://www.travelandleisure.com/trip-ideas/island-vacations/maldives-history |access-date=25 May 2021 |work=Travel + Leisure |archive-date=26 May 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210526033749/https://www.travelandleisure.com/trip-ideas/island-vacations/maldives-history |url-status=live }}</ref> The first resort in the Maldives was ] which welcomed the first guests on 3 October 1972.<ref>{{cite news |date=27 September 2020 |title=The Beginning of Maldives Tourism Industry – History of the First Resort, Kurumba Maldives |url=https://mvhotels.travel/the-beginning-of-maldives-tourism-industry-history-of-the-first-resort-kurumba-maldives |access-date=27 September 2020 |work=Maldives Travel |archive-date=21 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240221224056/https://mvhotels.travel/the-beginning-of-maldives-tourism-industry-history-of-the-first-resort-kurumba-maldives/ |url-status=live }}</ref> The first accurate census was held in December 1977 and showed 142,832 people living in the Maldives.<ref>" {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164344/http://countrystudies.us/maldives/4.htm |date=14 January 2021 }}</ref> | |||
| ===21st century=== | |||
| Political infighting during the 1970s between Nasir's faction and other political figures led to the 1975 arrest and exile of elected prime minister ] to a remote ].<ref>{{cite web |title=MODERN HISTORY OF THE MALDIVES: BECOMING A REPUBLIC AND INDEPENDENCE |url=https://factsanddetails.com/south-asia/Maldives/History_Maldives/entry-8035.html |access-date=16 May 2024 |website=Facts and Details |archive-date=16 April 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240416203537/https://factsanddetails.com/south-asia/Maldives/History_Maldives/entry-8035.html |url-status=live }}</ref> Economic decline followed the closure of the ] and the collapse of the market for dried fish, an important export. With support for his administration faltering, Nasir fled to Singapore in 1978, with millions of dollars from the treasury.<ref>{{cite web |date=5 December 2014 |title=Maldives |url=https://historygreatest.com/maldives |access-date=16 May 2024 |website=History's Greatest |quote=Economic decline followed the closure of the British airfield at Gan and the collapse of the market for dried fish, an important export. With support for his administration faltering, Nasir fled to Singapore in 1978, with millions of dollars from the treasury. |archive-date=16 April 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240416194539/https://historygreatest.com/maldives |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ] removing sand bags from a nearby construction site, to be used as a barrier to protect their homes from the flood, shortly after being hit by the ] generated by the ]]] | |||
| ] began his 30-year role as president in 1978, winning six consecutive elections without opposition. His election was seen as ushering in a period of political stability and economic development given Maumoon's priority to develop the poorer islands. Tourism flourished and increased foreign contact spurred development. However, Maumoon's rule was controversial, with some critics saying Maumoon was an autocrat who quelled dissent by limiting freedoms and practising political favouritism.<ref name="cnn_sinking">{{Cite news |date=11 November 2008 |title=Sinking island nation seeks new home |url=http://edition.cnn.com/2008/WORLD/asiapcf/11/11/maldives.president/index.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081206023636/http://edition.cnn.com/2008/WORLD/asiapcf/11/11/maldives.president/index.html |archive-date=6 December 2008 |access-date=12 November 2008 |website=]}}</ref> | |||
| On 26 December 2004, following the ], the ] by a tsunami. Only nine islands were reported to have escaped any flooding,<ref>{{cite web|title=Maldives – Country Review Report on the Implementation of the Brussels Programme of Action for LDCS|url=http://www.un.org/special-rep/ohrlls/ldc/MTR/Maldives.pdf}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Maldives Skyscraper – Floating States|url=http://www.evolo.us/architecture/maldives-skyscraper-floating-states/|work=UN.org}}</ref> while fifty-seven islands faced serious damage to critical infrastructure, fourteen islands had to be totally evacuated, and six islands were destroyed. A further twenty-one resort islands were forced to close because of serious damage. The total damage was estimated at more than US$400 million, or some 62% of the GDP.<ref>{{cite web|title=UNDP: Discussion Paper – Achieving Debt Sustainability and the MDGs in Small Island Developing States: The Case of the Maldives|url=http://wayback.archive.org/web/20120112232609/http://undp.org.mv/v2/publication_files/4d3d53b1f2a35.pdf}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|title=Maldives tsunami damage 62 percent of GDP: WB|url=http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/english/doc/2005-02/15/content_416614.htm}}</ref> 102 Maldivians and 6 foreigners reportedly died in the tsunami.<ref name="cnn_sinking" /> The destructive impact of the waves on the low-lying islands was mitigated by the fact there was no continental shelf or land mass upon which the waves could gain height. The tallest waves were reported to be {{convert|14|ft|m}} high.<ref>{{cite web|title=Republic of Maldives – Tsunami: Impact and Recovery|url=http://wayback.archive.org/web/20120328060124/http://www.undp.org.mv/v2/publication_files/4b36072ca065c.pdf|work=undp.org.mv}}</ref> | |||
| A series of coup attempts (in 1980, 1983, and 1988) by Nasir supporters and business interests tried to topple the government without success. While the first two attempts met with little success, the ] involved a roughly 80-strong mercenary force of the ] who seized the airport and caused Maumoon to flee from house to house until the intervention of 1,600 ] airlifted into Malé restored order. | |||
| During the later part of Gayoom's rule, independent political movements emerged in Maldives, which challenged the then-ruling ] (Maldivian People's Party) and demanded democratic reform. These movements brought about significant change in political structure. In 2008 a new constitution was approved and the first direct presidential elections occurred, which were won by ] and ] (as Vice-President) in the second round. The 2009 parliamentary election saw the ] of President Nasheed receive the most votes with 30.81%, gaining 26 seats, however the Dhivehi Rayyithunge Party with 24.62% of the vote received the most seats (28). | |||
| The November 1988 coup d'état was headed by Ibrahim Lutfee, a businessman, and Sikka Ahmed Ismail Manik, the father of the former first lady of the Maldives ].<ref>{{cite news |date=7 December 2022 |title=Nov 3rd attack mastermind Sikka arrives in the Maldives after more than a decade |url=https://themaldivesjournal.com/44422 |access-date=7 December 2022 |work=The Maldives Journal |archive-date=8 December 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221208093749/https://themaldivesjournal.com/44422 |url-status=live }}</ref> The attackers were defeated by then ].<ref name="three">{{cite news |last1=Banka |first1=Neha |date=3 November 2022 |title=Operation Cactus: How India helped Maldives thwart coup bid backed by Lankan militants |url=https://indianexpress.com/article/research/operation-cactus-how-india-helped-maldives-end-a-coup-backed-by-lankan-militants-7605322/ |access-date=3 November 2022 |work=] |location=Kolkata |archive-date=18 September 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220918132434/https://indianexpress.com/article/research/operation-cactus-how-india-helped-maldives-end-a-coup-backed-by-lankan-militants-7605322/ |url-status=live }}</ref> On the night of 3 November 1988, the ] airlifted a ] from ] and flew them over {{convert|2000|km|mi}} to the Maldives.<ref name="three" /> By the time Indian armed forces reached the Maldives, the mercenary forces has already left Malé on the hijacked ship MV Progress Light.<ref name="three" /> The Indian ] landed at ] and secured the airfield and restored the government rule at Malé within hours.<ref name="three" /> The brief operation labelled ''Operation Cactus'', also involved the ] that assisted in capturing the freighter MV Progress Light and rescued the hostages and crew.<ref name="three" /> | |||
| The government of President Mohamed Nasheed faced many challenges, including the huge debts left by the previous government, the economic downturn following the 2004 tsunami, overspending (by means of overprinting of local currency rufiyaa) during his regime, unemployment, corruption, and increasing drug use.<ref>{{cite news |title=he Quality of Political Appointees in the Nasheed Administration |author=Raajje News |url=http://raajjenews.blogspot.com/2009/06/quality-of-political-appointees-in.html |accessdate=21 February 2012 |date=7 May 2009}}</ref>{{verify credibility|date=April 2013}} | |||
| ===21st century=== | |||
| Taxation on goods was imposed for the first time in the country, and import duties were reduced in many goods and services. Social welfare benefits were given to those above 65 years of age, single parents, and those with special needs. On 10 November 2008, Nasheed announced an intent to create a ] with money earned from tourism that could be used to purchase land elsewhere for the Maldives people to relocate should rising sea levels due to ] inundate the country. The government reportedly considered locations in Sri Lanka and India due to cultural and climate similarities, and as far away as Australia.<ref name="cnn_sinking"/> | |||
| {{Main|History of the Maldives#21st century}} | |||
| ] in ], Maldives]] | |||
| The ] by a ] on 26 December 2004, following the ]. Only nine islands were reported to have escaped any flooding,<ref>{{Cite report |url=http://www.un.org/special-rep/ohrlls/ldc/MTR/Maldives.pdf |title=Maldives - Country Review Report on the implementation of the Brussels Programme of Action for LDCs |date=January 2009 |publisher=Ministry of Planning and National Development |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130921081046/http://www.un.org/special-rep/ohrlls/ldc/MTR/Maldives.pdf |archive-date=21 September 2013 |via=] |url-status=dead}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Aldridge |first=Paul |date=24 March 2010 |title=Maldives Skyscraper - Floating States |url=https://www.evolo.us/maldives-skyscraper-floating-states/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171010152057/http://www.evolo.us/architecture/maldives-skyscraper-floating-states/ |archive-date=10 October 2017 |access-date=27 July 2011 |website=eVolo}}</ref> while fifty-seven islands faced serious damage to critical infrastructure, fourteen islands had to be totally evacuated, and six islands were destroyed. A further twenty-one resort islands were forced to close because of tsunami damage. The total damage was estimated at more than US$400 million, or some 62% of the GDP.<ref>{{Cite web |date=20 December 2010 |title=UNDP: Discussion Paper - Achieving Debt Sustainability and the MDGs in Small Island Developing States: The Case of the Maldives |url=http://undp.org.mv/v2/publication_files/4d3d53b1f2a35.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120112232609/http://undp.org.mv/v2/publication_files/4d3d53b1f2a35.pdf |archive-date=12 January 2012 |website=]}}</ref> 102 Maldivians and 6 foreigners reportedly died in the tsunami.<ref name="cnn_sinking" /> The destructive impact of the waves on the low-lying islands was mitigated by the fact there was no continental shelf or land mass upon which the waves could gain height. The tallest waves were reported to be {{convert|14|ft|m}} high.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Republic of Maldives - Tsunami: Impact and Recovery |url=http://www.undp.org.mv/v2/publication_files/4b36072ca065c.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120328060124/http://www.undp.org.mv/v2/publication_files/4b36072ca065c.pdf |archive-date=28 March 2012 |access-date=18 September 2015 |website=]}}</ref> | |||
| On 23 December 2011, the opposition held a mass symposium with as many as 20,000 people in the name of protecting Islam, which they believed Nasheed's government was unable to maintain in the country. The mass event became the foundation of a campaign that brought about social unrest within the capital city. | |||
| On 16 January 2012,<ref>{{cite news |title=Q&A: The Maldives – Trouble in paradise |author=Voigt, Kevin |work=CNN |url=http://articles.cnn.com/2012-02-08/asia/world_asia_maldives-dispute-explainer_1_president-maumoon-abdul-gayoom-maldives-president-mohamed-nasheed?_s=PM:ASIA |accessdate=10 February 2012 |date=8 February 2012}}</ref> the Maldives military, on orders from the interior ministry, un-constitutionally arrested Judge ], the chief justice of the Maldives Criminal Court, on charges he was blocking the prosecution of corruption and human rights cases against allies of former President Gayoom. On 7 February, Nasheed ordered the police and army to subdue the anti-government protesters and allegedly told them to use force against the public. Police came out to protest against the government instead.<ref>{{cite web|title=The truth about the alleged coup … a series of deliberate actions by Nasheed?|url=http://web.archive.org/web/20120426091046/http://dhiislam.com/eng/7036|date=1 March 2012}}</ref> | |||
| During the later part of Maumoon's rule, independent political movements emerged in the Maldives, which challenged the then-ruling ] (Maldivian People's Party, MPP) and demanded democratic reform. The dissident journalist and activist ] founded the ] (MDP) in 2003 and pressured Maumoon into allowing gradual political reforms.<ref name="brownpoliticalreview.org">{{Cite web |last1=Brecehenmacher |first1=Victor |last2=Mendis |first2=Nikhita |date=22 April 2015 |title=Autocracy and Back Again: The Ordeal of the Maldives |url=https://brownpoliticalreview.org/2015/04/autocracy-and-back-again-the-ordeal-of-the-maldives/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164352/https://brownpoliticalreview.org/2015/04/autocracy-and-back-again-the-ordeal-of-the-maldives/ |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=16 May 2024 |website=Brown Political Review |language=en-US}}</ref> In 2008, a new constitution was approved and the ] occurred, which were won by Nasheed in the second round. His administration faced many challenges, including the huge debt left by the previous government, the economic downturn following the 2004 tsunami, overspending by means of overprinting of local currency (the ]), unemployment, corruption, and increasing drug use.<ref>{{Cite news |last= |date=7 June 2009 |title=The Quality of Political Appointees in the Nasheed Administration |url=https://raajjenews.blogspot.com/2009/06/quality-of-political-appointees-in.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164400/http://raajjenews.blogspot.com/2009/06/quality-of-political-appointees-in.html |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=21 February 2012 |work=Raajje News Blog}}</ref>{{unreliable source?|date=April 2013}} Taxation on goods was imposed for the first time in the country, and import duties were reduced on many goods and services. Universal health insurance (]) and social welfare benefits were given to those aged 65 years or older, single parents, and those with special needs.<ref name="cnn_sinking" /> | |||
| President Mohamed Nasheed resigned on 7 February 2012 by letter, and followed that with a televised public address informing Maldivians of his resignation. Later Nasheed told foreign media that he was deposed by a military coup led by President Waheed. There have been disputes over exactly what happened that day. Nasheed's vice president, Mohammed Waheed Hassan, was sworn in as President in accordance with the Constitution at the Peoples majlis in front of the Chief Justice.<ref>{{cite news |title=Maldives president quits after protests |author=Al Jazeera |url=http://www.aljazeera.com/news/asia/2012/02/20122765334806442.html |accessdate=6 February 2012 |date=9 February 2012}}</ref> | |||
| Social and ], following opposition campaigns in the name of protecting Islam. Nasheed controversially resigned from office after large number of police and army mutinied in February 2012. Nasheed's vice-president, ], was sworn in as president.<ref>{{Cite news |last= |date=7 February 2012 |title=Maldives president quits after protests |url=https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2012/2/7/maldives-president-quits-after-protests |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164507/https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2012/2/7/maldives-president-quits-after-protests |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=6 February 2012 |work=]}}</ref> | |||
| On 23 February 2012, the Commonwealth suspended the Maldives from its democracy and human rights ] while the ousting was being investigated, and backed Nasheed's call for elections before the end of 2012.<ref>{{cite news|last=Griffiths |first=Peter |url=http://in.reuters.com/article/2012/02/22/maldives-commonwealth-idINDEE81L0JO20120222 |title=Commonwealth suspends Maldives from rights group, seeks elections |publisher=In.reuters.com |date= 22 February 2012}}</ref> | |||
| Nasheed was later arrested,<ref>{{Cite news |last=Mallawarachi |first=Bharatha |date=8 October 2012 |title=Mohamed Nasheed, Former Maldives President, Arrested after Failing to Appear in Court |url=http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2012/10/08/mohamed-nasheed-maldives-former-president-arrested_n_1947348.html |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160310062645/http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2012/10/08/mohamed-nasheed-maldives-former-president-arrested_n_1947348.html |archive-date=10 March 2016 |work=] |agency=]}}</ref> convicted of terrorism, and sentenced to 13 years. The trial was widely seen as flawed and political. The ] called for Nasheed's immediate release.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Naafiz |first=Ali |date=20 October 2015 |title=Maldives opposition seeks India's help in jailed leader's release |url=http://www.haveeru.com.mv/news/63227 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151021134808/http://www.haveeru.com.mv/news/63227 |archive-date=21 October 2015 |access-date=24 October 2015 |work=]}}</ref> | |||
| The ] were highly contested. Former president Nasheed won the most votes in the first round, but the ] annulled it despite the positive assessment of international election observers. In the re-run vote ], half-brother of the former president Maumoon, assumed the presidency.<ref name="brownpoliticalreview.org" /> Yameen survived an assassination attempt in late 2015.<ref>{{Cite magazine |last=Iyengar |first=Rishi |date=28 September 2015 |title=Maldives President Abdulla Yameen Escapes Unhurt After Explosion on His Boat |url=https://time.com/4051674/maldives-president-abdulla-yameen-boat-blast/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164358/https://time.com/4051674/maldives-president-abdulla-yameen-boat-blast/ |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=16 May 2024 |magazine=]}}</ref> Vice president ] was removed from office after a ] from the People's Majlis, it was alleged that he was conspiring with opposition political parties and planning riots.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Muhsin |first=Mohamed Fathih Abdul |date=15 February 2021 |title=Was removed from office without being allowed a proper defense: Dr Jameel |url=https://timesofaddu.com/2021/02/15/was-removed-from-office-without-being-allowed-a-proper-defense-dr-jameel/ |access-date=16 May 2024 |work=The Times of Addu |archive-date=9 May 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240509182244/https://timesofaddu.com/2021/02/15/was-removed-from-office-without-being-allowed-a-proper-defense-dr-jameel/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Vice-president ] was later arrested together with 17 supporters for "public order offences" and the government instituted a broader crackdown against his accomplices. A ] was later declared ahead of a planned anti-government rally,<ref>{{Cite news |date=4 November 2015 |title=Maldives declares 30-day emergency |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-34718916 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164358/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-34718916 |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=16 May 2024 |work=] |language=en-GB}}</ref> and the People's Majlis (parliament) accelerated the removal of Adeeb.<ref name="majlis.gov.mv">{{Cite web |date=5 November 2015 |title=Majlis passes declaration to remove VP from office |url=http://www.majlis.gov.mv/en/2015/11/05/majlis-passes-declaration-to-remove-ahmed-adeeb-abdul-gafoor-from-the-post-of-vice-president/ |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160714204131/http://www.majlis.gov.mv/en/2015/11/05/majlis-passes-declaration-to-remove-ahmed-adeeb-abdul-gafoor-from-the-post-of-vice-president/ |archive-date=14 July 2016 |website=People's Majlis}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |date=10 November 2015 |title=Maldives revokes state of emergency amid global outcry and tourism worries |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2015/nov/10/maldives-revokes-state-of-emergency |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164354/https://www.theguardian.com/world/2015/nov/10/maldives-revokes-state-of-emergency |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=10 November 2015 |work=] |publication-place=Malé, Maldives |agency=Associated Press}}</ref> | |||
| Though in March 2012 the new regime promised new elections; in April the state minister of foreign affairs announced that elections would not be held in the near future.<ref>{{cite news|last=Lawson |first=Alastair |url=http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-17636199 |title=Maldives elections will not be in 'foreseeable future' |publisher=Bbc.co.uk |date=6 April 2012 |accessdate=2 April 2013}}</ref> | |||
| ], ] won the most votes, and was sworn in as the Maldives' new president in November 2018. Adeeb was freed by courts in Male in July 2019 after his conviction on charges of terrorism and corruption was overruled, but was placed under a ] after the state prosecutor appealed the order in a corruption and money laundering case. Adeeb escaped in a ] to ] in India. It is understood that the ] escorted the tugboat to the International Maritime Boundary Line (IMBL) and he was then "transferred" to a ] ship, where officials took him into custody.<ref>{{Cite news |last1=Haidar |first1=Suhasini |last2=Radhakrishnan |first2=Hariprasad |date=3 August 2019 |title=Adeeb returns to Maldives, arrested with quiet help from India |url=https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/former-maldives-vice-president-ahmed-adeeb-transferred-to-countrys-authorities-sources/article28806538.ece |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164429/https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/former-maldives-vice-president-ahmed-adeeb-transferred-to-countrys-authorities-sources/article28806538.ece |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=3 August 2019 |work=]}}</ref> | |||
| On 8 October, Nasheed was arrested after failing to appear in court to face charges that he ordered the illegal arrest of a judge while in office. However, his supporters claim that this detention was politically motivated in order to prevent him from campaigning for the 2013 presidential elections.<ref>{{cite news|title=Mohamed Nasheed, Former Maldives President, Arrested After Failing To Appear In Court|editor=The Huffington Post|url=http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2012/10/08/mohamed-nasheed-maldives-former-president-arrested_n_1947348.html | date=8 October 2012}}</ref> | |||
| Former president Abdulla Yameen was sentenced to five years in prison in November 2019 for money laundering. The ] upheld the jail sentence in January 2021.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Zalif |first=Zunana |date=21 January 2021 |title=High Court upholds ex-president's five-year jail sentence |url=https://raajje.mv/94119 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210122005946/https://raajje.mv/94119 |archive-date=22 January 2021 |access-date=16 May 2024 |work=]}}</ref> However, Supreme Court overturned Yameen's conviction in November 2021.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Junayd |first=Mohamed |date=30 November 2021 |title=Maldives' ex-president Yameen walks free after graft conviction overturned |url=https://www.reuters.com/world/asia-pacific/maldives-ex-president-yameen-walks-free-after-graft-conviction-overturned-2021-11-30/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220303175531/https://www.reuters.com/world/asia-pacific/maldives-ex-president-yameen-walks-free-after-graft-conviction-overturned-2021-11-30/ |archive-date=3 March 2022 |access-date=5 March 2022 |work=] |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| In the ], ] (PNC) candidate ] won the second-round runoff of the Maldives presidential election, beating incumbent president, Ibrahim Solih, with 54% of the vote.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Junayd |first=Mohamed |date=2023-10-01 |title=Maldives opposition candidate Muizzu wins presidential vote |url=https://www.reuters.com/world/asia-pacific/maldives-opposition-candidate-muizzu-wins-presidential-vote-2023-10-01/ |access-date=2023-11-10 |work=] |language=en |archive-date=10 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231110101533/https://www.reuters.com/world/asia-pacific/maldives-opposition-candidate-muizzu-wins-presidential-vote-2023-10-01/ |url-status=live }}</ref> On 17 October 2023, Mohamed Muizzu was sworn in as the eighth President of the Republic of Maldives.<ref>{{Cite news |date=2023-11-18 |title=Mohamed Muizzu sworn in as Maldives president, says will remove 'foreign' troops |url=https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/world/south-asia/mohamed-muizzu-sworn-in-as-maldives-president-says-will-remove-foreign-troops/articleshow/105303033.cms?from=mdr |access-date=2023-11-24 |work=] |issn=0971-8257 |agency=] |archive-date=24 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231124110555/https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/world/south-asia/mohamed-muizzu-sworn-in-as-maldives-president-says-will-remove-foreign-troops/articleshow/105303033.cms?from=mdr |url-status=live }}</ref> Mohamed Muizzu is widely seen to be pro-China, meaning souring relations with India.<ref>{{cite news |last=Eguegu |first=Ovigwe |date=24 January 2024 |title=What the China-Maldives-India Triangle Tells Us About 21st Century Balancing |url=https://thediplomat.com/2024/01/what-the-china-maldives-india-triangle-tells-us-about-21st-century-balancing/ |access-date=16 May 2024 |work=] |archive-date=22 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240322102506/https://thediplomat.com/2024/01/what-the-china-maldives-india-triangle-tells-us-about-21st-century-balancing/ |url-status=live }}</ref> In 2024, ex-President Abdulla Yameen Abdul Gayoom was freed from his 11-year conviction and the High Court ordered a new trial.<ref>{{Cite news |date=18 April 2024 |title=Maldives High Court overturns ex-President Abdulla Yameen's prison sentence |url=https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2024/4/18/maldives-high-court-frees-jailed-ex-president-abdulla-yameen |access-date=16 May 2024 |work=Al Jazeera |archive-date=2 May 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240502161416/https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2024/4/18/maldives-high-court-frees-jailed-ex-president-abdulla-yameen |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
| {{main|Geography of the Maldives}} | {{main|Geography of the Maldives}} | ||
| ] and ] can be seen in this picture.]] | |||
| {{see also|Atolls of the Maldives|List of islands of the Maldives}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] can be seen in this picture.]] | |||
| Maldives consists of 1,192 ] islands grouped in a double chain of 26 ]s, along the north-south direction, spread over roughly {{convert|90000|km²}}, making this one of the world's most dispersed countries. It lies between latitudes ] and ], and longitudes ] and ]. The atolls are composed of live ]s and ]s, situated atop a submarine ridge {{convert|960|km}} long that rises abruptly from the depths of the Indian Ocean and runs north to south. Only near the southern end of this natural coral barricade do two open passages permit safe ship navigation from one side of the Indian Ocean to the other through the territorial waters of Maldives. For administrative purposes the Maldivian government organised these atolls into twenty one ]. The largest island of Maldives is ], which belongs to Laamu Atoll or Hahdhummathi Maldives. In ] the westernmost islands are connected by roads over the reef (collectively called ]) and the total length of the road is {{convert|14|km|0|abbr=on}}. | |||
| The Maldives consists of 1,192 ]s grouped in a double chain of 26 atolls, that stretch along a length of {{convert|871|km|mi|abbr=off}} north to south, {{convert|130|km|mi|abbr=off}} east to west, spread over roughly {{convert|90000|km²}}, of which only {{convert|298|km2|sqmi|abbr=on}} is dry land, making this one of the world's most dispersed countries. It lies between latitudes ] and ], and longitudes ] and ]. The atolls are composed of live ]s and ]s, situated atop a submarine ridge {{convert|960|km}} long that rises abruptly from the depths of the Indian Ocean and runs north to south. | |||
| Maldives is the lowest country in the world, with maximum and average natural ground levels of only {{convert|2.4|m}} and {{convert|1.5|m}} above sea level, respectively. In areas where construction exists, however, this has been increased to several metres. More than 80 per cent of the country's land is composed of coral islands which rise less than one metre above sea level.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.aljazeera.com/news/asia/2010/06/201062915490741700.html |title=Entire Maldives cabinet resigns |publisher=Al Jazeera English |date=29 June 2010 |accessdate=30 June 2010}}</ref> | |||
| Only near the southern end of this natural coral barricade do two open passages permit safe ship navigation from one side of the Indian Ocean to the other through the territorial waters of the Maldives. For administrative purposes, the Maldivian government organised these atolls into 21 ]. The largest island of the Maldives is that of ], which belongs to Laamu Atoll or Hahdhummathi Maldives. In Addu Atoll, the westernmost islands are connected by roads over the reef (collectively called Link Road) and the total length of the road is {{convert|14|km|0|abbr=on}}. | |||
| ===Protected areas of Maldives=== | |||
| The Maldives is the lowest country in the world, with maximum and average natural ground levels of only {{convert|2.4|m}} and {{convert|1.5|m}} above sea level, respectively. In areas where construction exists, however, this has been increased to several metres. More than 80 per cent of the country's land is composed of coral islands which rise less than one metre above sea level.<ref>{{Cite news |date=29 June 2010 |title=Entire Maldives cabinet resigns |url=https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2010/6/29/entire-maldives-cabinet-resigns |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120111052220/http://www.aljazeera.com/news/asia/2010/06/201062915490741700.html |archive-date=11 January 2012 |access-date=30 June 2010 |work=Al Jazeera}}</ref> As a result, the Maldives are in danger of being submerged due to ]. The ] has warned that, at current rates, sea-level rise would be high enough to make the Maldives uninhabitable by 2100.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Angelo |first=Megan |date=1 May 2009 |title=Honey, I Sunk the Maldives: Environmental changes could wipe out some of the world's most well-known travel destinations |url=http://travel.yahoo.com/p-interests-27384279 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120717041919/http://travel.yahoo.com/p-interests-27384279 |archive-date=17 July 2012 |website=]}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |date=19 April 2009 |title=Climate refugees in Pacific flee rising sea |url=https://www.washingtontimes.com/news/2009/apr/19/rising-sea-levels-in-pacific-create-wave-of-migran/ |access-date=28 August 2015 |work=] |archive-date=6 September 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150906033747/http://www.washingtontimes.com/news/2009/apr/19/rising-sea-levels-in-pacific-create-wave-of-migran/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Protected areas of Maldives are administrated by ] and Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) of Maldives. There are ] in Maldives.<ref name="Maldives Protected Areas">{{cite web|url=http://epa.gov.mv/index.php?option=com_content&view=category&id=5&Itemid=25&limitstart=1|title=Protected Areas – Maldives|work=epa.gov.mv|publisher=Environmental Protection Agency|accessdate=25 May 2013}}</ref> | |||
| ===Climate=== | ===Climate=== | ||
| ] island]] | |||
| The Maldives has a ] (Am) under the ], which is affected by the large landmass of South Asia to the north. Because the Maldives has the lowest elevation of any country in the world, the temperature is constantly hot and often humid. The presence of this landmass causes differential heating of land and water. These factors set off a rush of moisture-rich air from the Indian Ocean over South Asia, resulting in the southwest ]. Two seasons dominate the Maldives' weather: the dry season associated with the winter northeastern monsoon and the rainy season associated with the southwest monsoon which brings strong winds and storms.<ref name="Climate">{{Cite web |title=Climate |url=https://www.meteorology.gov.mv/climate |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211213020544/https://www.meteorology.gov.mv/climate |archive-date=13 December 2021 |access-date=13 December 2021 |website=Maldives Meteorological Service}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| The Maldives has a tropical-monsoon climate, which is affected by the large landmass of South Asia to the north. The presence of this landmass causes differential heating of land and water. These factors set off a rush of moisture-rich air from the Indian Ocean over South Asia, resulting in the southwest ]. Two seasons dominate Maldives' weather: the dry season associated with the winter northeastern monsoon and the rainy season which brings strong winds and storms. | |||
| The shift from the |
The shift from the dry northeast monsoon to the moist southwest monsoon occurs during April and May. During this period, the southwest winds contribute to the formation of the southwest monsoon, which reaches the Maldives at the beginning of June and lasts until the end of November. However, the weather patterns of the Maldives do not always conform to the monsoon patterns of South Asia. The annual rainfall averages {{convert|254|cm}} in the north and {{convert|381|cm}} in the south.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Maldives |url=http://www.atlapedia.com/online/countries/maldives.htm |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171010151307/http://www.atlapedia.com/online/countries/maldives.htm |archive-date=10 October 2017 |access-date=27 July 2011 |website=Atlapedia}}</ref><ref name="Climate" /> | ||
| {{-}} | |||
| The monsoonal influence is greater in the north of the Maldives than in the south, more influenced by the ]. | |||
| {{Weather box | |||
| |location = ] | |||
| The average high temperature is 31.5 degrees Celsius and the average low temperature is 26.4 degrees Celsius.<ref name="Climate" /> | |||
| |metric first = yes | |||
| |single line = yes | |||
| {{Clear}} | |||
| |temperature colour = pastel | |||
| |Jan record high C = 32 | |||
| {{Weather box|location = Malé (1981–2010) | |||
| |Feb record high C = 32 | |||
| |collapsed = | |||
| |Mar record high C = 33 | |||
| |metric first = y | |||
| |Apr record high C = 35 | |||
| |single line = y | |||
| |May record high C = 35 | |||
| | |
|Jan high C = 30.3 | ||
| | |
|Feb high C = 30.7 | ||
| | |
|Mar high C = 31.4 | ||
| | |
|Apr high C = 31.6 | ||
| | |
|May high C = 31.2 | ||
| | |
|Jun high C = 30.6 | ||
| | |
|Jul high C = 30.5 | ||
| | |
|Aug high C = 30.4 | ||
| | |
|Sep high C = 30.2 | ||
| | |
|Oct high C = 30.2 | ||
| |Mar high C = 31.2 | |||
| |Apr high C = 31.5 | |||
| |May high C = 31.0 | |||
| |Jun high C = 30.5 | |||
| |Jul high C = 30.4 | |||
| |Aug high C = 30.2 | |||
| |Sep high C = 30.0 | |||
| |Oct high C = 30.0 | |||
| |Nov high C = 30.1 | |Nov high C = 30.1 | ||
| |Dec high C = 30. |
|Dec high C = 30.1 | ||
| |year high C = | |year high C = | ||
| |Jan |
|Jan mean C = 28.0 | ||
| |Feb |
|Feb mean C = 28.3 | ||
| |Mar |
|Mar mean C = 28.9 | ||
| |Apr |
|Apr mean C = 29.2 | ||
| |May |
|May mean C = 28.8 | ||
| |Jun |
|Jun mean C = 28.3 | ||
| |Jul |
|Jul mean C = 28.2 | ||
| |Aug |
|Aug mean C = 28.0 | ||
| |Sep |
|Sep mean C = 27.8 | ||
| |Oct |
|Oct mean C = 27.8 | ||
| |Nov |
|Nov mean C = 27.7 | ||
| |Dec |
|Dec mean C = 27.8 | ||
| |year |
|year mean C = 28.2 | ||
| |Jan |
|Jan low C = 25.7 | ||
| |Feb |
|Feb low C = 25.9 | ||
| |Mar |
|Mar low C = 26.4 | ||
| |Apr |
|Apr low C = 26.8 | ||
| |May |
|May low C = 26.3 | ||
| |Jun |
|Jun low C = 26.0 | ||
| |Jul |
|Jul low C = 25.8 | ||
| |Aug |
|Aug low C = 25.5 | ||
| |Sep |
|Sep low C = 25.3 | ||
| |Oct |
|Oct low C = 25.4 | ||
| |Nov |
|Nov low C = 25.2 | ||
| |Dec |
|Dec low C = 25.4 | ||
| |year |
|year low C = 25.8 | ||
| | |
|rain colour = green | ||
| |Jan |
|Jan rain mm = 114.2 | ||
| |Feb |
|Feb rain mm = 38.1 | ||
| |Mar |
|Mar rain mm = 73.9 | ||
| |Apr |
|Apr rain mm = 122.5 | ||
| |May |
|May rain mm = 218.9 | ||
| |Jun |
|Jun rain mm = 167.3 | ||
| |Jul |
|Jul rain mm = 149.9 | ||
| |Aug |
|Aug rain mm = 175.5 | ||
| |Sep |
|Sep rain mm = 199.0 | ||
| |Oct |
|Oct rain mm = 194.2 | ||
| |Nov |
|Nov rain mm = 231.1 | ||
| |Dec |
|Dec rain mm = 216.8 | ||
| |year |
|year rain mm = 1901.4 | ||
| |Jan humidity = 78.0 | |Jan humidity = 78.0 | ||
| |Feb humidity = 77.0 | |Feb humidity = 77.0 | ||
| Line 298: | Line 325: | ||
| |Dec humidity = 80.9 | |Dec humidity = 80.9 | ||
| |year humidity = 79.7 | |year humidity = 79.7 | ||
| |unit precipitation days = 1.0 |
|unit precipitation days = 1.0 mm | ||
| |Jan precipitation days = |
|Jan precipitation days = 6 | ||
| |Feb precipitation days = 3 |
|Feb precipitation days = 3 | ||
| |Mar precipitation days = |
|Mar precipitation days = 5 | ||
| |Apr precipitation days = 9 |
|Apr precipitation days = 9 | ||
| |May precipitation days = |
|May precipitation days = 15 | ||
| |Jun precipitation days = |
|Jun precipitation days = 13 | ||
| |Jul precipitation days = |
|Jul precipitation days = 12 | ||
| |Aug precipitation days = |
|Aug precipitation days = 13 | ||
| |Sep precipitation days = 15 |
|Sep precipitation days = 15 | ||
| |Oct precipitation days = |
|Oct precipitation days = 15 | ||
| |Nov precipitation days = 13 |
|Nov precipitation days = 13 | ||
| |Dec precipitation days = |
|Dec precipitation days = 12 | ||
| |year precipitation days = |
|year precipitation days = 131 | ||
| |Jan sun = 248. |
|Jan sun = 248.4 | ||
| |Feb sun = |
|Feb sun = 257.8 | ||
| |Mar sun = 279. |
|Mar sun = 279.6 | ||
| |Apr sun = 246. |
|Apr sun = 246.8 | ||
| |May sun = 223.2 | |May sun = 223.2 | ||
| |Jun sun = |
|Jun sun = 202.3 | ||
| |Jul sun = 226. |
|Jul sun = 226.6 | ||
| |Aug sun = |
|Aug sun = 211.5 | ||
| |Sep sun = |
|Sep sun = 200.4 | ||
| |Oct sun = |
|Oct sun = 234.8 | ||
| |Nov sun = |
|Nov sun = 226.1 | ||
| |Dec sun = 220. |
|Dec sun = 220.7 | ||
| |year sun = 2778.2 | |year sun = 2778.2 | ||
| |source 1 = ]<ref name="WMO">{{Cite web |title=World Weather Information Service – Malé |url=http://worldweather.wmo.int/en/city.html?cityId=228 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181226044058/http://worldweather.wmo.int/en/city.html?cityId=228 |archive-date=26 December 2018 |access-date=17 March 2016 |publisher=WMO}}</ref> | |||
| |source 1 =http://www.tutiempo.net/en/Climate/Male/435550.htm | |||
| |source 2 = ]<ref>{{Cite web |title=Malé Climate 1961–90 |url=ftp://ftp.atdd.noaa.gov/pub/GCOS/WMO-Normals/TABLES/REG_II/MV/43555.TXT |url-status=live |archive-url=https://wayback.archive-it.org/all/20171010150911/ftp://ftp.atdd.noaa.gov/pub/GCOS/WMO-Normals/TABLES/REG_II/MV/43555.TXT |archive-date=10 October 2017 |access-date=17 March 2016 |publisher=]}}</ref> | |||
| |date=November 2010 | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| === |
===Sea level rise=== | ||
| {{Main|Climate change in the Maldives}} | |||
| {{see also|Effects of climate change on island nations|The Island President}} | |||
| In 1988, Maldivian authorities claimed that sea rise would "completely cover this Indian Ocean nation of 1,196 small islands within the next 30 years."<ref>{{Cite news |date=26 September 1988 |title=Threat to islands |language=en |page=6 |work=] |agency=] |issue=19348, Vol. 63 |url=https://trove.nla.gov.au/newspaper/article/102074798 |access-date=15 November 2021 |quote=A gradual rise in average sea level is threatening to completely cover this Indian Ocean nation of 1196 small islands with- in the next 30 years, ac- cording to authorities. The Environmental Affairs Director, Mr Hussein Shihab, said an estimated rise of 20 to 30 centimetres in the next 20 to 40 years could be "catastrophic" |archive-date=15 November 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211115033208/https://trove.nla.gov.au/newspaper/article/102074798 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| {{see also|The Island President}} | |||
| According to former ] ], the Maldives are ranked the third most endangered nation due to flooding from ].<ref>{{cite news | first = Marcus | last = Stephen | url = http://www.thefreelibrary.com/A+sinking+feeling%3A+why+is+the+president+of+the+tiny+Pacific+island...-a0273079165 | title = A sinking feeling: Why is the president of the tiny Pacific island nation of Nauru so concerned about climate change?| work = ] | accessdate = 17 March 2013| accessdate = 9 February 2015 | authorlink = Marcus Stephen | date = 14 November 2011 | quote = Most Endangered Island nations at highest risk for flooding due to climate change 3 Maldives (Indian Ocean) }}</ref> In March and April 2012, Nasheed stated: "If carbon emissions were to stop today, the planet would not see a difference for 60 to 70 years," Nasheed said. "If carbon emissions continue at the rate they are climbing today, my country will be underwater in seven years." He called for more ] action while on the American television shows ] <ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.thedailyshow.com/watch/mon-april-2-2012/exclusive---mohamed-nasheed-extended-interview-pt--2 |title=Exclusive – Mohamed Nasheed Extended Interview Pt. 2 |publisher=Thedailyshow.com |date=2 April 2012 |accessdate=2 April 2013}}</ref> and the ].<ref>{{cite web|author=World Nation |url=http://www.guilfordian.com/worldnation/2012/04/06/endangered-island-nations-call-for-global-action-on-climate-change/ |title=Endangered island nations call for global action on climate change |publisher=Guilfordian.com |date=6 April 2012}}</ref> | |||
| The ]'s 2007 report predicted the upper limit of the sea level |
The ]'s 2007 report predicted the upper limit of the ] will be {{convert|59|cm}} by 2100, which means that most of the republic's 200 inhabited islands may need to be abandoned.<ref>{{Cite news |date=9 January 2012 |title=Where climate change threatens survival |url=https://www.smh.com.au/politics/federal/where-climate-change-threatens-survival-20120108-1pq4c.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164406/https://www.smh.com.au/politics/federal/where-climate-change-threatens-survival-20120108-1pq4c.html |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=18 September 2015 |work=]}}</ref> According to researchers from the ], the Maldives are the third most endangered island nation due to flooding from ] as a percentage of population.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Stephen |first=Marcus |author-link=Marcus Stephen |date=14 November 2011 |title=A sinking feeling: Why is the president of the tiny Pacific island nation of Nauru so concerned about climate change? |url=https://www.thefreelibrary.com/A+sinking+feeling%3A+why+is+the+president+of+the+tiny+Pacific+island...-a0273079165 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150209212434/http://www.thefreelibrary.com/A+sinking+feeling%3A+why+is+the+president+of+the+tiny+Pacific+island...-a0273079165 |archive-date=9 February 2015 |access-date=9 February 2015 |work=] |quote=Most Endangered Island nations at highest risk for flooding due to climate change 3 Maldives (Indian Ocean)}}</ref> | ||
| In |
In 2008, Nasheed announced plans to look into purchasing new land in India, Sri Lanka, and Australia because of his concerns about global warming, and the possibility of much of the islands being inundated with water from rising sea levels. The purchase of land will be made from a fund generated by tourism. The president explained his intentions: "We do not want to leave the Maldives, but we also do not want to be ] living in tents for decades".<ref name="Guardian">{{Cite news |last=Ramesh |first=Randeep |date=10 November 2008 |title=Paradise almost lost: Maldives seek to buy a new homeland |url=https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2008/nov/10/maldives-climate-change |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164412/https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2008/nov/10/maldives-climate-change |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=12 May 2010 |work=] |location=London}}</ref> | ||
| At the 2009 International Climate Talks, Nasheed stated that:<blockquote>For us swearing off fossil fuels is not only the right thing to do, but it is also in our economic self-interest... Pioneering countries will free themselves from the unpredictable price of foreign oil; they will capitalise on the new green economy of the future, and they will enhance their moral standing giving them greater political influence on the world stage.<ref>{{Cite news |date=28 June 2011 |title=Climate Change Gridlock: Where Do We Go From Here? (Part 1) |url=https://www.radioproject.org/2011/06/climate-change-gridlock-where-do-we-go-from-here-part-1/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164424/https://www.radioproject.org/2011/06/climate-change-gridlock-where-do-we-go-from-here-part-1/ |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=30 June 2011 |work=Making Contact |agency=National Radio Project}}</ref></blockquote> | |||
| Former president ] said in 2012 that "If carbon emissions continue at the rate they are climbing today, my country will be under water in seven years."<ref name="Guilfordian">{{Cite news |last=Catoe |first=Linda |title=Endangered island nations call for global action on climate change |work=The Guilfordian |url=https://www.guilfordian.com/worldnation/2012/04/06/endangered-island-nations-call-for-global-action-on-climate-change/ |url-status=live |access-date=30 December 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164407/https://www.guilfordian.com/worldnation/2012/04/06/endangered-island-nations-call-for-global-action-on-climate-change/ |archive-date=14 January 2021}}</ref> He has called for more ] action while on the American television shows '']''<ref>{{Cite web |date=2 April 2012 |title=Exclusive - Mohamed Nasheed Extended Interview Pt. 2 |url=http://www.cc.com/video-clips/ptdix5/the-daily-show-with-jon-stewart-exclusive---mohamed-nasheed-extended-interview-pt--2 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164433/http://www.cc.com/video-clips/ptdix5/the-daily-show-with-jon-stewart-exclusive---mohamed-nasheed-extended-interview-pt--2 |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=14 February 2017 |website=The Daily Show |publisher=Comedy Central}}</ref> and the '']'',<ref name="Guilfordian" /> and hosted "the world's first underwater cabinet meeting" in 2009 to raise awareness of the threats posed by climate change.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Lang |first=Olivia |date=17 October 2009 |title=Maldives leader in climate change stunt |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/8312320.stm |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100701130145/http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/8312320.stm |archive-date=1 July 2010 |access-date=19 October 2010 |work=]}}</ref><ref name=":1" /> Concerns over rising sea levels have also been expressed by Nasheed's predecessor, ].<ref>{{Cite web |last=Gayoom |first=Maumoon Abdul |author-link=Maumoon Abdul Gayoom |title=Address by his Excellency Mr. Maumoon Abdul Gayoom, President of the Republic of Maldives, at the nineteenth special session of the United Nations General Assembly for the purpose of an overall review and appraisal of the implementation of agenda 21 - 24 June 1997 |url=http://www.un.int/maldives/ungass.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060613232908/http://www.un.int/maldives/ungass.htm |archive-date=13 June 2006 |access-date=6 January 2006 |website=Permanent Mission of the Republic of Maldives to the United Nations}}</ref> | |||
| By 2020, Maldives plans to eliminate or offset all of its greenhouse gas emissions. At the 2009 International Climate Talks, President Mohamed Nasheed explained that: <blockquote>For us swearing off fossil fuels is not only the right thing to do, it is in our economic self-interest... Pioneering countries will free themselves from the unpredictable price of foreign oil; they will capitalize on the new green economy of the future, and they will enhance their moral standing giving them greater political influence on the world stage.<ref>{{cite news|title=Climate Change Gridlock: Where Do We Go From Here? (Part 1)|url=http://www.radioproject.org/2011/06/climate-change-gridlock-where-do-we-go-from-here-part-1/|accessdate=30 June 2011|newspaper=Making Contact|date=28 June 2011|agency=National Radio Project}}</ref></blockquote> | |||
| In 2020, a three-year study at the ] which looked at the Maldives and the ], found that tides move sediment to create a higher elevation, a morphological response that the researchers suggested could help low-lying islands adjust to sea level rise and keep the islands habitable. The research also reported that ] were compromising islands' ability to adjust to rising sea levels and that island drowning is an inevitable outcome for islands with coastal structures like sea walls.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Physical impacts of climate change on coral reef islands |url=https://www.plymouth.ac.uk/research/support/funding/global-challenges-research-fund/gerd-masselink-gcrf-project-2020 |access-date=2023-03-11 |website=University of Plymouth |language=en |archive-date=11 March 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230311121844/https://www.plymouth.ac.uk/research/support/funding/global-challenges-research-fund/gerd-masselink-gcrf-project-2020 |url-status=live }}</ref> Hideki Kanamaru, natural resources officer with the ] in Asia-Pacific, said the study provided a "new perspective" on how island nations could tackle the challenge of sea-level rise, and that even if islands can adapt naturally to higher seas by raising their own crests, humans still needed to double down on global warming and protection for island populations.<ref name=":1">{{Cite news |last=Taylor |first=Michael |date=10 June 2020 |title=Small islands may not disappear under rising seas, researchers find |url=https://news.trust.org/item/20200610171616-1ul7a |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164424/https://news.trust.org/item/20200610171616-1ul7a |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=18 May 2024 |work=]}}</ref> | |||
| Other environmental issues include bad waste disposal and ]. Although the Maldives are kept relatively pristine and little litter can be found on the islands, no good waste disposal sites exist. Most trash from Male and other resorts is simply dumped at ].<ref>{{cite news|author=Hall, Chris |url=http://www.dailymail.co.uk/home/moslive/article-2162653/Maldives-island-paradise-Thilafushi-trashed-reduced-pile-rubbish.html |title=Paradise trashed: The beautiful island in the Maldives that's been reduced to a pile of rubbish |publisher=Dailymail.co.uk |date= 23 June 2012 |location=London}}</ref> | |||
| ===Environment{{anchor|Environmental issues}}=== | |||
| ===Marine ecosystem=== | |||
| Environmental issues other than ] include bad waste disposal and ]. Although the Maldives are kept relatively pristine and little ] can be found on the islands, most ] sites are often substandard. The bulk of the waste from Malé and nearby resorts in the Maldives are disposed of at ], an industrial island on top of a lagoon reclaimed in the early '90s to sort waste management issues which had plagued the capital and surrounding islands.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Evans |first=Judith |date=24 April 2015 |title=Maldives island swamped by rising tide of waste |url=https://www.ft.com/content/29399966-e80b-11e4-9960-00144feab7de |url-access=subscription |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164426/https://www.ft.com/content/29399966-e80b-11e4-9960-00144feab7de |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=14 February 2017 |work=]}}</ref> | |||
| ] are administered by the Ministry of Climate Change, Environment and Energy and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) of the Maldives.<ref name="Maldives Protected Areas">{{Cite web |title=Protected Areas - Maldives |url=http://epa.gov.mv/index.php?option=com_content&view=category&id=5&Itemid=25&limitstart=1 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304134336/http://epa.gov.mv/index.php?option=com_content&view=category&id=5&Itemid=25&limitstart=1 |archive-date=4 March 2016 |access-date=25 May 2013 |website=Environmental Protection Agency}}</ref> | |||
| ===Marine ecosystem=== | |||
| {{further|Wildlife of Maldives}} | {{further|Wildlife of Maldives}} | ||
| ] (''Plectorhinchus vittatus'') at ], North Male Atoll]] | ] | ||
| ] (''Plectorhinchus vittatus'') at ], North Male Atoll]] | |||
| The Maldives have a range of different habitats including deep sea, shallow coast, and reef ecosystems, fringing mangroves, wetlands and dry land. There are 187 species of coral forming the ]. This area of the Indian Ocean, alone, houses 1,100 ] of fish, 5 species of ], 21 species of whale and dolphin, 400 species of mollusc, and 83 species of echinoderms. The area is also populated by a number of crustacean species: 120 copepods, 15 amphipods, as well as more than 145 crab and 48 shrimp species.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Fourth National Report to the Convention on Biological Diversity of Maldives |url=https://www.cbd.int/doc/world/mv/mv-nr-04-en.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20151104002542/https://www.cbd.int/doc/world/mv/mv-nr-04-en.pdf |archive-date=4 November 2015 |access-date=2 April 2013 |website=Convention on Biological Diversity |publisher=Ministry of Housing and Environment |page=7}}</ref> | |||
| Among the many marine families represented are ], ], ], ], ], reef sharks, ]s, ]s, ], ], ], ], ]s, ], ]s, ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ] |
Among the many marine families represented are ], ], ], ], ], ], ]s, ]s, ], ], ], ], ]s, ], ]s, ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ].<ref name="scuba">{{Cite web |title=Maldives Marine Life |url=http://www.scubadivemaldives.com/category/maldives-marine-life/ |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111222080727/http://www.scubadivemaldives.com/category/maldives-marine-life/ |archive-date=22 December 2011 |access-date=2 April 2013 |website=Scuba Dive Maldives}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Sharks of the Maldives |url=http://www.themaldives.com/diving/maldives-sharks.html |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170110131054/http://www.themaldives.com/diving/maldives-sharks.html |archive-date=10 January 2017 |access-date=12 February 2017 |website=The Maldives}}</ref> | ||
| These coral reefs are home to a variety of marine ecosystems that vary from ] organisms to whale sharks. Sponges have gained importance as five species have displayed anti-tumor and anti-cancer properties.<ref name="Coral reefs">{{ |
These coral reefs are home to a variety of marine ecosystems that vary from ] organisms to whale sharks. Sponges have gained importance as five species have displayed anti-tumor and anti-cancer properties.<ref name="Coral reefs">{{Cite web |title=Regional Workshop on the Conservation and Sustainable Management of Coral Reefs |url=http://www.fao.org/docrep/X5627E/X5627E00.htm |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164420/http://www.fao.org/3/X5627E/X5627E00.htm |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=2 April 2013 |website=]}}</ref> | ||
| In 1998, sea-temperature warming of as much as {{convert|5|C-change}} due to a single ] event caused ], killing |
In 1998, sea-temperature warming of as much as {{convert|5|C-change}} due to a single ] event caused ], killing two-thirds of the nation's coral reefs.<ref name="Wheatley">{{Cite web |last=Wheatley |first=Alan |date=2 May 2004 |title=Maldives Nurses Its Coral Reefs Back to Life |url=http://www.globalcoral.org/Maldives%20Nurses%20Its%20Coral%20Reefs%20Back%20to%20Life.htm |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130921010958/http://www.globalcoral.org/Maldives%20Nurses%20Its%20Coral%20Reefs%20Back%20to%20Life.htm |archive-date=21 September 2013 |access-date=2 April 2013 |website=Global Coral Reef Alliance}}</ref> | ||
| In an effort to induce the regrowth of the reefs, scientists placed electrified cones anywhere from {{convert|20|–|60|ft}} below the surface to provide a substrate for larval coral attachment. In 2004, scientists witnessed corals regenerating. Corals began to eject pink-orange eggs and sperm. The growth of these electrified corals was five times faster than |
In an effort to induce the regrowth of the reefs, scientists placed electrified cones anywhere from {{convert|20|–|60|ft}} below the surface to provide a substrate for larval coral attachment. In 2004, scientists witnessed corals regenerating. Corals began to eject pink-orange eggs and sperm. The growth of these electrified corals was five times faster than untreated corals.<ref name=Wheatley/> Scientist Azeez Hakim stated: | ||
| {{Blockquote|before 1998, we never thought that this reef would die. We had always taken for granted that these animals would be there, that this reef would be there forever. El Niño gave us a wake-up call that these things are not going to be there forever. Not only this, but they also act as a natural barrier against tropical storms, floods and tsunamis. Seaweeds grow on the skeletons of dead coral.|<ref name="scuba" />}} | |||
| ==Government== | |||
| Again, in 2016, the coral reefs of the Maldives experienced a ]. Up to 95% of coral around some islands have died, and, even after six months, 100% of young coral transplants died. The surface water temperatures reached an all-time high in 2016, at 31 degrees Celsius in May.<ref>{{Cite web |date=31 July 2016 |title=Coral Bleaching Updates |url=http://marinesavers.com/2016/07/coral-bleaching-updates/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164516/https://marinesavers.com/2016/07/coral-bleaching-updates/ |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=12 February 2017 |website=MarineSavers |publisher=Marine Savers and Four Seasons Resorts Maldives (2012–2017)}}</ref> | |||
| {{main|Politics of the Maldives}} | |||
| ]: the Presidential Palace of Malé, Maldives]] | |||
| Recent scientific studies suggest that the faunistic composition can vary greatly between neighbour atolls, especially in terms of benthic fauna. Differences in terms of fishing pressure (including poaching) could be the cause.<ref name="Ducarme between">{{Cite journal |last=Ducarme |first=Frédéric |date=2016 |title=Field Observations of Sea Cucumbers in Ari Atoll, and Comparison with Two Nearby Atolls in Maldives |url=http://www.spc.int/DigitalLibrary/Doc/FAME/InfoBull/BDM/36/BDM36_09_Ducarme.pdf |url-status=live |journal=SPC Beche-de-mer Information Bulletin |volume=36 |archive-url=https://wayback.archive-it.org/all/20171010151307/http://www.spc.int/DigitalLibrary/Doc/FAME/InfoBull/BDM/36/BDM36_09_Ducarme.pdf |archive-date=10 October 2017 |access-date=31 March 2016}}</ref> | |||
| Maldives is a ] republic, with the President as ] and ]. The President heads the executive branch and appoints the cabinet which is approved by the ]. Following the introduction of a new constitution in 2008, direct elections for the President take place every five years, with a limit of two terms in office for any individual. The current President is ].<ref name="Hassan sworn">{{cite news |url=http://www.utsandiego.com/news/2012/feb/07/maldives-vp-hassan-takes-oath-as-president/|title=Maldives' VP Hassan Takes Oath as President |agency=Associated Press |work=Time Magazine |date=7 February 2012 |accessdate=7 February 2012 |location=Male, Maldives}}</ref> Members of the ] Majlis serve five-year terms, with the total number of members determined by atoll populations. At the ], 77 members were elected. The People's Majlis, located in Male, houses members from all over the country.<ref name=r1>{{cite web|url=http://www.maldives-ethnography.com/ |title=Maldives Enthongraphy |publisher=Maldives-ethnography.com|accessdate=30 June 2010}}</ref> | |||
| ===Wildlife=== | |||
| The republican constitution came into force in 1968, and was amended in 1970, 1972, and 1975. On 27 November 1997 it was replaced by another Constitution assented to by the President ]. This Constitution came into force on 1 January 1998. All stated that the ] was the Head of State, Head of Government and the Commander-in-Chief of the ] and the Police of the Maldives. A third ] was ratified on 7 August 2008, which separated the ] from the head of state. | |||
| {{Main|Wildlife of the Maldives}} | |||
| {{Multiple image | |||
| | total_width = 300 | |||
| | image1 = Rekiny wąsate, Malediwy.jpg | |||
| | alt1 = Sharks | |||
| | image2 = Addu City, Maldives (Unsplash UWCIzF2gkdg).jpg | |||
| | alt2 = Nature Park | |||
| | align = left | |||
| | image3 = Maldives 09642.JPG | |||
| | alt3 = Flower | |||
| | image4 = Maldives 00345.JPG | |||
| | alt4 = Bird | |||
| | perrow = 2/2 | |||
| | footer = Clockwise from top left: ]s near ], pier in ], '']'', and ''] sp.'' | |||
| }} | |||
| The ] includes the ] and ] of the ], reefs, and the surrounding ocean. Recent scientific studies suggest that the fauna varies greatly between ] following a north–south gradient, but important differences between neighbouring atolls were also found (especially in terms of sea animals), which may be linked to differences in fishing pressure — including poaching.<ref name=Ducarme-2016-V36>{{cite report |first=Frédéric |last=Ducarme |date=2016 |title=Field observations of sea cucumbers in Ari Atoll, and comparison with two nearby atolls in Maldives |series=Beche-de-mer Information Bulletin |volume=36 |publisher=] |url=http://www.spc.int/DigitalLibrary/Doc/FAME/InfoBull/BDM/36/BDM36_09_Ducarme.pdf |access-date=31 March 2016 |archive-date=10 October 2017 |archive-url=https://wayback.archive-it.org/all/20171010151307/http://www.spc.int/DigitalLibrary/Doc/FAME/InfoBull/BDM/36/BDM36_09_Ducarme.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| The terrestrial habitats of the Maldives are confronted with a significant threat as extensive development encroaches swiftly upon the limited land resources. Once seldom frequented, previously uninhabited islands now teeter on the brink of extinction, virtually devoid of untouched expanses. Over recent decades of intensive development, numerous natural environments crucial to indigenous species have suffered severe endangerment or outright destruction. | |||
| ===Law=== | |||
| Coral reef habitats had been damaged, as the pressure for land has brought about the creation of artificial islands. Some reefs have been filled with rubble with little regard for the changes in the currents on the reef shelf and how the new pattern would affect coral growth and its related life forms on the reef edges.<ref>{{cite journal |title=Coral recovery in the central Maldives archipelago since the last major mass-bleaching, in 1998 |url=https://www.nature.com/articles/srep34720.pdf |journal=Scientific Reports |date=2016 |doi=10.1038/srep34720 |access-date=3 October 2016 |last1=Pisapia |first1=C. |last2=Burn |first2=D. |last3=Yoosuf |first3=R. |last4=Najeeb |first4=A. |last5=Anderson |first5=K. D. |last6=Pratchett |first6=M. S. |volume=6 |page=34720 |pmid=27694823 |pmc=5046149 |bibcode=2016NatSR...634720P |archive-date=21 January 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220121004942/https://www.nature.com/articles/srep34720.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> Mangroves thrive in brackish or muddy regions of the Maldives. The archipelago hosts fourteen species spanning ten genera, among which is the fern Acrostichum aureum, indigenous to these islands.<ref name="Hingun-2015">{{cite report |url=https://www.cbd.int/doc/world/mv/mv-nr-05-en.pdf |title=Fifth National Report of Maldives to the Convention on Biological Diversity |last=Hingun |first=Handuvaree |publisher=Ministry of Environment and Energy |page=24 |isbn=978-99915-59-11-7 |access-date=2018-10-13 |year=2015 |place=Maldives |archive-date=6 December 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171206151108/https://www.cbd.int/doc/world/mv/mv-nr-05-en.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| {{See also|Judiciary in the Maldives}} | |||
| The waters surrounding the Maldives boast an extensive array of marine life, showcasing a vibrant tapestry of corals and over 2,000 species of fish.<ref>{{cite web |date=3 December 2023 |title=Discovering the Maldives Underwater Marine Life |url=https://www.mymaldives.com/maldives/marine-life/ |access-date=18 May 2024 |website=My Maldives |archive-date=25 February 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240225150457/https://www.mymaldives.com/maldives/marine-life/ |url-status=live }}</ref> From the dazzling hues of reef fish to the majestic presence of the ], ], and a diverse range of rays including ], ], and ], the seas teem with life. Notably, the Maldivian waters harbor the magnificent ]. Renowned for its biodiversity, these waters host rare species of both biological and commercial significance, with ] representing a longstanding traditional resource. Within the limited freshwater habitats such as ponds and marshes, freshwater fish such as the ] (]) and various smaller species thrive. Additionally, the introduction of the tilapia or mouth-breeder, facilitated by a ] agency in the 1970s, further enriches the aquatic diversity of the Maldives. | |||
| According to the ], "The judges are independent, and subject only to the Constitution and the law. When deciding matters on which the Constitution or the law is silent, judges must consider Islamic ]." Article 15 of the Act Number 1/81 (Penal Code) gives provision for ] punishments.<ref>{{cite web|title=Maldives Penal Code|url=http://www.agoffice.gov.mv/pdf/sublawe/PC1.pdf|accessdate=19 February 2013}}</ref> Article 156 of the constitution states that law includes the norms and provisions of sharia.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.law.emory.edu/ifl/legal/maldives.htm |title=Maldives |publisher=Law.emory.edu |date=16 March 1983 |accessdate=18 February 2013}}</ref> | |||
| ]'' in the Maldives]] | |||
| Due to their diminutive size, land-dwelling reptiles are scarce on the Maldivian islands. Among the limited terrestrial reptilian inhabitants are a species of gecko and the oriental garden lizard (Calotes versicolor), alongside the white-spotted supple skink (Riopa albopunctata), the Indian wolf snake (]), and the brahminy blind snake (]). | |||
| In the surrounding seas, however, a more diverse array of reptilian life thrives. Maldivian beaches serve as nesting grounds for the green sea turtle (Chelonia mydas), the hawksbill ], and the leatherback sea turtle. Furthermore, saltwater ] have been reported to occasionally reach the islands, taking residence in marshy regions.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Howard |first1=Jake |title=Crocs In Paradise! (aka The Maldives) |url=https://stabmag.com/news/crocs-in-paradise-aka-the-maldives |access-date=8 March 2016 |agency=Stab |date=8 March 2016 |archive-date=29 May 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160529080418/http://stabmag.com/news/crocs-in-paradise-aka-the-maldives/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Islam is the official religion of the Maldives and open practice of any other religion is forbidden and liable to prosecution. Article 2 of the revised constitution says that the republic "is based on the principles of Islam." Article nine says that "a non-Muslim may not become a citizen"; Article ten says that "no law contrary to any principle of Islam can be applied". Article nineteen states that "citizens are free to participate in or carry out any activity that is not expressly prohibited by sharia or by the law." | |||
| The location of this Indian Ocean archipelago means that its avifauna is mainly restricted to ]s.<ref>{{cite web |title=Wildlife of Maldives |url=https://www.maladweep.com/wildlife-of-maldives.html |access-date=18 May 2024 |website=Maladweep |archive-date=16 August 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220816160145/https://www.maladweep.com/wildlife-of-maldives.html |url-status=live }}</ref> Most of the species are Eurasian migratory birds, only a few being typically associated with the Indian sub-continent. Some, like the ] are seasonal. There are also birds that dwell in marshes and island bush, like the ] and the ]. ] are found occasionally on the southern islands due to their rich habitats.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Phillips |first=W.W.A. |year=1963 |title=The birds of the Maldive Islands, Indian Ocean |journal=] |volume=60 |pages=546–584}}</ref> | |||
| The requirement to adhere to a particular religion and prohibition of public worship following other religions is contrary to Article 18 of the ] and Article 18 of the ] to which Maldives has recently become party<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.foreign.gov.mv/v3/?p=menu_item&sub_id=21&submenu=Human%20Rights%20and%20Democracy |title=Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Maldives |publisher=Foreign.gov.mv |accessdate=30 June 2010}}</ref> and was addressed in Maldives' reservation in adhering to the Covenant claiming that "The application of the principles set out in Article 18 of the Covenant shall be without prejudice to the Constitution of the Republic of the Maldives."<ref>{{cite book|author=Davis, Thomas W. D. |title=Human Rights in Asia|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=LOHDoJO_b0EC&pg=PA33|year=2011|publisher=Edward Elgar Publishing|isbn=978-1-84844-680-9|page=33}}</ref> | |||
| ==Government and politics== | |||
| The ] of Maldives is headed by a Chief Justice, who is the head of judiciary. As of 2008 the President had appointed 5 judges, who were approved by the Parliament. The interim court will sit until a new permanent Supreme Court is nominated under the constitution. Underneath the Supreme Court sit a ] and a ]. The constitution requires an odd number of judges in the High Court of Maldives, leading to the current three appointed ]. Verdicts must be reached by a majority, but must also include a minority report. | |||
| {{main|Politics of the Maldives}} | |||
| {{multiple image | |||
| | align = right | |||
| | total_width = 320 | |||
| | image1 = Dr Muizzu in December 2023.jpg | |||
| | caption1 = ], ] since 2023 | |||
| | image2 = Hussain_Mohamed_Latheef_official_portrait_January_2024.jpg | |||
| | caption2 = ], ] since 2023 | |||
| }} | |||
| The Maldives is a ] ], with extensive influence of the president as ] and ]. The president heads the ], and appoints the ] which is approved by the ]. He leads the ]. The current president serving since 17 November 2023 is ].<ref>{{cite web |title=President Dr Mohamed Muizzu |url=https://presidency.gov.mv/PO/President/156 |website=] |access-date=17 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231128132252/https://presidency.gov.mv/PO/President/156 |archive-date=28 November 2023 |url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Dr Mohamed Muizzu sworn in as the 8th President of the Maldives |url=https://presidency.gov.mv/Press/Article/29036 |website=] |access-date=17 November 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231215142839/https://presidency.gov.mv/Press/Article/29036 |archive-date=15 December 2023 |url-status=live}}</ref> ] and Members of the ] Majlis serve five-year terms.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Maldives - History |url=https://countrystudies.us/maldives/1.htm |access-date=18 May 2024 |website=] |publisher=] |archive-date=12 May 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240512051834/https://countrystudies.us/maldives/1.htm |url-status=live }}</ref> The total number of members are determined by atoll populations. At the ], the ] (PNC) won a super-majority over the 93 constituencies.<ref>{{Cite news |date=22 April 202 |title=Pro-China party on course for landslide victory in Maldives election |url=https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2024/4/22/pro-china-party-on-course-for-landslide-victory-in-maldives-election |access-date=18 April 2024 |work=Al Jazeera |archive-date=22 April 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240422041229/https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2024/4/22/pro-china-party-on-course-for-landslide-victory-in-maldives-election |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Magistrate courts are located in the administrative divisions of the atolls of the Maldives, with a Magistrate Court in each inhabited island. At the moment, there are 194 Magistrate Courts in the country. | |||
| The republican constitution came into force in 1968 and was amended in 1970, 1972, and 1975.<ref>{{cite web |title=Government of the Maldives: Branches, History, The President |url=https://factsanddetails.com/south-asia/Maldives/Government_Justice_Maldives/entry-8047.html |website=Facts and Details |access-date=1 February 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240326095904/https://factsanddetails.com/south-asia/Maldives/Government_Justice_Maldives/entry-8047.html |archive-date=26 March 2024 |url-status=live}}</ref> On 27 November 1997 it was replaced by another Constitution assented to by then-President ]. This Constitution came into force on 1 January 1998.<ref>{{cite web |title=Constitution of the Republic of Maldives 1998 |url=http://www.asianlii.org/mv/legis/const/1998/1.html |website=AsianLII |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080824031014/http://www.asianlii.org/mv/legis/const/1998/1.html |archive-date=24 August 2008 |language=En |date=1998 |url-status=live}}</ref> The current ] was ratified by President Maumoon on 7 August 2008, and came into effect immediately, replacing and repealing the constitution of 1998. This new constitution includes a judiciary run by an independent commission, and independent commissions to oversee elections and fight corruption. It also reduces the executive powers vested under the president and strengthens the parliament. All state that the ] is head of state, head of government and Commander-in-Chief of the ] of the Maldives. | |||
| An appointed ] (PG) is responsible for initiating court proceedings on behalf of the government, overseeing how investigations are being conducted and having a say in criminal prosecutions, duties previously held by the ]. The PG has the power to order investigations, monitor detentions, lodge appeals and review existing cases. The PG is appointed by the President and has to be approved by the Parliament. | |||
| In 2018, the then ruling ] (PPM-Y)'s tensions with opposition parties and subsequent crackdown was termed as an "assault on democracy" by the ] chief.<ref>{{Cite news |date=8 February 2018 |title=Maldives crackdown an 'assault on democracy': UN rights chief |url=http://www.newindianexpress.com/world/2018/feb/08/maldives-crackdown-an-assault-on-democracy-un-rights-chief-1770198.html |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164433/https://www.newindianexpress.com/world/2018/feb/08/maldives-crackdown-an-assault-on-democracy-un-rights-chief-1770198.html |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=8 February 2018 |work=]}}</ref> | |||
| The Maldives, in cooperation with the ] (UNDP), wrote the world's first Islamic criminal code. As of 2008 the code awaited action by the parliament. | |||
| ] Speaker of the People's Majlis in May 2019]] | |||
| In April 2019 parliamentary ] The ] (MDP) of president Ibrahim Mohamed Solih won a landslide victory. It took 65 of 87 seats of the parliament.<ref>{{Cite news |date=6 April 2019 |title=Maldives election: Early results show victory for president's party |url=https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-47842303 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201211121842/https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-47842303 |archive-date=11 December 2020 |access-date=25 February 2021 |work=]}}</ref> This was the first time a single party was able to get such a high number of seats in the parliament in Maldivian history.<ref>{{Cite news |date=11 April 2019 |title=Majlis 19: An overview in numbers |url=https://avas.mv/en/62819 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190526094313/https://avas.mv/en/62819 |archive-date=26 May 2019 |access-date=18 May 2024 |work=Avas}}</ref> | |||
| ] is the Maldives' highest civilian honor that can be bestowed upon a person. It is awarded by the president, usually in an elaborate ceremony.<ref>{{Cite web |date=8 June 2019 |title=PM Modi conferred with Maldives' highest honour, Order of Nishanizzuddeen |url=https://www.narendramodi.in/pm-modi-conferred-with-maldives-highest-honour-order-of-nishanizzuddeen-545218 |access-date=28 February 2022 |website=narendramodi.in |archive-date=11 July 2021 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210711131559/https://www.narendramodi.in/pm-modi-conferred-with-maldives-highest-honour-order-of-nishanizzuddeen-545218 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ===Human rights=== | |||
| In April 2024, President Mohamed Muizzu's pro-China People's National Congress (PNC) won 66 seats in the 2024 ], while its allies took nine, giving the president the backing of 75 legislators in the 93-member house, meaning a super-majority and enough to change the constitution.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Rasheed |first1=Zaheena |title='Absolute power': After pro-China Maldives leader's big win, what's next? |url=https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2024/4/24/absolute-power-after-pro-china-maldives-leaders-big-win-whats-next |work=Al Jazeera |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| {{main|Human rights in the Maldives}} | |||
| ===Law=== | |||
| In February 2013, the judiciary sentenced a fifteen-year-old girl to 100 lashes and house arrest for 8 months in Vilimale's orphanage for engaging in premarital sex. The international media caught the story when her fornication case came alongside her rape case. Charges were brought against her in 2012 after police investigated accusations that her stepfather had raped her and killed their baby. He is still to face trial. Prosecutors stated her conviction did not relate to the rape case; she was sentenced for fornication, "which is a different matter."<ref name="Lang">{{cite news |url=http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-21595814 |title=Maldives girl to get 100 lashes for pre-marital sex |last=Lang |first=Olivia |date=26 February 2013 |work=BBC |accessdate=26 February 2013}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Maldives government does not agree with flogging rape victim: BBC|url=http://web.archive.org/web/20130728220842/http://english.cnm.mv/news/1095|author=Shinan, Ali |date=27 February 2013}}</ref> The government said it did not agree with the punishment and that it would look into changing the law.<ref name="Lang"/> The case generated a global petition which may damage the Maldivian tourism industry.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://globalvoicesonline.org/2013/03/26/maldives-rape-victims-flogging-sentence-touches-off-anti-tourism-campaign/ |last=Faroog |first=Saffah |title=Maldive Rape Victim's Flogging Sentence Touches Off Anti-Tourism Campaign |date=26 March 2013}}</ref> Homosexuality and nudism are illegal in the country. | |||
| {{See also|Judiciary of the Maldives|Law enforcement in the Maldives}} | |||
| According to the ], "the judges are independent, and subject only to the Constitution and the law. When deciding matters on which the Constitution or the law is silent, judges must consider Islamic ]".<ref>{{cite web |title=Maldives 2008 Constitution |url=https://www.constituteproject.org/constitution/Maldives_2008 |website=constituteproject.org |date=2008 |access-date=25 December 2021 |archive-date=23 January 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220123232052/https://www.constituteproject.org/constitution/Maldives_2008 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| An American citizen linked to the Bangladeshi who was caught bringing books on Christianity written in Dhivehi into the country, has been blacklisted and banned from entering the Maldives. | |||
| Maldives Customs said that the American, Kevin Thomas Greenson, was blacklisted following the collection of sufficient evidence by the Police of his connection with the Bangladeshi, Jathis Biswas, 44. | |||
| Jathis Biswas has also been deported, following accusations of spreading other religions in Maldives in cooperation with a group of Maldivians. | |||
| Customs found 11 books on Christianity with Jathis Biswas, who arrived in Maldives on 27 September 2012 on Sri Lankan Airlines.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://sun.mv/english/7224 |title=Man linked to bringing in Christianity books |publisher=Sun.mv |accessdate=2 April 2013}}</ref> | |||
| Islam is the official religion of the Maldives and open practice of any other religion is forbidden.<ref>{{Cite web |title=International Religious Freedom Report for 2017 |url=https://2009-2017.state.gov/j/drl/rls/irf/religiousfreedom/index.htm?year=2017&dlid=281028 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164405/https://2009-2017.state.gov/j/drl/rls/irf/religiousfreedom/index.htm?year=2017&dlid=281028 |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=30 December 2018 |website=]}}</ref> The 2008 constitution says that the republic "is based on the principles of Islam" and that "no law contrary to any principle of Islam can be applied". Non-Muslims are prohibited from becoming citizens.<ref name="Hirschl2011">{{Cite book |last=Ran Hirschl |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=OgIhbPBWlkwC&pg=PA34 |title=Constitutional Theocracy |date=5 May 2011 |publisher=Harvard University Press |isbn=978-0-674-05937-5 |page=34 |access-date=30 December 2018 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164433/https://books.google.com/books?id=OgIhbPBWlkwC&pg=PA34 |archive-date=14 January 2021 |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The Maldives ranks high on the ]. | |||
| The requirement to adhere to a particular religion and prohibition of public worship following other religions is contrary to Article 18 of the ] and Article 18 of the ] to which the Maldives has recently become party<ref>{{Cite web |title=Human Rights and Democracy |url=http://www.foreign.gov.mv/v3/?p=menu_item&sub_id=21&submenu=Human%20Rights%20and%20Democracy |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130921022819/http://www.foreign.gov.mv/v3/?p=menu_item&sub_id=21&submenu=Human%20Rights%20and%20Democracy |archive-date=21 September 2013 |access-date=30 June 2010 |website=]}}</ref> and was addressed in the Maldives' reservation in adhering to the Covenant claiming that "The application of the principles set out in Article 18 of the Covenant shall be without prejudice to the Constitution of the Republic of Maldives."<ref>{{Cite book |last=Davis, Thomas W. D. |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=LOHDoJO_b0EC&pg=PA33 |title=Human Rights in Asia |publisher=Edward Elgar Publishing |year=2011 |isbn=978-1-84844-680-9 |page=33 |access-date=20 June 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150915160814/https://books.google.com/books?id=LOHDoJO_b0EC&pg=PA33 |archive-date=15 September 2015 |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ===Foreign relations=== | |||
| A new ] came into effect on 16 July 2015, replacing the 1968 law, the first modern, comprehensive penal code to incorporate the major tenets and principles of Islamic law.<ref>{{Cite web |title=New penal code comes into effect |date=16 July 2015 |url=https://minivannewsarchive.com/tag/new-penal-code |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164404/https://minivannewsarchive.com/tag/new-penal-code |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=10 July 2020}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Maldives Penal Code - Law No. 9/2014 |url=https://www.law.upenn.edu/live/files/4203-maldives-penal-code-2014.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164342/https://www.law.upenn.edu/live/files/4203-maldives-penal-code-2014.pdf |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=10 July 2020 |website=]}}</ref> | |||
| {{main|Foreign relations of the Maldives}} | |||
| ] are illegal in the Maldives, although tourist resorts typically operate as exceptions to this law.<ref>{{Cite web |date=17 May 2016 |title=State Sponsored Homophobia 2016: A world survey of sexual orientation laws: criminalisation, protection and recognition |url=http://ilga.org/downloads/02_ILGA_State_Sponsored_Homophobia_2016_ENG_WEB_150516.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170902183618/http://ilga.org/downloads/02_ILGA_State_Sponsored_Homophobia_2016_ENG_WEB_150516.pdf |archive-date=2 September 2017 |access-date=20 June 2017 |website=]}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |last=Bloom |first=Laura Begley |date=25 November 2019 |title=20 Most Dangerous Places For Gay Travelers (And The 5 Safest) |url=https://www.forbes.com/sites/laurabegleybloom/2019/11/25/most-dangerous-places-safest-lgbtq-gay-travelers/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164459/https://www.forbes.com/sites/laurabegleybloom/2019/11/25/most-dangerous-places-safest-lgbtq-gay-travelers/ |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=19 November 2020 |website=] |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |date=19 October 2016 |title=From South Africa to the Maldives: Surprising holiday destinations for LGBT travellers |url=https://www.independent.co.uk/travel/news-and-advice/gay-holidays-lgbt-friendly-safety-bali-buenos-aires-cape-town-iceland-maldives-honeymoons-a7369316.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164430/https://www.independent.co.uk/travel/news-and-advice/gay-holidays-lgbt-friendly-safety-bali-buenos-aires-cape-town-iceland-maldives-honeymoons-a7369316.html |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=18 May 2024 |work=]}}</ref> | |||
| Since 1996, the Maldives has been the official progress monitor of the ]. In 2002, the Maldives began to express interest in the Commission but as of 2008 had not applied for membership. Maldive's interest relates to its identity as a small island state, especially economic development and environmental preservation, and its desire for closer relations with France, a main actor in the IOC region. The Maldives is a founding member of the ], SAARC. The young Republic joined the ] in 1982, some 17 years after gaining independence from Great Britain. The Maldives enjoys close ties with Commonwealth members ] and ]. The Maldives and ] are also both members of the ]. | |||
| === |
===Foreign relations=== | ||
| {{main|Foreign relations of the Maldives}} | |||
| Since 1996, the Maldives has been the official progress monitor of the ]. In 2002, the Maldives began to express interest in the commission but {{As of|2008|lc=y}} had not applied for membership. Maldives' interest relates to its identity as a small island state, especially economic development and environmental preservation, and its desire for closer relations with France, a main actor in the IOC region. | |||
| The Maldives is a founding member of the ] (]). The republic joined the Commonwealth in 1982, some 17 years after gaining independence from the United Kingdom. In October 2016, the Maldives announced its withdrawal from the Commonwealth<ref>{{Cite web |date=13 October 2016 |title=Secretary-General statement on Maldives decision to leave the Commonwealth |url=https://thecommonwealth.org/news/secretary-general-statement-maldives-decision-leave-commonwealth |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200517085315/https://thecommonwealth.org/media/news/secretary-general-statement-maldives-decision-leave-commonwealth |archive-date=17 May 2020 |access-date=18 May 2024 |website=The Commonwealth}}</ref> in protest at allegations of human rights abuse and failing democracy.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161013143856/https://www.theguardian.com/world/2016/oct/13/maldives-quits-commonwealth-over-alleged-rights-abuses |date=13 October 2016 }}, '']'', 13 October 2016</ref> The Maldives enjoys close ties with Commonwealth members ] and ]. The Maldives and ] are also both members of the ]. Following his election as president in 2018, Ibrahim Mohamed Solih and his Cabinet decided that the Maldives would apply to rejoin the Commonwealth,<ref>{{Cite web |title=The President's Office |url=https://presidency.gov.mv/presidentNews/news/10346 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181121161727/https://presidency.gov.mv/presidentNews/news/10346 |archive-date=21 November 2018 |access-date=26 November 2018}}</ref> with readmission occurring on 1 February 2020.<ref>{{Cite news |date=1 February 2020 |title=Maldives rejoins Commonwealth after evidence of reforms |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/feb/01/maldives-rejoins-commonwealth-after-evidence-of-reforms |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200418002056/https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/feb/01/maldives-rejoins-commonwealth-after-evidence-of-reforms |archive-date=18 April 2020 |access-date=4 February 2020 |work=] |agency=]}}</ref> | |||
| {{main|Maldives National Defence Force}} | |||
| As a result of sanctions imposed upon the ] by the West in response to ]'s ] in February 2022, many of them sought refuge for their mega-yachts in the Maldives due to the absence of an extradition treaty with the United States and other countries.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Oltermann |first=Peter |date=3 March 2022 |title=Germany seizes Russian billionaire Alisher Usmanov's $600m superyacht - report |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2022/mar/03/germany-seizes-russian-billionaire-alisher-usmanovs-600m-superyacht-report |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220303014906/https://www.theguardian.com/world/2022/mar/03/germany-seizes-russian-billionaire-alisher-usmanovs-600m-superyacht-report |archive-date=3 March 2022 |access-date=3 March 2022 |work=] |location=London}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| Following a cabinet meeting, in June 2024, the government of the Maldives decided to ban ] holders from entering the country, as a response to the ongoing ] in the ].<ref>{{cite news |title=The Government decides to impose a ban on Israeli passports |url=https://presidency.gov.mv/Press/Article/30948 |access-date=2 June 2024 |agency=The President's Office |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240603105516/https://presidency.gov.mv/Press/Article/30948 |archive-date=3 June 2024}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Maldives bans Israeli passport holders over war on Gaza |url=https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2024/6/2/maldives-bans-israeli-passport-holders-from-entering-the-country |access-date=2 June 2024 |agency=] |archive-date=2 June 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240602195306/https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2024/6/2/maldives-bans-israeli-passport-holders-from-entering-the-country |url-status=live }}</ref><ref>{{cite news |title=Maldives to ban Israeli passport holders from entry in protest over Gaza war |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/article/2024/jun/03/maldives-israel-passport-holders-ban-gaza-war |access-date=3 June 2024 |agency=The Guardian}}</ref> | |||
| The Maldives National Defence Force is the combined security organisation responsible for defending the security and sovereignty of the Maldives, having the primary task of being responsible for attending to all internal and external security needs of the Maldives, including the protection of the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and the maintenance of peace and security. The MNDF component branches are the Coast Guard, Marine Corps, Special Forces, Service Corps and the Corps of Engineers. | |||
| ===Military=== | |||
| As a water-bound nation much of the security concerns lie at sea. Almost 99% of the country is covered by sea and the remaining 1% land is scattered over an area of {{convert|800|km|0|abbr=on}} × {{convert|120|km|0|abbr=on}}, with the largest island being not more than {{convert|8|km2|0|abbr=on}}. Therefore the duties assigned to the MNDF of maintaining surveillance over Maldives' waters and providing protection against foreign intruders poaching in the EEZ and territorial waters, are immense tasks from both logistical and economic view points. Hence, for carrying out these functions, it is the Coast Guard that plays a vital role. To provide timely security its patrol boats are stationed at various MNDF Regional Headquarters. Coast Guard is also assigned to respond to the maritime distress calls and to conduct search and rescue operations in a timely manner. Maritime pollution control exercises are conducted regularly on an annual basis for familiarisation and handling of such hazardous situations. | |||
| {{main|Maldives National Defence Force}} | |||
| ] | |||
| The Maldives National Defence Force is the combined security organisation responsible for defending the security and sovereignty of the Maldives, having the primary task of being responsible for attending to all internal and external security needs of the Maldives, including the protection of the ] (EEZ) and the maintenance of peace and security.<ref>{{cite web |author1=Saruna; President’s Office |title=National Security Policy 2012 |url=http://saruna.mnu.edu.mv/jspui/bitstream/123456789/13946/1/national-security-policy.pdf |website=Digital Repository of Maldives National University |publisher=Government of the Republic of Maldives |pages=221 |date=2012 |access-date=18 May 2024 |archive-date=16 April 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240416191128/http://saruna.mnu.edu.mv/jspui/bitstream/123456789/13946/1/national-security-policy.pdf |url-status=live }}</ref> The MNDF component branches are the ], ], ], Service Corps, Defence Intelligence Service, Military Police, Corps of Engineers, Special Protection Group, Medical Corps, Adjutant General's Corps, Air Corps, and Fire and Rescue Service. The Maldives has an arrangement with India allowing cooperation on radar coverage. | |||
| ===Tourism=== | |||
| One of the mainsource of income, tourism is Maldives is brought about by honeymoon and wedding. has reported that Maldives is a lovely wedding destination. | |||
| As a water-bound nation, much of its security concerns life at sea. Almost 99% of the country is covered by sea and the remaining 1% land is scattered over an area of {{convert|800|km|0|abbr=on}} × {{convert|120|km|0|abbr=on}}, with the largest island being not more than {{convert|8|km2|0|abbr=on}}. Therefore, the duties assigned to the MNDF of maintaining surveillance over the Maldives' waters and providing protection against foreign intruders poaching in the EEZ and territorial waters, are immense tasks from both logistical and economic viewpoints. | |||
| ==Administrative divisions== | |||
| The Coast Guard plays a vital role in carrying out these functions. To provide timely security its patrol boats are stationed at various MNDF Regional Headquarters. The Coast Guard is also assigned to respond to maritime distress calls and to conduct search and rescue operations in a timely manner. | |||
| ] | |||
| In 2019, the Maldives signed the UN ].<ref>{{Cite web |date=7 July 2017 |title=Chapter XXVI: Disarmament – No. 9 Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons |url=https://treaties.un.org/Pages/ViewDetails.aspx?src=TREATY&mtdsg_no=XXVI-9&chapter=26&clang=_en |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190806220546/https://treaties.un.org/Pages/ViewDetails.aspx?src=TREATY&mtdsg_no=XXVI-9&chapter=26&clang=_en |archive-date=6 August 2019 |access-date=18 October 2019 |website=United Nations Treaty Collection |publisher=]}}</ref> | |||
| ===Human rights=== | |||
| {{main|Human rights in the Maldives}} | |||
| Human rights in the Maldives is a contentious issue. In its 2011 ] report, ] declared the Maldives "Partly Free", claiming a reform process which had made headway in 2009 and 2010 had stalled.<ref name="FH 2011">{{Cite web |last= |year= |title=Maldives: Freedom in the World |url=https://freedomhouse.org/country/maldives/freedom-world/2024 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240313104840/https://freedomhouse.org/country/maldives/freedom-world/2024 |archive-date=13 March 2024 |access-date=19 May 2024 |website=] }}</ref> The ] claims in their 2012 report on human rights practices in the country that the most significant problems are corruption, lack of ], abuse, and unequal treatment of women.<ref name="State 2012">{{Cite web |last= |year=2012 |title=Country Reports on Human Rights Practices for 2011: Maldives |url=https://2009-2017.state.gov/j/drl/rls/hrrpt/humanrightsreport/index.htm?dlid=186470 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164432/https://2009-2017.state.gov/j/drl/rls/hrrpt/humanrightsreport/index.htm?dlid=186470 |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=24 August 2012 |website=] |publisher=]}}</ref> | |||
| ===Administrative divisions=== | |||
| {{main|Administrative divisions of the Maldives}} | {{main|Administrative divisions of the Maldives}} | ||
| ] letter used to identify the atoll. Natural atolls are labelled in light blue. |
] letter used to identify the atoll. Natural atolls are labelled in light blue.]] | ||
| The Maldives has twenty-six natural ] and few island groups on isolated reefs, all of which have been divided into twenty-one administrative divisions ( |
The Maldives has twenty-six natural ] and few island groups on isolated reefs, all of which have been divided into twenty-one administrative divisions (17 administrative atolls and cities of Malé, Addu, ], ], and ]).<ref>{{Cite web |title=Atolls of Maldives |url=http://www.statoids.com/umv.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100102053209/http://statoids.com/umv.html |archive-date=2 January 2010 |access-date=30 June 2010 |website=Statoids}}</ref> | ||
| Each atoll is administered by an elected Atoll Council. The islands are administered by an elected Island Council. | |||
| Each atoll is administered by an ] (''Atholhu Veriyaa'') appointed by the President. The Ministry of Atoll Administration and its Northern and Southern Regional Offices, Atoll Offices and Island Offices are collectively responsible to the President for Atolls Administration. The administrative head of each island is the Island ] (Katheeb), appointed by the President. The ]'s immediate superior is the Atoll Chief. | |||
| In addition to a name, every administrative division is identified by the Maldivian code letters, such as "]" for ] (Thiladhunmathi North); and by a Latin code letter. The first corresponds to the geographical Maldivian name of the atoll; the second is a code adopted for convenience. As there are certain islands in different atolls that have the same name, for administrative purposes this code is quoted before the name of the island, for example: Baa Funadhoo, Kaafu Funadhoo, Gaafu-Alifu Funadhoo. Since most atolls have very long geographical names it is also used whenever the long name is inconvenient, for example in the atoll website names.<ref name="autogenerated1">''Divehiraajjege Jōgrafīge Vanavaru''. Muhammadu Ibrahim Lutfee</ref> | |||
| The Maldives has 7 provinces each consisting of the following administrative divisions (the capital Malé is its own administrative division): | |||
| #]; consists of ], ] and ]. | |||
| #]; consists of ], ], ] and ]. | |||
| #]; consists of ], ], ] and ]. | |||
| #]; consists of ], ] and ]. | |||
| #]; consists of ] and ]. | |||
| #]; consists of ] and ]. | |||
| #]; consists of ] and ]. | |||
| The introduction of code-letter names has been a source of much puzzlement and misunderstandings, especially among foreigners. Many people have come to think that the code-letter of the administrative atoll is its new name and that it has replaced its geographical name. Under such circumstances, it is hard to know which is the correct name to use.<ref name="autogenerated1" /> | |||
| In addition to a name, every administrative division is identified by the Maldivian code letters, such as "]" for ] (Thiladhunmathi North); and by a Latin code letter. The first corresponds to the geographical Maldivian name of the atoll; the second is a code adopted for convenience. As there are certain islands in different atolls that have the same name, for administrative purposes this code is quoted before the name of the island, for example: Baa Funadhoo, Kaafu Funadhoo, Gaafu-Alifu Funadhoo. Since most Atolls have very long geographical names it is also used whenever the long name is inconvenient, for example in the atoll website names.<ref name="autogenerated1">''Divehiraajjege Jōgrafīge Vanavaru''. Muhammadu Ibrahim Lutfee</ref> | |||
| The introduction of code-letter names has been a source of much puzzlement and misunderstandings, especially among foreigners. Many people have come to think that the code-letter of the administrative atoll is its new name and that it has replaced its geographical name. Under such circumstances it is hard to know which is the correct name to use.<ref name="autogenerated1" /> | |||
| ==Economy== | ==Economy== | ||
| {{main|Economy of the Maldives}} | {{main|Economy of the Maldives}} | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| Historically, the Maldives provided enormous quantities of ] shells, ]. From the 2nd century CE, the islands were known as the 'Money Isles' by the Arabs.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Lyon, James |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=hJD94VZweCIC&pg=PA9 |title=Maldives |date=October 2003 |publisher=Lonely Planet Publications Pty Ltd |isbn=978-1-74059-176-8 |page=9 |access-date=9 November 2015 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160412225337/https://books.google.com/books?id=hJD94VZweCIC&pg=PA9 |archive-date=12 April 2016 |url-status=live}}</ref> '']'' were used for centuries as a currency in Africa, and huge amounts of ] cowries were introduced into Africa by western nations during the period of ].<ref>Hogendorn, Jan and Johnson Marion (1986). ''The Shell Money of the Slave Trade''. African Studies Series 49, ], ] {{ISBN|0521541107}}.</ref> The cowry is now the symbol of the ]. | |||
| In ancient times the Maldives were renowned for ]s, ] rope, dried ] fish (Maldive Fish), ] (Maavaharu), and ] (Tavakkaashi). Local and foreign trading ships used to load these products in Sri Lanka and transport them to other harbours in the Indian Ocean. | |||
| In the early 1970s and 1980s, the Maldives was one of the world's 20 poorest countries, with a population of 100,000.<ref>{{cite journal |title=Republic of Maldives Maldivian Labor Market: Spotlight on youth, tourism, and fisheries Analysis based on census 2014 data |journal=World Bank |date=30 May 2017 |url=https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/126131536606781671/pdf/115743-REVISED-MV-LaborNote-final.pdf}}</ref> The economy at the time was largely dependent on fisheries and trading local goods such as ] rope, ] (Maavaharu), and ] (Tavakkaashi) with neighbouring countries and ] countries.<ref>{{cite web |last1=Shakoor |first1=Athif Ibrahim |title=The tourism industry of the Maldives, - have we gone beyond 'regulatory capture'? |url=http://saruna.mnu.edu.mv/jspui/bitstream/123456789/8586/1/The%20tourism%20industry%20of%20the%20Maldives%2C%20%E2%80%93%20have%20we%20gone%20beyond%20%E2%80%98regulatory%20capture%E2%80%99.pdf |website=The Maldives National Journal of Research |publisher=Saruna.mnu.edu.mv |access-date=1 August 2020}}</ref> | |||
| Historically Maldives provided enormous quantities of ] shells, ]. From the 2nd century AD the islands were known as the 'Money Isles' by the Arabs.<ref>{{cite book | url=http://books.google.com.my/books?id=hJD94VZweCIC&pg=PA9 | title=Maldives | author=Lyon, James | date=October 2003 | publisher=Lonely Planet Publications Pty Ltd | page=9 | isbn=978-1-74059-176-8}}</ref> '']'' were used for centuries as a currency in Africa, and huge amounts of ] cowries were introduced into Africa by western nations during the period of ].<ref>Hogendorn, Jan and Johnson Marion (1986). ''The Shell Money of the Slave Trade''. African Studies Series 49, ], ] ISBN 0521541107.</ref> The cowry is now the symbol of the ]. | |||
| The Maldivian government began |
The Maldivian government began a largely successful ] programme in the 1980s, initiated by lifting import quotas and giving more opportunities to the private sector. At the time ] sector which would play a significant role in the nation's development was at its infant stage. | ||
| Agriculture and manufacturing continue to play lesser roles in the economy, constrained by the limited availability of cultivable land and the shortage of domestic labour. | |||
| ===Tourism=== | |||
| The Maldivian economy is to a large degree based on tourism. In late December 2004, the ] ], 12,000 displaced, and property damage exceeding $400 million. As a result of the tsunami, the GDP contracted by about 3.6% in 2005. A rebound in tourism, post-tsunami reconstruction, and development of new resorts helped the economy recover quickly and showed an 18% increase on 2006. 2013 estimates show Maldivians enjoy the highest GDP (PPP) per capita $11,900 (2013 est) among south Asian countries. | |||
| {{main|Tourism in the Maldives|Diving in the Maldives|List of mosques in the Maldives}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Agriculture and manufacturing continue to play a lesser role in the economy, constrained by the limited availability of cultivable land and the shortage of domestic labour. Tourism gave a major boost to the country's fledgling traditional ] such as mat weaving, ] work, ], and coir rope making. New industries that have since emerged include printing, production of ] ], brick making, marine engine repairs, bottling of ], and garment production. | |||
| The Maldives remained largely unknown to tourists until the early 1970s. Only 200 islands are home to its 382,751 inhabitants.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Discover the islands |url=https://islands.mv/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190702120755/https://islands.mv/ |archive-date=2 July 2019 |access-date=7 January 2020 |website=islands.mv}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Inhabited islands |url=https://isles.gov.mv/Island/IslandListEn?CategoryId=1 |website=isles.gov.mv |publisher=The President's Office |access-date=26 July 2023 |archive-date=10 June 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230610184632/https://isles.gov.mv/Island/IslandListEn?CategoryId=1 |url-status=dead }}</ref> The other islands are used entirely for economic purposes, of which tourism and agriculture are the most dominant. ] accounts for 28% of the GDP and more than 60% of the Maldives' foreign exchange receipts. Over 90% of government tax revenue comes from import duties and tourism-related taxes. | |||
| ===Tourism=== | |||
| The development of tourism fostered the overall growth of the ]. It created direct and indirect employment and income generation opportunities in other related industries. The first tourist resorts were opened in 1972 with Bandos Island Resort and Kurumba Village (the current name is Kurumba Maldives),<ref>{{Cite news |date=13 February 2012 |title=Coup? What coup? Tourists ignore Maldives turmoil |url=https://www.theage.com.au/traveller/inspiration/coup-what-coup-tourists-ignore-maldives-turmoil-20120213-1t0wi.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120215200358/http://www.theage.com.au/travel/travel-news/coup-what-coup-tourists-ignore-maldives-turmoil-20120213-1t0wi.html |archive-date=15 February 2012 |access-date=26 February 2012 |work=] |location=Melbourne}}</ref> which transformed the Maldives' economy. | |||
| ] | |||
| ] of ] (Baa atoll)]] | |||
| {{main|Tourism in the Maldives|Diving in the Maldives}} | |||
| According to the ], the emergence of tourism in 1972 transformed the economy, moving rapidly from dependence on fisheries to tourism. In just three and a half decades, the industry became the main source of income. Tourism was also the country's biggest foreign currency earner and the single largest contributor to the GDP. {{As of|2008}}, 89 resorts in the Maldives offered over 17,000 beds and hosted over 600,000 tourists annually.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Home |url=http://www.tourism.gov.mv/ |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090417062328/http://www.tourism.gov.mv:80/ |archive-date=17 April 2009 |access-date=3 April 2009 |website=]}}</ref> In 2019, over 1.7 million visitors came to the islands.<ref>{{Cite web |title=1.7 million tourists visit the Maldives in 2019 |url=https://www.tourism.gov.mv/16009/1-7-million-tourists-visit-the-maldives-in-2019/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164454/https://www.tourism.gov.mv/16009/1-7-million-tourists-visit-the-maldives-in-2019/ |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=9 January 2020 |website=]}}</ref> | |||
| The Maldives remained largely unknown to tourists until the early 1970s. Only 185 islands are home to its 300,000 inhabitants. The other islands are used entirely for economic purposes, of which tourism and agriculture are the most dominant. Tourism accounts for 28% of the GDP and more than 60% of the Maldives' foreign exchange receipts. Over 90% of government tax revenue comes from import duties and tourism-related taxes. The development of tourism fostered the overall growth of the ]. It created direct and indirect employment and income generation opportunities in other related industries. The first tourist resorts were opened in 1972 with Bandos island resort and Kurumba Village (the current name is Kurumba Maldives),<ref>{{cite news| url=http://www.theage.com.au/travel/travel-news/coup-what-coup-tourists-ignore-maldives-turmoil-20120213-1t0wi.html | location=Melbourne | work=The Age | title=Coup? What coup? Tourists ignore Maldives turmoil | date=13 February 2012}}</ref> which transformed the Maldives economy. | |||
| The number of resorts increased from 2 to 92 between 1972 and 2007. {{As of|2007}}, over 8,380,000 tourists had visited the Maldives.<ref>{{Cite web |title=ހަތުރުވެރިކަމުގެ ތަރައްޤީގެ 35 އަހަރު |trans-title=35 years of tourism |url=http://tourism.gov.mv/pubs/35_years_of_tourism_final.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091122171606/http://www.tourism.gov.mv/pubs/35_years_of_tourism_final.pdf |archive-date=22 November 2009 |access-date=2 April 2013 |website=] |language=dv}}</ref> | |||
| ] of ] (Baa atoll).]] | |||
| According to the ], the emergence of tourism in 1972 transformed the economy, moving rapidly from dependence on fisheries to tourism. In just three and a half decades, the industry became the main source of income. Tourism was also the country's biggest foreign currency earner and the single largest contributor to the GDP. As of 2008, 89 resorts in the Maldives offered over 17,000 beds and hosted over 600,000 tourists annually.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.tourism.gov.mv/ |title=Ministry of Tourism. Retrieved 3 April 2009 |publisher=Tourism.gov.mv |accessdate=2 April 2013}}</ref> | |||
| The country has ] listed as ] tentative sites.<ref>{{Cite web |last= |first= |title=Coral Stone Mosques of Maldives |url=https://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/5812 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164509/https://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/5812 |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=26 December 2019 |website=UNESCO World Heritage Centre}}</ref> | |||
| The number of resorts increased from 2 to 92 between 1972 and 2007. As of 2007, over 8,380,000 tourists had visited Maldives.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://tourism.gov.mv/pubs/35_years_of_tourism_final.pdf |title=35 years of tourism |format=PDF |accessdate=2 April 2013}}</ref> Visitors to Maldives do not need to apply for a visa pre-arrival, regardless of their country of origin, provided they have a valid passport, proof of onward travel, and the money to be self-sufficient while in the country.<ref name=doi>{{cite web|title=Entry into Maldives|url=http://www.immigration.gov.mv/index.php/entry-to-maldives.html|publisher=Department of Immigration and Emigration, Republic of Maldives|accessdate=9 February 2012}}</ref> | |||
| ====Visitors==== | |||
| Most visitors arrive at ], on ] Island, adjacent to the capital Malé. The airport is served by flights to ], Sri Lanka, ], ], Singapore, Istanbul, and major airports in South-East Asia, as well as charters from Europe. ], on the southern atoll of ], also serves an international flight to ] several times a week. British Airways offer direct flights to the Maldives around 2–3 times per week. | |||
| {{see also|#Transportation|Visa policy of Maldives}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ===Fishing industry=== | |||
| Visitors to the Maldives do not need to apply for a ] pre-arrival, regardless of their country of origin, provided they have a valid ], proof of onward travel, and the money to be self-sufficient while in the country.<ref name="doi">{{Cite web |title=Entry into Maldives |url=https://immigration.gov.mv/tourist-visa/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164448/https://immigration.gov.mv/tourist-visa/ |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=9 February 2012 |website=Maldives Immigration}}</ref> | |||
| Most visitors arrive at ], on ] Island, adjacent to the capital Malé. The airport is served by flights to and from ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and major airports in ] like ] in ], as well as charters from ] like ] in ]. ], on the southern atoll of Addu, also serves an international flight to ] in ] several times a week. ] offers direct flights to the Maldives from ].<ref>{{cite web |title=Flights to Maldives |url=https://www.britishairways.com/en-gb/destinations/maldives/flights-to-maldives |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221020220431/https://www.britishairways.com/en-gb/destinations/maldives/flights-to-maldives |archive-date=20 October 2022 |access-date=20 October 2022 |website=]}}</ref> | |||
| ===Fishing industry=== | |||
| {{main|Fishing industry in the Maldives}} | {{main|Fishing industry in the Maldives}} | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| For many centuries the Maldivian economy was entirely dependent on fishing and other ] products. Fishing remains the main occupation of the people and the government gives priority to the fisheries sector. | For many centuries the Maldivian economy was entirely dependent on fishing and other ] products. Fishing remains the main occupation of the people and the government gives priority to the fisheries sector. | ||
| The ] of the traditional fishing boat called '']'' in 1974 was a major milestone in the development of the fisheries industry. A fish canning plant was installed on ] in 1977, as a joint venture with a Japanese firm. In 1979, a Fisheries Advisory Board was set up with the mandate of advising the government on policy guidelines for the overall development of the fisheries sector. Manpower development |
The ] of the ] called '']'' in 1974 was a major milestone in the development of the fisheries industry. A fish canning plant was installed on ] in 1977, as a joint venture with a Japanese firm. In 1979, a Fisheries Advisory Board was set up with the mandate of advising the government on policy guidelines for the overall development of the fisheries sector. Manpower development programmes began in the early 1980s, and fisheries education was incorporated into the school curriculum. ]s and navigational aids were located at various strategic points. Moreover, the opening up of the ] (EEZ) of the Maldives for fisheries has further enhanced the growth of the fisheries sector. | ||
| As of |
{{As of|2010}}, fisheries contributed over 15% of the country's GDP and engaged about 30% of the country's workforce. Fisheries were also the second-largest foreign exchange earner after ]. | ||
| ==Demographics== | ==Demographics== | ||
| {{main|Demographics of the Maldives}} | {{main|Demographics of the Maldives}} | ||
| {{refimprove section|date=April 2012}} | |||
| ], the capital of the Maldives]] | |||
| ] | |||
| The Maldivian ethnic identity is a blend of the cultures reflecting the peoples who settled on the islands, reinforced by religion and language. The earliest settlers were probably from ] and Sri Lanka. They are linguistically and ethnically related to the people in the ]. They are ethnically known as ]. | |||
| {{Bar chart | |||
| |title= Maldives population | |||
| |label_type= Year | |||
| |data_type= Population<ref>{{Cite web |title=Census Population by Sex and Sex - Ratio, and Inter-Censal Variation of Population, 1911 - 2014 |url=http://statisticsmaldives.gov.mv/yearbook/statisticalarchive/wp-content/uploads/sites/3/2017/02/table2.1.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164341/http://statisticsmaldives.gov.mv/yearbook/statisticalarchive/wp-content/uploads/sites/3/2017/02/table2.1.pdf |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=24 May 2020 |website=National Bureau of Statistics (Maldives)}}</ref><ref name="Maldives Population Projections 2014-2054">{{Cite web |title=Maldives Population Projections 2014–2054 |url=http://statisticsmaldives.gov.mv/nbs/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/Projected-Mid-Year-population-of-Maldives.xlsx |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164344/http://statisticsmaldives.gov.mv/nbs/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/Projected-Mid-Year-population-of-Maldives.xlsx |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=24 May 2020 |website=statisticsmaldives.gov.mv |publisher=National Bureau of Statistics}}</ref> | |||
| |data_max= 560,000 | |||
| |label1= 1911 |data1= 72,237 | |||
| |label2= 1966 |data2= 100,883 | |||
| |label3= 2000 |data3= 270,101 | |||
| |label4= 2020 est. |data4= 557,426 | |||
| }} | |||
| The largest ethnic group is ], i.e. the Maldivians, native to the historic region of the Maldive Islands comprising today's Republic of Maldives and the island of ] in ], India. They share the same culture and speak the ]. They are principally an ] people, having traces of Middle Eastern, South Asian, ] and African genes in the population. | |||
| In the past, there was also a small ] population known as the ]. This group has now been almost completely absorbed into the larger Maldivian society but were once native to the island of ], which was evacuated in 1968 due to heavy erosion of the island.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Jaleel |first1=Jana |title=An Untold Story - The Lost People of Giraavaru |url=https://maldivesvoice.mv/480 |access-date=20 July 2023 |agency=Maldives Voice |date=20 July 2023 |archive-date=16 April 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240416190912/https://maldivesvoice.mv/480 |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| Some social stratification exists on the islands. It is not rigid, since rank is based on varied factors, including occupation, wealth, Islamic virtue, and family ties. Instead of a complex ] system, there was merely a distinction between noble (bēfulhu) and common people in the Maldives. Members of the social elite are concentrated in Malé. | Some social stratification exists on the islands. It is not rigid, since rank is based on varied factors, including occupation, wealth, Islamic virtue, and family ties. Instead of a complex ] system, there was merely a distinction between noble (bēfulhu) and common people in the Maldives. Members of the social elite are concentrated in Malé. | ||
| ] | |||
| The population doubled by 1978, and the ] rate peaked at 3.4% in 1985. At the 2006 census, the population had reached 298,968,<ref>{{cite web|title=Islands by Population Size and Percentage Share of Total Population|url=http://www.planning.gov.mv/publications/census2006_island_level_tables/population/population/PP_05.htm|work=Maldives: Population and Housing Census 2006|publisher=Ministry of Planning and National Development|accessdate=8 February 2012}}</ref> although the census in 2000 showed that the population growth rate had declined to 1.9%. Life expectancy at birth stood at 46 years in 1978, and later rose to 72. Infant mortality has declined from 12.7% in 1977 to 1.2% today, and adult literacy reached 99%. Combined school enrollment reached the high 90s. The population was projected to have reached 317,280 in 2010.<ref>{{cite web|title=page 273|url=http://planning.gov.mv/en/images/stories/publications/analysiscd/pdf/13.pdf|accessdate=5 July 2014}}</ref> Within an area of 298 km<sup>2</sup> this gives a population density of 1,065/km<sup>2</sup>. To get this in a wider context, an average population density of 53/km<sup>2</sup> was found for the '''"'''World (land only, excluding ])'''"''' in Misplaced Pages's ] based on data from July 5, 2014. | |||
| The population doubled by 1978, and the ] rate peaked at 3.4% in 1985. By the 2006 census, the population had reached 298,968,<ref>{{Cite web |title=Islands by Population Size and Percentage Share of Total Population |url=http://www.planning.gov.mv/publications/census2006_island_level_tables/population/population/PP_05.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130919044405/http://www.planning.gov.mv/publications/census2006_island_level_tables/population/population/PP_05.htm |archive-date=19 September 2013 |access-date=8 February 2012 |website=Maldives: Population and Housing Census 2006 |publisher=Ministry of Planning and National Development}}</ref> although the census in 2000 showed that the population growth rate had declined to 1.9%. ] stood at 46 years in 1978, and later rose to 72. Infant mortality has declined from 12.7% in 1977 to 1.2% today, and adult literacy reached 99%. Combined school enrolment reached the high 90s. The population was projected to have reached 317,280 in 2010.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Census Analysis 2006. Population Projection 2006 – 2050 |url=http://planning.gov.mv/en/images/stories/publications/analysiscd/pdf/13.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160303224031/http://planning.gov.mv/en/images/stories/publications/analysiscd/pdf/13.pdf |archive-date=3 March 2016 |access-date=5 July 2014 |website=Ministry of Planning and National Development |page=273}}</ref> | |||
| The 2014 Population and Housing Census listed the total population in the Maldives as 437,535: 339,761 resident Maldivians and 97,774 resident foreigners, approximately 16% of the total population. However, it is believed that foreigners have been undercounted.<ref name="Maldives Population Projections 2014-2054" /><ref name="prb-maldives">{{Cite web |last1=May |first1=John F. |last2=Riyaza |first2=Fathimath |date=July 2017 |title=Maldives' Population Dynamics |url=https://www.prb.org/maldives-population-dynamics/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164442/https://www.prb.org/maldives-population-dynamics/ |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=1 February 2019 |website=]}}</ref> {{as of |May 2021}}, there were 281,000 expatriate workers, an estimated 63,000 of whom are undocumented in the Maldives: 3,506 Chinese, 5,029 Nepalese, 15,670 Sri Lankans, 28,840 Indians, and (the largest group of foreigners working in the country) 112,588 ].<ref>{{Cite web |date=2 May 2021 |title=International Labour Day 2021 |url=https://statisticsmaldives.gov.mv/international-labour-day-2021/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210502081211/https://statisticsmaldives.gov.mv/international-labour-day-2021/ |archive-date=2 May 2021 |access-date=2 May 2021 |website=National Bureau of Statistics |publisher=Ministry of Housing, Land & Urban Development}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web |title=Anti-Human Trafficking Action Plan 2020–2022 |url=https://www.gov.mv/en/files/maldives-national-anti-human-trafficking-action-plan-2020-2022.pdf |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164343/https://www.gov.mv/en/files/maldives-national-anti-human-trafficking-action-plan-2020-2022.pdf |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=18 May 2020 |website=Government of the Maldives |publisher=]}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news |date=13 September 2021 |title=Over 281,000 expats in the Maldives |url=https://avas.mv/en/106783 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210913095035/https://avas.mv/en/106783 |archive-date=13 September 2021 |access-date=19 May 2024 |work=Avas}}</ref> Other immigrants include ] as well as various Western foreign workers. | |||
| As of April 2008, more than 70,000 foreign employees, along with 33,000 illegal immigrants, comprised more than one third of the Maldivian population.{{Citation needed|reason=reliable source needed for the whole sentence|date=September 2013}} | |||
| ===Religion=== | ===Religion=== | ||
| {{See also|Religion in the Maldives}} | |||
| {{Pie chart | |||
| |thumb = right | |||
| |caption = Religion in the Maldives<ref name="religion"/> | |||
| |label1= Islam | |||
| |value1 = 98.69 | |||
| |color1 = Green | |||
| |label2 = Christianity | |||
| |value2 = 0.29 | |||
| |color2 = Purple | |||
| |label3 = ] | |||
| |value3 = 0.29 | |||
| |color3 = Red | |||
| |label4 = ] | |||
| |value4 = 0.29 | |||
| |color4 = Lightblue | |||
| |label5 = Others | |||
| |value5 = 0.74 | |||
| |color5 = White | |||
| }} | |||
| After the long ],<ref>{{Cite web |title=Conversion of the Maldives to Islam |url=http://www.maldivesstory.com.mv:80/site%20files/after%20islam/latest/conversion-frames.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20030509021536/http://www.maldivesstory.com.mv/site%20files/after%20islam/latest/conversion-frames.htm |archive-date=9 May 2003 |website=Maldives Story}}</ref> Muslim traders introduced Islam. Maldivians converted to Islam by the mid-12th century. The islands have had a long history of ] orders, as can be seen in the history of the country such as the building of tombs. They were used until as recently as the 1980s for seeking the help of buried ]s. They can be seen next to some old mosques and are considered a part of the Maldives's ]. | |||
| Other aspects of ], such as ritualised ] ceremonies called Maulūdu (]) – the ] of which included recitations and certain supplications in a melodic tone – existed until very recent times. These Maulūdu festivals were held in ornate tents specially built for the occasion. At present Islam is the official religion of the entire population, as adherence to it is required for citizenship. | |||
| {{see also|Islam in the Maldives|Buddhism in the Maldives|Freedom of religion in the Maldives}} | |||
| ]]] | |||
| After the long Buddhist<ref>{{Wayback |date=20110511114027 |url=http://www.maldivesstory.com.mv/site%20files/after%20islam/latest/conversion-frames.htm |title=Conversion of the Maldives to Islam }}. maldivesstory.com.mv</ref> period of Maldivian history, Muslim traders introduced ] Islam. Maldivians converted to Islam by the mid-12th century. The islands has had a long history of ]c orders, as can be seen in the history of the country such as the building of tombs. They were used until as recently as the 1980s for seeking the help of buried ]s. They can be seen today next to some old mosques and are considered today as ]. Other aspects of ], such as ritualised ] ceremonies called Maulūdu (])—the ] of which included recitations and certain supplications in a melodical tone—existed until very recent times. These Maulūdu festivals were held in ornate tents specially built for the occasion. At present Sunni Islam is the official religion of the entire population, as adherence to it is required for citizenship. | |||
| According to |
According to Arab traveller ], the person responsible for this conversion was a Sunni Muslim visitor named Abu al-Barakat Yusuf al-Barbari, sailing from what is today ]. He is also referred to as ]. His venerated tomb now stands on the grounds of Medhu Ziyaaraiy, across the street from the Friday Mosque, or ], in Malé. Originally built in 1153 and re-built in 1658,<ref>{{Cite web |last=Yoosuf |first=Muawwaz |date=2020-02-28 |title=Malé Friday Mosque |url=https://coralstonemosques.com/male-friday-mosque/ |access-date=2024-10-25 |website=Coral Stone Mosques of Maldives |language=en-US}}</ref> this is one of the country's oldest surviving mosques. | ||
| In 2013, scholar Felix Wilfred of ] estimates the number of Christians in Maldives as 1,400 or 0.4% of the country's population.<ref>{{cite book|title=The Oxford Handbook of Christianity in Asia| first=Felix |last=Wilfred|year= 2014| isbn= 9780199329069|page=45|publisher=Oxford University Press|quote=}}</ref> | |||
| Since the adoption of the ] citizens and anyone wishing to become a citizens are required by law to nominally follow ]<ref name=":0">{{Cite web |title=2022 Report on International Religious Freedom: Maldives |url=https://www.state.gov/reports/2022-report-on-international-religious-freedom/maldives/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240304134513/https://www.state.gov/reports/2022-report-on-international-religious-freedom/maldives/ |archive-date=4 March 2024 |access-date=18 February 2024 |website=] |publisher=Office of International Religious Freedom}}</ref> which would make Maldives a 100% Muslim country in theory. But residents, tourists and guest workers are free to be of any religion and practise them in private. However, in 2020, studies found that 0.29% of the population is Christian (roughly split between ] and ]).<ref>{{Cite web |title=National Profiles | World Religion |url=https://www.thearda.com/world-religion/national-profiles?REGION=0&u=146c&u=140c&u=23r |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230814204149/https://www.thearda.com/world-religion/national-profiles?REGION=0&u=146c&u=140c&u=23r |archive-date=14 August 2023 |accessdate=1 September 2023 |website=]}}</ref> | |||
| ===Languages=== | ===Languages=== | ||
| {{See also|Maldivian language}} | |||
| ] | |||
| The official and |
The official and national language is ], an ] closely related to the ] of Sri Lanka. The first known script used to write Dhivehi is the '']'' script, which is found in the historical recording of kings (''raadhavalhi''). Later a script called '']'' was used for a long period. The present-day script is called ] and is written from right to left. ] is derived from a mix of the old indigenous script of ] and ]. Thaana is said to have been introduced by the reign of ]. | ||
| English is widely spoken by the locals of the Maldives:<ref>{{Cite web |title=Maldives Languages - Languages of Maldives - Language Spoken In Maldives |url=http://maldives.tourism-srilanka.com/travel-tips/language.html |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181111021720/http://maldives.tourism-srilanka.com/travel-tips/language.html |archive-date=11 November 2018 |access-date=12 June 2017 |website=Maldives Tourism}}</ref> "Following the nation's opening to the outside world, the introduction of English as a medium of instruction at the secondary and tertiary levels of education, and its government's recognition of the opportunities offered through tourism, English has now firmly established itself in the country. As such, the Maldives are quite similar to the countries in the Gulf region .... The nation is undergoing vast societal change, and English is part of this."<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Meierkord |first=Christiane |date=March 2018 |title=English in paradise: the Maldives: English is rapidly establishing itself as a second language in a society transforming from fishing to tourism and trade |url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/english-today/article/english-in-paradise-the-maldives/84E0B35287213D3E1A7645FFD32BC16D |url-status=live |journal=English Today |volume=34 |issue=1 |pages=2–11 |doi=10.1017/S0266078417000475 |issn=0266-0784 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164430/https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/english-today/article/abs/english-in-paradise-the-maldives/84E0B35287213D3E1A7645FFD32BC16D |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=31 March 2019 |s2cid=148650495}}</ref> | |||
| ===Largest cities=== | |||
| Otherwise, ] is taught in schools and mosques, as ] is the ]. The Maldivian population has formal or informal education in the reading, writing and pronunciation of the Arabic language, as part of the compulsory religious education for all primary and secondary school students.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| {{Largest cities of the Maldives}} | |||
| ] | |||
| '''''Thikijehi Thaana''''' | |||
| ==Culture== | |||
| These additional letters were added to the Thaana alphabet by adding dots (]) to existing letters, to allow for transliteration of Arabic loanwords, as previously Arabic loanwords were written using the Arabic script. Their usage is inconsistent, and becoming less frequent as the spelling changes to reflect pronunciation by Maldivians, rather than the original Arabic pronunciation, as the words get absorbed into the Maldivian language. | |||
| ===Population by locality=== | |||
| {{Largest cities of the Maldives|class=info}} | |||
| ===Health=== | |||
| {{main|Health in the Maldives}} | |||
| The Human Rights Measurement Initiative reports that Maldives is meeting 5.1 of 10 of the expected fulfillment for the right to health considering its income level.<ref name="Hrm">{{Cite web |title=Maldives |url=https://rightstracker.org/country/MDV |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240519180326/https://rightstracker.org/country/MDV |archive-date=19 May 2024 |access-date=19 May 2024 |website=Human Rights Measurement Initiative }}</ref> Specifically for children's health rights, Maldives attains 98.0% of the anticipated level based on its current income.<ref name="Hrm"/> Regarding adult health rights, the country achieves 99.7% of the expected fulfillment considering its income level. However, in terms of reproductive health rights, Maldives falls into the "very bad" category, as it fulfills only 18.2% of the expected achievement based on its available resources.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Maldives - HRMI Rights Tracker |url=https://rightstracker.org/ |access-date=2022-03-25 |website=rightstracker.org |language=en |archive-date=19 May 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220519142734/https://rightstracker.org/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| ] in Maldives was 77 years in 2011.<ref>{{cite news |date=2018 |title=Maldives |url=http://www.commonwealthhealth.org/asia/maldives/ |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181120140446/http://www.commonwealthhealth.org/asia/maldives/ |archive-date=20 November 2018 |accessdate=20 November 2018 |publisher=Commonwealth Health online}}</ref> Infant mortality fell from 34 per 1,000 in 1990 to 15 in 2004. There is increasing disparity between health in the capital and on the other islands. There is also a problem of ]. Imported food is expensive.<ref>{{cite news |date=2010 |title=At a Glance: Health and Nutrition in the Maldives |url=https://www.unicef.org/maldives/media_3334.htm |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20181120140006/https://www.unicef.org/maldives/media_3334.htm |archive-date=20 November 2018 |accessdate=20 November 2018 |work=]}}</ref> | |||
| On 24 May 2021, the Maldives had the world's fastest-growing ], with the highest number of infections per million people over the prior 7 and 14 days, according to data compiled by ].<ref>{{Cite web |last=Bhuckory |first=Kamlesh |date=24 May 2021 |title=With Highest Covid Rate, Maldives Imposes 16-Hour Curfew |url=https://www.bloombergquint.com/global-economics/maldives-tightens-restrictions-as-virus-cases-deaths-climb |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210524215208/https://www.bloombergquint.com/global-economics/maldives-tightens-restrictions-as-virus-cases-deaths-climb |archive-date=24 May 2021 |access-date=24 May 2021 |website=BloombergQuint}}</ref> Doctors warned that increasing demand for COVID-19 care could hinder their ability to handle other health emergencies in the Maldives.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Rasheed |first=Aishath Hanaan Hussain |date=24 May 2021 |title=Maldives reports 61st Covid-19 death in ongoing month of May |url=https://raajje.mv/100460 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210524215216/https://raajje.mv/100460 |archive-date=24 May 2021 |access-date=19 May 2024 |work=]}}</ref> The reason for the outbreak was the ].<!-- it became dominant almost worldwide within some weeks--> | |||
| ===Transportation=== | |||
| {{main|Transport in the Maldives|List of airports in the Maldives}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] is the principal gateway to the Maldives; it is adjacent to the capital city Malé and is connected by a bridge. International travel is available on government-owned ] (branded as Maldivian), which operates ] seaplanes and to nearly all Maldivian domestic airports with several ] aircraft, and one ] with international service to India, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Malaysia and Thailand. | |||
| In the Maldives, there are three main ways to travel between islands: by domestic flight, by ], or by boat.<ref>{{Cite web |title=Maldives |url=http://www.elitedivingagency.com/maldives/ |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131218100252/http://www.elitedivingagency.com/maldives/ |archive-date=18 December 2013 |website=Elite Diving Agency}}</ref> For several years there were two seaplane companies operating: TMA (]) and ], but these merged in 2013 under the name TMA. The seaplane fleet is entirely made up of DHC-6 Twin Otters. There is also another airline, ], which operates using ] planes to domestic airports, principally ], ] and some others. ] began its first scheduled seaplane service in 2019. Its seaplane fleet is made up of DHC-6 Twin Otter aircraft. In addition to the seaplane service, ] utilises ] aircraft to operate domestic flights to ], ] and ] from the main ].<ref>{{Cite web |date=18 November 2019 |title=Manta Air begins its first scheduled seaplane service |url=https://corporatemaldives.com/manta-air-begins-its-first-scheduled-seaplane-service/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164448/https://corporatemaldives.com/manta-air-begins-its-first-scheduled-seaplane-service/ |archive-date=14 January 2021 |access-date=14 December 2019 |website=Corporate Maldives}}</ref> Depending on the distance of the destination island from the airport, resorts organise ] transfers or ] flights directly to the resort island jetty for their guests. Several daily flights operate from ] to the 18 domestic and international airports in the country. Scheduled ferries also operate from Malé to many of the atolls. The traditional Maldivian boat is called a ], one of the oldest known sea vessels in the Maldives.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Green |first1=Richard |title=The Commonwealth Yearbook 2005 |date=2005 |publisher=Nexus Strategic Partnerships |isbn=9780954962906 |page=209 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=7-NITbEo2-UC&dq=The+traditional+Maldivian+boat+is+called+a+dhoni.&pg=PA209}}</ref> Speedboats and seaplanes tend to be more expensive, while travel by dhoni, although slower, is relatively cheaper and convenient. | |||
| ===Education=== | |||
| {{main|Education in the Maldives}} | |||
| The Maldives National University is one of the country's institutions of higher education.{{efn|There are 209 registered Higher Education Institutes as of May 2022.}}<ref>{{citation |title=Registered Higher Education Institute as of 19.05.2022 |url=https://mohe.gov.mv/images/resources/resources/Registered%20Higher%20Education%20Institutes%20as%20of%2019.05.2022.pdf |website=Ministry of Higher Education, Labour and Skills Development |access-date=19 May 2022 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220617135106/https://mohe.gov.mv/images/resources/resources/Registered%20Higher%20Education%20Institutes%20as%20of%2019.05.2022.pdf |archive-date=17 June 2022 |url-status=live }}</ref> In 1973, the Allied Health Services Training Centre (the forerunner of the Faculty of Health Sciences) was established by the ].<ref>{{cite web |title=History |url=https://mnu.edu.mv/history/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240223004912/https://mnu.edu.mv/history/ |archive-date=23 February 2024 |access-date=18 May 2024 |website=Maldives National University |quote=1st September 1973 Allied Health Services Training Centre was established – Forerunner to the Faculty of Health Sciences established by the Ministry of Health}}</ref> The Vocational Training Centre was established in 1974, providing training for mechanical and electrical trades.<ref>{{cite web |date= |title=Faculty of Engineering, Science and Technology |url=https://courses.mnu.edu.mv/FEST |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240224113056/https://courses.mnu.edu.mv/fest |archive-date=24 February 2024 |access-date=18 May 2024 |website=Maldives National University |quote=The Vocational Training Center (VTC) was established on 14 October 1975 under the Department of Electricity to train a large number of workers required for the growing industrial and economic activities}}</ref> In 1984, the Institute for Teacher Education was created and the School of Hotel and Catering Services was established in 1987 to provide trained personnel for the tourist industry.<ref>{{cite journal |date=February 2019 |title=Education Sector Analysis Maldives – 6.1 Quick Historical Development Of Higher Education |url=https://support.moe.gov.mv/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/EDUCATION-SECTOR-ANALYSIS_ESA.pdf |url-status=live |journal=Ministry of Education |language=En |publisher=] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210428080715/https://support.moe.gov.mv/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/EDUCATION-SECTOR-ANALYSIS_ESA.pdf |archive-date=28 April 2021 |access-date=1 February 2019 |quote=The Vocational Training Center, the Institute for Teacher Education and the School of Hotel and Catering Services were also established prior to the amalgamation of such post- secondary institutions to form the Maldives College of Higher Education in 1998.}}</ref> In 1991, the Institute of Management and Administration was created to train staff for public and private services. In 1998, the Maldives College of Higher Education was founded. The Institute of Shar'ah and Law was founded in January 1999. In 2000 the college launched its first-degree programme, Bachelor of Arts. On 17 January 2011 the Maldives National University Act was passed by the President of the Maldives; The Maldives National University was named on 15 February 2011. In 2015 under a Presidential decree the College of Islamic Studies was changed into the Islamic University of Maldives (IUM).<ref>{{Cite web |title=Profile & History |url=https://www.ium.edu.mv/about-us |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240519175208/https://www.ium.edu.mv/about-us |archive-date=19 May 2024 |access-date=19 May 2024 |website=Islamic University of Maldives |language=en-US}}</ref> | |||
| The Maldivian government now offers 3 different scholarships to students that have completed their higher secondary education with results above a certain threshold, with ranks of the scholarship received depending on the merits achieved by students on their year 12 examinations.<ref>{{cite web |title=A new scholarship scheme called Merit Scholarship is being launched this year |url=https://mohe.gov.mv/news/a-new-scholarship-scheme-called-merit-scholarship-is-being-launched-this-year |website=Ministry of Higher Education, Labour and Skills Development |access-date=16 May 2023 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230702020052/https://mohe.gov.mv/news/a-new-scholarship-scheme-called-merit-scholarship-is-being-launched-this-year |archive-date=2 July 2023 |date=16 May 2023 |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ==Culture== | |||
| {{main|Culture of the Maldives}} | {{main|Culture of the Maldives}} | ||
| {{see also|Music of the Maldives|Maldivian Folklore}} | |||
| {{refimprove section|date=October 2011}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ], housing the mosque ''Masjid-al-Sultan ]'']] | |||
| {{see also|Maldivian cuisine|Folklore of the Maldives}} | |||
| Since the 12th century AD there were also influences from ] in the language and culture of the Maldives because of the conversion to Islam and its location as a crossroads in the central Indian Ocean. This was due to the long trading history between the ] and the ]. ] travellers discovered the island for gold in the 13th century, before the Portuguese. Their brief stay later ended in a bloody conflict known by the Somalis as "Dagaal Diig Badaaney" in 1424. | |||
| ] Festival in ]]] | |||
| However, unlike the Sinhalese of Sri Lanka and most of the Arabs, Africans and Europeans whose influence can be seen in borrow-words, material culture, and the diversity of Maldivian phenotype, Maldivians do not have the highly embedded patriarchal codes of honor, purity, corporate marriage, and sedentary private property that are typical of places where agriculture is the key form of subsistence and social relations have been built, historically, around tribute taking.{{Citation needed|date=November 2014}} | |||
| The culture of the Maldives is influenced by the cultures of the people of different ethnicities who have settled on the islands throughout the times. | |||
| Reflective of this is the fact that the Maldives has had the highest national divorce rate in the world for many decades. This, it is hypothesized, is due to a combination of liberal Islamic rules about divorce and the relatively loose marital bonds that have been identified as common in non and semi-sedentary peoples without a history of fully developed agrarian property and kinship relations.<ref>Marcus, Anthony. 2012. '''' in Chitra Raghavan and James Levine. Self-Determination and Women’s Rights in Muslim Societies. Lebanon, NH: Brandeis University Press</ref> | |||
| Since the 12th century AD, there were also influences from ] in the language and culture of the Maldives because of the conversion to Islam and its location as a crossroads in the central Indian Ocean.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Robinson |first1=J. J. |title=The Maldives: Islamic Republic, Tropical Autocracy |date=2015 |publisher=Hurst |isbn=978-1849045896 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=6u1vrgEACAAJ}}</ref> This was due to the long trading history between the far east and the middle east. | |||
| == Transportation == | |||
| Reflective of this is the fact that the Maldives has had the highest national divorce rate in the world for many decades. This, it is hypothesised, is due to a combination of liberal Islamic rules about divorce and the relatively loose marital bonds that have been identified as common in non- and semi-sedentary peoples without a history of fully developed agrarian property and kinship relations.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Marcus |first=Anothony |date=2012 |title=Reconsidering Talaq |url=http://snrg-nyc.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/reconsidering-talaq.pdf |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171010152111/http://snrg-nyc.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/reconsidering-talaq.pdf |archive-date=10 October 2017 |website=]}}</ref> | |||
| ] is the principal gateway to the Maldives. International travel is available on a number of major airlines. Two Maldives based airlines also operate international flights. Privately owned ] has Boeing 757 and 767 aircraft and operates frequent services to Beijing, Shanghai, and Hong Kong. Government owned ] (branded as Maldivian) operates to nearly all of Maldives domestic airports with several Dash-8 aircraft and one A320 with international service to Chennai and Thiruvananthapuram, India, and Dhaka, Bangladesh. | |||
| ===Media=== | |||
| In Maldives there are three main ways to move around: by domestic flight, by ] or by boat.<ref>. Elitedivingagency.com. Retrieved on 2014-01-29.</ref> For several years there were two seaplanes companies operating: TMA, ], and ], but these merged in 2013 under the name TMA. The seaplane fleet is entirely made up of DHC-6 "Twin Otters." There is also another airline, flyMe, which operates using ATRs to domestic airports, principally Maamagili and some others. The typical Maldivian boat is called ]. Depending on the distance of the destination island to the airport, resorts organise domestic flight plus boat transfers, seaplane flights directly to the resort island jetty, or speedboat trips for their guests. There are also locally run ferries by large dhoni boats. Speedboats and seaplanes tend to be more expensive, while travel by dhoni, although longer, is relatively cheaper. | |||
| {{main|Television Maldives|Voice of Maldives|List of newspapers in the Maldives}} | |||
| ] serves as the country's main media, owned by the ].<ref>{{cite web |title=Public Service Media |url=https://soegateway.finance.gov.mv/soes/psm |access-date=31 August 2024 |website=SOE Gateway |publisher=Ministry of Finance}}</ref> The newspaper was founded on 3 May 2017, in the celebration of ].<ref>{{Cite news |date=3 May 2024 |title=PSM News : Seven years of reliable reporting |url=https://psmnews.mv/en/136888 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240514184206/https://psmnews.mv/en/136888 |archive-date=14 May 2024 |access-date=19 May 2024 |work=]}}</ref> Maldives has been ranked one–hundred in the ] 2023 and 106 in 2024.<ref>{{cite web |year=2024 |title=2024 World Press Freedom Index |url=https://rsf.org/en/country/maldives |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220507020451/https://rsf.org/en/country/maldives |archive-date=7 May 2022 |access-date=12 May 2022 |work=]}}</ref> The country's first daily newspaper, ] News was the first and longest–serving newspaper in the history of the Maldives, which was registered on 28 December 1978, and dissolved in 2016.<ref>{{Cite news |date=24 May 2016 |title=Lost in translation: the story of Haveeru |url=https://maldivesindependent.com/feature-comment/lost-in-translation-the-story-of-haveeru-124392 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231016070200/https://maldivesindependent.com/feature-comment/lost-in-translation-the-story-of-haveeru-124392 |archive-date=16 October 2023 |access-date=19 May 2024 |work=Maldives Independent}}</ref> | |||
| == Education == | |||
| Article 28 of the ] guarantees freedom of the press and stipulates that: | |||
| {{blockquote|No person shall be compelled to disclose the source of any information that is espoused, disseminated or published by that person.<ref>{{cite web |title=Constitution of the Republic of Maldives |url=http://agoffice.gov.mv/#/Media/Constitution%20of%20the%20Republic%20of%20Maldives|website=] |page=7 |access-date=16 October 2020 |archive-date=6 June 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110606081747/http://www.agoffice.gov.mv/#/Media/Constitution%20of%20the%20Republic%20of%20Maldives |url-status=live }}</ref>}} | |||
| The ] was inaugurated on February 15, 2011. The university was previously known as the Maldives College of Higher Education which was established on January 1, 1999, as part of a restructuring and rationalization of all government-run post-secondary education in Maldives. The university is the only public degree-granting institution on the nation. The university offers a range of degrees, diplomas, and certificates, with particular emphasis on engineering, health science, education, tourism, and management.<ref name="mnu.e">{{cite web|url=http://www.mnu.edu.mv|title=The Maldives National University – Home|publisher=mnu.edu.mv|accessdate=14 September 2014}}</ref> | |||
| However, this protection is compromised by the Evidence Act, which came into effect in January 2023 and grants courts the authority to compel journalists to reveal their confidential sources. The Maldives Media Council (MMC) and the ] (MJA) serve as crucial watchdogs in addressing and combating these threats. Newspapers, Sun Online, ] and its English edition, '']'' and Avas serves one of the most well–known private news outlets.<ref>{{cite web |title=Maldives Newspapers Online – List of Maldives newspapers, magazines, and news sites covering business, finance, sports, travel, weather, jobs, and entertainments |url=https://www.w3newspapers.com/maldives/ |website=w3newspapers.com}}</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| === Sports === | |||
| *] | |||
| Sports in the Maldives are deeply ingrained in the culture of the island nation, with a diverse array of activities reflecting both traditional pastimes and modern sporting pursuits. Given its unique geography of scattered islands surrounded by the Indian Ocean, water sports naturally hold a prominent position. ], in particular, has gained international recognition, with waves that cater to both beginners and seasoned surfers. Locations such as the atolls of North and South Malé, ], and ] offer ideal conditions for enthusiasts to ride the waves throughout the years.<ref>{{cite web |title=Thulusdhoo Island Surf Guide – Maldives Local Island Surfing! |url=https://www.stokedfortravel.com/thulusdhoo-island-surf-guide-maldives-local-island/ |website=Stoked For Travel |date=15 September 2020 |access-date=15 September 2020 |archive-date=25 September 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200925030355/https://www.stokedfortravel.com/thulusdhoo-island-surf-guide-maldives-local-island/ |url-status=live }}</ref> Additionally, diving and snorkeling are immensely popular, allowing locals and tourists alike to explore the rich marine life that thrives in the crystal-clear waters surrounding the Maldives.<ref>{{cite web |title=SNORKELING IN THE MALDIVES |url=https://www.snorkeling-report.com/destination/snorkeling-maldives/ |access-date=19 May 2024 |website=Snorkeling Report |archive-date=1 March 2024 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240301023117/https://www.snorkeling-report.com/destination/snorkeling-maldives/ |url-status=live }}</ref> | |||
| *] | |||
| ] against ] at the ].]] | |||
| *] | |||
| ], or soccer, stands out as one of the most widely played and passionately followed sports in the Maldives.<ref>{{cite news |title=Future of Football: When will a country from South Asia emerge as a powerhouse in the global game? |url=https://www.skysports.com/football/news/11095/12932480/future-of-football-when-will-a-country-from-south-asia-emerge-as-a-powerhouse-in-the-global-game |access-date=4 August 2023 |agency=Sky Sports |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240110145607/https://www.skysports.com/football/news/11095/12932480/future-of-football-when-will-a-country-from-south-asia-emerge-as-a-powerhouse-in-the-global-game |archive-date=10 January 2024}}</ref> ] competes in regional and international tournaments, with a fervent fan base supporting their endeavors. The country has its own domestic football league, the Dhivehi Premier League, featuring clubs from various atolls vying for supremacy.<ref>{{cite web |title=Maldives |url=https://us.soccerway.com/teams/maldives/maldives/1443/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230326175708/https://us.soccerway.com/teams/maldives/maldives/1443/ |archive-date=26 March 2023 |access-date=18 May 2024 |website=Soccerway}}</ref> Matches often draw large crowds, contributing to the vibrant sporting atmosphere of the Maldives. Moreover, futsal enjoys popularity, especially among younger generations, with numerous indoor facilities providing spaces for friendly matches and competitive leagues. | |||
| * ] | |||
| ]ing in Maldives|left]] | |||
| {{portal bar|Geography|Asia|South Asia|SAARC|Commonwealth realms|Maldives|Islands}} | |||
| Traditional Maldivian sports also play a significant role in preserving cultural heritage and promoting physical activity. Bodu Beru, a rhythmic ]ming and ], often accompanies traditional sports events, adding to the festive ambiance. One such traditional sport is "Baibalaa", a game resembling ] but played with a woven ball made from dried coconut palm leaves. "Fenei Bashi", a form of ], is another traditional sport that showcases strength and agility. These indigenous sports serve as a reminder of the Maldives' rich cultural heritage and continue to be cherished by communities across the islands. | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| {{Portal|Maldives|Asia}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==Notes== | == Notes == | ||
| {{ |
{{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} | ||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{reflist |
{{reflist}} | ||
| ==Further reading== | ==Further reading== | ||
| {{Refbegin}} | |||
| * ''Divehiraajjege Jōgrafīge Vanavaru''. Muhammadu Ibrahim Lutfee. G.Sōsanī. Malé 1999. | * ''Divehiraajjege Jōgrafīge Vanavaru''. Muhammadu Ibrahim Lutfee. G.Sōsanī. Malé 1999. | ||
| * ], ''The Maldive Islands, An account of the Physical Features, History, Inhabitants, Productions and Trade''. Colombo 1883, ISBN |
* ], ''The Maldive Islands, An account of the Physical Features, History, Inhabitants, Productions and Trade''. Colombo 1883, {{ISBN|81-206-1222-1}}. | ||
| * H.C.P. Bell, ''The Maldive Islands; Monograph on the History, Archaeology and Epigraphy''. Reprint Colombo 1940. Council for Linguistic and Historical Research. Malé 1989. | * H.C.P. Bell, ''The Maldive Islands; Monograph on the History, Archaeology and Epigraphy''. Reprint Colombo 1940. Council for Linguistic and Historical Research. Malé 1989. | ||
| * H.C.P. Bell, ''Excerpta Maldiviana''. Reprint Colombo 1922/35 edn. Asian Educational Services. New Delhi 1999. | * H.C.P. Bell, ''Excerpta Maldiviana''. Reprint Colombo 1922/35 edn. Asian Educational Services. New Delhi 1999. | ||
| * ''Divehi Tārīkhah Au Alikameh. Divehi Bahāi Tārikhah Khidmaiykurā Qaumī Markazu''. Reprint 1958 edn. Malé 1990. | * ''Divehi Tārīkhah Au Alikameh. Divehi Bahāi Tārikhah Khidmaiykurā Qaumī Markazu''. Reprint 1958 edn. Malé, Maldives 1990. | ||
| * Christopher, William (1836–38). ''Transactions of the Bombay Geographical Society'', Vol. I. Bombay. | * Christopher, William (1836–38). ''Transactions of the Bombay Geographical Society'', Vol. I. Bombay. | ||
| * Lieut. I.A. Young & W. Christopher, ''Memoirs on the Inhabitants of the Maldive Islands''. | * Lieut. I.A. Young & W. Christopher, ''Memoirs on the Inhabitants of the Maldive Islands''. | ||
| * ]. ''Maldivian Linguistic Studies''. Reprint 1919 edn. Asian Educational Services. Delhi 1999. | * ]. ''Maldivian Linguistic Studies''. Reprint 1919 edn. Asian Educational Services. Delhi 1999. | ||
| * Hockly, T.W. ''The Two Thousand Isles''. Reprint 1835 edn. Asian Educational Services. Delhi 2003. | * Hockly, T.W. ''The Two Thousand Isles''. Reprint 1835 edn. Asian Educational Services. Delhi 2003. | ||
| * Hideyuki Takahashi, ''Maldivian National Security |
* Hideyuki Takahashi, ''Maldivian National Security - And the Threats of Mercenaries'', The Round Table (London), No. 351, July 1999, pp. 433–444. | ||
| * Malten, Thomas: Malediven und Lakkadiven. Materialien zur Bibliographie der Atolle im Indischen Ozean. Beiträge zur Südasien-Forschung Südasien-Institut Universität Heidelberg, Nr. 87. Franz Steiner Verlag. Wiesbaden, 1983. | * Malten, Thomas: Malediven und Lakkadiven. Materialien zur Bibliographie der Atolle im Indischen Ozean. Beiträge zur Südasien-Forschung Südasien-Institut Universität Heidelberg, Nr. 87. Franz Steiner Verlag. Wiesbaden, 1983. | ||
| * Vilgon, Lars: Maldive and Minicoy Islands Bibliography with the Laccadive Islands. Published by the author. Stockholm, 1994. | * Vilgon, Lars: Maldive and Minicoy Islands Bibliography with the Laccadive Islands. Published by the author. Stockholm, 1994. | ||
| * ], ''People of the Maldive Islands'', Orient Black Swan, 2013 | |||
| *Djan Sauerborn. , Spotlight South Asia, Heidelberg, 2012, ISSN 2195-2787 | |||
| * ], ''The Maldive Islanders: a study of the popular culture of an ancient ocean kingdom'', NEI, 1999 | |||
| *], ''People of the Maldive Islands'', Orient Black Swan, 2013 | |||
| * |
* Xavier Romero-Frias, ''Folk Tales of the Maldives'', Nordic Institute of Asian Studies, 2012 | ||
| * Djan Sauerborn, '' {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210114164455/https://css.ethz.ch/en/services.html |date=14 January 2021 }}'', International Relations and Security Network (ISN), Zürich, September 2013 | |||
| *Xavier Romero-Frias, ''Folk Tales of the Maldives'', Nordic Institute of Asian Studies, 2012 | |||
| * Djan Sauerborn, '''', South Asia Democratic Forum (SADF), February 2015 | |||
| {{Refend}} | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{Sister project links|voy=Maldives|b=no|v=no}} | {{Sister project links|voy=Maldives|b=no|v=no|The Maldives}} | ||
| * | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200116105604/https://visitmaldives.com/ |date=16 January 2020 }} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230530232213/https://www.presidencymaldives.gov.mv/ |date=30 May 2023 }} | |||
| *{{CIA World Factbook link|mv|Maldives}} | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200612131552/https://www.gov.mv/ |date=12 June 2020 }} | |||
| * from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs'' | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220729125757/https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/maldives/ |date=29 July 2022 }}. '']''. ]. | |||
| *{{Dmoz|Regional/Asia/Maldives}} | |||
| * from UCB Libraries GovPubs | |||
| * from the ] | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180729053826/https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-south-asia-12651486 |date=29 July 2018 }} from the ] | |||
| *{{Wikiatlas|Maldives}} | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221202175356/https://www.britannica.com/place/Maldives |date=2 December 2022 }} ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' entry | |||
| * from ] | |||
| * {{Wikiatlas|Maldives}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{OSM relation|536773}} | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120706030400/http://www.ifs.du.edu/ifs/frm_CountryProfile.aspx?Country=MV |date=6 July 2012 }} from ] | |||
| * {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110606081747/http://www.agoffice.gov.mv/#/Media/Constitution%20of%20the%20Republic%20of%20Maldives |date=6 June 2011 }} | |||
| {{Maldives topics}} | {{Maldives topics}} | ||
| {{Navboxes | {{Navboxes | ||
| |title= Articles related to the Maldives | |title = Articles related to the Maldives | ||
| |list= | |list = | ||
| {{Navboxes | |||
| |title= ]{{nbsp}} Geographic locale | |||
| |list= | |||
| {{Islands of the Maldives}} | {{Islands of the Maldives}} | ||
| {{Atolls of the Maldives}} | {{Atolls of the Maldives}} | ||
| Line 592: | Line 738: | ||
| {{Countries bordering the Arabian Sea}} | {{Countries bordering the Arabian Sea}} | ||
| {{Countries of Asia}} | {{Countries of Asia}} | ||
| {{South Asian topics}} | |||
| }} | |||
| {{The Commonwealth}} | |||
| {{Navboxes | |||
| |title= International membership | |||
| |list= | |||
| {{Organisation of Islamic Cooperation|state=collapsed}} | {{Organisation of Islamic Cooperation|state=collapsed}} | ||
| {{South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation}} | {{South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation}} | ||
| {{World Trade Organization|state=collapsed}} | {{World Trade Organization|state=collapsed}} | ||
| {{Commonwealth of Nations}} | |||
| {{Non-Aligned Movement}} | {{Non-Aligned Movement}} | ||
| {{Shanghai Cooperation Organisation}} | |||
| {{Portuguese overseas empire}} | |||
| }} | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| {{Coord|3.20|73.22|display=title}} | |||
| {{Coord|4.18|73.51|display=title}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:20, 18 December 2024
Island country in South Asia "Maldive Islands" redirects here. For other uses, see Maldives (disambiguation).
Republic of Maldives
| |
|---|---|
 Flag
Flag
 Emblem
Emblem
| |
| Motto: الدولة المحلديبية (Arabic) Ad-Dawlat Al-Mahaldibiyya "State of the Mahal Dibiyat" | |
| Anthem: ޤައުމީ ސަލާމް (Dhivehi) Qaumee Salaam "National Salute" | |
 Show globe Show globe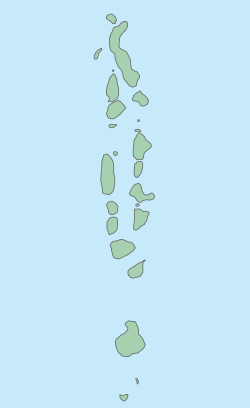 Show map of Maldives Show map of Maldives | |
| Capitaland largest city | Malé 4°10′31″N 73°30′32″E / 4.17528°N 73.50889°E / 4.17528; 73.50889 |
| Official language and national language | Dhivehi |
| Common languages | English |
| Religion | |
| Demonym(s) | Maldivian |
| Government | Unitary presidential republic |
| • President | Mohamed Muizzu |
| • Vice President | Hussain Mohamed Latheef |
| • Majlis Speaker | Abdul Raheem Abdulla |
| • Chief Justice | Ahmed Muthasim Adnan |
| Legislature | People's Majlis |
| Independence from the United Kingdom | |
| • Independence declared | 26 July 1965 |
| • First Republic | 1 January 1953 |
| • Second Republic | 11 November 1968 |
| • Current constitution | 7 August 2008 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 298 km (115 sq mi) (187th) |
| Population | |
| • 2022 census | 515,132 (167th) |
| • Density | 1,728.63/km (4,477.1/sq mi) (7th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
| • Total | |
| • Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
| • Total | |
| • Per capita | |
| Gini (2024) | medium inequality |
| HDI (2022) | high (87th) |
| Currency | Maldivian rufiyaa (MVR) |
| Time zone | UTC+5 (MVT) |
| Calling code | +960 |
| ISO 3166 code | MV |
| Internet TLD | .mv |
The Maldives, officially the Republic of Maldives, and historically known as the Maldive Islands, is a country and archipelagic state in South Asia in the Indian Ocean. The Maldives is southwest of Sri Lanka and India, about 750 kilometres (470 miles; 400 nautical miles) from the Asian continent's mainland. The Maldives' chain of 26 atolls stretches across the equator from Ihavandhippolhu Atoll in the north to Addu Atoll in the south.
The Maldives is the smallest country in Asia. Including the sea, the territory spans roughly 90,000 square kilometres (35,000 sq mi), with a land area of 298 square kilometres (115 sq mi). The Maldives is one of the world's most geographically dispersed sovereign states. With a population of 515,132 in the 2022 census, it is the second least populous country in Asia and the ninth-smallest country by area, but also one of the most densely populated countries. The Maldives has an average ground-level elevation of 1.5 metres (4 ft 11 in) above sea level, and a highest natural point of only 2.4 metres (7 ft 10 in), making it the world's lowest-lying country. Some sources state the highest point, Mount Villingili, as 5.1 metres or 17 feet.
Malé is the capital and the most populated city, traditionally called the "King's Island", where the ancient royal dynasties ruled from its central location. The Maldives has been inhabited for over 2,500 years. Documented contact with the outside world began around 947 AD when Arab travelers began visiting the islands. In the 12th century, partly due to the importance of the Arabs and Persians as traders in the Indian Ocean, Islam reached the Maldivian Archipelago. The Maldives was soon consolidated as a sultanate, developing strong commercial and cultural ties with Asia and Africa. From the mid-16th century, the region came under the increasing influence of European colonial powers, with the Maldives becoming a British protectorate in 1887. Independence from the United Kingdom came in 1965, and a presidential republic was established in 1968 with an elected People's Majlis. The ensuing decades have seen political instability, efforts at democratic reform, and environmental challenges posed by climate change and rising sea levels. The Maldives became a founding member of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC).
The Maldives is a member of the United Nations, the Commonwealth of Nations, the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, and the Non-Aligned Movement. The World Bank classifies the Maldives as having an upper-middle income economy. The Maldives is a Dialogue Partner of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation. Fishing has historically been the dominant economic activity, and remains the largest sector by far, followed by the rapidly growing tourism industry. The Maldives rates "high" on the Human Development Index, with per capita income significantly higher than other SAARC nations. The Maldives was a member of the Commonwealth of Nations from July 1982 until withdrawing from the organisation in October 2016 in protest of allegations of its human rights abuses and failing democracy. The Maldives rejoined the Commonwealth on 1 February 2020 after showing evidence of functioning democratic processes and popular support.
Etymology
See also: Names of the MaldivesAccording to legends, the first settlers of the Maldives were people known as Dheyvis. The first Kingdom of the Maldives was known as Kingdom of Dheeva Maari [bn]. During the 3rd century BCE visit of emissaries, it was noted that the Maldives was known as Dheeva Mahal.
During c. 1100 – 1166, the Maldives was also referred to as Diva Kudha and the Laccadive archipelago which was a part of the Maldives was then referred to as Diva Kanbar by the scholar and polymath al-Biruni.
The name Maldives may also derive from Sanskrit माला mālā (garland) and द्वीप dvīpa (island), or මාල දිවයින Maala Divaina ("Necklace Islands") in Sinhala. The Maldivian people are called Dhivehin. The word Dheeb/Deeb (archaic Dhivehi, related to Sanskrit द्वीप, dvīpa) means "island", and Dhives (Dhivehin) means "islanders" (i.e., Maldivians). In Tamil, "Garland of Islands" can be translated as Mālaitīvu (மாலைத்தீவு).
The venerable Sri Lankan chronicle Mahavamsa mentions an island designated as Mahiladiva ("Island of Women", महिलादिभ) in Pali, likely arising from an erroneous translation of the Sanskrit term, signifying "garland".
Jan Hogendorn, professor of economics at Colby College, theorised that the name Maldives derives from the Sanskrit mālādvīpa (मालाद्वीप), meaning "garland of islands". In Malayalam, "Garland of Islands" can be translated as Maladweepu (മാലദ്വീപ്). In Kannada, "Garland of Islands" can be translated as Maaledweepa (ಮಾಲೆದ್ವೀಪ). None of these names are mentioned in any literature, however, classical Sanskrit texts dating back to the Vedic period mention the "Hundred Thousand Islands" (Lakshadweepa), a generic name which would include not only the Maldives, but also the Laccadives, Aminidivi Islands, Minicoy, and the Chagos island groups.
Medieval Muslim travellers such as Ibn Battuta called the islands Maḥal Dībīyāt (محل ديبية) from the Arabic word maḥal ("palace"), which must be how the Berber traveller interpreted the name of Malé, having been through Muslim North India, where Perso-Arabic words were introduced to the local vocabulary. This is the name currently inscribed on the scroll in the Maldives state emblem. The classical Persian/Arabic name for the Maldives is Dibajat. The Dutch referred to the islands as the Maldivische Eilanden (pronounced [mɑlˈdivisə ˈʔɛilɑndə(n)]), while the British anglicised the local name for the islands first to the "Maldive Islands" and later to "Maldives".
In a conversational book published in 1563, Garcia de Orta writes: "I must tell you that I have heard it said that the natives do not call it Maldiva but Nalediva. In the Malabar language, nale means four and diva island. So that in that language, the word signifies 'four islands', while we, corrupting the name, call it Maldiva."
The local name for Maldives by the Maldivian people in Dhivehi language is "Dhivehi Raajje", (Dhivehi: ދިވެހިރާއްޖެ).
History
Main article: History of the MaldivesAncient history and settlement
Main article: History of the Maldives § Early AgeIn the 6th–5th century BCE, the Maldives already had their kingdoms. The country has an established history of over 2,500 years according to historical evidence and legends.
The Mahāvaṃsa (300 BCE) has records of people from Sri Lanka emigrating to the Maldives. Assuming that cowrie shells come from the Maldives, historians believe that there may have been people living in the Maldives during the Indus Valley civilisation (3300–1300 BCE). A number of artefacts show the presence of Hinduism in the country before the Islamic period.
According to the book Kitāb fi āthār Mīdhu al-qādimah (كتاب في آثار ميذو القديمة) (On the Ancient Ruins of Meedhoo), written in the 17th century in Arabic by Allama Ahmed Shihabuddine (Allama Shihab al-Din) of Meedhoo in Addu Atoll, the first settlers of the Maldives were people known as Dheyvis. They came from the Kalibanga in India. The time of their arrival is unknown but it was before Emperor Asoka's kingdom in 269–232 BCE. Shihabuddin's story tallies remarkably well with the recorded history of South Asia and that of the copperplate document of the Maldives known as Loamaafaanu.
The ancient history of the Maldives is told in copperplates, ancient scripts carved on coral artefacts, traditions, language and different ethnicities of Maldivians. The Maapanansa, the copper plates on which recorded the history of the first Kings of the Maldives from the Solar Dynasty, were lost quite early on.
A 4th-century notice written by Ammianus Marcellinus (362 CE) speaks of gifts sent to the Roman emperor Julian by a deputation from the nation of Divi. The name Divi is very similar to Dheyvi who were the first settlers of Maldives.
The first Maldivians did not leave any archaeological artefacts. Their buildings were probably built of wood, palm fronds, and other perishable materials, which would have quickly decayed in the salt and wind of the tropical climate. Moreover, chiefs or headmen did not reside in elaborate stone palaces, nor did their religion require the construction of large temples or compounds.
Comparative studies of Maldivian oral, linguistic, and cultural traditions confirm that the first settlers were people from the southern shores of the neighbouring Indian subcontinent, including the Giraavaru people, mentioned in ancient legends and local folklore about the establishment of the capital and kingly rule in Malé.
A strong underlying layer of Dravidian and North Indian cultures survives in Maldivian society, with a clear Elu substratum in the language, which also appears in place names, kinship terms, poetry, dance, and religious beliefs. The North Indian system was brought by the original Sinhalese from Sri Lanka. Malabar and Pandya seafaring culture led to the settlement of the Islands by Tamil and Malabar seafarers.
Buddhist period
Main articles: History of the Maldives § Buddhist period, and Buddhism in the Maldives
Despite being just mentioned briefly in most history books, the 1,400 year-long Buddhist period has a foundational importance in the history of the Maldives. It was during this period that the culture of the Maldives both developed and flourished, a culture that survives today. The Maldivian language, early Maldive scripts, architecture, ruling institutions, customs, and manners of the Maldivians originated at the time when the Maldives were a Buddhist kingdom.
Buddhism probably spread to the Maldives in the 3rd century BCE at the time of Emperor Ashoka's expansion and became the dominant religion of the people of the Maldives until the 12th century. The ancient Maldivian Kings promoted Buddhism, and the first Maldive writings and artistic achievements, in the form of highly developed sculpture and architecture, originate from that period. Nearly all archaeological remains in the Maldives are from Buddhist stupas and monasteries, and all artefacts found to date display characteristic Buddhist iconography.
Islamic period
See also: History of the Maldives § Islamic Period, Islam in Maldives, List of Maldivian monarchs, and Sultanate of MaldivesThe importance of the Arabs as traders in the Indian Ocean by the 12th century may partly explain why the last Buddhist king of the Maldives, Dhovemi, converted to Islam in the year 1153 (or 1193). Adopting the Muslim title of Sultan Muhammad al-Adil, he initiated a series of six Islamic dynasties that lasted until 1932 when the sultanate became elective. The formal title of the sultan up to 1965 was, Sultan of Land and Sea, Lord of the twelve-thousand islands and Sultan of the Maldives which came with the style Highness.
A Moroccan traveller named Abu al-Barakat Yusuf al-Barbari is traditionally cited for this conversion. According to the story told to Ibn Battutah, a mosque was built with the inscription: 'The Sultan Ahmad Shanurazah accepted Islam at the hand of Abu al-Barakat Yusuf al-Barbari.' Some scholars have suggested the possibility of Ibn Battuta misreading Maldive texts, and having a bias towards the North African, Maghrebi narrative of this Shaykh, instead of the Persian origins account that was known as well at the time.
Others have it that he may have been from the Persian town of Tabriz. This interpretation, held by the more reliable local historical chronicles, Raadavalhi and Taarikh, is that Abu al-Barakat Yusuf al-Barbari was Abdul Barakat Yusuf Shams ud-Dīn at-Tabrīzī, also locally known as Tabrīzugefānu. In the Arabic script the words al-Barbari and al-Tabrizi are very much alike, since at the time, Arabic had several consonants that looked identical and could only be differentiated by overall context (this has since changed by addition of dots above or below letters to clarify pronunciation – For example, the letter "B" in modern Arabic has a dot below, whereas the letter "T" looks identical except there are two dots above it). "ٮوسڡ الٮٮرٮرى" could be read as "Yusuf at-Tabrizi" or "Yusuf al-Barbari".
The venerated tomb of the scholar now stands on the grounds of Medhu Ziyaaraiy, across the street from the Friday Mosque, or Hukuru Miskiy, in Malé. Originally built in 1153 and re-built in 1658, this is one of the oldest surviving mosques in the Maldives. Following the Islamic concept that before Islam there was the time of Jahiliya (ignorance), in the history books used by Maldivians the introduction of Islam at the end of the 12th century is considered the cornerstone of the country's history. Nonetheless, the cultural influence of Buddhism remains, a reality directly experienced by Ibn Battuta during his nine months there sometime between 1341 and 1345, serving as a chief judge and marrying into the royal family of Omar I. For he became embroiled in local politics and left when his strict judgments in the laissez-faire island kingdom began to chafe with its rulers. In particular, he was angered at the local women going about with no clothing above the waist— a cultural epithet of the region at the time- was seen as a violation of Middle Eastern Islamic rules of modesty—and the locals taking no notice when he complained.
Compared to the other areas of South Asia, the conversion of the Maldives to Islam happened relatively late. The Maldives remained a Buddhist kingdom for another 500 years. Arabic became the prime language of administration (instead of Persian and Urdu), and the Maliki school of jurisprudence was introduced, both hinting at direct contact with the core of the Arab world.
Middle Eastern seafarers had just begun to take over the Indian Ocean trade routes in the 10th century and found the Maldives to be an important link in those routes as the first landfall for traders from Basra sailing to Southeast Asia. Trade involved mainly cowrie shells—widely used as a form of currency throughout Asia and parts of the East African coast—and coir fibre. The Bengal Sultanate, where cowrie shells were used as legal tender, was one of the principal trading partners of the Maldives. The Bengal–Maldives cowry shell trade was the largest shell currency trade network in history.
The other essential product of the Maldives was coir, the fibre of the dried coconut husk, resistant to saltwater. It stitched together and rigged the dhows that plied the Indian Ocean. Maldivian coir was exported to Sindh, China, Yemen, and the Persian Gulf.
Protectorate period



In 1558, the Portuguese established a small garrison with a Viador (Viyazoaru), or overseer of a factory (trading post) in the Maldives, which they administered from their main colony in Goa. Their attempts to forcefully impose Christianity with the threat of death provoked a local revolt led by Muhammad Thakurufaanu al-A'uẓam, his two brothers and Dhuvaafaru Dhandahele, who fifteen years later drove the Portuguese out of the Maldives. This event is now commemorated as National Day which is known as Qaumee Dhuvas (literally meaning "National" and "Day"). It is celebrated on 1st of Rabi' al-Awwal, the third month of Hijri (Islamic) calendar.
In the mid-17th century, the Dutch, who had replaced the Portuguese as the dominant power in Ceylon, established hegemony over Maldivian affairs without involving themselves directly in local matters, which were governed according to centuries-old Islamic customs.
The British expelled the Dutch from Ceylon in 1796 and included the Maldives as a British protectorate. The status of the Maldives as a British protectorate was officially recorded in an 1887 agreement in which the sultan Muhammad Mueenuddeen II accepted British influence over Maldivian external relations and defence while retaining home rule, which continued to be regulated by Muslim traditional institutions in exchange for an annual tribute. The status of the islands was akin to other British protectorates in the Indian Ocean region, including Zanzibar and the Trucial States.

In the British period, the Sultan's powers were taken over by the Chief Minister, much to the chagrin of the British Governor-General who continued to deal with the ineffectual Sultan. Consequently, Britain encouraged the development of a constitutional monarchy, and the first Constitution was proclaimed in 1932. However, the new arrangements favoured neither the Sultan nor the Chief Minister, but rather a young crop of British-educated reformists. As a result, angry mobs were instigated against the Constitution which was publicly torn up.
The Maldives remained a British crown protectorate until 1953 when the sultanate was suspended and the First Republic was declared under the short-lived presidency of Mohamed Amin Didi. While serving as prime minister during the 1940s, Didi nationalised the fish export industry. As president, he is remembered as a reformer of the education system and an advocate of women's rights. Conservatives in Malé ousted his government, and during a riot over food shortages, Didi was beaten by a mob and died on a nearby island.

Beginning in the 1950s, the political history in the Maldives was largely influenced by the British military presence on the islands. In 1954, the restoration of the sultanate perpetuated the rule of the past. Two years later, the United Kingdom obtained permission to reestablish its wartime RAF Gan airfield in the southernmost Addu Atoll, employing hundreds of locals. In 1957, however, the new prime minister, Ibrahim Nasir, called for a review of the agreement. Nasir was challenged in 1959 by a local secessionist movement in the three southernmost atolls that benefited economically from the British presence on Gan. This group cut ties with the Maldives government and formed an independent state, the United Suvadive Republic with Abdullah Afeef as president and Hithadhoo as its capital. One year later the Suvadive republic was scrapped after Nasir sent gunboats from Malé with government police, and Abdullah Afeef went into exile. Meanwhile, in 1960 the Maldives allowed the United Kingdom to continue to use both the Gan and the Hithadhoo facilities for thirty years, with the payment of £750,000 from 1960 to 1965 for the Maldives' economic development. The base was closed in 1976 as part of the larger British withdrawal of permanently-stationed forces 'East of Suez'.
Independence and republic
Main article: Independence of the Maldives

When the British became increasingly unable to continue their colonial hold on Asia and were losing their colonies to the indigenous populations who wanted freedom, on 26 July 1965 an agreement was signed on behalf of the Sultan by Ibrahim Nasir Rannabandeyri Kilegefan, Prime Minister, and on behalf of the British government by Sir Michael Walker, British Ambassador-designate to the Maldive Islands, which formally ended the British authority on the defence and external affairs of the Maldives. The islands thus achieved independence, with the ceremony taking place at the British High Commissioner's Residence in Colombo. After this, the sultanate continued for another three years under Sir Muhammad Fareed Didi, who declared himself King upon independence.
On 15 November 1967, a vote was taken in parliament to decide whether the Maldives should continue as a constitutional monarchy or become a republic. Of the 44 members of parliament, 40 voted in favour of a republic. On 15 March 1968, a national referendum was held on the question, and 93.34% of those taking part voted in favour of establishing a republic. The republic was declared on 11 November 1968, thus ending the 853-year-old monarchy, which was replaced by a republic under the presidency of Ibrahim Nasir. As the King had held little real power, this was seen as a cosmetic change and required few alterations in the structures of government.
Tourism began to be developed on the archipelago by the beginning of the 1970s. The first resort in the Maldives was Kurumba Maldives which welcomed the first guests on 3 October 1972. The first accurate census was held in December 1977 and showed 142,832 people living in the Maldives.
Political infighting during the 1970s between Nasir's faction and other political figures led to the 1975 arrest and exile of elected prime minister Ahmed Zaki to a remote atoll. Economic decline followed the closure of the British airfield at Gan and the collapse of the market for dried fish, an important export. With support for his administration faltering, Nasir fled to Singapore in 1978, with millions of dollars from the treasury.
Maumoon Abdul Gayoom began his 30-year role as president in 1978, winning six consecutive elections without opposition. His election was seen as ushering in a period of political stability and economic development given Maumoon's priority to develop the poorer islands. Tourism flourished and increased foreign contact spurred development. However, Maumoon's rule was controversial, with some critics saying Maumoon was an autocrat who quelled dissent by limiting freedoms and practising political favouritism.
A series of coup attempts (in 1980, 1983, and 1988) by Nasir supporters and business interests tried to topple the government without success. While the first two attempts met with little success, the 1988 coup attempt involved a roughly 80-strong mercenary force of the PLOTE who seized the airport and caused Maumoon to flee from house to house until the intervention of 1,600 Indian troops airlifted into Malé restored order.
The November 1988 coup d'état was headed by Ibrahim Lutfee, a businessman, and Sikka Ahmed Ismail Manik, the father of the former first lady of the Maldives Fazna Ahmed. The attackers were defeated by then National Security Services of Maldives. On the night of 3 November 1988, the Indian Air Force airlifted a parachute battalion group from Agra and flew them over 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) to the Maldives. By the time Indian armed forces reached the Maldives, the mercenary forces has already left Malé on the hijacked ship MV Progress Light. The Indian paratroopers landed at Hulhulé and secured the airfield and restored the government rule at Malé within hours. The brief operation labelled Operation Cactus, also involved the Indian Navy that assisted in capturing the freighter MV Progress Light and rescued the hostages and crew.
21st century
Main article: History of the Maldives § 21st century
The Maldives were devastated by a tsunami on 26 December 2004, following the Indian Ocean earthquake. Only nine islands were reported to have escaped any flooding, while fifty-seven islands faced serious damage to critical infrastructure, fourteen islands had to be totally evacuated, and six islands were destroyed. A further twenty-one resort islands were forced to close because of tsunami damage. The total damage was estimated at more than US$400 million, or some 62% of the GDP. 102 Maldivians and 6 foreigners reportedly died in the tsunami. The destructive impact of the waves on the low-lying islands was mitigated by the fact there was no continental shelf or land mass upon which the waves could gain height. The tallest waves were reported to be 14 feet (4.3 m) high.
During the later part of Maumoon's rule, independent political movements emerged in the Maldives, which challenged the then-ruling Dhivehi Rayyithunge Party (Maldivian People's Party, MPP) and demanded democratic reform. The dissident journalist and activist Mohamed Nasheed founded the Maldivian Democratic Party (MDP) in 2003 and pressured Maumoon into allowing gradual political reforms. In 2008, a new constitution was approved and the first direct presidential elections occurred, which were won by Nasheed in the second round. His administration faced many challenges, including the huge debt left by the previous government, the economic downturn following the 2004 tsunami, overspending by means of overprinting of local currency (the rufiyaa), unemployment, corruption, and increasing drug use. Taxation on goods was imposed for the first time in the country, and import duties were reduced on many goods and services. Universal health insurance (Aasandha) and social welfare benefits were given to those aged 65 years or older, single parents, and those with special needs.
Social and political unrest grew in late 2011, following opposition campaigns in the name of protecting Islam. Nasheed controversially resigned from office after large number of police and army mutinied in February 2012. Nasheed's vice-president, Mohamed Waheed Hassan Manik, was sworn in as president. Nasheed was later arrested, convicted of terrorism, and sentenced to 13 years. The trial was widely seen as flawed and political. The UN Working Group on Arbitrary Detention called for Nasheed's immediate release.
The election in late 2013 were highly contested. Former president Nasheed won the most votes in the first round, but the Supreme Court annulled it despite the positive assessment of international election observers. In the re-run vote Abdulla Yameen, half-brother of the former president Maumoon, assumed the presidency. Yameen survived an assassination attempt in late 2015. Vice president Mohamed Jameel Ahmed was removed from office after a no confidence motion from the People's Majlis, it was alleged that he was conspiring with opposition political parties and planning riots. Vice-president Ahmed Adeeb was later arrested together with 17 supporters for "public order offences" and the government instituted a broader crackdown against his accomplices. A state of emergency was later declared ahead of a planned anti-government rally, and the People's Majlis (parliament) accelerated the removal of Adeeb.
In the 2018 election, Ibrahim Mohamed Solih won the most votes, and was sworn in as the Maldives' new president in November 2018. Adeeb was freed by courts in Male in July 2019 after his conviction on charges of terrorism and corruption was overruled, but was placed under a travel ban after the state prosecutor appealed the order in a corruption and money laundering case. Adeeb escaped in a tugboat to seek asylum in India. It is understood that the Indian Coast Guard escorted the tugboat to the International Maritime Boundary Line (IMBL) and he was then "transferred" to a Maldivian Coast Guard ship, where officials took him into custody. Former president Abdulla Yameen was sentenced to five years in prison in November 2019 for money laundering. The High Court upheld the jail sentence in January 2021. However, Supreme Court overturned Yameen's conviction in November 2021.
In the 2023 election, People's National Congress (PNC) candidate Mohamed Muizzu won the second-round runoff of the Maldives presidential election, beating incumbent president, Ibrahim Solih, with 54% of the vote. On 17 October 2023, Mohamed Muizzu was sworn in as the eighth President of the Republic of Maldives. Mohamed Muizzu is widely seen to be pro-China, meaning souring relations with India. In 2024, ex-President Abdulla Yameen Abdul Gayoom was freed from his 11-year conviction and the High Court ordered a new trial.
Geography
Main article: Geography of the Maldives

The Maldives consists of 1,192 coral islands grouped in a double chain of 26 atolls, that stretch along a length of 871 kilometres (541 miles) north to south, 130 kilometres (81 miles) east to west, spread over roughly 90,000 square kilometres (35,000 sq mi), of which only 298 km (115 sq mi) is dry land, making this one of the world's most dispersed countries. It lies between latitudes 1°S and 8°N, and longitudes 72° and 74°E. The atolls are composed of live coral reefs and sand bars, situated atop a submarine ridge 960 kilometres (600 mi) long that rises abruptly from the depths of the Indian Ocean and runs north to south.
Only near the southern end of this natural coral barricade do two open passages permit safe ship navigation from one side of the Indian Ocean to the other through the territorial waters of the Maldives. For administrative purposes, the Maldivian government organised these atolls into 21 administrative divisions. The largest island of the Maldives is that of Gan, which belongs to Laamu Atoll or Hahdhummathi Maldives. In Addu Atoll, the westernmost islands are connected by roads over the reef (collectively called Link Road) and the total length of the road is 14 km (9 mi).
The Maldives is the lowest country in the world, with maximum and average natural ground levels of only 2.4 metres (7 ft 10 in) and 1.5 metres (4 ft 11 in) above sea level, respectively. In areas where construction exists, however, this has been increased to several metres. More than 80 per cent of the country's land is composed of coral islands which rise less than one metre above sea level. As a result, the Maldives are in danger of being submerged due to rising sea levels. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has warned that, at current rates, sea-level rise would be high enough to make the Maldives uninhabitable by 2100.
Climate

The Maldives has a tropical monsoon climate (Am) under the Köppen climate classification, which is affected by the large landmass of South Asia to the north. Because the Maldives has the lowest elevation of any country in the world, the temperature is constantly hot and often humid. The presence of this landmass causes differential heating of land and water. These factors set off a rush of moisture-rich air from the Indian Ocean over South Asia, resulting in the southwest monsoon. Two seasons dominate the Maldives' weather: the dry season associated with the winter northeastern monsoon and the rainy season associated with the southwest monsoon which brings strong winds and storms.
The shift from the dry northeast monsoon to the moist southwest monsoon occurs during April and May. During this period, the southwest winds contribute to the formation of the southwest monsoon, which reaches the Maldives at the beginning of June and lasts until the end of November. However, the weather patterns of the Maldives do not always conform to the monsoon patterns of South Asia. The annual rainfall averages 254 centimetres (100 in) in the north and 381 centimetres (150 in) in the south.
The monsoonal influence is greater in the north of the Maldives than in the south, more influenced by the equatorial currents.
The average high temperature is 31.5 degrees Celsius and the average low temperature is 26.4 degrees Celsius.
| Climate data for Malé (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 30.3 (86.5) |
30.7 (87.3) |
31.4 (88.5) |
31.6 (88.9) |
31.2 (88.2) |
30.6 (87.1) |
30.5 (86.9) |
30.4 (86.7) |
30.2 (86.4) |
30.2 (86.4) |
30.1 (86.2) |
30.1 (86.2) |
30.6 (87.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 28.0 (82.4) |
28.3 (82.9) |
28.9 (84.0) |
29.2 (84.6) |
28.8 (83.8) |
28.3 (82.9) |
28.2 (82.8) |
28.0 (82.4) |
27.8 (82.0) |
27.8 (82.0) |
27.7 (81.9) |
27.8 (82.0) |
28.2 (82.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 25.7 (78.3) |
25.9 (78.6) |
26.4 (79.5) |
26.8 (80.2) |
26.3 (79.3) |
26.0 (78.8) |
25.8 (78.4) |
25.5 (77.9) |
25.3 (77.5) |
25.4 (77.7) |
25.2 (77.4) |
25.4 (77.7) |
25.8 (78.4) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 114.2 (4.50) |
38.1 (1.50) |
73.9 (2.91) |
122.5 (4.82) |
218.9 (8.62) |
167.3 (6.59) |
149.9 (5.90) |
175.5 (6.91) |
199.0 (7.83) |
194.2 (7.65) |
231.1 (9.10) |
216.8 (8.54) |
1,901.4 (74.86) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 6 | 3 | 5 | 9 | 15 | 13 | 12 | 13 | 15 | 15 | 13 | 12 | 131 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 78.0 | 77.0 | 76.9 | 78.1 | 80.8 | 80.7 | 79.1 | 80.5 | 81.0 | 81.7 | 82.2 | 80.9 | 79.7 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 248.4 | 257.8 | 279.6 | 246.8 | 223.2 | 202.3 | 226.6 | 211.5 | 200.4 | 234.8 | 226.1 | 220.7 | 2,778.2 |
| Source 1: World Meteorological Organization | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: NOAA (relative humidity and sun 1961–1990) | |||||||||||||
Sea level rise
Main article: Climate change in the Maldives See also: Effects of climate change on island nations and The Island PresidentIn 1988, Maldivian authorities claimed that sea rise would "completely cover this Indian Ocean nation of 1,196 small islands within the next 30 years."
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change's 2007 report predicted the upper limit of the sea level rise will be 59 centimetres (23 in) by 2100, which means that most of the republic's 200 inhabited islands may need to be abandoned. According to researchers from the University of Southampton, the Maldives are the third most endangered island nation due to flooding from climate change as a percentage of population.
In 2008, Nasheed announced plans to look into purchasing new land in India, Sri Lanka, and Australia because of his concerns about global warming, and the possibility of much of the islands being inundated with water from rising sea levels. The purchase of land will be made from a fund generated by tourism. The president explained his intentions: "We do not want to leave the Maldives, but we also do not want to be climate refugees living in tents for decades".
At the 2009 International Climate Talks, Nasheed stated that:
For us swearing off fossil fuels is not only the right thing to do, but it is also in our economic self-interest... Pioneering countries will free themselves from the unpredictable price of foreign oil; they will capitalise on the new green economy of the future, and they will enhance their moral standing giving them greater political influence on the world stage.
Former president Mohamed Nasheed said in 2012 that "If carbon emissions continue at the rate they are climbing today, my country will be under water in seven years." He has called for more climate change mitigation action while on the American television shows The Daily Show and the Late Show with David Letterman, and hosted "the world's first underwater cabinet meeting" in 2009 to raise awareness of the threats posed by climate change. Concerns over rising sea levels have also been expressed by Nasheed's predecessor, Maumoon Abdul Gayoom.
In 2020, a three-year study at the University of Plymouth which looked at the Maldives and the Marshall Islands, found that tides move sediment to create a higher elevation, a morphological response that the researchers suggested could help low-lying islands adjust to sea level rise and keep the islands habitable. The research also reported that sea walls were compromising islands' ability to adjust to rising sea levels and that island drowning is an inevitable outcome for islands with coastal structures like sea walls. Hideki Kanamaru, natural resources officer with the Food and Agriculture Organization in Asia-Pacific, said the study provided a "new perspective" on how island nations could tackle the challenge of sea-level rise, and that even if islands can adapt naturally to higher seas by raising their own crests, humans still needed to double down on global warming and protection for island populations.
Environment
Environmental issues other than sea level rise include bad waste disposal and sand theft. Although the Maldives are kept relatively pristine and little litter can be found on the islands, most waste disposal sites are often substandard. The bulk of the waste from Malé and nearby resorts in the Maldives are disposed of at Thilafushi, an industrial island on top of a lagoon reclaimed in the early '90s to sort waste management issues which had plagued the capital and surrounding islands.
31 protected areas are administered by the Ministry of Climate Change, Environment and Energy and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) of the Maldives.
Marine ecosystem
Further information: Wildlife of Maldives

The Maldives have a range of different habitats including deep sea, shallow coast, and reef ecosystems, fringing mangroves, wetlands and dry land. There are 187 species of coral forming the coral reefs. This area of the Indian Ocean, alone, houses 1,100 species of fish, 5 species of sea turtle, 21 species of whale and dolphin, 400 species of mollusc, and 83 species of echinoderms. The area is also populated by a number of crustacean species: 120 copepods, 15 amphipods, as well as more than 145 crab and 48 shrimp species.
Among the many marine families represented are pufferfish, fusiliers, jackfish, lionfish, oriental sweetlips, reef sharks, groupers, eels, snappers, bannerfish, batfish, humphead wrasse, spotted eagle rays, scorpionfish, lobsters, nudibranches, angelfish, butterflyfish, squirrelfish, soldierfish, glassfish, surgeonfish, unicornfish, triggerfish, Napoleon wrasse, and barracuda.
These coral reefs are home to a variety of marine ecosystems that vary from planktonic organisms to whale sharks. Sponges have gained importance as five species have displayed anti-tumor and anti-cancer properties.
In 1998, sea-temperature warming of as much as 5 °C (9.0 °F) due to a single El Niño phenomenon event caused coral bleaching, killing two-thirds of the nation's coral reefs.
In an effort to induce the regrowth of the reefs, scientists placed electrified cones anywhere from 20–60 feet (6.1–18.3 m) below the surface to provide a substrate for larval coral attachment. In 2004, scientists witnessed corals regenerating. Corals began to eject pink-orange eggs and sperm. The growth of these electrified corals was five times faster than untreated corals. Scientist Azeez Hakim stated:
before 1998, we never thought that this reef would die. We had always taken for granted that these animals would be there, that this reef would be there forever. El Niño gave us a wake-up call that these things are not going to be there forever. Not only this, but they also act as a natural barrier against tropical storms, floods and tsunamis. Seaweeds grow on the skeletons of dead coral.
—
Again, in 2016, the coral reefs of the Maldives experienced a severe bleaching incident. Up to 95% of coral around some islands have died, and, even after six months, 100% of young coral transplants died. The surface water temperatures reached an all-time high in 2016, at 31 degrees Celsius in May.
Recent scientific studies suggest that the faunistic composition can vary greatly between neighbour atolls, especially in terms of benthic fauna. Differences in terms of fishing pressure (including poaching) could be the cause.
Wildlife
Main article: Wildlife of the Maldives


 Clockwise from top left: Tawny nurse sharks near Vaavu Atoll, pier in Addu City, Butorides striata, and Ixora sp.
Clockwise from top left: Tawny nurse sharks near Vaavu Atoll, pier in Addu City, Butorides striata, and Ixora sp.
The wildlife of the Maldives includes the flora and fauna of the islands, reefs, and the surrounding ocean. Recent scientific studies suggest that the fauna varies greatly between atolls following a north–south gradient, but important differences between neighbouring atolls were also found (especially in terms of sea animals), which may be linked to differences in fishing pressure — including poaching.
The terrestrial habitats of the Maldives are confronted with a significant threat as extensive development encroaches swiftly upon the limited land resources. Once seldom frequented, previously uninhabited islands now teeter on the brink of extinction, virtually devoid of untouched expanses. Over recent decades of intensive development, numerous natural environments crucial to indigenous species have suffered severe endangerment or outright destruction.
Coral reef habitats had been damaged, as the pressure for land has brought about the creation of artificial islands. Some reefs have been filled with rubble with little regard for the changes in the currents on the reef shelf and how the new pattern would affect coral growth and its related life forms on the reef edges. Mangroves thrive in brackish or muddy regions of the Maldives. The archipelago hosts fourteen species spanning ten genera, among which is the fern Acrostichum aureum, indigenous to these islands.
The waters surrounding the Maldives boast an extensive array of marine life, showcasing a vibrant tapestry of corals and over 2,000 species of fish. From the dazzling hues of reef fish to the majestic presence of the blacktip reef shark, moray eels, and a diverse range of rays including manta rays, stingrays, and eagle rays, the seas teem with life. Notably, the Maldivian waters harbor the magnificent whale shark. Renowned for its biodiversity, these waters host rare species of both biological and commercial significance, with tuna fisheries representing a longstanding traditional resource. Within the limited freshwater habitats such as ponds and marshes, freshwater fish such as the milkfish (Chanos chanos) and various smaller species thrive. Additionally, the introduction of the tilapia or mouth-breeder, facilitated by a United Nations agency in the 1970s, further enriches the aquatic diversity of the Maldives.

Due to their diminutive size, land-dwelling reptiles are scarce on the Maldivian islands. Among the limited terrestrial reptilian inhabitants are a species of gecko and the oriental garden lizard (Calotes versicolor), alongside the white-spotted supple skink (Riopa albopunctata), the Indian wolf snake (Lycodon aulicus), and the brahminy blind snake (Ramphotyphlops braminus).
In the surrounding seas, however, a more diverse array of reptilian life thrives. Maldivian beaches serve as nesting grounds for the green sea turtle (Chelonia mydas), the hawksbill sea turtle, and the leatherback sea turtle. Furthermore, saltwater crocodiles have been reported to occasionally reach the islands, taking residence in marshy regions.
The location of this Indian Ocean archipelago means that its avifauna is mainly restricted to pelagic birds. Most of the species are Eurasian migratory birds, only a few being typically associated with the Indian sub-continent. Some, like the frigatebird are seasonal. There are also birds that dwell in marshes and island bush, like the grey heron and the moorhen. White terns are found occasionally on the southern islands due to their rich habitats.
Government and politics
Main article: Politics of the Maldives Mohamed Muizzu, President since 2023
Mohamed Muizzu, President since 2023 Hussain Mohamed Latheef, Vice President since 2023
Hussain Mohamed Latheef, Vice President since 2023
The Maldives is a presidential constitutional republic, with extensive influence of the president as head of government and head of state. The president heads the executive branch, and appoints the cabinet which is approved by the People's Majlis (Parliament). He leads the armed forces. The current president serving since 17 November 2023 is Mohamed Muizzu. President of the Maldives and Members of the unicameral Majlis serve five-year terms. The total number of members are determined by atoll populations. At the 2024 parliamentary election, the People's National Congress (PNC) won a super-majority over the 93 constituencies.
The republican constitution came into force in 1968 and was amended in 1970, 1972, and 1975. On 27 November 1997 it was replaced by another Constitution assented to by then-President Maumoon. This Constitution came into force on 1 January 1998. The current Constitution of Maldives was ratified by President Maumoon on 7 August 2008, and came into effect immediately, replacing and repealing the constitution of 1998. This new constitution includes a judiciary run by an independent commission, and independent commissions to oversee elections and fight corruption. It also reduces the executive powers vested under the president and strengthens the parliament. All state that the president is head of state, head of government and Commander-in-Chief of the armed forces of the Maldives.
In 2018, the then ruling Progressive Party of Maldives (PPM-Y)'s tensions with opposition parties and subsequent crackdown was termed as an "assault on democracy" by the UN Human Rights chief.

In April 2019 parliamentary election The Maldivian Democratic Party (MDP) of president Ibrahim Mohamed Solih won a landslide victory. It took 65 of 87 seats of the parliament. This was the first time a single party was able to get such a high number of seats in the parliament in Maldivian history.
Order of Nishanizzuddeen is the Maldives' highest civilian honor that can be bestowed upon a person. It is awarded by the president, usually in an elaborate ceremony.
In April 2024, President Mohamed Muizzu's pro-China People's National Congress (PNC) won 66 seats in the 2024 Maldivian parliamentary election, while its allies took nine, giving the president the backing of 75 legislators in the 93-member house, meaning a super-majority and enough to change the constitution.
Law
See also: Judiciary of the Maldives and Law enforcement in the MaldivesAccording to the Constitution of Maldives, "the judges are independent, and subject only to the Constitution and the law. When deciding matters on which the Constitution or the law is silent, judges must consider Islamic Shari'ah".
Islam is the official religion of the Maldives and open practice of any other religion is forbidden. The 2008 constitution says that the republic "is based on the principles of Islam" and that "no law contrary to any principle of Islam can be applied". Non-Muslims are prohibited from becoming citizens.
The requirement to adhere to a particular religion and prohibition of public worship following other religions is contrary to Article 18 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and Article 18 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights to which the Maldives has recently become party and was addressed in the Maldives' reservation in adhering to the Covenant claiming that "The application of the principles set out in Article 18 of the Covenant shall be without prejudice to the Constitution of the Republic of Maldives."
A new penal code came into effect on 16 July 2015, replacing the 1968 law, the first modern, comprehensive penal code to incorporate the major tenets and principles of Islamic law.
Same-sex relations are illegal in the Maldives, although tourist resorts typically operate as exceptions to this law.
Foreign relations
Main article: Foreign relations of the MaldivesSince 1996, the Maldives has been the official progress monitor of the Indian Ocean Commission. In 2002, the Maldives began to express interest in the commission but as of 2008 had not applied for membership. Maldives' interest relates to its identity as a small island state, especially economic development and environmental preservation, and its desire for closer relations with France, a main actor in the IOC region.
The Maldives is a founding member of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC). The republic joined the Commonwealth in 1982, some 17 years after gaining independence from the United Kingdom. In October 2016, the Maldives announced its withdrawal from the Commonwealth in protest at allegations of human rights abuse and failing democracy. The Maldives enjoys close ties with Commonwealth members Seychelles and Mauritius. The Maldives and Comoros are also both members of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation. Following his election as president in 2018, Ibrahim Mohamed Solih and his Cabinet decided that the Maldives would apply to rejoin the Commonwealth, with readmission occurring on 1 February 2020.
As a result of sanctions imposed upon the Russian oligarchs by the West in response to Russia's invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, many of them sought refuge for their mega-yachts in the Maldives due to the absence of an extradition treaty with the United States and other countries.
Following a cabinet meeting, in June 2024, the government of the Maldives decided to ban Israeli passport holders from entering the country, as a response to the ongoing Israel–Hamas war in the Gaza Strip.
Military
Main article: Maldives National Defence Force
The Maldives National Defence Force is the combined security organisation responsible for defending the security and sovereignty of the Maldives, having the primary task of being responsible for attending to all internal and external security needs of the Maldives, including the protection of the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and the maintenance of peace and security. The MNDF component branches are the Coast Guard, Marine Corps, Special Forces, Service Corps, Defence Intelligence Service, Military Police, Corps of Engineers, Special Protection Group, Medical Corps, Adjutant General's Corps, Air Corps, and Fire and Rescue Service. The Maldives has an arrangement with India allowing cooperation on radar coverage.
As a water-bound nation, much of its security concerns life at sea. Almost 99% of the country is covered by sea and the remaining 1% land is scattered over an area of 800 km (497 mi) × 120 km (75 mi), with the largest island being not more than 8 km (3 sq mi). Therefore, the duties assigned to the MNDF of maintaining surveillance over the Maldives' waters and providing protection against foreign intruders poaching in the EEZ and territorial waters, are immense tasks from both logistical and economic viewpoints. The Coast Guard plays a vital role in carrying out these functions. To provide timely security its patrol boats are stationed at various MNDF Regional Headquarters. The Coast Guard is also assigned to respond to maritime distress calls and to conduct search and rescue operations in a timely manner.

In 2019, the Maldives signed the UN treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
Human rights
Main article: Human rights in the MaldivesHuman rights in the Maldives is a contentious issue. In its 2011 Freedom in the World report, Freedom House declared the Maldives "Partly Free", claiming a reform process which had made headway in 2009 and 2010 had stalled. The United States Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor claims in their 2012 report on human rights practices in the country that the most significant problems are corruption, lack of religious freedom, abuse, and unequal treatment of women.
Administrative divisions
Main article: Administrative divisions of the Maldives
The Maldives has twenty-six natural atolls and few island groups on isolated reefs, all of which have been divided into twenty-one administrative divisions (17 administrative atolls and cities of Malé, Addu, Fuvahmulah, Thinadhoo, and Kulhudhuffushi).
Each atoll is administered by an elected Atoll Council. The islands are administered by an elected Island Council.
In addition to a name, every administrative division is identified by the Maldivian code letters, such as "Haa Alif" for Thiladhunmati Uthuruburi (Thiladhunmathi North); and by a Latin code letter. The first corresponds to the geographical Maldivian name of the atoll; the second is a code adopted for convenience. As there are certain islands in different atolls that have the same name, for administrative purposes this code is quoted before the name of the island, for example: Baa Funadhoo, Kaafu Funadhoo, Gaafu-Alifu Funadhoo. Since most atolls have very long geographical names it is also used whenever the long name is inconvenient, for example in the atoll website names.
The introduction of code-letter names has been a source of much puzzlement and misunderstandings, especially among foreigners. Many people have come to think that the code-letter of the administrative atoll is its new name and that it has replaced its geographical name. Under such circumstances, it is hard to know which is the correct name to use.
Economy
Main article: Economy of the Maldives
Historically, the Maldives provided enormous quantities of cowry shells, an international currency of the early ages. From the 2nd century CE, the islands were known as the 'Money Isles' by the Arabs. Monetaria moneta were used for centuries as a currency in Africa, and huge amounts of Maldivian cowries were introduced into Africa by western nations during the period of slave trade. The cowry is now the symbol of the Maldives Monetary Authority.
In the early 1970s and 1980s, the Maldives was one of the world's 20 poorest countries, with a population of 100,000. The economy at the time was largely dependent on fisheries and trading local goods such as coir rope, ambergris (Maavaharu), and coco de mer (Tavakkaashi) with neighbouring countries and East Asian countries.
The Maldivian government began a largely successful economic reform programme in the 1980s, initiated by lifting import quotas and giving more opportunities to the private sector. At the time tourism sector which would play a significant role in the nation's development was at its infant stage. Agriculture and manufacturing continue to play lesser roles in the economy, constrained by the limited availability of cultivable land and the shortage of domestic labour.
Tourism
Main articles: Tourism in the Maldives, Diving in the Maldives, and List of mosques in the Maldives
The Maldives remained largely unknown to tourists until the early 1970s. Only 200 islands are home to its 382,751 inhabitants. The other islands are used entirely for economic purposes, of which tourism and agriculture are the most dominant. Tourism accounts for 28% of the GDP and more than 60% of the Maldives' foreign exchange receipts. Over 90% of government tax revenue comes from import duties and tourism-related taxes.
The development of tourism fostered the overall growth of the country's economy. It created direct and indirect employment and income generation opportunities in other related industries. The first tourist resorts were opened in 1972 with Bandos Island Resort and Kurumba Village (the current name is Kurumba Maldives), which transformed the Maldives' economy.

According to the Ministry of Tourism, the emergence of tourism in 1972 transformed the economy, moving rapidly from dependence on fisheries to tourism. In just three and a half decades, the industry became the main source of income. Tourism was also the country's biggest foreign currency earner and the single largest contributor to the GDP. As of 2008, 89 resorts in the Maldives offered over 17,000 beds and hosted over 600,000 tourists annually. In 2019, over 1.7 million visitors came to the islands.
The number of resorts increased from 2 to 92 between 1972 and 2007. As of 2007, over 8,380,000 tourists had visited the Maldives.
The country has six heritage Maldivian coral mosques listed as UNESCO tentative sites.
Visitors
See also: § Transportation, and Visa policy of Maldives
Visitors to the Maldives do not need to apply for a visa pre-arrival, regardless of their country of origin, provided they have a valid passport, proof of onward travel, and the money to be self-sufficient while in the country.
Most visitors arrive at Velana International Airport, on Hulhulé Island, adjacent to the capital Malé. The airport is served by flights to and from India, Sri Lanka, Doha, Dubai, Abu Dhabi, Singapore, Dhaka, Istanbul, and major airports in South-East Asia like Kuala Lumpur International in Malaysia, as well as charters from Europe like Charles De Gaulle in France. Gan Airport, on the southern atoll of Addu, also serves an international flight to Malpensa in Milan several times a week. British Airways offers direct flights to the Maldives from Heathrow Airport.
Fishing industry
Main article: Fishing industry in the Maldives
For many centuries the Maldivian economy was entirely dependent on fishing and other marine products. Fishing remains the main occupation of the people and the government gives priority to the fisheries sector.
The mechanisation of the traditional fishing boat called dhoni in 1974 was a major milestone in the development of the fisheries industry. A fish canning plant was installed on Felivaru in 1977, as a joint venture with a Japanese firm. In 1979, a Fisheries Advisory Board was set up with the mandate of advising the government on policy guidelines for the overall development of the fisheries sector. Manpower development programmes began in the early 1980s, and fisheries education was incorporated into the school curriculum. Fish aggregating devices and navigational aids were located at various strategic points. Moreover, the opening up of the exclusive economic zone (EEZ) of the Maldives for fisheries has further enhanced the growth of the fisheries sector.
As of 2010, fisheries contributed over 15% of the country's GDP and engaged about 30% of the country's workforce. Fisheries were also the second-largest foreign exchange earner after tourism.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of the Maldives
| Year | Population |
|---|---|
| 1911 | 72,237 |
| 1966 | 100,883 |
| 2000 | 270,101 |
| 2020 est. | 557,426 |
The largest ethnic group is Dhivehin, i.e. the Maldivians, native to the historic region of the Maldive Islands comprising today's Republic of Maldives and the island of Minicoy in Union territory of Lakshadweep, India. They share the same culture and speak the Dhivehi language. They are principally an Indo-Aryan people, having traces of Middle Eastern, South Asian, Austronesian and African genes in the population.
In the past, there was also a small Tamil population known as the Giraavaru people. This group has now been almost completely absorbed into the larger Maldivian society but were once native to the island of Giraavaru, which was evacuated in 1968 due to heavy erosion of the island.
Some social stratification exists on the islands. It is not rigid, since rank is based on varied factors, including occupation, wealth, Islamic virtue, and family ties. Instead of a complex caste system, there was merely a distinction between noble (bēfulhu) and common people in the Maldives. Members of the social elite are concentrated in Malé.

The population doubled by 1978, and the population growth rate peaked at 3.4% in 1985. By the 2006 census, the population had reached 298,968, although the census in 2000 showed that the population growth rate had declined to 1.9%. Life expectancy at birth stood at 46 years in 1978, and later rose to 72. Infant mortality has declined from 12.7% in 1977 to 1.2% today, and adult literacy reached 99%. Combined school enrolment reached the high 90s. The population was projected to have reached 317,280 in 2010.
The 2014 Population and Housing Census listed the total population in the Maldives as 437,535: 339,761 resident Maldivians and 97,774 resident foreigners, approximately 16% of the total population. However, it is believed that foreigners have been undercounted. As of May 2021, there were 281,000 expatriate workers, an estimated 63,000 of whom are undocumented in the Maldives: 3,506 Chinese, 5,029 Nepalese, 15,670 Sri Lankans, 28,840 Indians, and (the largest group of foreigners working in the country) 112,588 Bangladeshis. Other immigrants include Filipinos as well as various Western foreign workers.
Religion
See also: Religion in the MaldivesReligion in the Maldives
Islam (98.69%) Christianity (0.29%) Agnostics (0.29%) Hindu (0.29%) Others (0.74%)After the long Buddhist period of Maldivian history, Muslim traders introduced Islam. Maldivians converted to Islam by the mid-12th century. The islands have had a long history of Sufic orders, as can be seen in the history of the country such as the building of tombs. They were used until as recently as the 1980s for seeking the help of buried saints. They can be seen next to some old mosques and are considered a part of the Maldives's cultural heritage.
Other aspects of tassawuf, such as ritualised dhikr ceremonies called Maulūdu (Mawlid) – the liturgy of which included recitations and certain supplications in a melodic tone – existed until very recent times. These Maulūdu festivals were held in ornate tents specially built for the occasion. At present Islam is the official religion of the entire population, as adherence to it is required for citizenship.
According to Arab traveller Ibn Battuta, the person responsible for this conversion was a Sunni Muslim visitor named Abu al-Barakat Yusuf al-Barbari, sailing from what is today Morocco. He is also referred to as Tabrizugefaanu. His venerated tomb now stands on the grounds of Medhu Ziyaaraiy, across the street from the Friday Mosque, or Hukuru Miskiy, in Malé. Originally built in 1153 and re-built in 1658, this is one of the country's oldest surviving mosques.
In 2013, scholar Felix Wilfred of Oxford University estimates the number of Christians in Maldives as 1,400 or 0.4% of the country's population.
Since the adoption of the 2008 constitution citizens and anyone wishing to become a citizens are required by law to nominally follow Sunni Islam which would make Maldives a 100% Muslim country in theory. But residents, tourists and guest workers are free to be of any religion and practise them in private. However, in 2020, studies found that 0.29% of the population is Christian (roughly split between Catholic and Protestant).
Languages
See also: Maldivian language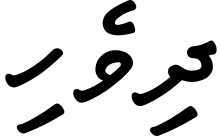
The official and national language is Dhivehi, an Indo-Aryan language closely related to the Sinhala language of Sri Lanka. The first known script used to write Dhivehi is the eveyla akuru script, which is found in the historical recording of kings (raadhavalhi). Later a script called Dhives akuru was used for a long period. The present-day script is called Thaana and is written from right to left. Thaana is derived from a mix of the old indigenous script of Dhives akuru and Arabic abjad. Thaana is said to have been introduced by the reign of Mohamed Thakurufaanu.
English is widely spoken by the locals of the Maldives: "Following the nation's opening to the outside world, the introduction of English as a medium of instruction at the secondary and tertiary levels of education, and its government's recognition of the opportunities offered through tourism, English has now firmly established itself in the country. As such, the Maldives are quite similar to the countries in the Gulf region .... The nation is undergoing vast societal change, and English is part of this."
Otherwise, Arabic is taught in schools and mosques, as Sunni Islam is the state religion. The Maldivian population has formal or informal education in the reading, writing and pronunciation of the Arabic language, as part of the compulsory religious education for all primary and secondary school students.
Thikijehi Thaana
These additional letters were added to the Thaana alphabet by adding dots (nukuthaa) to existing letters, to allow for transliteration of Arabic loanwords, as previously Arabic loanwords were written using the Arabic script. Their usage is inconsistent, and becoming less frequent as the spelling changes to reflect pronunciation by Maldivians, rather than the original Arabic pronunciation, as the words get absorbed into the Maldivian language.
Population by locality
| Largest localities in Maldives by registered population as of December 31, 2018 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Name | Division | Pop. | ||||||
 Malé  Addu City |
1 | Malé | Malé | 252,768 |  Fuvahmulah  Kulhudhuffushi | ||||
| 2 | Addu City | Addu Atoll | 34,503 | ||||||
| 3 | Fuvahmulah | Gnaviyani Atoll | 13,037 | ||||||
| 4 | Kulhudhuffushi | Haa Dhaalu | 10,210 | ||||||
| 5 | Thinadhoo | Gaafu Dhaalu | 7,487 | ||||||
| 6 | Naifaru | Lhaviyani | 5,542 | ||||||
| 7 | Hinnavaru | Lhaviyani | 4,901 | ||||||
| 8 | Dhuvaafaru | Raa | 4,760 | ||||||
| 9 | Dhidhdhoo | Haa Alifu | 4,246 | ||||||
| 10 | Gan | Laamu | 3,860 | ||||||
Health
Main article: Health in the MaldivesThe Human Rights Measurement Initiative reports that Maldives is meeting 5.1 of 10 of the expected fulfillment for the right to health considering its income level. Specifically for children's health rights, Maldives attains 98.0% of the anticipated level based on its current income. Regarding adult health rights, the country achieves 99.7% of the expected fulfillment considering its income level. However, in terms of reproductive health rights, Maldives falls into the "very bad" category, as it fulfills only 18.2% of the expected achievement based on its available resources.
Life expectancy at birth in Maldives was 77 years in 2011. Infant mortality fell from 34 per 1,000 in 1990 to 15 in 2004. There is increasing disparity between health in the capital and on the other islands. There is also a problem of malnutrition. Imported food is expensive.
On 24 May 2021, the Maldives had the world's fastest-growing COVID-19 outbreak, with the highest number of infections per million people over the prior 7 and 14 days, according to data compiled by Bloomberg. Doctors warned that increasing demand for COVID-19 care could hinder their ability to handle other health emergencies in the Maldives. The reason for the outbreak was the Delta variant.
Transportation
Main articles: Transport in the Maldives and List of airports in the Maldives

Velana International Airport is the principal gateway to the Maldives; it is adjacent to the capital city Malé and is connected by a bridge. International travel is available on government-owned Island Aviation Services (branded as Maldivian), which operates DHC-6 Twin Otter seaplanes and to nearly all Maldivian domestic airports with several Bombardier Dash 8 aircraft, and one Airbus A320 with international service to India, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Malaysia and Thailand.
In the Maldives, there are three main ways to travel between islands: by domestic flight, by seaplane, or by boat. For several years there were two seaplane companies operating: TMA (Trans Maldivian Airways) and Maldivian Air Taxi, but these merged in 2013 under the name TMA. The seaplane fleet is entirely made up of DHC-6 Twin Otters. There is also another airline, Flyme, which operates using ATR planes to domestic airports, principally Villa-Maamigili, Dharavandhoo and some others. Manta Air began its first scheduled seaplane service in 2019. Its seaplane fleet is made up of DHC-6 Twin Otter aircraft. In addition to the seaplane service, Manta Air utilises ATR 72–600 aircraft to operate domestic flights to Dhaalu Airport, Dharavandhoo Airport and Kooddoo Airport from the main Velana International Airport. Depending on the distance of the destination island from the airport, resorts organise speedboat transfers or seaplane flights directly to the resort island jetty for their guests. Several daily flights operate from Velana International Airport to the 18 domestic and international airports in the country. Scheduled ferries also operate from Malé to many of the atolls. The traditional Maldivian boat is called a dhoni, one of the oldest known sea vessels in the Maldives. Speedboats and seaplanes tend to be more expensive, while travel by dhoni, although slower, is relatively cheaper and convenient.
Education
Main article: Education in the MaldivesThe Maldives National University is one of the country's institutions of higher education. In 1973, the Allied Health Services Training Centre (the forerunner of the Faculty of Health Sciences) was established by the Ministry of Health. The Vocational Training Centre was established in 1974, providing training for mechanical and electrical trades. In 1984, the Institute for Teacher Education was created and the School of Hotel and Catering Services was established in 1987 to provide trained personnel for the tourist industry. In 1991, the Institute of Management and Administration was created to train staff for public and private services. In 1998, the Maldives College of Higher Education was founded. The Institute of Shar'ah and Law was founded in January 1999. In 2000 the college launched its first-degree programme, Bachelor of Arts. On 17 January 2011 the Maldives National University Act was passed by the President of the Maldives; The Maldives National University was named on 15 February 2011. In 2015 under a Presidential decree the College of Islamic Studies was changed into the Islamic University of Maldives (IUM).
The Maldivian government now offers 3 different scholarships to students that have completed their higher secondary education with results above a certain threshold, with ranks of the scholarship received depending on the merits achieved by students on their year 12 examinations.
Culture
Main article: Culture of the Maldives See also: Maldivian cuisine and Folklore of the Maldives
The culture of the Maldives is influenced by the cultures of the people of different ethnicities who have settled on the islands throughout the times.
Since the 12th century AD, there were also influences from Arabia in the language and culture of the Maldives because of the conversion to Islam and its location as a crossroads in the central Indian Ocean. This was due to the long trading history between the far east and the middle east.
Reflective of this is the fact that the Maldives has had the highest national divorce rate in the world for many decades. This, it is hypothesised, is due to a combination of liberal Islamic rules about divorce and the relatively loose marital bonds that have been identified as common in non- and semi-sedentary peoples without a history of fully developed agrarian property and kinship relations.
Media
Main articles: Television Maldives, Voice of Maldives, and List of newspapers in the MaldivesPSM News serves as the country's main media, owned by the government of the Maldives. The newspaper was founded on 3 May 2017, in the celebration of World Press Freedom Day. Maldives has been ranked one–hundred in the World Press Freedom Index 2023 and 106 in 2024. The country's first daily newspaper, Haveeru Daily News was the first and longest–serving newspaper in the history of the Maldives, which was registered on 28 December 1978, and dissolved in 2016. Article 28 of the Maldives Constitution guarantees freedom of the press and stipulates that:
No person shall be compelled to disclose the source of any information that is espoused, disseminated or published by that person.
However, this protection is compromised by the Evidence Act, which came into effect in January 2023 and grants courts the authority to compel journalists to reveal their confidential sources. The Maldives Media Council (MMC) and the Maldives Journalists Association (MJA) serve as crucial watchdogs in addressing and combating these threats. Newspapers, Sun Online, Mihaaru and its English edition, The Edition and Avas serves one of the most well–known private news outlets.
Sports
Sports in the Maldives are deeply ingrained in the culture of the island nation, with a diverse array of activities reflecting both traditional pastimes and modern sporting pursuits. Given its unique geography of scattered islands surrounded by the Indian Ocean, water sports naturally hold a prominent position. Surfing, in particular, has gained international recognition, with waves that cater to both beginners and seasoned surfers. Locations such as the atolls of North and South Malé, Thulusdhoo, and Himmafushi offer ideal conditions for enthusiasts to ride the waves throughout the years. Additionally, diving and snorkeling are immensely popular, allowing locals and tourists alike to explore the rich marine life that thrives in the crystal-clear waters surrounding the Maldives.

Football, or soccer, stands out as one of the most widely played and passionately followed sports in the Maldives. The Maldives national football team competes in regional and international tournaments, with a fervent fan base supporting their endeavors. The country has its own domestic football league, the Dhivehi Premier League, featuring clubs from various atolls vying for supremacy. Matches often draw large crowds, contributing to the vibrant sporting atmosphere of the Maldives. Moreover, futsal enjoys popularity, especially among younger generations, with numerous indoor facilities providing spaces for friendly matches and competitive leagues.

Traditional Maldivian sports also play a significant role in preserving cultural heritage and promoting physical activity. Bodu Beru, a rhythmic drumming and dance performance, often accompanies traditional sports events, adding to the festive ambiance. One such traditional sport is "Baibalaa", a game resembling volleyball but played with a woven ball made from dried coconut palm leaves. "Fenei Bashi", a form of wrestling, is another traditional sport that showcases strength and agility. These indigenous sports serve as a reminder of the Maldives' rich cultural heritage and continue to be cherished by communities across the islands.
See also
- List of Maldives-related topics
- Outline of the Maldives
- Maldives Sign Language
- Maldives Inland Revenue Authority
Notes
- The total area, including its exclusive economic zone territory is approximately 89,999 square kilometers, behind Jordan (89,342 square kilometers) and ahead of Portugal (92,220 square kilometers). With the EEZ, the Maldives would be the 110th largest country.
- The Maldives predominantly utilizes the Maldivian Rufiyaa (MVR) as its official currency. However, United States dollars are commonly accepted in tourist establishments due to the high number of visitors from USD-based countries.
- /ˈmɔːldivz/ MAWL-deevz; Dhivehi: ދިވެހިރާއްޖެ, romanized: Dhivehi Raajje, pronounced [diʋehi ɾaːd͡ʒːe].
- ދިވެހިރާއްޖޭގެ ޖުމްހޫރިއްޔާ, Dhivehi Raajjeyge Jumhooriyyaa, pronounced [diʋehi ɾaːd͡ʒːeːge d͡ʒumhuːɾijjaː].
- There are 209 registered Higher Education Institutes as of May 2022.
References
- ^ "National Emblems of the Maldives". Maldives Mission to the United Nations. Archived from the original on 6 June 2011. Retrieved 29 October 2010.
- ^ "Regional Profiles: Maldives". The Association of Religion Data Archives. World Religion Database. Archived from the original on 6 May 2024. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- "Economic Profile". Embassy of the Republic of Maldives. Archived from the original on 13 August 2022. Retrieved 13 August 2022.
- "Maldives". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Archived from the original on 29 July 2022. Retrieved 30 November 2023.
- "Census Results Summary". Maldives Population and Housing Census. National Bureau of Statistics. Archived from the original on 1 September 2023. Retrieved 30 November 2023.
- ^ "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2023 Edition. (Maldives)". International Monetary Fund. 10 October 2023. Archived from the original on 29 October 2023. Retrieved 19 October 2023.
- "Gini Index coefficient". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Archived from the original on 17 July 2021. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- "Human Development Report 2023/24" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 13 March 2024. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 March 2024. Retrieved 13 March 2024.
- ^ Henley, Jon (11 November 2008). "The last days of paradise". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on 4 September 2013. Retrieved 12 May 2010.
holds the record for the country with the lowest high point on earth: nowhere on any of the islands on Maldives does the natural ground level exceed 5.1m. Most of land mass, which totals roughly one-fifth of Greater London, is a great deal lower , averaging around 1.5m.
- "Male | Geography, Facts, & Points of Interest". Britannica. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 11 June 2020.
- "Home". Permanent Mission of the Republic of the Maldives to the United Nations. Archived from the original on 15 March 2024. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- "Maldives – Country report – Freedom in the World – 2015". Freedom House. 21 January 2015. Archived from the original on 14 August 2016. Retrieved 19 June 2016.
- National Adaptation Program of Action: Republic of Maldives (PDF) (Report). Ministry of Environment, Energy and Water. 2007. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 24 February 2019.
- "Data for Upper middle income, Maldives". World Bank. Archived from the original on 15 May 2024. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- "Nepal, Maldives To Join Shanghai Cooperation Organisation.As Observer". Spotlight. Xinhua News Agency. 1 August 2022. Archived from the original on 15 March 2024. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- Human Development Report 2020 The Next Frontier: Human Development and the Anthropocene (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 15 December 2020. pp. 343–346. ISBN 978-92-1-126442-5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 January 2021. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- "2016 Human Development Report Statistical Annex" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 2016. p. 13. Archived from the original on 25 December 2018. Retrieved 4 May 2019.
- Safi, Michael (13 October 2016). "Maldives quits Commonwealth over alleged rights abuses". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on 13 October 2016. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- "Maldives rejoins Commonwealth after evidence of reforms". The Guardian. 1 February 2020. Archived from the original on 18 April 2020. Retrieved 4 February 2020.
- ^ Mohamed, Naseema (2005). "First Settlers". Note on the Early History of the Maldives. 70 (1): 7–14. doi:10.3406/arch.2005.3970. ISSN 0044-8613. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 28 November 2019.
- "The Long Road From Islam to Islamism: A Short History". Dhivehi Sitee. 30 May 2014. Archived from the original on 29 August 2014. Retrieved 30 May 2014.
- Hogendorn, Jan. The Shell Money of the Slave Trade. pp. 23–24.
- ^ Hogendorn, Jan and Johnson Marion (1986). The Shell Money of the Slave Trade. African Studies Series 49, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge ISBN 0521541107, pp. 20–22
- P.E.P Deraniyagala in Senarat Paranavitana; Leelananda Prematilleka; Johanna Engelberta van Lohuizen-De Leeuw (1978). Senarat Paranavitana Commemoration Volume. Brill. pp. 52–. ISBN 978-90-04-05455-4. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 1 August 2013.
- Wilhelm Geiger, trans. Mrs. J. C. Willis, Máldivian Linguistic Studies, Journal of the Ceylon Branch of the Royal Asiatic Society 27 (Colombo: 1911), 149–52. ISBN 8120612019
- "Altername Names for Republic of Maldives". GeoNames. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 23 September 2013.
- Melton, Gregory (16 April 2024). "How did Maldives get its name?". Geographic FAQ Hub. Archived from the original on 16 April 2024. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- "Maldives - Summary". Studocu. University of Sydney. Retrieved 15 May 2024.
- Apte, Vaman Shivram (1985). Sanskrit–English Dictionary. Motilal Banarsidass, New Delhi.
- "Minicoy in English dictionary". Glosbe. Archived from the original on 16 April 2024. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- Battuta, Ibn (1929) Travels in Asia and Africa 1325–1354, translated by A. R. Gibb. London: Routledge and Keegan Paul.
- Akhbar al-Sin wa 'l-Hind (Notes on China and India), which dates from 851.
- Lunde, Paul (July–August 2005). "The Seas of Sinbad". Saudi Aramco World. Vol. 56, no. 4. pp. 20–29. Archived from the original on 8 February 2007. Retrieved 24 September 2008.
- ^ Pacific Islands Business Law Handbook Volume 1 Strategic Information, Regulations, Contact. Global Pro Info USA. June 2015. p. 69. ISBN 978-1-5145-0229-7. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 16 November 2020.
IBPUS.com
- Orta, Garcia (2016). Colloquies on the Simple and Drugs of India. India: Sri Satguru Publications. p. 22. ISBN 978-81-7030-117-2.
- Dhivehi Bahaai Thareekhah Khidhumaikuraa Qaumee Marukazu (1 August 1990). "Dhivehiraajje". Digital Repository of the Maldives National University. Dhivehi Bahaai Thareekhah Khidhumaikuraa Qaumee Marukazu. Archived from the original on 16 April 2024. Retrieved 18 May 2024 – via Saruna.
- ދިވެހީންގެ އަސްލު (in Divehi). Maldives: ދިވެހިތާރީޚަށް ޚިދުމަތްކުރާ ޤައުމީ މަރުކަޒު. 1998. p. 3.
- ދިވެހީންގެ އަސްލު (in Divehi). ދިވެހިތާރީޚަށް ޚިދުމަތްކުރާ ޤައުމީ މަރުކަޒު.
- Kalpana Ram (1993). Mukkuvar Women. Macquarie University.
- Xavier Romero-Frias, The Maldive Islanders, A Study of the Popular Culture of an Ancient Ocean Kingdom
- Ellis, Royston (2008). Maldives. Bradt Travel Guides. ISBN 9781841622668. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 16 November 2020.
- ^ Maloney, Clarence. "Where Did the Maldives People Come From?". International Institute for Asian Studies. Archived from the original on 29 January 2002. Retrieved 22 June 2008.
- Maloney, Clarence. People of the Maldive Islands. Orient Longman.
- ^ Battutah, Ibn (2002). The Travels of Ibn Battutah. London: Picador. pp. 235–236, 320. ISBN 9780330418799.
- The Adventures of Ibn Battuta: A Muslim Traveller of the Fourteenth Century Archived 12 April 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- Honchell, Stephanie (2018), Sufis, Sea Monsters, and Miraculous Circumcisions: Comparative Conversion Narratives and Popular Memories of Islamization (PDF), Fairleigh Dickinson University and the University of Cape Town, p. 5, archived (PDF) from the original on 16 May 2024, retrieved 16 May 2024,
In reference to Ibn Batuta's Moroccan theory of this figure, citation 8 of this text mentions, that other accounts identify Yusuf Al Barbari as East African or Persian. But as a fellow Maghribi, Ibn Battuta likely felt partial to the Moroccan version.
- Paul, Ludwig (2003). Persian Origins: Early Judaeo-Persian and the Emergence of New Persian : Collected Papers of the Symposium, Göttingen 1999. Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. p. 31. ISBN 978-3-447-04731-9. Archived from the original on 15 September 2015. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- Kamala Visweswaran (6 May 2011). Perspectives on Modern South Asia: A Reader in Culture, History, and Representation. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 164–. ISBN 978-1-4051-0062-5. Archived from the original on 3 May 2021. Retrieved 2 October 2020.
- Ishtiaq Ahmed (2002). Ingvar Svanberg; David Westerlund (eds.). Islam Outside the Arab World. Routledge. p. 250. ISBN 9780253022608. Archived from the original on 3 May 2021. Retrieved 2 October 2020.
- HCP Bell, The Máldive Islands. Monograph on the History, Archæology, and Epigraphy with W. L. De Silva, Colombo 1940
- Paul, Ludwig (2003). Persian Origins--: Early Judaeo-Persian and the Emergence of New Persian: Collected Papers of the Symposium, Göttingen 1999. Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. p. 31. ISBN 978-3-447-04731-9. Archived from the original on 15 September 2015. Retrieved 30 April 2017.
- Yoosuf, Muawwaz (28 February 2020). "Malé Friday Mosque". Coral Stone Mosques of Maldives. Retrieved 25 October 2024.
- Buchan, James (21 December 2002). Mackintosh-Smith, Tim (ed.). "The Travels of Ibn Battutah". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on 7 December 2017. Retrieved 6 December 2017.
- Jerry Bently, Old World Encounters Cross-Cultural Contacts and Exchanges in Pre-Modern Times (New York: Oxford University Press, 1993), 126.
- Boomgaard, P. (1 January 2008). Linking Destinies: Trade, Towns and Kin in Asian History. BRILL. ISBN 9789004253995. Archived from the original on 6 January 2017. Retrieved 23 August 2016 – via Google Books.
- "BOCARRO, António, 1594–1642? Livro das plantas de todas as fortalezas, cidades e povoaçoens do Estado da India Oriental / António Bocarro [1635]". Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 20 June 2020.
- Geary, Peter (17 May 1971). "The Sun never sets on the British Empire". gan.philliptsmall.me.uk. Archived from the original on 19 September 2013. Retrieved 2 April 2013.
- Davies, Laura (26 July 2015). "Maldives at Fifty: penning a chapter in history". Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office. Archived from the original on 25 April 2021. Retrieved 26 July 2015.
- Hadi, Ahmedulla Abdul (26 July 2019). "The independence gained by the unyielding determination of Nasir". Sun News. Archived from the original on 23 September 2023. Retrieved 26 July 2019.
- People's Majlis Archive
- Riyaz, Ahmed (11 November 2012). "ރާއްޖޭގެ ވެރިކަން ޖުމުހުރީ ވެރިކަމަކަށް ބަދަލުވުން" [Maldives Becomes a republic]. Utheemu (in Divehi). Archived from the original on 11 August 2014. Retrieved 11 November 2012.
- Walker, James (26 July 2023). "How Maldives gained independence from the British empire". The National. Archived from the original on 30 July 2023. Retrieved 26 July 2023.
- Kachroo-Levine, Maya (25 May 2021). "How the Maldives Transformed From a Fishing Archipelago to a Tropical Hot Spot in 50 Years". Travel + Leisure. Archived from the original on 26 May 2021. Retrieved 25 May 2021.
- "The Beginning of Maldives Tourism Industry – History of the First Resort, Kurumba Maldives". Maldives Travel. 27 September 2020. Archived from the original on 21 February 2024. Retrieved 27 September 2020.
- "Maldives - Population". Library of Congress Country Studies Archived 14 January 2021 at the Wayback Machine
- "MODERN HISTORY OF THE MALDIVES: BECOMING A REPUBLIC AND INDEPENDENCE". Facts and Details. Archived from the original on 16 April 2024. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- "Maldives". History's Greatest. 5 December 2014. Archived from the original on 16 April 2024. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
Economic decline followed the closure of the British airfield at Gan and the collapse of the market for dried fish, an important export. With support for his administration faltering, Nasir fled to Singapore in 1978, with millions of dollars from the treasury.
- ^ "Sinking island nation seeks new home". CNN. 11 November 2008. Archived from the original on 6 December 2008. Retrieved 12 November 2008.
- "Nov 3rd attack mastermind Sikka arrives in the Maldives after more than a decade". The Maldives Journal. 7 December 2022. Archived from the original on 8 December 2022. Retrieved 7 December 2022.
- ^ Banka, Neha (3 November 2022). "Operation Cactus: How India helped Maldives thwart coup bid backed by Lankan militants". The Indian Express. Kolkata. Archived from the original on 18 September 2022. Retrieved 3 November 2022.
- Maldives - Country Review Report on the implementation of the Brussels Programme of Action for LDCs (PDF) (Report). Ministry of Planning and National Development. January 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 September 2013 – via United Nations.
- Aldridge, Paul (24 March 2010). "Maldives Skyscraper - Floating States". eVolo. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 27 July 2011.
- "UNDP: Discussion Paper - Achieving Debt Sustainability and the MDGs in Small Island Developing States: The Case of the Maldives" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 20 December 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 January 2012.
- "Republic of Maldives - Tsunami: Impact and Recovery" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 March 2012. Retrieved 18 September 2015.
- ^ Brecehenmacher, Victor; Mendis, Nikhita (22 April 2015). "Autocracy and Back Again: The Ordeal of the Maldives". Brown Political Review. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- "The Quality of Political Appointees in the Nasheed Administration". Raajje News Blog. 7 June 2009. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 21 February 2012.
- "Maldives president quits after protests". Al Jazeera. 7 February 2012. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 6 February 2012.
- Mallawarachi, Bharatha (8 October 2012). "Mohamed Nasheed, Former Maldives President, Arrested after Failing to Appear in Court". The Huffington Post. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 10 March 2016.
- Naafiz, Ali (20 October 2015). "Maldives opposition seeks India's help in jailed leader's release". Haveeru Daily. Archived from the original on 21 October 2015. Retrieved 24 October 2015.
- Iyengar, Rishi (28 September 2015). "Maldives President Abdulla Yameen Escapes Unhurt After Explosion on His Boat". TIME. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- Muhsin, Mohamed Fathih Abdul (15 February 2021). "Was removed from office without being allowed a proper defense: Dr Jameel". The Times of Addu. Archived from the original on 9 May 2024. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- "Maldives declares 30-day emergency". BBC News. 4 November 2015. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- "Majlis passes declaration to remove VP from office". People's Majlis. 5 November 2015. Archived from the original on 14 July 2016.
- "Maldives revokes state of emergency amid global outcry and tourism worries". The Guardian. Malé, Maldives. Associated Press. 10 November 2015. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 10 November 2015.
- Haidar, Suhasini; Radhakrishnan, Hariprasad (3 August 2019). "Adeeb returns to Maldives, arrested with quiet help from India". The Hindu. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 3 August 2019.
- Zalif, Zunana (21 January 2021). "High Court upholds ex-president's five-year jail sentence". Raajje TV. Archived from the original on 22 January 2021. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- Junayd, Mohamed (30 November 2021). "Maldives' ex-president Yameen walks free after graft conviction overturned". Reuters. Archived from the original on 3 March 2022. Retrieved 5 March 2022.
- Junayd, Mohamed (1 October 2023). "Maldives opposition candidate Muizzu wins presidential vote". Reuters. Archived from the original on 10 November 2023. Retrieved 10 November 2023.
- "Mohamed Muizzu sworn in as Maldives president, says will remove 'foreign' troops". The Times of India. Press Trust of India. 18 November 2023. ISSN 0971-8257. Archived from the original on 24 November 2023. Retrieved 24 November 2023.
- Eguegu, Ovigwe (24 January 2024). "What the China-Maldives-India Triangle Tells Us About 21st Century Balancing". The Diplomat. Archived from the original on 22 March 2024. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- "Maldives High Court overturns ex-President Abdulla Yameen's prison sentence". Al Jazeera. 18 April 2024. Archived from the original on 2 May 2024. Retrieved 16 May 2024.
- "Entire Maldives cabinet resigns". Al Jazeera. 29 June 2010. Archived from the original on 11 January 2012. Retrieved 30 June 2010.
- Angelo, Megan (1 May 2009). "Honey, I Sunk the Maldives: Environmental changes could wipe out some of the world's most well-known travel destinations". Yahoo! Travel. Archived from the original on 17 July 2012.
- "Climate refugees in Pacific flee rising sea". The Washington Times. 19 April 2009. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 28 August 2015.
- ^ "Climate". Maldives Meteorological Service. Archived from the original on 13 December 2021. Retrieved 13 December 2021.
- "Maldives". Atlapedia. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 27 July 2011.
- "World Weather Information Service – Malé". WMO. Archived from the original on 26 December 2018. Retrieved 17 March 2016.
- "Malé Climate 1961–90". NOAA. Archived from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 17 March 2016.
- "Threat to islands". The Canberra Times. No. 19348, Vol. 63. Agence France-Presse. 26 September 1988. p. 6. Archived from the original on 15 November 2021. Retrieved 15 November 2021.
A gradual rise in average sea level is threatening to completely cover this Indian Ocean nation of 1196 small islands with- in the next 30 years, ac- cording to authorities. The Environmental Affairs Director, Mr Hussein Shihab, said an estimated rise of 20 to 30 centimetres in the next 20 to 40 years could be "catastrophic"
- "Where climate change threatens survival". The Sydney Morning Herald. 9 January 2012. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 18 September 2015.
- Stephen, Marcus (14 November 2011). "A sinking feeling: Why is the president of the tiny Pacific island nation of Nauru so concerned about climate change?". The New York Times Upfront. Archived from the original on 9 February 2015. Retrieved 9 February 2015.
Most Endangered Island nations at highest risk for flooding due to climate change 3 Maldives (Indian Ocean)
- Ramesh, Randeep (10 November 2008). "Paradise almost lost: Maldives seek to buy a new homeland". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 12 May 2010.
- "Climate Change Gridlock: Where Do We Go From Here? (Part 1)". Making Contact. National Radio Project. 28 June 2011. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 30 June 2011.
- ^ Catoe, Linda. "Endangered island nations call for global action on climate change". The Guilfordian. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 30 December 2018.
- "Exclusive - Mohamed Nasheed Extended Interview Pt. 2". The Daily Show. Comedy Central. 2 April 2012. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 14 February 2017.
- Lang, Olivia (17 October 2009). "Maldives leader in climate change stunt". BBC News. Archived from the original on 1 July 2010. Retrieved 19 October 2010.
- ^ Taylor, Michael (10 June 2020). "Small islands may not disappear under rising seas, researchers find". Thomson Reuters Foundation. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- Gayoom, Maumoon Abdul. "Address by his Excellency Mr. Maumoon Abdul Gayoom, President of the Republic of Maldives, at the nineteenth special session of the United Nations General Assembly for the purpose of an overall review and appraisal of the implementation of agenda 21 - 24 June 1997". Permanent Mission of the Republic of Maldives to the United Nations. Archived from the original on 13 June 2006. Retrieved 6 January 2006.
- "Physical impacts of climate change on coral reef islands". University of Plymouth. Archived from the original on 11 March 2023. Retrieved 11 March 2023.
- Evans, Judith (24 April 2015). "Maldives island swamped by rising tide of waste". Financial Times. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 14 February 2017.
- "Protected Areas - Maldives". Environmental Protection Agency. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 25 May 2013.
- "Fourth National Report to the Convention on Biological Diversity of Maldives" (PDF). Convention on Biological Diversity. Ministry of Housing and Environment. p. 7. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 November 2015. Retrieved 2 April 2013.
- ^ "Maldives Marine Life". Scuba Dive Maldives. Archived from the original on 22 December 2011. Retrieved 2 April 2013.
- "Sharks of the Maldives". The Maldives. Archived from the original on 10 January 2017. Retrieved 12 February 2017.
- "Regional Workshop on the Conservation and Sustainable Management of Coral Reefs". Food and Agriculture Organization. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 2 April 2013.
- ^ Wheatley, Alan (2 May 2004). "Maldives Nurses Its Coral Reefs Back to Life". Global Coral Reef Alliance. Archived from the original on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 2 April 2013.
- "Coral Bleaching Updates". MarineSavers. Marine Savers and Four Seasons Resorts Maldives (2012–2017). 31 July 2016. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 12 February 2017.
- Ducarme, Frédéric (2016). "Field Observations of Sea Cucumbers in Ari Atoll, and Comparison with Two Nearby Atolls in Maldives" (PDF). SPC Beche-de-mer Information Bulletin. 36. Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 31 March 2016.
- Ducarme, Frédéric (2016). Field observations of sea cucumbers in Ari Atoll, and comparison with two nearby atolls in Maldives (PDF) (Report). Beche-de-mer Information Bulletin. Vol. 36. South Pacific Commission. Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 October 2017. Retrieved 31 March 2016.
- Pisapia, C.; Burn, D.; Yoosuf, R.; Najeeb, A.; Anderson, K. D.; Pratchett, M. S. (2016). "Coral recovery in the central Maldives archipelago since the last major mass-bleaching, in 1998" (PDF). Scientific Reports. 6: 34720. Bibcode:2016NatSR...634720P. doi:10.1038/srep34720. PMC 5046149. PMID 27694823. Archived (PDF) from the original on 21 January 2022. Retrieved 3 October 2016.
- Hingun, Handuvaree (2015). Fifth National Report of Maldives to the Convention on Biological Diversity (PDF) (Report). Maldives: Ministry of Environment and Energy. p. 24. ISBN 978-99915-59-11-7. Archived (PDF) from the original on 6 December 2017. Retrieved 13 October 2018.
- "Discovering the Maldives Underwater Marine Life". My Maldives. 3 December 2023. Archived from the original on 25 February 2024. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- Howard, Jake (8 March 2016). "Crocs In Paradise! (aka The Maldives)". Stab. Archived from the original on 29 May 2016. Retrieved 8 March 2016.
- "Wildlife of Maldives". Maladweep. Archived from the original on 16 August 2022. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- Phillips, W.W.A. (1963). "The birds of the Maldive Islands, Indian Ocean". Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society. 60: 546–584.
- "President Dr Mohamed Muizzu". The President's Office. Archived from the original on 28 November 2023. Retrieved 17 November 2023.
- "Dr Mohamed Muizzu sworn in as the 8th President of the Maldives". The President's Office. Archived from the original on 15 December 2023. Retrieved 17 November 2023.
- "Maldives - History". Country Studies. Library of Congress. Archived from the original on 12 May 2024. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- "Pro-China party on course for landslide victory in Maldives election". Al Jazeera. 22 April 202. Archived from the original on 22 April 2024. Retrieved 18 April 2024.
- "Government of the Maldives: Branches, History, The President". Facts and Details. Archived from the original on 26 March 2024. Retrieved 1 February 2022.
- "Constitution of the Republic of Maldives 1998". AsianLII. 1998. Archived from the original on 24 August 2008.
- "Maldives crackdown an 'assault on democracy': UN rights chief". The New Indian Express. 8 February 2018. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 8 February 2018.
- "Maldives election: Early results show victory for president's party". BBC News. 6 April 2019. Archived from the original on 11 December 2020. Retrieved 25 February 2021.
- "Majlis 19: An overview in numbers". Avas. 11 April 2019. Archived from the original on 26 May 2019. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- "PM Modi conferred with Maldives' highest honour, Order of Nishanizzuddeen". narendramodi.in. 8 June 2019. Archived from the original on 11 July 2021. Retrieved 28 February 2022.
- Rasheed, Zaheena. "'Absolute power': After pro-China Maldives leader's big win, what's next?". Al Jazeera.
- "Maldives 2008 Constitution". constituteproject.org. 2008. Archived from the original on 23 January 2022. Retrieved 25 December 2021.
- "International Religious Freedom Report for 2017". United States Department of State. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 30 December 2018.
- Ran Hirschl (5 May 2011). Constitutional Theocracy. Harvard University Press. p. 34. ISBN 978-0-674-05937-5. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 30 December 2018.
- "Human Rights and Democracy". Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Maldives). Archived from the original on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 30 June 2010.
- Davis, Thomas W. D. (2011). Human Rights in Asia. Edward Elgar Publishing. p. 33. ISBN 978-1-84844-680-9. Archived from the original on 15 September 2015. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- "New penal code comes into effect". 16 July 2015. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 10 July 2020.
- "Maldives Penal Code - Law No. 9/2014" (PDF). University of Pennsylvania. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 10 July 2020.
- "State Sponsored Homophobia 2016: A world survey of sexual orientation laws: criminalisation, protection and recognition" (PDF). International Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Trans and Intersex Association. 17 May 2016. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 September 2017. Retrieved 20 June 2017.
- Bloom, Laura Begley (25 November 2019). "20 Most Dangerous Places For Gay Travelers (And The 5 Safest)". Forbes. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 19 November 2020.
- "From South Africa to the Maldives: Surprising holiday destinations for LGBT travellers". The Independent. 19 October 2016. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- "Secretary-General statement on Maldives decision to leave the Commonwealth". The Commonwealth. 13 October 2016. Archived from the original on 17 May 2020. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
- Maldives quits Commonwealth over alleged rights abuses Archived 13 October 2016 at the Wayback Machine, The Guardian, 13 October 2016
- "The President's Office". Archived from the original on 21 November 2018. Retrieved 26 November 2018.
- "Maldives rejoins Commonwealth after evidence of reforms". The Guardian. PA Media. 1 February 2020. Archived from the original on 18 April 2020. Retrieved 4 February 2020.
- Oltermann, Peter (3 March 2022). "Germany seizes Russian billionaire Alisher Usmanov's $600m superyacht - report". The Guardian. London. Archived from the original on 3 March 2022. Retrieved 3 March 2022.
- "The Government decides to impose a ban on Israeli passports". The President's Office. Archived from the original on 3 June 2024. Retrieved 2 June 2024.
- "Maldives bans Israeli passport holders over war on Gaza". Al Jazeera English. Archived from the original on 2 June 2024. Retrieved 2 June 2024.
- "Maldives to ban Israeli passport holders from entry in protest over Gaza war". The Guardian. Retrieved 3 June 2024.
- Saruna; President’s Office (2012). "National Security Policy 2012" (PDF). Digital Repository of Maldives National University. Government of the Republic of Maldives. p. 221. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 April 2024. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "Chapter XXVI: Disarmament – No. 9 Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons". United Nations Treaty Collection. United Nations. 7 July 2017. Archived from the original on 6 August 2019. Retrieved 18 October 2019.
- "Maldives: Freedom in the World". Freedom House. Archived from the original on 13 March 2024. Retrieved 19 May 2024.
- "Country Reports on Human Rights Practices for 2011: Maldives". United States Department of State. Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor. 2012. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 24 August 2012.
- "Atolls of Maldives". Statoids. Archived from the original on 2 January 2010. Retrieved 30 June 2010.
- ^ Divehiraajjege Jōgrafīge Vanavaru. Muhammadu Ibrahim Lutfee
- Lyon, James (October 2003). Maldives. Lonely Planet Publications Pty Ltd. p. 9. ISBN 978-1-74059-176-8. Archived from the original on 12 April 2016. Retrieved 9 November 2015.
- Hogendorn, Jan and Johnson Marion (1986). The Shell Money of the Slave Trade. African Studies Series 49, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge ISBN 0521541107.
- "Republic of Maldives Maldivian Labor Market: Spotlight on youth, tourism, and fisheries Analysis based on census 2014 data" (PDF). World Bank. 30 May 2017.
- Shakoor, Athif Ibrahim. "The tourism industry of the Maldives, - have we gone beyond 'regulatory capture'?" (PDF). The Maldives National Journal of Research. Saruna.mnu.edu.mv. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- "Discover the islands". islands.mv. Archived from the original on 2 July 2019. Retrieved 7 January 2020.
- "Inhabited islands". isles.gov.mv. The President's Office. Archived from the original on 10 June 2023. Retrieved 26 July 2023.
- "Coup? What coup? Tourists ignore Maldives turmoil". The Age. Melbourne. 13 February 2012. Archived from the original on 15 February 2012. Retrieved 26 February 2012.
- "Home". Ministry of Tourism. Archived from the original on 17 April 2009. Retrieved 3 April 2009.
- "1.7 million tourists visit the Maldives in 2019". Ministry of Tourism. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 9 January 2020.
- "ހަތުރުވެރިކަމުގެ ތަރައްޤީގެ 35 އަހަރު" [35 years of tourism] (PDF). Ministry of Tourism (in Divehi). Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 November 2009. Retrieved 2 April 2013.
- "Coral Stone Mosques of Maldives". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 26 December 2019.
- "Entry into Maldives". Maldives Immigration. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 9 February 2012.
- "Flights to Maldives". British Airways. Archived from the original on 20 October 2022. Retrieved 20 October 2022.
- "Census Population by Sex and Sex - Ratio, and Inter-Censal Variation of Population, 1911 - 2014" (PDF). National Bureau of Statistics (Maldives). Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 24 May 2020.
- ^ "Maldives Population Projections 2014–2054". statisticsmaldives.gov.mv. National Bureau of Statistics. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 24 May 2020.
- Jaleel, Jana (20 July 2023). "An Untold Story - The Lost People of Giraavaru". Maldives Voice. Archived from the original on 16 April 2024. Retrieved 20 July 2023.
- "Islands by Population Size and Percentage Share of Total Population". Maldives: Population and Housing Census 2006. Ministry of Planning and National Development. Archived from the original on 19 September 2013. Retrieved 8 February 2012.
- "Census Analysis 2006. Population Projection 2006 – 2050" (PDF). Ministry of Planning and National Development. p. 273. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 5 July 2014.
- May, John F.; Riyaza, Fathimath (July 2017). "Maldives' Population Dynamics". Population Reference Bureau. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 1 February 2019.
- "International Labour Day 2021". National Bureau of Statistics. Ministry of Housing, Land & Urban Development. 2 May 2021. Archived from the original on 2 May 2021. Retrieved 2 May 2021.
- "Anti-Human Trafficking Action Plan 2020–2022" (PDF). Government of the Maldives. Ministry of Defence. Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 18 May 2020.
- "Over 281,000 expats in the Maldives". Avas. 13 September 2021. Archived from the original on 13 September 2021. Retrieved 19 May 2024.
- "Conversion of the Maldives to Islam". Maldives Story. Archived from the original on 9 May 2003.
- Yoosuf, Muawwaz (28 February 2020). "Malé Friday Mosque". Coral Stone Mosques of Maldives. Retrieved 25 October 2024.
- Wilfred, Felix (2014). The Oxford Handbook of Christianity in Asia. Oxford University Press. p. 45. ISBN 9780199329069.
- ^ "2022 Report on International Religious Freedom: Maldives". United States Department of State. Office of International Religious Freedom. Archived from the original on 4 March 2024. Retrieved 18 February 2024.
- "National Profiles | World Religion". Association of Religion Data Archives. Archived from the original on 14 August 2023. Retrieved 1 September 2023.
- "Maldives Languages - Languages of Maldives - Language Spoken In Maldives". Maldives Tourism. Archived from the original on 11 November 2018. Retrieved 12 June 2017.
- Meierkord, Christiane (March 2018). "English in paradise: the Maldives: English is rapidly establishing itself as a second language in a society transforming from fishing to tourism and trade". English Today. 34 (1): 2–11. doi:10.1017/S0266078417000475. ISSN 0266-0784. S2CID 148650495. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 31 March 2019.
- ^ "Maldives". Human Rights Measurement Initiative. Archived from the original on 19 May 2024. Retrieved 19 May 2024.
- "Maldives - HRMI Rights Tracker". rightstracker.org. Archived from the original on 19 May 2022. Retrieved 25 March 2022.
- "Maldives". Commonwealth Health online. 2018. Archived from the original on 20 November 2018. Retrieved 20 November 2018.
- "At a Glance: Health and Nutrition in the Maldives". UNICEF. 2010. Archived from the original on 20 November 2018. Retrieved 20 November 2018.
- Bhuckory, Kamlesh (24 May 2021). "With Highest Covid Rate, Maldives Imposes 16-Hour Curfew". BloombergQuint. Archived from the original on 24 May 2021. Retrieved 24 May 2021.
- Rasheed, Aishath Hanaan Hussain (24 May 2021). "Maldives reports 61st Covid-19 death in ongoing month of May". Raajje TV. Archived from the original on 24 May 2021. Retrieved 19 May 2024.
- "Maldives". Elite Diving Agency. Archived from the original on 18 December 2013.
- "Manta Air begins its first scheduled seaplane service". Corporate Maldives. 18 November 2019. Archived from the original on 14 January 2021. Retrieved 14 December 2019.
- Green, Richard (2005). The Commonwealth Yearbook 2005. Nexus Strategic Partnerships. p. 209. ISBN 9780954962906.
- "Registered Higher Education Institute as of 19.05.2022" (PDF), Ministry of Higher Education, Labour and Skills Development, archived (PDF) from the original on 17 June 2022, retrieved 19 May 2022
- "History". Maldives National University. Archived from the original on 23 February 2024. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
1st September 1973 Allied Health Services Training Centre was established – Forerunner to the Faculty of Health Sciences established by the Ministry of Health
- "Faculty of Engineering, Science and Technology". Maldives National University. Archived from the original on 24 February 2024. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
The Vocational Training Center (VTC) was established on 14 October 1975 under the Department of Electricity to train a large number of workers required for the growing industrial and economic activities
- "Education Sector Analysis Maldives – 6.1 Quick Historical Development Of Higher Education" (PDF). Ministry of Education. Ministry of Education (Maldives). February 2019. Archived (PDF) from the original on 28 April 2021. Retrieved 1 February 2019.
The Vocational Training Center, the Institute for Teacher Education and the School of Hotel and Catering Services were also established prior to the amalgamation of such post- secondary institutions to form the Maldives College of Higher Education in 1998.
- "Profile & History". Islamic University of Maldives. Archived from the original on 19 May 2024. Retrieved 19 May 2024.
- "A new scholarship scheme called Merit Scholarship is being launched this year". Ministry of Higher Education, Labour and Skills Development. 16 May 2023. Archived from the original on 2 July 2023. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- Robinson, J. J. (2015). The Maldives: Islamic Republic, Tropical Autocracy. Hurst. ISBN 978-1849045896.
- Marcus, Anothony (2012). "Reconsidering Talaq" (PDF). Brandeis University Press. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 October 2017.
- "Public Service Media". SOE Gateway. Ministry of Finance. Retrieved 31 August 2024.
- "PSM News : Seven years of reliable reporting". PSM News. 3 May 2024. Archived from the original on 14 May 2024. Retrieved 19 May 2024.
- "2024 World Press Freedom Index". Reporters Without Borders. 2024. Archived from the original on 7 May 2022. Retrieved 12 May 2022.
- "Lost in translation: the story of Haveeru". Maldives Independent. 24 May 2016. Archived from the original on 16 October 2023. Retrieved 19 May 2024.
- "Constitution of the Republic of Maldives". Attorney General. p. 7. Archived from the original on 6 June 2011. Retrieved 16 October 2020.
- "Maldives Newspapers Online – List of Maldives newspapers, magazines, and news sites covering business, finance, sports, travel, weather, jobs, and entertainments". w3newspapers.com.
- "Thulusdhoo Island Surf Guide – Maldives Local Island Surfing!". Stoked For Travel. 15 September 2020. Archived from the original on 25 September 2020. Retrieved 15 September 2020.
- "SNORKELING IN THE MALDIVES". Snorkeling Report. Archived from the original on 1 March 2024. Retrieved 19 May 2024.
- "Future of Football: When will a country from South Asia emerge as a powerhouse in the global game?". Sky Sports. Archived from the original on 10 January 2024. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- "Maldives". Soccerway. Archived from the original on 26 March 2023. Retrieved 18 May 2024.
Further reading
- Divehiraajjege Jōgrafīge Vanavaru. Muhammadu Ibrahim Lutfee. G.Sōsanī. Malé 1999.
- H. C. P. Bell, The Maldive Islands, An account of the Physical Features, History, Inhabitants, Productions and Trade. Colombo 1883, ISBN 81-206-1222-1.
- H.C.P. Bell, The Maldive Islands; Monograph on the History, Archaeology and Epigraphy. Reprint Colombo 1940. Council for Linguistic and Historical Research. Malé 1989.
- H.C.P. Bell, Excerpta Maldiviana. Reprint Colombo 1922/35 edn. Asian Educational Services. New Delhi 1999.
- Divehi Tārīkhah Au Alikameh. Divehi Bahāi Tārikhah Khidmaiykurā Qaumī Markazu. Reprint 1958 edn. Malé, Maldives 1990.
- Christopher, William (1836–38). Transactions of the Bombay Geographical Society, Vol. I. Bombay.
- Lieut. I.A. Young & W. Christopher, Memoirs on the Inhabitants of the Maldive Islands.
- Geiger, Wilhelm. Maldivian Linguistic Studies. Reprint 1919 edn. Asian Educational Services. Delhi 1999.
- Hockly, T.W. The Two Thousand Isles. Reprint 1835 edn. Asian Educational Services. Delhi 2003.
- Hideyuki Takahashi, Maldivian National Security - And the Threats of Mercenaries, The Round Table (London), No. 351, July 1999, pp. 433–444.
- Malten, Thomas: Malediven und Lakkadiven. Materialien zur Bibliographie der Atolle im Indischen Ozean. Beiträge zur Südasien-Forschung Südasien-Institut Universität Heidelberg, Nr. 87. Franz Steiner Verlag. Wiesbaden, 1983.
- Vilgon, Lars: Maldive and Minicoy Islands Bibliography with the Laccadive Islands. Published by the author. Stockholm, 1994.
- Clarence Maloney, People of the Maldive Islands, Orient Black Swan, 2013
- Xavier Romero-Frias, The Maldive Islanders: a study of the popular culture of an ancient ocean kingdom, NEI, 1999
- Xavier Romero-Frias, Folk Tales of the Maldives, Nordic Institute of Asian Studies, 2012
- Djan Sauerborn, The Perils of Rising Fundamentalism in the Maldives Archived 14 January 2021 at the Wayback Machine, International Relations and Security Network (ISN), Zürich, September 2013
- Djan Sauerborn, Failing to Transition: Democratization under Stress in the Maldives, South Asia Democratic Forum (SADF), February 2015
External links
- Official tourist guide to Maldives Archived 16 January 2020 at the Wayback Machine
- President's Office Archived 30 May 2023 at the Wayback Machine
- Official website of the Government of Maldives Archived 12 June 2020 at the Wayback Machine
- Maldives Archived 29 July 2022 at the Wayback Machine. The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
- Maldives from UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Maldives Archived 29 July 2018 at the Wayback Machine from the BBC News
- Maldives Archived 2 December 2022 at the Wayback Machine Encyclopædia Britannica entry
 Wikimedia Atlas of Maldives
Wikimedia Atlas of Maldives Geographic data related to Maldives at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Maldives at OpenStreetMap- Key Development Forecasts for the Maldives Archived 6 July 2012 at the Wayback Machine from International Futures
- Constitution of the Republic of Maldives Archived 6 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine
| Maldives articles | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| History |  | ||
| Geography | |||
| Politics | |||
| Economy | |||
| Society | |||
4°11′N 73°31′E / 4.18°N 73.51°E / 4.18; 73.51
Categories:- 1965 establishments in Asia
- Archipelagoes of the Indian Ocean
- Countries in Asia
- Former kingdoms
- Former least developed countries
- Former protectorates
- Former sultanates
- Island countries of the Indian Ocean
- Island countries
- Landforms of South Asia
- Maldives
- Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations
- Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
- Member states of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
- Member states of the United Nations
- Republics in the Commonwealth of Nations
- Republics
- Small Island Developing States
- South Asian countries
- States and territories established in 1965
- Western Indo-Pacific