| Revision as of 15:09, 5 March 2010 editGlobalreporter8876 (talk | contribs)2 edits →Demographics← Previous edit | Revision as of 02:01, 6 March 2010 edit undoThe Blade of the Northern Lights (talk | contribs)Edit filter managers, Autopatrolled, Oversighters, Administrators55,784 edits →DemographicsNext edit → | ||
| Line 173: | Line 173: | ||
| *] (derived from ''boer'', the ] word for ''farmer'') are descendants of ] nineteenth-century immigrant farmers. Most Boeres left after independence in 1975. | *] (derived from ''boer'', the ] word for ''farmer'') are descendants of ] nineteenth-century immigrant farmers. Most Boeres left after independence in 1975. | ||
| *]ians, many of them gold miners.<ref>"". Radio Netherlands Worldwide. December 26, 2009.</ref> Most of the nearly 40,000 Brazilians living in Suriname arrived during the past several years.<ref>"". The New York Times. March 30, 2000.</ref> | *]ians, many of them gold miners.<ref>"". Radio Netherlands Worldwide. December 26, 2009.</ref> Most of the nearly 40,000 Brazilians living in Suriname arrived during the past several years.<ref>"". The New York Times. March 30, 2000.</ref> | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Revision as of 02:01, 6 March 2010
| Republic of SurinameRepubliek Suriname Template:Nl icon Ripoliku Sranan (Sranan Tongo) | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Coat of arms of Suriname
Coat of arms
Flag
Coat of arms of Suriname
Coat of arms
| |
| Motto: Justitia - Pietas - Fides Template:La icon "Justice - Duty - Loyalty" | |
| Anthem: God zij met ons Suriname Template:Nl icon ('God be with our Suriname') | |
 | |
| Capitaland largest city | Paramaribo |
| Official languages | Dutch |
| Recognised regional languages | Sranan Tongo, Hindi, English, Sarnami, Javanese, Indonesian, Bhojpuri, Hakka, Cantonese, Saramaccan, Paramaccan, Ndyuka, Kwinti, Matawai, Cariban, Arawakan Kalina |
| Demonym(s) | Surinamese |
| Government | |
| • President | Ronald Venetiaan |
| Independence From the Netherlands | |
| • Date | November 25, 1975 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 163,821 km (63,252 sq mi) (91st) |
| Population | |
| • July 2009 estimate | 481,267 (167th) |
| • 2004 census | 456,829 |
| • Density | 2.9/km (7.5/sq mi) (231st) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2008 estimate |
| • Total | $4.364 billion |
| • Per capita | $8,187 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2008 estimate |
| • Total | $2.933 billion |
| • Per capita | $5,504 |
| HDI (2007) | Error: Invalid HDI value (97th) |
| Currency | Surinamese dollar (SRD) |
| Time zone | UTC-3 (ART) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-3 (not observed) |
| Drives on | left |
| Calling code | 597 |
| ISO 3166 code | SR |
| Internet TLD | .sr |
| Suriname's ISO 3166 code is SR | |
Suriname (Dutch: Suriname; Sarnami: शर्नम् Sarnam, Sranan Tongo: Sranangron), officially the Republic of Suriname, is a country in northern South America.
Suriname is situated between French Guiana to the east and Guyana to the west. The southern border is shared with Brazil and the northern border is the Atlantic coast. The southernmost borders with French Guiana and Guyana are disputed along the Marowijne and Corantijn rivers, respectively; while a part of the disputed maritime boundary with Guyana was arbitrated by the United Nations Convention on Law of the Sea on September 20, 2007.
Suriname is the smallest sovereign state in terms of area and population in South America. The country is the only Dutch-speaking region in the Western Hemisphere that is not a part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. Suriname has a typical multicultural society with extreme ethnic, linguistic, and religious diversity. Suriname's geographical size is just under 165,000 km (64,000 sq mi), and it has an estimated population of about 470,000 people. About a quarter of the population live on less than US$ 2 a day.
Etymology
The name, Suriname, may derive from a Taino (Arawak-speaking) group called "Surinen" who first inhabited the region prior to European arrival.
Originally, the country was spelt Surinam by English settlers who founded the first colony at Marshall's Creek, along the Suriname River, and was formerly known as Nederlands Guyana, Netherlands Guiana or Dutch Guiana. "Surinam" can still be found in English. A notable example of this is Suriname's own national airline, Surinam Airways. The older English name is reflected in the English pronunciation of "Suriname", /ˈsʊrɨnæm/ or /ˈsʊrɨnɑːm/. In Dutch, the official language of Suriname, the pronunciation is [ˌsyriˈnamə], with the main stress on the first syllable.
Geography
Main article: Geography of Suriname
Suriname is the smallest independent country in South America. Situated on the Guiana Shield, the country can be divided into two main geographic regions. The northern, lowland coastal area (roughly above the line Albina-Paranam-Wageningen) has been cultivated, and most of the population lives here. The southern part consists of tropical rainforest and sparsely inhabited savanna along the border with Brazil, covering about 80% of Suriname's land surface.
There are two main mountain ranges in the Bakhuys Mountains and the Van Asch Van Wijck Mountains. Julianatop is the highest mountain in the country at 1,286 metres (4,219 ft) above sea level. Other mountains include Tafelberg at 1,026 metres (3,366 ft), Mount Kasikasima at 718 metres (2,356 ft), Goliathberg at 358 metres (1,175 ft) and Voltzberg at 240 metres (790 ft).
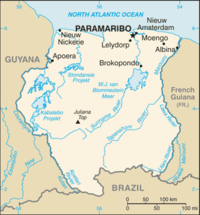
Districts and resorts


| Suriname is divided into ten districts: |
Suriname is further subdivided into 62 resorts (ressorten).
Climate
Lying 2 to 5 degrees north of the equator, Suriname has a very hot tropical climate, and temperatures do not vary much throughout the year. The year has two wet seasons, from April to August and from November to February. It also has two dry seasons, from August to November and February to April.
Nature reserves
In the upper Coppename River watershed, the Central Suriname Nature Reserve is a UNESCO World Heritage Site cited for its unspoiled rainforest biodiversity. There are many national parks in the country: Galibi National Reserve, Coppename Manding National Park and Wia Wia NR along the coast, Brownsberg NR, Raleighvallen/Voltzeberg NR, Tafelberg NR and Eilerts de Haan NP in the centre and the Sipaliwani NR on the Brazilian border. In all, 12.6% of the country's land area are national parks and lakes, according to the UNEP World Conservation Monitoring Centre.
Landmarks

The Jules Wijdenbosch Bridge is a bridge over the river Suriname between Paramaribo and Meerzorg in the Commewijne district. The bridge was built during the tenure of President Jules Albert Wijdenbosch (1996–2000) and was completed in 2000. The bridge is 52 metres (171 ft) high, and 1,504 metres (4,934 ft) long. It connects Paramaribo with Commewijne, a connection which previously could only be made by ferry. The purpose of the bridge was to facilitate and promote the development of the eastern part of Suriname. The bridge consists of two lanes and is not accessible to pedestrians.
The Cathedral of St. Peter and Paul is 114 years old. Before it became a cathedral it was a theatre and was owned by La Parra. The theatre was built in 1809 and burned down in 1820. The construction of the Sts. Peter and Paul Cathedral started on January, 13, 1883.

Suriname is one of the few countries in the world where a synagogue is located next to a mosque (another place is Sofia, Bulgaria). The two buildings are located next to each other in the centre of Paramaribo and have been known to share a parking facility during their respective religious rites, should they happen to coincide with one another.
History
Main article: History of SurinameBeginning in the 16th century, the area was discovered by, French, Spanish and English explorers. A century later, plantation colonies were established by the Dutch and English along the many rivers in the fertile Guyana plains. The earliest documented colony in Guiana was along the Suriname River and called Marshall's Creek. The area was named after an Englishman. Disputes arose between the Dutch and the English. In 1667, the Dutch decided to keep the nascent plantation colony of Suriname conquered from the English, resulting from the Treaty of Breda. The English were left with New Amsterdam, a small trading post in North America, which later became New York City.
The Dutch planters relied heavily on African slaves to cultivate the coffee, cocoa, sugar cane and cotton plantations along the rivers. Treatment of the slaves by their owners was notoriously bad, and many slaves escaped the plantations. With the help of the native South Americans living in the adjoining rain forests, these runaway slaves established a new and unique culture that was highly successful in its own right. Known collectively in English as the Maroons, in French as the Nèg'Marrons and in Dutch as "Bosnegers" (literally meaning "bush negroes"), they actually established several independent tribes, among them the Saramaka, the Paramaka, the Ndyuka or Aukan, the Kwinti, the Aluku or Boni, and the Matawai.
The Maroons would often raid the plantations to recruit new members, acquire women, weapons, food and supplies. These attacks were often deadly for the planters and their families, and after several unsuccessful campaigns against the Maroons, the European authorities signed several peace treaties with them in the 19th century, granting the Maroons sovereign status and trade rights.

Slavery was abolished by the Netherlands in Suriname in 1863, but the slaves in Suriname were not fully released until 1873, after a mandatory 10 year transition period during which time they were required to work on the plantations for minimal pay and without state sanctioned torture. As soon as they became truly free, the slaves largely abandoned the plantations where they had suffered for several generations, in favor of the city, Paramaribo. As a plantation colony, Suriname was still heavily dependent on manual labor, and to make up for the shortfall, the Dutch brought in contract laborers from the Dutch East Indies (modern Indonesia) and India (through an arrangement with the British). In addition, during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, small numbers of mostly men were brought in from China and the Middle East. Although Suriname's population remains relatively small, because of this history it is one of the most ethnically and culturally diverse in the world.

In 1954, the Dutch placed Suriname under a system of limited self-government, with the Netherlands retaining control of defense and foreign affairs. In 1973, the local government, led by the NPK (a largely Creole, meaning ethnically African or mixed African-European, party) started negotiations with the Dutch government leading towards full independence, which was granted on 25 November 1975. The severance package was very substantial, and a large part of Suriname's economy for the first decade following independence was fueled by foreign aid provided by the Dutch government.
The first President of the country was Johan Ferrier, the former governor, with Henck Arron (the then leader of the Nationale Partij Suriname (Suriname's National Party)) as Prime Minister. Nearly one third of the population of Suriname at that time emigrated to the Netherlands in the years leading up to independence, as many people feared that the new country would fare worse under independence than it did as an overseas colony of the Netherlands. Suriname's diaspora therefore includes more than a quarter of one million people of Suriname origin living in the Netherlands today, including several recent members of the Dutch national football (soccer) team.
On February 25, 1980, a military coup sidelined the democratic government and declared a Socialist Republic, and with it began a period of economic and social hardship for the country. On 8 December 1982, the military, then under the leadership of Desi Bouterse, rounded up several prominent citizens who were accused of plotting against the government. They were allegedly tortured and certainly killed during the night, and the Netherlands quickly suspended all foreign aid to Suriname after this event. (As of August 2008, Desi Bouterse is currently standing trial in Suriname for his role in these killings.)
Elections were held in 1987 and a new constitution was adopted, which among other things allowed the dictator to remain in charge of the army. Dissatisfied with the government, Bouterse summarily dismissed them in 1990, by telephone. This event became popularly known as "the telephone coup". Bouterse's power began to wane after the 1991 elections however, and a brutal civil war between the Suriname army and the Maroons, loyal to the rebel leader Ronnie Brunswijk, further weakened his position during the 1990s.
Suriname's democracy gained some strength after the turbulent 1990s, and its economy became more diversified and less dependent on Dutch financial assistance. Bauxite (Aluminum ore) mining continues to be a strong revenue source, but the discovery and exploitation of oil and gold has added substantially to Suriname's economic independence. Agriculture, especially of rice and bananas, remains a strong component of the economy, and ecotourism is providing new economic opportunities. More than 80% of Suriname's land-mass consists of unspoiled rain forest, and with the establishment of the Central Suriname Nature Reserve in 1998, Suriname signaled its commitment to conservation of this precious resource. The Central Suriname Nature Reserve became a World Heritage Site in 2000.
Economy

The economy of Suriname is dominated by the bauxite industry, which accounts for more than 15% of GDP and 70% of export earnings. Other main export products include rice, bananas and shrimp. Suriname has recently started exploiting some of its sizeable oil and gold reserves. About a quarter of the people work in the agricultural sector. The Surinamese economy is very dependent on commerce, its main trade partners being the Netherlands, the United States, Canada and Caribbean countries.
After assuming power in the fall of 1996, the Wijdenbosch government ended the structural adjustment program of the previous government, claiming it was unfair to the poorer elements of society. Tax revenues fell as old taxes lapsed and the government failed to implement new tax alternatives. By the end of 1997, the allocation of new Dutch development funds was frozen as Surinamese Government relations with the Netherlands deteriorated. Economic growth slowed in 1998, with decline in the mining, construction, and utility sectors. Rampant government expenditures, poor tax collection, a bloated civil service, and reduced foreign aid in 1999 contributed to the fiscal deficit, estimated at 11% of GDP. The government sought to cover this deficit through monetary expansion, which led to a dramatic increase in inflation.
- GDP (2006 est.): U.S. $2.11 billion.
- Annual growth rate real GDP (2006 est.): 5.8%.
- Per capita GDP (2006 est.): U.S. $4,000.
- Inflation (2006): 5.6%.
- Natural resources: Bauxite, gold, oil, iron ore, other minerals; forests; hydroelectric potential; fish and shrimp.
- Agriculture: Products—rice, bananas, timber, and citrus fruits.
- Industry: Types—alumina, oil, gold, fish, shrimp, lumber.
- Trade (2005):
- Exports—U.S. $929.1 million: alumina, gold, crude oil, wood and wood products, rice, bananas, fish, and shrimp. Major markets—Norway (23.9%), U.S. (16.8%), Canada (16.4%), France (8.1%), Iceland (2.9%).
- Imports--$1.1 billion: capital equipment, petroleum, iron and steel products, agricultural products, and consumer goods. Major suppliers—U.S. (24.4%), Netherlands (14.5%), Trinidad and Tobago (10.5%), China (5.4%), Japan (4.3%), Brazil (3.6%).
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Suriname
In November 2007, Suriname's population was estimated to be 494,347. It is made up of several distinct ethnic groups.
- Hindoestanen form the largest major group at 27% of the population. They are descendants of nineteenth-century contract workers from India. They are from the Indian states of Bihar and Eastern Uttar Pradesh, in Northern India, along the Nepali border.
- The Surinamese Creoles form the middle group 18% of the population. They are the mixed descendants of West African slaves and Europeans (mostly Dutch).
- The Javanese (descendants of contract workers from the former Dutch East Indies on the island of Java, Indonesia) make up 15% (close to 90,000) of the population.
- Surinamese Maroons (descendants of escaped West African slaves) make up 15% and are divided into five main groups: Ndyuka (Aucans), Kwinti, Matawai, Saramaccans and Paramaccans.
- Mixed 12.5%
- Amerindians form 3.7% of the population, the main groups being the Akuriyo, Arawak, Carib/Kaliña, Trío (Tiriyó), and Wayana.
- Chinese, mainly descendants of the earliest nineteenth-century contract workers, 1.8% and number about 14,000.
- Boeres (derived from boer, the Dutch word for farmer) are descendants of Dutch nineteenth-century immigrant farmers. Most Boeres left after independence in 1975.
- Brazilians, many of them gold miners. Most of the nearly 40,000 Brazilians living in Suriname arrived during the past several years.

There is no predominant religion in the country. Christianity, both in the form of Roman Catholicism and various denominations of Protestantism, is dominant among Creoles and Maroons. The Creoles and to a lesser degree the Maroons, both descendants of enslaved Africans, were forced to convert to Christianity, but a lot of them still retain their Afro-American religion called Winti. Most of the Hindustani are Hindu, but some practice Islam or Christianity. The Javanese practice either Islam or Christianity. Suriname's population is 20% Muslim, which is the highest minority-percentage of Muslims of any country in the New World(after India having Muslims 13.4%).
The makeup of Suriname's population is similar to that of neighboring Guyana, with the exception of the large Indonesian population (which is not present in Guyana). French Guiana, which is a part of France, does not collect ethnic statistics, but is believed to contain much smaller Hindustani and Indonesian populations.
The vast majority of people (about 90%) live in Paramaribo or on the coast. There is also a significant Surinamese population in the Netherlands. In 2005 there were 328,300 Surinamese people living in the Netherlands, which is about 2% of the total population of the Netherlands, compared to 438,000 Surinamese in Suriname itself.

These groups are all represented in the old flag of Suriname.
Languages
A variety of languages are spoken in Suriname. Dutch is the sole official language, and is the language of education, government, business and the media. Over 60 percent of the population speak it as a mother tongue, and most of the rest speak it as a second or third language. In 2004, Suriname became an associate member of the Dutch Language Union. In Paramaribo, Dutch is the main home language in two-thirds of households.. The recognition of "Surinaams Nederlands" ("Surinam Dutch") as a natiolect equal to "Nederlands Nederlands" ("Dutch Dutch") and "Vlaams Nederlands" ("Flemish Dutch") was expressed in 2009 by the publication of the Woordenboek Surinaams Nederlands (Surinamese Dutch Dictionary) . Only in the interior of Suriname is Dutch seldom used.
Sranan Tongo, a local creole language originally spoken by the Creole population group, is the most widely used language in the streets and often interchangeably with Dutch depending on the formality of the setting.
Surinamese Hindi or Sarnami, a dialect of Bhojpuri, is the third-most used language, spoken by the descendants of British Asian contract workers. Javanese is used by the descendants of Javanese contract workers. The Maroon languages, somewhat intelligible with Sranan Tongo, include Saramaka, Paramakan, Ndyuka, Aukan, Kwinti and Matawai. Amerindian languages, spoken by Amerindians, include Carib and Arawak. Hakka and Cantonese are spoken by the descendants of the Chinese contract (koelie, coolie) workers. Mandarin is spoken by some few recent Chinese immigrants. English, Spanish and Portuguese are also used. Spanish and Portuguese are spoken by Latin American residents and their descendants and sometimes also taught in schools.
The public discourse about Suriname's languages is a part of an ongoing debate about the country's national identity. While Dutch is perceived as a remnant of colonialism by some, the use of the popular Sranan became associated with nationalist politics after its public use by former dictator Dési Bouterse in the 1980s, and groups descended from escaped slaves might resent it. Some propose to change the national language to English, so as to improve links to the Caribbean and North America, or to Spanish, as a nod to Suriname's location in South America, although it has no Spanish-speaking neighbours.
Health
Fertility rate was at 2.6 births per woman. Public expenditure was at 3.6 % of the GDP in 2004, whereas private expenditure was at 4.2 %. There were 45 physicians per 100,000 in the early 2000s. Infant mortality was at 30 per 1,000 live births. Male life expectancy at birth was at 66.4 years, whereas female life expectancy at birth was at 73 years.
Transport
See also: Transport in Suriname and East-West Link (Suriname)Suriname and neighboring Guyana are the only two countries on the (in-land) American continent who still drive on the left. In Guyana this practice is inherited from United Kingdom colonial authorities. The reason for the left hand drive in Suriname is explained by several sources. It is thought that this is because the first cars imported were from England, but this is yet undocumented. In addition, this view does not make statements on traffic before the automobile era. Another explanation is that the Netherlands, at the time of colonization of Suriname, used the left-hand side of the road for traffic, or that Suriname was first colonized by the English. Although the Netherlands converted to driving to the right at the end of the 18th century (Peter Kincaid, and ), Suriname did not. An interesting viewpoint on this is forwarded by Peter Kincaid, and further explored by Ian Watson, in that territories such as Suriname, with no neighbors or no connecting roads to neighbour countries, had no external pressure to either change or to maintain the status quo on driving sides.
Politics


The Republic of Suriname is a constitutional democracy based on the 1987 constitution.
The legislative branch of government consists of a 51-member unicameral National Assembly, simultaneously and popularly elected for a five-year term.
The president, who is elected for a five-year term by a two-thirds majority of the National Assembly or, failing that, by a majority of the People's Assembly, heads the executive branch. If at least two-thirds of the National Assembly cannot agree to vote for one presidential candidate, a People's Assembly is formed from all National Assembly delegates and regional and municipal representatives who were elected by popular vote in the most recent national election. As head of government, the president appoints a 16-minister cabinet. There is no constitutional provision for removal or replacement of the president unless he resigns.
The judiciary is headed by the Court of Justice (Supreme Court). This court supervises the magistrate courts. Members are appointed for life by the president in consultation with the National Assembly, the State Advisory Council and the National Order of Private Attorneys. In April 2005, the regional Caribbean Court of Justice, based in Trinidad, was inaugurated. As the final court of appeal, it was intended to replace the London-based Privy Council.
The country is divided into 10 administrative districts, each headed by a district commissioner appointed by the president. The commissioner is similar to the governor of a United States-type state, but is appointed and removed by the president.
Culture
Main articles: Roman Catholicism in Suriname, Music of Suriname, and Hinduism in South America
Owing to the country's multicultural heritage, Suriname celebrates a variety of distinct ethnic and religious festivals.
National celebrations
January 1 - New Year's Day
March 1 (varies) - Holi/ Phagwa
May 1 - Labour Day
June 5 - Immigration of the Indians
July 1 - Keti Koti, Emancipation Day (end of slavery)
August 8 - Day of the indigenous people
August 9 - Immigration of the Javanese
November 25 - Independence Day
December 5 - Children's day (Sinterklaas)
December 25 - Christmas Day
December 26 - Second Christmas Day
There are several Hindu and Islamic national holidays like Divali (deepavali), Phagwa and Eid ul-Fitr and Eid-ul-adha. These holidays do not have specific dates on the Gregorian calendar as they are based on the Hindu and Islamic calendars, respectively.
There are several holidays which are unique to Suriname. These include the Indian, Javanese and Chinese arrival days. They celebrate the arrival of the first ships with their respective immigrants.
New Year's Eve

New Year's Eve in Suriname is called Oud jaar, or "old year". It is during this period that the Surinamese population goes to the city's commercial district to watch demonstrational fireworks. The bigger stores invest in these firecrackers and display them out in the streets. Every year the length of them is compared, and high praises are held for the company that has managed to import the largest ribbon. These celebrations start at 10 in the morning and finish the next day. The day is usually filled with laughter, dance, music, and drinking. When the night starts, the big street parties are already at full capacity. The most popular fiesta is the one that is held at café 't Vat in the main tourist district. The parties there stop between 10 and 11 at night. After which the people go home to light their pagaras (red-firecracker-ribbons) at midnight. After 12, the parties continue and the streets fill again until daybreak.
Sports
Some of the greatest football players to represent the Netherlands, such as Frank Rijkaard, Ruud Gullit, Patrick Kluivert, Edgar Davids, Clarence Seedorf, Aron Winter, Jimmy Floyd Hasselbaink, Stanley Menzo, Ryan Babel, Ken Monkou, Edson Braafheid,, Regi Blinker and Fabian Wilnis are of Surinamese descent. Davids in particular has written of his passionate pride in his Surinamese heritage and his love of attending football matches there. There are a number of local heroes in other sports as well, like Primraj Binda, best known as the athlete who dominated the local 10 km for nearly a decade, Steven Vismale and Letitia Vriesde. Another notable track athlete from Suriname was Tommy Asinga.
Anthony Nesty is the only person to win a medal (for swimming) for Suriname at the Olympics. Originally from Trinidad and Tobago, not Suriname, he now lives in Gainesville, Florida, USA, and is a coach of the University of Florida. He is mainly a distance coach.
Multiple K-1 champion and legend, Ernesto Hoost, was born in Suriname. Remy Bonjasky also a multiple K-1 champion is also from Surinamese descent. MMA and Kickboxing champions Melvin Manhoef, Gilbert Yvel and Alistair Overeem were born in Suriname or from Surinamese descent. Retired female kickboxer Ilonka Elmont was also born in Suriname. Another notable up and comer kickboxer and K-1 fighter, Tyrone Spong, was born in Suriname. Ginty Vrede, a former Muay Thai Heavy Weight Champion who passed away in 2008 aged 22, was born in Suriname.
Education
Main article: Education in SurinameThe net primary enrollment rate was 94 % in 2004. Education is compulsory until the age of 12. Literacy is very common, particularly among males. The university of the country is the Anton de Kom University of Suriname. Boy Waterman
Media
A popular newspaper is De Ware Tijd. Suriname has 24 radio stations from which a couple broadcast through the Internet (Apintie and Radio10). There are also a dozen television networks including STVS, RBN, ABC, ATV, Mustika, and Garuda). Also listened to is mArt, a broadcaster from Amsterdam founded by people from Suriname. Kondreman is one of the popular cartoons in Suriname.
Tourism
Royal Torarica, was opened in the night district of Paramaribo on the Suriname River. The hotel industry is important to Suriname's economy. The rental of apartments, or the rent-a-house phenomenon, is also popular in Suriname.
Most tourists visit Suriname for the outstanding biodiversity of the pristine Amazonian rain forests in the south of the country, which are noted for their flora and fauna. The Central Suriname Nature Reserve is the biggest and one of the most popular reserves, along with the Brownsberg Nature Park which overlooks the Brokopondo Reservoir, the latter being one of the largest man-made lakes in the world. Tonka Island in the reservoir is home to a rustic eco-tourism project run by the Saramaccaner Maroons. There are also many waterfalls throughout the country: Raleighvallen, or Raleigh Falls, is a 56,000 hectare nature reserve on the Coppename River, rich in bird life. Also are the Blanche Marie Falls on the Nickerie River and the Wonotobo Falls. Tafelberg Mountain in the centre of the country is surrounded by its own reserve- the Tafelberg Nature Reserve- around the source of the Saramacca River, as is the Voltzberg Nature Reserve further north on the Coppename River at Raleighvallen. In the interior are many Maroon and Amerindian villages which often have their own reserves and are open to visitors.
Suriname is one of the few countries in the world where at least one of each biome that the state possesses has been declared a wildlife reserve. Around 30% of the total land area of Suriname is protected by law as reserves.
Other attractions include plantations such as Laarwijk, which is situated along the Suriname River. This plantation can only be reached by boat via Domburg, in the north central Wanica District of Suriname.
Airlines
Airlines from Suriname
Airlines operating to Suriname
- Caribbean Airlines, (Trinidad & Tobago)
- Insel Air, (Curaçao)
- KLM, (the Netherlands)
- Meta Linhas Aéreas, (Brazil)
See also
Main article: Outline of SurinameReferences
- ^ Central Intelligence Agency (2009). "Suriname". The World Factbook. Retrieved January 23, 2010.
- Suriname Population UN Stats. Pg. 47, Appendix 1. Retrieved 26 June 2009
- ^ "Suriname". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 2009-10-01.
- "Human Development Report 2009. Human development index trends: Table G" (PDF). The United Nations. Retrieved 2009-10-18.
- ISO 3166
- United Nations Development Programme
- ^ Encyclopedia Britannica: A Dictionary of Arts, Sciences, and General Literature, Volume XI (Ninth Edition—Popular Reprint ed.). Retrieved 2008-05-04.
In 1614 the states of Holland granted to any Dutch citizen a four years' monopoly of any harbour or place of commerce which he might discover in that region (Guiana). The first settlement, however, in Suriname (in 1630) was made by an Englishman, whose name is still preserved by Marshall's Creek.
- Transclusion error: {{En}} is only for use in File namespace. Use {{langx|en}} or {{in lang|en}} instead. UNEP World Conservation Monitoring Centre World Databbase on Protected Areas
- Transclusion error: {{En}} is only for use in File namespace. Use {{langx|en}} or {{in lang|en}} instead. Rigzone Staatsolie Launches Tender for 3 Offshore Blocks
- Transclusion error: {{En}} is only for use in File namespace. Use {{langx|en}} or {{in lang|en}} instead. Cambior Development of the Gross Rosebel Mine in Suriname
- ^ Joshuaproject.net
- "Violence erupts in Surinam". Radio Netherlands Worldwide. December 26, 2009.
- "Guyana: Caught in Brazil's Net?; Small Nation, New to Free Markets, Fears Loss of Its Identity". The New York Times. March 30, 2000.
- Muslim Minorities in the West: Visible and Invisible By Yvonne Yazbeck Haddad, Jane I. Smith, pg 271
- Template:Nl icon "Het Nederlandse taalgebied". Nederlandse Taalunie. 2005. Retrieved 2008-11-04.
- Template:Nl icon Nederlandse Taalunie
- Algemeen Bureau voor de Statistiek. "Update Census 7" (PDF). ABS. Retrieved 2008-07-24.
- Prisma Woordenboek Surinaams Nederlands, edited by Renata de Bies, in cooperation with Willy Martin and Willy Smedts, ISBN: 978-90-491-0054-4
- ^ Simon Romero (March 23, 2008). "In Babel of Tongues, Suriname Seeks Itself". New York Times.
- ^ United Nations Development Programme
- unreferenced
- The UN Refugee Agency
External links
- Government
- Government of the Republic of Suriname Template:Nl icon
- "Districts of Suriname". Statoids.
- Chief of State and Cabinet Members
- General information
- "Suriname". The World Factbook (2024 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Travel information for the independent traveller
- Suriname at UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Dictionaries of Suriname languages
- Template:Dmoz
- Suriname, an external wiki
 Wikimedia Atlas of Suriname
Wikimedia Atlas of Suriname- Perry-Castañeda Library Map Collection
- History of the Suriname Jewish Community
- Template:Wikitravel
| Geographic locale | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||
Template:Austronesian-speaking
Categories: