| Revision as of 15:09, 19 May 2023 edit2402:3a80:19f5:4a3e::2 (talk) Mackenzie, Charles E. (1980). Coded Character Sets, History and Development (PDF). The Systems Programming Series (1 ed.). Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc. pp. 247–253. ISBN 978-0-201-14460-4. LCCN 77-90165. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 26, 2016. Retrieved December 29, 2022.Tags: Reverted Mobile edit Mobile web edit← Previous edit | Revision as of 15:09, 19 May 2023 edit undoSeventh Ward Dragon (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users1,515 edits Restored revision 1155753868 by WhichUserAmI (talk): Persistent vandalismTags: Twinkle UndoNext edit → | ||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
| *] industrial camera protocol over Coax | *] industrial camera protocol over Coax | ||
| *] control of theatrical lighting | *] control of theatrical lighting | ||
| *] |
*] | ||
| Atari SIO (Joe Decuir credits his work on Atari SIO as the basis of USB) | |||
| Binary Synchronous Communications BSC - Binary Synchronous Communications | |||
| CAN Control Area Network Vehicle Bus | |||
| ccTalk Used in the money transaction and point-of-sale industry | |||
| CoaXPress industrial camera protocol over Coax | |||
| DMX512 control of theatrical lighting | |||
| Ethernet | |||
| Fibre Channel (high-speed, for connecting computers to mass storage devices) | |||
| FireWire | |||
| HDMI | |||
| HyperTransport | |||
| InfiniBand (very high speed, broadly comparable in scope to PCI) | |||
| I²C multidrop serial bus | |||
| MIDI control of electronic musical instruments | |||
| MIL-STD-1553A/B | |||
| Morse code telegraphy | |||
| PCI Express | |||
| Profibus | |||
| RS-232 (low-speed, implemented by serial ports) | |||
| RS-422 multidrop serial bus | |||
| RS-423 | |||
| RS-485 multidrop multimaster serial bus | |||
| SDI-12 industrial sensor protocol | |||
| SERCOM | |||
| Serial ATA | |||
| Serial Attached SCSI | |||
| Shift Register with serial-in and serial-out configuration | |||
| SONET and SDH (high speed telecommunication over optical fibers) | |||
| SpaceWire Spacecraft communication network | |||
| SPI | |||
| T-1, E-1 and variants (high speed telecommunication over copper pairs) | |||
| Universal Serial Bus (for connecting peripherals to computers) | |||
| UNI/O multidrop serial bus | |||
| 1-Wire multidrop serial bus | |||
| *] (high-speed, for connecting computers to mass storage devices) | *] (high-speed, for connecting computers to mass storage devices) | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| Line 127: | Line 93: | ||
| * ] (UART) | * ] (UART) | ||
| ==References== | |||
| ==References==Mackenzie, Charles E. (1980). Coded Character Sets, History and Development (PDF). The Systems Programming Series (1 ed.). Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc. pp. 247–253. ISBN 978-0-201-14460-4. LCCN 77-90165. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 26, 2016. Retrieved December 29, 2022. | |||
| {{Reflist}} | {{Reflist}} | ||
Revision as of 15:09, 19 May 2023
Type of data transfer| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Serial communication" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
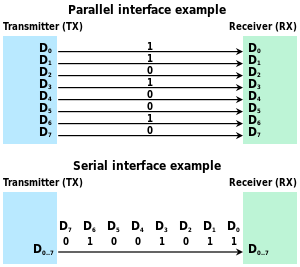
In telecommunication and data transmission, serial communication is the process of sending data one bit at a time, sequentially, over a communication channel or computer bus. This is in contrast to parallel communication, where several bits are sent as a whole, on a link with several parallel channels.

Serial communication is used for all long-haul communication and most computer networks, where the cost of cable and synchronization difficulties make parallel communication impractical. Serial computer buses are becoming more common even at shorter distances, as improved signal integrity and transmission speeds in newer serial technologies have begun to outweigh the parallel bus's advantage of simplicity (no need for serializer and deserializer, or SerDes) and to outstrip its disadvantages (clock skew, interconnect density). The migration from PCI to PCI Express is an example.
Cables
Main article: data cableMany serial communication systems were originally designed to transfer data over relatively large distances through some sort of data cable.
Practically all long-distance communication transmits data one bit at a time, rather than in parallel, because it reduces the cost of the cable. The cables that carry this data (other than "the" serial cable) and the computer ports they plug into are usually referred to with a more specific name, to reduce confusion.
Keyboard and mouse cables and ports are almost invariably serial—such as PS/2 port, Apple Desktop Bus and USB.
The cables that carry digital video are also mostly serial—such as coax cable plugged into a HD-SDI port, a webcam plugged into a USB port or FireWire port, Ethernet cable connecting an IP camera to a Power over Ethernet port, FPD-Link, digital telephone lines (ex. ISDN), etc.
Other such cables and ports, transmitting data one bit at a time, include Serial ATA, Serial SCSI, Ethernet cable plugged into Ethernet ports, the Display Data Channel using previously reserved pins of the VGA connector or the DVI port or the HDMI port.
Serial buses

Many communication systems were generally designed to connect two integrated circuits on the same printed circuit board, connected by signal traces on that board (rather than external cables).
Integrated circuits are more expensive when they have more pins. To reduce the number of pins in a package, many ICs use a serial bus to transfer data when speed is not important. Some examples of such low-cost serial buses include RS-232, SPI, I²C, UNI/O, 1-Wire and PCI Express.
Serial versus parallel
The communication links, across which computers (or parts of computers) talk to one another, may be either serial or parallel. A parallel link transmits several streams of data simultaneously along multiple channels (e.g., wires, printed circuit tracks, or optical fibers); whereas, a serial link transmits only a single stream of data.
Although a serial link may seem inferior to a parallel one, since it can transmit less data per clock cycle, it is often the case that serial links can be clocked considerably faster than parallel links in order to achieve a higher data rate. Several factors allow serial to be clocked at a higher rate:
- Clock skew between different channels is not an issue (for unclocked asynchronous serial communication links).
- A serial connection requires fewer interconnecting cables (e.g., wires/fibers) and hence occupies less space. The extra space allows for better isolation of the channel from its surroundings.
- Crosstalk is less of an issue, because there are fewer conductors in proximity.
- Budgets for power use, power dissipation, cable cost, component cost, IC die area, PC board area, ESD protection, etc. can be focused on a single link.
In many cases, serial is cheaper to implement than parallel. Many ICs have serial interfaces, as opposed to parallel ones, so that they have fewer pins and are therefore less expensive.
Examples of architectures
- ARINC 818 Avionics Digital Video Bus
- Atari SIO (Joe Decuir credits his work on Atari SIO as the basis of USB)
- Binary Synchronous Communications BSC - Binary Synchronous Communications
- CAN Control Area Network Vehicle Bus
- ccTalk Used in the money transaction and point-of-sale industry
- CoaXPress industrial camera protocol over Coax
- DMX512 control of theatrical lighting
- Ethernet
- Fibre Channel (high-speed, for connecting computers to mass storage devices)
- FireWire
- HDMI
- HyperTransport
- InfiniBand (very high speed, broadly comparable in scope to PCI)
- I²C multidrop serial bus
- MIDI control of electronic musical instruments
- MIL-STD-1553A/B
- Morse code telegraphy
- PCI Express
- Profibus
- RS-232 (low-speed, implemented by serial ports)
- RS-422 multidrop serial bus
- RS-423
- RS-485 multidrop multimaster serial bus
- SDI-12 industrial sensor protocol
- SERCOM
- Serial ATA
- Serial Attached SCSI
- Shift Register with serial-in and serial-out configuration
- SONET and SDH (high speed telecommunication over optical fibers)
- SpaceWire Spacecraft communication network
- SPI
- T-1, E-1 and variants (high speed telecommunication over copper pairs)
- Universal Serial Bus (for connecting peripherals to computers)
- UNI/O multidrop serial bus
- 1-Wire multidrop serial bus
See also
- 8N1
- Asynchronous serial communication
- Comparison of synchronous and asynchronous signalling
- Computer bus
- Data transmission
- Federal Standard 1037C
- High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC)
- List of device bandwidths
- MIL-STD-188
- Serial Peripheral Interface Bus
- Serial port
- Synchronous serial communication
- Universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter (UART)
References
- Mackenzie, Charles E. (1980). Coded Character Sets, History and Development (PDF) (1 ed.). Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Inc. pp. 247–253. ISBN 978-0-201-14460-4. LCCN 77-90165. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 26, 2016. Retrieved December 29, 2022.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help)
External links
- Serial Interface Tutorial for Robotics (contains many practical examples)
- Serial interfaces listing (with pinouts)
- Wiki: Serial Ports
- Visual studio 2008 coding for Serial communication
- Introduction to I²C and SPI protocols
- Serial communication introduction
- Serial Port Programming in Linux
| Technical and de facto standards for wired computer buses | |
|---|---|
| General | |
| Standards |
|
| Storage |
|
| Peripheral | |
| Audio | |
| Portable | |
| Embedded | |
| Interfaces are listed by their speed in the (roughly) ascending order, so the interface at the end of each section should be the fastest. | |
| Line coding (digital baseband transmission) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Main articles |  | |
| Basic line codes | ||
| Extended line codes | ||
| Optical line codes | ||