| Revision as of 22:06, 6 June 2015 editAubmn (talk | contribs)1,347 edits trim article almost reaching 11,000 words← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 10:53, 25 December 2024 edit undo103.84.176.43 (talk) Louis XVI changed to Louis Auguste because he was Dauphin of France when he married Marie AntoinetteTags: Visual edit Mobile edit Mobile web edit | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Queen of France from 1774 to 1792}} | |||
| {{Other uses|Marie Antoinette (disambiguation)}} | {{Other uses|Marie Antoinette (disambiguation)}} | ||
| {{pp-move}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=August 2012}} | |||
| {{Use British English|date=April 2022}} | |||
| {{Infobox royalty | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=October 2021}} | |||
| |consort=yes | |||
| {{Infobox royalty | |||
| | name = Marie Antoinette of Austria | |||
| | image = Marie-Antoinette, 1775 - Musée Antoine Lécuyer.jpg | |||
| | title = Queen consort of France and Navarre<br/>Queen consort of the French | |||
| | caption = Portrait, {{circa|1775}} | |||
| | image = Marie167.jpg | |||
| | succession = ] | |||
| | caption = ''Marie Antoinette with the Rose''<br/>Portrait by | |||
| | reign = 10 May 1774 – 21 September 1792 | |||
| ], 1783. | |||
| | birth_name = Archduchess Maria Antonia of Austria | |||
| | succession = ] | |||
| | birth_date = {{birth date|df=yes|1755|11|2}} | |||
| | reign = 10 May 1774 – 21 September 1792 | |||
| | birth_place = ], Vienna, Archduchy of Austria, Holy Roman Empire | |||
| | spouse = ] | |||
| | death_date = {{death date and age|df=yes|1793|10|16|1755|11|2}} | |||
| | issue = ] <br /> ] <br /> ] <br /> ] | |||
| | death_place = ], Paris, France | |||
| | house = ]<br/>] | |||
| {{Infobox person | embed = yes | |||
| | father = ] | |||
| | death_cause = ]}} | |||
| | mother = ] | |||
| | burial_date = 21 January 1815 | |||
| | birth_date = {{Birth date|df=yes|1755|11|2}} | |||
| | burial_place = ] | |||
| | birth_place = ], ], ], ] | |||
| | consort = yes | |||
| | death_date = 16 October 1793 (aged 37) | |||
| | spouse = {{Marriage|]|19 April 1770|21 January 1793|end=d}} | |||
| | death_place = ], ], ] | |||
| | issue = {{Indented plainlist| | |||
| | place of burial = ], France | |||
| * ] | |||
| | religion = ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| | date of burial = 21 January 1815 | |||
| * ] | |||
| | full name = Maria Antonia Josepha Johanna | |||
| * Sophie | |||
| | signature = Marie-AntoinetteSignature.png | |||
| }} | |||
| | full name = {{Unbulleted list|{{langx|de|link=no|Maria Antonia Josefa Johanna}}|{{langx|fr|link=no|Marie Antoinette Josèphe Jeanne}}}} | |||
| | house = ] | |||
| | father = ] | |||
| | mother = ] | |||
| | signature = Marie-AntoinetteSignature.png | |||
| | module = {{Infobox noble | child = yes | |||
| | CoA = ]}} | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Marie Antoinette |
'''Marie Antoinette''' ({{IPAc-en|ˌ|æ|n|t|w|ə|ˈ|n|ɛ|t|,_|ˌ|ɒ̃|t|-}};<ref>{{Citation |last=Jones |first=Daniel |title=English Pronouncing Dictionary |year=2003 |editor=Peter Roach |place=Cambridge |publisher=Cambridge University Press |isbn=978-3-12-539683-8 |author-link=Daniel Jones (phonetician) |editor2=James Hartmann |editor3=Jane Setter |orig-year=1917}}.</ref> {{IPA|fr|maʁi ɑ̃twanɛt|lang|LL-Q150 (fra)-Exilexi-Marie-Antoinette.wav}}; Maria Antonia Josefa Johanna; 2 November 1755 – 16 October 1793) was the last ] prior to the ] and the establishment of the ]. Marie Antoinette was the wife of ]. Born '''Archduchess Maria Antonia of Austria''', she was the penultimate child and youngest daughter of ] and ]. She married Louis Auguste, ], in May 1770 at the age of 14. She then became the ]. On 10 May 1774, her husband ascended the throne as Louis XVI and she became queen. | ||
| As queen, Marie Antoinette became increasingly a target of criticism by opponents of the domestic and foreign policies of Louis XVI, and those opposed to the monarchy in general. The French '']'' accused her of being profligate,<ref>Royal household spending in 1788 was 13% of total state expenses(excluding interest on debts). Finances of Louis XVI (1788) | Nicholas E. Bomba https://blogs.nvcc.edu {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110420130803/http://blogs.nvcc.edu/ |date=20 April 2011 }} › nbomba › files › 2016/10, https://books.google.com/books?id=ixJWG9q0Eo4C</ref> promiscuous, having illegitimate children, and harboring sympathies for France's perceived enemies, including her native ]. She was falsely accused of defrauding the Crown's jewelers in the ], but the accusations damaged her reputation further. During the French Revolution, she became known as ''Madame Déficit'' because the country's ] was blamed on her lavish spending and her opposition to social and financial reforms proposed by ] and ]. | |||
| In April 1770, upon her marriage to Louis-Auguste, ], she became Dauphine of France. She assumed the title ] when her husband ascended the throne as ] upon the death of his grandfather ] on 10 May 1774. After seven years of marriage, she gave birth to a daughter, ], the first of her four children. | |||
| Several events were linked to Marie Antoinette during the Revolution after the government placed the royal family under house arrest in the ] in October 1789. The June 1791 attempted ] and her role in the ] were immensely damaging to her image among French citizens. On 10 August 1792, the attack on the Tuileries forced the royal family to take refuge at the ], and they were imprisoned in the ] on 13 August 1792. On 21 September 1792, France was declared a republic and ]. ] by ] on 21 January 1793. Marie Antoinette's trial began on 14 October 1793; two days later, she was convicted by the ] of high treason and executed by beheading by guillotine on 16 October 1793 at the ] during the French Revolution. | |||
| Within the kingdom of France, a growing number of the population eventually came to dislike her, accusing ''L'Autrichienne'', "the Austrian woman", (a nickname given her upon her arrival to France by Louis XV's daughters, ]), of being ], promiscuous,<ref>C. f. "It is both impolitic and immoral for palaces to belong to a Queen of France" (part of a speech by a councilor in the ''Parlement de Paris'', early 1785, after Louis XVI bought the ] for the personal use of Marie Antoinette), quoted in {{harvnb|Castelot|1957|p=233}}</ref> and of harbouring sympathies for France's enemies, particularly Austria, her country of origin.<ref>C.f. the following quote: "She (Marie Antoinette) thus obtained promises from Louis XVI which were in contradiction with the Council's (of Louis XVI's ministers) decisions", quoted in {{harvnb|Castelot|1957|p=186}}</ref> The ] damaged her reputation further. She later became known as ] because France's financial crisis was blamed on her lavish spending and her opposition to the social and financial reforms of ] and ]. | |||
| ==Early life (1755–1770)== | |||
| During the ], after the government had placed the royal family under house arrest in the ] in October 1789, several events linked to Marie Antoinette, in particular the June 1791 ], and her role in the ], had disastrous effects on French popular opinion: over a year later, on 10 August 1792, the attack on the Tuileries forced the royal family to take refuge at the Assembly. On 13 August, the family was imprisoned in the ]. On 21 September 1792, Louis XVI was deposed and the ]. After a two-day trial begun on 14 October 1793, Marie Antoinette was convicted by the ] of ] to the principles of the revolution, and executed by ] on ''Place de la Révolution'' on 16 October 1793. | |||
| ]]] | |||
| Marie Antoinette, full name Maria Antonia Josepha Johanna, was born on 2 November 1755 at the ] Palace in ], Archduchy of Austria, at 20:30.<ref>{{Cite web |title=The Birth of Marie Antoinette {{!}} History Today |url=https://www.historytoday.com/archive/birth-marie-antoinette |access-date=2022-11-20 |website=historytoday.com}}</ref> She was the youngest daughter and 15th child | |||
| ==Early life== | |||
| of Empress ], ruler of the ], and her husband ].<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2002|p=5}}</ref> Maria Theresa gave birth to all of her previous children without any problems. During the birth of her last daughter, serious complications arose, and doctors even feared for the life of the mother. Her godparents were ] and ], King and Queen of Portugal; Archduke ] and Archduchess ] acted as proxies for their newborn sister.<ref name="Fraser 2002 5–6">{{Harvnb|Fraser|2002|pp=5–6}}</ref><ref name="liaisons">{{cite book|first=Michel|last=de Decker|title=Marie-Antoinette, les dangereuses liaisons de la reine|publisher=Belfond|location=Paris, France|date=2005|isbn=978-2714441416|pages=12–20}}</ref> | |||
| ], ca. 1767-1768.]] | |||
| ], by ] (1768).]] | |||
| Maria Antonia was born on ], a ] day of mourning, and during her childhood her birthday was instead celebrated the day before, on ], due to the connotations of the date. Shortly after her birth she was placed under the care of the governess of the imperial children, Countess von Brandeis.<ref name="d'Armaillé">{{cite book|first=Marie Célestine Amélie|last=de Ségur d'Armaillé |author-link=Marie Célestine Amélie d'Armaillé |title=Marie-Thérèse et Marie-Antoinette|publisher=]|date=1870|location=Paris, France|pages=34, 47}}</ref> Maria Antonia was raised together with her sister, ], who was three years older, and with whom she had a lifelong close relationship.<ref>{{Harvnb|Lever|2006|p=10}}</ref> Maria Antonia had a difficult but ultimately loving relationship with her mother,<ref name="Fraser 2001 166–170">{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=22–23, 166–70}}</ref> who referred to her as "the little Madame Antoine". | |||
| Maria Antonia was born on 2 November 1755, in ] as the youngest daughter of ] and ].<ref name="Lever2006p1" /><ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2002|p=5}}</ref> Her godparents were ] and ], King and Queen of Portugal; Archduke ] and Archduchess ] acted as proxies for their newborn sister.<ref name="Fraser 2002 5–6">{{Harvnb|Fraser|2002|pp=5–6}}</ref><ref name="Fraser 2002 5–6"/><ref>Michel de Decker: ''Marie-Antoinette, les dangereuses liaisons de la reine'', France Loisirs, 2005, p. 12.</ref> | |||
| Maria Antonia spent her formative years between the Hofburg Palace and ], the imperial summer residence in Vienna,<ref name="liaisons" /> where on 13 October 1762, when she was seven, she met ], two months her junior and a child prodigy.<ref>{{cite book|first=Philippe|last=Delorme|author-link=Philippe Delorme|title=Marie-Antoinette. Épouse de Louis XVI, mère de Louis XVII|publisher=Pygmalion Éditions|date=1999|page=13}}</ref><ref name="liaisons" /><ref name="d'Armaillé" /><ref>{{cite book|first=Évelyne|last=Lever|author-link=Évelyne Lever|title='C'état Marie-Antoinette|publisher=]|location=Paris, France|date=2006|page=14|ref=none}}</ref> Despite the private tutoring she received, the results of her schooling were less than satisfactory.<ref name="Cronin 1989 45">{{Harvnb|Cronin|1989|p=45}}</ref> At the age of 10 she could not write correctly in German or in any language commonly used at court, such as French or Italian,<ref name="liaisons" /> and conversations with her were stilted.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2002|pp=32–33}}</ref><ref name="liaisons" /> Under the teaching of ], Maria Antonia developed into a good musician. She learned to play the ],<ref name="Cronin 1989 45" /> the ] and the ]. She sang during the family's evening gatherings, as she was known to have had a beautiful voice.<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1989|p=46}}</ref> She also excelled at dancing, had "exquisite" poise, and loved dolls.<ref name="Weber2007">{{harvnb|Weber|2007|pp=13–14}}</ref> | |||
| She was raised jointly with her her three-year older sister ], with whom Maria Antonia had a lifelong close relationship.<ref>{{Harvnb|Lever|2006|p=10}}</ref> As to her relationship with her mother, it was difficult but both the empress and her daughter loved each other; Maria Theresa raised her with the firm intention of her becoming a Queen.<ref name="Fraser 2001 166–170">{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=22–23,166–170}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| On 13 October 1762 she meet ], then a child prodigy;<ref>]: ''Marie-Antoinette. Épouse de Louis XVI, mère de Louis XVII'', Pygmalion Éditions, 1999, p. 13.</ref>.<ref>Michel de Decker: ''Marie-Antoinette, les dangereuses liaisons de la reine'', France Loisirs, 2005, p. 15.</ref><ref>Marie Célestine Amélie de Ségur d'Armaillé: ''Marie-Thérèse et Marie-Antoinette'', Didier, 1870, p. 34.</ref><ref>]: ''C'était Marie-Antoinette'', Fayard, 2006, p. 14.</ref> | |||
| ] c.1767-1768]] | |||
| In spite of the private tutoring she received, results of her schooling were less than satisfactory.<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1989|p=45}}</ref> At the age of ten, she could not write correctly in German or in any language commonly used at court, such as French and Italian.<ref>France Loisirs, Michel de Decker, 2005, p.16</ref> Conversations with her were stilted.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2002|pp=32–33}}</ref><ref>France Loisirs, Michel de Decker, 2005, p.17</ref>. | |||
| The death of her older sister ] from ] during the epidemic in Vienna in October 1767 made an everlasting impression on the young Maria Antonia.{{Sfn|Fraser|2002|p=28}} Maria Antonia, in her later life, recalled the ailing Maria Josepha taking her in her arms. She told her that she would not be traveling to Naples to marry King ], to whom she was betrothed, but for the ].{{Sfn|Fraser|2002|p=28}} | |||
| Later in 1768, Mathieu-Jacques de Vermond was dispatched by ] to tutor Marie Antoinette as she became the future wife to Louis XVI. Serving as an educator, Abbé de Vermond found her to be unsatisfactorily educated and lacking in, at the age of 13, important writing skills. Nonetheless, he also complimented her, stating "her character, her heart, are excellent". He found her "more intelligent than has been generally supposed," but since "she is rather lazy and extremely frivolous, she is hard to teach".<ref name="Marie Antoinette">{{cite web|url=https://www.smithsonianmag.com/history/marie-antoinette-134629573/|title=Marie Antoinette |date=November 2006|publisher=Smithsonian Magazine |first1= Richard |last1=Covington |url-status=live |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20240124074106/https://www.smithsonianmag.com/history/marie-antoinette-134629573/ |archive-date= Jan 24, 2024 }}</ref> | |||
| However, Maria Antonia was a good musician. She learned to play the ],<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1989|p=45}}</ref> the ] and the ]. During the family's gatherings in the evenings, she would sing, as she had a beautiful voice.<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1989|p=46}}</ref> She also excelled at dancing,<ref name="Weber2007">{{harvnb|Weber|2007}}{{Page needed|date=April 2011}}</ref> had an "exquisite" poise,<ref name="Weber2007" /> and loved dolls.<ref name="Weber2007" /><ref name="Weber2007" /> | |||
| Under the recommendation of ], a strong supporter of her prospective marriage, Maria Antonia also received a makeover to bring her more in line with the fashion of French royalty. This included the straightening of her teeth by a French dentist, the diversification of her wardrobe, and hairstyles reminiscent of ].<ref>{{harvnb|Weber|2007|pp=15–16}}</ref> She was also instructed by ], who taught her to walk in the gliding fashion characteristic of the court of Versailles.<ref>{{harvnb|Erickson|1991|pp=40–41}}</ref> | |||
| ==Marriage to Louis: 1770–1793== | |||
| ] (1769).]] | |||
| On 17 April 1770 Maria Antonia formally renounced to her Habsburg rights and two days later, on 19 April, she was ] to the Dauphin of France at the ] in ] with her brother ] representing the groom in the ceremony.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=51–53}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Pierre Nolhac|La Dauphine Marie Antoinette,1929|pp=46–48|}}</ref><ref>Michel de Decker: ''Marie-Antoinette, les dangereuses liaisons de la reine'', France Loisirs, 2005, p. 21.</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| On 7 May 1770, on the ''Île aux Épis'', an island on the ] between ] and ], Marie Antoinette was officially handed over to ], her lady in waiting until 1775, in charge of the proper court ] Marie-Antoinette was to follow.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=58–62}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Edmond and Jules de Goncourt|Histoire de Marie Antoinette preface Robert Kopp, 1990|pp=30–36}}</ref> On 14 May, at the edge of the ], she met king Louis XV, her husband the Dauphin, the king's daughters, ''Mesdames de France'', ], ], ], the following day, her brothers-in-law, ]; and ], at the '']'',<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=64–69}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Nolhac|1929|pp=50–55}}</ref> and on 16 May, her husband's younger sisters, ] and ], at Versailles. | |||
| ==Dauphine of France (1770–1774)== | |||
| The ceremonial wedding took place on 16 May 1770, in the ], and, after the festivities, the day ended with the ritual bedding.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=70–71}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Nolhac|1929|pp=55–61}}</ref> The lack of consummation of the marriage plagued the reputation of both Louis-Auguste and Marie Antoinette for the next seven years.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=157}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Alfred et Geffroy D'Arneth| Correspondance Secrete entre Marie-Therese et le Comte de Mercy-Argenteau,vol 3|1874|pp=80–90,110–115}}</ref> | |||
| ], which was sent to the ] in May 1769{{Sfn|Fraser|2001|p=37}}]] | |||
| ] by ] and sent to her mother, Empress Maria Theresa, in Austria]] | |||
| Following the ] and the ] of 1756, Empress Maria Theresa decided to end hostilities with her longtime enemy, King Louis XV of France. Their common desire to destroy the ambitions of ] and ], and to secure a definitive peace between their respective countries led them to seal their alliance with a marriage: on 7 February 1770, Louis XV formally requested the hand of Maria Antonia for his eldest surviving grandson and heir, ], ] and ].<ref name="liaisons"/> | |||
| Maria Antonia formally renounced her rights to ] domains, and on 19 April 1770 she was ] with Louis Auguste at the ], with her brother Archduke ] standing in for the Dauphin.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=51–53}}</ref><ref>{{citation |first=Pierre |last=Nolhac |title=La Dauphine Marie Antoinette |date=1929 |pages=46–48}}</ref><ref name="liaisons" /> On 14 May 1770 she met her husband at the edge of the ]. Upon her arrival in France, she adopted the French version of her name: Marie Antoinette. A further ceremonial wedding took place on 16 May 1770 in the ] and, after the festivities, the day ended with the ].<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=70–71}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Nolhac|1929|pp=55–61}}</ref> The couple's longtime failure to ] the marriage plagued the reputations of the royal couple for the next seven years.{{sfnm|Fraser|2001|1p=157|2a1=d'Arneth|2a2=Geffroy|2y=1874|2pp=80–90, 110–115}} | |||
| The initial reaction to the marriage between Marie Antoinette and Louis-Auguste was mixed. On the one hand, the Dauphine herself was popular among the people. Her first official appearance in Paris on 8 June 1773 was a resounding success. She and the Dauphin had been acclaimed throughout the day with climax taking place at the ] before their return to Versailles. With her fair skin, straw-blond hair, blue eyes, beautiful smile and majestic figure, people could not help but be charmed by the personality and beauty of the not yet 18-year old princess. On the other hand, those opposed to the alliance with Austria, and others on personal grounds, such as the ], had a tenuous relationship with the Dauphine.<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1974|pp=61–63}}</ref> | |||
| The initial reaction to the marriage between Marie Antoinette and Louis XVI was mixed. On the one hand, the Dauphine was beautiful, personable and well-liked by the common people. Her first official appearance in Paris on 8 June 1773 was a resounding success. On the other hand, those opposed to the alliance with Austria had a difficult relationship with Marie Antoinette, as did others who disliked her for more personal or petty reasons.<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1974|pp=61–63}}</ref> | |||
| ==Relationship of the Dauphine with Mme du Barry== | |||
| ], Vienna.]] | |||
| Her relationship with Mme du Barry was politically important to improve, at least on the surface, because Mme du Barry was Louis XV's mistress, with considerable political influence over the king. In fact, the favorite had been instrumental in ousting the ], who had helped orchestrate the Franco-Austrian alliance and Marie Antoinette's marriage.<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1974|p=61}}</ref> After months of continued pressure from her mother and the Austrian minister, the ], who was sending Maria-Theresa secret reports on Marie-Antoinette's behavior,<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=80–81}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|ALfred and Geffroy d'Arneth|1874|pp=65–75}}</ref> the Dauphine grudgingly agreed to speak to Mme du Barry on New Year's Day 1772 in order to stop any French protest about the partition of Poland. Although the limit of the conversation was Marie Antoinette's banal comment to the royal mistress: "There are a lot of people at Versailles today", Mme du Barry was satisfied by her victory, and the crisis, for the most part, dissipated.<ref>{{Harvnb|Lever|2006}}</ref> Afterwards, Marie Antoinette never addressed a word to the ''comtesse''. Mme Du Barry, who dominated court life, had much influence on the king who, in spite of Marie-Antoinette's strong objection, exiled in 1770 one of her ladies-in-waiting, the ''duchesse de Gramont'', sister of Choiseul. Mercy the Austrian ambassador and the dauphin occasionally visited Mme du Barry in order to please the king. In 1772, the Dauphine, whose influence on the king was non-existent, could not make her planned entrance in Paris because of a conflict of ''étiquette'' between Mesdames aunts and the ''comtesse de Noailles''.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=104}}</ref> Although she, the Dauphin and his brothers had been allowed to attend incognito the previous carnival ball at the Opera, it was only after their official entrance in the capital on 8 June 1773 that the young couple had more freedom to visit Paris.<ref>Lever, Evelyne, ''Marie-Antoinette'', Fayard, Paris, 1991, p. 95.</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Castelot|1957|pp=70–85,100–105}}</ref> | |||
| ] (1769).]] | |||
| ] proved a troublesome foe to the new dauphine. She was Louis XV's mistress and had considerable political influence over him. In 1770 she was instrumental in ousting ], who had helped orchestrate the ] and Marie Antoinette's marriage,<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1974|p=61}}</ref> and in exiling his sister, the ], one of Marie Antoinette's ladies-in-waiting. Marie Antoinette was persuaded by her husband's aunts to refuse to acknowledge du Barry, which some saw as a political blunder that jeopardized Austria's interests at the French court. Marie Antoinette's mother and the Austrian ambassador to France, ], who sent the Empress secret reports on Marie Antoinette's behaviour, pressured Marie Antoinette to speak to Madame du Barry, which she grudgingly agreed to do on New Year's Day 1772.{{sfnm|Fraser|2001|1pp=80–81|2a1=d'Arneth|2a2=Geffroy|2y=1874|2pp=65–75}} She merely commented to her, "There are a lot of people at Versailles today", but it was enough for Madame du Barry, who was satisfied with this recognition, and the crisis passed.<ref>{{Harvnb|Lever|2006|p=38}}</ref> | |||
| On 10 May 1774, Louis XV died. On May 12, by '']'', the new king, Louis XVI, "under the influence of his pious aunts", and to the satisfaction of Marie-Antoinette who get her revenge on the favorite.<ref>Fraser, ''Marie Antoinette'', 2001, p. 124.</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Jackes Levron|Madame du Barry|1973|pp=75–85}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Evelyne Lever|Marie Antoinette|1991|pp=124}}</ref> exiled Mme du Barry at the ''abbaye de Pont-aux-Dames'', in ].,<ref name="Goncourt 1880, pp. 195-196">Goncourt, Edmond de, ''La Du Barry'', Ed. G. Charpentier, Paris, 1880, pp. 195-196</ref><ref>Lever, Evelyne, ''Louis XV'', Fayard, Paris, 1985, p. 96</ref> On 14 May, Marie-Antoinette wrote to her mother: "The public expected lots of changes at the moment;: the king simply sent the creature to the convent and chased away from the court all that bear this name of scandal. (In a letter to Mercy dated 18 May, Marie-Thérèse mentions Marie-Antoinette's letter to her complaining of her vehemence in treating Mme Du Barry whom the empress describes as a "poor creature": "she wrote to me about it with vehemence, treating her of creature...")<ref name="Goncourt 1880, pp. 195-196"/><ref>''Correspondance secrète entre Marie-Thérèse et le cte de Mercy-Argenteau : avec les lettres de Marie-Thérèse et de Marie-Antoinette.'' T. 2 / publiée avec une introduction et des notes par M. le chevalier Alfred d'Arneth,... et M. A. Geffroy,..., pp. 139, 149, 150-151. http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k200372g/f155.image</ref><ref>Fraser, Antonia (2002). Marie Antoinette: The Journey (2nd ed.), p. 124</ref><ref>Lever, Evelyne, ''Louis XVI'', Fayard, Paris, 1985, p. 96</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Correspondance de Marie Antoinette(1770-1793)|Evelyne Lever(1770-1793),2005|pp=173}}</ref> In April 1775, Mme du Barry was allowed to leave ''Pont-aux-Dames'' and to reside in her newly-acquired house at ], but with the interdiction to return to the court and to visit Paris. In October 1776, thanks to the intervention of Maurepas, she was allowed to return to her estate in ] and to visit Paris, but the court remained forbidden to her. Marie Antoinette and the Empress did not approve of the visit made by Joseph to her in Louveciennes in 1777. | |||
| Two days after the death of Louis XV in 1774, Louis XVI exiled du Barry to the ] in ], pleasing both his wife and aunts.<ref>Fraser, ''Marie Antoinette'', 2001, p. 124.</ref><ref>{{cite book |first=Jacques |last=Levron |title=Madame du Barry |date=1973 |pages=75–85}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Lever|1991|p=124}}</ref><ref name="Goncourt 1880, pp. 195–196">{{cite book|first=Edmond de|last=Goncourt|title=La Du Barry|publisher=G. Charpentier|location=Paris, France|date=1880|pages=195–96}}</ref><ref>Lever, Evelyne, ''Louis XV'', Fayard, Paris, 1985, p. 96</ref> Two and a half years later, at the end of October 1776, Madame du Barry's exile ended and she was allowed to return to her beloved château at ], but she was never permitted to return to Versailles.<ref>{{cite book|first=Charles|last=Vatel|title=Histoire de Madame du Barry: d'après ses papiers personnels et les documents d'archives|publisher=Hachette Livre|location=Paris, France|date=1883|isbn=978-2013020077|page=410}}</ref> | |||
| ==Queenship: 1774–1792== | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ==Queen of France and Navarre (1774–1792)== | |||
| ===1774–1778: Early years=== | |||
| ] | |||
| On 11 June 1775, Louis was crowned king Louis XVI of France at the cathedral of ]. Following the custom, Marie Antoinette was not crowned alongside him.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=132–137}}</ref> Had she been crowned Queen of France, the ceremony would have taken place at the ]. | |||
| ===Early years (1774–1778)=== | |||
| At the outset, the new queen had limited political influence with her husband. Louis blocked several of her candidates, including ],<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=136–137}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Arneth and Geffroy ii|1874|pp475-480}}</ref> from taking important positions, with the support of his two most important ministers, Chief Minister ] and Foreign Minister ]. However, the queen played a decisive role in the disgrace and exile of the most powerful of Louis XV ministers, the ].<ref>Castelot, André, ''Marie-Antoinette'', Librairie académique Perrin, Paris, 1962, pp. 107-108</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=124–127}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Lever|Marie Antoinette 1991|pp=125}}</ref> | |||
| On 10 May 1774, upon the death of ], the Dauphin ascended the throne as King Louis XVI of ] and ] with Marie Antoinette as his ]. At the outset, the new queen had limited political influence with her husband, who, with the support of his two most important ministers, Chief Minister ] and Foreign Minister ], blocked several of her candidates from assuming important positions, including Choiseul.{{sfnm|Fraser|2001|1pp=136–37|2a1=d'Arneth|2a2=Geffroy|2y=1874|2pp=475–480}} The queen did play a decisive role in the disgrace and exile of the most powerful of Louis XV's ministers, the ].{{sfnm|Castelot|1962|1pp=107–108|Fraser|2001|2pp=124–27|Lever|1991|3p=125}} | |||
| On 24 May 1774, two weeks after the death of Louis XV, the king gave his wife the ], a small château on the grounds of Versailles that had been built by Louis XV for his mistress, ]. Louis XVI allowed Marie Antoinette to renovate it to suit her own tastes; soon rumours circulated that she had plastered the walls with gold and diamonds.<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1974|p=215}}</ref> | |||
| ] visited Marie Antoinette and Louis XVI on 7 February 1775 at the ].]] | |||
| ] by Jean-Baptiste André Gautier-Dagoty c.1775]] | |||
| Opening the door to more criticism in a time when the country was facing a grave financial problem, and the population suffering from difficult economical conditions and the ] where a lot of hungry people lost their lives, the queen plunged further into the costly diversions of buying her dresses from ] and gambling with the result that the image of the monarchy and specially Marie Antoinette was largely tarnished in the eyes of both the middle and lower classes. For formal occasions, she adopted hair styles, the '']'' and the ''panache'' (bundle of feathers); created by Rose Bertin making her a model to the other ladies to follow at least among the nobility in addition to being a launcher of fashions, and which, with the wearing of high-heels, added at least one foot to her height. She also began to befriend various male admirers, such as the ], the ], and the ].<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=140–145}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Arneth and Geffroy i|1874|pp=400–410}}</ref> | |||
| The Queen spent heavily on fashion, luxuries, and gambling, though the country was facing a grave financial crisis and the population was suffering. ] created dresses for her, and hairstyles such as '']s'', up to three feet (90 cm) high, and the '']—''a spray of feather plumes. She and her court also adopted the English fashion of dresses made of ], a material banned in France from 1686 until 1759 to protect local French woolen and silk industries, ] and ].<ref>{{cite book|first1=Michael|last1=Batterberry|first2=Ariane|last2=Ruskin Batterberry|title=Fashion, the mirror of history|publisher=Greenwich House|location=Greenwich, Connecticut|date=1977|isbn=978-0-517-38881-5|page=190}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=150–51}}</ref> As a result of all these fashion activities, Marie Antoinette presided over one of the most important and fashionable courts in history and she was dominant over all of the other ladies of the court; as for her bearing and appearance the queen was very majestic and charismatic in spite of the fact that she gained much weight over the years due to her many pregnancies. | |||
| By the time of the ] of 1775, a series of riots, due to the high price of flour and bread, had damaged her reputation among the general public. Eventually, Marie Antoinette's reputation was no better than that of the favourites of previous kings. Many French people were beginning to blame her for the degrading economic situation, suggesting the country's inability to pay off its debt was the result of her wasting the crown's money.<ref>{{harvnb|Erickson|1991|pp=163}}</ref> In her correspondence, Marie Antoinette's mother, Maria Theresa, expressed concern over her daughter's spending habits, citing the civil unrest it was beginning to cause.<ref>Thomas, Chantal. ''The Wicked Queen: The Origins of the Myth of Marie Antoinette''. Translated by Julie Rose. New York: Zone Books, 2001, p. 51.</ref> | |||
| Marie Antoinette formed deep friendships with various ladies at court. Most noted was the ], who, as the daughter-in-law of the ], was a cousin of the members of the royal family, and whom, on 19 September 1774, the new queen appointed as Superintendent of her Household,<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=129–131}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=131–132}}; {{harvnb|Bonnet|1981}}</ref> charge she gave later on to the ]. | |||
| As early as 1774, Marie Antoinette had begun to befriend some of her male admirers, such as the ], the ], and ],<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=140–45}}</ref>{{sfn|d'Arneth|Geffroy|1874|pp=400–410}} and also formed deep friendships with various ladies at court. Most noted was ], related to the royal family through her marriage into the ]. On 19 September 1774, she appointed her superintendent of her household,<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=129–31}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=131–32}}; {{harvnb|Bonnet|1981}}</ref> an appointment she soon transferred to her new favourite, the ]. | |||
| In 1774, she took under her patronage her former music teacher, the German composer of operas ], who remained in France until 1779.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=111–113}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Howard Patricia, Gluck|1995|pp=105–115,240–245}}</ref> | |||
| In 1774, she took under her patronage her former music teacher, the German opera composer ], who remained in France until 1779.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=111–13}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Howard |first1=Patricia |title=Gluck: An Eighteenth-century Portrait in Letters and Documents |date=1995 |publisher=Clarendon Press |isbn=978-0-19-816385-5 |pages=105–15, 240–45}}</ref> | |||
| She was given free rein to renovate the '']'', a gift to her by Louis XVI on 15 August 1774;<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1974|p=215}}</ref> The ''Petit Trianon'' became associated with Marie Antoinette's perceived extravagance. With the "]", Marie Antoinette and her court adopted the English dress of ], of ] or ].<ref>Fashion, the mirror of history, page 190, Michael Batterberry, Ariane Ruskin Batterberry, Greenwich House, 1977. ISBN 978-0-517-38881-5</ref> The tradition of costume at the court at Versailles was broken after more than ten years.<ref>20,000 years of fashion: the history of costume and personal adornment, page 350, François Boucher, Yvonne Deslandres, H.N. Abrams, 1987. ISBN 978-0-8109-1693-7</ref> Rumors circulated that she plastered the walls with gold and diamonds.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=150–151}}</ref> Her lady-in-waiting ] defended her reputation and simplicity.<ref>A History of the Gardens of Versailles, page 218, Michel Baridon, University of Pennsylvania Press, 2008. ISBN 978-0-8122-4078-8</ref> | |||
| === |
===Motherhood, changes at court and intervention in politics (1778–1781)=== | ||
| Amidst the atmosphere of a wave of '']'', the Holy Roman Emperor ] came to France incognito, using the name Comte de Falkenstein, for a six-week visit during which he toured Paris extensively and was a guest at Versailles. He met his sister and her husband on 18 April 1777 at the ], and spoke frankly to his brother-in-law, curious as to why the royal marriage had not been consummated, arriving at the conclusion that no obstacle to the couple's conjugal relations existed save the Queen's lack of interest and the King's unwillingness to exert himself.<ref>Lever, Evelyne, ''Louis XVI'', Fayard, Paris, 1985, pp. 289–91</ref> | |||
| ] showing her majestic presence, by ] (1778).]] | |||
| Amidst the atmosphere of a wave of ''libelles'', the Holy Roman ] came to France incognito and visited his sister and brother-in-law on 18 April 1777. During the subsequent six-week visit to Versailles, Joseph investigated why the royal marriage had not been consummated. He soon came to the conclusion that no obstacle to the couple's conjugal relations existed, save the queen's lack of interest and the king's unwillingness to exert himself in that arena. In a letter to his brother Leopold, Joseph graphically described them as "a couple of complete blunderers."<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1974|pp=158–159}}</ref> Due to Joseph's intervention, the marriage was finally consummated in August 1777.<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1974|p=159}}</ref> Eight months later, in April, it was suspected that the queen was pregnant with her first child, which was confirmed on 16 May 1778.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=160–161}}</ref> | |||
| In a letter to his brother ], Joseph II described them as "a couple of complete blunderers."<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1974|pp=158–59}}</ref> He disclosed to Leopold that the inexperienced—then still only 22-year-old—Louis XVI had confided in him the course of action he had been undertaking in their marital bed; saying Louis XVI "introduces the member," but then "stays there without moving for about two minutes," withdraws without having completed the act and "bids goodnight."{{sfn|Fraser|2002b|p=156}} | |||
| In the middle of the queen's pregnancy, two events occurred which had a profound impact on her later life: the return of the handsome Swede, ], to Versailles for two years, and her brother's claims on the throne of ].<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1974|pp=162–164}}</ref> Marie Antoinette pleaded with her husband for the French to help intercede on behalf of Austria. The ], signed on 13 May 1779, ended the brief conflict, with the queen imposing French mediation on the demand of her mother, and Austria's gaining a territory of at least 100,000 inhabitants - a strong retreat from the early French position which was hostile towards Austria with the impression, partially justified, that the queen sided with Austria against France .<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=164–168}}</ref> | |||
| Marie Antoinette's daughter, ], was born at Versailles on 19 December 1778.<ref name="Fraser 2001 166–170"/><ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1974|p=161}}</ref><ref>{{harvnb|Hibbert|2002|p=23}}</ref> The child's paternity was contested in the |
Suggestions that Louis suffered from ], which was relieved by ], have been discredited.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.historyofcircumcision.net/index.php?option=content&task=view&id=80|title=Circumcision and phimosis in eighteenth century France|website=History of Circumcision|access-date=16 December 2016}}</ref> Nevertheless, following Joseph's intervention, the marriage was finally consummated in August 1777.<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1974|p=159}}</ref> Eight months later, in April 1778, it was suspected that the queen was pregnant, which was officially announced on 16 May.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=160–61}}</ref> Marie Antoinette's daughter, ], ''Madame Royale'', was born at Versailles on 19 December 1778.<ref name="Fraser 2001 166–170"/><ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1974|p=161}}</ref><ref>{{harvnb|Hibbert|2002|p=23}}</ref> The child's paternity was contested in the ''libelles'', as were all her children's.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=169}}</ref><ref name=":0">{{Cite book |last=Fraser |first=Antonia |title=Marie Antoinette: The Journey |publisher=Phoenix |year=2006 |isbn=9780753821404 |pages=182–193}}</ref> | ||
| In the middle of the queen's pregnancy, two events occurred which had a profound effect on her later life: the return of her friend, the Swedish diplomat Count ]<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/europe/france/12096119/Marie-Antoinettes-torrid-affair-with-Swedish-count-revealed-in-decoded-letters.html|title=Marie-Antoinette's torrid affair with Swedish count revealed in decoded letters|website=The Telegraph|last=Samuel|first=Henry|date=12 January 2016}}</ref> to Versailles for two years, and her brother's ] of ], contested by ] and Prussia.<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1974|pp=162–64}}</ref> Marie Antoinette pleaded with her husband for the French to intercede on behalf of Austria. The ], signed on 13 May 1779, ended the brief conflict, with the Queen imposing French mediation at her mother's insistence and Austria's gaining the ] territory of at least 100,000 inhabitants—a strong retreat from the early French position which was hostile towards Austria. This gave the impression, partially justified, that the Queen had sided with Austria against France.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=158–71}}</ref>{{sfn|d'Arneth|Geffroy|1874|pp=168–170, 180–182, 210–212}} | |||
| Meanwhile, the queen began to institute changes in the customs practiced at court. Some changes had been met with disapproval from the older generation. More importantly was the abandonment of heavy make-up and the popular wide-hooped ] for a more simple feminine look, typified first by the rustic ] and later by the ''gaulle'', a simple muslin dress she wore in a 1783 ] portrait.<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1974|pp=127–128}}</ref> She also began to participate in amateur plays and musicals, starting in 1780, in a theatre built for her.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=174–179}}</ref> | |||
| Meanwhile, the Queen began to institute changes in court customs. Some of them met with the disapproval of the older generation, such as the abandonment of heavy make-up and the popular wide-hooped ].<ref>{{Cite book|title=Fashion: The Definitive History of Costume and Style|last=Kindersley|first=Dorling|publisher=DK Publishing|year=2012|location=New York|pages=146–49}}</ref> The new fashion called for a simpler feminine look, typified first by the rustic ] style and later by the '']'', a layered muslin dress Marie Antoinette wore in a 1783 ] portrait.<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1974|pp=127–28}}</ref> In 1780 she began to participate in amateur plays and musicals in the ] built for her by ].<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=174–79}}</ref> | |||
| Repayment of the French debt remained a difficult problem, further exacerbated by Vergennes and also Marie Antoinette's prodding Louis XVI to involve France in Great Britain's war with its ]; the queen played a very important role in supporting the ] by, first, securing Austrian and Russian support for France which resulted in the establishment of a neutral league which stopped England's attack on international trade; second, sending part of her retinue to fight in America; third, supporting both ] and ] in their social lives in Paris and Versailles during the time they were Ministers to France, and finally, weighing in decisively for the nomination of ], as Minister of War and ], Secretary of the Navy in 1780, who helped ] in defeating the British in the American Revolutionary War, which ended in 1783.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=152}}</ref> | |||
| ]'', a 1783 portrait of Marie Antoinette that was criticised for showing what was described as improper and informal attire for a queen. In response to the criticism, it was repainted with the queen in a blue silk dress.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150318103947/http://digitalcommons.providence.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1047&context=art_journal|date=18 March 2015}} Kelly Hall: "Impropriety, Informality and Intimacy in Vigée Le Brun's Marie Antoinette en Chemise", pp. 21–28. Providence College Art Journal, 2014.</ref>]] | |||
| Finally, the queen played in 1783 a decisive role in the nomination of ], a close friend of the Polignacs, as Financial Minister, and the ] as the Minister of the Royal Household, making him perhaps the strongest and most conservative minister of the reign. The result of these two nominations was that Marie Antoinette's influence became paramount in government and the new ministers rejected any major to change the structure of the old regime more than that a decree by the minister of war blocked the middle classes to achieve important positions in the armed forces posing the concept of equality one of the main grievances and causes of the French Revolution.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp218-220}}</ref> | |||
| Repayment of the French debt remained a difficult problem, further exacerbated by Vergennes and also by Marie Antoinette prodding<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Larkin|first=T. Lawrence|date=2010|title=A "Gift" Strategically Solicited and Magnanimously Conferred|journal=Winterthur Portfolio|volume=44|issue=1|pages=31–76|doi=10.1086/651087|jstor=10.1086/651087|s2cid=142922208|url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/10.1086/651087 | issn = 0084-0416}}</ref> Louis XVI to involve France in the ]. The primary motive for the queen's involvement in political affairs in this period may arguably have had more to do with court factionalism than any true interest on her part in politics themselves,<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.britannica.com/biography/Marie-Antoinette-queen-of-France|title=Marie-Antoinette {{!}} Biography & French Revolution|work=Encyclopædia Britannica|access-date=3 February 2018}}</ref> but she played an important role in aiding the ] by securing Austrian and ] support for France, which resulted in the establishment of the ] that stopped Britain's attack, and by weighing in decisively for the nomination of ], as Minister of War and ] as Secretary of the Navy in 1780, who helped ] defeat the British in the American Revolutionary War, which ended in 1783.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=152, 171, 194–95}}</ref> | |||
| Marie Antoinette's second pregnancy ended in a miscarriage early in July 1779, as confirmed by letters between the Queen and her mother, although some historians believed that she may have experienced bleeding related to an irregular menstrual cycle, which she mistook for a lost pregnancy.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170202001555/http://scholarworks.umass.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1965&context=theses|date=2 February 2017}} (retrieved 1 October 2016).</ref> | |||
| ]'', portrait of the queen in a "muslin" dress, by ] (1783). This controversial portrait was viewed by her critics to be improper for a queen.]] | |||
| Her third pregnancy was affirmed in March 1781, and on 22 October she gave birth to ], Dauphin of France.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.ntv.co.jp/marie/works/catalog_en.pdf|title=From Vienna to Versailles: from Imperial Princess to Crown Prince}}</ref> | |||
| Empress Maria Theresa died on 29 November 1780, in Vienna. Marie Antoinette feared that the death of her mother would jeopardise the Franco-Austrian alliance (as well as, ultimately, herself), but her brother, ], reassured her through his own letters that he had no intention of breaking the alliance. | |||
| Empress Maria Theresa died on 29 November 1780 in Vienna. Marie Antoinette feared that the death of her mother would jeopardise the Franco-Austrian alliance, as well as, ultimately, herself, but her brother, Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor, wrote to her that he had no intention of breaking the alliance.<ref>{{Cite book |url=https://archive.org/details/bub_gb_JD1AAQAAMAAJ |title=Marie Antoinette; Joseph II, und Leopold II |last=Arneth |first=Alfred |date=1866 |location=Leipzig / Paris / Vienna |publisher=K.F. Köhler / Ed. Jung-Treuttel / Wilhelm Braumüller |page= (footnote) |language=fr, de}}</ref> | |||
| Marie Antoinette's second pregnancy was confirmed in March 1781. On 22 October 1781, the queen gave birth to ], who bore the title Dauphin of France. | |||
| A second visit from Joseph II, which |
A second visit from Joseph II, which took place in July 1781 to reaffirm the Franco-Austrian alliance and also to see his sister, was tainted by false rumours{{Sfn|Fraser|2002|p=186}} that Marie Antoinette was sending money to him from the French treasury.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=184–87}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Price|1995|pp=55–60}}</ref> | ||
| ===Declining popularity (1782–1785)=== | |||
| With time, Marie Antoinette, especially after 1778, gained a lot of weight with a full fullness below the chin, as was noticed and commented by both her brother Joseph (For him she has the fine face of a good fat German), the king of Sweden (He described her as too fat) and observers at court, such as the count of Tilly (according to her dressmaker, her bosom was well over 40 inches); yet she retained a majestic presence and a great charisma which imposed itself on her court and visitors; she dominated all other figures at court with her proud and regal carriage as a great oak rises above all the other trees of the forest according to the Comte d'Hezecques.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=187–188}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=191}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1974|p=190}}</ref><ref>{{Harnvb|Fraser|2001|pp=240,256}}</ref><ref>{{Harnvb|Tilly|Memoirs of the Comte Alexandre de Tilly,introd Havelock Ellis|1933|pp=68,70=75}}</ref> | |||
| Despite the general celebration over the birth of an heir, Marie Antoinette's political influence, such as it was, was perceived to greatly benefit Austria.<ref>Fraser, pp. 232–36</ref> During the ], in which her brother Joseph attempted to open the ] river for naval passage, Marie Antoinette succeeded in obliging Vergennes to pay huge financial compensation to Austria. Finally, the Queen was able to obtain her brother's support against ] in the American Revolution and she neutralized French hostility to his alliance with Russia.<ref>{{cite book |title=Lettres de Marie Antoinette |author=Le Marquis de Beaucourt |date=1895 |volume=ii |pages=42–44}}</ref>{{sfn|Lever|1991|pp=350–353}} | |||
| In 1782, after the governess of the royal children, the ], went bankrupt and resigned, Marie Antoinette appointed her favourite, the ], to the position.<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1974|p=193}}</ref> This decision met with disapproval from the court as the duchess was considered to be of too modest origins to occupy such an exalted position. In contrast, both the king and the queen trusted Madame de Polignac completely, gave her a thirteen-room apartment in Versailles and paid her well.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=198–201}}</ref> The entire Polignac family benefited greatly from royal favour in titles and positions, but its sudden wealth and lavish lifestyle outraged most aristocratic families, who resented the Polignacs' dominance at court, and also fueled the increasing popular disapproval of Marie Antoinette, mostly in Paris.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Price |first1=Munro |title=The Road from Versailles: Louis XVI, Marie Antoinette, and the Fall of the French Monarchy |date=2003 |publisher=Macmillan |isbn=978-0-312-26879-4 |pages=14–15, 72}}</ref> De Mercy wrote to the empress: "It is almost unexampled that in so short a time, the royal favour should have brought such overwhelming advantages to a family".<ref>{{Harvnb|Zweig|2002|p=121}}</ref> | |||
| ===1782–1785: Declining popularity, Friends, Fersen and support of arts and sciences === | |||
| ]'s gardens, by ] (1785).]] | |||
| ], 1783.]] | |||
| In June 1783, Marie Antoinette's new pregnancy was announced, but on the night of 1–2 November, her 28th birthday, she suffered a miscarriage.<ref>{{Cite book |last1=Wheeler |first1=Bonnie |title=Eleanor of Aquitaine: Lord and Lady |last2=Parsons |first2=John Carmi |year=2003 |pages=288}}</ref> | |||
| Despite the general celebration over the birth of the Dauphin, Marie Antoinette's political influence, such as it was, did greatly benefit Austria.<ref>Fraser, pp.232-6</ref> During the ], in which her brother Joseph attempted to open the ] for naval passage; Marie Antoinette succeeded in obliging Vergennes to pay a huge financial compensation to Austria. Finally, the queen was able to obtain her brother's support against ] in the ] and she neutralized French hostility to his alliance with Russia.<ref>{{Harvnb|Lettres de Marie Antoinette|Le Marquis de Beaucourt|1895|Vol ii|pp=42–44}}</ref> | |||
| In 1783 the Queen played a decisive role in the nomination of ], a close friend of ], as ], and of the ] as the Minister of the Royal Household, making him perhaps the strongest and most conservative minister of the reign.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Charles-Alexandre de Calonne {{!}} French statesman |url=https://www.britannica.com/biography/Charles-Alexandre-de-Calonne|access-date=2021-12-16|website=Britannica |language=en}}</ref> The result of these two nominations was that Marie Antoinette's influence became paramount in government, and the new ministers rejected any major change to the structure of the old regime. More than that, the ], the minister of war, requiring four ] of nobility as a condition for the appointment of officers, mainly served the interest of older noble families including poorer provincial ones, who were widely seen as a reactionary interest group by ambitious members of the middle and professional classes, by some more recent nobility, and even by the Parisian populace and press. The measure also blocked the access of 'commoners', mainly sons of members of the professional classes, and of more recently elevated nobility to important positions in the armed forces. As such, the decree became an important grievance for social classes that had been habitually supportive of the monarchy and established order, and which went on to supply the bulk of the early leadership of the French Revolution.<ref name="Fraser 2001 218–20">{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=218–20}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Price |first1=Munro |title=Preserving the Monarchy: The Comte de Vergennes 1774-1787 |date=1995 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |isbn=978-0-521-46566-3 |pages=30–35, 145–50}}</ref> | |||
| After the royal governess of the Dauphin's, the ], went bankrupt and was forced to resign; Marie Antoinette appointed her favourite, the ], to the position.<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1974|p=193}}</ref> This decision met with disapproval from the court, as the duchess was considered to be of too "immodest" a birth to occupy such an exalted position.<ref>{{Harvnb|Hector Fleischman|Madame de Polignac|1910|pp=60–62}}</ref> On the other hand, the Queen trusted Mme de Polignac completely and gave her millions of 'livres' every year.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=198–201}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| Count ], after his return from America in June 1783, was accepted into the Queen's private society. There were claims that the two were romantically involved,<ref>{{cite book |last=Farr |first=Evelyn |title=Marie-Antoinette and Count Fersen: The Untold Love Story |date=12 October 2013 |publisher=Peter Owen Publishers |isbn=978-0720610017 |edition=2nd Revised}}</ref> but since most of their correspondence has been lost, destroyed, or redacted, for many years there was no conclusive evidence.<ref name="Fraser202">{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=202}}</ref> Starting in 2016, scientists at the ] (CRCC), uncovered some of the redacted text of the queen's letters to Fersen.<ref>{{Cite web |author=Joseph Bamat |date=12 January 2016 |title=Science sheds new light on Marie Antoinette 'love affair' |url=https://www.france24.com/en/20160112-marie-antoinette-love-letters-science-france |publisher=France24}}</ref> The revealed texts do not mention a physical relationship, but do confirm a very strong emotional relationship.<ref>{{cite book |last=Farr |first=Evelyn |title=I Love You Madly: Marie-Antoinette and Count Fersen: The Secret Letters |date=1 July 2016 |publisher=Peter Owen Publishers |isbn=978-0720618778}}</ref> | |||
| In June 1783, Marie Antoinette was pregnant again. Later that month, Count Axel von Fersen returned from America, he was accepted into her private society, probably becoming her affective lover without a full physical relation between the two. Marie Antoinette suffered a miscarriage on the night of 1–2 November 1783.<ref name="Fraser202">{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=202}}</ref> | |||
| Around this time, ] describing farcical sexual deviance including the Queen and her friends in the court were growing in popularity around the country. The ''Portefeuille d'un talon rouge'' was one of the earliest, including the queen and a variety of other nobles in a political statement decrying the immoral practices of the court. As time went on, these came to focus more on the queen. They described amorous encounters with a wide range of figures, from the Duchess of Polignac to Louis XV. As these attacks increased, they were connected with the public's dislike of her association with the rival nation of Austria. It was publicly suggested that her supposed behaviour was learned at the Austrian court, particularly lesbianism, which was known as the "German vice".<ref>Hunt, Lynn. "The Many Bodies of Marie Antoinette: Political Pornography and the Problem of the Feminine in the French Revolution". In ''The French Revolution: Recent Debates and New Controversies'' 2nd edition, ed. ]. New York and London: Routledge, 1998, pp. 201–18.</ref> Her mother again expressed concern for the safety of her daughter, and she began to use Austria's ambassador to France, ], to provide information on Marie Antoinette's safety and movements.<ref>Thomas, Chantal. ''The Wicked Queen: The Origins of the Myth of Marie Antoinette''. Translated by Julie Rose. New York: Zone Books, 2001, pp. 51–52.</ref> | |||
| Trying to calm her mind, the queen occupied herself with the creation of the '']'', built to the designs of her favoured architect, ].<ref>{{Harvnb|Lever|2006|p=158}}</ref> Its creation, however, caused another uproar when the price of the ''Hameau'' was justly criticized by her critics.<ref>Fraser, pp. 245-7.</ref> | |||
| In 1783, the Queen was busy with the creation of her "]", a rustic retreat built by her favoured architect, ], according to the designs of the painter ].<ref>{{Harvnb|Lever|2006|p=158}}</ref> Its creation, however, caused another uproar when its cost became widely known.<ref>Fraser, pp. 206–08</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Gutwirth |first1=Madelyn |title=The Twilight of the Goddesses: Women and Representation in the French Revolutionary Era |date=1992 |publisher=Rutgers University Press |isbn=978-0-8135-1787-2 |pages=103, 178–85, 400–05}}</ref> However, the hamlet was not an eccentricity of Marie Antoinette's. It was en vogue at the time for nobles to have recreations of small villages on their properties. In fact, the design was copied from that of ]. It was also significantly smaller and less intricate than many other nobles'.{{sfn|Fraser|2002b|p=207}} Around this time she accumulated a library of 5,000 books. Those on music, often dedicated to her, were the most read, though she also liked to read history.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=208}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Bombelles |first1=Marc-Marie marquis de |title=Journal |volume=1: 1780-1784 |date=1977 |publisher=Droz |pages=258–65 |language=fr}}</ref> | |||
| Marie Antoinette became an avid reader of historical novels, and her scientific interest was strong enough to become a witness and supporting to the first launching of ], rendering a major service for humanity.<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1974|pp=204–205}}</ref> She had many books in her library.,<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=208}}</ref> and was able to write in imperfect English to her friend, the ].<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1974|pp=133–134}}</ref> The queen supported and sponsored a lot of arts and science activities specially ] works.{{citation needed|date=June 2015}} | |||
| She sponsored the arts, in particular music. Marie Antoinette preferred to hold her musicales in the salon of her '']'' in the Palace of Versailles, or in the ]. She limited the audience to her intimate circle and a few musicians, among them the ]. "Admitted to perform music with the Queen,"{{sfn|Banat|2006|p=151-152}} Saint-Georges probably played his violin sonatas for two instruments, with Her Majesty playing the ]. She also supported some scientific endeavours, encouraging and witnessing the first launch of a '']'', a ] for the first time in human history; this extraordinary feat which represented a turning point in human civilization was done by ].<ref>{{Harvnb|Cronin|1974|pp=204–05}}</ref> | |||
| In 1784, it was widely thought that the sickly Dauphin would not reach adulthood.<ref name="Fraser202"/> During this time, on 27 April 1784, ]'s play '']'' premiered in Paris. After initially having been banned by the king due to its negative portrayal of the nobility, the play was ironically finally allowed to be publicly performed because of the queen's support and its overwhelming popularity at court, where secret readings of it had been given by Marie Antoinette. The play was a disaster for the image of the monarchy and aristocracy. It did inspire ]'s ], which premiered in Vienna on 1 May 1786.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=214–215}}</ref> | |||
| On 27 April 1784, ]'s play '']'' premiered in Paris. Initially banned by the king due to its negative portrayal of the nobility, the play was finally allowed to be publicly performed because of the Queen's support and its overwhelming popularity at court, where secret readings of it had been given by Marie Antoinette. The play was a disaster for the image of the monarchy and aristocracy. It inspired ]'s '']'', which premiered in Vienna on 1 May 1786.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=214–15}}</ref> | |||
| In August 1784, it wa announced that the queen was pregnant again. Her husband bought for her the ] from the ], the father of the previously disgraced ]. This was an unpopular acquisition, particularly with some factions of the nobility who already disliked her, but also with a growing percentage of the population who disapproved that a French queen might own her own residence, independently of the king. Despite having the ] working on her behalf, the purchase did not help improve the public's image of the queen as frivolous. The château's expensive price, almost 6\10million ], plus the substantial extra cost of redecorating it, ensured that there was much less money going towards repaying France's substantial debt.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=216–220}}</ref> | |||
| ], by ]]] | |||
| On 27 March 1785, Marie Antoinette gave birth to a second son, ], who bore the title of Duke of Normandy.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=224–225}}</ref> The fact that the birth occurred exactly nine months following Fersen's visit did not escape the attention of many, and though there is much doubt and historical speculation about the parentage of this child, public opinion towards her decreased noticeably.<ref>{{Harvnb|Lever|2006|p=189}}</ref> It is the belief of most of Marie-Antoinette's biographers, and of the young prince, that he was the biological son of Louis XVI and not Axel von Fersen's.<ref>Stefan Zweig and Antonia Fraser, who believe Fersen and the queen were romantically involved with one another, argue that there is no evidence whatsoever to suggest that Louis XVI was not the child's father - see Stefan Zweig, ''Marie Antoinette: The portrait of an average woman'' (New York, 1933), pp. 143, 244-7, and Fraser, pp. 267-9. This is also the view taken in biographies like Ian Dunlop, ''Marie-Antoinette: A Portrait'' (London, 1993), Évelyne Lever, ''Marie-Antoinette : la dernière reine'' (Paris, 2000), Simone Bertière, ''Marie-Antoinette: l'insoumise'' (Paris, 2003), and Jonathan Beckman, ''How to ruin a Queen: Marie Antoinette, the Stolen Diamonds and the Scandal that shook the French throne'' (London, 2014), all of which argue that the Queen was not romantically or sexually involved with von Fersen. Beckman argues that 'there was speculation that he had an affair with the queen. To keep such a liaison hidden for years would have required a talent for logistics and discretion well beyond Marie Antoinette.' Munro Price, ''The Fall of the French Monarchy: Louis XVI, Marie Antoinette and the baron de Breteuil'' (London, 2002) argues that it is impossible to know one way or the other how the queen and von Fersen felt about one another, but that if they ever did consummate their union, it took place after the birth of all four of her children and quite possibly only in the final few weeks of her freedom. The prince's biographer, Deborah Cadbury, in ''The Lost King of France: The tragic story of Marie-Antoinette's Favourite Son'' (London, 2003), pp. 22-4 also argues strongly that Louis XVI was the younger son's biological father.</ref> Courtiers at Versailles noted in their diaries at the time that the date of the child's conception in fact corresponded perfectly with a period when the king and queen had spent a lot of time together, but these details were ignored amid attacks on the queen's character.<ref>Cadbury, p. 23</ref> These suspicions of illegitimacy, along with the continued publication of the ''libelles'', a never-ending cavalcade of court intrigues, the actions of Joseph II in the Kettle War, and her purchase of Saint-Cloud combined to turn popular opinion sharply against the queen, and the image of a licentious, spendthrift, empty-headed foreign queen was quickly taking root in the French psyche.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=226}}</ref> | |||
| On 24 October 1784, putting the Baron de Breteuil in charge of its acquisition, Louis XVI bought the ] from ] in the name of his wife, which she wanted due to their expanding family. She wanted to be able to own her own property, one that was actually hers, to then have the authority to bequeath it to "whichever of my children I wish,"{{Sfn|Fraser|2002|p=217}} choosing the child she thought could use it rather than it going through patriarchal inheritance laws or whims. It was proposed that the cost could be covered by other sales, such as that of the ''château Trompette'' in Bordeaux.{{sfn|Fraser|2002b|p=217}} This was unpopular, particularly with those factions of the nobility who disliked the Queen, but also with a growing percentage of the population, who disapproved of a queen of France independently owning a private residence. The purchase of Saint-Cloud thus damaged the public's image of the Queen even further. The château's high price, almost 6 million ], plus the substantial extra cost of redecorating, ensured that much less money was going towards repaying France's substantial debt.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=216–20}}</ref>{{sfn|Lever|1991|pp=358–360}} | |||
| On 27 March 1785, Marie Antoinette gave birth to a second son, Louis Charles, who bore the title of ].<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=224–25}}</ref> The fact that the birth occurred exactly nine months after Fersen's return did not escape the attention of many, leading to doubt as to the parentage of the child and to a noticeable decline of the Queen's reputation in public opinion.<ref>{{Harvnb|Lever|2006|p=189}}</ref> The majority of Marie Antoinette's and Louis XVII's biographers believe that the young prince was the biological son of Louis XVI, including ] and ], who believe that Fersen and Marie Antoinette were indeed romantically involved.<ref>Stefan Zweig, ''Marie Antoinette: The portrait of an average woman'', New York, 1933, pp. 143, 244–47</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=267–69}}</ref><ref>], ''Marie-Antoinette: A Portrait'', London, 1993</ref><ref>Évelyne Lever, ''Marie-Antoinette : la dernière reine'', Fayard, Paris, 2000</ref><ref>Simone Bertière, ''Marie-Antoinette: l'insoumise'', Le Livre de Poche, Paris, 2003</ref><ref>Jonathan Beckman, ''How to ruin a Queen: Marie Antoinette, the Stolen Diamonds and the Scandal that shook the French throne'', London, 2014</ref><ref>Munro Price, ''The Fall of the French Monarchy: Louis XVI, Marie Antoinette and the baron de Breteuil'', London, 2002</ref><ref>Deborah Cadbury, ''The Lost King of France: The tragic story of Marie-Antoinette's Favourite Son'', London, 2003, pp. 22–24</ref> Fraser has also noted that the birthdate matches up perfectly with a known conjugal visit from the King.{{Sfn|Fraser|2002|p=217}} | |||
| A second daughter, ] was born on 9 July 1786, but she died on 19 June 1787, before reaching her first year of life. This was Marie Antoinette's last child. | |||
| Courtiers at Versailles noted in their diaries that the date of the child's conception corresponded perfectly with a period when the King and the Queen had spent much time together, but these details were ignored amid attacks on the Queen's character.<ref>Cadbury, p. 23</ref> These suspicions of illegitimacy, along with the continued publication of the ''libelles'' and never-ending cavalcades of court intrigues, the actions of Joseph II in the ], the purchase of Saint-Cloud and the ] combined to turn popular opinion sharply against the Queen, and the image of a licentious, spendthrift, empty-headed foreign queen was quickly taking root in the French psyche.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=226}}</ref> | |||
| ===1786–1789: Prelude to the Revolution: high spending, scandals and the failure of reforms=== | |||
| A second daughter, her last child, ], ''Madame Sophie'', was born on 9 July 1786 and lived only eleven months until 19 June 1787. She was named after the King's aunt, ].{{Sfn|Fraser|2002|p=244}} | |||
| ] (1787) of Marie Antoinette and her children Marie Thérèse, Louis Charles (on her lap), and Louis Joseph, was meant to help her reputation by depicting her as a mother and in simple, yet stately attire.]] | |||
| Continuing deterioration of the French financial situation, despite cutbacks to the royal retinue, ultimately forced the king, the queen and their Minister of Finance, ], to call the ], after a hiatus of 160 years. The assembly was held to attempt passing some reforms required to alleviate the financial situation, on which the ]s refused to cooperate. The first meeting of the assembly took place on 22 February 1787, at which Marie Antoinette was not present. Later, this absence resulted in accusations that the queen was trying to undermine the purpose of the assembly.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=246–248}}</ref> | |||
| ===Prelude to the Revolution: scandals and the failure of reforms (1786–1789)=== | |||
| However, the Assembly was a failure, as it did not pass any reforms and instead fell into a pattern of defying the king. The king, on the urging of the queen, dismissed Calonne on 8 April 1787; Vergennes died on 13 February.<ref name="Fraser248-250">{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=248–250}}</ref> | |||
| ====Diamond necklace scandal==== | |||
| {{Main|Affair of the Diamond Necklace}} | |||
| ], in France]] | |||
| Marie Antoinette began to abandon her more carefree activities to become increasingly involved in politics in her role as queen of France.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=248–52}}</ref> By publicly showing her attention to the education and care of her children, the queen sought to improve the dissolute image she had acquired in 1785 from the "Diamond Necklace Affair", in which public opinion had falsely accused her of criminal participation in defrauding the jewelers Boehmer and Bassenge of the price of an expensive diamond necklace they had originally created for ]. | |||
| The main actors in the scandal were ], ], ], and ], Countess de La Motte, a descendant of an illegitimate child of ] of the ]. Marie Antoinette had profoundly disliked Rohan since the time he had been the French ambassador to Vienna when she was a child. Despite his high clerical position at the Court, she never addressed a word to him. Others involved were ], alias ''Baronne d'Oliva'', a prostitute who happened to look like Marie Antoinette; ], a forger; ], an Italian adventurer; and the Count de La Motte, Jeanne de Valois' husband. Madame de La Motte tricked Rohan into buying the necklace as a gift to Marie Antoinette, for him to gain the queen's favour. | |||
| During this time, the queen began to abandon her more carefree activities to become increasingiy involved in politics, and mostly with the interests of Austria and her children.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=248–252}}</ref> This was for a variety of reasons. First, her children were '']'', and thus their future as leaders of France needed to be assured. Second, by concentrating on her children, the queen sought to improve the dissolute image she had acquired from the "]", in which she had been accused of participating in a crime to defraud the crown jewelers of the cost of a very expensive diamond necklace, and this incident in which she insisted on the arrest and trial of the ] destroyed her reputation specially when she imprisoned and exiled the cardinal in spite of the parliament decision to exonerate him. Third, the king had begun to withdraw from a decision-making role in government due to the onset of an acute case of depression. As a result, Marie Antoinette finally emerged as a politically viable entity. In her new capacity as a politician with a very high degree of power, the queen tried to help the situation brewing between the assembly and the king.<ref name="Fraser248-250"/> | |||
| When the affair was discovered, those involved, except de La Motte and Rétaux de Villette, who both managed to flee, were arrested, tried, convicted, and either imprisoned or exiled. Madame de La Motte was sentenced for life to confinement in the ], which also served as a prison for women. Judged by the ], Rohan was found innocent of any wrongdoing and allowed to leave the ]. Marie Antoinette, who had insisted on the arrest of the Cardinal, was dealt a heavy personal blow, as was the monarchy, and despite the fact that the guilty parties were tried and convicted, the affair proved to be extremely damaging to her reputation, which never recovered from it.{{citation needed|date=December 2016}} | |||
| This change in the queen's political role signalled the beginning of the end of the influence of the duchesse de Polignac, as Marie Antoinette began to dislike the duchesse's huge expenditures and their impact on the finances of the Crown. The duchesse left for England in May, leaving her children behind in Versailles. Also in May, ], the ] and one of the queen's political allies, was appointed by the king, on Marie Antoinette's urging and orders, to replace Calonne first as the Finance Minister and then as Prime Minister. He began to institute more cutbacks at court and to restore the absolute power of the king and queen who were weakened by parliaments .<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=250–260}}</ref> | |||
| ====Failure of political and financial reforms==== | |||
| Brienne, though, was not able to improve the financial situation. Since he was the queen's ally and creature, this failure adversely affected her political position. The continued poor financial climate of the country resulted in the 25 May dissolution of the Assembly of Notables because of its inability to get things done. This lack of solutions was fairly blamed on the queen.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001pp=218-220}}</ref> The financial problems resulted from a combination of several factors: too many expensive wars; a too-large royal family headed by the queen whose large frivolous expenditures far exceeded the resources of the state; and an unwillingness on the part of many of the aristocrats and Marie Antoinette who were in charge to help defray the costs of the government out of their own pockets with higher taxes. Marie Antoinette earned the nickname of "Madame Déficit" in the summer of 1787 as a result of the public perception that she had singlehandedly ruined the national finances.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=254–255}}</ref> | |||
| Suffering from an acute case of depression, the King began to seek the advice of his wife. In her new role and with increasing political power, the Queen tried to improve the awkward situation brewing between the Parlement and the King.<ref name="Fraser248-250"/> This change of the queen's position signaled the end of the Polignacs' influence and their impact on the finances of the Crown. | |||
| While sole fault for the financial crisis did not lie with the queen, Marie Antoinette was the biggest obstacle to any major reform effort. She played a decisive role in the disgrace, exile and partial imprisonment of the Reformer Ministers of Finance, ] and ]. She spent a lot of money on her favorites and on herself, more than any other person in France. Finally the expense of the court was much higher than the official estimate of 7% of the state budget, if the secret expenses of the queen were taken into account.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp254-260}}</ref> | |||
| The queen attempted to fight back with propaganda portraying her as a caring mother, most notably the premier at ] in August 1787 of a portrait of her and her children by ].<ref>Facos, p. 12.</ref><ref>Schama, p. 221.</ref> Around the same time, ] escaped from ] in France and fled to London, where she published more damaging lies concerning her supposed "affair" with the Queen.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=255–258}}</ref> | |||
| Continuing deterioration of the financial situation despite cutbacks to the royal retinue and court expenses ultimately forced the King, the Queen and the Controller-General of Finances, ], at the urging of Vergennes, to call a session of the ], after a hiatus of 160 years. The assembly was held for the purpose of initiating necessary financial reforms, but the Assembly refused to cooperate. The first meeting took place on 22 February 1787, nine days after the death of Vergennes on 13 February. Marie Antoinette did not attend the meeting and her absence resulted in accusations that the Queen was trying to undermine its purpose.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=246–48}}</ref>{{sfn|Lever|1991|pp=419–420}} The Assembly was a failure. It did not pass any reforms and, instead, fell into a pattern of defying the King. On the urging of the Queen, Louis XVI dismissed Calonne on 8 April 1787.<ref name="Fraser248-250">{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=248–50}}</ref> | |||
| ] (1788).]] | |||
| The political situation in 1787 began to worsen when on Marie Antoinette's urging, the '']'' was exiled, and further deteriorated when the King tried to use a '']'' to force through legislation on 11 November. The new duc d'Orléans publicly protested the king's actions, and was subsequently exiled.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp 257-258}}</ref> The May Edicts issued on 8 May 1788 were also opposed by the public and parliaments. Finally, on 8 July and 8 August, the King announced his intention to bring back the ], the traditional elected legislature of the country, which had not been convened since 1614.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=258–259}}</ref> | |||
| On 1 May 1787 ], ] and one of the queen's political allies was appointed by the King at her urging to replace Calonne, first as Controller-General of Finances and then as ]. He began to institute more cutbacks at court while trying to restore the royal absolute power weakened by the Parlement.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=250–60}}</ref> Brienne was unable to improve the financial situation, and since he was the Queen's ally, this failure adversely affected her political position. The continued poor financial climate of the country resulted in the 25 May dissolution of the Assembly of Notables because of its inability to function, and the lack of solutions was blamed on the Queen.<ref name="Fraser 2001 218–20"/> | |||
| Marie Antoinette was directly involved with the exile of the ''Parlement'', the May Edicts or with the announcement regarding the Estates General, she did participate in the King Council, the first queen to do this in the last hundred years, and she was making the major decisions behind the scene and in Council . Her primary concern in late 1787 and 1788 was the improved health of the Dauphin, who suffered from ] and his condition continued to deteriorate.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=260–261}}</ref> | |||
| France's financial problems were the result of a combination of factors: several expensive wars; a large royal family whose expenditures were paid for by the state; and an unwillingness on the part of most members of the privileged classes, aristocracy, and clergy, to help defray the costs of the government out of their own pockets by relinquishing some of their financial privileges. As a result of the public perception that she had single-handedly ruined the national finances, Marie Antoinette was given the nickname of "Madame Déficit" in the summer of 1787.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=254–55}}</ref> While the sole fault for the financial crisis did not lie with her, Marie Antoinette was the biggest obstacle to any major reform effort. She had played a decisive role in the disgrace of the reformer ministers of finance, ] (in 1776), and ] (first dismissal in 1781). If the secret expenses of the Queen were taken into account, court expenses were much higher than the official estimate of 7% of the state budget.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=254–60}}</ref> | |||
| The queen was instrumental in the recall of Jacques Necker as Finance Minister on 26 August, a popular move, even though she herself was worried that the recall would again go against her if Necker proved unsuccessful in reforming the country's finances.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=263–265}}</ref> | |||
| ] of Marie Antoinette by ], 1792.]] | |||
| ], 1787.]] | |||
| The queen prepared for the Mass celebrating the return of the Estates General on 4 May 1789. She knew that her rival, the duc d'Orléans, who had given money and bread to the people during the winter, would be popularly acclaimed by the crowd much to her detriment.<ref>{{Harvnb|A diary of the French Revolution 1789-93|Morris Gouverneur|1939|pp=66,67}}</ref> The Estates General convened the next day.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=270–273}}</ref> During the month of May, the Estates General began to fracture between the democratic ] (consisting of the bourgeoisie and radical nobility), and the royalist nobility of the ]. | |||
| The queen attempted to fight back with propaganda portraying her as a caring mother, most notably in the painting by ] exhibited at the ] in August 1787, showing her with her children.<ref>Facos, p. 12.</ref><ref>Schama, p. 221.</ref> Around the same time, Jeanne de Valois-Saint-Rémy escaped from prison and fled to London, where she published damaging slander concerning her supposed amorous affair with the Queen.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=255–58}}</ref> | |||
| The death of the Dauphin on 4 June, which deeply affected his mother was virtually ignored by the French people,<ref>{{Louis Nicorlardet|Journal de Louis Seize|1873|p=133-138}}</ref> who were instead preparing for the next meeting of the Estates General and hoping for a resolution to the bread crisis. As the Third Estate declared itself a ] and took the ], and as others listened to rumors that the queen wished to bathe in their blood, Marie Antoinette went into mourning for her eldest son.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=274–278}}</ref> Marie Antoinette's role was decisive in urging the king to remain firm and to not concede to popular demands for reforms. In addition, the queen was ready to use force to crush the revolution.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp279-282}}</ref> | |||
| The political situation in 1787 worsened when, at Marie Antoinette's urging, the '']'' was exiled to ] on 15 August. It further deteriorated when Louis XVI tried to use a '']'' on 11 November to impose legislation. The new ] publicly protested the king's actions, and was subsequently exiled to his ].<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=257–58}}</ref> The May Edicts issued on 8 May 1788 were also opposed by the public and parlement. Finally, on 8 August, Louis XVI announced his intention to bring back the ], the traditional elected legislature of the country, which had not been convened since 1614.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=258–59}}</ref> | |||
| ===July 1789–1791: The French Revolution before Varennes=== | |||
| ] and arrest of the Governor ], 14 July 1789. Museum of the History of France.]] | |||
| While from late 1787 up to his death in June 1789 Marie Antoinette's primary concern was the continued deterioration of the health of the Dauphin, who suffered from ],<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=260–61}}</ref> she was directly involved in the exile of the ''Parlement'', the May Edicts, and the announcement regarding the Estates General. She did participate in the ], the first queen to do this in over 175 years (since ] had been named ''Chef du Conseil du Roi'', between 1614 and 1617), and she was making the major decisions behind the scene and in the Royal Council. | |||
| The situation began to escalate violently in June as the National Assembly began to demand more rights, and Louis XVI began to push back with efforts to suppress the Third Estate. However, the king's ineffectiveness and the queen's unpopularity undermined the monarchy as an institution, and so these attempts failed. Then, on 11 July, on Marie Antoinette's urging and orders, Necker was dismissed to be replaced by Breteuil, the queen's choice to crush the Revolution with mercenary Germanic troops under the command of one of her favorites Besenval.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp280-285}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Letters vol 2|pp=130–140}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Morris|1939|pp=130–135}}</ref> At the news, Paris was besieged by riots which culminated in the ] on ].<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=282–284}}</ref> | |||
| Marie Antoinette was instrumental in the reinstatement of ] as Finance Minister on 26 August 1788, a popular move, even though she herself was worried that it would go against her if Necker proved unsuccessful in reforming the country's finances. She accepted Necker's proposition to double the representation of the Third Estate (''tiers état'') in an attempt to check the power of the aristocracy.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=263–65}}</ref>{{sfn|Lever|2001|pp=448–453}} | |||
| In the days and weeks that followed, many of the most conservative, reactionary royalists, including the ] and the ], fled France for fear of assassination. Marie Antoinette, whose life was the most in danger, stayed behind in order to help the king promote stability, even as his power was gradually being taken away by the ], which was now ruling Paris and conscripting men to serve in the '']''.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=284–289}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Despaches of Earl Grower|Oscar Browning|Cambridge 1885|pp=70–75,245–250}}</ref> | |||
| On the eve of the opening of the ] the Queen attended the mass celebrating its return. As soon as it opened on 5 May 1789, the fracture between the democratic Third Estate (consisting of bourgeois and radical aristocrats) and the conservative nobility of the Second Estate widened, and Marie Antoinette knew that her rival, the Duke of Orléans, who had given money and bread to the people during the winter, would be acclaimed by the crowd, much to her detriment.<ref>{{cite book |title=A diary of the French Revolution 1789–93 |last=Morris |first=Gouverneur |date=1939 |pages=66–67 |editor=Beatrix Cary Davenport |location=Boston |publisher=Houghton Mifflin |url=https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=mdp.39015011239764&seq=9}}</ref> | |||
| ], 1789.]] | |||
| The death of the Dauphin on 4 June, which deeply affected his parents, was virtually ignored by the French people,<ref>Nicolardot, Louis, ''Journal de Louis Seize'', 1873, pp. 133–38</ref> who were instead preparing for the next meeting of the Estates General and hoping for a resolution to the bread crisis. As the Third Estate declared itself a ] and took the ], and as people either spread or believed rumours that the Queen wished to bathe in their blood, Marie Antoinette went into mourning for her eldest son.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=274–78}}</ref> Her role was decisive in urging the King to remain firm and not concede to popular demands for reforms. In addition, she showed her determination to use force to crush the forthcoming revolution.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=279–82}}</ref>{{sfn|Lever|1991|pp=462–467}} | |||
| By the end of August, the ] (''La Déclaration des Droits de l'Homme et du Citoyen''), drafted by La Fayette, was adopted, which officially began a constitutional monarchy in France.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=289}}</ref> Despite this, the king was still required to perform certain court ceremonies, even as the situation in Paris worsened due to a bread shortage in September. On 5 October, a ] and forced the royal family, along with the ], his wife and ], to move to Paris under the watchful eye of the ''Garde Nationale''. The king and queen were installed in the ] under strong surveillance.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=298–304}}</ref> During this house arrest, Marie Antoinette conveyed to her friends that she did not intend to involve herself any further in French politics, as everything, whether or not she was involved, would inevitably be attributed to her anyway and she feared the repercussions of further involvement.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=304}}</ref> | |||
| ==French Revolution before Varennes (1789–1791)== | |||
| Despite the situation, Marie Antoinette was still required to perform charitable functions and to attend certain religious ceremonies, which she did. Most of her time, however, was dedicated to her children.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=304–308}}</ref> In spite of her status as an effective state prisoner, Marie Antoinette played a very important political role in the period extending between 1789 and 1791. That role was not public because there was a political and public rejection of the queen who tried to crush the revolution in July 1789. During this period, Marie Antoinette had a complex set of relationships with several key leaders of the early period of the French Revolution. One of the most important politicians of that period was Necker the prime minister who was in charge of financial policy, the queen hated Necker in spite that she played a decisive role in his return to power. Marie Antoinette blamed Necker for the role he played in supporting the Revolution and she was very happy when he was obliged to resign in 1790.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=315}}</ref> | |||
| The situation escalated on 20 June as the Third Estate, which had been joined by several members of the clergy and radical nobility, found the door to its appointed meeting place closed by order of the King.<ref>{{Cite book|last=Doyle|first=William|title=The Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford University Press|year=1990|pages=100–105}}</ref> It thus met at the tennis court in Versailles and took the ] not to separate before it had given a constitution to the nation. | |||
| On 11 July at Marie Antoinette's urging, Necker was dismissed and replaced by Breteuil, the queen's choice to crush the Revolution with mercenary Swiss troops under the command of one of her favourites, ].<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=280–85}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Morris|1939|pp=130–35}}</ref> At the news, Paris was besieged by riots that culminated in the ] on 14 July.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=282–84}}</ref>{{sfn|Lever|1991|pp=474–478}} On 15 July ] was named commander-in-chief of the newly formed ].<ref name="Fraser 2001 284–289">{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=284–89}}</ref><ref name="Browning1885">{{cite book |title=Despatches of Earl Gower |editor-first1=Oscar |editor-last1=Browning |location=Cambridge |publisher =Cambridge University Press|date=1885 |pages=70–75, 245–50}}</ref> | |||
| ] the leader of the National Guard (and military leader in the American Revolution) hated the queen and served as her jailer and even considered sending her to a convent. However, he was persuaded by the mayor of Paris, ], to try to work with her. La Fayette's relation with the King was acceptable and being a liberal aristocrat he did not want the destruction of the monarchy but instead the installation of a liberal system of government. At times La Fayette worked in the queen's favor. La Fayette sent the Duke of Orleans, who was accused by the queen of fomenting trouble, into exile for a period of time. La Fayette even boasted, as the queen's jailer, that he allowed Marie Antoinette to see Axel de Fersen, albeit under strong surveillance. The queen who did not have any direct political power during that period because the king's powers were suspended until the constitution was adopted. Marie Antoinette strongly resented her status as an effective prisoner who needed the approval of her guards for any physical or public activity and suffered a lot during these "sad years" as she described them in her letters, while never losing hope that one day she'd recover her liberty and absolute power.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp310-314}}</ref> | |||
| ] in Paris, and the arrest of its Governor ], 14 July 1789]] | |||
| A significant achievement for Marie Antoinette in that period was the establishment of an alliance with ], the most important lawmaker in the assembly. Like La Fayette, Mirabeau was a liberal aristocrat. While Mirabeau was elected on the lower-class list, he was not fundamentally against the monarchy and dreamed of reconciling the monarchy with the revolution. Mirabeau wanted also to be a minister and he was not immune to corruption. On the advice of Count Mercy, Marie Antoinette opened secret negotiations with Mirabeau and they agreed to meet in secret in the castle of Saint Cloud in the summer of 1790. At the meeting, Mirabeau was much impressed by the queen, saying that she was the only man in her husband's court. A deal was reached turning Mirabeau into one of her political allies. Marie Antoinette also accepted to pay Mirabeau 6000 livres per month and many millions if he succeeded in his mission to restore the king's authority. | |||
| In the days following the storming of the Bastille, for fear of assassination, and ordered by the King, the ] began on 17 July with the departure of the ], the ], cousins of the King,<ref>''Journal d'émigration du prince de Condé. 1789–1795'', publié par le comte de Ribes, Bibliothèque nationale de France. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160307191951/http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k6530679p/f28.image|date=7 March 2016}}</ref> and the unpopular Polignacs. Marie Antoinette, whose life was as much in danger, remained with the King, whose power was gradually being taken away by the ].<ref name="Fraser 2001 284–289"/><ref>Castelot, ''Charles X'', Librairie Académique Perrin, Paris, 1988, pp. 78–79</ref><ref name="Browning1885" /> | |||
| The summer of 1790 brought to Marie Antoinette and her family a limited amount of relief, as they were allowed to spend it in the castle of Saint Cloud, which belonged to the queen. While her situation as a prisoner did not change, she had much greater personal freedom than in Paris, since she was free from the radical elements who surrounded her and followed all her movements in the capital. During this time, she met Mirabeau in secret, an event which could not have happened in Paris. | |||
| The ] by the National Constituent Assembly on 4 August 1789 and the ] (''La Déclaration des Droits de l'Homme et du Citoyen''), drafted by Lafayette with the help of ] and adopted on 26 August, paved the way to a ] (4 September 1791 – 21 September 1792).<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=289}}</ref>{{sfn|Lever|1991|pp=484–485}} Despite these dramatic changes, life at the court continued, while the situation in Paris was becoming critical because of bread shortages in September. On 5 October, a ] and forced the royal family to move to the ] in Paris, where they lived under a form of house arrest under the watch of Lafayette's National Guard, while the ] and ] were allowed to reside in the ], where they remained until they went into exile on 20 June 1791.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.senat.fr/evenement/archives/presidence1.html|title=dossiers d'histoire – Le Palais du Luxembourg – Sénat|website=senat.fr|access-date=18 October 2015|archive-date=4 March 2016|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304093643/http://www.senat.fr/evenement/archives/presidence1.html|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| The only time the royal couple returned to Paris in that period was in 14 July 1790 for the official celebration of the Fall of the Bastille, "The Fete de la Federation". The Abbe ] said a commemorative Mass in Paris and at least 300,000 persons participated from all over France including 18,000 National Guards. At the event, the king was greeted with numerous cries of "Long Live The King ", especially when he took the oath to protect the Nation and to apply the laws voted by the Constitutional Assembly. There were even some cheers to the queen, particularly when she presented her son to the Public. Mirabeau advised Marie Antoinette to leave Paris and to travel inside France to profit from the commemoration of the 14 of July, but the queen was already thinking of leaving France and turning for Foreign Powers to help her crush the Revolution.<ref>{{Harvnb|2001|Fraser|pp=314–316}}</ref> | |||
| Marie Antoinette continued to perform charitable functions and attend religious ceremonies, but dedicated most of her time to her children.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=304–08}}</ref> She also played an important political, albeit not public, role between 1789 and 1791 when she had a complex set of relationships with several key actors of the early period of the French Revolution. One of the most important was Necker, the Prime Minister of Finances (''Premier ministre des finances'').<ref>''Discours prononcé par M. Necker, Premier Ministre des Finances, à l'Assemblée Nationale, le 24. Septembre 1789''. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221203145325/https://books.google.fr/books?id=OSh8riUvV_UC&pg=PP1&lpg=PP1&dq=necker+premier+ministre+des+finances&source=bl&ots=j1FO3K8sSy&sig=deQBeYTngT_4IybHN8BCis-xEIA&hl=fr&sa=X&ved=0CDsQ6AEwA2oVChMI8JShrtiSxwIVxVUUCh1I_wCi#v=onepage&q=necker%20premier%20ministre%20des%20finances&f=false|date=3 December 2022}}</ref> Despite her dislike of him, she played a decisive role in his return to the office. She blamed him for his support of the Revolution and did not regret his resignation in 1790.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=315}}</ref>{{sfn|Lever|1991|pp=536–537}} | |||
| Mirabeau sincerely wanted to reconcile the queen with the people, but the Queen was still attempting to restore as much of the king's authority as possible and to liberate herself from her captivity. Marie Antoinette was happy to see Mirabeau restoring much of the King's powers in the assembly. The king's authority over foreign policy was restored and the right to propose the declaration of war was also given to the king. Over the objections of La Fayette and his allies, the king was given a suspensive veto allowing him to veto any laws for a period of four years. With time, Mirabeau would support the queen even more, going as far as to agree with her escape plans but perhaps not to the extent of demanding the help of foreign powers.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp315-319}}</ref> However, this leverage with the Assembly ended with the death of Mirabeau in April 1791, though many moderate leaders of the French Revolution tried to contact the queen and to establish some kind of cooperation with her. | |||
| Lafayette, one of the former ] (1775–1783), served as the warden of the royal family in his position as commander-in-chief of the National Guard. Despite his dislike of the Queen—he detested her as much as she detested him and at one time had even threatened to send her to a convent—he was persuaded by the ], ], to work and collaborate with her, and allowed her to see Fersen a number of times. He even went as far as exiling the Duke of Orléans, who was accused by the queen of fomenting trouble. His relationship with the King was more cordial. As a liberal aristocrat, he did not want the fall of the monarchy but rather the establishment of a liberal one, similar to that of ], based on cooperation between the King and the people, as was to be defined in the ]. | |||
| Just before Mirabeau's death, the Pope condemned the civil constitution of the clergy in March 1791, which reduced the number of bishops from 132 to 93, imposed the election of bishops and monks by the French people, and finally reduced the Pope's authority over the Church. Marie Antoinette was raised in the Catholic Faith and while she was not pious as her husband, religion played a decisive role in her life especially after her pregnancies. The queen's political ideas and her belief in the absolute power of monarchs were based on the simple assumption that queens and kings were the representatives of God on earth and that their subjects should obey them in an absolute way. When the people in Paris felt that the queen was against the new religious laws, Marie Antoinette was publicly insulted and she was not allowed to leave Paris. This incident fortified the queen's determination to leave Paris.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp321-323}}</ref> | |||
| Despite her attempts to remain out of the public eye, Marie Antoinette was falsely accused in the ''libelles'' of having an affair with Lafayette, whom she loathed,<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=319}}</ref> and, as was published in ''Le Godmiché Royal'' ("The Royal Dildo"), of having a sexual relationship with the English baroness Lady Sophie Farrell of Bournemouth, a well-known lesbian of the time. Publication of such calumnies continued to the end, climaxing at her trial with an accusation of incest with her son. There is no evidence to support the accusations. | |||
| ].]] | |||
| ===Mirabeau=== | |||
| Despite her attempts to remain out of the public eye, she was falsely accused in the ''libelles'' of conducting an affair with the commander of the ''Garde Nationale'', the ], whom in reality she loathed for his liberal tendencies and his role in the royal family's forced departure from Versailles.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=319}}</ref> This was not the only accusation Marie Antoinette faced from such "libelles." In such pamphlets as "''Le Godmiché Royal''" (translated, "''The Royal Dildo''"), it was suggested that she routinely engaged in deviant sexual acts of various sorts, most famously with the English Baroness 'Lady Sophie Farrell' of Bournemouth, a renowned lesbian of the time.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://muse.jhu.edu/journals/early_american_literature/v040/40.1comment.pdf |title=Project MUSE — Early American Literature — Charles Brockden Brown's Ormond and Lesbian Possibility in the Early Republic |publisher=Muse.jhu.edu |accessdate=1 August 2010}}</ref> From acting as a ] (in her case, in the lesbian sense), to sleeping with her son, Marie Antoinette was constantly an object of rumor and false accusations of committing sexual acts with partners other than the King. Later, allegations of this sort (from incest to orgiastic excesses) were used to justify her execution.<ref name="Zimmerman">{{cite book|title =Lesbian histories and cultures: an encyclopedia (Volume 1)|publisher=Taylor & Francis|year=2000|pages=776–777| author =Bonnie Zimmerman|isbn =9780815319207|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=0EUoCrFolGcC&pg=PA777&dq=Lesbian+histories+and+cultures+tribadism&hl=en&sa=X&ei=rn5OT9_zDI30sQK9gsUF&ved=0CDIQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q=Lesbian%20histories%20and%20cultures%20tribadism&f=false|accessdate=February 29, 2012}}</ref><ref name="Goodman">{{cite book|title=Marie-Antoinette: writings on the body of a queen|author=Dena Goodman|publisher=Psychology Press|year=2003|pages=144–145|accessdate=February 19, 2012|isbn=9780415933957|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=VA9oTIyrWr4C&pg=PA145&dq=Marie+Antoinette+was+tried+and+roundly+convicted+in+the+press+as+a+tribade.&hl=en&sa=X&ei=TShBT9y_KJOA2AXKhs2JCA&ved=0CDAQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q=Marie%20Antoinette%20was%20tried%20and%20roundly%20convicted%20in%20the%20press%20as%20a%20tribade.&f=false}}</ref> Ultimately, none of the charges of sexual depravity has any credible evidentiary support; Marie Antoinette was simply an easy target for rumor and criticism. | |||
| A significant achievement of Marie Antoinette in that period was the establishment of an alliance with ], the most important lawmaker in the assembly. Like Lafayette, Mirabeau was a liberal aristocrat. He had joined the Third Estate and was not against the monarchy, but wanted to reconcile it with the Revolution. He also wanted to be a minister and was not immune to corruption. On the advice of Mercy, Marie Antoinette opened secret negotiations with him and both agreed to meet privately at the ] on 3 July 1790, where the royal family was allowed to spend the summer, free of the radical elements who watched their every move in Paris.{{sfnm|Castelot|1962|1p=334|Lever|1991|2pp=528–530}} At the meeting, Mirabeau was much impressed by the queen, and remarked in a letter to ], ], that she was the only person the King had by him: ''La Reine est le seul homme que le Roi ait auprès de Lui.''<ref>''Mémoires de Mirabeau'', tome VII, p. 342.</ref> An agreement was reached turning Mirabeau into one of her political allies: Marie Antoinette promised to pay him 6000 ] per month and one million if he succeeded in his mission to restore the King's authority.{{sfn|Lever|1991|pp=524–527}} | |||
| The only time the royal couple returned to Paris in that period was on 14 July to attend the '']'', an official ceremony held at the ] in commemoration of the fall of the Bastille one year earlier. At least 300,000 persons participated from all over France, including 18,000 National Guards, with ], bishop of ], celebrating a mass at the ''autel de la Patrie'' ("altar of the fatherland"). The King was greeted at the event with loud cheers of "Long live the King!", especially when he took the oath to protect the nation and to enforce the laws voted by the Constitutional Assembly. There were even cheers for the Queen, particularly when she presented the dauphin to the public.{{sfnm|Fraser|2001|1pp=314–316|Castelot|1962|2p=335}} | |||
| Marie Antoinette at that period of time had in general very good relations with her husband, who was passing through a depressive phase and who was letting her make all the major political and personnel decisions affecting their lives. Marie Antoinette's priority in the spring of 1791 was to escape her captivity but with her family; she refused to be separated from her children and especially from her husband. Even Fersen could not convince her to leave without the king; the queen wanted the king to come with her both because she loved the king, the father of her children, and because she was aware that without the king, she would lose all her political powers. Marie Antoinette asked and ordered Fersen and Breteuil (who represented her in the courts of Europe) to prepare an escape plan while she continued her negotiations with some moderate leaders of the French Revolution.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp321-325}}</ref> | |||
| Mirabeau sincerely wanted to reconcile the Queen with the people, and she was happy to see him restoring much of the King's powers, such as his authority over foreign policy, and the right to declare war. Over the objections of Lafayette and his allies, the King was given a suspensive veto allowing him to veto any laws for a period of four years. With time, Mirabeau would support the Queen, even more, going as far as to suggest that Louis XVI "adjourn" to ] or ].<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=313}}</ref> This leverage with the Assembly ended with the death of Mirabeau in April 1791, despite the attempt of several moderate leaders of the Revolution to contact the queen to establish some basis of cooperation with her. | |||
| ==1791–1792: The Radicalization of the Revolution after Varennes== | |||
| ===Civil Constitution of the Clergy=== | |||
| ] | |||
| In March 1791 ] had condemned the ], reluctantly signed by Louis XVI, which reduced the number of bishops from 132 to 93, imposed the election of bishops and all members of the clergy by departmental or district assemblies of electors, and reduced the pope's authority over the Church. Religion played an important role in the life of Marie Antoinette and Louis XVI, both raised in the Roman Catholic faith. The Queen's political ideas and her belief in the absolute power of monarchs were based on France's long-established tradition of the ].<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Zevin |first=Alexander |date=Spring 2007 |title=Marie Antoinette and The Ghosts of the French Revolution |journal=Cineaste |volume=32 |issue=2 |pages=32–34 |via=Academic Search Ultimate}}</ref> | |||
| During this time, there were many plots designed to help members of the royal family escape. The queen rejected several because she would not leave without the king. Other opportunities to rescue the family were ultimately frittered away by the indecisive king. Once the king finally did commit to a plan, his indecision played an important role in its poor execution and ultimate failure. In an ] to the ] stronghold of ] planned by ] and the ], some members of the royal family were to pose as the servants of a wealthy Russian baroness. Initially, the queen rejected the plan because it required her to leave with only her son, as she wished the rest of the royal family to accompany her. The king wasted time deciding upon which members of the family should be included in the venture, what the departure date should be, and the exact path of the route to be used. After many delays, the escape ultimately occurred on 21 June 1791, but the entire family was captured twenty-four hours later at ] and taken back to Paris within a week. The escape attempt destroyed much of the remaining support of the populace for the King<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=325–348}}</ref> | |||
| On 18 April, as the royal family prepared to leave for Saint-Cloud to attend Easter mass celebrated by a refractory priest, a crowd, soon joined by the National Guard (disobeying Lafayette's orders), prevented their departure from Paris, prompting Marie Antoinette to declare to Lafayette that she and her family were no longer free. This incident fortified her in her determination to leave Paris for personal and political reasons, not alone, but with her family. Even the King, who had been hesitant, accepted his wife's decision to flee with the help of foreign powers and counter-revolutionary forces.{{sfnm|Fraser|2001|1pp=321–323|Lever|1991|2pp=542–552|Castelot|1962|3pp=336–339}} Fersen and Breteuil, who represented her in the courts of Europe, were put in charge of the escape plan, while Marie Antoinette continued her negotiations with some of the moderate leaders of the French Revolution.{{sfnm|Fraser|2001|1pp=321–325|Castelot|1962|2pp=340–341}} | |||
| When the queen was captured with her family, the assembly sent three representatives to escort the royal family back to Paris. Marie Antoinette was humiliated by the people as never before; she was beaten and pushed by the crowds; people spat on her and her hands were put forcefully behind her back under the excuse of escorting her. ], the representative of the moderate party in the constitutional assembly, protected the Queen from the crowds at the peril of his own life. Even ], the representative of the Girondin radical republican party of ], took pity on the royal family. Marie Antoinette was brought safely to Paris; in addition, thanks to Barnave, she was not brought to trial and publicly exonerated of any crimes in relation with her attempt of escape. | |||
| ==Flight, arrest at Varennes and return to Paris (21–25 June 1791)== | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Main|Flight to Varennes}} | |||
| ] on the night of 21–22 June 1791, by ], 1854]] | |||
| There had been several plots designed to help the royal family escape, which the Queen had rejected because she would not leave without the King, or which had ceased to be viable because of the King's indecision. Once Louis XVI finally did commit to a plan, its poor execution was the cause of its failure. In an elaborate attempt known as the Flight to Varennes to reach the ] stronghold of ], some members of the royal family were to pose as the servants of an imaginary "Mme de Korff", a wealthy Russian baroness, a role played by ], governess of the royal children. | |||
| Using her connection with the moderate leader Barnave, Marie Antoinette played a leading but indirect role in the establishment of the ]. In its details, the constitution of 1791 was a compromise between the ideas of the Old Regime and the ideals of the French Revolution. It was not directed against the king but certainly against the old nobility. This constitution called for the establishment of a constitutional monarchy where the king was given important but not full powers. The king was given substantial powers according to the articles of the Constitution. Executive power was under the control of the king, who was also the head the army, in charge of foreign policy and chose ministers. While the king could not declare war, the new Legislative Assembly, which replaced the previous Constituent Assembly on 1 October, could go to war only if requested to do so by the king. The king was also considered to have immunity for actions he might take as a monarch, but this did not extend to other members of his family. An English visitor in the Tuileries gardens would witness two soldiers observing and guarding the queen keeping their hats on in her presence while singing disgusting songs, on the grounds that there was no mention of her in the Constitution. Finally, the king was given the right to veto any law for four years.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=355–356}}</ref> The King, who was considered the head of state, was given a budget of 25 millions livres every year in order to allow him to pay the functions of his court. | |||
| ] | |||
| As her letters show, the queen was incompletely sincere in this cooperation with the moderate leaders of the French Revolution, which ultimately ended any chance to establish a moderate government in France.,<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=353–354}}</ref> as it led to a further decline in the popularity of both the king and queen. The view that the unpopular queen was controlling the king further degraded their standing with the people. The ] Party successfully exploited the failed escape to advance its radical agenda. Its members called for the end to any type of monarchy in France.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=350–352}}</ref> | |||
| After many delays, the escape was ultimately attempted on 21 June 1791, but the entire family was arrested less than 24 hours later at ] and taken back to Paris within a week. The escape attempt destroyed much of the remaining support of the population for the King.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=325–48}}</ref>{{sfn|Lever|1991|pp=555–568}} | |||
| The constitution called for a moderate system of government. Barnave, who believed in the sincerity of the queen, took great political risks in the hope of producing a stable social and political structure. Barnave established a system of voting that was based on the middle-class vote. In addition, the civil constitution of the clergy, which greatly displeased Marie Antoinette because it created a national church outside the influence of the Papacy, was not considered a constitutional act. Barnave was able to secure a moderate majority that was ready to work with the queen in spite of her unpopularity. This situation lasted a few months until the spring of 1792.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp357-358}}</ref> | |||
| Upon learning of the capture of the royal family, the ] sent three representatives, ], ] and ] to Varennes to escort Marie Antoinette and her family back to Paris. On the way to the capital they were jeered and insulted by the people as never before. The prestige of the French monarchy had never been at such a low level. During the trip, Barnave, the representative of the moderate party in the Assembly, protected Marie Antoinette from the crowds, and even ] took pity on the royal family. Brought safely back to Paris, they were met with total silence by the crowd. Thanks to Barnave, the royal couple was not brought to trial and was publicly ] of any crime in relation with the attempted escape.{{sfnm|Lever|1991|1pp=569–575|Castelot|1962|2pp=385–398}} | |||
| During these years at the Tuileries, the queen was a prisoner guarded night and day by many soldiers who never left her for a moment, not even in her bedroom and kept her a lot of times under great restrain stopping her completely from any physical activity or movement. Many of these jailers were radicals who openly disrespected her, smoking in her face, denying her any privacy and maximally restricting her movements. Marie Antoinette was never allowed to visit her palace of Saint Cloud and was required to seek her guards' permission to see her children or husband, who sometimes refused her request. If permission was granted to leave her rooms, she was escorted by soldiers who surrounded her on all sides, restraining her completely and who were present in all her meetings. This occurred despite the fact that she and her husband were still legally ruling sovereigns. However, over the course of her strict captivity, in poor spirits and with restrictions on her social life, the health of Marie Antoinette began to deteriorate rapidly. The hair of the Queen turned at least partially white,she began to lose a lot of blood but she remained a very big charismatic woman who was able to charm even some of her enemies. She developed problems in at least one of her legs, necessitating assistance when walking and further reducing her activities.<ref>{{Harvnb|Lettres de Marie Antoinette vol 2|1895|pp=364–378|}}</ref> | |||
| Marie Antoinette's first Lady of the Bedchamber, ], wrote about what happened to the Queen's hair on the night of 21–22 June, "...in a single night, it had turned white as that of a seventy-year-old woman." (''En une seule nuit ils étaient devenus blancs comme ceux d'une femme de soixante-dix ans.'')<ref>''Mémoires de Madame Campan, première femme de chambre de Marie-Antoinette'', Le Temps retrouvé, Mercure de France, Paris, 1988, p. 272, {{ISBN|2-7152-1566-5}}</ref> | |||
| In February 1792, Ferson was able to see the queen a final time in spite of the strong measures of restriction around the prisoner queen. Beyond doubt, Fersen bribed some of the guards, but was not able to pass more than a short period of time in the palace where the queen was effectively imprisoned. Marie Antoinette would acknowledge that the security measures were so strong that it was impossible to escape with barred windows in her rooms and an escort of soldiers following her day and night dictating her every move. | |||
| ==Radicalization of the Revolution after Varennes (1791–92)== | |||
| Barnave advised the queen to recall the Austrian ambassador Count Mercy, who had played such a huge part in her life, in addition to the Princess de Lamballe. Count Mercy, who was appointed in a high position in the Austrian Empire, refused to return for a variety of reasons. This saddened the queen greatly, leaving the impression that she was left to her demise, especially that Mercy was a paternal figure for her sent by her mother to take care of her since her coming to France. She was more lucky with the Princess de Lamballe, who returned and filled a great void in the affective and social life of the captive Queen. As for her social life, it was difficult for the queen, effectively a prisoner guarded night and day, to have an effective social life. Wherever Marie Antoinette went, there was a soldier before her and one after her; it was in the night that she was the more controlled, as she was obliged to keep the door of her bedroom open so that she can be seen by her guards, who did not always respect her and invaded frequently her privacy.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=360–363}}</ref> | |||
| ], damaged with a pike by a revolutionary.]] | |||
| After their return from Varennes and until the ] on 10 August 1792, the Queen, her family and entourage were held under tight surveillance by the National Guard in the Tuileries, where the royal couple was guarded night and day. Four guards accompanied the Queen wherever she went, and her bedroom door had to be left open at night. Her health also began to deteriorate, thus further reducing her physical activities.<ref>{{cite book |title=Lettres de Marie Antoinette |author=Le Marquis de Beaucourt |date=1895 |volume=ii |pages=364–78}}</ref>{{sfn|Lever|1991|pp=576–580}} | |||
| Marie Antoinette hoped that the armies sent by the rulers of Europe would be able to crush the Revolution even if the cost was the blood of her own people. The queen particularly counted on the support of her Austrian family. After her brother Joseph who was attached to her died in 1790, Léopold her brother who was cool towards Marie Antoinette was ready to support the queen but to only a limited degree. Her nephew Francis, who succeeded his father Leopold in 1792, was a very conservative ruler who was ready to support Marie Antoinette because he hated and feared the French Revolution. When the queen asked him to declare war on France, he accepted out of monarchical solidarity and because he wanted to establish Austrian influence over Western Europe. To be fair to Marie Antoinette, she was not the only person who wanted war, as many radical leaders of the French Revolution also wanted war for their own reasons. The Jacobin party itself was split into two factions; the radicals under the leadership of Robespierre did not want to participate in the war, fearing a union of the Monarchies against them. The Moderate ] or ], as they were called under the leadership of ] and ], were for the war because they wanted to spread the ideals of the French Revolution all over Europe and they also believed that a war would unite the French People against their internal and external enemies. While the role of Madame Roland was the most important as de facto-leader of the Girondins, ], the leader of the foreign comity in the National Assembly, played a key role in the drafting of the war resolution. Yet according to the simple facts and description of events, the most important actor remained the queen because according to the constitution, only the king could propose to the Assembly to declare war. The facts speak for themselves: not only did the queen push Austria to declare war as we know from her letters, she also pushed her husband to propose the declaration of war to the National Assembly.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=364–365}}</ref> | |||
| ] : ''Madame Veto...'']] | |||
| However, as the result of Leopold's aggressive tendencies, and those of his son ] on the queen's behalf, who succeeded him in March, it was that France declared war on Austria on 20 April 1792. This caused the queen to be viewed as an enemy, even though she was personally against Austrian claims on French lands. That summer, the situation was compounded by multiple defeats of French armies by the Austrians, in part because Marie Antoinette betrayed her country's military secrets<ref>{{Harvnb|2001|pp365-368}}</ref> to the foreign powers. In addition, the king on the orders of the queen vetoed several measures that would have restricted his power even further. During this time, due to his political activities, Louis received the nickname "Monsieur Veto" and the name "Madame Veto" was likewise subsequently bequeathed on Marie Antoinette.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=365–368}}</ref> These names were then prominently featured in different contexts, including ]. | |||
| On 17 July 1791, with the support of Barnave and his friends, Lafayette's ''Garde Nationale'' ] on the crowd that had assembled on the ] to sign a petition demanding the ] of the King. The estimated number of those killed varies between 12 and 50. Lafayette's reputation never recovered from the event and, on 8 October, he resigned as commander of the National Guard. Their enmity continuing, Marie Antoinette played a decisive role in defeating him in his aims to become the mayor of Paris in November 1791.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=350, 360–71}}</ref> | |||
| ==1792–1793: Royal Deposition, "Widow Capet", trial, and execution== | |||
| Up until the deposition of the royal family in August 1792 and his own fall from grace, Barnave remained the most important advisor and supporter of the queen inside France. Marie Antoinette was ready to work with Barnave as long as he was ready to follow her orders, which Barnave did to a large extent and over a long period of time. Goaded by the queen, Barnave convinced Lafayette to use force against the radical elements of the French Revolution. As a result, tens of thousands of political opponents of Marie Antoinette were either killed, exiled or sent to prison. Rather than cooperating with Lafayette, Marie Antoinette refused to be helped by him and played a decisive role in defeating him in his aims to become the mayor of Paris in October 1791.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=350,360–371}}</ref> | |||
| As her correspondence shows, while Barnave was taking great political risks in the belief that the Queen was his political ally and had managed, despite her unpopularity, to secure a moderate majority ready to work with her, Marie Antoinette was not considered sincere in her cooperation with the moderate leaders of the French Revolution, which ultimately ended any chance to establish a moderate government.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=353–54}}</ref> Moreover, the view that the unpopular queen was controlling the King further degraded the royal couple's standing with the people, which the ] successfully exploited after their return from Varennes to advance their radical agenda to abolish the monarchy.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=350–52}}</ref> This situation lasted until the spring of 1792.{{sfnm|Fraser|2001|1pp=357–358|Castelot|1962|2pp=408–409}} | |||
| Barnave and the moderates made up about 260 lawmakers in the new ]; the radicals numbered around 136, and the rest (around 350) were in the middle. At first, the majority was with Barnave, but the queen's policy led to the radicalization of the assembly and the moderates lost control of the legislative process. The moderate government collapsed in April 1792 and a radical ministry headed by the Girondins was formed. Worse than that, the assembly passed a series of laws concerning the Church, the aristocracy and the formation of new national guard units which were vetoed by the king on the orders of the queen. The radical Girondin government who was formed in April 1792 controlled the legislative assembly with 330 members, while Marie Antoinette and Barnave were not supported by more than 120 members.The two strongest members of that government were ],the husband of ], who was minister of interior, and General ], the minister of foreign affairs. Dumouriez sympathized with the royal couple and wanted to save them. However, he was rebuffed by the queen, who wanted to crush the Revolution by counting on the support of foreign powers.<ref>{{Harvnb|Castelot|1957|pp=295–298}}</ref> | |||
| Marie Antoinette continued to hope that the military coalition of European kingdoms would succeed in crushing the Revolution. She counted most on the support of her Austrian family. After the death of her brother Joseph II in 1790, his successor and younger brother, ],<ref>{{Cite web|title=Marie Antoinette as queen of France|url=https://www.habsburger.net/en/chapter/marie-antoinette-queen-france|access-date=15 December 2020|website=Die Welt der Habsburger|language=en}}</ref> was willing to support her to a limited degree.<ref>{{Cite web |last=Mark |first=Harrison W. |date=2022-09-09 |title=Declaration of Pillnitz |url=https://www.worldhistory.org/Declaration_of_Pillnitz/ |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20240404071650/https://www.worldhistory.org/Declaration_of_Pillnitz/ |archive-date=2024-04-04 |access-date=2024-06-01 |website=World History Encyclopedia |language=en}}</ref> It was her hope that the threat of Austria's advancing military would deter further escalation of revolutionary violence. In a letter to her brother, penned in September 1791, Marie Antoinette expressed how she expected the revolution to react: "...it will be effected by the approach of the war and not by the war itself. The King, his powers restored, will be entrusted with negotiations with the foreign powers, and the princes will return, in the general tranquillity, to reassume their ranks at his court and in the nation."<ref>{{cite web|title=Marie Antoinette's View of the Revolution (8 September 1791)|url=https://revolution.chnm.org/d/331|access-date=21 January 2024|website=LIBERTY, EQUALITY, FRATERNITY: EXPLORING THE FRENCH REVOLUTION|date=8 September 1791 |language=en}}</ref> In the same letter, she wrote that the fall of France's monarchy and the subsequent rise of revolutionary principles would be "destructive to all governments." | |||
| Marie Antoinette's actions in refusing to collaborate with the ] radical ministry who were in power between April and June 1792 led the Girondins to denounce the treason of the Austrian comity, a direct allusion to the Queen. After Madame Roland sent a letter to the King denouncing the Queen's role in these matters, the King sacked the Government on the order of Marie Antoinette, losing his majority in the Assembly. Dumouriez resigned and refused a post in any new government. At this point, most of the French people and political parties turned against the royal authority. Marie Antoinette even collaborated with ] using the ], the leader of the constitutional guard and the lover of Madame du Barry, as an intermediate to fund and prepare a counterrevolution in the ]. This counterrevolution would interrupt in 1793, causing hundred of thousands of deaths and bring the Revolution to a quick end in 1799. In addition, Marie Antoinette pushed the king to refuse the new laws voted by the Legislative Assembly in 1792.<ref>{{Harvnb|Castelot|1957|pp=299–305}}</ref> and continued her plots with the foreign powers by pushing them to issue the ] in August 1791, which threatened invasion of France. This led in turn to a French declaration of war in April 1792 and the ] and the popular revolution of August 1792 which ended the monarchy.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp371-373}}</ref> | |||
| Upon Leopold's death in 1792, his son, ], a conservative ruler, was ready to support the cause of the French royal couple more vigorously because he feared the consequences of the French Revolution and its ideas for the monarchies of Europe, particularly, for Austria's influence in the continent.{{Citation needed|date=August 2016}} | |||
| ] on 20 June 1792.]] | |||
| Barnave had advised the Queen to call back Mercy, who had played such an important role in her life before the Revolution, but Mercy had been appointed to another foreign diplomatic position{{Where|date=August 2016}} and could not return to France. At the end of 1791, ignoring the danger she faced, the ''Princesse de Lamballe'', who was in London, returned to the Tuileries. As for Fersen, despite the strong restrictions imposed on the Queen, he was able to see her a final time in February 1792.{{sfn|Lever|1991|pp=599–601}} | |||
| On 20 June, "a mob of terrifying aspect" broke in to the Tuileries, made the King wear the '']'' (red Phrygian cap) to show his loyalty to France, insulted Marie Antoinette, accused her of betraying France and threatened her life. In consequence, the queen ordered Fersen first to push foreign powers to activate their invasion of France and second to issue a manifesto in which the foreign powers threatened to destroy Paris if anything happened to the queen and her family. This manifesto triggered the events of 10 August <ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=368,375–378}}</ref> when an armed mob, on the verge of forcing its way into the Tuileries Palace, forced the King and the royal family to seek refuge at the Legislative Assembly. An hour and a half later, the palace was invaded by the mob, who massacred the ]s.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=373–379}}</ref> On 13 August, the royal family was imprisoned in the tower of the ] in the ] under conditions considerably harsher than their previous confinement in the Tuileries.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=382–386}}</ref> | |||
| ==Events leading to the abolition of the monarchy on 10 August 1792== | |||
| A week later, many of the royal family's attendants, among them the '']'', were taken in for interrogation by the ]. Transferred to the ''La Force'' prison, the ''princesse de Lamballe'' was a victim of the ], killed on 3 September. Her head was affixed on a pike and marched through the city; Marie Antoinette did not see this but fainted upon learning of it.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=389}}</ref> | |||
| Leopold's and Francis II's strong action on behalf of Marie Antoinette led to France's declaration of war on Austria on 20 April 1792. This resulted in the Queen being viewed as an enemy, although she was personally against Austrian claims to French territories on European soil. That summer, the situation was compounded by multiple defeats of the ] by the Austrians, in part because Marie Antoinette passed on military secrets to them.<ref name="Fraser365–68">{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=365–68}}</ref> In addition, at the insistence of his wife, Louis XVI vetoed several measures that would have further restricted his power, earning the royal couple the nicknames "Monsieur Veto" and "Madame Veto",<ref name="Fraser365–68" />{{sfn|Lever|1991|pp=607–609}} nicknames then prominently featured in different contexts, including La ]. | |||
| Barnave remained the most important advisor and supporter of the Queen, who was willing to work with him as long as he met her demands, which he did to a large extent. Barnave and the moderates comprised about 260 lawmakers in the new ]; the radicals numbered around 136, and the rest around 350. Initially, the majority was with Barnave, but the Queen's policies led to the radicalization of the Assembly and the moderates lost control of the legislative process. The moderate government collapsed in April 1792 to be replaced by a radical majority headed by the '']''. The Assembly then passed a series of laws concerning the Church, the aristocracy and the formation of new National Guard units; all were vetoed by Louis XVI. While Barnave's faction had dropped to 120 members, the new ''Girondin'' majority controlled the legislative assembly with 330 members. The two strongest members of that government were ], who was minister of interior, and General ], the minister of foreign affairs. Dumouriez sympathized with the royal couple and wanted to save them but he was rebuffed by the Queen.{{sfnm|Castelot|1962|1pp=415–416|Lever|1991|2pp=591–592}} | |||
| ] | |||
| Marie Antoinette's actions in refusing to collaborate with the ''Girondins'', in power between April and June 1792, led them to denounce the treason of the Austrian comity, a direct allusion to the Queen. After ] sent a letter to the King denouncing the Queen's role in these matters, urged by the Queen, Louis XVI disbanded{{citation needed|date=July 2015}} the government, thus losing his majority in the Assembly. Dumouriez resigned and refused a post in any new government. At this point, the tide against royal authority intensified in the population and political parties, while Marie Antoinette encouraged the King to veto the new laws voted by the Legislative Assembly in 1792.{{sfn|Castelot|1962|p=418}} In August 1791, the ] threatened an invasion of France. This led in turn to a French declaration of war in April 1792, which led to the ] and to the events of August 1792, which ended the monarchy.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=371–73}}</ref> | |||
| On 21 September, the fall of the monarchy was officially declared, and the ] became the legal authority of France. The royal family was re-styled as the non-royal "]". Preparations began for the trial of the king in a court of law.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=392}}</ref> | |||
| ], facing the mob that had broken into the ] on 20 June 1792: ] ]] | |||
| Charged with undermining the ], Louis was separated from his family and tried in December. He was found guilty by the Convention, led by the Jacobins who rejected the idea of keeping him as a hostage. A month later, he was condemned to death by guillotine and executed on 21 January 1793.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=395–399}}</ref> | |||
| On 20 June 1792, "a mob of terrifying aspect" broke into the Tuileries, made the King wear the '']'' (red Phrygian cap) to show his loyalty to the Revolution, insulted Marie Antoinette, accusing her of betraying France, and threatened her life. In consequence, the Queen asked Fersen to urge the foreign powers to carry out their plans to invade France and to issue a manifesto in which they threatened to destroy Paris if anything happened to the royal family. The ], issued on 25 July 1792, triggered the ]<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=368, 375–78}}</ref> when the approach of an armed mob on its way to the Tuileries Palace forced the royal family to seek refuge at the Legislative Assembly. Ninety minutes later, the palace was invaded by the mob, who massacred the ].{{sfnm|Fraser|2001|1pp=373–379|Castelot|1962|2pp=428–435}} On 13 August the royal family was imprisoned in the tower of the ] in the ] under conditions considerably harsher than those of their previous confinement in the Tuileries.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=382–86}}</ref> | |||
| ]"—French engraving.]] | |||
| A week later, several of the royal family's attendants, among them the ''Princesse de Lamballe'', were taken for interrogation by the ]. Transferred to the ], after a rapid judgment, ] was ] on 3 September. Her head was affixed on a pike and paraded through the city to the Temple for the Queen to see. Marie Antoinette was prevented from seeing it, but fainted upon learning of it.{{sfnm|Fraser|2001|1p=389|Castelot|1962|2pp=442–446}} | |||
| The queen, now called the "Widow Capet", plunged into deep mourning and refused to eat or do any exercise. She proclaimed her son as ] hoping to rule France in his name as Regent; the ], in exile, recognised his nephew as the new King of France. The royalists, especially those preparing the insurrection in ] and the clergy, supported Marie Antoinette, who wished to used this support in order to free herself from prison and subsequently crush the revolution, counting on a civil war inside France and the pressure of foreign armies and powers to achieve this. The queen could count on the sympathy of many conservative factions and social-religious groups who were turning against the Revolution, and on many wealthy figures who were ready to corrupt republican officials in order to facilitate the escape of the queen, which was a necessary step in order to form a new legal political entity.<ref>{{Harvnb|Castelot|1957|pp=305–315}}</ref> While all this plots and activity failed in their attempts to change the fate of the prisoner queen and her family nevertheless they formed a network of royal activists strong enough to corrupt republican officials, to launch the war in ] in the name of the son of Marie Antoinette Louis seventeen and to defend the Catholic Religion by giving a true and strong popular base for the royalists and other conservatives whose activity in the long run will undermine the Revolution and oblige ] to restore the ] in France and Europe.<ref>{{Harvnb|Gobry|1989|pp=461–464}}</ref> Marie Antoinette was treated badly by her jailors who smoked in her face and insulted her. She was imprisoned in a dark cell with few luxuries except her books and high heels. The queen had little social contact with no privacy, she was allowed to see her family on a very limited basis. Her health deteriorated through inactivity and forced restraint, she found difficulty in walking and developed ] and possibly ], and she suffered frequent hemorrhages.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=404–405, 408}}</ref> Marie Antoinette wanted to escape at all cost, the ] plot which consisted in the queen putting the cloth of one of her guards because of her very big size failed due to the massive presence of guards, to the great desperation and sadness of the queen as we know from her letters.<ref>{{Harvnb|Thelast days of Marie Antoinette and Louis sixteen|Rupert Furneaux|1971|pp=120–130}}</ref> | |||
| On 21 September 1792, France was declared a republic, the monarchy was abolished and the ] became the governing body of the ]. The royal family name was downgraded to the non-royal "]". Preparations began for the trial of the former king in a court of law.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=392}}</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| ===Louis XVI's trial and execution=== | |||
| After Louis' death, Marie Antoinette's fate became a central question of the National Convention. While some continually advocated for her death, others proposed exchanging her for French prisoners of war or for a ransom from the Holy Roman Emperor. ] advocated exile to America.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=398, 408}}</ref> Starting in April, however, a ] was formed, and men such as ] were beginning to call for Antoinette's trial; by the end of May, the ] had been chased from power and arrested.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=411–412}}</ref> Other calls were made to "retrain" the Dauphin, to make him more pliant to revolutionary ideas. To carry this out, the eight-year-old Louis Charles was separated from Antoinette on 3 July and given to the care of a cobbler named Antoine Simon.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=412–414}}</ref> On 1 August, following various plots for her escape, Marie Antoinette was taken restrained with her hands behind her back out of the tower under a lot of insults, she was pushed and her head was injured. The queen was moved to an isolated underground cell in the ] as Prisoner No. 280. This period of time was the most difficult period of her captivity, Marie Antoinette was always attended by guards who restrained her, did not allow her any privacy and treated her very badly; an attempt to escape was foiled due to the inability to corrupt all the guards, to fear and also to the large numbers of iron doors which totally cut the unground cell where Marie Antoinette was imprisoned from the rest of the prison.<ref>{{Harvnb|Furneaux|19711|pp=139–142}}</ref> There she was attended by ] and at at least once received a Catholic priest.<ref>G. Lenotre: ''The Last Days of Marie Antoinette'', 1907.</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=416–420}}</ref> | |||
| {{main|Execution of Louis XVI}} | |||
| Charged with treason against the French Republic, Louis XVI was separated from his family and ] in December. He was found guilty by the Convention, led by the Jacobins who rejected the idea of keeping him as a hostage. On 15 January 1793, by a majority of six votes, he was condemned to death by ] and executed on 21 January 1793.{{sfnm|Fraser|2001|1pp=395–399|Castelot|1962|2pp=447–453}} | |||
| ==Marie Antoinette in the Temple== | |||
| ] | |||
| The former queen, now called "Widow Capet", plunged into deep mourning. She still hoped her son ], whom the exiled ], Louis XVI's brother, had recognized as Louis XVI's successor, would one day rule France. The royalists and the ], including those preparing the insurrection in ], supported Marie Antoinette and the return to the monarchy. Throughout her imprisonment and up to her execution, Marie Antoinette could count on the sympathy of conservative factions and social-religious groups which had turned against the Revolution, and also on wealthy individuals ready to bribe republican officials to facilitate her escape.{{sfn|Castelot|1962|pp=453–457}} These plots all failed. While imprisoned in the Tower of the Temple, Marie Antoinette, her children and ] were insulted, some of the guards going as far as blowing smoke in the former queen's face. Strict security measures were taken to assure that Marie Antoinette was not able to communicate with the outside world. Despite these measures, several of her guards were open to bribery and a line of communication was kept with the outside world.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Marie Antoinette: Last Queen of France|url=https://janeausten.co.uk/blogs/society-figures/marie-antoinette-last-queen-of-france|access-date=2021-12-13|website=Jane Austen Centre and the Jane Austen Online Gift Shop|language=en|archive-date=13 December 2021|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211213021603/https://janeausten.co.uk/blogs/society-figures/marie-antoinette-last-queen-of-france|url-status=dead}}</ref> | |||
| After Louis's execution, Marie Antoinette's fate became a central question of the National Convention. While some advocated her death, others proposed exchanging her for French prisoners of war or for a ransom from the Holy Roman Emperor. ] advocated exile to America.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=398, 408}}</ref> In April 1793, during the ], a ], dominated by ], was formed, and men such as ] began to call for Marie Antoinette's trial. By the end of May, the ''Girondins'' had been chased from power.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=411–12}}</ref> Calls were also made to "retrain" the eight-year-old Louis XVII, to make him pliant to revolutionary ideas. To carry this out, Louis Charles was separated from his mother on 3 July after a struggle during which his mother fought in vain to retain her son, who was handed over to ], a cobbler and representative of the ]. Until her removal from the Temple, Marie Antoinette spent hours trying to catch a glimpse of her son, who, within weeks, had been made to turn against her, accusing his mother of wrongdoing.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=412–14}}</ref> | |||
| She was finally tried by the Revolutionary Tribunal on 14 October. Some historians believe the outcome of the trial had been decided in advance by the Committee of Public Safety around the time the Carnation Plot was uncovered.<ref>{{Harvnb|Castelot|1957|pp=425–435}}</ref> She was given less than one day to prepare her defence. Among the accusations, many previously published in the ''libelles'', were orchestrating orgies in Versailles, sending millions of livres of treasury money to Austria, plotting to kill the Duke of Orléans, orchestrating the massacre of the Swiss Guards in 1792, declaring her son to be the new King of France, and - by her son Louis Charles himself (pushed by radical elements who controlled him) - of sexually abusing him which draw an emotional response from Marie Antoinette strongly rebuking that charge and calling on all mothers to support her which brought her a lot of comfort from some of her enemies even on a temporary basis. .<ref>{{Harvnb|Castelot|1957|pp=380–385}}</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=429–435}}</ref> She refused to respond to this charge. | |||
| ===Conciergerie=== | |||
| ] and Queen Marie Antoinette, sculptures by ] and ] in the ].]] | |||
| On the night of 1 August, at 1:00 in the morning, Marie Antoinette was transferred from the Temple to an isolated cell in the ] as 'Prisoner nº 280'. Leaving the Tower she bumped her head against the ] of a door, which prompted one of her guards to ask her if she was hurt, to which she answered, "No! Nothing now can hurt me."<ref>Funck-Brentano, Frantz: ''Les Derniers jours de Marie-Antoinette'', Flammarion, Paris, 1933</ref> This was the most difficult period of her captivity. She was under constant surveillance with no privacy. The "]" ({{lang|fr|Le complot de l'œillet}}), an attempt to help her escape at the end of August, was foiled due to the inability to corrupt all the guards.<ref>{{Harvnb|Furneaux|1971|pp=139–42}}</ref> She was attended by ], who took care of her as much as she could.{{sfn|Fraser|2001|p=437}} At least once she received a visit by a Catholic priest.<ref>G. Lenotre: ''The Last Days of Marie Antoinette'', 1907.</ref><ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=416–20}}</ref> | |||
| ==Trial and execution (14–16 October 1793)== | |||
| After two days she was declared guilty of treason to her great sadness and surprise because she expected life imprisonment .<ref>{{Harvnb|Furneaus|1971|pp=150–154}}</ref> In her cell she composed a letter to her sister-in-law ], affirming her clear conscience, her Catholic faith and her feelings for her children. The letter did not reach Élisabeth.<ref>{{citation|url=http://teaattrianon.blogspot.com/2007/05/last-letter-of-marie-antoinette.html|title=Last Letter of Marie-Antoinette |date=26 May 2007|work=Tea at Trianon}}</ref> Later that same day, Marie Antoinette was forced to undress before her guards and clothed in a plain white dress, her hair shorn. Her hands bound painfully behind her back causing her a lot of pains and tears and leashed on a rope (as shown in the last drawing of her from life, by the painter ] ), she was driven through Paris to the place of execution in an open cart through crowds which were partly jeering calling her "chienne"(meaning dog in that language), partly silent.<ref>{{Harvnb|Furneaus|1971|pp==155–156|}}</ref> Despite this humiliation, the people of Paris saw on that day a very large bounded woman who was leashed, who looked very sad and under great pains but also a person who was able to maintain partially her composure. While many described her as arrogant, others granted her their respects.<ref>{{Harvnb|Castelot|1957|pp=395–405,435–445}}</ref> For her final confession she was given a priest recognized not by Rome but by the local constitutional church in France; in this and other matters, she was treated more harshly than the king had been.<ref>{{Harvnb|Castelot|1957|pp=395–405}}</ref> | |||
| ], 16 October 1793]] | |||
| ] on 16 October 1793: at left, Sanson, the executioner, showing Marie Antoinette's head to the people. Anonymous, 1793]] | |||
| Marie Antoinette was tried by the ] on 14 October 1793. Some historians believe the outcome of the trial had been decided in advance by the ] around the time the Carnation Plot was uncovered.{{sfn|Castelot|1962|pp=496–500}} She and her lawyers were given less than one day to prepare her defense. Among the accusations, many previously published in the ], were: orchestrating orgies in Versailles, sending millions of livres of treasury money to Austria, planning the massacre of the National Guards in 1792,<ref>''Procès de Louis XVI, de Marie-Antoinette, de Marie-Elisabeth et de Philippe d'Orléans'', Recueil de pièces authentiques, Années 1792, 1793 et 1794, De Mat, imprimeur-libraire, Bruxelles, 1821, p. 473</ref> declaring her son to be the new king of France, and ], a charge made by her son Louis-Charles, pressured into doing so by the radical ] who controlled him. | |||
| This last accusation drew an emotional response from Marie Antoinette, who refused to respond to this charge, instead appealing to all mothers present in the room. Their reaction comforted her since these women were not otherwise sympathetic to her.{{sfnm|Castelot|1957|1pp=380–385|Fraser|2001|2pp=429–435}} Upon being pressed further by a juror to address the accusations of incest, the queen replied, "If I did not respond, it was because it would be against nature for a mother to reply to such an accusation. On this I appeal to all mothers who may be here." When a juror, ], told Robespierre of this over dinner, Robespierre broke his plate in anger, declaring "That imbecile Hébert!"<ref>{{cite book|last=Hardman|first=John|title=Marie-Antoinette: The Making of a French Queen|publisher=Yale University Press|year=2019|page=304}}</ref> | |||
| ], 16 October 1793)]] | |||
| ] | |||
| Early on 16 October, Marie Antoinette was declared guilty of the three main charges against her: depletion of the national treasury, conspiracy against the internal and external security of the State, and ] because of her intelligence activities in the interest of the enemy; the latter charge alone was enough to condemn her to death.<ref>''Le procès de Marie-Antoinette'', Ministère de la Justice, 17 October 2011, (French) {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20150921132933/http://www.justice.gouv.fr/histoire-et-patrimoine-10050/proces-historiques-10411/le-proces-de-marie-antoinette-22697.html|date=21 September 2015}}</ref> At worst, she and her lawyers had expected life imprisonment.<ref>{{Harvnb|Furneaux|1971|pp=150–54}}</ref> In the hours left to her, she composed a letter to her sister-in-law ], affirming her clear conscience, her Catholic faith, and her love and concern for her children. The letter did not reach Élisabeth.<ref>{{citation |author=Elena Maria Vidal |author-link=Elena Maria Vidal |url=http://teaattrianon.blogspot.com/2007/05/last-letter-of-marie-antoinette.html |title=Last Letter of Marie-Antoinette |date=26 May 2007 |work=Tea at Trianon}}</ref> Her will was part of the collection of papers of ] found under his bed and was published by ].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Zwx_FBzaUxEC&q=Courtois&pg=PA101|title=Papiers inédits trouvés chez Robespierre, Saint-Just, Payan, etc. supprimés ou omis par Courtois...|first1=Edme-Bonaventure|last1=Courtois|first2=Maximilien de|last2=Robespierre|date=31 January 2019|publisher=Baudoin|via=Google Books}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|title=Documents intéressant E.B. Courtois. In: Annales historiques de la Révolution française, 55e Année, No. 254 (Octobre–Décembre 1983), pp. 624–28|journal=Annales Historiques de la Révolution Française|volume=55|issue=254|pages=624–35|jstor = 41915129|last1 = Chevrier|first1 = M. -R|last2=Alexandre|first2=J.|last3=Laux|first3=Christian|last4=Godechot|first4=Jacques|last5=Ducoudray|first5=Emile|year=1983}}</ref> | |||
| She was guillotined at 12:15 p.m. on 16 October 1793, at the ''Place de la Révolution'' (present-day '']'').<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=440}}</ref><ref>, ].</ref> Her last words were "Pardon me, sir, I meant not to do it", to ] the executioner, whose foot she had accidentally stepped on after climbing the scaffold. Her body was thrown into an ] in the ], rue d'Anjou (which was closed the following year).{{citation needed|date = October 2013}} | |||
| Preparing for her execution, she had to change clothes in front of her guards. She wanted to wear a black dress but was forced to wear a plain white dress, white being the colour worn by widowed queens of France. Her hair was shorn, her hands bound painfully behind her back and she was put on a rope leash. Unlike her husband, who had been taken to his execution in a carriage (''carrosse''), she had to sit in an open cart (''charrette'') for the hour it took to convey her from the Conciergerie via the ] thoroughfare to reach the guillotine erected in the Place de la Révolution, the present-day ].<ref>{{Harvnb|Furneaux|1971|pp=155–56|}}</ref> She maintained her composure, despite the insults of the jeering crowd. A ] priest was assigned to hear her final confession. He sat by her in the cart, but she ignored him all the way to the scaffold as he had pledged his allegiance to the republic.{{sfnm|Castelot|1957|1pp=550–558|Lever|1991|2p=660}} | |||
| Her sister-in-law Élisabeth was executed in 1794 and her son died in prison in 1795. Her daughter returned to Austria in a prisoner exchange, married and died childless in 1851.<ref>{{citation|url=http://www.smithsonianmag.com/history-archaeology/biography/marieantoinette.html|title=Marie Antoinette |author=Richard Covington|date=November 2006|magazine=Smithsonian magazine}}</ref> | |||
| Marie Antoinette was executed by beheading by guillotine at 12:15pm on 16 October 1793 during the French Revolution.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|p=440}}</ref><ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20091101184818/http://archive.timesonline.co.uk/tol/viewArticle.arc?articleId=ARCHIVE-The_Times-1793-10-23-03-001&pageId=ARCHIVE-The_Times-1793-10-23-03&pageId=undefined |date=1 November 2009 }}, '']''.</ref> Her last words are recorded as, "Pardonnez-moi, monsieur. Je ne l'ai pas fait exprès" or "Pardon me, sir, I did not do it on purpose", after accidentally stepping on her executioner's shoe.<ref>{{cite web|url=https://thoughtcatalog.com/oliver-miller/2012/05/famous-last-words-2/|title=Famous Last Words|date=23 May 2012}}</ref> ] was employed to make a ] of her head.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.encyclopedia.com/topic/Marie_Tussaud.aspx|title=Marie Tussaud|website=encyclopedia.com|access-date=28 March 2016}}</ref> Her body was thrown into an ] in the ], located close by in rue d'Anjou. Because its capacity was exhausted the cemetery was closed the following year, on 25 March 1794.<ref>Ragon, Michel, ''L'espace de la mort, Essai sur l'architecture, la décoration et l'urbanisme funéraires'', Michel Albin, Paris, 1981, {{ISBN|978-2-226-22871-0}} {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221203145327/https://books.google.fr/books?id=a9ZY3Kv0jtYC&pg=PT125&lpg=PT125&dq=cimeti%C3%A8re+de+la+madeleine+ferm%C3%A9+en+1794&source=bl&ots=U55hqYOABk&sig=A-0nSU6aAWpd__C0Cu9pFaSQGlA&hl=fr&sa=X&ved=0CDYQ6AEwAmoVChMIvcHKqZ7dyAIVg1YaCh2zww8Z#v=onepage&q=cimeti%C3%A8re%20de%20la%20madeleine%20ferm%C3%A9%20en%201794&f=false|date=3 December 2022}}</ref> | |||
| Both Marie Antoinette's body and that of Louis XVI were exhumed on 18 January 1815, during the ], when the ''comte de Provence'' had become king ]. Christian burial of the royal remains took place three days later, on 21 January, in the necropolis of French kings at the ].<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=411, 447}}</ref>{{clear left}} | |||
| ===Foreign response=== | |||
| ==After death and legacy== | |||
| After her execution, Marie Antoinette became a symbol abroad, and a controversial figure of the French Revolution. Some used her as a scapegoat to blame for the events of the Revolution. ], writing in 1821, claimed that "Her inordinate gambling and dissipations, with those of the Count d'Artois, and others of her clique, had been a sensible item in the exhaustion of the treasury, which called into action the reforming hand of the nation; and her opposition to it, her inflexible perverseness, and dauntless spirit, led herself to the Guillotine," adding that "I have ever believed that, had there been no Queen, there would have been no revolution."<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.bartleby.com/400/prose/471.html |title=Passages from his autobiography |date=1854 |language=en |publisher=] |access-date=17 May 2021}}</ref> | |||
| Long after her death, Marie Antoinette remains a major historical figure linked with ] and the ] positions; and a major ] associated with high ], ] and a certain style of life based on luxury and ] appealing today to the social and ] elites; ],<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.chevroncars.com/learn/famous-people/marie-antoinette |title=Marie Antoinette Biography |publisher=Chevroncars.com |date= |accessdate=17 July 2011}}</ref> being the subject of several books, films and other forms of media. Most academics and scholars, have deemed her the quintessential representative of ], western ] and ] government in addition to being frivolous, superficial; and have attributed the start of the ] to her in addition to the beginning of the ] of 1792 which ended with the ] with their millions of victims and the introduction of ] and ] ideas.<ref name="Jefferson">{{cite book|last=Jefferson|first=Thomas|title=Autobiography of Thomas Jefferson|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=IJpuhuAIzo8C&pg=PA92&lpg=PA92&dq=%E2%80%9CI+have+ever+believed+that+had+there+been+no+queen,+there+would+have+been+no+revolution.%E2%80%9D+%E2%80%A6Thomas+Jefferson&source=bl&ots=6qCoaHJzNX&sig=JW-5di0FHYxABrPxJQvW6JjyWwE&hl=en&sa=X&ei=jbNVUeHFF-KDywHWpoGwBQ&ved=0CDAQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q=%E2%80%9CI%20have%20ever%20believed%20that%20had%20there%20been%20no%20queen%2C%20there%20would%20have%20been%20no%20revolution.%E2%80%9D%20%E2%80%A6Thomas%20Jefferson&f=false|publisher=Courier Dover Publications|accessdate=March 29, 2013|quote=I have ever believed that had there been no queen, there would have been no revolution.}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.marie-antoinette.org/category/reputation/ |title=A Reputation in Shreds - Marie Antoinette Online |publisher=Marie-antoinette.org |date= |accessdate=17 July 2011}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.antoniafraser.com/antoinette.aspx |title=Marie Antoinette |publisher=Antonia Fraser |date= |accessdate=17 July 2011}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|last=Konigsberg |first=Eric |url=http://www.nytimes.com/2006/10/22/weekinreview/22marie.html |title=Marie Antoinette, Citoyenne |publisher=NYTimes.com |date=22 October 2006 |accessdate=17 July 2011}}</ref><ref>|Harvnb|Les Martyrs de la Révolution Française|Ivan Gobry,1989|pp=450-455</ref> On the other hand, Marie Antoinette supported the ] in 1776 and the ], and helped inspire a conservative reaction in France after 1791, which saw its greatest manifestation in the ] which led, several years after the death of the queen, to the end of the Revolution and to the return of conservative and religious ideas in France and in Europe.<ref>{{Harvnb|Gobry|1989|pp=456–462}}</ref> That tendency saw its first manifestation in the writing of ], the most important theorist of modern conservative thought, who criticized the Revolution as early as 1790 and defended Marie Antoinette in his various books. | |||
| For some, Marie Antoinette was a victim of her family ambition and the general situation in France, in addition, even some of her critics recognize her qualities as a mother, her courage in dying, even her charisma. She also patronized the arts, sciences and fashion. | |||
| ], the chapel constructed on the grounds where she was initially buried]] | |||
| In his 1790 treatise, '']'', which was written during Marie Antoinette's imprisonment in Paris, but prior to her execution, ] lamented that "the age of chivalry is gone. That of sophisters, economists, and calculators has succeeded, and the glory of Europe is extinguished forever" and now "Never, never more, shall we behold that generous loyalty to rank and sex."<ref>{{cite book |last=Burke|first=Edmund|year=1790 |title= Reflections on the Revolution in France, And on the Proceedings in Certain Societies in London Relative to that Event. In a Letter Intended to Have Been Sent to a Gentleman in Paris |edition= 1|publisher= J.Dodsley in Pall Mall |publication-date=1790 |location=London |url=https://archive.org/details/reflections00burkuoft/page/n119/mode/2up |access-date=7 September 2021}}</ref> After receiving the news, ], Queen of Naples and close sister to Marie Antoinette, spiraled into a state of mourning and an anger against the revolutionaries. She quickly suspended protections of reformers and intellectuals in Naples, allowed Neapolitan bishops wide latitude to halt the secularization of the country, and offered succor to the overflowing number of '']'' fleeing from revolutionary France, many of whom were granted pensions.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.encyclopedia.com/women/encyclopedias-almanacs-transcripts-and-maps/maria-carolina-1752-1814#:~:text=On%20October%2015%2C%201767%2C%20the,journey%20to%20Italy%2C%20Josepha%20died.&text=Maria%20Carolina%20cried%20and%20entreated,Neapolitan%20match%20must%20be%20cursed |title=Maria Carolina (1752–1814) |date= 2019 |language=en |publisher=] |access-date=17 May 2021}}</ref> | |||
| ===Bourbon Restoration=== | |||
| Both Marie Antoinette's and Louis XVI's bodies were exhumed on 18 January 1815, during the ], when the Count of Provence ascended the newly reestablished throne as ], King of France and of ]. Christian burial of the royal remains took place three days later, on 21 January, in the necropolis of French kings at the ].<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=411, 447}}</ref> | |||
| ==Legacy== | |||
| For many revolutionary figures, Marie Antoinette was the symbol of what was wrong with the old regime in France. The onus of having caused the financial difficulties of the nation was placed on her shoulders by the revolutionary tribunal,<ref>{{cite book|first=Lynn|last=Hunt|chapter=The Many Bodies of Marie Antoinette: Political Pornography and the Problem of the Feminine in the French Revolution|title=The French Revolution: Recent Debates and New Controversies|edition=2nd|editor-first=Gary|editor-last=Kates|pages=|publisher=]|location=London, England|date=1998|isbn=978-0415358330|chapter-url=https://archive.org/details/frenchrevolution00kate/page/201}}</ref> and under the new republican ideas of what it meant to be a member of a nation, her Austrian descent and continued correspondence with the competing nation made her a traitor.<ref>{{cite journal|first=Thomas|last=Kaiser|title=From the Austrian Committee to the Foreign Plot: Marie-Antoinette, Austrophobia, and the Terror|journal=French Historical Studies|publisher=]|location=Durham, North Carolina|volume=26|issue=4|date=Fall 2003|pages=579–617|doi=10.1215/00161071-26-4-579|s2cid=154852467}}</ref> The people of France saw her death as a necessary step toward completing the revolution. Furthermore, her execution was seen as a sign that the revolution had done its work.<ref>{{cite book|first=Chantal|last=Thomas|title=The Wicked Queen: The Origins of the Myth of Marie Antoinette|translator=Julie Rose|publisher=Zone Books|location=New York City|date=2001|isbn=0942299396|page=149}}</ref> | |||
| Marie Antoinette is also known for her taste for fine things, and her commissions from famous craftsmen, such as ], suggest more about her enduring legacy as a woman of taste and patronage. For instance, a writing table attributed to Riesener, now located at ], bears witness to Marie Antoinette's desire to escape the oppressive formality of court life, when she decided to move the table from the queen's boudoir, de la Meridienne, at Versailles to her humble interior, the ]. Her favourite objects filled her small, private chateau and reveal aspects of Marie Antoinette's character that have been obscured by satirical political prints, such as those in Les Tableaux de la Révolution.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://waddesdon.org.uk/blog/celebrating-marie-antoinette-on-her-birthday/|title=Celebrating Marie-Antoinette on her birthday|last=Jenner|first=Victoria|date=12 November 2019|website=Waddesdon Manor|access-date=18 November 2019}}</ref> She owned several instruments.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.rouillac.com/snf1264|title=Le 13e piano de Marie-Antoinette ? - Mardi 09 mai 2017|website=www.rouillac.com}}</ref> In 1788 she bought a piano made by ].<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.cobbecollection.co.uk/collection/12-marie-antoinettes-square-piano/|title=MARIE ANTOINETTE'S PIANO}}</ref> | |||
| A catalog of Marie Antoinette's personal library of 736 volumes was published by ] in 1863, using his pseudonym P. L. Jacob.<ref>P. L. Jacob. ''Bibliothèque de la reine Marie-Antoinette au Petit Trianon d'après l'inventaire original dressé par ordre de la convention : catalogue avec des notes inédites du marquis de Paulmy''. Paris: Jules Gay, 1863.</ref> The listed books were from her library at the Petit Trianon, including many found in her boudoir, and mostly consist of novels and plays. A random selection of her books includes ''Histoire de Mademoiselle de Terville'' by ], ''Le Philosophe parvenu ou Lettres et pièces originales contenant les aventures d'Eugène Sans-Pair'' by ], and ''Oeuvres mêlées... contenant des tragédies et différents ouvrages en vers et en prose'' by ]. A larger and more official library belonging to Marie Antoinette was kept at the ] in ].<ref>"Marie Antoinette", ''LibraryThing'' https://www.librarything.com/profile/MarieAntoinette {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20211024000721/https://www.librarything.com/profile/MarieAntoinette |date=24 October 2021 }} Accessed October 23, 2021.</ref> | |||
| Long after her death, Marie Antoinette remains a major historical figure linked with conservatism, the ], wealth and fashion. She has been the subject of a number of books, films, and other media. Politically engaged authors have deemed her the quintessential representative of ], western ] and ]. Some of her contemporaries, such as Thomas Jefferson, attributed to her the start of the French Revolution.<ref name="Jefferson">{{cite book|first=Thomas|last=Jefferson|author-link=Thomas Jefferson|title=Autobiography of Thomas Jefferson|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=IJpuhuAIzo8C&q=%E2%80%9CI+have+ever+believed+that+had+there+been+no+queen%2C+there+would+have+been+no+revolution.%E2%80%9D+%E2%80%A6Thomas+Jefferson&pg=PA92|publisher=Courier Dover Publications|location=Mineola, New York|access-date=29 March 2013|quote=I have ever believed that had there been no queen, there would have been no revolution.|isbn=978-0486137902|date=2012}}</ref> | |||
| ==In popular culture== | ==In popular culture== | ||
| {{Main| |
{{Main|Cultural depictions of Marie Antoinette}} | ||
| The phrase "]" is often conventionally attributed to Marie Antoinette, but there is no evidence that she ever uttered it, and it is now generally regarded as a journalistic cliché.<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=xviii, 160}}; {{Harvnb|Lever|2006|pp=63–65}}; {{Harvnb|Lanser|2003|pp=273–90}}.</ref> This phrase originally appeared in Book VI of the first part of ]'s autobiographical work '']'', finished in 1767 and published in 1782: "''Enfin Je me rappelai le pis-aller d'une grande Princesse à qui l'on disait que les paysans n'avaient pas de pain, et qui répondit: Qu'ils mangent de la brioche''" ("Finally I recalled the stopgap solution of a great princess who was told that the peasants had no bread, and who responded: 'Let them eat ]{{'"}}). Rousseau ascribes these words to a "great princess", but the purported writing date precedes Marie Antoinette's arrival in France. Some think that he invented it altogether.<ref>{{Harvnb|Johnson|1990|p=17}}.</ref> | |||
| In the United States, expressions of gratitude to France for its help in the American Revolution included naming a city ], in 1788.<ref>Sturtevant, pp. 14, 72.</ref> Her life has been the subject of many films, such as '']'' (1938) and '']'' (2006).<ref>{{Citation |last=Dyke |first=W. S. Van |title=Marie Antoinette |date=1938-08-26 |type=Biography, Drama, History |url=https://www.imdb.com/title/tt0030418/ |access-date=2024-06-01 |others=Norma Shearer, Tyrone Power, John Barrymore |publisher=Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer (MGM) |last2=Duvivier |first2=Julien}}</ref><ref>{{Citation |last=Coppola |first=Sofia |title=Marie Antoinette |date=2006-10-20 |type=Biography, Drama, History |url=https://www.imdb.com/title/tt0422720/ |access-date=2024-06-01 |others=Kirsten Dunst, Jason Schwartzman, Rip Torn |publisher=Columbia Pictures, Pricel, Tohokushinsha Film Corporation (TFC)}}</ref> There is a book about Marie Antoinette by ] called '']''.<ref name="msnbc">{{cite news |url=https://www.nbcnews.com/id/wbna15292100 |title=Dunst puts fresh face on 'Marie Antoinette' |date=October 23, 2006 |agency=Associated Press |publisher=] |access-date=December 11, 2008 |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120916205912/http://today.msnbc.msn.com/id/15292100/ |archive-date=September 16, 2012}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.foxnews.com/story/0,2933,208285,00.html |title=Kirsten Dunst Poses as Marie Antoinette in Vogue |date=August 14, 2006 |agency=Associated Press |publisher=] |access-date=December 10, 2008 |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070128001838/http://www.foxnews.com/story/0%2C2933%2C208285%2C00.html |archive-date=January 28, 2007}}</ref> | |||
| The phrase "]" is often attributed to Marie Antoinette, but there is no evidence she ever uttered it, and it is now generally regarded as a "journalistic cliché".<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2001|pp=xviii, 160}}; {{Harvnb|Lever|2006|pp=63–5}}; {{Harvnb|Lanser|2003|pp=273–290}}</ref> It may have been a rumor started by angry French peasants as a form of ]. This phrase originally appeared in Book VI of the first part (finished in 1767, published in 1782) of ]'s putative autobiographical work, '']'': "''Enfin je me rappelai le pis-aller d'une grande princesse à qui l'on disait que les paysans n'avaient pas de pain, et qui répondit: Qu'ils mangent de la brioche''" ("Finally I recalled the stopgap solution of a great princess who was told that the peasants had no bread, and who responded: 'Let them eat ]{{'"}}). Apart from the fact that Rousseau ascribes these words to an unknown princess, vaguely referred to as a "great princess", some think that he invented it altogether as ''Confessions'' was largely inaccurate.<ref>{{Harvnb|Johnson|1990|p=17}}</ref> | |||
| In 2020, a silk shoe that belonged to her was sold in an auction in the Palace of Versailles for 43,750 euros ($51,780).<ref>{{Cite news |url=https://www.ctvnews.ca/lifestyle/marie-antoinette-s-silk-slipper-fetches-us-50-000-at-auction-1.5189823 |title=Marie Antoinette's silk slipper fetches US$50,000 at auction |date=15 November 2020 |language=en |publisher=] |access-date=26 February 2021}}</ref> | |||
| In America, expressions of gratitude to France for its help in the ] included the naming of the city of ], founded in 1788. The ] chose the name Marietta after an affectionate nickname for Marie Antoinette.<ref>Sturtevant, pp. 14, 72.</ref> | |||
| In 2022, her story was dramatised by a ] and ] English-language ]. | |||
| Marie Antoinette is referenced in the lyrics of the song "]" by the rock band ]. | |||
| In the ] in ], ] band ]'s performance showed a depiction of the freshly severed head of Marie Antoinette singing, in reference to the French Revolution. | |||
| ==Titles from birth to death== | |||
| * '''2 November 1755 – 19 April 1770''': ''Her Royal Highness'' Archduchess Maria Antonia of Austria, Princess of Hungary and Bohemia | |||
| * '''19 April 1770 – 10 May 1774''': ''Her Royal Highness'' The Dauphine of France, Archduchess of Austria, Princess of Hungary and Bohemia | |||
| * '''10 May 1774 – 1 October 1791''': ''Her Most Christian Majesty'' The Queen of France and Navarre | |||
| * '''1 October 1791 – 21 September 1792''': ''Her Most Christian Majesty'' The Queen of the French | |||
| == |
== Family tree == | ||
| <div style="margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto; overflow:auto; width: 90%;"> | |||
| {{ahnentafel top|width=100%}} | |||
| {{chart top |width=100%|Simplified family tree illustrating the Bourbon-Habsburg-Lorraine connections<ref>{{Harvnb|Fraser|2002}}</ref>}} | |||
| {{ahnentafel-compact5 | |||
| |style= |
{{Tree chart/start |style= line-height:100% |align=center | ||
| |border=1 | |||
| |boxstyle=padding-top: 0; padding-bottom: 0; | |||
| |boxstyle_1=background-color: #fcc; | |||
| |boxstyle_2=background-color: #fb9; | |||
| |boxstyle_3=background-color: #ffc; | |||
| |boxstyle_4=background-color: #bfc; | |||
| |boxstyle_5=background-color: #9fe; | |||
| |1= 1. '''Marie Antoinette''' <!-- Please do not add "Queen of France". The title of the article is Marie Antoinette, so it's well known that the woman mentioned here as Marie Antoinette is Queen Marie Antoinette of France. Besides, her ancestresses do not have marital titles included in the ahnentafel. --> | |||
| |2= 2. ] | |||
| |3= 3. ] | |||
| |4= 4. ] | |||
| |5= 5. ] | |||
| |6= 6. ] | |||
| |7= 7. ] | |||
| |8= 8. ] | |||
| |9= 9. ] | |||
| |10= 10. ] | |||
| |11= 11. ] | |||
| |12= 12. ] | |||
| |13= 13. ] | |||
| |14= 14. ] | |||
| |15= 15. ] | |||
| |16= 16. ] | |||
| |17= 17. ] | |||
| |18= 18. ] | |||
| |19= 19. ] | |||
| |20= 20. ] | |||
| |21= 21. ] | |||
| |22= 22. ] | |||
| |23= 23. ] | |||
| |24= 24. Ferdinand III, Holy Roman Emperor (= 18) | |||
| |25= 25. ] | |||
| |26= 26. ] | |||
| |27= 27. ] | |||
| |28= 28. ] | |||
| |29= 29. Duchess Elisabeth of Schleswig-Holstein-Sønderburg-Norburg | |||
| |30= 30. Albert Ernest I, Prince of Oettingen-Oettingen | |||
| |31= 31. Duchess Christine Frederica of Württemburg | |||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{chart |border=0| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |Louis|Louis=]}} | |||
| {{ahnentafel bottom}} | |||
| {{chart |border=0| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |,|-|-|^|-|-|-|.|}} | |||
| {{chart |border=0| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |Leopold| |Louis| |Henrietta|j|Philip|j|-|-|-|-|-|-|v|Liselotte|Leopold=]|Louis=]|Philip=]|Liselotte=]|Henrietta=]}} | |||
| {{chart |border=0| | | | | | | |,|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|-|^|-|-|-|-|*|-|-|-|-|*|-|-|-|*|-|-|.| | | |!|}} | |||
| {{chart |border=0| | | | | | |Joseph| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |D|~|~|~|~|J| | | |:| |Charles| |Liselotte|v|Leo|Joseph=]|Charles=]|grandson=<small>great-grandson</small>|Liselotte=]|Leo=]<!---<br><small>Duke of Lorraine</small>--->}} | |||
| {{chart |border=0| |,|-|-|-|-|-|^|-|-|-|.| | | | | | | | | | |Marie|v|Louis| | | | | | | | |:| | |!| | | | | |!||Louis=]|Marie=]}} | |||
| {{chart |border=0|Amalia|v|Charles| | | |Josepha|v|August| | | | |,|-|-|-|+|-|-|-|.| | | | | | | |:| | |!| | | | | |!|Amalia=]|Josepha=]|Louis=]|Charles=]|August=]}} | |||
| {{chart |border=0| |,|-|^|-|.| | | |,|-|-|-|+|-|-|-|.| | | |!| | |Mesdames| |Louise| | | | | | |:| |Theresa|-|v|-|Francis|Mesdames='']''|Louise=]|Theresa=]|Francis=]}} | |||
| {{chart |border=0|Josepha| |MaxJos| |Clemens| |Albert| |Josephe|v|Louis| | |,|-|-|-|+|-|-|-|.| | | |:| | | | | |!|Josepha=]<br><small>m. {{nowrap|Joseph II}}</small>|MaxJos=]|Clemens=]|Albert=]<br><small>m. Maria Christina</small>|Josephe=]|Louis=]|Louise=]}} | |||
| {{chart |border=0| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |!| | | | |Isabella| |Ferdinand| |Luisa| |Philip| | | | |!|Isabella=]<br><small>m. {{nowrap|Joseph II}}</small>|Ferdinand=]<br><small>m. Maria Amalia</small>|Luisa=]|Philip=]}} | |||
| {{chart |border=0| | | | | |,|-|-|-|v|-|-|-|v|-|-|-|v|-|^|-|.| | | |,|-|-|-|v|-|-|-|v|-|-|-|v|-|-|-|v|-|^|-|v|-|-|v|-|-|-|.|}} | |||
| {{chart |border=0| | | | |Provence| |Artois| |Clotilde| |Elisabeth| |Louis|-|Antonia| |Joseph| |Christina| |Leopold| |Amalia| |Carolina| |Ferdinand| |Max|Joseph=]|Christina=]|Leopold=]|Amalia=]|Carolina=]|Ferdinand=]|Antonia='''Marie Antoinette'''|Max=]|Louis=''']'''|Provence=]|Artois=]|Clotilde=]|Elisabeth=]}} | |||
| {{chart |border=0| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |!|}} | |||
| {{chart |border=0| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |Francis|Francis=]}} | |||
| {{chart/end}} | |||
| <div style="text-align:left;"> | |||
| '''Notes:''' | |||
| Solid vertical lines indicate parent-child relationship, while dashed lines represent more distant ancestor-descendant connections. | |||
| </div> | |||
| {{chart bottom}} | |||
| </div> | |||
| == |
==Children== | ||
| {{Hidden top|expanded=yes|title=Children of Marie Antoinette|titlestyle=text-align:center; background: #CCDDCC; border:1px solid black}} | |||
| {{portal bar|Kingdom of France}} | |||
| {| style="text-align:center; width:100%" class="wikitable" | |||
| * ] | |||
| ! width=20% | Name !! width=100px | Portrait !! Lifespan !! Age !! Notes | |||
| |- | |||
| | ''']'''<br /> ''Madame Royale'' | |||
| || ] | |||
| ||19 December 1778 –<br /> 19 October 1851 | |||
| ||{{Age in years, months and days|1778|12|19|1851|10|19}} | |||
| ||Married her cousin, ], the eldest son of the future ]. | |||
| |- | |||
| | ''']'''<br />''Dauphin de France'' | |||
| || ] | |||
| ||22 October 1781 –<br /> 4 June 1789 | |||
| ||{{Age in years, months and days|1781|10|22|1789|6|4}} | |||
| || Contracted tuberculosis and died in childhood on the very day the Estates General convened. | |||
| |- | |||
| | ''']'''<br /> ''(nominally) King of France and Navarre'' | |||
| || ] | |||
| || 27 March 1785 –<br /> 8 June 1795 | |||
| ||{{Age in years, months and days|1785|3|27|1795|6|8}} | |||
| || Died in childhood; no issue. He was never officially king, nor did he rule. His title was bestowed by his royalist supporters and acknowledged implicitly by his uncle's later adoption of the regnal name Louis XVIII rather than Louis XVII, upon the restoration of the Bourbon monarchy in 1814. | |||
| |- | |||
| | ''']''' | |||
| || ] | |||
| || 9 July 1786 –<br /> 19 June 1787 | |||
| ||{{Age in years, months and days|1786|7|9|1787|6|19}} | |||
| || Died in the Palace of Versailles at the age of 11 months after suffering several days of convulsions, possibly related to tuberculosis.<ref>Fraser, Antonia, ''Marie Antoinette, The Journey'', Anchor Books, USA, 2001, p. 257, {{ISBN|0-385-48949-8}}.</ref> | |||
| |- | |||
| |} | |||
| {{hidden bottom}} | |||
| In addition to her biological children, Marie Antoinette adopted four children: "Armand" ], a poor orphan adopted in 1776; ], a Senegalese ] boy given to the queen as a present by ] in 1787, but whom she instead freed, baptized, adopted and placed in a pension; ], daughter of two servants at the palace, who was raised as the playmate of her daughter Marie-Thérèse and whom she adopted after the death of her mother in 1788; and "Zoe" ], who was adopted in 1790 along with her two older sisters when her parents, an usher and his wife in service of the King, had died.<ref name="ReferenceA">Philippe Huisman, Marguerite Jallut: ''Marie Antoinette'', Stephens, 1971.</ref> | |||
| ==References== | |||
| Of these, only Armand, Ernestine, and Zoe actually lived with the royal family: Jean Amilcar, along with the elder siblings of Zoe and Armand who were also formally foster children of the royal couple, simply lived at the queen's expense until her imprisonment, which proved fatal for at least Amilcar, as he was evicted from the boarding school when the fee was no longer paid, and reportedly starved to death on the street.<ref name="ReferenceA"/> | |||
| === Notes === | |||
| Armand and Zoe had a position which was more similar to that of Ernestine; Armand lived at court with the king and queen until he left them at the outbreak of the Revolution because of his republican sympathies, and Zoe was chosen to be the playmate of the dauphin, just as Ernestine had once been selected as the playmate of Marie-Thérèse, and later sent away to her sisters in a convent boarding school before the Flight to Varennes in 1791.<ref name="ReferenceA"/> | |||
| ==References== | |||
| ===Notes=== | |||
| {{Reflist|20em}} | {{Reflist|20em}} | ||
| === |
===Bibliography=== | ||
| {{refbegin |
{{refbegin}} | ||
| * {{cite book |editor-last1=d'Arneth |editor-first1=Alfred Ritter |editor-last2=Geffroy |editor-first2=A. |title=Correspondance secrète entre Marie-Thérèse et le comte de Mercy-Argenteau, avec les lettres de Marie-Thérèse et de Marie-Antoinette |date=1874 |publisher=Firmin-Didot |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=72cvAAAAMAAJ |language=fr |volume=3}} | |||
| * {{cite book|title=Un choix sans équivoque: recherches historiques sur les relations amoureuses entre les femmes, XVIe-XXe siècle |first=Marie-Jo |last=Bonnet|year=1981|location=Paris|publisher=Denoël|language=French|oclc=163483785| ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Banat |first1=Gabriel |title=The Chevalier de Saint-Georges: Virtuoso of the Sword and the Bow |date=2006 |publisher=Pendragon Press |isbn=978-1-57647-109-8 |location=Hillsdale, New York |oclc= |url=https://archive.org/details/chevalierdesaint0000bana/page/n5/mode/2up |url-access=registration}} | |||
| * {{cite book|title=Queen of France: a biography of Marie Antoinette|first=André|last=Castelot|authorlink=André Castelot|location=New York |publisher=Harper & Brothers|year=1957|others=trans. Denise Folliot|oclc=301479745| ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book |title=Un choix sans équivoque: recherches historiques sur les relations amoureuses entre les femmes, XVIe–XXe siècle |first=Marie-Jo |last=Bonnet |year=1981 |location=Paris |publisher=Denoël |language=fr |oclc=163483785}} | |||
| * {{cite book | last = Cronin | first = Vincent | authorlink = Vincent Cronin | title = Louis and Antoinette | publisher=The Harvill Press | location = London | year = 1989 | isbn = 978-0-00-272021-2 | ref = harv }} | |||
| * {{cite book |title=Queen of France: a biography of Marie Antoinette |url=https://archive.org/details/queenoffrancebio00cast |url-access=registration |first=André |last=Castelot |author-link=André Castelot |location=New York |publisher=Harper & Brothers |year=1957 |others=trans. Denise Folliot |oclc=301479745}} | |||
| * {{cite book|title=La folie de bâtir: pavillons d'agrément et folies sous l'Ancien Régime|first1=Bernd H. |last1=Dams|first2=Andrew |last2=Zega| authorlink2 = Andrew Zega | others=trans. Alexia Walker|publisher=Flammarion|year=1995|isbn=978-2-08-201858-6| ref=harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book |first=André |last=Castelot |title=Marie-Antoinette |publisher=Librairie académique Perrin |location=Paris, France |date=1962 |isbn=978-2262048228}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last=Facos|first=Michelle|authorlink=Michelle Facos|title=An Introduction to Nineteenth-Century Art|year=2011|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=Vk4WgsO2OZsC&pg=PA12|accessdate=1 September 2011|publisher=Taylor & Francis|isbn=978-1-136-84071-5}} | |||
| * {{cite book | |
* {{cite book |last1=Cronin |first1=Vincent |title=Louis and Antoinette |date=1974 |publisher=Collins |isbn=978-0-00-211494-3 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=6CMxAQAAIAAJ |language=en}} | ||
| * {{cite book | |
** {{cite book |last=Cronin |first=Vincent |author-link=Vincent Cronin |title=Louis and Antoinette |publisher=The Harvill Press |location=London |year=1989 |isbn=978-0-00-272021-2}} | ||
| * {{cite book |title=La folie de bâtir: pavillons d'agrément et folies sous l'Ancien Régime |first1=Bernd H. |last1=Dams |first2=Andrew |last2=Zega |author-link2=Andrew Zega |others=trans. Alexia Walker |publisher=Flammarion |year=1995 |isbn=978-2-08-201858-6}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last= Hermann|first= Eleanor|title= Sex With The Queen|year= 2006|publisher=Harper/Morrow |isbn=0-06-084673-9}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last= |
* {{cite book |last=Facos |first=Michelle |author-link=Michelle Facos |title=An Introduction to Nineteenth-Century Art |year=2011 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Vk4WgsO2OZsC&pg=PA12 |access-date=1 September 2011 |publisher=Taylor & Francis |isbn=978-1-136-84071-5}} | ||
| * {{cite book | |
* {{cite book |last=Farr |first=Evelyn |title=Marie-Antoinette and Count Fersen: The Untold Love Story |year=2013 |publisher=Peter Owen Publishers |isbn=978-0720610017 |edition=2nd Revised}} | ||
| * {{cite book | |
* {{cite book |last1=Furneaux |first1=Rupert |title=The Last Days of Marie Antoinette and Louis XVI. |date=1971 |publisher=John Day Company |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=kutnAAAAMAAJ |language=en}} | ||
| * {{cite book | |
* {{cite book |last=Fraser |first=Antonia |author-link=Antonia Fraser |title=Marie Antoinette |edition=1st |publisher=N.A. Talese/Doubleday |location=New York |year=2001 |isbn=978-0-385-48948-5 |url=https://archive.org/details/marieantoinettej00fras}} | ||
| * {{cite book |last= |
* {{cite book |last=Fraser |first=Antonia |title=Marie Antoinette: The Journey |edition=2nd |publisher=Anchor Books |location=Garden City |year=2002 |isbn=978-0-385-48949-2 |url=https://archive.org/details/marieantoinette00anto_0}} | ||
| ** {{Cite book |last=Fraser |first=Antonia |title=Marie Antoinette: The Journey |publisher=Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group |year=2002b |isbn=9781400033287}} | |||
| * {{cite journal|last=Seulliet|first=Philippe|work=World Of Interiors |title=Swan Song: Music Pavillion of the Last Queen of France|date=July 2008 |number= 7| ref = harv}} | |||
| * {{cite book|last= |
* {{cite book |last=Hermann |first=Eleanor |title=Sex with the Queen |year=2006 |publisher=Harper/Morrow |isbn=978-0-06-084673-2 |url=https://archive.org/details/sexwithqueen900y00herm}} | ||
| * {{cite book | |
* {{cite book |last=Hibbert |first=Christopher |author-link=Christopher Hibbert |title=The Days of the French Revolution |year=2002 |publisher=Harper Perennial |isbn=978-0-688-16978-7 |url=https://archive.org/details/daysoffrenchre00hibb}} | ||
| * {{cite book |last=Johnson |first=Paul |author-link=Paul Johnson (writer) |title=Intellectuals |publisher=Harper & Row |location=New York |year=1990 |isbn=978-0-06-091657-2 |url-access=registration |url=https://archive.org/details/intellectuals00johnrich}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last= Wollstonecraft|first= Mary| authorlink = Mary Wollstonecraft | title = An Historical and Moral View of the Origin and Progress of the French Revolution and the Effect it Has Produced in Europe|year= 1795|publisher=St. Paul's}} | |||
| * {{cite book |first=Susan S. |last=Lanser |chapter=Eating Cake: The (Ab)uses of Marie-Antoinette |title=Marie-Antoinette: Writings on the Body of a Queen |editor-first=Dena |editor-last=Goodman |publisher=Psychology Press |year=2003 |isbn=978-0-415-93395-7}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Lever |first1=Evelyne |title=Marie Antoinette |date=1991 |publisher=Fayard |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=nZulswEACAAJ |language=en}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Lever |first1=Evelyne |title=Marie Antoinette: The Last Queen of France |date=24 September 2001 |publisher=Macmillan |isbn=978-0-312-28333-9 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=WNX1tQCA-w0C |language=en}} | |||
| ** {{cite book |last=Lever |first=Évelyne |author-link=Évelyne Lever |title=Marie Antoinette: The Last Queen of France |publisher=Portrait |location=London |year=2006 |isbn=978-0-7499-5084-2}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Schama |first=Simon |author-link=Simon Schama |title=Citizens: A Chronicle of the French Revolution |year=1989 |publisher=Vintage |location=New York |isbn=978-0-679-72610-4 |title-link=Citizens: A Chronicle of the French Revolution}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Seulliet |first=Philippe |journal=World of Interiors |title=Swan Song: Music Pavilion of the Last Queen of France |date=July 2008 |number=7}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Sturtevant |first=Lynne |title=A Guide to Historic Marietta, Ohio |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mm08vgAACAAJ |access-date=1 September 2011 |year=2011 |publisher=The History Press |isbn=978-1-60949-276-2}} | |||
| * {{cite book |title=Queen of Fashion: What Marie Antoinette Wore to the Revolution |isbn=978-0-312-42734-4 |first=Caroline |last=Weber |author-link=Caroline Weber (author) |publisher=Picador |year=2007}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Wollstonecraft |first=Mary |author-link=Mary Wollstonecraft |title=An Historical and Moral View of the Origin and Progress of the French Revolution and the Effect it Has Produced in Europe |year=1795 |publisher=St. Paul's}} | |||
| {{refend}} | {{refend}} | ||
| == |
==Further reading== | ||
| {{refbegin}} | {{refbegin}} | ||
| * {{cite book | |
* {{cite book |title=Marie Antoinette's Head: The Royal Hairdresser, the Queen, and the Revolution |last=Bashor |first=Will |publisher=Lyons Press |year=2013 |isbn=978-0762791538 |page=320 |author-link=Will Bashor}} | ||
| * {{Cite book |title=To the Scaffold |last=Erickson |first=Carolly |publisher=William Morrow and Company, Inc. |year=1991 |isbn=0-312-32205-4 |location=New York |url=https://archive.org/details/toscaffoldlifeof00eric}} | |||
| * {{cite book | last = Lasky | first = Kathryn | authorlink = Kathryn Lasky | title = The Royal Diaries: Marie Antoinette, Princess of Versailles: Austria-France, 1769 | publisher=Scholastic | location = New York | year = 2000 | isbn = 978-0-439-07666-1 }} | |||
| * {{cite book | |
* {{cite book |title=I Love You Madly: Marie-Antoinette and Count Fersen: The Secret Letters |last=Farr |first=Evelyn |year=2016 |publisher=Peter Owen Publishers |isbn=978-0720618778}} | ||
| * {{cite book |title=Bibliothèque de la reine Marie-Antoinette au Petit Trianon d'après l'inventaire original dressé par ordre de la convention : catalogue avec des notes inédites du marquis de Paulmy |last=Jacob |first=P.L. |year=1863 |publisher=Jules Gay |oclc=12097301}} | |||
| * {{cite book | last = MacLeod | first = Margaret Anne | title = There Were Three of Us in the Relationship: The Secret Letters of Marie Antoinette | publisher=Isaac MacDonald | location = Irvine, Scotland | year = 2008 | isbn = 978-0-9559991-0-9 }} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |author=Kaiser, Thomas |title=From the Austrian Committee to the Foreign Plot: Marie-Antoinette, Austrophobia, and the Terror |journal=French Historical Studies |volume=26 |issue=4 |date=Fall 2003 |pages=579–617 |doi=10.1215/00161071-26-4-579 |s2cid=154852467}} | |||
| * {{cite book | last = Naslund | first = Sena Jeter | authorlink = Sena Jeter Naslund | title = Abundance: A Novel of Marie Antoinette | publisher=William Morrow | location = New York | year = 2006 | isbn = 978-0-06-082539-3 }} | |||
| * {{Cite book |title=The French Revolution: Recent Debates and New Controversies 2nd ed |last=Kates |first=Gary |publisher=Routledge |year=1998 |isbn=0-415-35833-7 |pages= |url=https://archive.org/details/frenchrevolution00kate/page/201}} | |||
| * {{cite book | last = Romijn | first = André | title = Vive Madame la Dauphine: A Biographical Novel | publisher=Roman House | location = Ripon | year = 2008 | isbn = 978-0-9554100-2-4 }} | |||
| * {{cite book | |
* {{cite book |title=The Royal Diaries: Marie Antoinette, Princess of Versailles: Austria-France, 1769 |last=Lasky |first=Kathryn |publisher=Scholastic |year=2000 |isbn=978-0-439-07666-1 |location=New York |author-link=Kathryn Lasky |url=https://archive.org/details/marieantoinettep00lask}} | ||
| * {{cite book | |
* {{cite book |title=The Fatal Friendship: Marie Antoinette, Count Fersen and the flight to Varennes |last=Loomis |first=Stanley |publisher=Davis-Poynter |year=1972 |isbn=978-0-7067-0047-3 |location=London |author-link=Stanley Loomis}} | ||
| * {{cite book | |
* {{cite book |title=There Were Three of Us in the Relationship: The Secret Letters of Marie Antoinette |last=MacLeod |first=Margaret Anne |publisher=Isaac MacDonald |year=2008 |isbn=978-0-9559991-0-9 |location=Irvine, Scotland}} | ||
| * {{cite book |title=Abundance: A Novel of Marie Antoinette |last=Naslund |first=Sena Jeter |publisher=William Morrow |year=2006 |isbn=978-0-06-082539-3 |location=New York |author-link=Sena Jeter Naslund |url=https://archive.org/details/abundancenovelof00nasl}} | |||
| * {{cite book |title=Vive Madame la Dauphine: A Biographical Novel |last=Romijn |first=André |publisher=Roman House |year=2008 |isbn=978-0-9554100-2-4 |location=Ripon}} | |||
| * {{cite book |title=The Wicked Queen: The Origins of the Myth of Marie-Antoinette |last=Thomas |first=Chantal |publisher=Zone Books |others=Trans. Julie Rose |year=1999 |isbn=978-0-942299-40-3 |location=New York |author-link=Chantal Thomas}} | |||
| * {{cite book |title=Trianon: A Novel of Royal France |last=Vidal |first=Elena Maria |publisher=Neumann Press |year=1997 |isbn=978-0-911845-96-9 |location=Long Prairie, MN |author-link=Elena Maria Vidal}} | |||
| * {{cite book |title=Marie Antoinette: The Portrait of an Average Woman |last=Zweig |first=Stefan |publisher=Grove Press |year=2002 |isbn=978-0-8021-3909-2 |location=New York |author-link=Stefan Zweig |url=https://archive.org/details/marieantoinettep00zwei_0}} | |||
| {{refend}} | {{refend}} | ||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{ |
{{sisterlinks|d=y|s=Author:Marie Antoinette|c=Marie Antoinette of Austria|n=no|b=no|v=no|voy=no|m=no|mw=no|wikt=no}} | ||
| * on | |||
| {{Wikiquote}} | |||
| * on | |||
| * in the '']'' | |||
| * | * on | ||
| * on | |||
| * | |||
| * on | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * —A site with a sympathetic bend, and contains a great deal of information. | |||
| * sur parismarais.com | |||
| * —Many articles on all things Antoinette, from Versailles to Trianon to the most obscure details of life in Royal France, by historian and author ]. | |||
| * {{CathEncy|wstitle=Marie Antoinette}} | |||
| * from the Petit-Trianon palace, based on 1863 printed catalog, online at ]. | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| {{Navboxes | |||
| |title=Articles and topics related to Marie Antoinette | |||
| |state=collapsed | |||
| |list1=</span> | |||
| {{s-start}} | {{s-start}} | ||
| {{s-break}} | {{s-break}} | ||
| {{S-hou|]|2 November|1755|16 October|1793}} | {{S-hou|]|2 November|1755|16 October|1793|] and ]}} | ||
| {{s-break}} | {{s-break}} | ||
| {{S-roy|fr}} | {{S-roy|fr}} | ||
| {{s-break}} | {{s-break}} | ||
| {{S-vac|last=]}} | {{S-vac|last=]}} | ||
| {{S-ttl|title=]|years= |
{{S-ttl|title=]|years=1774–1792<br>from 1791 ''Queen of the French''}} | ||
| {{S- |
{{S-vac|reason=]|next=]|as=]}} | ||
| {{s-break}} | |||
| {{S-non|reason=Herself<br><small>as Queen of France</small>}} | |||
| {{S-ttl|title=]|years=1 October 1791 – 21 September 1792}} | |||
| {{S-vac|reason=]|next=]|as=]}} | |||
| {{s-break}} | {{s-break}} | ||
| {{S-pre|}} | {{S-pre|}} | ||
| {{s-break}} | {{s-break}} | ||
| {{S-new|loss|reason=]}} | {{S-new|loss|reason=]}} | ||
| {{S-tul|title=]/<br />]|years= |
{{S-tul|title=]|years=4 September 1791 – 21 January 1793}} | ||
| {{S-vac|next=]}} | {{S-vac|next=]}} | ||
| {{s-end}} | |||
| {{s-ref|Weber, Caroline. Queen of Fashion: What Marie Antoinette Wore to the Revolution. New York: Henry Holt and Company, 2006.}} | |||
| {{Navboxes | |||
| |title=Articles and topics related to Marie Antoinette | |||
| |state=collapsed | |||
| |list1= | |||
| {{Austrian archduchesses}} | {{Austrian archduchesses}} | ||
| {{Tuscan princesses}} | {{Tuscan princesses}} | ||
| Line 414: | Line 451: | ||
| {{French Revolution navbox}} | {{French Revolution navbox}} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| {{Portal bar|France|Biography|Law}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | {{Authority control}} | ||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Maria Antonia Of Austria}} | |||
| {{Persondata | |||
| | NAME =Antoinette, Marie | |||
| | ALTERNATIVE NAMES =Maria Antonia Josefa Johanna von Habsburg-Lothringen | |||
| | SHORT DESCRIPTION =Archduchess of Austria, and Queen of France | |||
| | DATE OF BIRTH =2 November 1755 | |||
| | PLACE OF BIRTH =] in Vienna | |||
| | DATE OF DEATH =16 October 1793 | |||
| | PLACE OF DEATH =Paris, France | |||
| }} | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Marie Antoinette Of Austria}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| Line 444: | Line 481: | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:53, 25 December 2024
Queen of France from 1774 to 1792 For other uses, see Marie Antoinette (disambiguation).
| Marie Antoinette | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Portrait, c. 1775 Portrait, c. 1775 | |||||
| Queen consort of France | |||||
| Tenure | 10 May 1774 – 21 September 1792 | ||||
| Born | Archduchess Maria Antonia of Austria (1755-11-02)2 November 1755 Hofburg, Vienna, Archduchy of Austria, Holy Roman Empire | ||||
| Died | 16 October 1793(1793-10-16) (aged 37) Place de la Révolution, Paris, France | ||||
| Cause of death | Execution by guillotine | ||||
| Burial | 21 January 1815 Basilica of Saint-Denis | ||||
| Spouse |
Louis XVI
(m. 1770; died 1793) | ||||
| Issue | |||||
| |||||
| House | Habsburg-Lorraine | ||||
| Father | Francis I, Holy Roman Emperor | ||||
| Mother | Maria Theresa | ||||
| Signature | |||||
| Coat of arms |  | ||||
Marie Antoinette (/ˌæntwəˈnɛt, ˌɒ̃t-/; French: [maʁi ɑ̃twanɛt] ; Maria Antonia Josefa Johanna; 2 November 1755 – 16 October 1793) was the last Queen of France prior to the French Revolution and the establishment of the French First Republic. Marie Antoinette was the wife of Louis XVI. Born Archduchess Maria Antonia of Austria, she was the penultimate child and youngest daughter of Empress Maria Theresa and Emperor Francis I. She married Louis Auguste, Dauphin of France, in May 1770 at the age of 14. She then became the Dauphine of France. On 10 May 1774, her husband ascended the throne as Louis XVI and she became queen.
As queen, Marie Antoinette became increasingly a target of criticism by opponents of the domestic and foreign policies of Louis XVI, and those opposed to the monarchy in general. The French libelles accused her of being profligate, promiscuous, having illegitimate children, and harboring sympathies for France's perceived enemies, including her native Austria. She was falsely accused of defrauding the Crown's jewelers in the Affair of the Diamond Necklace, but the accusations damaged her reputation further. During the French Revolution, she became known as Madame Déficit because the country's financial crisis was blamed on her lavish spending and her opposition to social and financial reforms proposed by Anne Robert Jacques Turgot and Jacques Necker.
Several events were linked to Marie Antoinette during the Revolution after the government placed the royal family under house arrest in the Tuileries Palace in October 1789. The June 1791 attempted flight to Varennes and her role in the War of the First Coalition were immensely damaging to her image among French citizens. On 10 August 1792, the attack on the Tuileries forced the royal family to take refuge at the Assembly, and they were imprisoned in the Temple Prison on 13 August 1792. On 21 September 1792, France was declared a republic and the monarchy was abolished. Louis XVI was executed by guillotine on 21 January 1793. Marie Antoinette's trial began on 14 October 1793; two days later, she was convicted by the Revolutionary Tribunal of high treason and executed by beheading by guillotine on 16 October 1793 at the Place de la Révolution during the French Revolution.
Early life (1755–1770)

Marie Antoinette, full name Maria Antonia Josepha Johanna, was born on 2 November 1755 at the Hofburg Palace in Vienna, Archduchy of Austria, at 20:30. She was the youngest daughter and 15th child of Empress Maria Theresa, ruler of the Habsburg monarchy, and her husband Francis I, Holy Roman Emperor. Maria Theresa gave birth to all of her previous children without any problems. During the birth of her last daughter, serious complications arose, and doctors even feared for the life of the mother. Her godparents were Joseph I and Mariana Victoria, King and Queen of Portugal; Archduke Joseph and Archduchess Maria Anna acted as proxies for their newborn sister.
Maria Antonia was born on All Souls' Day, a Catholic day of mourning, and during her childhood her birthday was instead celebrated the day before, on All Saints' Day, due to the connotations of the date. Shortly after her birth she was placed under the care of the governess of the imperial children, Countess von Brandeis. Maria Antonia was raised together with her sister, Maria Carolina of Austria, who was three years older, and with whom she had a lifelong close relationship. Maria Antonia had a difficult but ultimately loving relationship with her mother, who referred to her as "the little Madame Antoine".
Maria Antonia spent her formative years between the Hofburg Palace and Schönbrunn, the imperial summer residence in Vienna, where on 13 October 1762, when she was seven, she met Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, two months her junior and a child prodigy. Despite the private tutoring she received, the results of her schooling were less than satisfactory. At the age of 10 she could not write correctly in German or in any language commonly used at court, such as French or Italian, and conversations with her were stilted. Under the teaching of Christoph Willibald Gluck, Maria Antonia developed into a good musician. She learned to play the harp, the harpsichord and the flute. She sang during the family's evening gatherings, as she was known to have had a beautiful voice. She also excelled at dancing, had "exquisite" poise, and loved dolls.

The death of her older sister Maria Josepha from smallpox during the epidemic in Vienna in October 1767 made an everlasting impression on the young Maria Antonia. Maria Antonia, in her later life, recalled the ailing Maria Josepha taking her in her arms. She told her that she would not be traveling to Naples to marry King Ferdinand IV of Naples, to whom she was betrothed, but for the family vault.
Later in 1768, Mathieu-Jacques de Vermond was dispatched by Louis XV to tutor Marie Antoinette as she became the future wife to Louis XVI. Serving as an educator, Abbé de Vermond found her to be unsatisfactorily educated and lacking in, at the age of 13, important writing skills. Nonetheless, he also complimented her, stating "her character, her heart, are excellent". He found her "more intelligent than has been generally supposed," but since "she is rather lazy and extremely frivolous, she is hard to teach".
Under the recommendation of Étienne François de Choiseul, Duke of Choiseul, a strong supporter of her prospective marriage, Maria Antonia also received a makeover to bring her more in line with the fashion of French royalty. This included the straightening of her teeth by a French dentist, the diversification of her wardrobe, and hairstyles reminiscent of Madame de Pompadour. She was also instructed by Jean-Georges Noverre, who taught her to walk in the gliding fashion characteristic of the court of Versailles.
Dauphine of France (1770–1774)


Following the Seven Years' War and the Diplomatic Revolution of 1756, Empress Maria Theresa decided to end hostilities with her longtime enemy, King Louis XV of France. Their common desire to destroy the ambitions of Prussia and Great Britain, and to secure a definitive peace between their respective countries led them to seal their alliance with a marriage: on 7 February 1770, Louis XV formally requested the hand of Maria Antonia for his eldest surviving grandson and heir, Louis Auguste, Duke of Berry and Dauphin of France.
Maria Antonia formally renounced her rights to Habsburg domains, and on 19 April 1770 she was married by proxy with Louis Auguste at the Augustinian Church, Vienna, with her brother Archduke Ferdinand standing in for the Dauphin. On 14 May 1770 she met her husband at the edge of the forest of Compiègne. Upon her arrival in France, she adopted the French version of her name: Marie Antoinette. A further ceremonial wedding took place on 16 May 1770 in the Palace of Versailles and, after the festivities, the day ended with the ritual bedding. The couple's longtime failure to consummate the marriage plagued the reputations of the royal couple for the next seven years.
The initial reaction to the marriage between Marie Antoinette and Louis XVI was mixed. On the one hand, the Dauphine was beautiful, personable and well-liked by the common people. Her first official appearance in Paris on 8 June 1773 was a resounding success. On the other hand, those opposed to the alliance with Austria had a difficult relationship with Marie Antoinette, as did others who disliked her for more personal or petty reasons.
Madame du Barry proved a troublesome foe to the new dauphine. She was Louis XV's mistress and had considerable political influence over him. In 1770 she was instrumental in ousting Étienne François, duc de Choiseul, who had helped orchestrate the Franco-Austrian Alliance and Marie Antoinette's marriage, and in exiling his sister, the Duchess of Gramont, one of Marie Antoinette's ladies-in-waiting. Marie Antoinette was persuaded by her husband's aunts to refuse to acknowledge du Barry, which some saw as a political blunder that jeopardized Austria's interests at the French court. Marie Antoinette's mother and the Austrian ambassador to France, Comte de Mercy-Argenteau, who sent the Empress secret reports on Marie Antoinette's behaviour, pressured Marie Antoinette to speak to Madame du Barry, which she grudgingly agreed to do on New Year's Day 1772. She merely commented to her, "There are a lot of people at Versailles today", but it was enough for Madame du Barry, who was satisfied with this recognition, and the crisis passed.
Two days after the death of Louis XV in 1774, Louis XVI exiled du Barry to the Abbaye du Pont-aux-Dames in Meaux, pleasing both his wife and aunts. Two and a half years later, at the end of October 1776, Madame du Barry's exile ended and she was allowed to return to her beloved château at Louveciennes, but she was never permitted to return to Versailles.
Queen of France and Navarre (1774–1792)

Early years (1774–1778)
On 10 May 1774, upon the death of Louis XV, the Dauphin ascended the throne as King Louis XVI of France and Navarre with Marie Antoinette as his queen consort. At the outset, the new queen had limited political influence with her husband, who, with the support of his two most important ministers, Chief Minister Maurepas and Foreign Minister Vergennes, blocked several of her candidates from assuming important positions, including Choiseul. The queen did play a decisive role in the disgrace and exile of the most powerful of Louis XV's ministers, the Duc d'Aiguillon.
On 24 May 1774, two weeks after the death of Louis XV, the king gave his wife the Petit Trianon, a small château on the grounds of Versailles that had been built by Louis XV for his mistress, Madame de Pompadour. Louis XVI allowed Marie Antoinette to renovate it to suit her own tastes; soon rumours circulated that she had plastered the walls with gold and diamonds.

The Queen spent heavily on fashion, luxuries, and gambling, though the country was facing a grave financial crisis and the population was suffering. Rose Bertin created dresses for her, and hairstyles such as poufs, up to three feet (90 cm) high, and the panache—a spray of feather plumes. She and her court also adopted the English fashion of dresses made of indienne, a material banned in France from 1686 until 1759 to protect local French woolen and silk industries, percale and muslin. As a result of all these fashion activities, Marie Antoinette presided over one of the most important and fashionable courts in history and she was dominant over all of the other ladies of the court; as for her bearing and appearance the queen was very majestic and charismatic in spite of the fact that she gained much weight over the years due to her many pregnancies.
By the time of the Flour War of 1775, a series of riots, due to the high price of flour and bread, had damaged her reputation among the general public. Eventually, Marie Antoinette's reputation was no better than that of the favourites of previous kings. Many French people were beginning to blame her for the degrading economic situation, suggesting the country's inability to pay off its debt was the result of her wasting the crown's money. In her correspondence, Marie Antoinette's mother, Maria Theresa, expressed concern over her daughter's spending habits, citing the civil unrest it was beginning to cause.
As early as 1774, Marie Antoinette had begun to befriend some of her male admirers, such as the Baron de Besenval, the Duc de Coigny, and Count Valentin Esterházy, and also formed deep friendships with various ladies at court. Most noted was Marie-Louise, Princesse de Lamballe, related to the royal family through her marriage into the Penthièvre family. On 19 September 1774, she appointed her superintendent of her household, an appointment she soon transferred to her new favourite, the Duchess of Polignac.
In 1774, she took under her patronage her former music teacher, the German opera composer Christoph Willibald Gluck, who remained in France until 1779.
Motherhood, changes at court and intervention in politics (1778–1781)
Amidst the atmosphere of a wave of libelles, the Holy Roman Emperor Joseph II came to France incognito, using the name Comte de Falkenstein, for a six-week visit during which he toured Paris extensively and was a guest at Versailles. He met his sister and her husband on 18 April 1777 at the Château de la Muette, and spoke frankly to his brother-in-law, curious as to why the royal marriage had not been consummated, arriving at the conclusion that no obstacle to the couple's conjugal relations existed save the Queen's lack of interest and the King's unwillingness to exert himself.
In a letter to his brother Leopold, Grand Duke of Tuscany, Joseph II described them as "a couple of complete blunderers." He disclosed to Leopold that the inexperienced—then still only 22-year-old—Louis XVI had confided in him the course of action he had been undertaking in their marital bed; saying Louis XVI "introduces the member," but then "stays there without moving for about two minutes," withdraws without having completed the act and "bids goodnight."
Suggestions that Louis suffered from phimosis, which was relieved by circumcision, have been discredited. Nevertheless, following Joseph's intervention, the marriage was finally consummated in August 1777. Eight months later, in April 1778, it was suspected that the queen was pregnant, which was officially announced on 16 May. Marie Antoinette's daughter, Marie-Thérèse Charlotte, Madame Royale, was born at Versailles on 19 December 1778. The child's paternity was contested in the libelles, as were all her children's.
In the middle of the queen's pregnancy, two events occurred which had a profound effect on her later life: the return of her friend, the Swedish diplomat Count Axel von Fersen the Younger to Versailles for two years, and her brother's claim to the throne of Bavaria, contested by Saxony and Prussia. Marie Antoinette pleaded with her husband for the French to intercede on behalf of Austria. The Peace of Teschen, signed on 13 May 1779, ended the brief conflict, with the Queen imposing French mediation at her mother's insistence and Austria's gaining the Innviertel territory of at least 100,000 inhabitants—a strong retreat from the early French position which was hostile towards Austria. This gave the impression, partially justified, that the Queen had sided with Austria against France.
Meanwhile, the Queen began to institute changes in court customs. Some of them met with the disapproval of the older generation, such as the abandonment of heavy make-up and the popular wide-hooped panniers. The new fashion called for a simpler feminine look, typified first by the rustic robe à la polonaise style and later by the gaulle, a layered muslin dress Marie Antoinette wore in a 1783 Vigée-Le Brun portrait. In 1780 she began to participate in amateur plays and musicals in the Théâtre de la Reine built for her by Richard Mique.

Repayment of the French debt remained a difficult problem, further exacerbated by Vergennes and also by Marie Antoinette prodding Louis XVI to involve France in the American Revolutionary War. The primary motive for the queen's involvement in political affairs in this period may arguably have had more to do with court factionalism than any true interest on her part in politics themselves, but she played an important role in aiding the American Revolution by securing Austrian and Russian support for France, which resulted in the establishment of the First League of Armed Neutrality that stopped Britain's attack, and by weighing in decisively for the nomination of Philippe Henri, Marquis de Ségur, as Minister of War and Charles Eugène Gabriel de La Croix as Secretary of the Navy in 1780, who helped George Washington defeat the British in the American Revolutionary War, which ended in 1783.
Marie Antoinette's second pregnancy ended in a miscarriage early in July 1779, as confirmed by letters between the Queen and her mother, although some historians believed that she may have experienced bleeding related to an irregular menstrual cycle, which she mistook for a lost pregnancy.
Her third pregnancy was affirmed in March 1781, and on 22 October she gave birth to Louis Joseph Xavier François, Dauphin of France.
Empress Maria Theresa died on 29 November 1780 in Vienna. Marie Antoinette feared that the death of her mother would jeopardise the Franco-Austrian alliance, as well as, ultimately, herself, but her brother, Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor, wrote to her that he had no intention of breaking the alliance.
A second visit from Joseph II, which took place in July 1781 to reaffirm the Franco-Austrian alliance and also to see his sister, was tainted by false rumours that Marie Antoinette was sending money to him from the French treasury.
Declining popularity (1782–1785)
Despite the general celebration over the birth of an heir, Marie Antoinette's political influence, such as it was, was perceived to greatly benefit Austria. During the Kettle War, in which her brother Joseph attempted to open the Scheldt river for naval passage, Marie Antoinette succeeded in obliging Vergennes to pay huge financial compensation to Austria. Finally, the Queen was able to obtain her brother's support against Great Britain in the American Revolution and she neutralized French hostility to his alliance with Russia.
In 1782, after the governess of the royal children, the Princesse de Guéméné, went bankrupt and resigned, Marie Antoinette appointed her favourite, the Duchess of Polignac, to the position. This decision met with disapproval from the court as the duchess was considered to be of too modest origins to occupy such an exalted position. In contrast, both the king and the queen trusted Madame de Polignac completely, gave her a thirteen-room apartment in Versailles and paid her well. The entire Polignac family benefited greatly from royal favour in titles and positions, but its sudden wealth and lavish lifestyle outraged most aristocratic families, who resented the Polignacs' dominance at court, and also fueled the increasing popular disapproval of Marie Antoinette, mostly in Paris. De Mercy wrote to the empress: "It is almost unexampled that in so short a time, the royal favour should have brought such overwhelming advantages to a family".
In June 1783, Marie Antoinette's new pregnancy was announced, but on the night of 1–2 November, her 28th birthday, she suffered a miscarriage.
In 1783 the Queen played a decisive role in the nomination of Charles Alexandre de Calonne, a close friend of the Polignacs, as Controller-General of Finances, and of the Baron de Breteuil as the Minister of the Royal Household, making him perhaps the strongest and most conservative minister of the reign. The result of these two nominations was that Marie Antoinette's influence became paramount in government, and the new ministers rejected any major change to the structure of the old regime. More than that, the decree by de Ségur, the minister of war, requiring four quarterings of nobility as a condition for the appointment of officers, mainly served the interest of older noble families including poorer provincial ones, who were widely seen as a reactionary interest group by ambitious members of the middle and professional classes, by some more recent nobility, and even by the Parisian populace and press. The measure also blocked the access of 'commoners', mainly sons of members of the professional classes, and of more recently elevated nobility to important positions in the armed forces. As such, the decree became an important grievance for social classes that had been habitually supportive of the monarchy and established order, and which went on to supply the bulk of the early leadership of the French Revolution.
Count Axel von Fersen, after his return from America in June 1783, was accepted into the Queen's private society. There were claims that the two were romantically involved, but since most of their correspondence has been lost, destroyed, or redacted, for many years there was no conclusive evidence. Starting in 2016, scientists at the Centre for Research and Restoration of Museums of France (CRCC), uncovered some of the redacted text of the queen's letters to Fersen. The revealed texts do not mention a physical relationship, but do confirm a very strong emotional relationship.
Around this time, pamphlets describing farcical sexual deviance including the Queen and her friends in the court were growing in popularity around the country. The Portefeuille d'un talon rouge was one of the earliest, including the queen and a variety of other nobles in a political statement decrying the immoral practices of the court. As time went on, these came to focus more on the queen. They described amorous encounters with a wide range of figures, from the Duchess of Polignac to Louis XV. As these attacks increased, they were connected with the public's dislike of her association with the rival nation of Austria. It was publicly suggested that her supposed behaviour was learned at the Austrian court, particularly lesbianism, which was known as the "German vice". Her mother again expressed concern for the safety of her daughter, and she began to use Austria's ambassador to France, Comte de Mercy, to provide information on Marie Antoinette's safety and movements.
In 1783, the Queen was busy with the creation of her "hamlet", a rustic retreat built by her favoured architect, Richard Mique, according to the designs of the painter Hubert Robert. Its creation, however, caused another uproar when its cost became widely known. However, the hamlet was not an eccentricity of Marie Antoinette's. It was en vogue at the time for nobles to have recreations of small villages on their properties. In fact, the design was copied from that of Louis Joseph, Prince of Condé. It was also significantly smaller and less intricate than many other nobles'. Around this time she accumulated a library of 5,000 books. Those on music, often dedicated to her, were the most read, though she also liked to read history.
She sponsored the arts, in particular music. Marie Antoinette preferred to hold her musicales in the salon of her Petit appartement de la reine in the Palace of Versailles, or in the Théâtre de la Reine. She limited the audience to her intimate circle and a few musicians, among them the Chevalier de Saint-Georges. "Admitted to perform music with the Queen," Saint-Georges probably played his violin sonatas for two instruments, with Her Majesty playing the fortepiano. She also supported some scientific endeavours, encouraging and witnessing the first launch of a Montgolfière, a hot air balloon for the first time in human history; this extraordinary feat which represented a turning point in human civilization was done by Jean-François Pilâtre de Rozier.
On 27 April 1784, Pierre Beaumarchais's play The Marriage of Figaro premiered in Paris. Initially banned by the king due to its negative portrayal of the nobility, the play was finally allowed to be publicly performed because of the Queen's support and its overwhelming popularity at court, where secret readings of it had been given by Marie Antoinette. The play was a disaster for the image of the monarchy and aristocracy. It inspired Mozart's The Marriage of Figaro, which premiered in Vienna on 1 May 1786.
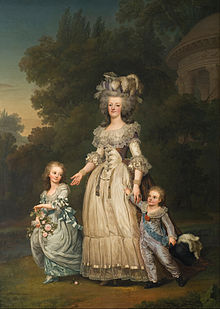
On 24 October 1784, putting the Baron de Breteuil in charge of its acquisition, Louis XVI bought the Château de Saint-Cloud from Louis Philippe I, Duke of Orléans in the name of his wife, which she wanted due to their expanding family. She wanted to be able to own her own property, one that was actually hers, to then have the authority to bequeath it to "whichever of my children I wish," choosing the child she thought could use it rather than it going through patriarchal inheritance laws or whims. It was proposed that the cost could be covered by other sales, such as that of the château Trompette in Bordeaux. This was unpopular, particularly with those factions of the nobility who disliked the Queen, but also with a growing percentage of the population, who disapproved of a queen of France independently owning a private residence. The purchase of Saint-Cloud thus damaged the public's image of the Queen even further. The château's high price, almost 6 million livres, plus the substantial extra cost of redecorating, ensured that much less money was going towards repaying France's substantial debt.
On 27 March 1785, Marie Antoinette gave birth to a second son, Louis Charles, who bore the title of Duke of Normandy. The fact that the birth occurred exactly nine months after Fersen's return did not escape the attention of many, leading to doubt as to the parentage of the child and to a noticeable decline of the Queen's reputation in public opinion. The majority of Marie Antoinette's and Louis XVII's biographers believe that the young prince was the biological son of Louis XVI, including Stefan Zweig and Antonia Fraser, who believe that Fersen and Marie Antoinette were indeed romantically involved. Fraser has also noted that the birthdate matches up perfectly with a known conjugal visit from the King.
Courtiers at Versailles noted in their diaries that the date of the child's conception corresponded perfectly with a period when the King and the Queen had spent much time together, but these details were ignored amid attacks on the Queen's character. These suspicions of illegitimacy, along with the continued publication of the libelles and never-ending cavalcades of court intrigues, the actions of Joseph II in the Kettle War, the purchase of Saint-Cloud and the Affair of the Diamond Necklace combined to turn popular opinion sharply against the Queen, and the image of a licentious, spendthrift, empty-headed foreign queen was quickly taking root in the French psyche.
A second daughter, her last child, Marie Sophie Hélène Béatrix, Madame Sophie, was born on 9 July 1786 and lived only eleven months until 19 June 1787. She was named after the King's aunt, Princess Sophie of France.
Prelude to the Revolution: scandals and the failure of reforms (1786–1789)
Diamond necklace scandal
Main article: Affair of the Diamond Necklace
Marie Antoinette began to abandon her more carefree activities to become increasingly involved in politics in her role as queen of France. By publicly showing her attention to the education and care of her children, the queen sought to improve the dissolute image she had acquired in 1785 from the "Diamond Necklace Affair", in which public opinion had falsely accused her of criminal participation in defrauding the jewelers Boehmer and Bassenge of the price of an expensive diamond necklace they had originally created for Madame du Barry.
The main actors in the scandal were Cardinal de Rohan, Prince de Rohan-Guéméné, Grand Almoner of France, and Jeanne de Valois-Saint-Rémy, Countess de La Motte, a descendant of an illegitimate child of Henry II of France of the House of Valois. Marie Antoinette had profoundly disliked Rohan since the time he had been the French ambassador to Vienna when she was a child. Despite his high clerical position at the Court, she never addressed a word to him. Others involved were Nicole Lequay, alias Baronne d'Oliva, a prostitute who happened to look like Marie Antoinette; Rétaux de Villette, a forger; Alessandro Cagliostro, an Italian adventurer; and the Count de La Motte, Jeanne de Valois' husband. Madame de La Motte tricked Rohan into buying the necklace as a gift to Marie Antoinette, for him to gain the queen's favour.
When the affair was discovered, those involved, except de La Motte and Rétaux de Villette, who both managed to flee, were arrested, tried, convicted, and either imprisoned or exiled. Madame de La Motte was sentenced for life to confinement in the Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital, which also served as a prison for women. Judged by the Parlement of Paris, Rohan was found innocent of any wrongdoing and allowed to leave the Bastille. Marie Antoinette, who had insisted on the arrest of the Cardinal, was dealt a heavy personal blow, as was the monarchy, and despite the fact that the guilty parties were tried and convicted, the affair proved to be extremely damaging to her reputation, which never recovered from it.
Failure of political and financial reforms
Suffering from an acute case of depression, the King began to seek the advice of his wife. In her new role and with increasing political power, the Queen tried to improve the awkward situation brewing between the Parlement and the King. This change of the queen's position signaled the end of the Polignacs' influence and their impact on the finances of the Crown.
Continuing deterioration of the financial situation despite cutbacks to the royal retinue and court expenses ultimately forced the King, the Queen and the Controller-General of Finances, Charles Alexandre de Calonne, at the urging of Vergennes, to call a session of the Assembly of Notables, after a hiatus of 160 years. The assembly was held for the purpose of initiating necessary financial reforms, but the Assembly refused to cooperate. The first meeting took place on 22 February 1787, nine days after the death of Vergennes on 13 February. Marie Antoinette did not attend the meeting and her absence resulted in accusations that the Queen was trying to undermine its purpose. The Assembly was a failure. It did not pass any reforms and, instead, fell into a pattern of defying the King. On the urging of the Queen, Louis XVI dismissed Calonne on 8 April 1787.
On 1 May 1787 Étienne Charles de Loménie de Brienne, Archbishop of Toulouse and one of the queen's political allies was appointed by the King at her urging to replace Calonne, first as Controller-General of Finances and then as Chief Minister. He began to institute more cutbacks at court while trying to restore the royal absolute power weakened by the Parlement. Brienne was unable to improve the financial situation, and since he was the Queen's ally, this failure adversely affected her political position. The continued poor financial climate of the country resulted in the 25 May dissolution of the Assembly of Notables because of its inability to function, and the lack of solutions was blamed on the Queen.
France's financial problems were the result of a combination of factors: several expensive wars; a large royal family whose expenditures were paid for by the state; and an unwillingness on the part of most members of the privileged classes, aristocracy, and clergy, to help defray the costs of the government out of their own pockets by relinquishing some of their financial privileges. As a result of the public perception that she had single-handedly ruined the national finances, Marie Antoinette was given the nickname of "Madame Déficit" in the summer of 1787. While the sole fault for the financial crisis did not lie with her, Marie Antoinette was the biggest obstacle to any major reform effort. She had played a decisive role in the disgrace of the reformer ministers of finance, Anne-Robert-Jacques Turgot (in 1776), and Jacques Necker (first dismissal in 1781). If the secret expenses of the Queen were taken into account, court expenses were much higher than the official estimate of 7% of the state budget.

The queen attempted to fight back with propaganda portraying her as a caring mother, most notably in the painting by Élisabeth Vigée Le Brun exhibited at the Royal Académie Salon de Paris in August 1787, showing her with her children. Around the same time, Jeanne de Valois-Saint-Rémy escaped from prison and fled to London, where she published damaging slander concerning her supposed amorous affair with the Queen.
The political situation in 1787 worsened when, at Marie Antoinette's urging, the Parlement of Paris was exiled to Troyes on 15 August. It further deteriorated when Louis XVI tried to use a lit de justice on 11 November to impose legislation. The new Duke of Orléans publicly protested the king's actions, and was subsequently exiled to his Château de Villers-Cotterêts. The May Edicts issued on 8 May 1788 were also opposed by the public and parlement. Finally, on 8 August, Louis XVI announced his intention to bring back the Estates General, the traditional elected legislature of the country, which had not been convened since 1614.
While from late 1787 up to his death in June 1789 Marie Antoinette's primary concern was the continued deterioration of the health of the Dauphin, who suffered from tuberculosis, she was directly involved in the exile of the Parlement, the May Edicts, and the announcement regarding the Estates General. She did participate in the King Council, the first queen to do this in over 175 years (since Marie de' Medici had been named Chef du Conseil du Roi, between 1614 and 1617), and she was making the major decisions behind the scene and in the Royal Council.
Marie Antoinette was instrumental in the reinstatement of Jacques Necker as Finance Minister on 26 August 1788, a popular move, even though she herself was worried that it would go against her if Necker proved unsuccessful in reforming the country's finances. She accepted Necker's proposition to double the representation of the Third Estate (tiers état) in an attempt to check the power of the aristocracy.
On the eve of the opening of the Estates General the Queen attended the mass celebrating its return. As soon as it opened on 5 May 1789, the fracture between the democratic Third Estate (consisting of bourgeois and radical aristocrats) and the conservative nobility of the Second Estate widened, and Marie Antoinette knew that her rival, the Duke of Orléans, who had given money and bread to the people during the winter, would be acclaimed by the crowd, much to her detriment.
The death of the Dauphin on 4 June, which deeply affected his parents, was virtually ignored by the French people, who were instead preparing for the next meeting of the Estates General and hoping for a resolution to the bread crisis. As the Third Estate declared itself a National Assembly and took the Tennis Court Oath, and as people either spread or believed rumours that the Queen wished to bathe in their blood, Marie Antoinette went into mourning for her eldest son. Her role was decisive in urging the King to remain firm and not concede to popular demands for reforms. In addition, she showed her determination to use force to crush the forthcoming revolution.
French Revolution before Varennes (1789–1791)
The situation escalated on 20 June as the Third Estate, which had been joined by several members of the clergy and radical nobility, found the door to its appointed meeting place closed by order of the King. It thus met at the tennis court in Versailles and took the Tennis Court Oath not to separate before it had given a constitution to the nation.
On 11 July at Marie Antoinette's urging, Necker was dismissed and replaced by Breteuil, the queen's choice to crush the Revolution with mercenary Swiss troops under the command of one of her favourites, Pierre Victor, Baron de Besenval de Brünstatt. At the news, Paris was besieged by riots that culminated in the storming of the Bastille on 14 July. On 15 July Gilbert du Motier, Marquis de Lafayette was named commander-in-chief of the newly formed National Guard.

In the days following the storming of the Bastille, for fear of assassination, and ordered by the King, the emigration of members of the high aristocracy began on 17 July with the departure of the Count of Artois, the Condés, cousins of the King, and the unpopular Polignacs. Marie Antoinette, whose life was as much in danger, remained with the King, whose power was gradually being taken away by the National Constituent Assembly.
The abolition of feudal privileges by the National Constituent Assembly on 4 August 1789 and the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen (La Déclaration des Droits de l'Homme et du Citoyen), drafted by Lafayette with the help of Thomas Jefferson and adopted on 26 August, paved the way to a Constitutional Monarchy (4 September 1791 – 21 September 1792). Despite these dramatic changes, life at the court continued, while the situation in Paris was becoming critical because of bread shortages in September. On 5 October, a crowd from Paris descended upon Versailles and forced the royal family to move to the Tuileries Palace in Paris, where they lived under a form of house arrest under the watch of Lafayette's National Guard, while the Count of Provence and his wife were allowed to reside in the Petit Luxembourg, where they remained until they went into exile on 20 June 1791.
Marie Antoinette continued to perform charitable functions and attend religious ceremonies, but dedicated most of her time to her children. She also played an important political, albeit not public, role between 1789 and 1791 when she had a complex set of relationships with several key actors of the early period of the French Revolution. One of the most important was Necker, the Prime Minister of Finances (Premier ministre des finances). Despite her dislike of him, she played a decisive role in his return to the office. She blamed him for his support of the Revolution and did not regret his resignation in 1790.
Lafayette, one of the former military leaders in the American War of Independence (1775–1783), served as the warden of the royal family in his position as commander-in-chief of the National Guard. Despite his dislike of the Queen—he detested her as much as she detested him and at one time had even threatened to send her to a convent—he was persuaded by the mayor of Paris, Jean Sylvain Bailly, to work and collaborate with her, and allowed her to see Fersen a number of times. He even went as far as exiling the Duke of Orléans, who was accused by the queen of fomenting trouble. His relationship with the King was more cordial. As a liberal aristocrat, he did not want the fall of the monarchy but rather the establishment of a liberal one, similar to that of Great Britain, based on cooperation between the King and the people, as was to be defined in the Constitution of 1791.
Despite her attempts to remain out of the public eye, Marie Antoinette was falsely accused in the libelles of having an affair with Lafayette, whom she loathed, and, as was published in Le Godmiché Royal ("The Royal Dildo"), of having a sexual relationship with the English baroness Lady Sophie Farrell of Bournemouth, a well-known lesbian of the time. Publication of such calumnies continued to the end, climaxing at her trial with an accusation of incest with her son. There is no evidence to support the accusations.
Mirabeau
A significant achievement of Marie Antoinette in that period was the establishment of an alliance with Honoré Gabriel Riqueti, Comte de Mirabeau, the most important lawmaker in the assembly. Like Lafayette, Mirabeau was a liberal aristocrat. He had joined the Third Estate and was not against the monarchy, but wanted to reconcile it with the Revolution. He also wanted to be a minister and was not immune to corruption. On the advice of Mercy, Marie Antoinette opened secret negotiations with him and both agreed to meet privately at the Château de Saint-Cloud on 3 July 1790, where the royal family was allowed to spend the summer, free of the radical elements who watched their every move in Paris. At the meeting, Mirabeau was much impressed by the queen, and remarked in a letter to Auguste Marie Raymond d'Arenberg, Comte de la Marck, that she was the only person the King had by him: La Reine est le seul homme que le Roi ait auprès de Lui. An agreement was reached turning Mirabeau into one of her political allies: Marie Antoinette promised to pay him 6000 livres per month and one million if he succeeded in his mission to restore the King's authority.
The only time the royal couple returned to Paris in that period was on 14 July to attend the Fête de la Fédération, an official ceremony held at the Champ de Mars in commemoration of the fall of the Bastille one year earlier. At least 300,000 persons participated from all over France, including 18,000 National Guards, with Talleyrand, bishop of Autun, celebrating a mass at the autel de la Patrie ("altar of the fatherland"). The King was greeted at the event with loud cheers of "Long live the King!", especially when he took the oath to protect the nation and to enforce the laws voted by the Constitutional Assembly. There were even cheers for the Queen, particularly when she presented the dauphin to the public.
Mirabeau sincerely wanted to reconcile the Queen with the people, and she was happy to see him restoring much of the King's powers, such as his authority over foreign policy, and the right to declare war. Over the objections of Lafayette and his allies, the King was given a suspensive veto allowing him to veto any laws for a period of four years. With time, Mirabeau would support the Queen, even more, going as far as to suggest that Louis XVI "adjourn" to Rouen or Compiègne. This leverage with the Assembly ended with the death of Mirabeau in April 1791, despite the attempt of several moderate leaders of the Revolution to contact the queen to establish some basis of cooperation with her.
Civil Constitution of the Clergy
In March 1791 Pope Pius VI had condemned the Civil Constitution of the Clergy, reluctantly signed by Louis XVI, which reduced the number of bishops from 132 to 93, imposed the election of bishops and all members of the clergy by departmental or district assemblies of electors, and reduced the pope's authority over the Church. Religion played an important role in the life of Marie Antoinette and Louis XVI, both raised in the Roman Catholic faith. The Queen's political ideas and her belief in the absolute power of monarchs were based on France's long-established tradition of the divine right of kings.
On 18 April, as the royal family prepared to leave for Saint-Cloud to attend Easter mass celebrated by a refractory priest, a crowd, soon joined by the National Guard (disobeying Lafayette's orders), prevented their departure from Paris, prompting Marie Antoinette to declare to Lafayette that she and her family were no longer free. This incident fortified her in her determination to leave Paris for personal and political reasons, not alone, but with her family. Even the King, who had been hesitant, accepted his wife's decision to flee with the help of foreign powers and counter-revolutionary forces. Fersen and Breteuil, who represented her in the courts of Europe, were put in charge of the escape plan, while Marie Antoinette continued her negotiations with some of the moderate leaders of the French Revolution.
Flight, arrest at Varennes and return to Paris (21–25 June 1791)
Main article: Flight to Varennes
There had been several plots designed to help the royal family escape, which the Queen had rejected because she would not leave without the King, or which had ceased to be viable because of the King's indecision. Once Louis XVI finally did commit to a plan, its poor execution was the cause of its failure. In an elaborate attempt known as the Flight to Varennes to reach the royalist stronghold of Montmédy, some members of the royal family were to pose as the servants of an imaginary "Mme de Korff", a wealthy Russian baroness, a role played by Louise-Élisabeth de Croÿ de Tourzel, governess of the royal children.
After many delays, the escape was ultimately attempted on 21 June 1791, but the entire family was arrested less than 24 hours later at Varennes and taken back to Paris within a week. The escape attempt destroyed much of the remaining support of the population for the King.
Upon learning of the capture of the royal family, the National Constituent Assembly sent three representatives, Antoine Barnave, Jérôme Pétion de Villeneuve and Charles César de Fay de La Tour-Maubourg to Varennes to escort Marie Antoinette and her family back to Paris. On the way to the capital they were jeered and insulted by the people as never before. The prestige of the French monarchy had never been at such a low level. During the trip, Barnave, the representative of the moderate party in the Assembly, protected Marie Antoinette from the crowds, and even Pétion took pity on the royal family. Brought safely back to Paris, they were met with total silence by the crowd. Thanks to Barnave, the royal couple was not brought to trial and was publicly exonerated of any crime in relation with the attempted escape.
Marie Antoinette's first Lady of the Bedchamber, Jeanne-Louise-Henriette Campan, wrote about what happened to the Queen's hair on the night of 21–22 June, "...in a single night, it had turned white as that of a seventy-year-old woman." (En une seule nuit ils étaient devenus blancs comme ceux d'une femme de soixante-dix ans.)
Radicalization of the Revolution after Varennes (1791–92)

After their return from Varennes and until the storming of the Tuileries on 10 August 1792, the Queen, her family and entourage were held under tight surveillance by the National Guard in the Tuileries, where the royal couple was guarded night and day. Four guards accompanied the Queen wherever she went, and her bedroom door had to be left open at night. Her health also began to deteriorate, thus further reducing her physical activities.
On 17 July 1791, with the support of Barnave and his friends, Lafayette's Garde Nationale opened fire on the crowd that had assembled on the Champ de Mars to sign a petition demanding the deposition of the King. The estimated number of those killed varies between 12 and 50. Lafayette's reputation never recovered from the event and, on 8 October, he resigned as commander of the National Guard. Their enmity continuing, Marie Antoinette played a decisive role in defeating him in his aims to become the mayor of Paris in November 1791.
As her correspondence shows, while Barnave was taking great political risks in the belief that the Queen was his political ally and had managed, despite her unpopularity, to secure a moderate majority ready to work with her, Marie Antoinette was not considered sincere in her cooperation with the moderate leaders of the French Revolution, which ultimately ended any chance to establish a moderate government. Moreover, the view that the unpopular queen was controlling the King further degraded the royal couple's standing with the people, which the Jacobins successfully exploited after their return from Varennes to advance their radical agenda to abolish the monarchy. This situation lasted until the spring of 1792.
Marie Antoinette continued to hope that the military coalition of European kingdoms would succeed in crushing the Revolution. She counted most on the support of her Austrian family. After the death of her brother Joseph II in 1790, his successor and younger brother, Leopold II, was willing to support her to a limited degree. It was her hope that the threat of Austria's advancing military would deter further escalation of revolutionary violence. In a letter to her brother, penned in September 1791, Marie Antoinette expressed how she expected the revolution to react: "...it will be effected by the approach of the war and not by the war itself. The King, his powers restored, will be entrusted with negotiations with the foreign powers, and the princes will return, in the general tranquillity, to reassume their ranks at his court and in the nation." In the same letter, she wrote that the fall of France's monarchy and the subsequent rise of revolutionary principles would be "destructive to all governments."
Upon Leopold's death in 1792, his son, Francis, a conservative ruler, was ready to support the cause of the French royal couple more vigorously because he feared the consequences of the French Revolution and its ideas for the monarchies of Europe, particularly, for Austria's influence in the continent.
Barnave had advised the Queen to call back Mercy, who had played such an important role in her life before the Revolution, but Mercy had been appointed to another foreign diplomatic position and could not return to France. At the end of 1791, ignoring the danger she faced, the Princesse de Lamballe, who was in London, returned to the Tuileries. As for Fersen, despite the strong restrictions imposed on the Queen, he was able to see her a final time in February 1792.
Events leading to the abolition of the monarchy on 10 August 1792
Leopold's and Francis II's strong action on behalf of Marie Antoinette led to France's declaration of war on Austria on 20 April 1792. This resulted in the Queen being viewed as an enemy, although she was personally against Austrian claims to French territories on European soil. That summer, the situation was compounded by multiple defeats of the French Revolutionary Army by the Austrians, in part because Marie Antoinette passed on military secrets to them. In addition, at the insistence of his wife, Louis XVI vetoed several measures that would have further restricted his power, earning the royal couple the nicknames "Monsieur Veto" and "Madame Veto", nicknames then prominently featured in different contexts, including La Carmagnole.
Barnave remained the most important advisor and supporter of the Queen, who was willing to work with him as long as he met her demands, which he did to a large extent. Barnave and the moderates comprised about 260 lawmakers in the new Legislative Assembly; the radicals numbered around 136, and the rest around 350. Initially, the majority was with Barnave, but the Queen's policies led to the radicalization of the Assembly and the moderates lost control of the legislative process. The moderate government collapsed in April 1792 to be replaced by a radical majority headed by the Girondins. The Assembly then passed a series of laws concerning the Church, the aristocracy and the formation of new National Guard units; all were vetoed by Louis XVI. While Barnave's faction had dropped to 120 members, the new Girondin majority controlled the legislative assembly with 330 members. The two strongest members of that government were Jean Marie Roland, who was minister of interior, and General Charles François Dumouriez, the minister of foreign affairs. Dumouriez sympathized with the royal couple and wanted to save them but he was rebuffed by the Queen.
Marie Antoinette's actions in refusing to collaborate with the Girondins, in power between April and June 1792, led them to denounce the treason of the Austrian comity, a direct allusion to the Queen. After Madame Roland sent a letter to the King denouncing the Queen's role in these matters, urged by the Queen, Louis XVI disbanded the government, thus losing his majority in the Assembly. Dumouriez resigned and refused a post in any new government. At this point, the tide against royal authority intensified in the population and political parties, while Marie Antoinette encouraged the King to veto the new laws voted by the Legislative Assembly in 1792. In August 1791, the Declaration of Pillnitz threatened an invasion of France. This led in turn to a French declaration of war in April 1792, which led to the French Revolutionary Wars and to the events of August 1792, which ended the monarchy.

On 20 June 1792, "a mob of terrifying aspect" broke into the Tuileries, made the King wear the bonnet rouge (red Phrygian cap) to show his loyalty to the Revolution, insulted Marie Antoinette, accusing her of betraying France, and threatened her life. In consequence, the Queen asked Fersen to urge the foreign powers to carry out their plans to invade France and to issue a manifesto in which they threatened to destroy Paris if anything happened to the royal family. The Brunswick Manifesto, issued on 25 July 1792, triggered the Insurrection of 10 August when the approach of an armed mob on its way to the Tuileries Palace forced the royal family to seek refuge at the Legislative Assembly. Ninety minutes later, the palace was invaded by the mob, who massacred the Swiss Guards. On 13 August the royal family was imprisoned in the tower of the Temple in the Marais under conditions considerably harsher than those of their previous confinement in the Tuileries.
A week later, several of the royal family's attendants, among them the Princesse de Lamballe, were taken for interrogation by the Paris Commune. Transferred to the La Force Prison, after a rapid judgment, Marie Louise de Lamballe was savagely killed on 3 September. Her head was affixed on a pike and paraded through the city to the Temple for the Queen to see. Marie Antoinette was prevented from seeing it, but fainted upon learning of it.
On 21 September 1792, France was declared a republic, the monarchy was abolished and the National Convention became the governing body of the French First Republic. The royal family name was downgraded to the non-royal "Capets". Preparations began for the trial of the former king in a court of law.
Louis XVI's trial and execution
Main article: Execution of Louis XVICharged with treason against the French Republic, Louis XVI was separated from his family and tried in December. He was found guilty by the Convention, led by the Jacobins who rejected the idea of keeping him as a hostage. On 15 January 1793, by a majority of six votes, he was condemned to death by guillotine and executed on 21 January 1793.
Marie Antoinette in the Temple
The former queen, now called "Widow Capet", plunged into deep mourning. She still hoped her son Louis-Charles, whom the exiled Count of Provence, Louis XVI's brother, had recognized as Louis XVI's successor, would one day rule France. The royalists and the refractory clergy, including those preparing the insurrection in Vendée, supported Marie Antoinette and the return to the monarchy. Throughout her imprisonment and up to her execution, Marie Antoinette could count on the sympathy of conservative factions and social-religious groups which had turned against the Revolution, and also on wealthy individuals ready to bribe republican officials to facilitate her escape. These plots all failed. While imprisoned in the Tower of the Temple, Marie Antoinette, her children and Élisabeth were insulted, some of the guards going as far as blowing smoke in the former queen's face. Strict security measures were taken to assure that Marie Antoinette was not able to communicate with the outside world. Despite these measures, several of her guards were open to bribery and a line of communication was kept with the outside world.
After Louis's execution, Marie Antoinette's fate became a central question of the National Convention. While some advocated her death, others proposed exchanging her for French prisoners of war or for a ransom from the Holy Roman Emperor. Thomas Paine advocated exile to America. In April 1793, during the Reign of Terror, a Committee of Public Safety, dominated by Maximilien Robespierre, was formed, and men such as Jacques Hébert began to call for Marie Antoinette's trial. By the end of May, the Girondins had been chased from power. Calls were also made to "retrain" the eight-year-old Louis XVII, to make him pliant to revolutionary ideas. To carry this out, Louis Charles was separated from his mother on 3 July after a struggle during which his mother fought in vain to retain her son, who was handed over to Antoine Simon, a cobbler and representative of the Paris Commune. Until her removal from the Temple, Marie Antoinette spent hours trying to catch a glimpse of her son, who, within weeks, had been made to turn against her, accusing his mother of wrongdoing.
Conciergerie
On the night of 1 August, at 1:00 in the morning, Marie Antoinette was transferred from the Temple to an isolated cell in the Conciergerie as 'Prisoner nº 280'. Leaving the Tower she bumped her head against the lintel of a door, which prompted one of her guards to ask her if she was hurt, to which she answered, "No! Nothing now can hurt me." This was the most difficult period of her captivity. She was under constant surveillance with no privacy. The "Carnation Plot" (Le complot de l'œillet), an attempt to help her escape at the end of August, was foiled due to the inability to corrupt all the guards. She was attended by Rosalie Lamorlière, who took care of her as much as she could. At least once she received a visit by a Catholic priest.
Trial and execution (14–16 October 1793)


Marie Antoinette was tried by the Revolutionary Tribunal on 14 October 1793. Some historians believe the outcome of the trial had been decided in advance by the Committee of Public Safety around the time the Carnation Plot was uncovered. She and her lawyers were given less than one day to prepare her defense. Among the accusations, many previously published in the libelles, were: orchestrating orgies in Versailles, sending millions of livres of treasury money to Austria, planning the massacre of the National Guards in 1792, declaring her son to be the new king of France, and incest, a charge made by her son Louis-Charles, pressured into doing so by the radical Jacques Hébert who controlled him.
This last accusation drew an emotional response from Marie Antoinette, who refused to respond to this charge, instead appealing to all mothers present in the room. Their reaction comforted her since these women were not otherwise sympathetic to her. Upon being pressed further by a juror to address the accusations of incest, the queen replied, "If I did not respond, it was because it would be against nature for a mother to reply to such an accusation. On this I appeal to all mothers who may be here." When a juror, Joachim Vilate, told Robespierre of this over dinner, Robespierre broke his plate in anger, declaring "That imbecile Hébert!"
Early on 16 October, Marie Antoinette was declared guilty of the three main charges against her: depletion of the national treasury, conspiracy against the internal and external security of the State, and high treason because of her intelligence activities in the interest of the enemy; the latter charge alone was enough to condemn her to death. At worst, she and her lawyers had expected life imprisonment. In the hours left to her, she composed a letter to her sister-in-law Madame Élisabeth, affirming her clear conscience, her Catholic faith, and her love and concern for her children. The letter did not reach Élisabeth. Her will was part of the collection of papers of Robespierre found under his bed and was published by Edme-Bonaventure Courtois.
Preparing for her execution, she had to change clothes in front of her guards. She wanted to wear a black dress but was forced to wear a plain white dress, white being the colour worn by widowed queens of France. Her hair was shorn, her hands bound painfully behind her back and she was put on a rope leash. Unlike her husband, who had been taken to his execution in a carriage (carrosse), she had to sit in an open cart (charrette) for the hour it took to convey her from the Conciergerie via the rue Saint-Honoré thoroughfare to reach the guillotine erected in the Place de la Révolution, the present-day Place de la Concorde. She maintained her composure, despite the insults of the jeering crowd. A constitutional priest was assigned to hear her final confession. He sat by her in the cart, but she ignored him all the way to the scaffold as he had pledged his allegiance to the republic.
Marie Antoinette was executed by beheading by guillotine at 12:15pm on 16 October 1793 during the French Revolution. Her last words are recorded as, "Pardonnez-moi, monsieur. Je ne l'ai pas fait exprès" or "Pardon me, sir, I did not do it on purpose", after accidentally stepping on her executioner's shoe. Marie Tussaud was employed to make a death mask of her head. Her body was thrown into an unmarked grave in the Madeleine cemetery, located close by in rue d'Anjou. Because its capacity was exhausted the cemetery was closed the following year, on 25 March 1794.
Foreign response
After her execution, Marie Antoinette became a symbol abroad, and a controversial figure of the French Revolution. Some used her as a scapegoat to blame for the events of the Revolution. Thomas Jefferson, writing in 1821, claimed that "Her inordinate gambling and dissipations, with those of the Count d'Artois, and others of her clique, had been a sensible item in the exhaustion of the treasury, which called into action the reforming hand of the nation; and her opposition to it, her inflexible perverseness, and dauntless spirit, led herself to the Guillotine," adding that "I have ever believed that, had there been no Queen, there would have been no revolution."

In his 1790 treatise, Reflections on the Revolution in France, which was written during Marie Antoinette's imprisonment in Paris, but prior to her execution, Edmund Burke lamented that "the age of chivalry is gone. That of sophisters, economists, and calculators has succeeded, and the glory of Europe is extinguished forever" and now "Never, never more, shall we behold that generous loyalty to rank and sex." After receiving the news, Maria Carolina, Queen of Naples and close sister to Marie Antoinette, spiraled into a state of mourning and an anger against the revolutionaries. She quickly suspended protections of reformers and intellectuals in Naples, allowed Neapolitan bishops wide latitude to halt the secularization of the country, and offered succor to the overflowing number of émigrés fleeing from revolutionary France, many of whom were granted pensions.
Bourbon Restoration
Both Marie Antoinette's and Louis XVI's bodies were exhumed on 18 January 1815, during the Bourbon Restoration, when the Count of Provence ascended the newly reestablished throne as Louis XVIII, King of France and of Navarre. Christian burial of the royal remains took place three days later, on 21 January, in the necropolis of French kings at the Basilica of Saint-Denis.
Legacy
For many revolutionary figures, Marie Antoinette was the symbol of what was wrong with the old regime in France. The onus of having caused the financial difficulties of the nation was placed on her shoulders by the revolutionary tribunal, and under the new republican ideas of what it meant to be a member of a nation, her Austrian descent and continued correspondence with the competing nation made her a traitor. The people of France saw her death as a necessary step toward completing the revolution. Furthermore, her execution was seen as a sign that the revolution had done its work.
Marie Antoinette is also known for her taste for fine things, and her commissions from famous craftsmen, such as Jean Henri Riesener, suggest more about her enduring legacy as a woman of taste and patronage. For instance, a writing table attributed to Riesener, now located at Waddesdon Manor, bears witness to Marie Antoinette's desire to escape the oppressive formality of court life, when she decided to move the table from the queen's boudoir, de la Meridienne, at Versailles to her humble interior, the Petit Trianon. Her favourite objects filled her small, private chateau and reveal aspects of Marie Antoinette's character that have been obscured by satirical political prints, such as those in Les Tableaux de la Révolution. She owned several instruments. In 1788 she bought a piano made by Sébastien Érard.
A catalog of Marie Antoinette's personal library of 736 volumes was published by Paul Lacroix in 1863, using his pseudonym P. L. Jacob. The listed books were from her library at the Petit Trianon, including many found in her boudoir, and mostly consist of novels and plays. A random selection of her books includes Histoire de Mademoiselle de Terville by Madeleine d'Arsant de Puisieux, Le Philosophe parvenu ou Lettres et pièces originales contenant les aventures d'Eugène Sans-Pair by Robert-Martin Lesuire, and Oeuvres mêlées... contenant des tragédies et différents ouvrages en vers et en prose by Madeleine-Angélique de Gomez. A larger and more official library belonging to Marie Antoinette was kept at the Tuileries Palace in Paris.
Long after her death, Marie Antoinette remains a major historical figure linked with conservatism, the Catholic Church, wealth and fashion. She has been the subject of a number of books, films, and other media. Politically engaged authors have deemed her the quintessential representative of class conflict, western aristocracy and absolutism. Some of her contemporaries, such as Thomas Jefferson, attributed to her the start of the French Revolution.
In popular culture
Main article: Cultural depictions of Marie AntoinetteThe phrase "let them eat cake" is often conventionally attributed to Marie Antoinette, but there is no evidence that she ever uttered it, and it is now generally regarded as a journalistic cliché. This phrase originally appeared in Book VI of the first part of Jean-Jacques Rousseau's autobiographical work Les Confessions, finished in 1767 and published in 1782: "Enfin Je me rappelai le pis-aller d'une grande Princesse à qui l'on disait que les paysans n'avaient pas de pain, et qui répondit: Qu'ils mangent de la brioche" ("Finally I recalled the stopgap solution of a great princess who was told that the peasants had no bread, and who responded: 'Let them eat brioche'"). Rousseau ascribes these words to a "great princess", but the purported writing date precedes Marie Antoinette's arrival in France. Some think that he invented it altogether.
In the United States, expressions of gratitude to France for its help in the American Revolution included naming a city Marietta, Ohio, in 1788. Her life has been the subject of many films, such as Marie Antoinette (1938) and Marie Antoinette (2006). There is a book about Marie Antoinette by Antonia Fraser called Marie Antoinette: The Journey.
In 2020, a silk shoe that belonged to her was sold in an auction in the Palace of Versailles for 43,750 euros ($51,780).
In 2022, her story was dramatised by a Canal+ and BBC English-language television series.
In the 2024 Summer Olympics opening ceremony in Paris, heavy metal band Gojira's performance showed a depiction of the freshly severed head of Marie Antoinette singing, in reference to the French Revolution.
Family tree
| Simplified family tree illustrating the Bourbon-Habsburg-Lorraine connections |
|---|
|
Notes: Solid vertical lines indicate parent-child relationship, while dashed lines represent more distant ancestor-descendant connections. |
Children
Children of Marie Antoinette| Name | Portrait | Lifespan | Age | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marie-Thérèse Charlotte Madame Royale |

|
19 December 1778 – 19 October 1851 |
72 years and 10 months | Married her cousin, Louis Antoine, Duke of Angoulême, the eldest son of the future Charles X of France. |
| Louis Joseph Xavier François Dauphin de France |

|
22 October 1781 – 4 June 1789 |
7 years, 7 months and 13 days | Contracted tuberculosis and died in childhood on the very day the Estates General convened. |
| Louis XVII of France (nominally) King of France and Navarre |

|
27 March 1785 – 8 June 1795 |
10 years, 2 months and 12 days | Died in childhood; no issue. He was never officially king, nor did he rule. His title was bestowed by his royalist supporters and acknowledged implicitly by his uncle's later adoption of the regnal name Louis XVIII rather than Louis XVII, upon the restoration of the Bourbon monarchy in 1814. |
| Marie Sophie Hélène Béatrix | 
|
9 July 1786 – 19 June 1787 |
11 months and 10 days | Died in the Palace of Versailles at the age of 11 months after suffering several days of convulsions, possibly related to tuberculosis. |
In addition to her biological children, Marie Antoinette adopted four children: "Armand" Francois-Michel Gagné, a poor orphan adopted in 1776; Jean Amilcar, a Senegalese slave boy given to the queen as a present by Chevalier de Boufflers in 1787, but whom she instead freed, baptized, adopted and placed in a pension; Ernestine Lambriquet, daughter of two servants at the palace, who was raised as the playmate of her daughter Marie-Thérèse and whom she adopted after the death of her mother in 1788; and "Zoe" Jeanne Louise Victoire, who was adopted in 1790 along with her two older sisters when her parents, an usher and his wife in service of the King, had died.
Of these, only Armand, Ernestine, and Zoe actually lived with the royal family: Jean Amilcar, along with the elder siblings of Zoe and Armand who were also formally foster children of the royal couple, simply lived at the queen's expense until her imprisonment, which proved fatal for at least Amilcar, as he was evicted from the boarding school when the fee was no longer paid, and reportedly starved to death on the street.
Armand and Zoe had a position which was more similar to that of Ernestine; Armand lived at court with the king and queen until he left them at the outbreak of the Revolution because of his republican sympathies, and Zoe was chosen to be the playmate of the dauphin, just as Ernestine had once been selected as the playmate of Marie-Thérèse, and later sent away to her sisters in a convent boarding school before the Flight to Varennes in 1791.
References
Notes
- Jones, Daniel (2003) , Peter Roach; James Hartmann; Jane Setter (eds.), English Pronouncing Dictionary, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-3-12-539683-8.
- Royal household spending in 1788 was 13% of total state expenses(excluding interest on debts). Finances of Louis XVI (1788) | Nicholas E. Bomba https://blogs.nvcc.edu Archived 20 April 2011 at the Wayback Machine › nbomba › files › 2016/10, https://books.google.com/books?id=ixJWG9q0Eo4C
- "The Birth of Marie Antoinette | History Today". historytoday.com. Retrieved 20 November 2022.
- Fraser 2002, p. 5
- Fraser 2002, pp. 5–6
- ^ de Decker, Michel (2005). Marie-Antoinette, les dangereuses liaisons de la reine. Paris, France: Belfond. pp. 12–20. ISBN 978-2714441416.
- ^ de Ségur d'Armaillé, Marie Célestine Amélie (1870). Marie-Thérèse et Marie-Antoinette. Paris, France: Editions Didier Millet. pp. 34, 47.
- Lever 2006, p. 10
- ^ Fraser 2001, pp. 22–23, 166–70
- Delorme, Philippe (1999). Marie-Antoinette. Épouse de Louis XVI, mère de Louis XVII. Pygmalion Éditions. p. 13.
- Lever, Évelyne (2006). 'C'état Marie-Antoinette. Paris, France: Fayard. p. 14.
- ^ Cronin 1989, p. 45
- Fraser 2002, pp. 32–33
- Cronin 1989, p. 46
- Weber 2007, pp. 13–14
- ^ Fraser 2002, p. 28.
- Covington, Richard (November 2006). "Marie Antoinette". Smithsonian Magazine. Archived from the original on 24 January 2024.
- Weber 2007, pp. 15–16
- Erickson 1991, pp. 40–41
- Fraser 2001, p. 37.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 51–53
- Nolhac, Pierre (1929), La Dauphine Marie Antoinette, pp. 46–48
- Fraser 2001, pp. 70–71
- Nolhac 1929, pp. 55–61
- Fraser 2001, p. 157; d'Arneth & Geffroy 1874, pp. 80–90, 110–115.
- Cronin 1974, pp. 61–63
- Cronin 1974, p. 61
- Fraser 2001, pp. 80–81; d'Arneth & Geffroy 1874, pp. 65–75.
- Lever 2006, p. 38
- Fraser, Marie Antoinette, 2001, p. 124.
- Levron, Jacques (1973). Madame du Barry. pp. 75–85.
- Lever 1991, p. 124
- Goncourt, Edmond de (1880). La Du Barry. Paris, France: G. Charpentier. pp. 195–96.
- Lever, Evelyne, Louis XV, Fayard, Paris, 1985, p. 96
- Vatel, Charles (1883). Histoire de Madame du Barry: d'après ses papiers personnels et les documents d'archives. Paris, France: Hachette Livre. p. 410. ISBN 978-2013020077.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 136–37; d'Arneth & Geffroy 1874, pp. 475–480.
- Castelot 1962, pp. 107–108; Fraser 2001, pp. 124–27; Lever 1991, p. 125.
- Cronin 1974, p. 215
- Batterberry, Michael; Ruskin Batterberry, Ariane (1977). Fashion, the mirror of history. Greenwich, Connecticut: Greenwich House. p. 190. ISBN 978-0-517-38881-5.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 150–51
- Erickson 1991, pp. 163
- Thomas, Chantal. The Wicked Queen: The Origins of the Myth of Marie Antoinette. Translated by Julie Rose. New York: Zone Books, 2001, p. 51.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 140–45
- d'Arneth & Geffroy 1874, pp. 400–410.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 129–31
- Fraser 2001, pp. 131–32; Bonnet 1981
- Fraser 2001, pp. 111–13
- Howard, Patricia (1995). Gluck: An Eighteenth-century Portrait in Letters and Documents. Clarendon Press. pp. 105–15, 240–45. ISBN 978-0-19-816385-5.
- Lever, Evelyne, Louis XVI, Fayard, Paris, 1985, pp. 289–91
- Cronin 1974, pp. 158–59
- Fraser 2002b, p. 156.
- "Circumcision and phimosis in eighteenth century France". History of Circumcision. Retrieved 16 December 2016.
- Cronin 1974, p. 159
- Fraser 2001, pp. 160–61
- Cronin 1974, p. 161
- Hibbert 2002, p. 23
- Fraser 2001, p. 169
- Fraser, Antonia (2006). Marie Antoinette: The Journey. Phoenix. pp. 182–193. ISBN 9780753821404.
- Samuel, Henry (12 January 2016). "Marie-Antoinette's torrid affair with Swedish count revealed in decoded letters". The Telegraph.
- Cronin 1974, pp. 162–64
- Fraser 2001, pp. 158–71
- d'Arneth & Geffroy 1874, pp. 168–170, 180–182, 210–212.
- Kindersley, Dorling (2012). Fashion: The Definitive History of Costume and Style. New York: DK Publishing. pp. 146–49.
- Cronin 1974, pp. 127–28
- Fraser 2001, pp. 174–79
- Archived 18 March 2015 at the Wayback Machine Kelly Hall: "Impropriety, Informality and Intimacy in Vigée Le Brun's Marie Antoinette en Chemise", pp. 21–28. Providence College Art Journal, 2014.
- Larkin, T. Lawrence (2010). "A "Gift" Strategically Solicited and Magnanimously Conferred". Winterthur Portfolio. 44 (1): 31–76. doi:10.1086/651087. ISSN 0084-0416. JSTOR 10.1086/651087. S2CID 142922208.
- "Marie-Antoinette | Biography & French Revolution". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 3 February 2018.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 152, 171, 194–95
- Meagen Elizabeth Moreland: The Performance of Motherhood in the Correspondence of Madame de Sévigné, Marie-Thérèse of Austria and Joséphine Bonaparte to their Daughters. Chapter I: Contextualizing the correspondence, p. 11 Archived 2 February 2017 at the Wayback Machine (retrieved 1 October 2016).
- "From Vienna to Versailles: from Imperial Princess to Crown Prince" (PDF).
- Arneth, Alfred (1866). Marie Antoinette; Joseph II, und Leopold II (in French and German). Leipzig / Paris / Vienna: K.F. Köhler / Ed. Jung-Treuttel / Wilhelm Braumüller. p. 23 (footnote).
- Fraser 2002, p. 186.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 184–87
- Price 1995, pp. 55–60
- Fraser, pp. 232–36
- Le Marquis de Beaucourt (1895). Lettres de Marie Antoinette. Vol. ii. pp. 42–44.
- Lever 1991, pp. 350–353.
- Cronin 1974, p. 193
- Fraser 2001, pp. 198–201
- Price, Munro (2003). The Road from Versailles: Louis XVI, Marie Antoinette, and the Fall of the French Monarchy. Macmillan. pp. 14–15, 72. ISBN 978-0-312-26879-4.
- Zweig 2002, p. 121
- Wheeler, Bonnie; Parsons, John Carmi (2003). Eleanor of Aquitaine: Lord and Lady. p. 288.
- "Charles-Alexandre de Calonne | French statesman". Britannica. Retrieved 16 December 2021.
- ^ Fraser 2001, pp. 218–20
- Price, Munro (1995). Preserving the Monarchy: The Comte de Vergennes 1774-1787. Cambridge University Press. pp. 30–35, 145–50. ISBN 978-0-521-46566-3.
- Farr, Evelyn (12 October 2013). Marie-Antoinette and Count Fersen: The Untold Love Story (2nd Revised ed.). Peter Owen Publishers. ISBN 978-0720610017.
- Fraser 2001, p. 202
- Joseph Bamat (12 January 2016). "Science sheds new light on Marie Antoinette 'love affair'". France24.
- Farr, Evelyn (1 July 2016). I Love You Madly: Marie-Antoinette and Count Fersen: The Secret Letters. Peter Owen Publishers. ISBN 978-0720618778.
- Hunt, Lynn. "The Many Bodies of Marie Antoinette: Political Pornography and the Problem of the Feminine in the French Revolution". In The French Revolution: Recent Debates and New Controversies 2nd edition, ed. Gary Kates. New York and London: Routledge, 1998, pp. 201–18.
- Thomas, Chantal. The Wicked Queen: The Origins of the Myth of Marie Antoinette. Translated by Julie Rose. New York: Zone Books, 2001, pp. 51–52.
- Lever 2006, p. 158
- Fraser, pp. 206–08
- Gutwirth, Madelyn (1992). The Twilight of the Goddesses: Women and Representation in the French Revolutionary Era. Rutgers University Press. pp. 103, 178–85, 400–05. ISBN 978-0-8135-1787-2.
- Fraser 2002b, p. 207.
- Fraser 2001, p. 208
- Bombelles, Marc-Marie marquis de (1977). Journal (in French). Vol. 1: 1780-1784. Droz. pp. 258–65.
- Banat 2006, p. 151-152.
- Cronin 1974, pp. 204–05
- Fraser 2001, pp. 214–15
- ^ Fraser 2002, p. 217.
- Fraser 2002b, p. 217.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 216–20
- Lever 1991, pp. 358–360.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 224–25
- Lever 2006, p. 189
- Stefan Zweig, Marie Antoinette: The portrait of an average woman, New York, 1933, pp. 143, 244–47
- Fraser 2001, pp. 267–69
- Ian Dunlop, Marie-Antoinette: A Portrait, London, 1993
- Évelyne Lever, Marie-Antoinette : la dernière reine, Fayard, Paris, 2000
- Simone Bertière, Marie-Antoinette: l'insoumise, Le Livre de Poche, Paris, 2003
- Jonathan Beckman, How to ruin a Queen: Marie Antoinette, the Stolen Diamonds and the Scandal that shook the French throne, London, 2014
- Munro Price, The Fall of the French Monarchy: Louis XVI, Marie Antoinette and the baron de Breteuil, London, 2002
- Deborah Cadbury, The Lost King of France: The tragic story of Marie-Antoinette's Favourite Son, London, 2003, pp. 22–24
- Cadbury, p. 23
- Fraser 2001, p. 226
- Fraser 2002, p. 244.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 248–52
- ^ Fraser 2001, pp. 248–50
- Fraser 2001, pp. 246–48
- Lever 1991, pp. 419–420.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 250–60
- Fraser 2001, pp. 254–55
- Fraser 2001, pp. 254–60
- Facos, p. 12.
- Schama, p. 221.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 255–58
- Fraser 2001, pp. 257–58
- Fraser 2001, pp. 258–59
- Fraser 2001, pp. 260–61
- Fraser 2001, pp. 263–65
- Lever 2001, pp. 448–453.
- Morris, Gouverneur (1939). Beatrix Cary Davenport (ed.). A diary of the French Revolution 1789–93. Boston: Houghton Mifflin. pp. 66–67.
- Nicolardot, Louis, Journal de Louis Seize, 1873, pp. 133–38
- Fraser 2001, pp. 274–78
- Fraser 2001, pp. 279–82
- Lever 1991, pp. 462–467.
- Doyle, William (1990). The Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford University Press. pp. 100–105.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 280–85
- Morris 1939, pp. 130–35
- Fraser 2001, pp. 282–84
- Lever 1991, pp. 474–478.
- ^ Fraser 2001, pp. 284–89
- ^ Browning, Oscar, ed. (1885). Despatches of Earl Gower. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 70–75, 245–50.
- Journal d'émigration du prince de Condé. 1789–1795, publié par le comte de Ribes, Bibliothèque nationale de France. Archived 7 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- Castelot, Charles X, Librairie Académique Perrin, Paris, 1988, pp. 78–79
- Fraser 2001, p. 289
- Lever 1991, pp. 484–485.
- "dossiers d'histoire – Le Palais du Luxembourg – Sénat". senat.fr. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 18 October 2015.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 304–08
- Discours prononcé par M. Necker, Premier Ministre des Finances, à l'Assemblée Nationale, le 24. Septembre 1789. Archived 3 December 2022 at the Wayback Machine
- Fraser 2001, p. 315
- Lever 1991, pp. 536–537.
- Fraser 2001, p. 319
- Castelot 1962, p. 334; Lever 1991, pp. 528–530.
- Mémoires de Mirabeau, tome VII, p. 342.
- Lever 1991, pp. 524–527.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 314–316; Castelot 1962, p. 335.
- Fraser 2001, p. 313
- Zevin, Alexander (Spring 2007). "Marie Antoinette and The Ghosts of the French Revolution". Cineaste. 32 (2): 32–34 – via Academic Search Ultimate.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 321–323; Lever 1991, pp. 542–552; Castelot 1962, pp. 336–339.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 321–325; Castelot 1962, pp. 340–341.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 325–48
- Lever 1991, pp. 555–568.
- Lever 1991, pp. 569–575; Castelot 1962, pp. 385–398.
- Mémoires de Madame Campan, première femme de chambre de Marie-Antoinette, Le Temps retrouvé, Mercure de France, Paris, 1988, p. 272, ISBN 2-7152-1566-5
- Le Marquis de Beaucourt (1895). Lettres de Marie Antoinette. Vol. ii. pp. 364–78.
- Lever 1991, pp. 576–580.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 350, 360–71
- Fraser 2001, pp. 353–54
- Fraser 2001, pp. 350–52
- Fraser 2001, pp. 357–358; Castelot 1962, pp. 408–409.
- "Marie Antoinette as queen of France". Die Welt der Habsburger. Retrieved 15 December 2020.
- Mark, Harrison W. (9 September 2022). "Declaration of Pillnitz". World History Encyclopedia. Archived from the original on 4 April 2024. Retrieved 1 June 2024.
- "Marie Antoinette's View of the Revolution (8 September 1791)". LIBERTY, EQUALITY, FRATERNITY: EXPLORING THE FRENCH REVOLUTION. 8 September 1791. Retrieved 21 January 2024.
- Lever 1991, pp. 599–601.
- ^ Fraser 2001, pp. 365–68
- Lever 1991, pp. 607–609.
- Castelot 1962, pp. 415–416; Lever 1991, pp. 591–592.
- Castelot 1962, p. 418.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 371–73
- Fraser 2001, pp. 368, 375–78
- Fraser 2001, pp. 373–379; Castelot 1962, pp. 428–435.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 382–86
- Fraser 2001, p. 389; Castelot 1962, pp. 442–446.
- Fraser 2001, p. 392
- Fraser 2001, pp. 395–399; Castelot 1962, pp. 447–453.
- Castelot 1962, pp. 453–457.
- "Marie Antoinette: Last Queen of France". Jane Austen Centre and the Jane Austen Online Gift Shop. Archived from the original on 13 December 2021. Retrieved 13 December 2021.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 398, 408
- Fraser 2001, pp. 411–12
- Fraser 2001, pp. 412–14
- Funck-Brentano, Frantz: Les Derniers jours de Marie-Antoinette, Flammarion, Paris, 1933
- Furneaux 1971, pp. 139–42
- Fraser 2001, p. 437.
- G. Lenotre: The Last Days of Marie Antoinette, 1907.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 416–20
- Castelot 1962, pp. 496–500.
- Procès de Louis XVI, de Marie-Antoinette, de Marie-Elisabeth et de Philippe d'Orléans, Recueil de pièces authentiques, Années 1792, 1793 et 1794, De Mat, imprimeur-libraire, Bruxelles, 1821, p. 473
- Castelot 1957, pp. 380–385; Fraser 2001, pp. 429–435.
- Hardman, John (2019). Marie-Antoinette: The Making of a French Queen. Yale University Press. p. 304.
- Le procès de Marie-Antoinette, Ministère de la Justice, 17 October 2011, (French) Archived 21 September 2015 at the Wayback Machine
- Furneaux 1971, pp. 150–54
- Elena Maria Vidal (26 May 2007), "Last Letter of Marie-Antoinette", Tea at Trianon
- Courtois, Edme-Bonaventure; Robespierre, Maximilien de (31 January 2019). "Papiers inédits trouvés chez Robespierre, Saint-Just, Payan, etc. supprimés ou omis par Courtois..." Baudoin – via Google Books.
- Chevrier, M. -R; Alexandre, J.; Laux, Christian; Godechot, Jacques; Ducoudray, Emile (1983). "Documents intéressant E.B. Courtois. In: Annales historiques de la Révolution française, 55e Année, No. 254 (Octobre–Décembre 1983), pp. 624–28". Annales Historiques de la Révolution Française. 55 (254): 624–35. JSTOR 41915129.
- Furneaux 1971, pp. 155–56
- Castelot 1957, pp. 550–558; Lever 1991, p. 660.
- Fraser 2001, p. 440
- The Times 23 October 1793 Archived 1 November 2009 at the Wayback Machine, The Times.
- "Famous Last Words". 23 May 2012.
- "Marie Tussaud". encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 28 March 2016.
- Ragon, Michel, L'espace de la mort, Essai sur l'architecture, la décoration et l'urbanisme funéraires, Michel Albin, Paris, 1981, ISBN 978-2-226-22871-0 Archived 3 December 2022 at the Wayback Machine
- "Passages from his autobiography". bartleby. 1854. Retrieved 17 May 2021.
- Burke, Edmund (1790). Reflections on the Revolution in France, And on the Proceedings in Certain Societies in London Relative to that Event. In a Letter Intended to Have Been Sent to a Gentleman in Paris (1 ed.). London: J.Dodsley in Pall Mall. Retrieved 7 September 2021.
- "Maria Carolina (1752–1814)". Cengage. 2019. Retrieved 17 May 2021.
- Fraser 2001, pp. 411, 447
- Hunt, Lynn (1998). "The Many Bodies of Marie Antoinette: Political Pornography and the Problem of the Feminine in the French Revolution". In Kates, Gary (ed.). The French Revolution: Recent Debates and New Controversies (2nd ed.). London, England: Routledge. pp. 201–18. ISBN 978-0415358330.
- Kaiser, Thomas (Fall 2003). "From the Austrian Committee to the Foreign Plot: Marie-Antoinette, Austrophobia, and the Terror". French Historical Studies. 26 (4). Durham, North Carolina: Duke University Press: 579–617. doi:10.1215/00161071-26-4-579. S2CID 154852467.
- Thomas, Chantal (2001). The Wicked Queen: The Origins of the Myth of Marie Antoinette. Translated by Julie Rose. New York City: Zone Books. p. 149. ISBN 0942299396.
- Jenner, Victoria (12 November 2019). "Celebrating Marie-Antoinette on her birthday". Waddesdon Manor. Retrieved 18 November 2019.
- "Le 13e piano de Marie-Antoinette ? - Mardi 09 mai 2017". www.rouillac.com.
- "MARIE ANTOINETTE'S PIANO".
- P. L. Jacob. Bibliothèque de la reine Marie-Antoinette au Petit Trianon d'après l'inventaire original dressé par ordre de la convention : catalogue avec des notes inédites du marquis de Paulmy. Paris: Jules Gay, 1863.
- "Marie Antoinette", LibraryThing https://www.librarything.com/profile/MarieAntoinette Archived 24 October 2021 at the Wayback Machine Accessed October 23, 2021.
- Jefferson, Thomas (2012). Autobiography of Thomas Jefferson. Mineola, New York: Courier Dover Publications. ISBN 978-0486137902. Retrieved 29 March 2013.
I have ever believed that had there been no queen, there would have been no revolution.
- Fraser 2001, pp. xviii, 160; Lever 2006, pp. 63–65; Lanser 2003, pp. 273–90.
- Johnson 1990, p. 17.
- Sturtevant, pp. 14, 72.
- Dyke, W. S. Van; Duvivier, Julien (26 August 1938), Marie Antoinette (Biography, Drama, History), Norma Shearer, Tyrone Power, John Barrymore, Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer (MGM), retrieved 1 June 2024
- Coppola, Sofia (20 October 2006), Marie Antoinette (Biography, Drama, History), Kirsten Dunst, Jason Schwartzman, Rip Torn, Columbia Pictures, Pricel, Tohokushinsha Film Corporation (TFC), retrieved 1 June 2024
- "Dunst puts fresh face on 'Marie Antoinette'". MSNBC. Associated Press. 23 October 2006. Archived from the original on 16 September 2012. Retrieved 11 December 2008.
- "Kirsten Dunst Poses as Marie Antoinette in Vogue". Fox News Channel. Associated Press. 14 August 2006. Archived from the original on 28 January 2007. Retrieved 10 December 2008.
- "Marie Antoinette's silk slipper fetches US$50,000 at auction". CTV News. 15 November 2020. Retrieved 26 February 2021.
- Fraser 2002
- Fraser, Antonia, Marie Antoinette, The Journey, Anchor Books, USA, 2001, p. 257, ISBN 0-385-48949-8.
- ^ Philippe Huisman, Marguerite Jallut: Marie Antoinette, Stephens, 1971.
Bibliography
- d'Arneth, Alfred Ritter; Geffroy, A., eds. (1874). Correspondance secrète entre Marie-Thérèse et le comte de Mercy-Argenteau, avec les lettres de Marie-Thérèse et de Marie-Antoinette (in French). Vol. 3. Firmin-Didot.
- Banat, Gabriel (2006). The Chevalier de Saint-Georges: Virtuoso of the Sword and the Bow. Hillsdale, New York: Pendragon Press. ISBN 978-1-57647-109-8.
- Bonnet, Marie-Jo (1981). Un choix sans équivoque: recherches historiques sur les relations amoureuses entre les femmes, XVIe–XXe siècle (in French). Paris: Denoël. OCLC 163483785.
- Castelot, André (1957). Queen of France: a biography of Marie Antoinette. trans. Denise Folliot. New York: Harper & Brothers. OCLC 301479745.
- Castelot, André (1962). Marie-Antoinette. Paris, France: Librairie académique Perrin. ISBN 978-2262048228.
- Cronin, Vincent (1974). Louis and Antoinette. Collins. ISBN 978-0-00-211494-3.
- Cronin, Vincent (1989). Louis and Antoinette. London: The Harvill Press. ISBN 978-0-00-272021-2.
- Dams, Bernd H.; Zega, Andrew (1995). La folie de bâtir: pavillons d'agrément et folies sous l'Ancien Régime. trans. Alexia Walker. Flammarion. ISBN 978-2-08-201858-6.
- Facos, Michelle (2011). An Introduction to Nineteenth-Century Art. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-136-84071-5. Retrieved 1 September 2011.
- Farr, Evelyn (2013). Marie-Antoinette and Count Fersen: The Untold Love Story (2nd Revised ed.). Peter Owen Publishers. ISBN 978-0720610017.
- Furneaux, Rupert (1971). The Last Days of Marie Antoinette and Louis XVI. John Day Company.
- Fraser, Antonia (2001). Marie Antoinette (1st ed.). New York: N.A. Talese/Doubleday. ISBN 978-0-385-48948-5.
- Fraser, Antonia (2002). Marie Antoinette: The Journey (2nd ed.). Garden City: Anchor Books. ISBN 978-0-385-48949-2.
- Fraser, Antonia (2002b). Marie Antoinette: The Journey. Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group. ISBN 9781400033287.
- Hermann, Eleanor (2006). Sex with the Queen. Harper/Morrow. ISBN 978-0-06-084673-2.
- Hibbert, Christopher (2002). The Days of the French Revolution. Harper Perennial. ISBN 978-0-688-16978-7.
- Johnson, Paul (1990). Intellectuals. New York: Harper & Row. ISBN 978-0-06-091657-2.
- Lanser, Susan S. (2003). "Eating Cake: The (Ab)uses of Marie-Antoinette". In Goodman, Dena (ed.). Marie-Antoinette: Writings on the Body of a Queen. Psychology Press. ISBN 978-0-415-93395-7.
- Lever, Evelyne (1991). Marie Antoinette. Fayard.
- Lever, Evelyne (24 September 2001). Marie Antoinette: The Last Queen of France. Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-312-28333-9.
- Lever, Évelyne (2006). Marie Antoinette: The Last Queen of France. London: Portrait. ISBN 978-0-7499-5084-2.
- Schama, Simon (1989). Citizens: A Chronicle of the French Revolution. New York: Vintage. ISBN 978-0-679-72610-4.
- Seulliet, Philippe (July 2008). "Swan Song: Music Pavilion of the Last Queen of France". World of Interiors (7).
- Sturtevant, Lynne (2011). A Guide to Historic Marietta, Ohio. The History Press. ISBN 978-1-60949-276-2. Retrieved 1 September 2011.
- Weber, Caroline (2007). Queen of Fashion: What Marie Antoinette Wore to the Revolution. Picador. ISBN 978-0-312-42734-4.
- Wollstonecraft, Mary (1795). An Historical and Moral View of the Origin and Progress of the French Revolution and the Effect it Has Produced in Europe. St. Paul's.
Further reading
- Bashor, Will (2013). Marie Antoinette's Head: The Royal Hairdresser, the Queen, and the Revolution. Lyons Press. p. 320. ISBN 978-0762791538.
- Erickson, Carolly (1991). To the Scaffold. New York: William Morrow and Company, Inc. ISBN 0-312-32205-4.
- Farr, Evelyn (2016). I Love You Madly: Marie-Antoinette and Count Fersen: The Secret Letters. Peter Owen Publishers. ISBN 978-0720618778.
- Jacob, P.L. (1863). Bibliothèque de la reine Marie-Antoinette au Petit Trianon d'après l'inventaire original dressé par ordre de la convention : catalogue avec des notes inédites du marquis de Paulmy. Jules Gay. OCLC 12097301.
- Kaiser, Thomas (Fall 2003). "From the Austrian Committee to the Foreign Plot: Marie-Antoinette, Austrophobia, and the Terror". French Historical Studies. 26 (4): 579–617. doi:10.1215/00161071-26-4-579. S2CID 154852467.
- Kates, Gary (1998). The French Revolution: Recent Debates and New Controversies 2nd ed. Routledge. pp. 201–218. ISBN 0-415-35833-7.
- Lasky, Kathryn (2000). The Royal Diaries: Marie Antoinette, Princess of Versailles: Austria-France, 1769. New York: Scholastic. ISBN 978-0-439-07666-1.
- Loomis, Stanley (1972). The Fatal Friendship: Marie Antoinette, Count Fersen and the flight to Varennes. London: Davis-Poynter. ISBN 978-0-7067-0047-3.
- MacLeod, Margaret Anne (2008). There Were Three of Us in the Relationship: The Secret Letters of Marie Antoinette. Irvine, Scotland: Isaac MacDonald. ISBN 978-0-9559991-0-9.
- Naslund, Sena Jeter (2006). Abundance: A Novel of Marie Antoinette. New York: William Morrow. ISBN 978-0-06-082539-3.
- Romijn, André (2008). Vive Madame la Dauphine: A Biographical Novel. Ripon: Roman House. ISBN 978-0-9554100-2-4.
- Thomas, Chantal (1999). The Wicked Queen: The Origins of the Myth of Marie-Antoinette. Trans. Julie Rose. New York: Zone Books. ISBN 978-0-942299-40-3.
- Vidal, Elena Maria (1997). Trianon: A Novel of Royal France. Long Prairie, MN: Neumann Press. ISBN 978-0-911845-96-9.
- Zweig, Stefan (2002). Marie Antoinette: The Portrait of an Average Woman. New York: Grove Press. ISBN 978-0-8021-3909-2.
External links
- Marie Antoinette's official Versailles profile on en.chateauversailles.fr
- Marie Antoinette:history and appearance on Royalty Now Studios
- The marais of Marie-Antoinette on parismarais.com
- Celebrating Marie-Antoinette blog article on waddesdon.org.uk
- Marie Antoinette: a childhood overshadowed by politics on habsburger.net
| Marie Antoinette House of Habsburg-LorraineCadet branch of the House of Habsburg and House of LorraineBorn: 2 November 1755 Died: 16 October 1793 | ||
| French royalty | ||
|---|---|---|
| VacantTitle last held byMarie Leszczyńska | Queen consort of France 1774–1792 from 1791 Queen of the French |
VacantMonarchy abolishedTitle next held byJoséphine de Beauharnais as Empress of the French |
| Titles in pretence | ||
| Loss of title Republic declared |
— TITULAR — Queen consort of France 4 September 1791 – 21 January 1793 |
VacantTitle next held byMarie Joséphine of Savoy |
- Marie Antoinette
- 1755 births
- 1793 deaths
- 18th-century Austrian people
- 18th-century Austrian women
- 18th-century French people
- 18th-century French women
- 18th-century German people
- Austrian people executed abroad
- Austrian princesses
- Austrian Roman Catholics
- Burials at the Basilica of Saint-Denis
- Children of Maria Theresa
- Daughters of counts
- Daughters of duchesses regnant
- Daughters of dukes
- Daughters of emperors
- Daughters of kings
- Daughters of queens regnant
- Dauphines of France
- Dauphines of Viennois
- Executed Austrian women
- Executed French women
- Executed royalty
- French people executed by guillotine during the French Revolution
- French people of Austrian descent
- French Roman Catholics
- French socialites
- House of Habsburg-Lorraine
- Louis XVI
- Navarrese royal consorts
- Nobility from Vienna
- People executed for treason against France
- People of the War of the First Coalition
- Princesses of France (Bourbon)
- Pupils of Metastasio
- Queens consort of France
- Royal reburials
- Women in the French Revolution
