| Revision as of 02:55, 13 June 2023 view sourceNeveselbert (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers80,902 editsm →top: fmt cr.← Previous edit | Revision as of 17:25, 13 June 2023 view source GhostInTheMachine (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Page movers85,785 editsm remove invalid infobox param /residence/Next edit → | ||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
| {{Use New Zealand English|date=August 2016}} | {{Use New Zealand English|date=August 2016}} | ||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=August 2022}} | {{Use dmy dates|date=August 2022}} | ||
| {{Infobox scientist | {{Infobox scientist | ||
| | honorific-prefix = ] | | honorific-prefix = ] | ||
| Line 19: | Line 18: | ||
| | death_place = ], England | | death_place = ], England | ||
| | resting_place = ] | | resting_place = ] | ||
| | residence = New Zealand, United Kingdom | |||
| | citizenship = <!-- use only when necessary per ] --> | | citizenship = <!-- use only when necessary per ] --> | ||
| | nationality = | | nationality = | ||
Revision as of 17:25, 13 June 2023
New Zealand physicist (1871–1937) "Lord Rutherford" redirects here. Not to be confused with Lord Rutherfurd or Andrew Rutherford, 1st Earl of Teviot.
Ernest Rutherford, 1st Baron Rutherford of Nelson, OM, PRS, HonFRSE (30 August 1871 – 19 October 1937) was a Nobel Prize winning New Zealand physicist who was a pioneering researcher in both atomic and nuclear physics. Decsribed as "the father of nuclear physics", and "one of the greatest scientists of all time", he spent a substantial amount of his career abroad, in both Canada and the United Kingdom.
In 1898, Rutherford moved to Canada and joined McGill University, in Montreal, where he discovered the concept of radioactive half-life, the radioactive element radon, and differentiated and named alpha and beta radiation. For this work he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1908 "for his investigations into the disintegration of the elements, and the chemistry of radioactive substances". He was the first Oceanian Nobel laureate, and the first to perform the awarded work in Canada.
Rutherford moved in 1907 to the Victoria University of Manchester (today University of Manchester) in the UK, where he and Thomas Royds proved that alpha radiation is helium nuclei. In 1911, although he could not prove that it was positive or negative, he theorized that atoms have their charge concentrated in a very small nucleus, and thereby pioneered the Rutherford model of the atom, through his discovery and interpretation of Rutherford scattering by the gold foil experiment of Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden.
He performed the first artificially induced nuclear reaction in 1917 in experiments where nitrogen nuclei were bombarded with alpha particles. As a result, he discovered the emission of a subatomic particle which, in 1919, he called the "hydrogen atom" but, in 1920, he more accurately named the proton.
Rutherford became Director of the Cavendish Laboratory at the University of Cambridge in 1919. Under his leadership the neutron was discovered by James Chadwick in 1932 and in the same year the first experiment to split the nucleus in a fully controlled manner was performed by students working under his direction, John Cockcroft and Ernest Walton.
After his death in 1937, he was buried in Westminster Abbey near Charles Darwin and Isaac Newton. Encyclopædia Britannica considers him to be the greatest experimentalist since Michael Faraday (1791–1867). The chemical element rutherfordium (element 104) was named after him in 1997.
Early life and education
Ernest Rutherford was the son of James Rutherford, a farmer, and his wife Martha Thompson, originally from Hornchurch, Essex, England. James had emigrated to New Zealand from Perth, Scotland, "to raise a little flax and a lot of children". Ernest was born at Brightwater, near Nelson, New Zealand. His first name was mistakenly spelled 'Earnest' when his birth was registered. Rutherford's mother Martha Thompson was a schoolteacher.

He studied at Havelock School and then Nelson College and won a scholarship to study at Canterbury College, University of New Zealand, where he participated in the debating society and played rugby. He was awarded an MA in Mathematics and Physical Science from the Canterbury College in 1893 and received a BSc from the same institution in 1894.
Thereafter, he invented a new form of radio receiver, and in 1895 Rutherford was awarded an 1851 Research Fellowship from the Royal Commission for the Exhibition of 1851, to travel to England for postgraduate study at the Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge. In 1897, he was awarded a BA Research Degree and the Coutts-Trotter Studentship from Trinity College, Cambridge.
Scientific career
At Cambridge, he was among the first of the 'aliens' (those without a Cambridge degree) allowed to do research at the university, under the leadership of J. J. Thomson, which aroused jealousies from the more conservative members of the Cavendish fraternity.
With Thomson's encouragement, he detected radio waves at 0.5 miles (800 m), and briefly held the world record for the distance over which electromagnetic waves could be detected, though when he presented his results at the British Association meeting in 1896, he discovered he had been outdone by Guglielmo Marconi, who was also lecturing.
McGill years
In 1898, Thomson recommended Rutherford for a position at McGill University in Montreal, Canada, to replace Hugh Longbourne Callendar who held the chair of Macdonald Professor of physics, and was coming to Cambridge. Rutherford was accepted, which meant that in 1900 he could marry his fiancé of two years, Mary Georgina Newton (1876–1954) In 1901, Rutherford gained a DSc from the University of New Zealand.
At Cambridge, Rutherford had worked with J. J. Thomson on the conductive effects of X-rays on gases, work which led to the discovery of the electron which Thomson presented to the world in 1897. Hearing of Becquerel's experience with uranium, Rutherford started to explore its radioactivity, discovering two types that differed from X-rays in their penetrating power. Continuing his research in Canada, he coined the terms alpha ray and beta ray in 1899 to describe the two distinct types of radiation.
In conjunction with R.B. Owens, Rutherford discovered thoron (Rn), a noble gas emitted by the radioactive element thorium which was itself radioactive and would coat other substances. He found that a sample of this radioactive material of any size invariably took the same amount of time for half the sample to decay, for which he coined the term "half-life", (111⁄2 minutes in this case).
From 1900 to 1903, he was joined at McGill by the young chemist Frederick Soddy (Nobel Prize in Chemistry, 1921) for whom he set the problem of identifying the thorium emanations. Once he had eliminated all the normal chemical reactions, Soddy suggested that it must be one of the inert gases, which they named thoron (later found to be an isotope of radon). They also found another type of thorium they called Thorium X, and kept on finding traces of helium. They also worked with samples of "Uranium X" from William Crookes and radium from Marie Curie.

In 1903, they published their "Law of Radioactive Change", to account for all their experiments. Until then, atoms were assumed to be the indestructible basis of all matter and although Curie had suggested that radioactivity was an atomic phenomenon, the idea of the atoms of radioactive substances breaking up was a radically new idea. Rutherford and Soddy demonstrated that radioactivity involved the spontaneous disintegration of atoms into other, as yet, unidentified matter. The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1908 was awarded to Ernest Rutherford "for his investigations into the disintegration of the elements, and the chemistry of radioactive substances".
In 1903, Rutherford considered a type of radiation discovered (but not named) by French chemist Paul Villard in 1900, as an emission from radium, and realised that this observation must represent something different from his own alpha and beta rays, due to its very much greater penetrating power. Rutherford therefore gave this third type of radiation the name of gamma ray. All three of Rutherford's terms are in standard use today – other types of radioactive decay have since been discovered, but Rutherford's three types are among the most common.
In 1904, Rutherford suggested that radioactivity provides a source of energy sufficient to explain the existence of the Sun for the many millions of years required for the slow biological evolution on Earth proposed by biologists such as Charles Darwin. The physicist Lord Kelvin had argued earlier for a much younger Earth (see also William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin#Age of the Earth: geology) based on the insufficiency of known energy sources, but Rutherford pointed out at a lecture attended by Kelvin that radioactivity could solve this problem.
In 1904, he was elected as a member to the American Philosophical Society, and in 1907, he returned to Britain to take the chair of physics at the Victoria University of Manchester.
Manchester years
In Manchester, he continued to work with alpha radiation. In conjunction with Hans Geiger, he developed zinc sulfide scintillation screens and ionisation chambers to count alphas. By dividing the total charge they produced by the number counted, Rutherford decided that the charge on the alpha was two. In late 1907, Ernest Rutherford and Thomas Royds allowed alphas to penetrate a very thin window into an evacuated tube. As they sparked the tube into discharge, the spectrum obtained from it changed, as the alphas accumulated in the tube. Eventually, the clear spectrum of helium gas appeared, proving that alphas were at least ionised helium atoms, and probably helium nuclei.
Gold foil experiment
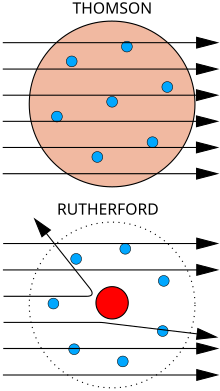
Bottom: Observed results: a small portion of the particles were deflected, indicating a small, concentrated charge. Diagram is not to scale; in reality the nucleus is vastly smaller than the electron shell.
Rutherford continued to make ground breaking discoveries long after receiving the Nobel prize in 1908. Along with Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden in 1909, he carried out the Geiger–Marsden experiment, which demonstrated the nuclear nature of atoms by deflecting alpha particles passing through a thin gold foil. Rutherford was inspired to ask Geiger and Marsden in this experiment to look for alpha particles with very high deflection angles, of a type not expected from any theory of matter at that time. Such deflections, though rare, were found, and proved to be a smooth but high-order function of the deflection angle. It was Rutherford's interpretation of this data that led him to formulate the Rutherford model of the atom in 1911 – that a very small charged nucleus, containing much of the atom's mass, was orbited by low-mass electrons.
Further advancements
In 1912, Rutherford was joined by Niels Bohr (who postulated that electrons moved in specific orbits). Bohr adapted Rutherford's nuclear structure to be consistent with Max Planck's quantum theory, and the resulting Rutherford–Bohr model is considered valid to this day.
Together with H.G. Moseley, Rutherford developed the atomic numbering system in 1913. Rutherford and Moseley's experiments used cathode rays to bombard various elements with a stream of electrons and observed that each element responded in a consistent and distinct manner. Their research was the first to assert that each element could be defined by the properties of its inner structures – an observation which later led to the discovery of the atomic nucleus.
Rutherford was knighted in 1914. During World War I, he worked on a top secret project to solve the practical problems of submarine detection by sonar. In 1916, he was awarded the Hector Memorial Medal.
Back to Cambridge
In 1919, he returned to the Cavendish succeeding J. J. Thomson as the Cavendish professor and Director. Under him, Nobel Prizes were awarded to James Chadwick for discovering the neutron (in 1932), John Cockcroft and Ernest Walton for an experiment which was to be known as splitting the atom using a particle accelerator, and Edward Appleton for demonstrating the existence of the ionosphere.
Discovery of protons and neutrons
In 1919–1920, Rutherford found that nitrogen and other light elements ejected a proton, which he called a "hydrogen atom", when hit with α (alpha) particles. This result showed Rutherford that hydrogen nuclei were a part of nitrogen nuclei (and by inference, probably other nuclei as well). Such a construction had been suspected for many years on the basis of atomic weights which were whole numbers of that of hydrogen; see Prout's hypothesis. Hydrogen was known to be the lightest element, and its nuclei presumably the lightest nuclei. Now, because of all these considerations, Rutherford decided that a hydrogen nucleus was possibly a fundamental building block of all nuclei, and also possibly a new fundamental particle as well, since nothing was known from the nucleus that was lighter. Thus, confirming and extending the work of Wilhelm Wien who in 1898 discovered the proton in streams of ionized gas, Rutherford postulated the hydrogen nucleus to be a new particle in 1920, which he dubbed the proton.
In 1921, while working with Niels Bohr, Rutherford theorized about the existence of neutrons, (which he had christened in his 1920 Bakerian Lecture), which could somehow compensate for the repelling effect of the positive charges of protons by causing an attractive nuclear force and thus keep the nuclei from flying apart from the repulsion between protons. The only alternative to neutrons was the existence of "nuclear electrons" which would counteract some of the proton charges in the nucleus, since by then it was known that nuclei had about twice the mass that could be accounted for if they were simply assembled from hydrogen nuclei (protons). But how these nuclear electrons could be trapped in the nucleus, was a mystery. Rutherford is widely quoted as saying, regarding the results of these experiments: "It was quite the most incredible event that has ever happened to me in my life. It was almost as incredible as if you fired a 15-inch shell at a piece of tissue paper and it came back and hit you."
Rutherford's theory of neutrons was proved in 1932 by his associate James Chadwick, who recognized neutrons immediately when they were produced by other scientists and later himself, in bombarding beryllium with alpha particles. In 1935, Chadwick was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for this discovery.
Re-evaluation of nuclear transmutation credit
A long-standing myth existed, at least as early as 1948, running at least to 2017, that Rutherford was the first scientist to observe and report an artificial transmutation of a stable element into another element: nitrogen into oxygen. It was thought by many people to be one of Rutherford's greatest accomplishments. The New Zealand government even issued a commemorative stamp in the belief that the nitrogen-to-oxygen discovery belonged to Rutherford. Beginning in 2017, many scientific institutions corrected their versions of this history to indicate that the discovery credit for the reaction belongs to Patrick Blackett. Rutherford did detect the ejected proton in 1919 and interpreted it as evidence for disintegration of the nitrogen nucleus (to lighter nuclei). In 1925, Blackett showed that the actual product is oxygen and identified the true reaction as N + α → O + p. Rutherford therefore recognized "that the nucleus may increase rather than diminish in mass as the result of collisions in which the proton is expelled".
Later years and honours
In 1925, Rutherford pushed calls to the New Zealand Government to support education and research, which led to the formation of the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research (DSIR) in the following year. Between 1925 and 1930, he served as President of the Royal Society, and later as president of the Academic Assistance Council which helped almost 1,000 university refugees from Germany. He was appointed to the Order of Merit in the 1925 New Year Honours and raised to the peerage as Baron Rutherford of Nelson, New Zealand and of Cambridge in the County of Cambridge in 1931, a title that became extinct upon his unexpected death in 1937. In 1933, Rutherford was one of the two inaugural recipients of the T. K. Sidey Medal, set up by the Royal Society of New Zealand as an award for outstanding scientific research.
Personal life and death

In 1900 he married Mary Georgina Newton (1876–1954) to whom he had become engaged before leaving New Zealand; they married at St Paul's Anglican Church, Papanui in Christchurch. They had one daughter, Eileen Mary (1901–1930), who married the physicist Ralph Fowler.
Beyond science, Rutherford's hobbies included golf and motoring.
For some time before his death, Rutherford had a small hernia, which he had neglected to have fixed, and it became strangulated, causing him to be violently ill. Despite an emergency operation in London, he died four days afterwards at age 66 of what physicians termed "intestinal paralysis", at Cambridge on 19 October 1937. After cremation at Golders Green Crematorium, he was given the high honour of burial in Westminster Abbey, near Isaac Newton and other illustrious British scientists such as Charles Darwin.
Legacy

Rutherford is considered to have been among the greatest scientists in history. At the opening session of the 1938 Indian Science Congress, which Rutherford had been expected to preside over before his death, astrophysicist James Jeans spoke in his place and deemed him "one of the greatest scientists of all time", saying:
In his flair for the right line of approach to a problem, as well as in the simple directness of his methods of attack, often reminds us of Faraday, but he had two great advantages which Faraday did not possess, first, exuberant bodily health and energy, and second, the opportunity and capacity to direct a band of enthusiastic co-workers. Great though Faraday's output of work was, it seems to me that to match Rutherford's work in quantity as well as in quality, we must go back to Newton. In some respects he was more fortunate than Newton. Rutherford was ever the happy warrior – happy in his work, happy in its outcome, and happy in its human contacts.
Nuclear physics

Rutherford is known as "the father of nuclear physics", because his research, and work done under him as laboratory director, established the nuclear structure of the atom and the essential nature of radioactive decay as a nuclear process. Patrick Blackett, a research fellow working under Rutherford, using natural alpha particles, demonstrated induced nuclear transmutation. Rutherford's team later, using protons from an accelerator, demonstrated artificially-induced nuclear reactions and transmutation.
Rutherford died too early to see Leó Szilárd's idea of controlled nuclear chain reactions come into being. However, a speech of Rutherford's about his artificially-induced transmutation in lithium, printed on 12 September 1933 London paper The Times, was reported by Szilárd to have been his inspiration for thinking of the possibility of a controlled energy-producing nuclear chain reaction. Szilard had this idea while walking in London, on the same day.
Rutherford's speech touched on the 1932 work of his students John Cockcroft and Ernest Walton in "splitting" lithium into alpha particles by bombardment with protons from a particle accelerator they had constructed. Rutherford realized that the energy released from the split lithium atoms was enormous, but he also realized that the energy needed for the accelerator, and its essential inefficiency in splitting atoms in this fashion, made the project an impossibility as a practical source of energy (accelerator-induced fission of light elements remains too inefficient to be used in this way, even today). Rutherford's speech in part, read:
We might in these processes obtain very much more energy than the proton supplied, but on the average we could not expect to obtain energy in this way. It was a very poor and inefficient way of producing energy, and anyone who looked for a source of power in the transformation of the atoms was talking moonshine. But the subject was scientifically interesting because it gave insight into the atoms.
Items named in honour of Rutherford's life and work

- Scientific discoveries
- The element rutherfordium, Rf, Z=104. (1997)
- The rutherford (Rd), an obsolete unit of radioactivity equivalent to one megabecquerel.
- Institutions
- Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, a scientific research laboratory near Didcot, Oxfordshire.
- Rutherford College, Auckland, a school in Auckland, New Zealand
- Rutherford College, Kent, a college at the University of Kent in Canterbury, England
- Rutherford Institute for Innovation at the University of Cambridge
- Rutherford Intermediate School, Wanganui, New Zealand
- Rutherford Hall, a hall of residence at Loughborough University
- Awards
- Rutherford Medal, the highest science medal awarded by the Royal Society of New Zealand
- Rutherford Award at Thomas Carr College for excellence in Victorian Certificate of Education chemistry, Australia.
- Rutherford Memorial Medal is an award for research in the fields of physics and chemistry by the Royal Society of Canada.
- Rutherford Medal and Prize is awarded once every two years by the Institute of Physics for "distinguished research in nuclear physics or nuclear technology".
- Rutherford Memorial Lecture is an international lecture tour under the auspices of the Royal Society created under the Rutherford Memorial Scheme in 1952.
- Rutherford Discovery Fellowships are awarded annually by the Royal Society of New Zealand
- Buildings
- Rutherford House, a boarding house at Nelson College
- Rutherford Hotel, Nelson's largest hotel, which incorporates the Rutherford Cafe and Bar
- The physics and chemistry building at the University of Canterbury, New Zealand
- Rochester and Rutherford Hall at the University of Canterbury, New Zealand
- Rutherford House, the primary building of Victoria University of Wellington's Pipitea Campus, originally the headquarters of the New Zealand Electricity Department, in Wellington, New Zealand.
- A building of the modern Cavendish Laboratory at the University of Cambridge
- The Ernest Rutherford Physics Building at McGill University, Montreal
- The Coupland Building at the University of Manchester, where Rutherford worked, was renamed "The Rutherford Building" in 2006.
- The Rutherford lecture theatre in the Schuster Laboratory at the University of Manchester
- Streets
- Lord Rutherford Road (the location of his birthplace in Brightwater, New Zealand)
- Route Rutherford, a street at CERN, Geneva, Switzerland.
- Rutherford Street, a major thoroughfare in central Nelson, New Zealand
- Rutherfordstraße, a street in Berlin near the BESSY synchrotron
- Rutherford Close, a residential street in Abingdon, Oxfordshire
- Rutherford Road in the biotechnology district of Carlsbad, California
- Rutherford Road, commercial/residential street in Vaughan, Ontario, Canada
- Other

- Rutherford – Pickering Memorial, Havelock, New Zealand
- Rutherford Park, a sports ground in Nelson, New Zealand
- The Rutherford Memorial at the site of his birth in Brightwater, New Zealand
- His image is on the obverse of the New Zealand one hundred-dollar note (since 1992).
- The Rutherford Foundation, a charitable trust set up by the Royal Society of New Zealand to support research in science and technology.
- Rutherford House, at Macleans College, Auckland, New Zealand
- Rutherford House, at Hillcrest High School, Hamilton, New Zealand
- Rutherford House, at Rotorua Intermediate School, Rotorua, New Zealand
- Rutherford House, at Rangiora High School
- The crater Rutherford on the Moon, and the crater Rutherford on the planet Mars
- Ernest Rutherford was the subject of a play by Stuart Hoar.
- On the side of the Mond Laboratory on the site of the original Cavendish Laboratory in Cambridge, there is an engraving in Rutherford's memory in the form of a crocodile, this being the nickname given to him by its commissioner, his colleague Peter Kapitza.
- Rutherford rocket engine, an engine developed in New Zealand by Rocket Lab and the first to use the electric pump feed cycle.
- His image is depicted in the stained glass window of the Presbyterian chapel at Lindisfarne College in Hastings, New Zealand. The window, unveiled in 2007, is dedicated to the college's concept of men with supreme content of character, and depicts Rutherford along with Charles Upham VC and Bar, the conqueror of Mount Everest Edmund Hillary, and the Maori academic and leader John Rangihau as iconic examples.
- Mount Rutherford in New Zealand's Paparoa Range was named after him in 1970 by the Department of Scientific and Industrial Research.
Publications
- Radio-activity (1904), 2nd ed. (1905), ISBN 978-1-60355-058-1
- Radioactive Transformations (1906), ISBN 978-1-60355-054-3
- Radioaktive Substanzen und ihre Strahlungen. Cambridge: University press. 1933.
- Radioaktive Substanzen und ihre Strahlungen (in German). Leipzig: Akademische Verlaggesellschaft. 1913.
- Radioactive Substances and their Radiations (1913)
- The Electrical Structure of Matter (1926)
- The Artificial Transmutation of the Elements (1933)
- The Newer Alchemy (1937)
-
 Title page to Radioactive Transformations (1906)
Title page to Radioactive Transformations (1906)
-
 First page to Radioactive Transformations (1906)
First page to Radioactive Transformations (1906)
-
 Title page to Radio-activity (1904)
Title page to Radio-activity (1904)
-
 First page to Radio-activity (1904)
First page to Radio-activity (1904)
-
 Title page to Radioactive Substances and their Radiations (1913)
Title page to Radioactive Substances and their Radiations (1913)
Articles
- "Disintegration of the Radioactive Elements" Harper's Monthly Magazine, January 1904, pages 279 to 284.
Arms
See also
- Bateman equation
- Hydrophone
- Magnetic detector
- Neutron generator
- Rutherford–Bohr model
- Rutherfordine
- The Rutherford Journal
- List of presidents of the Royal Society
References
- ^ Ernest Rutherford and Frederick Soddy American Physical Society 2017
- Grodzins, Lee (February 1994). "Obituaries: Zhang Wen-Yu". Physics Today. 47 (2): 116. doi:10.1063/1.2808417. Retrieved 28 January 2023.
Zhang studied under Ernest Rutherford in the mid-1930s, receiving his degree from Cambridge University in 1938.
- Zhang Wenyu (张文裕) (28 March 2018). 高能实验物理学家张文裕:回忆导师卢瑟福生命中的最后两年. thepaper.com (in Chinese). Retrieved 12 August 2021.
- Eve, A. S.; Chadwick, J. (1938). "Lord Rutherford 1871–1937". Obituary Notices of Fellows of the Royal Society. 2 (6): 394. doi:10.1098/rsbm.1938.0025.
- ^ "Ernest Rutherford, Baron Rutherford of Nelson". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- Nicholas P. Cheremisinoff (20 April 2016). Pollution Control Handbook for Oil and Gas Engineering. Wiley. pp. 886–. ISBN 978-1-119-11788-9.
- "The Discovery of Radioactivity". lbl.gov. 9 August 2000.
- "Ernest Rutherford – Biography". NobelPrize.org. Retrieved 21 February 2013.
- Campbell, John. "Rutherford – A Brief Biography". Rutherford.org.nz. Retrieved 4 March 2013.
- Rutherford, E.; Royds, T. (1908). "Spectrum of the radium emanation". Philosophical Magazine. Series 6. 16 (92): 313. doi:10.1080/14786440808636511.
- ^ Rutherford, E. (1911). "The scattering of α and β particles by matter and the structure of the atom". The London, Edinburgh, and Dublin Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science. Series 6. 21 (125): 669–688. doi:10.1080/14786440508637080.
- Longair, M. S. (2003). Theoretical concepts in physics: an alternative view of theoretical reasoning in physics. Cambridge University Press. pp. 377–378. ISBN 978-0-521-52878-8.
- Rutherford, E. (1919). "Collision of α particles with light atoms. IV. An anomalous effect in nitrogen". The London, Edinburgh, and Dublin Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science. Series 6. 37 (222): 581–587. doi:10.1080/14786440608635919.
- Rutherford, E. (1920). "Bakerian Lecture. Nuclear Constitution of Atoms". Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences. 97 (686): 374–400. Bibcode:1920RSPSA..97..374R. doi:10.1098/rspa.1920.0040.
- McLintock, A.H. (18 September 2007). "Rutherford, Sir Ernest (Baron Rutherford of Nelson, O.M., F.R.S.)". An Encyclopaedia of New Zealand (1966 ed.). Te Ara – The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. ISBN 978-0-478-18451-8. Retrieved 2 April 2008.
- Campbell, John. "Rutherford, Ernest 1871–1937". Dictionary of New Zealand Biography. Ministry for Culture and Heritage. Retrieved 4 April 2011.
- By J.L. Heilbron – Ernest Rutherford And the Explosion of Atoms – Oxford University Press – ISBN 0-19-512378-6
- Campbell, John (30 October 2012). "Rutherford, Ernest". An Encyclopaedia of New Zealand. Te Ara – The Encyclopaedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 1 October 2013.
- ^ "Ernest Rutherford Biographical". The Nobel Prize. Nobel Prize Outreach AB. Archived from the original on 3 June 2023. Retrieved 13 June 2023.
- 1851 Royal Commission Archives
- ^ "Rutherford, Ernest (RTRT895E)". A Cambridge Alumni Database. University of Cambridge.
- McKown, Robin (1962). Giant of the Atom, Ernest Rutherford. Julian Messner Inc, New York. p. 57.
- ^ Campbell, John (January 2002). "Rutherford, Ernest". Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Retrieved 8 February 2023.
- Trenn, Thaddeus J. (1976). "Rutherford on the Alpha-Beta-Gamma Classification of Radioactive Rays". Isis. 67 (1): 61–75. doi:10.1086/351545. JSTOR 231134. S2CID 145281124.
- Kragh, Helge (5 February 2012). "Rutherford, Radioactivity, and the Atomic Nucleus". arXiv:1202.0954 .
- "The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1908". The Nobel Prize. The Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2 April 2020.
- England, P.; Molnar, P.; Righter, F. (January 2007). "John Perry's neglected critique of Kelvin's age for the Earth: A missed opportunity in geodynamics". GSA Today. 17 (1): 4–9. Bibcode:2007GSAT...17R...4E. doi:10.1130/GSAT01701A.1.
- "APS Member History". search.amphilsoc.org. Retrieved 28 June 2021.
- "No. 12647". The Edinburgh Gazette. 27 February 1914. p. 269.
- Alan Selby (9 November 2014). "Manchester scientist Ernest Rutherford revealed as top secret mastermind behind sonar technology". Manchester Evening News. Retrieved 13 November 2014.
- "Atop the Physics Wave: Rutherford back in Cambridge, 1919–1937". Rutherford's Nuclear World: The Story of the Discovery of the Nucleus. American Institute of Physics. Retrieved 25 June 2018.
- Wien, W. (1904). "Über positive Elektronen und die Existenz hoher Atomgewichte". Annalen der Physik. 318 (4): 669–677. Bibcode:1904AnP...318..669W. doi:10.1002/andp.18943180404.
- E. N. da C. Andrade, Rutherford and the Nature of the Atom (1964), cited in Ratcliffe, Susan, ed. (2016). "Ernest Rutherford 1871–1937, New Zealand physicist". Oxford Essential Quotations (4th ed.). ISBN 9780191826719.
- "Nobel Prize for Physics : Prof. P. M. S. Blackett, F.R.S". Nature. 162 (4126): 841. 1948. Bibcode:1948Natur.162R.841.. doi:10.1038/162841b0.
- "Exploring the atom". The Manhattan Project – Adventures Inside the Atom. U.S. Department of Energy – Office of History and Heritage Resources. Retrieved 19 June 2019.
- Dacey, James (1 September 2011). "What was Rutherford's greatest discovery?". Physics World. Retrieved 18 June 2019.
- Allibone, Thomas Edward (1964). "Rutherford Memorial Lecture, 1963 The industrial development of nuclear power". Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A. Mathematical and Physical Sciences. 282 (1391): 447–463. Bibcode:1964RSPSA.282..447A. doi:10.1098/rspa.1964.0245. S2CID 97303563.
- Campbell, John (2009). "Inside Story: The genius of Rutherford revisited". CERN Courier. 49 (2): 46–48.
- "Exploring the atom". The Manhattan Project – an interactive history. U.S. Department of Energy – Office of History and Heritage Resources. Retrieved 18 June 2019.
- Rutherford, Sir Ernest (27 March 1925). "Studies of Atomic Nuclei". Science. 62 (1601). Physical Sciences Volume 9: The Royal Institution Library of Sciences: 73–76. Bibcode:1925Sci....62..209R. doi:10.1126/science.62.1601.209. PMID 17748045. Retrieved 29 June 2019.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - Brewerton, Emma (15 December 2014). "Ernest Rutherford". Ministry for Culture and Heritage.
- "No. 14089". The Edinburgh Gazette. 2 January 1925. p. 4.
- "No. 33683". The London Gazette. 23 January 1931. p. 533.
- "The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1908". NobelPrize.org. Retrieved 16 April 2022.
- "Background of the Medal". Royal Society of New Zealand. Retrieved 7 August 2015.
- "Recipients". Royal Society of New Zealand. Retrieved 7 August 2015.
- Intergen. "General". www.bdmhistoricalrecords.dia.govt.nz. Retrieved 8 February 2023.
- "Family history in from the cold". 18 March 2009.
- Summerfield, Fiona (9 November 2012). "Historic St Paul's Church in the Christchurch suburb of Papanui is being fully restored". Anglican Taonga.
- ^ The Complete Peerage, Volume XIII – Peerage Creations, 1901–1938. St Catherine's Press. 1949. p. 495.
- Heilbron, J. L. (12 June 2003). Ernest Rutherford: And the Explosion of Atoms. Oxford University Press. pp. 123–124. ISBN 978-0-19-512378-4.
- "Viceroy Opens The Congress – Sir James Jeans's Address". The Times. Calcutta. 3 January 1938.
- "The British association – breaking down the atom". The Times. 12 September 1933.
- Rhodes, Richard (1986). The Making of the Atomic Bomb. New York: Simon and Schuster. p. 27. ISBN 0-671-44133-7.
- Freemantle, Michael (2003). "ACS Article on Rutherfordium". Chemical & Engineering News. American Chemical Society. Retrieved 2 April 2008.
- "Sanger Institute researcher among first to receive Rutherford Discovery Fellowship". Wellcome Sanger Institute. 17 November 2010. Retrieved 8 April 2021.
- "Rutherford House History". Nelson College. Nelson College. Retrieved 1 April 2018.
- "ErnestRutherford Physics Building". Virtual McGill. McGill University. 24 January 2000. Retrieved 2 April 2008.
- Phillips, Jock; Palmer, Andy (2011). "Rutherford – Pickering memorial, Havelock". New Zealand History Nga korero a ipurangi o Aotearoa. Retrieved 18 January 2023.
- Lord Rutherford may have left a deadly legacy « Lord Rutherford may have left a deadly legacy « News « Royal Society of New Zealand Archived 14 October 2008 at the Wayback Machine. Royalsociety.org.nz. Retrieved on 26 January 2011.
- "'Good Kiwi men' reflected in chapel window". Hawke's Bay Today. NZPA. 25 July 2007. Retrieved 6 December 2016.
- "Place name detail: Mount Rutherford". New Zealand Gazetteer. New Zealand Geographic Board. Retrieved 21 August 2022.
- "Review of Radio-activity by Ernest Rutherford". The Oxford Magazine. 23. The Proprietors: 347. 25 January 1905.
- Carmichael, R. D. (1916). "Book Review: Radioactive Substances and their Radiations" (PDF). Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society. 22 (4): 200. doi:10.1090/s0002-9904-1916-02762-5.
- Pais, Abraham (1988) . Inward Bound. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 216. ISBN 978-0-19-851997-3.
- "Coat-of-Arms of Ernest Rutherford". Escutcheons of Science. Numericana.
Further reading
- Badash, Lawrence (2008) . "Rutherford, Ernest". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (online ed.). Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/35891. (Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
- Cragg, R. H. (1971). "Lord Ernest Rutherford of Nelson (1871–1937)". Royal Institute of Chemistry, Reviews. 4 (2): 129. doi:10.1039/RR9710400129.
- Campbell, John. (1999) Rutherford: Scientist Supreme, AAS Publications, Christchurch, ISBN 0-4730-5700-X
- Marsden, E. (1954). "The Rutherford Memorial Lecture, 1954. Rutherford-His Life and Work, 1871–1937". Proceedings of the Royal Society A. 226 (1166): 283–305. Bibcode:1954RSPSA.226..283M. doi:10.1098/rspa.1954.0254. S2CID 73381519.
- Reeves, Richard (2008). A Force of Nature: The Frontier Genius of Ernest Rutherford. New York: W. W. Norton. ISBN 0-393-33369-8
- Rhodes, Richard (1986). The Making of the Atomic Bomb. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0-671-44133-7
- Wilson, David (1983). Rutherford. Simple Genius, Hodder & Stoughton, ISBN 0-340-23805-4
External links
- Biography and web exhibit from the American Institute of Physics
- Ernest Rutherford on Nobelprize.org
 including the Nobel Lecture, 11 December 1908 The Chemical Nature of the Alpha Particles from Radioactive Substances
including the Nobel Lecture, 11 December 1908 The Chemical Nature of the Alpha Particles from Radioactive Substances - The Rutherford Museum
- Rutherford Scientist Supreme
- Newspaper clippings about Ernest Rutherford in the 20th Century Press Archives of the ZBW
| Academic offices | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded byArthur Schuster | Langworthy Professor at the University of Manchester 1907–1919 |
Succeeded byLawrence Bragg |
| 1908 Nobel Prize laureates | |
|---|---|
| Chemistry |
|
| Literature (1908) |
|
| Peace |
|
| Physics |
|
| Physiology or Medicine |
|
| Dalton Medallists | |
|---|---|
| Recipients |
|
 Media from Commons
Media from Commons Quotations from Wikiquote
Quotations from Wikiquote Texts from Wikisource
Texts from Wikisource
- Ernest Rutherford
- 1871 births
- 1937 deaths
- Experimental physicists
- New Zealand physicists
- New Zealand nuclear physicists
- Radio pioneers
- Nobel laureates in Chemistry
- Recipients of the Copley Medal
- Academic staff of McGill University
- Presidents of the Royal Society
- New Zealand Fellows of the Royal Society
- Foreign associates of the National Academy of Sciences
- Members of the Pontifical Academy of Sciences
- Honorary Members of the Russian Academy of Sciences (1917–1925)
- Honorary Members of the USSR Academy of Sciences
- Fellows of Trinity College, Cambridge
- University of Canterbury alumni
- Academics of the Victoria University of Manchester
- Barons in the Peerage of the United Kingdom
- Knights Bachelor
- People from Brightwater
- New Zealand people of English descent
- New Zealand people of Scottish descent
- British Nobel laureates
- English Nobel laureates
- New Zealand Nobel laureates
- Burials at Westminster Abbey
- Fellows of the Royal Society of New Zealand
- Persons of National Historic Significance (Canada)
- People educated at Nelson College
- Faraday Lecturers
- Presidents of the Institute of Physics
- Honorary Fellows of the Royal Society of Edinburgh
- Corresponding Members of the Russian Academy of Sciences (1917–1925)
- Barons created by George V
- New Zealand recipients of a British peerage
- New Zealand emigrants to the United Kingdom
- 20th-century British physicists
- 19th-century British physicists
- 20th-century British scientists
- 19th-century New Zealand scientists
- New Zealand members of the Order of Merit
- Recipients of the Matteucci Medal
- Recipients of the Dalton Medal
- Members of the American Philosophical Society
- Discoverers of chemical elements
- Cavendish Professors of Physics


