| Revision as of 01:16, 31 August 2006 view sourceAltenmann (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers217,231 edits →History: rm controversial phrase until clarification← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 12:57, 18 December 2024 view source Bastun (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, New page reviewers, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers26,080 edits Undid revision 1263704333 by Thereppy (talk) Restore referenced section.Tag: Undo | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{short description|Clear distilled alcoholic beverage}} | |||
| {{wiktionary}} | |||
| {{redirect|Wodka|other uses|Wódka (disambiguation){{!}}wódka|and|vodka (disambiguation)}} | |||
| ], ]]] | |||
| {{pp-semi-indef|small=yes}} | |||
| '''Vodka''' is a typically ]less ], usually ] from ] ] or ] but also from other raw materials (see "Production" below). It is thought that the term is a ] of the ] word "voda" (woda, вода) for "]." | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=January 2023}} | |||
| {{Infobox beverage | |||
| | name = Vodka | |||
| | image = Smirnoff Red Label 8213.jpg | |||
| | image_size = 200px | |||
| | caption = ] Red Label vodka | |||
| | alternate_name = | |||
| | origin = ], ], ]<ref name="auto">{{Cite web|url=https://vocal.media/proof/the-history-of-vodka|title=The History of Vodka|website=Proof}}</ref><ref name="auto1">{{Cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=LGWEDwAAQBAJ&dq=sweden+russia+poland+vodka+15th+century&pg=PA82|isbn=9781631595554|title=The Art of Distilling, Revised and Expanded: An Enthusiast's Guide to the Artisan Distilling of Whiskey, Vodka, Gin and other Potent Potables|date=January 2019|publisher=Quarry Books}}</ref> | |||
| | region = Central, Northern and Eastern Europe | |||
| | type = ] | |||
| | abv = 35–40% | |||
| | proof = 70–80° | |||
| | color = clear | |||
| | ingredients = ], ] | |||
| | related = Flavored vodka, ] | |||
| }} | |||
| '''Vodka''' ({{langx|pl|wódka}} {{IPA|pl|ˈvutka|}}; {{langx|ru|водка}} {{IPA|ru|ˈvotkə|}}; {{langx|sv|vodka}} {{IPA|sv|vɔdkɑː|}}) is a clear ]. Different varieties originated in ], ], and ].<ref name="auto"/><ref name="auto1"/> Vodka is composed mainly of water and ] but sometimes with traces of impurities and flavourings.<ref name="Vodka: A Global History" >{{cite book |last1=Herlihy |first1=Patricia |title=Vodka: A Global History |date=2012 |publisher=Reaktion Books |isbn=9781861899293|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=362bfAtl3g8C&pg=PA12|page=12 }}</ref> Traditionally, it is made by distilling liquid from ] ] and ]es since the latter was introduced in Europe in the 18th century. Some modern brands use ], ], ], ], and ] as the base. | |||
| Since the 1890s, standard vodkas have been 40% ] (ABV) (80 ]).<ref name=Evseev2011>{{cite web|last=Evseev|first=Anton|title=Dmitry Mendeleev and 40 degrees of Russian vodka|work=Science|publisher=English Pravda.Ru|location=Moscow|date=21 November 2011|url=http://english.pravda.ru/science/mysteries/21-11-2011/119683-dmitry_mendeleev_vodka-0/|access-date=6 July 2014}}</ref> The ] has established a minimum alcohol content of 37.5% for vodka.<ref name="ginvodka1">{{cite web | access-date=20 January 2007 | archive-date=22 January 2008 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080122091206/http://www.ginvodka.org/history/vodkaproduction.html | url=http://www.ginvodka.org/history/vodkaproduction.html | title=The Production of Vodka | url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name=europarl/> Vodka in the United States must have a minimum alcohol content of 40%.<ref name="cfra1">{{cite web |url=http://ecfr.gpoaccess.gov/cgi/t/text/text-idx?c=ecfr;sid=a405a5761091de13308884c6cc36ee89;rgn=div6;view=text;node=27%3A1.0.1.1.3.3;idno=27;cc=ecfr |title=United States Code of Federal Regulations Title 27, Section 5.22(a)(1) |publisher=United States Government Printing Office |access-date=31 May 2011 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20111123093631/http://ecfr.gpoaccess.gov/cgi/t/text/text-idx?c=ecfr;sid=a405a5761091de13308884c6cc36ee89;rgn=div6;view=text;node=27%3A1.0.1.1.3.3;idno=27;cc=ecfr |archive-date=23 November 2011 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| Except for various types of flavorings, vodka consists of water and ] (]). Vodka usually has an alcohol content ranging from 35% to 70% by ]. The classic Russian vodka is 40% (80 ]). This can be attributed to the Russian standards for vodka production introduced in 1894 by ] from research undertaken by the famous Russian ] ]. According to the Vodka Museum in ], Mendeleev found the perfect percentage to be 38, but since spirits in his time were taxed on their strength the percentage was rounded up to 40 to simplify the tax computation. At strengths less than this vodka drunk neat can taste 'watery' and above this strength the taste of vodka can have more 'burn'. Under US Federal law, the minimum alcohol strength of vodka is also 40% by volume, whilst in Europe the minimum is 37.5% by volume. | |||
| Vodka is traditionally drunk "]" (not mixed with water, ice, or other ]), and it is often served freezer chilled in the ] of Belarus, Estonia, Finland, Iceland, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and Ukraine.<ref name="Vodka: A Global History"/> It is also used in ]s, such as the ], ], ], ], ], ] or ], ], ], and ]. | |||
| ==Etymology== | ==Etymology== | ||
| The name ''vodka'' is a ] form of the ] word ''voda'' (water), interpreted as "waterkin": ] ''vod''- + -''k''- (diminutive ], among other functions) + -''a'' (] of ]).<ref name="eb">{{Britannica|631781}}</ref><ref name="ety">{{cite dictionary|url=http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?term=vodka |title=vodka |dictionary=Online Etymology Dictionary |access-date=22 November 2008}}</ref><ref>Etymology of the word "vodka" in Черных П. Я.: Историко-этимологический словарь современного русского языка. Москва, Русский язык-Медиа, 2004.</ref> | |||
| In English literature, the word vodka appeared in around the late 18th century. In a book of travels published in English in 1780 (presumably, a translation from German), ] correctly explained that "''kabak'' in the Russian language signifies a public house for the common people to drink ''vodka'' (a sort of brandy) in".<ref>{{Cite book |first=Johann Gottlieb |last=Georgi |title=Russia: or, a compleat historical account of all the nations which compose that Empire. |publisher=printed for J. Nichols: T. Cadell; H. Payne; and N. Conant |year=1780 |url=https://archive.org/details/russiaoracomple00georgoog |page= }}</ref> In 1799, ] glossed ''vodka'' as "rectified corn-spirits",<ref>{{Cite book |first=William |last=Tooke |title=View of the Russian empire during the reign of Catharine the Second, and to the close of the present century, Volume 1 |publisher=T.N. Longman and O. Rees, Pater-Noster-Row, and J. Debrett|place= Piccadilly|year= 1799 |url= https://books.google.com/books?id=wBIbAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA362 |page=362 }}</ref> using the traditional English sense of the word "corn" to refer to any grain, not just ]. In 1800, French poet ] glossed it as a "grain liquor" served with meals in Poland (''] de grain'').<ref>{{Cite book |first=Théophile |last=Gautier|publisher=G. Charpentier et cie. |year=1800 |title=Voyage en Russie |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9lBEAAAAIAAJ&q=vodka |pages=354, 406 }}</ref> | |||
| The origins of vodka (and of its name) cannot be traced definitively, but it is believed to have originated in the grain-growing region that now embraces ], ], ], and western ]. It also has a long tradition in ]. | |||
| Another possible connection of ''vodka'' with "water" is the name of the medieval alcoholic beverage '']'' (], literally, "water of life"), which is reflected in Polish {{Lang|pl|okowita}}, Ukrainian {{lang|uk|оковита}}, Belarusian {{lang|be|акавіта}}, and Scandinavian '']''. ] has a similar etymology, from the ] and ] '']''/uisge-beatha. | |||
| The word can be found in the ] chronicle in records dated ], where the term "vodka" is used in the context of herbal alcoholic ]s. A number of ] lists contain the terms "vodka of bread wine" (водка хлебного вина) and "vodka in half of bread wine" (водка вполу хлебного вина). As alcohol had long been used as a basis for medicines, this implies that the term vodka is a noun derived from the verb "vodit,'" "razvodit'" ("водить", "разводить"), "to dilute with water." "Bread Wine" was a spirit distilled from alcohol made from grain (as opposed to "Grape Wine") and hence "vodka of bread wine" would be a water dilution of a distilled grain spirit. | |||
| People in the area of vodka's probable origin have names for vodka with roots meaning "to burn": {{langx|pl|gorzała}}; {{langx|uk|горілка|horilka}}; {{langx|be|гарэлка|harelka}}; {{langx|lt|degtinė}}; {{langx|sgs|degtėnė}} is also in use, colloquially and in ]s;<ref>{{cite web | access-date=11 March 2008 | archive-date=11 April 2008 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080411121714/http://www.lki.lt/php/English/publications/angliskos_santraukos_KK.doc | url=http://www.lki.lt/php/English/publications/angliskos_santraukos_KK.doc | title=The heritage of professor Juozas Balčikonis, the great educator of the native language | url-status=dead}}</ref> {{langx|lv|degvīns}}; {{langx|fi|]}}. In ] during the 17th and 18th centuries, {{lang|ru|горящѣе вино or горячее вино}} (''goryashchee vino'', "burning wine" or "hot wine") was widely used. Others languages include the German ''Branntwein'', ] ''brændevin'', {{langx|nl|brandewijn}}, {{langx|sv|]}}, and {{langx|no|]}} (although the latter terms refer to any strong alcoholic beverage). | |||
| While the word could be found in manuscripts and in '']'' (лубок, pictures with text explaining the plot, a Russian predecessor of the ]), it began to appear in Russian dictionaries in the mid-]. | |||
| Interestingly, other peoples in the area of vodka's probable origin have names for vodka with roots meaning "to burn": (]: '''gorzałka'''; ]: '''горілка''', '']''; ]: '''гарэлка''', ''harelka''; ]: '''degtinė'''; ]: '''degvīns''').'' | |||
| ==History== | ==History== | ||
| ]" countries of Northern, Central, and Eastern Europe are the historic home of vodka. These countries have the highest vodka consumption in the world.]] | |||
| Scholars debate the beginnings of vodka<ref name="smith_companion">{{Cite book |author=Smith, A. F. |title=The Oxford companion to American food and drink |publisher=Oxford University Press |year=2007 |page= |isbn=978-0-19-530796-2 |url=https://archive.org/details/oxfordcompaniont0000unse_e9i9/page/693 }}</ref> because there is little historical material available.<ref name=Blocker>Blocker, Jack S; Fahey, David M, and Tyrrell, Ian R (2003). '''' Vol. 1 A – L, ABC-CLIO, pp. 389, 636 {{ISBN|1-57607-833-7}}.</ref><ref name=Ermochkin>Ermochkine, Nicholas, and Iglikowski, Peter (2003). ''40 degrees east : an anatomy of vodka'', Nova Publishers, p. 217, {{ISBN|1-59033-594-5}}.</ref> For many centuries, beverages differed significantly compared to the vodka of today, as the spirit at that time had a different flavor, color, and smell, and was originally used as medicine. It contained little alcohol, an estimated maximum of about 14%. ] techniques were developed in ] by the 3rd century, but the description of ''aqua ardens'' ("burning water", i.e., alcohol) made by distilling wine with salt appears in Latin works only by the 12th century. The process was well known among European medieval chemists by about 1300.<ref name=Multhauf>{{Cite book |last=Multhauf |first=Robert P. |title=The Origins of Chemistry |publisher=Oldbourne |year=1966 |isbn=9782881245947 |location=London |author-link=Robert P. Multhauf}} pp. 204-206.<!--] (1919). ''The Making of Humanity'', .--></ref> | |||
| ===Poland=== | |||
| Little is known about the early history of the drink. The first written record of vodka in Poland dates from ] in the ] Court Registry. In Russia, the first written usage of the word ''vodka'' in an official document in its modern meaning is dated by the decree of ] ] of ], ] that regulated the ownership of vodka distilleries. | |||
| The world's first written mention of the word ''wódka'' was in 1405 from ''Akta Grodzkie'' ],<ref name="KRPS">{{cite web|url=http://krps.pl/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=17&Itemid=27|title=History of vodka production, at the official page of Polish Spirit Industry Association (KRPS), 2007|language=pl|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070930131416/http://krps.pl/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=17&Itemid=27 |archive-date=30 September 2007}}</ref> in the court documents from the ] in Poland.<ref name="KRPS" /> At the time, the word ''wódka'' referred to chemical compounds such as ]s and ]' cleansers. The production of ] begins in the mid-15th century, with varied local traditions emerging throughout Europe, in Poland as vodka ({{langx|pl|wódka}} or {{lang|pl|gorzałka}}). In the 16th century, the Polish word for the beverage was ''gorzałka'' (from the ] verb ''gorzeć'' meaning "to burn"), which is also the source of Ukrainian {{Lang|uk|horilka}} ({{Lang|uk|горілка}}). The word written in ] appeared first in 1533, about a medicinal drink brought from Poland to Russia by the Russian merchants.<ref name="KRPS" /> | |||
| Vodka is now one of the world's most popular spirits. It was rarely drunk outside ] before the ], but its popularity spread to the ] by way of post-war ]. (] once defined the most notable features of post-war France as "], modern ], Polish vodka.") By ] vodka sales in the ] overtook those of ], previously the most popular hard liquor,and the native spirit of that country. In the second half of the 20th century, vodka owed its popularity in part to its reputation as an alcoholic beverage that "leaves you breathless," as one ad put it — no smell of liquor remaining detectable on the breath. | |||
| In these early days, the spirits were used mostly as medicines. ] asserted in his 1534 works on ]s that vodka could serve "to increase fertility and awaken lust". ''Wodka lub gorzałka'' (1614), by Jerzy Potański, contains valuable information on the production of vodka. Jakub Kazimierz Haur, in his book ''Skład albo skarbiec znakomitych sekretów ekonomii ziemiańskiej'' (''A Treasury of Excellent Secrets about Landed Gentry's Economy'', Kraków, 1693), gave detailed recipes for making vodka from ]. | |||
| According to ''The Penguin Book of Spirits and Liqueurs'', "Its low level of ]s and congenerics — impurities that flavor spirits but that can contribute to the after-effects of heavy consumption — led to its being considered among the 'safer' spirits, though not in terms of its powers of intoxication, which, depending on strength, may be considerable." (Pamela Vandyke Price, , pp. 196ff.) | |||
| {| align="right" | |||
| |- | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |- style="text-align: center;" | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |] | |||
| |} | |||
| Some Polish vodka blends go back centuries. Most notable are '']'', from about the 16th century; '']'', from the early 17th century; and aged '']'' vodka, from the 16th century. In the mid-17th century, the '']'' (nobility of Poland) were granted a monopoly on producing and selling vodka in their territories. This privilege was a source of substantial profits. One of the most famous distilleries of the aristocracy was established by ] and later operated by her grandson, ]. The Vodka Industry Museum, located at the park of the Potocki country estate has an original document attesting that the distillery already existed in 1784. Today, it operates as "]".<ref name="Polmos">{{cite web |url=http://www.muzeumgorzelnictwa.pl/museum.html |title=Count Alfred Potocki Factory Museum of Liqueurs, Rosolios and Rum |publisher=Polmos Distillery |access-date=25 November 2013 |archive-date=26 December 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20131226213147/http://muzeumgorzelnictwa.pl/museum.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| A Russian culinary book writer ] in the book '']'' made the first historical analysis of the history of ''production'' of vodka in Russia, The research was initiated by the following events, as described by the author. The second half of the 1970s witnessed two massive attacks on the priority and rights of the ] to market liquors named "vodka". The first assault was along the lines that the ] "discontinued" Russia's rights to use the name "vodka", which were "naturally" transferred to emigrated manufacturers of vodka, ] in particular, because of prohibition by Soviets, so that officially the ] started manufacturing vodka in ]. This was refuted fairly easily. The second assault, around 1977, by ], was more serious, and the ] undertook the historical research to substantiate Russia's priority, which was completed by ], and in ] the international arbitrage considered it convincing enough to grant the ] the trademark motto "Only vodka from Russia is genuine Russian vodka". The author of the research published his findings under the alias in the book ''A History of Vodka''. He noted that while there was a wealth of publications about the history of ''consumption and distribution'' of vodka, there was virtually no literature in the history of the production of vodka. Despite the clear bias of the exposition in the book towards the goal (to prove the Russian priority), it is a serious, substantiated research and reveals quite a few facts, as well as debunks a number of myths, on the origins of vodka, both as product and as name. | |||
| Vodka production on a much larger scale began in Poland at the end of the 16th century, initially at ], whence spirits were exported to ] before 1550. Silesian cities also bought vodka from ], a city that in 1580 had 498 working spirits distilleries. Soon, however, ] outpaced both these cities. In the 17th and 18th centuries, Polish vodka was known in the Netherlands, Denmark, England, Russia, Germany, Austria, Hungary, ], ], ] and the ] basin. | |||
| Early production methods were rudimentary. The beverage was usually low-proof, and the distillation process had to be repeated several times (a three-stage distillation process was common). The first distillate was called ''brantówka'', the second was ''szumówka'', and the third was ''okowita'' (from ''aqua vitae''), which generally contained 70–80% ABV. Then the beverage was watered down, yielding a simple vodka (30–35% ABV), or a stronger one if the watering was done using an ]. The exact production methods were described in 1768 by ] and in 1774 by ]. The late 18th century inaugurated the production of vodka from various unusual substances including even the ].<ref name="Wiwała">{{cite book | url= | title=Od gorzałki do wódki – zarys historii polskiej wódki (History of Polish vodka) | publisher=Wydawnictwo Leon | author=Leszek Wiwała | year=2010 | isbn=978-83-928861-0-5}}{{page needed|date=February 2023}}</ref> | |||
| Though there was a substantial vodka cottage industry in Poland back to the 16th century, the end of the 18th century marked the start of real industrial production of vodka in Poland (], the eastern part of Poland was controlled ] at that time). Vodkas produced by the nobility and clergy became a mass product. The first industrial distillery was opened in 1782 in ] by ]. He was soon followed by Jakub Haberfeld, who in 1804 established a factory at ], and by Hartwig Kantorowicz, who started producing ] in 1823 at ]. The implementation of new technologies in the latter half of the 19th century, which allowed the production of clear vodkas, contributed to their success. The first rectification distillery was established in 1871. In 1925, the production of clear vodkas was made a ] monopoly.<ref name="Wiwała" /> | |||
| After ], all vodka distilleries were taken over by Poland's ]. During the martial law of the 1980s, the sale of vodka was rationed. Following the success of the ] movement and the ], many distilleries began struggling financially. Some filed for bankruptcy, but many were privatized, leading to the creation of various new brands.<ref name="Wiwała" /> | |||
| ===Russia=== | |||
| ] | |||
| ==== Russian Empire ==== | |||
| A type of distilled liquor designated by the Russian word ''vodka'' came to Russia in the late 14th century. In 1386, the ] ambassadors brought the first ''aqua vitae'' ("water of life") to Moscow and presented it to ], the grand prince. The liquid obtained by distillation of grape ] was thought to be a concentrate and a "spirit" of wine (''spiritus vini'' in Latin), whence came to the name of this substance in many European languages (like English ], or Russian {{lang|ru|спирт}}, {{lang|ru-Latn|spirt}}). | |||
| Perhaps one of the earliest terms linked to vodka production was ''varenoe vino'' ("distilled wine") which appears in a 1399 document. Another term used was ''perevara'', a precursor to vodka, which last appears in official documents in 1495. The term ''korchma'' is one of the oldest official terms used for vodka, which was used alongside ''varenoe vino'', but later came to denote illegally produced vodka by the 16th century. Other terms that referred to vodka included ''goriachee vino'' ("burning wine"), ''zhzhenoe vino'' ("burnt wine"), and ''khlebnoe vino'' ("bread wine").<ref>{{cite book |last1=Pokhlyobkin |first1=William |author-link1=William Pokhlyobkin |title=A History of Vodka |date=17 December 1992 |publisher=Verso |isbn=978-0-86091-359-7 |pages=100–107 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=esHVFxS0F8YC |language=en}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last1=Goldstein |first1=Darra |title=The Kingdom of Rye: A Brief History of Russian Food |date=24 May 2022 |publisher=Univ of California Press |isbn=978-0-520-38389-0 |pages=24–26 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=h1tZEAAAQBAJ |language=en}}</ref><ref name="Schrad"/> | |||
| According to ], in around 1430, a monk named ] from the ] inside the ] made a recipe of the first Russian vodka.<ref name="pohlebkin_history">{{Cite book |author=] / Похлёбкин В. В. |title=The history of vodka / История водки |place=Moscow |publisher=Tsentrpoligraph / Центрполиграф |year=2007 |page=272 |isbn=978-5-9524-1895-0}}</ref> Having a special knowledge and distillation devices, he became the creator of a new, higher quality type of alcoholic beverage. This "bread wine", as it was initially known, was for a long time produced exclusively in the Moscow grand principality and in no other Russian principality (this situation persisted until the era of industrial production). Thus, this beverage was closely associated with Moscow. In 1474, ] created the first Russian state monopoly on vodka.<ref name="distilled">{{cite book |last1=DeSalle |first1=Rob |last2=Tattersall |first2=Ian |title=Distilled: A Natural History of Spirits |date=12 July 2022 |publisher=Yale University Press |isbn=978-0-300-26510-1 |pages=140–141 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=F8ZyEAAAQBAJ |language=en}}</ref> In 1505, the first exports of distilled Russian vodka arrived in Sweden.<ref name="distilled"/> By the 16th century, government-run taverns known as ''kabaks'' replaced privately-run ''korchmas''.<ref name="Schrad">{{cite book |last1=Schrad |first1=Mark |title=Vodka Politics: Alcohol, Autocracy, and the Secret History of the Russian State |date=March 2014 |publisher=OUP USA |isbn=978-0-19-975559-2 |pages=79–83 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=rkRDAgAAQBAJ |language=en}}</ref> ], who was the English ambassador in Russia, wrote: | |||
| {{Blockquote | |||
| |text = In every great towne of his Realme he hath a ''Caback'' or drinking house, where is sold ''aquavitæ'' (which they call ''Russewine'') ''mead'', ''beere'', ''&c.'' Out of these hee receiveth rent that amounteth to a great summe of money. | |||
| |source = ''Of the Russe Common Wealth'' (1591)<ref name="Schrad"/> | |||
| }} | |||
| Until the mid-18th century, the drink remained relatively low in alcohol content, not exceeding 40% ABV. Multiple terms for the drink were recorded, sometimes reflecting different levels of quality, alcohol concentration, filtering, and the number of distillations; most commonly, it was referred to as "burning wine", "bread wine", or even in some locations simply "wine". In some locations, grape wine may have been so expensive that it was a drink only for aristocrats. Burning wine was usually diluted with water to 24% ABV or less before drinking. It was mostly sold in taverns and was quite expensive. At the same time, the word ''vodka'' was already in use, but it described herbal ]s (similar to ]), containing up to 75% ABV, and made for medicinal purposes. | |||
| ].]] | |||
| The first written usage of the word ''vodka'' in an official Russian document in its modern meaning is dated by the decree of Empress ] of 8 June 1751, which regulated the ownership of vodka distilleries. By the 1860s, a government policy of promoting the consumption of state-manufactured vodka made it the drink of choice for many Russians. In 1863, the government monopoly on vodka production was repealed, causing prices to plummet and making vodka available even to low-income citizens. The taxes on vodka became a key element of government finances in Tsarist Russia, providing at times up to 40% of state revenue.<ref>{{cite book|author=Bromley, Jonathan |title=Russia 1848–1917|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=vuFjmDQPG7kC&pg=PA40|year=2002|publisher=Heinemann|isbn=978-0-435-32718-7|pages=40–}}</ref> By 1911, vodka comprised 89% of all alcohol consumed in Russia. This level has fluctuated somewhat during the 20th century but remained quite high at all times. The most recent estimates put it at 70% (2001). | |||
| ==== Post-Soviet Russia ==== | |||
| Vodka remains a major source of state revenue and therefore of power. Seizing control of the state spirits monopoly ] and its ] distillery was instrumental for ] to consolidate his power as prime minister and president.<ref name=":0">{{Cite web |last=Schrad |first=Mark Lawrence |title=Russia Has a Vodka Addiction. So Does Vladimir Putin – But Not the Same Way. |url=https://www.politico.com/news/magazine/2023/05/05/vladimir-putin-vodka-empire-00095109 |access-date=2023-05-07 |website=POLITICO |date=5 May 2023 |language=en}}</ref> Under his rule, the "]" ("little Putin") brand of vodka became a bestseller, partly to Putin's financial benefit.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
| Other popular Russian vodka producers or brands include ] and ].<ref>{{cite web |title=Some vodka manufacturers |url=http://www.onlinevodka.net/vodka-manufacturers |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20090413034541/http://www.onlinevodka.net/vodka-manufacturers |archive-date=13 April 2009 |work=onlinevodka.net}}</ref> | |||
| ==== William Pokhlebin's ''A History of Vodka'' ==== | |||
| During the late 1970s, Russian culinary author ] compiled a history of the production of vodka in Russia, as part of the ] case in a trade dispute; this was later published as '']''. Pokhlebkin wrote that while there is a wealth of publications about the history of consumption and distribution of vodka, virtually nothing had been written about vodka production. One of his assertions was that the word "vodka" was used in popular speech in Russia considerably earlier than the middle of the 18th century, but the word did not appear in print until the 1860s. | |||
| Pokhlebkin's sources were challenged by David Christian in the ''Slavic Review'' in 1994, who criticized the lack of valid references in Pokhlebkin's works and its pro-Russian bias. Pokhlebkin is also known for his Pan-Slavic sympathies under the leadership of Russia and sentiments that, in David Christian's opinion, discredit most of his work, especially his ''History of Vodka''.<ref>''Slavic Review'' Vol. 53, no. 1 (1994), pp. 245–247.</ref> | |||
| ===Sweden=== | |||
| Up until the 1950s, vodka was not used as a designation for Swedish distilled beverages, which were instead called '']'' ("burn-wine"), the word having the same etymology as the Dutch ''Brandewijn'', which is the base for the word ]. This beverage has been produced in Sweden since the late 15th century, although the total production was still small in the 17th century.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130621022712/http://runeberg.org/nfbd/0235.html |date=21 June 2013 }} in '']'', volume 4 (1905)</ref> From the early 18th century, production expanded, although production was prohibited several times, during grain shortages. Although initially a grain product, ]es started to be used in production in the late 18th century and became dominant from the early 19th century.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130621032823/http://runeberg.org/nfbd/0233.html |date=21 June 2013 }} in '']'', volume 4 (1905)</ref> From the early 1870s, distillery equipment was improved. | |||
| Progressively from the 1960s, unflavoured Swedish ''brännvin'' also came to be called vodka. The first Swedish product to use this term was ], which was created in 1958 and initially was intended for the American export market. Although it ultimately failed in that market, it remains one of the most popular vodka brands in Sweden today.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.conaxesstrade.com/brand/explorer-vodka/|title=Conaxess Trade: Explorer Vodka|website=Conaxess Trade|access-date=5 December 2019|archive-date=5 December 2019|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20191205152651/https://www.conaxesstrade.com/brand/explorer-vodka/|url-status=dead}} Retrieved 12 December 2019.</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.statista.com/statistics/757098/sales-volume-of-the-leading-spirits-brands-in-systembolaget-stores-in-sweden/|title=Sweden: sales volume of the leading spirits brands in Systembolaget stores 2018|website=Statista|language=en|access-date=5 December 2019}}</ref> In 1979, ] was launched, reusing the name of the old ''Absolut Rent Brännvin'' ("absolutely pure ''brännvin''") created in 1879. | |||
| After Sweden joined the European Union in 1995, the regulations were changed so that privately owned companies could produce Vodka.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.riksdagen.se/sv/dokument-lagar/dokument/kommittedirektiv/oversyn-av-vissa-bestammelser-i-alkohollagen-samt_GMB119|title=Översyn av vissa bestämmelser i alkohollagen samt av bestämmelserna om försäljning av teknisk sprit m.m. Kommittédirektiv 1998:19 - Riksdagen|website=www.riksdagen.se}}</ref> | |||
| Vodka has become popular among young people, with a flourishing ].<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160204011728/http://www.thelocal.se/20120210/39046 |date=4 February 2016 }}. Thelocal.se (10 February 2012). Retrieved on 19 July 2013.</ref> In 2013, the organizers of the so-called "vodka car" were jailed for two and a half years for having illegally provided thousands of liters to young people, some as young as 13.<ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130606074744/http://www.expressen.se/nyheter/atalade-for-vodkabilen-domda-till-fangelse/ |date=6 June 2013 }}. Expressen.se (3 May 2013). Retrieved on 19 July 2013.</ref> | |||
| ==Production== | ==Production== | ||
| ] | |||
| ]) ]] | |||
| Vodka may be distilled from any ]- or ]-rich plant matter; most vodka today is produced from ] such as ], ], ], or ]. Among grain vodkas, rye and wheat vodkas are generally considered superior. Some vodkas are made from ]es, ], ]s, ]s, ], ]s and sometimes even byproducts of oil refining<ref name=ermochkine>Ermochkine, Nicholas and Iglikowski, Peter (2003). ''40 degrees east : an anatomy of vodka'', Nova Publishers, p. 65, {{ISBN|1-59033-594-5}}.</ref> or wood pulp processing. In some Central European countries, such as Poland, some vodka is produced by just fermenting a solution of crystal sugar and yeast. In the ], there are talks about the standardization of vodka, and the ] countries insist that only spirits produced from grains, potato, and sugar beet molasses be allowed to be branded as "vodka", following the traditional methods of production.<ref name="reuters">{{cite web | access-date=10 March 2007 | archive-date=10 March 2007 | archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070310191503/http://www.flexnews.com/pages/5412/European_Union/Spirits/eu_farm_chief_warns_legal_action_vodka_row.html | url=http://www.flexnews.com/pages/5412/European_Union/Spirits/eu_farm_chief_warns_legal_action_vodka_row.html | title=EU Farm Chief Warns of Legal Action in Vodka Row | url-status=dead}}</ref><ref name=stubb>], {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120215005220/http://www.alexstubb.com/artikkelit/bw_vodka.pdf |date=15 February 2012 }}, a December 2006 '']'' article</ref> | |||
| In the United States, many vodkas are made from 95% pure ] produced in large quantities by agricultural-industrial giants ], Grain Processing Corporation,<ref>{{cite web|url=https://www.grainprocessing.com/alcohol/|title=Ethyl Alcohol – Alcohol – Markets|website=www.grainprocessing.com}}</ref> and Midwest Grain Products (MGP).<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.mgpingredients.com/product-list/|title=Product – MGP|website=www.mgpingredients.com}}</ref> Bottlers purchase the base spirits in bulk, then filter, dilute, distribute and market the end product under a variety of vodka brand names.<ref>{{cite news|last=Nasaw|first=Daniel|title=Why are there so many brands of vodka on sale?|url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/magazine-18360315|access-date=14 July 2012|newspaper=BBC News|date=7 June 2012}}</ref> Similar methods are used in other regions such as Europe.<ref name="Akwawit-Polmos">{{Cite web |url=http://www.akwawit.com.pl/en/spirits_in_bulk.html |title=Spirits in bulk |website=Akwawit-Polmos |access-date=4 August 2017 |quote=The agricultural ethyl alcohol we produce is the basic component of clear and fine vodkas. Our product is used for manufacturing vodkas of the best brand in Poland. |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170805030216/http://www.akwawit.com.pl/en/spirits_in_bulk.html |archive-date=5 August 2017 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| Vodka may be distilled from any ]/]-rich plant matter; most vodka today is produced from ] such as ], ], ] or ]. Among grain vodkas, rye and wheat vodkas are generally considered superior. Some vodka is made from ]es, ], ]s, ]s and sometimes even byproducts of oil refining or wood pulp processing. In some Central European countries like Poland some vodka is produced by just fermenting a solution of crystal sugar and some <!--nutrious (?)--> salts for the yeast and distilling this after a few weeks. Today vodka is produced throughout the world, see ]. | |||
| This pure grain alcohol, also known as ''rectified spirit'', ''neutral spirit'', or ''ethyl alcohol of agricultural origin'', is also available directly to consumers in some areas, as products such as ], Polmos ''spirytus rektyfikowany'', and others. In contrast to very high ABV vodkas such as the Bulgarian ''Balkan 176°'' with 88% ABV, these grain alcohol products are not considered vodka; they have not (yet) gone through the filtration and refining process used to produce vodka.<ref name=ginvodka1 /><ref name="Akwawit-Polmos" /><ref name="Everclear">{{Cite web |url=http://www.makeityourown.com/faq |title=Everclear Uses and Products FAQs |website=Make it Your Own with Everclear |publisher=Luxco |access-date=4 August 2017}}</ref> | |||
| ===Distilling and filtering=== | |||
| A common property of vodkas produced in the USA and Europe is the extensive use of filtration prior to any additional processing, such as the addition of ]. Filtering is sometimes done in the ] during ], as well as afterward, where the distilled vodka is filtered through ] and other media. This is because under U.S. and European law vodka must not have any distinctive aroma, character, color or flavor. However, this is not the case in the traditional vodka producing nations, so many distillers from these countries prefer to use very accurate distillation but minimal filtering, thus preserving the unique flavors and characteristics of their products. | |||
| A study conducted on ]'s '']'' podcast revealed negligible differences in taste between various brands of vodka, leading to speculation as to how much branding contributes to the concept of "super-premium vodkas".<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.npr.org/2018/03/01/590022606/is-there-really-a-difference-between-expensive-vodka-and-cheap-vodka |title=Is There Really A Difference Between Expensive Vodka And Cheap Vodka? |website=NPR.org |language=en |access-date=19 March 2018}}</ref> | |||
| The "stillmaster" is the person in charge of distilling the vodka and directing its filtration. When done correctly, much of the "fore-shots" or "heads" and the "tails" separated in distillation process are discarded. These portions of the distillate contain flavor compounds such as ] and ] (heads) as well as the ]s (tails) that alter the clean taste of vodka. Through numerous rounds of distillation, the taste of the vodka is improved and its clarity is enhanced. In some distilled liquors such as ] and ], some of the heads and tails are not removed in order to give the liquor its unique flavor and mouth-feel. | |||
| ===Distilling and filtering=== | |||
| Proper distillation and excluding some of the heads also removes ] from vodka (and other distilled liquors), which can be poisonous in larger amounts. Methanol is formed when cellulose is fermented. This can be avoided by fermenting sugar with a high quality Turbo Yeast, so little methanol is formed. A fermentation of sugar, water, and Turbo Yeast will typically produce 1 ppm (one millionth) in the mash. This is much less methanol than found in ordinary orange juice, and about one twentieth of that found in commercial whisky and cognac. | |||
| {{unreferenced section|date=August 2017}} | |||
| A common property of the vodkas produced in the United States and Europe is the extensive use of filtration before any additional processing including the addition of ]s. Filtering is sometimes done in the ] during ], as well as afterward, where the distilled vodka is filtered through ] and other media to absorb trace amounts of substances that alter or impart off-flavors to the vodka. However, this is not the case in the traditional vodka-producing nations, so many distillers from these countries prefer to use very accurate distillation but minimal filtering, thus preserving the unique flavors and characteristics of their products. | |||
| The master distiller is in charge of distilling the vodka and directing its filtration, which includes the removal of the "fore-shots", "heads" and "tails". These components of the distillate contain flavor compounds such as ] and ] (heads) as well as the ]s (tails) that impact the usually desired clean taste of vodka. Through numerous rounds of distillation, or the use of a fractioning still, the taste is modified and clarity is increased. In contrast, the distillery process for liquors such as ], ], and ] allow portions of the "heads" and "tails" to remain, giving them their unique flavors. | |||
| Repeated distillation of vodka will make its ethanol level much higher than |
Repeated distillation of vodka will make its ethanol level much higher than is acceptable to most end users, whether legislation determines strength limits or not. Depending on the distillation method and the technique of the still master, the final filtered and distilled vodka may have as much as 95–96% ethanol. As such, most vodka is diluted with water before bottling. | ||
| ===Flavoring=== | ===Flavoring=== | ||
| {{Main|Flavored liquor}} | |||
| Apart from the alcoholic content, vodkas may be classified into two main groups: | |||
| ], Poland, where the bison grass vodka "]" is produced]] | |||
| ''clear vodkas'' and ''flavored vodkas''. From the latter ones, one can separate ''bitter tinctures'', such as Russian ''Yubileynaya'' (jubilee vodka) and ''Pertsovka'' (pepper vodka). | |||
| ]]] | |||
| While most vodkas are unflavored, many flavored vodkas have been produced in traditional vodka-drinking areas, often as home-made recipes to improve vodka's taste or for medicinal purposes. Flavorings include red pepper, ginger, fruit flavors, vanilla, chocolate (without sweetener), and cinnamon. In Russia, vodka flavored with honey and pepper, ''pertsovka'' in Russian, is also very popular. In Poland and Belarus, the leaves of the local ] are added to produce '']'' (Polish) and '']'' (Belarusian) vodka, with slightly sweet flavors and light amber colors. In Lithuania and Poland, a famous vodka containing honey is called '']''. | |||
| This tradition of flavoring is also prevalent in the ], where vodka seasoned with herbs, fruits, and spices is the appropriate strong drink for several seasonal festivities. Sweden has forty-odd common varieties of herb-flavored vodka (''kryddat brännvin''). In Poland and Ukraine, a separate category ({{lang|uk|nalyvka}} in Ukraine and '']'' in Poland) is used for vodka-based spirits with fruit, root, flower, or herb extracts, which are often home-made or produced by small commercial distilleries. Their alcohol contents vary between 15 and 75%. In ], vodkas are available with barberry, blackcurrant, cherry, green apple, lemon, vanilla, and watermelon flavors.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.therealculture.com/estonian-culture/estonian-vodka-2/|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100401100638/http://www.therealculture.com/estonian-culture/estonian-vodka-2/ |archive-date=1 April 2010|title=Estonian Vodka flavors|work=therealculture.com}}</ref> | |||
| While most vodkas are unflavored, a wide variety of flavored vodkas has long been produced in traditional vodka-drinking areas, often as homemade recipes to improve vodka's taste, or for medicinal purposes. Flavorings include red pepper, ginger, various fruit flavors, vanilla, chocolate (without sweetener), and cinnamon. ] produce a commercial vodka that includes ]. ]s and ]s add the leaves of the local ] to produce '']'' (Polish) and '']'' (Belarussian) vodka, with slightly sweet flavor and light amber color. In ] and Russia, vodka flavored with honey and pepper (''Pertsovka'', in Russian, ''Z pertsem'', in Ukrainian) is also very popular. In Poland, a famous vodka containing honey is called ]. | |||
| In most cases, vodka flavoring comes from a post-distillation infusion of flavors. Through the fermentation process, grain mash is transformed into a neutral alcohol beverage that is unflavored. The process of flavoring vodka so that it tastes like fruits, chocolate, and other foods occurs after fermentation and distillation. Various chemicals that reproduce the flavor profiles of foods are added into vodka to give it a specific taste. | |||
| This tradition of flavoring is also prevalent in the ], where vodka seasoned with various herbs, fruits and spices is the appropriate strong drink for all traditional seasonal festivities, ] in particular. In ] alone there are some forty-odd common varieties of herb-flavored vodka (''kryddat brännvin''). In Poland there is a separate category, '']'', for vodka-based spirits with fruit, root, flower, or herb extracts, which are often homemade or produced commercially by small distilleries. Its alcohol content may vary from 15 to 75%. | |||
| ==Today== | |||
| The Poles also make a very pure (95%, 190 proof) ] (Polish language: ]), which is used in a variety of ways. Technically a form of vodka, it is sold in liquor stores, not pharmacies. Similarly, the German market often carries German-/Hungarian-/Polish-/Ukrainian- made varieties of vodka of 90 to 95% alcohol content (as well as ] rum (a spiced rum) of the same potency). | |||
| Vodka is less likely than other spirits to produce the ] | |||
| (though no less likely to intoxicate) because of its low level of ]s and ], which are impurities that flavor spirits.<ref>*{{cite book|last=Price|first=Pamela Vandyke|title=The Penguin Book of Spirits and Liqueurs|year=1980|publisher=Penguin Books|isbn=0-14-046335-6|pages=196 ff}}</ref> | |||
| Since the year 2000, because of evolving consumer tastes and regulatory changes, several 'artisanal vodka' or even 'ultra premium vodka' brands have appeared. | |||
| ===Other processing=== | |||
| Due to the high alcohol content of certain brands of vodka, it can be stored in ice or a freezer without any crystallization of water. In countries where alcohol levels are generally low (the USA for example, due to alcohol taxation levels varying directly with alcohol content), individuals sometimes increase the alcohol percentage by a form of ]. This is done by placing the vodka in an open vessel (bowl, etc) in the freezer, and then after it has reached a temperature below the freezing point of water, adding one or more ice cubes, to which the free water within the vodka will crystallize, leaving a higher alcohol concentration behind. | |||
| ===European Union regulation=== | |||
| In some countries, ] or "]" vodka is widespread, as it can be produced easily to avoid taxation. However, severe poisoning, ], or death have been said to happen as a result of impurities, notably ]. This pervasive poisoning belief is due to ] lore, which abounds with myths of blindness, but few actual documented cases. The concern is due to the presence of ] (wood alcohol), an optic nerve poison, which can be present in small amounts when fermenting grains or fruits high in pectin. | |||
| The success of ]-based vodka in the United States in the early twenty-first century prompted traditional vodka producers in the Vodka Belt countries of ], ], ], ], and ] to campaign for ] that would define ''vodka'' as only spirits made from grain or potatoes.<ref name=reuters/><ref name=stubb/> This proposition provoked heavy criticism from South European countries, which often distill used ] from wine-making into spirits; although higher-quality mash is usually distilled into some variety of ], the lower-quality mash is better turned into neutral-flavored spirits instead. Any vodka not made from either grain or potatoes would have to display the products used in its production. This regulation entered into force in 2008.<ref name="europarl">{{cite web|url=https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/en/ALL/?uri=CELEX%3A32008R0110|title=Regulation (EC) No 110/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 15 January 2008 on the definition, description, presentation, labelling and the protection of geographical indications of spirit drinks and repealing Council Regulation (EEC) No 1576/89|website=EUR-Lex|access-date=17 February 2020}}</ref> | |||
| ===Canadian regulations=== | |||
| ==Vodka and the EU== | |||
| Under ] regulations, vodka is a potable alcoholic distillate obtained from potatoes, cereal grain, or any other material of agricultural origin fermented by the action of yeast or a mixture of yeast and other microorganisms.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://laws.justice.gc.ca/eng/regulations/C.R.C.,_c._870/page-31.html#h-569931|title=Consolidated federal laws of canada, Food and Drug Regulations|last=Branch|first=Legislative Services|date=3 June 2019|website=laws.justice.gc.ca|access-date=15 July 2019}}</ref> | |||
| Vodka producers in ], ] and ] are campaigning for ] that will categorize only spirits made from grain and potatoes as "Vodka" instead of any spirit made from any ] (provided, for example, from apples and grapes). This proposition has provoked heavy criticism from south European countries, which often distill used ] from wine-making into vodka. Any drink then not made from either grain or potatoes would then have to be labeled as "Spirit Drinks" instead. | |||
| === |
===United States regulations=== | ||
| In 1956, it was put into revenue ruling that sugar not more than 0.2% and trace amounts of citric acid are not considered flavoring agent. The meaning of "trace amounts" of citric acid was clarified as not more than 1,000ppm in 1995.<ref>{{Cite web |date=December 29, 1995 |title=ATF Ruling 97-1 |url=https://www.ttb.gov/images/pdfs/rulings/97-1.htm}}</ref> | |||
| The brands that would be affected if the law is passed include: | |||
| It is no longer defined as "to be without distinctive character, aroma, taste, or color."<ref>{{Cite news |last=Allan |first=M. Carrie |date=2021-10-28 |title=Vodka has a new definition — it's still neutral, but no longer flavorless |language=en-US |newspaper=Washington Post |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/voraciously/wp/2020/06/12/vodka-has-a-new-definition-its-still-neutral-but-no-longer-flavorless/ |access-date=2023-12-27 |issn=0190-8286}}</ref> The law includes other requirements: Vodka cannot be aged in wood; it may or may not be charcoal filtered; and it must meet minimum distillation and bottling proofs.<ref name="27 CFR 5.22">{{Cite web |title=27 CFR § 5.22 – The standards of identity. |url=https://www.law.cornell.edu/cfr/text/27/5.22 |access-date=22 January 2021 |website=LII / Legal Information Institute |language=en}}</ref> | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| == Boycotts == | |||
| ==Gallery of vodka brands== | |||
| {{Globalize|section|North America|date=January 2024}} | |||
| <gallery> | |||
| In summer 2013, American ] targeted Russian vodka brands for boycott over ].<ref>{{Cite news|date=1 August 2013|title=Vodka boycott in U.S. spreads on concerns over gay rights in Russia|language=en|work=Reuters|url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-usa-vodka-boycott-idINBRE97000C20130801|access-date=26 February 2022}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|last=Abad-Santos|first=Alexander|date=8 August 2013|title=The Russian Vodka Boycott Is Working, Whether You Like It or Not|url=https://www.theatlantic.com/international/archive/2013/08/russian-vodka-boycott-working-whether-you-it-or-not/312367/|access-date=26 February 2022|website=The Atlantic|language=en}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|date=31 July 2013|title=Stoli CEO Speaks Out On How Company Will Respond To Vodka Boycott|url=https://www.huffpost.com/entry/stoli-vodka-gay-boycott_n_3682365|access-date=26 February 2022|website=HuffPost|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| Image:Stoli.jpg|] ("Capital"), Russia | |||
| Image:Solidarnosc vodka.jpg|Solidarność ("Solidarity"), Poland | |||
| In late February 2022, with the ], some North American liquor stores and bars expressed symbolic solidarity with Ukraine, and opposition to Russia, by boycotting Russian vodka brands.<ref>{{Cite news|date=26 February 2022|title=Canadian liquor stores remove Russian vodka from shelves after Ukraine invasion|language=en|work=Reuters|url=https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/canadas-ontario-province-orders-russian-liquor-off-store-shelves-2022-02-25/|access-date=26 February 2022}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|title=Boycotting Russian vodka brands: How big of an impact does it have and on who?|url=https://www.msn.com/en-us/news/technology/boycotting-russian-vodka-brands-how-big-of-an-impact-does-it-have-and-on-who/ar-AAUjJiH|access-date=26 February 2022|website=MSN|language=en-US}}</ref> | |||
| Image:zodiac_bottle.jpg|], United States | |||
| Image:Absolut vodka.jpg| ], Sweden | |||
| One critic argued that boycotts of Russian-branded vodka may inadvertently affect U.S. vodka manufacturers and noted that only 1.2 percent of U.S. vodka imports come from Russia.<ref name="reason.com">{{Cite web|title=Why Are You Boycotting American Vodka To Punish Russia?|url=https://reason.com/2022/02/28/why-are-you-boycotting-american-vodka-to-punish-russia/|date=28 February 2022}}</ref> | |||
| Image:Monopolowa.jpg| Monopolowa, Poland | |||
| Image:Hollandse Graanjenever 0495.JPG| Hollandse Graanjenever vodka, Netherlands | |||
| ==Illegal production== | |||
| Image:Żubrówka.jpg|], Poland | |||
| In some countries, ] or "]" vodka is widespread because it can be produced easily and avoids taxation. However, severe poisoning, ], or death can occur as a result of dangerous industrial ethanol substitutes being added by black-market producers.<ref>{{cite news|first=Steven |last=Eke |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/6157015.stm |title='People's vodka' urged for Russia |work=BBC News |date=29 November 2006 |access-date=22 November 2008}}</ref> In March 2007 in a documentary, ] UK sought to find the cause of severe ] among imbibers of a "bathtub" vodka in Russia.<ref>{{cite news|first=John |last=Sweeney |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/programmes/from_our_own_correspondent/6434789.stm |title=When vodka is your poison |work=BBC News |date=10 March 2007 |access-date=22 November 2008}}</ref> The cause was suspected to be an industrial disinfectant (])—95% ethanol but also containing a highly toxic chemical—added to the vodka by the illegal traders because of its high alcohol content and low price. Death toll estimates list at least 120 dead and more than 1,000 poisoned{{Vague|reason=Over what time span?|date=October 2023}}. The death toll is expected to rise due to the chronic nature of the ] that is causing jaundice.{{Citation needed|date=March 2021}} | |||
| Image:Vodka, Finlandia.jpg| ], Finland | |||
| Image:Wodka_gorbatschow.jpg |Wodka Gorbatschow, Germany | |||
| ==Public health effects== | |||
| Image:Chopamer1.jpg | Chopin Vodka, Poland | |||
| {{See also|Alcohol and health}} | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| Estimates of the annual death toll resulting from ] extend up to the thousands in Russia.<ref>See, e.g., ], ] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190604225120/https://www.academia.edu/32754260/Russian_Demographic_Crisis_in_Cross-National_Perspective._In_Russia_and_Globalization._Baltimore_John_Hopkins_University_Press |date=4 June 2019 }}. Ed. by D. W. Blum. Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2008. P. 37–78; Khaltourina, D. A., & Korotayev, A. V. {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180701002031/http://cliodynamics.ru/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=376&Itemid=1 |date=1 July 2018 }}.</ref><ref> {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210108180042/https://www.academia.edu/41473801/Distilled_Spirits_Overconsumption_as_the_Most_Important_Factor_of_Excessive_Adult_Male_Mortality_in_Europe_Alcohol_and_Alcoholism_2018_53_6_742_752 |date=8 January 2021 }}.</ref> | |||
| == Cooking == | |||
| ]]] | |||
| Vodka can also be used in cooking and various recipes are improved by the addition of vodka or rely on it as a key ingredient. ] is a pasta sauce made from tomato sauce, cream, and vodka that gained popularity in the 1970s. Vodka can be used in baking as a substitute for water: pie crusts can be made flakier with vodka.<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.epicurious.com/expert-advice/how-to-use-alcohol-in-baking-article|title=The Boozy Ingredient Your Baked Goods Are Missing|work=Epicurious|access-date=6 March 2018|language=en-US}}</ref> It may be used in seafood dishes, cheesecake, or ].<ref>{{Cite news|url=https://feastandwest.com/2015/05/27/how-to-cook-with-vodka/|title=How to Cook with Vodka » Feast + West|date=27 May 2015|work=Feast + West|access-date=6 March 2018|language=en-US}}</ref><ref>{{Cite news|url=https://www.chowhound.com/food-news/54862/10-recipes-using-vodka/|title=10 Recipes Using Vodka|last=Chowhound|work=Chowhound|access-date=6 March 2018|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| *] | |||
| {{Commons|Category:Vodka}} | |||
| * |
*] | ||
| *] | |||
| * ], which includes flavoured vodkas | |||
| * |
*] | ||
| {{clear right}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ], sometimes called "]ese vodka" | |||
| * ], a ] distilled liquor sometimes called "Chinese vodka" | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{Reflist|30em}} | |||
| <!--See http://en.wikipedia.org/Wikipedia:Footnotes for an explanation of how to generate footnotes using the <ref(erences/)> tags--> | |||
| <div class="references-small"> | |||
| ==Further reading== | |||
| <references /> | |||
| * |
*{{cite book|last=Begg|first=Desmond|title=The Vodka Companion: A Connoisseur's Guide|year=1997|publisher=Running|isbn=0-7624-0252-0}} | ||
| *{{cite book|last=Broom|first=Dave|title=Complete Book of Spirits and Cocktails|year=1998|publisher=Carlton Books Ltd.|location=Italy|isbn=1-85868-485-4|url-access=registration|url=https://archive.org/details/spiritscocktails0000broo}} | |||
| *] and Clarke, Renfrey (translator). '']''. Verso: 1992. ISBN 0-86091-359-7. | |||
| *Delos |
*{{cite book|last=Delos|first=Gilbert|title=Vodkas of the World|year=1998|publisher=Wellfleet Press|location=Edison, New Jersey|isbn=0-7858-1018-8}} | ||
| *{{cite book|last=Elborn|first=Geoffrey|title=The Dedalus Book of Vodka|year=2013|publisher=Dedalus|isbn=978-1-907650-04-8|url-access=registration|url=https://archive.org/details/dedalusbookofvod0000elbo}} | |||
| *Lingwood, William, and Ian Wisniewski. ''Vodka: Discovering, Exploring, Enjoying''. Ryland, Peters, & Small: 2003. ISBN 1-84172-506-4. | |||
| *{{cite book|last=Faith|first=Nicholas|title=Classic Vodka|year=1977|publisher=Prion Books Ltd|location=London|isbn=1-85375-234-7|author2=Ian Wisniewski }} | |||
| *Price, Pamela Vandyke. ''The Penguin Book of Spirits and Liqueurs''. Penguin Books, 1980. | |||
| *{{cite book|last=Lingwood|first=William|title=Vodka: Discovering, Exploring, Enjoying|year=2003|publisher=Ryland Peters & Small|location=New York|isbn=1-84172-506-4|author2=Ian Wisniewski }} | |||
| </div> | |||
| *{{cite book|last=Rogala|first=Jan|title=Gorzałka czyli historia i zasady wypalania mocnych trunków |year=2004 |publisher=Baobab |isbn=83-89642-70-0}} | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * | |||
| * - ] | |||
| * | |||
| {{Vodkas}} | |||
| {{Alcoholic beverages}} | {{Alcoholic beverages}} | ||
| {{Subject bar|Liquor|Drink|auto=1|wikt=y}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 12:57, 18 December 2024
Clear distilled alcoholic beverage "Wodka" redirects here. For other uses, see wódka and vodka (disambiguation).
 Smirnoff Red Label vodka Smirnoff Red Label vodka | |
| Type | Distilled alcoholic beverage |
|---|---|
| Country of origin | Poland, Russia, Sweden |
| Region of origin | Central, Northern and Eastern Europe |
| Alcohol by volume | 35–40% |
| Proof (US) | 70–80° |
| Color | clear |
| Ingredients | Water, grains |
| Related products | Flavored vodka, nalewka |
Vodka (Polish: wódka [ˈvutka]; Russian: водка [ˈvotkə]; Swedish: vodka [vɔdkɑː]) is a clear distilled alcoholic beverage. Different varieties originated in Poland, Russia, and Sweden. Vodka is composed mainly of water and ethanol but sometimes with traces of impurities and flavourings. Traditionally, it is made by distilling liquid from fermented cereal grains and potatoes since the latter was introduced in Europe in the 18th century. Some modern brands use maize, sugar cane, fruit, honey, and maple sap as the base.
Since the 1890s, standard vodkas have been 40% alcohol by volume (ABV) (80 U.S. proof). The European Union has established a minimum alcohol content of 37.5% for vodka. Vodka in the United States must have a minimum alcohol content of 40%.
Vodka is traditionally drunk "neat" (not mixed with water, ice, or other mixers), and it is often served freezer chilled in the vodka belt of Belarus, Estonia, Finland, Iceland, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and Ukraine. It is also used in cocktails and mixed drinks, such as the vodka martini, Cosmopolitan, vodka tonic, screwdriver, greyhound, Black or White Russian, Moscow mule, Bloody Mary, and Caesar.
Etymology
The name vodka is a diminutive form of the Slavic word voda (water), interpreted as "waterkin": root vod- + -k- (diminutive suffix, among other functions) + -a (ending of feminine gender).
In English literature, the word vodka appeared in around the late 18th century. In a book of travels published in English in 1780 (presumably, a translation from German), Johann Gottlieb Georgi correctly explained that "kabak in the Russian language signifies a public house for the common people to drink vodka (a sort of brandy) in". In 1799, William Tooke glossed vodka as "rectified corn-spirits", using the traditional English sense of the word "corn" to refer to any grain, not just maize. In 1800, French poet Théophile Gautier glossed it as a "grain liquor" served with meals in Poland (eau-de-vie de grain).
Another possible connection of vodka with "water" is the name of the medieval alcoholic beverage aqua vitae (Latin, literally, "water of life"), which is reflected in Polish okowita, Ukrainian оковита, Belarusian акавіта, and Scandinavian akvavit. Whiskey has a similar etymology, from the Irish and Scottish Gaelic uisce beatha/uisge-beatha.
People in the area of vodka's probable origin have names for vodka with roots meaning "to burn": Polish: gorzała; Ukrainian: горілка, romanized: horilka; Belarusian: гарэлка, romanized: harelka; Lithuanian: degtinė; Samogitian: degtėnė is also in use, colloquially and in proverbs; Latvian: degvīns; Finnish: paloviina. In Russian during the 17th and 18th centuries, горящѣе вино or горячее вино (goryashchee vino, "burning wine" or "hot wine") was widely used. Others languages include the German Branntwein, Danish brændevin, Dutch: brandewijn, Swedish: brännvin, and Norwegian: brennevin (although the latter terms refer to any strong alcoholic beverage).
History
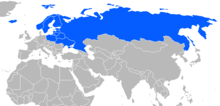
Scholars debate the beginnings of vodka because there is little historical material available. For many centuries, beverages differed significantly compared to the vodka of today, as the spirit at that time had a different flavor, color, and smell, and was originally used as medicine. It contained little alcohol, an estimated maximum of about 14%. Distillation techniques were developed in Roman Egypt by the 3rd century, but the description of aqua ardens ("burning water", i.e., alcohol) made by distilling wine with salt appears in Latin works only by the 12th century. The process was well known among European medieval chemists by about 1300.
Poland
The world's first written mention of the word wódka was in 1405 from Akta Grodzkie recorder of deeds, in the court documents from the Palatinate of Sandomierz in Poland. At the time, the word wódka referred to chemical compounds such as medicines and cosmetics' cleansers. The production of liquor begins in the mid-15th century, with varied local traditions emerging throughout Europe, in Poland as vodka (Polish: wódka or gorzałka). In the 16th century, the Polish word for the beverage was gorzałka (from the Old Polish verb gorzeć meaning "to burn"), which is also the source of Ukrainian horilka (горілка). The word written in Cyrillic appeared first in 1533, about a medicinal drink brought from Poland to Russia by the Russian merchants.
In these early days, the spirits were used mostly as medicines. Stefan Falimierz asserted in his 1534 works on herbs that vodka could serve "to increase fertility and awaken lust". Wodka lub gorzałka (1614), by Jerzy Potański, contains valuable information on the production of vodka. Jakub Kazimierz Haur, in his book Skład albo skarbiec znakomitych sekretów ekonomii ziemiańskiej (A Treasury of Excellent Secrets about Landed Gentry's Economy, Kraków, 1693), gave detailed recipes for making vodka from rye.

|

|

|

|
| Chopin | Wyborowa | Żubrówka | Luksusowa |
Some Polish vodka blends go back centuries. Most notable are Żubrówka, from about the 16th century; Goldwasser, from the early 17th century; and aged Starka vodka, from the 16th century. In the mid-17th century, the szlachta (nobility of Poland) were granted a monopoly on producing and selling vodka in their territories. This privilege was a source of substantial profits. One of the most famous distilleries of the aristocracy was established by Elżbieta Izabela Lubomirska and later operated by her grandson, Alfred Wojciech Potocki. The Vodka Industry Museum, located at the park of the Potocki country estate has an original document attesting that the distillery already existed in 1784. Today, it operates as "Polmos Łańcut".
Vodka production on a much larger scale began in Poland at the end of the 16th century, initially at Kraków, whence spirits were exported to Silesia before 1550. Silesian cities also bought vodka from Poznań, a city that in 1580 had 498 working spirits distilleries. Soon, however, Gdańsk outpaced both these cities. In the 17th and 18th centuries, Polish vodka was known in the Netherlands, Denmark, England, Russia, Germany, Austria, Hungary, Romania, Ukraine, Bulgaria and the Black Sea basin.
Early production methods were rudimentary. The beverage was usually low-proof, and the distillation process had to be repeated several times (a three-stage distillation process was common). The first distillate was called brantówka, the second was szumówka, and the third was okowita (from aqua vitae), which generally contained 70–80% ABV. Then the beverage was watered down, yielding a simple vodka (30–35% ABV), or a stronger one if the watering was done using an alembic. The exact production methods were described in 1768 by Jan Paweł Biretowski and in 1774 by Jan Chryzostom Pasek. The late 18th century inaugurated the production of vodka from various unusual substances including even the carrot.
Though there was a substantial vodka cottage industry in Poland back to the 16th century, the end of the 18th century marked the start of real industrial production of vodka in Poland (Kresy, the eastern part of Poland was controlled by the Russian empire at that time). Vodkas produced by the nobility and clergy became a mass product. The first industrial distillery was opened in 1782 in Lwów by J. A. Baczewski. He was soon followed by Jakub Haberfeld, who in 1804 established a factory at Oświęcim, and by Hartwig Kantorowicz, who started producing Wyborowa in 1823 at Poznań. The implementation of new technologies in the latter half of the 19th century, which allowed the production of clear vodkas, contributed to their success. The first rectification distillery was established in 1871. In 1925, the production of clear vodkas was made a Polish government monopoly.
After World War II, all vodka distilleries were taken over by Poland's Marxist–Leninist government. During the martial law of the 1980s, the sale of vodka was rationed. Following the success of the Solidarity movement and the abolition of single-party rule in Poland, many distilleries began struggling financially. Some filed for bankruptcy, but many were privatized, leading to the creation of various new brands.
Russia

Russian Empire
A type of distilled liquor designated by the Russian word vodka came to Russia in the late 14th century. In 1386, the Genoese ambassadors brought the first aqua vitae ("water of life") to Moscow and presented it to Dmitry Donskoy, the grand prince. The liquid obtained by distillation of grape must was thought to be a concentrate and a "spirit" of wine (spiritus vini in Latin), whence came to the name of this substance in many European languages (like English spirit, or Russian спирт, spirt).
Perhaps one of the earliest terms linked to vodka production was varenoe vino ("distilled wine") which appears in a 1399 document. Another term used was perevara, a precursor to vodka, which last appears in official documents in 1495. The term korchma is one of the oldest official terms used for vodka, which was used alongside varenoe vino, but later came to denote illegally produced vodka by the 16th century. Other terms that referred to vodka included goriachee vino ("burning wine"), zhzhenoe vino ("burnt wine"), and khlebnoe vino ("bread wine").
According to William Pokhlyobkin, in around 1430, a monk named Isidore from the Chudov Monastery inside the Moscow Kremlin made a recipe of the first Russian vodka. Having a special knowledge and distillation devices, he became the creator of a new, higher quality type of alcoholic beverage. This "bread wine", as it was initially known, was for a long time produced exclusively in the Moscow grand principality and in no other Russian principality (this situation persisted until the era of industrial production). Thus, this beverage was closely associated with Moscow. In 1474, Ivan III created the first Russian state monopoly on vodka. In 1505, the first exports of distilled Russian vodka arrived in Sweden. By the 16th century, government-run taverns known as kabaks replaced privately-run korchmas. Giles Fletcher, who was the English ambassador in Russia, wrote:
In every great towne of his Realme he hath a Caback or drinking house, where is sold aquavitæ (which they call Russewine) mead, beere, &c. Out of these hee receiveth rent that amounteth to a great summe of money.
— Of the Russe Common Wealth (1591)
Until the mid-18th century, the drink remained relatively low in alcohol content, not exceeding 40% ABV. Multiple terms for the drink were recorded, sometimes reflecting different levels of quality, alcohol concentration, filtering, and the number of distillations; most commonly, it was referred to as "burning wine", "bread wine", or even in some locations simply "wine". In some locations, grape wine may have been so expensive that it was a drink only for aristocrats. Burning wine was usually diluted with water to 24% ABV or less before drinking. It was mostly sold in taverns and was quite expensive. At the same time, the word vodka was already in use, but it described herbal tinctures (similar to Nalewka), containing up to 75% ABV, and made for medicinal purposes.

The first written usage of the word vodka in an official Russian document in its modern meaning is dated by the decree of Empress Elizabeth of 8 June 1751, which regulated the ownership of vodka distilleries. By the 1860s, a government policy of promoting the consumption of state-manufactured vodka made it the drink of choice for many Russians. In 1863, the government monopoly on vodka production was repealed, causing prices to plummet and making vodka available even to low-income citizens. The taxes on vodka became a key element of government finances in Tsarist Russia, providing at times up to 40% of state revenue. By 1911, vodka comprised 89% of all alcohol consumed in Russia. This level has fluctuated somewhat during the 20th century but remained quite high at all times. The most recent estimates put it at 70% (2001).
Post-Soviet Russia
Vodka remains a major source of state revenue and therefore of power. Seizing control of the state spirits monopoly Rosspirtprom and its Kristall distillery was instrumental for Vladimir Putin to consolidate his power as prime minister and president. Under his rule, the "Putinka" ("little Putin") brand of vodka became a bestseller, partly to Putin's financial benefit.
Other popular Russian vodka producers or brands include Stolichnaya and Russian Standard.
William Pokhlebin's A History of Vodka
During the late 1970s, Russian culinary author William Pokhlebkin compiled a history of the production of vodka in Russia, as part of the Soviet case in a trade dispute; this was later published as A History of Vodka. Pokhlebkin wrote that while there is a wealth of publications about the history of consumption and distribution of vodka, virtually nothing had been written about vodka production. One of his assertions was that the word "vodka" was used in popular speech in Russia considerably earlier than the middle of the 18th century, but the word did not appear in print until the 1860s.
Pokhlebkin's sources were challenged by David Christian in the Slavic Review in 1994, who criticized the lack of valid references in Pokhlebkin's works and its pro-Russian bias. Pokhlebkin is also known for his Pan-Slavic sympathies under the leadership of Russia and sentiments that, in David Christian's opinion, discredit most of his work, especially his History of Vodka.
Sweden
Up until the 1950s, vodka was not used as a designation for Swedish distilled beverages, which were instead called brännvin ("burn-wine"), the word having the same etymology as the Dutch Brandewijn, which is the base for the word brandy. This beverage has been produced in Sweden since the late 15th century, although the total production was still small in the 17th century. From the early 18th century, production expanded, although production was prohibited several times, during grain shortages. Although initially a grain product, potatoes started to be used in production in the late 18th century and became dominant from the early 19th century. From the early 1870s, distillery equipment was improved.
Progressively from the 1960s, unflavoured Swedish brännvin also came to be called vodka. The first Swedish product to use this term was Explorer Vodka, which was created in 1958 and initially was intended for the American export market. Although it ultimately failed in that market, it remains one of the most popular vodka brands in Sweden today. In 1979, Absolut Vodka was launched, reusing the name of the old Absolut Rent Brännvin ("absolutely pure brännvin") created in 1879.
After Sweden joined the European Union in 1995, the regulations were changed so that privately owned companies could produce Vodka.
Vodka has become popular among young people, with a flourishing black market. In 2013, the organizers of the so-called "vodka car" were jailed for two and a half years for having illegally provided thousands of liters to young people, some as young as 13.
Production


Vodka may be distilled from any starch- or sugar-rich plant matter; most vodka today is produced from grains such as sorghum, corn, rye, or wheat. Among grain vodkas, rye and wheat vodkas are generally considered superior. Some vodkas are made from potatoes, molasses, soybeans, grapes, rice, sugar beets and sometimes even byproducts of oil refining or wood pulp processing. In some Central European countries, such as Poland, some vodka is produced by just fermenting a solution of crystal sugar and yeast. In the European Union, there are talks about the standardization of vodka, and the Vodka Belt countries insist that only spirits produced from grains, potato, and sugar beet molasses be allowed to be branded as "vodka", following the traditional methods of production.
In the United States, many vodkas are made from 95% pure grain alcohol produced in large quantities by agricultural-industrial giants Archer Daniels Midland, Grain Processing Corporation, and Midwest Grain Products (MGP). Bottlers purchase the base spirits in bulk, then filter, dilute, distribute and market the end product under a variety of vodka brand names. Similar methods are used in other regions such as Europe.
This pure grain alcohol, also known as rectified spirit, neutral spirit, or ethyl alcohol of agricultural origin, is also available directly to consumers in some areas, as products such as Everclear, Polmos spirytus rektyfikowany, and others. In contrast to very high ABV vodkas such as the Bulgarian Balkan 176° with 88% ABV, these grain alcohol products are not considered vodka; they have not (yet) gone through the filtration and refining process used to produce vodka.
A study conducted on NPR's Planet Money podcast revealed negligible differences in taste between various brands of vodka, leading to speculation as to how much branding contributes to the concept of "super-premium vodkas".
Distilling and filtering
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (August 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
A common property of the vodkas produced in the United States and Europe is the extensive use of filtration before any additional processing including the addition of flavorants. Filtering is sometimes done in the still during distillation, as well as afterward, where the distilled vodka is filtered through activated charcoal and other media to absorb trace amounts of substances that alter or impart off-flavors to the vodka. However, this is not the case in the traditional vodka-producing nations, so many distillers from these countries prefer to use very accurate distillation but minimal filtering, thus preserving the unique flavors and characteristics of their products.
The master distiller is in charge of distilling the vodka and directing its filtration, which includes the removal of the "fore-shots", "heads" and "tails". These components of the distillate contain flavor compounds such as ethyl acetate and ethyl lactate (heads) as well as the fusel oils (tails) that impact the usually desired clean taste of vodka. Through numerous rounds of distillation, or the use of a fractioning still, the taste is modified and clarity is increased. In contrast, the distillery process for liquors such as whiskey, rum, and baijiu allow portions of the "heads" and "tails" to remain, giving them their unique flavors.
Repeated distillation of vodka will make its ethanol level much higher than is acceptable to most end users, whether legislation determines strength limits or not. Depending on the distillation method and the technique of the still master, the final filtered and distilled vodka may have as much as 95–96% ethanol. As such, most vodka is diluted with water before bottling.
Flavoring
Main article: Flavored liquor

While most vodkas are unflavored, many flavored vodkas have been produced in traditional vodka-drinking areas, often as home-made recipes to improve vodka's taste or for medicinal purposes. Flavorings include red pepper, ginger, fruit flavors, vanilla, chocolate (without sweetener), and cinnamon. In Russia, vodka flavored with honey and pepper, pertsovka in Russian, is also very popular. In Poland and Belarus, the leaves of the local bison grass are added to produce żubrówka (Polish) and zubrovka (Belarusian) vodka, with slightly sweet flavors and light amber colors. In Lithuania and Poland, a famous vodka containing honey is called krupnik.
This tradition of flavoring is also prevalent in the Nordic countries, where vodka seasoned with herbs, fruits, and spices is the appropriate strong drink for several seasonal festivities. Sweden has forty-odd common varieties of herb-flavored vodka (kryddat brännvin). In Poland and Ukraine, a separate category (nalyvka in Ukraine and nalewka in Poland) is used for vodka-based spirits with fruit, root, flower, or herb extracts, which are often home-made or produced by small commercial distilleries. Their alcohol contents vary between 15 and 75%. In Estonia, vodkas are available with barberry, blackcurrant, cherry, green apple, lemon, vanilla, and watermelon flavors.
In most cases, vodka flavoring comes from a post-distillation infusion of flavors. Through the fermentation process, grain mash is transformed into a neutral alcohol beverage that is unflavored. The process of flavoring vodka so that it tastes like fruits, chocolate, and other foods occurs after fermentation and distillation. Various chemicals that reproduce the flavor profiles of foods are added into vodka to give it a specific taste.
Today
Vodka is less likely than other spirits to produce the undesirable aftereffects of heavy consumption (though no less likely to intoxicate) because of its low level of fusel oils and congeners, which are impurities that flavor spirits.
Since the year 2000, because of evolving consumer tastes and regulatory changes, several 'artisanal vodka' or even 'ultra premium vodka' brands have appeared.
European Union regulation
The success of grape-based vodka in the United States in the early twenty-first century prompted traditional vodka producers in the Vodka Belt countries of Poland, Finland, Estonia, Lithuania, and Sweden to campaign for EU legislation that would define vodka as only spirits made from grain or potatoes. This proposition provoked heavy criticism from South European countries, which often distill used mash from wine-making into spirits; although higher-quality mash is usually distilled into some variety of pomace brandy, the lower-quality mash is better turned into neutral-flavored spirits instead. Any vodka not made from either grain or potatoes would have to display the products used in its production. This regulation entered into force in 2008.
Canadian regulations
Under Canadian regulations, vodka is a potable alcoholic distillate obtained from potatoes, cereal grain, or any other material of agricultural origin fermented by the action of yeast or a mixture of yeast and other microorganisms.
United States regulations
In 1956, it was put into revenue ruling that sugar not more than 0.2% and trace amounts of citric acid are not considered flavoring agent. The meaning of "trace amounts" of citric acid was clarified as not more than 1,000ppm in 1995.
It is no longer defined as "to be without distinctive character, aroma, taste, or color." The law includes other requirements: Vodka cannot be aged in wood; it may or may not be charcoal filtered; and it must meet minimum distillation and bottling proofs.
Boycotts
| The examples and perspective in this section deal primarily with North America and do not represent a worldwide view of the subject. You may improve this section, discuss the issue on the talk page, or create a new section, as appropriate. (January 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
In summer 2013, American LGBT rights activists targeted Russian vodka brands for boycott over Russia's anti-gay policies.
In late February 2022, with the Russian invasion of Ukraine, some North American liquor stores and bars expressed symbolic solidarity with Ukraine, and opposition to Russia, by boycotting Russian vodka brands.
One critic argued that boycotts of Russian-branded vodka may inadvertently affect U.S. vodka manufacturers and noted that only 1.2 percent of U.S. vodka imports come from Russia.
Illegal production
In some countries, black-market or "bathtub" vodka is widespread because it can be produced easily and avoids taxation. However, severe poisoning, blindness, or death can occur as a result of dangerous industrial ethanol substitutes being added by black-market producers. In March 2007 in a documentary, BBC News UK sought to find the cause of severe jaundice among imbibers of a "bathtub" vodka in Russia. The cause was suspected to be an industrial disinfectant (Extrasept)—95% ethanol but also containing a highly toxic chemical—added to the vodka by the illegal traders because of its high alcohol content and low price. Death toll estimates list at least 120 dead and more than 1,000 poisoned. The death toll is expected to rise due to the chronic nature of the cirrhosis that is causing jaundice.
Public health effects
See also: Alcohol and healthEstimates of the annual death toll resulting from vodka consumption extend up to the thousands in Russia.
Cooking

Vodka can also be used in cooking and various recipes are improved by the addition of vodka or rely on it as a key ingredient. Vodka sauce is a pasta sauce made from tomato sauce, cream, and vodka that gained popularity in the 1970s. Vodka can be used in baking as a substitute for water: pie crusts can be made flakier with vodka. It may be used in seafood dishes, cheesecake, or bitters.
See also
References
- ^ "The History of Vodka". Proof.
- ^ The Art of Distilling, Revised and Expanded: An Enthusiast's Guide to the Artisan Distilling of Whiskey, Vodka, Gin and other Potent Potables. Quarry Books. January 2019. ISBN 9781631595554.
- ^ Herlihy, Patricia (2012). Vodka: A Global History. Reaktion Books. p. 12. ISBN 9781861899293.
- Evseev, Anton (21 November 2011). "Dmitry Mendeleev and 40 degrees of Russian vodka". Science. Moscow: English Pravda.Ru. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ^ "The Production of Vodka". Archived from the original on 22 January 2008. Retrieved 20 January 2007.
- ^ "Regulation (EC) No 110/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 15 January 2008 on the definition, description, presentation, labelling and the protection of geographical indications of spirit drinks and repealing Council Regulation (EEC) No 1576/89". EUR-Lex. Retrieved 17 February 2020.
- "United States Code of Federal Regulations Title 27, Section 5.22(a)(1)". United States Government Printing Office. Archived from the original on 23 November 2011. Retrieved 31 May 2011.
- Vodka at the Encyclopædia Britannica
- "vodka". Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved 22 November 2008.
- Etymology of the word "vodka" in Черных П. Я.: Историко-этимологический словарь современного русского языка. Москва, Русский язык-Медиа, 2004.
- Georgi, Johann Gottlieb (1780). Russia: or, a compleat historical account of all the nations which compose that Empire. printed for J. Nichols: T. Cadell; H. Payne; and N. Conant. p. 115.
- Tooke, William (1799). View of the Russian empire during the reign of Catharine the Second, and to the close of the present century, Volume 1. Piccadilly: T.N. Longman and O. Rees, Pater-Noster-Row, and J. Debrett. p. 362.
- Gautier, Théophile (1800). Voyage en Russie. G. Charpentier et cie. pp. 354, 406.
- "The heritage of professor Juozas Balčikonis, the great educator of the native language". Archived from the original on 11 April 2008. Retrieved 11 March 2008.
- Smith, A. F. (2007). The Oxford companion to American food and drink. Oxford University Press. p. 693. ISBN 978-0-19-530796-2.
- Blocker, Jack S; Fahey, David M, and Tyrrell, Ian R (2003). Alcohol and Temperance in Modern History: An International Encyclopedia Vol. 1 A – L, ABC-CLIO, pp. 389, 636 ISBN 1-57607-833-7.
- Ermochkine, Nicholas, and Iglikowski, Peter (2003). 40 degrees east : an anatomy of vodka, Nova Publishers, p. 217, ISBN 1-59033-594-5.
- Multhauf, Robert P. (1966). The Origins of Chemistry. London: Oldbourne. ISBN 9782881245947. pp. 204-206.
- ^ "History of vodka production, at the official page of Polish Spirit Industry Association (KRPS), 2007" (in Polish). Archived from the original on 30 September 2007.
- "Count Alfred Potocki Factory Museum of Liqueurs, Rosolios and Rum". Polmos Distillery. Archived from the original on 26 December 2013. Retrieved 25 November 2013.
- ^ Leszek Wiwała (2010). Od gorzałki do wódki – zarys historii polskiej wódki (History of Polish vodka). Wydawnictwo Leon. ISBN 978-83-928861-0-5.
- Pokhlyobkin, William (17 December 1992). A History of Vodka. Verso. pp. 100–107. ISBN 978-0-86091-359-7.
- Goldstein, Darra (24 May 2022). The Kingdom of Rye: A Brief History of Russian Food. Univ of California Press. pp. 24–26. ISBN 978-0-520-38389-0.
- ^ Schrad, Mark (March 2014). Vodka Politics: Alcohol, Autocracy, and the Secret History of the Russian State. OUP USA. pp. 79–83. ISBN 978-0-19-975559-2.
- Pokhlyobkin, William / Похлёбкин В. В. (2007). The history of vodka / История водки. Moscow: Tsentrpoligraph / Центрполиграф. p. 272. ISBN 978-5-9524-1895-0.
- ^ DeSalle, Rob; Tattersall, Ian (12 July 2022). Distilled: A Natural History of Spirits. Yale University Press. pp. 140–141. ISBN 978-0-300-26510-1.
- Bromley, Jonathan (2002). Russia 1848–1917. Heinemann. pp. 40–. ISBN 978-0-435-32718-7.
- ^ Schrad, Mark Lawrence (5 May 2023). "Russia Has a Vodka Addiction. So Does Vladimir Putin – But Not the Same Way". POLITICO. Retrieved 7 May 2023.
- "Some vodka manufacturers". onlinevodka.net. Archived from the original on 13 April 2009.
- Slavic Review Vol. 53, no. 1 (1994), pp. 245–247.
- Brännvinslagstiftning Archived 21 June 2013 at the Wayback Machine in Nordisk familjebok, volume 4 (1905)
- Brännvinsbränning Archived 21 June 2013 at the Wayback Machine in Nordisk familjebok, volume 4 (1905)
- "Conaxess Trade: Explorer Vodka". Conaxess Trade. Archived from the original on 5 December 2019. Retrieved 5 December 2019. Retrieved 12 December 2019.
- "Sweden: sales volume of the leading spirits brands in Systembolaget stores 2018". Statista. Retrieved 5 December 2019.
- "Översyn av vissa bestämmelser i alkohollagen samt av bestämmelserna om försäljning av teknisk sprit m.m. Kommittédirektiv 1998:19 - Riksdagen". www.riksdagen.se.
- 'Vodka-mobile' selling booze to Swedish kids Archived 4 February 2016 at the Wayback Machine. Thelocal.se (10 February 2012). Retrieved on 19 July 2013.
- Åtalade för vodkabilen dömda till fängelse Archived 6 June 2013 at the Wayback Machine. Expressen.se (3 May 2013). Retrieved on 19 July 2013.
- Ermochkine, Nicholas and Iglikowski, Peter (2003). 40 degrees east : an anatomy of vodka, Nova Publishers, p. 65, ISBN 1-59033-594-5.
- ^ "EU Farm Chief Warns of Legal Action in Vodka Row". Archived from the original on 10 March 2007. Retrieved 10 March 2007.
- ^ Alexander Stubb, The European Vodka Wars Archived 15 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine, a December 2006 Blue Wings article
- "Ethyl Alcohol – Alcohol – Markets". www.grainprocessing.com.
- "Product – MGP". www.mgpingredients.com.
- Nasaw, Daniel (7 June 2012). "Why are there so many brands of vodka on sale?". BBC News. Retrieved 14 July 2012.
- ^ "Spirits in bulk". Akwawit-Polmos. Archived from the original on 5 August 2017. Retrieved 4 August 2017.
The agricultural ethyl alcohol we produce is the basic component of clear and fine vodkas. Our product is used for manufacturing vodkas of the best brand in Poland.
- "Everclear Uses and Products FAQs". Make it Your Own with Everclear. Luxco. Retrieved 4 August 2017.
- "Is There Really A Difference Between Expensive Vodka And Cheap Vodka?". NPR.org. Retrieved 19 March 2018.
- "Estonian Vodka flavors". therealculture.com. Archived from the original on 1 April 2010.
- *Price, Pamela Vandyke (1980). The Penguin Book of Spirits and Liqueurs. Penguin Books. pp. 196 ff. ISBN 0-14-046335-6.
- Branch, Legislative Services (3 June 2019). "Consolidated federal laws of canada, Food and Drug Regulations". laws.justice.gc.ca. Retrieved 15 July 2019.
- "ATF Ruling 97-1". 29 December 1995.
- Allan, M. Carrie (28 October 2021). "Vodka has a new definition — it's still neutral, but no longer flavorless". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved 27 December 2023.
- "27 CFR § 5.22 – The standards of identity". LII / Legal Information Institute. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- "Vodka boycott in U.S. spreads on concerns over gay rights in Russia". Reuters. 1 August 2013. Retrieved 26 February 2022.
- Abad-Santos, Alexander (8 August 2013). "The Russian Vodka Boycott Is Working, Whether You Like It or Not". The Atlantic. Retrieved 26 February 2022.
- "Stoli CEO Speaks Out On How Company Will Respond To Vodka Boycott". HuffPost. 31 July 2013. Retrieved 26 February 2022.
- "Canadian liquor stores remove Russian vodka from shelves after Ukraine invasion". Reuters. 26 February 2022. Retrieved 26 February 2022.
- "Boycotting Russian vodka brands: How big of an impact does it have and on who?". MSN. Retrieved 26 February 2022.
- "Why Are You Boycotting American Vodka To Punish Russia?". 28 February 2022.
- Eke, Steven (29 November 2006). "'People's vodka' urged for Russia". BBC News. Retrieved 22 November 2008.
- Sweeney, John (10 March 2007). "When vodka is your poison". BBC News. Retrieved 22 November 2008.
- See, e.g., Korotayev A., Khaltourina D. Russian Demographic Crisis in Cross-National Perspective. Russia and Globalization: Identity, Security, and Society in an Era of Change Archived 4 June 2019 at the Wayback Machine. Ed. by D. W. Blum. Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2008. P. 37–78; Khaltourina, D. A., & Korotayev, A. V. 'Potential for alcohol policy to decrease the mortality crisis in Russia', Evaluation & the Health Professions, vol. 31, no. 3, Sep 2008. pp. 272–281 Archived 1 July 2018 at the Wayback Machine.
- Korotayev, A., Khaltourina, D., Meshcherina, K., & Zamiatnina, E. Distilled Spirits Overconsumption as the Most Important Factor of Excessive Adult Male Mortality in Europe. Alcohol and Alcoholism, 2018, 53(6), 742-752 Archived 8 January 2021 at the Wayback Machine.
- "The Boozy Ingredient Your Baked Goods Are Missing". Epicurious. Retrieved 6 March 2018.
- "How to Cook with Vodka » Feast + West". Feast + West. 27 May 2015. Retrieved 6 March 2018.
- Chowhound. "10 Recipes Using Vodka". Chowhound. Retrieved 6 March 2018.
Further reading
- Begg, Desmond (1997). The Vodka Companion: A Connoisseur's Guide. Running. ISBN 0-7624-0252-0.
- Broom, Dave (1998). Complete Book of Spirits and Cocktails. Italy: Carlton Books Ltd. ISBN 1-85868-485-4.
- Delos, Gilbert (1998). Vodkas of the World. Edison, New Jersey: Wellfleet Press. ISBN 0-7858-1018-8.
- Elborn, Geoffrey (2013). The Dedalus Book of Vodka. Dedalus. ISBN 978-1-907650-04-8.
- Faith, Nicholas; Ian Wisniewski (1977). Classic Vodka. London: Prion Books Ltd. ISBN 1-85375-234-7.
- Lingwood, William; Ian Wisniewski (2003). Vodka: Discovering, Exploring, Enjoying. New York: Ryland Peters & Small. ISBN 1-84172-506-4.
- Rogala, Jan (2004). Gorzałka czyli historia i zasady wypalania mocnych trunków. Baobab. ISBN 83-89642-70-0.
External links
| Vodkas by country | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asia |
| ||||||||
| Europe |
| ||||||||
| North America |
| ||||||||
| Oceania |
| ||||||||
| Alcoholic beverages | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
 Definitions from Wiktionary
Definitions from Wiktionary Media from Commons
Media from Commons