| Revision as of 15:04, 11 April 2011 editEmausBot (talk | contribs)Bots, Template editors2,856,786 editsm r2.6.4) (robot Modifying: eu:Antioquia← Previous edit | Revision as of 20:24, 30 April 2011 edit undoPolylerus (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers53,393 edits grammarNext edit → | ||
| Line 99: | Line 99: | ||
| After the debate initiated by the idea of Jewish origin of Antioquia from mid-nineteenth century to the twentieth century, came the hypothesis of Basque origin. From this it commissioned especially two American historians: Everett Hagen and Leonard Kasdan. Hagen looked up the phone in Medellin in 1957 and found that 15% of the surnames were Basques, of Basque origin, finding then that employers in the percentage of surnames was up to 25%, which led it to conclude that the inheritance Basque was very important to explain the increased industrial development of Antioquia in the Colombian context. These ideas were supported by representatives of developmental theories, who sought to justify business growth based on "the character of social groups." | After the debate initiated by the idea of Jewish origin of Antioquia from mid-nineteenth century to the twentieth century, came the hypothesis of Basque origin. From this it commissioned especially two American historians: Everett Hagen and Leonard Kasdan. Hagen looked up the phone in Medellin in 1957 and found that 15% of the surnames were Basques, of Basque origin, finding then that employers in the percentage of surnames was up to 25%, which led it to conclude that the inheritance Basque was very important to explain the increased industrial development of Antioquia in the Colombian context. These ideas were supported by representatives of developmental theories, who sought to justify business growth based on "the character of social groups." | ||
| ⚫ | Euskera (Basque language) in Antioquia | ||
| ⚫ | ===Euskera (Basque language) in Antioquia.=== | ||
| The use of the Basque language (Euskera) in the present territory of Colombia goes back to the early exploration occurred in 1499, during the third voyage of Columbus, it is said that from that time the territory was felt a strong presence of Basques. Some figures such as the pilot and geographer Juan de la Cosa, nicknamed "El Vizcaino" (although some sources claim that reputable and solvent was not a native of |
The use of the ] (Euskera) in the present territory of Colombia goes back to the early exploration occurred in 1499, during the ], it is said that from that time the territory was felt a strong presence of ]. Some figures such as the pilot and geographer ], nicknamed "El Vizcaino" (although some sources claim that reputable and solvent was not a native of the ], but was born in ], ]). | ||
| Thereafter, the Basques began to come regularly and are distributed throughout the country. Due to this presence is that the Colombian department of Antioquia has been considered a major route of the Basque-Navarre immigration, mainly during the colonial era, when hundreds of Basque migrated to be linked to the Spanish colonization companies. | Thereafter, the Basques began to come regularly and are distributed throughout the country. Due to this presence is that the Colombian department of Antioquia has been considered a major route of the Basque-] immigration, mainly during the colonial era, when hundreds of Basque migrated to be linked to the Spanish colonization companies. | ||
| People who were interested in investigating the presence of Euskal Herria in the department of Antioquia and Colombia, one of the questions that troubled them relates to the use and retention of the Basque language in their current territories. | People who were interested in investigating the presence of Euskal Herria in the department of Antioquia and Colombia, one of the questions that troubled them relates to the use and retention of the Basque language in their current territories. | ||
| It is estimated (for example for small Antioquia, a region where hundreds of Spaniards arrived |
It is estimated (for example for small Antioquia, a region where hundreds of Spaniards arrived, of which a good portion were Basque, some limited aspects of the culture and traditions brought by Basque settlers, without even mention his particular language, it has been unclear to track the use of Euskara in the current Antioquia and Colombia, because the Basque language was always an outcast, which apparently left no written evidence in Antioquia. | ||
| In this regard, it is hardly likely that the Spanish crown to maintain the monopoly of overseas companies, to maintain policies that restrict citizens not belonging to the then Spanish rule, much less allow it to speak languages other than Castilian language . Basques so that those invited to participate in the colonization of Indian companies, and foreigners in general, had to learn the official language, ie, Castilian, hence the dominance of Castilian-Basque-speaking or bilingual. | In this regard, it is hardly likely that the Spanish crown to maintain the monopoly of overseas companies, to maintain policies that restrict citizens not belonging to the then Spanish rule, much less allow it to speak languages other than Castilian language . Basques so that those invited to participate in the colonization of Indian companies, and foreigners in general, had to learn the official language, ie, Castilian, hence the dominance of Castilian-Basque-speaking or bilingual. | ||
| Despite these restrictions, it is still possible to trace the history of Colombia present references to the ancient language of the Basques. A reference that has very ancient use of Euskara in Colombian territory, occurred in relation to Lope de Aguirre, a |
Despite these restrictions, it is still possible to trace the history of Colombia present references to the ancient language of the Basques. A reference that has very ancient use of Euskara in Colombian territory, occurred in relation to ], a native of ] nicknamed "The Madman". Aguirre's rebellion defied the Spanish empire, carrying out acts against the subjects of the Spanish crown. ], a Navarrese faithful to the Spanish king, who was also the founder of ] in eastern Colombia, said that he could persuade the soldiers to be told of Aguirre's revolt, if they spoke in Euskera. | ||
| After the ], several Basque families migrated to Colombia. Many of these families were Basque-speakers and were wrote works in Euskera, and likewise, translated from Castilian Euskera literary works of Colombian authors.{{citation}} | |||
| === Antioquia Basque speech === | |||
| ⚫ | The current Spanish dialect in Antioquia, closely observed, has obvious influences from Basque. Basque origin are the words 'love' or 'ma' (mother), 'coscorria' (useless, inept) and 'tap' (tap), to name only a few cases . Basque also for example the pronunciation of the letter 's' apico-alveolar, so in the Antioquia, and the letter "ll" (double L) Africa, not to overlook the inclusion of the letter "a" before certain initial Rs: arrecostarse, arrecoger, arrecordarse, instead of lying down, collect, remember, etc.. See also Spanish Antioquia. | ||
| ⚫ | The current |
||
| ===The Spaniards in Antioquia=== | ===The Spaniards in Antioquia=== | ||
| The first Spaniard that came to Antioquia was ] who was in Darién in the year 1500. Ten years later, ] founded ], 2 km from the present-day town of ], which would be destroyed later by the natives. However, the first Spanish incursion in Antioquia only took place in 1537, when an expedition commanded by ] traveled the lands of Indian chief Dabeiba, arriving at the ] and taking an important treasure from the indigenous tombs. However, men of chief Nutibara harassed the Spaniards, forcing them to return to ]. | The first Spaniard that came to Antioquia was ] who was in Darién in the year 1500. Ten years later, ] founded ], 2 km from the present-day town of ], which would be destroyed later by the natives. However, the first Spanish incursion in Antioquia only took place in 1537, when an expedition commanded by ] traveled the lands of Indian chief Dabeiba, arriving at the ] and taking an important treasure from the indigenous tombs. However, men of chief Nutibara harassed the Spaniards, forcing them to return to ]. | ||
Revision as of 20:24, 30 April 2011
| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Antioquia Department" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (August 2010) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Department of Antioquia Departamento de Antioquia | |
|---|---|
| Department | |
 Flag Flag Coat of arms Coat of arms | |
| Motto(s): New Antioquia, a Home for Life (Template:Lang-es) | |
| Anthem: Himno de Antioquia | |
 Antioquia shown in red Antioquia shown in red | |
| Country | |
| Region | Andean Region |
| Established | 1826 |
| Capital | Medellín |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Luis Alfredo Ramos (Conservative Party) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 63,612 km (24,561 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 6 |
| Population | |
| • Total | 5,671,689 |
| • Rank | 2 |
| • Density | 89/km (230/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC-05 |
| ISO 3166 code | CO-ANT |
| Provinces | 9 |
| Municipalities | 125 |
| Website | www.gobant.gov.co |
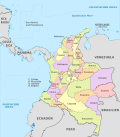
Antioquia (Spanish pronunciation: [anˈtjokja]) is one of the 32 departments of Colombia, located in the central northwestern part of Colombia with a narrow section that borders the Caribbean Sea. Most of its territory is mountainous with some valleys, much of which is part of the Andes mountain range. Antioquia has been part of many territorial divisions of former countries created over the present day territory of Colombia, and prior to the Colombian Constitution of 1886, Antioquia State was a sovereign government in their own right.
The department covers an area of 63,612 km² (24,427 sq mi), and has a population of 5,819,358 (2006 estimate); 6,6 million (2010 estimate). Antioquia borders with the Córdoba Department and the Caribbean Sea to the north, Chocó to the west, to the east it borders the departments of Bolivar, Santander and Boyaca, and to the south the departments of Caldas and Risaralda.
Medellín is Antioquia's capital city, and the second largest city in the country. Other important towns are Santa Fe de Antioquia, the old capital located on the Cauca, and Puerto Berrío on the Magdalena.
Geography
Antioquia is the 6th largest Department of Colombia. It is predominantly mountainous, crossed by the Cordillera Central and the Cordillera Occidental of the Andes. The Cordillera Central, further divides to form the Aburrá valley, in which the capital Medellín is located. The Cordillera Central forms the plateaus of Santa Rosa de Osos and Rionegro.
Despite 80% of the department's territory being mountainous, Antioquia also has a coast on the Caribbean Sea, in the lowland area of the Urabá. This area has a tropical climate and is of high strategical importance due to its location.
History
The aboriginal peoples of Antioquia
Before Spanish colonization (a time referred to as the prehispanic era), two large tribes, the Caribs and the Muiscas, inhabited this part of modern day Colombia. There is still much uncertainty regarding the origin of these tribes–historical evidence suggests that both groups migrated from Brazil.
Antioquia was primarily populated by Caribs, although some scattered groups of Muiscas were present in the Darién region (in modern day Panama), a coastal region in the far north of Antioquia. However, there are no historical records for these groups of Muiscas in Antioquia.
The Caribs present in Antioquia were further classified into smaller groups, called families. Some of the most prominent indigenous families in the region include the Catías, Nutabes and Tahamíes, which all inhabited the central region of Antioquia.
An important group that inhabited southern Antioquia was the Quimbaya.
There were other groups, but the Quimbaya, Carib and Muisca tribes were the most prominent groupings that were found by the conquistadors upon their arrival in Antioquia. The Quimbayas had little to do with the evolution of the department, because Jorge Robledo, the main conquistador of Antioquia, quickly subjected the few Quimbaya that he found and the rest disappeared.
The history was centered then in the turbulent relationships of the Spaniards with the Caribs. Despite the number of Caribs and their well-known warring culture, they would end up dominated or exterminated by the Spaniards in the process of conquest and colonization.
During these processes bloody confrontations were presented that caused the surviving natives to disperse, and even commit suicide, before they were subjected. Many of the survivors fled to the department of Chocó. Thus, in Antioquia, the natives disappeared almost completely. At present, the indigenous population of the department of Antioquia scarcely reaches 0.5% of the total population.
Basque influence in Antioquia
After the debate initiated by the idea of Jewish origin of Antioquia from mid-nineteenth century to the twentieth century, came the hypothesis of Basque origin. From this it commissioned especially two American historians: Everett Hagen and Leonard Kasdan. Hagen looked up the phone in Medellin in 1957 and found that 15% of the surnames were Basques, of Basque origin, finding then that employers in the percentage of surnames was up to 25%, which led it to conclude that the inheritance Basque was very important to explain the increased industrial development of Antioquia in the Colombian context. These ideas were supported by representatives of developmental theories, who sought to justify business growth based on "the character of social groups."
Euskera (Basque language) in Antioquia.
The use of the Basque language (Euskera) in the present territory of Colombia goes back to the early exploration occurred in 1499, during the third voyage of Columbus, it is said that from that time the territory was felt a strong presence of Basques. Some figures such as the pilot and geographer Juan de la Cosa, nicknamed "El Vizcaino" (although some sources claim that reputable and solvent was not a native of the Basque Country, but was born in Santona, Cantabria).
Thereafter, the Basques began to come regularly and are distributed throughout the country. Due to this presence is that the Colombian department of Antioquia has been considered a major route of the Basque-Navarre immigration, mainly during the colonial era, when hundreds of Basque migrated to be linked to the Spanish colonization companies.
People who were interested in investigating the presence of Euskal Herria in the department of Antioquia and Colombia, one of the questions that troubled them relates to the use and retention of the Basque language in their current territories.
It is estimated (for example for small Antioquia, a region where hundreds of Spaniards arrived, of which a good portion were Basque, some limited aspects of the culture and traditions brought by Basque settlers, without even mention his particular language, it has been unclear to track the use of Euskara in the current Antioquia and Colombia, because the Basque language was always an outcast, which apparently left no written evidence in Antioquia.
In this regard, it is hardly likely that the Spanish crown to maintain the monopoly of overseas companies, to maintain policies that restrict citizens not belonging to the then Spanish rule, much less allow it to speak languages other than Castilian language . Basques so that those invited to participate in the colonization of Indian companies, and foreigners in general, had to learn the official language, ie, Castilian, hence the dominance of Castilian-Basque-speaking or bilingual.
Despite these restrictions, it is still possible to trace the history of Colombia present references to the ancient language of the Basques. A reference that has very ancient use of Euskara in Colombian territory, occurred in relation to Lope de Aguirre, a native of Gipuzkoa nicknamed "The Madman". Aguirre's rebellion defied the Spanish empire, carrying out acts against the subjects of the Spanish crown. Pedro de Ursua, a Navarrese faithful to the Spanish king, who was also the founder of Pamplona in eastern Colombia, said that he could persuade the soldiers to be told of Aguirre's revolt, if they spoke in Euskera.
After the Spanish Civil War, several Basque families migrated to Colombia. Many of these families were Basque-speakers and were wrote works in Euskera, and likewise, translated from Castilian Euskera literary works of Colombian authors. {{citation}}: Empty citation (help)
Antioquia Basque speech
The current Spanish dialect in Antioquia, closely observed, has obvious influences from Basque. Basque origin are the words 'love' or 'ma' (mother), 'coscorria' (useless, inept) and 'tap' (tap), to name only a few cases . Basque also for example the pronunciation of the letter 's' apico-alveolar, so in the Antioquia, and the letter "ll" (double L) Africa, not to overlook the inclusion of the letter "a" before certain initial Rs: arrecostarse, arrecoger, arrecordarse, instead of lying down, collect, remember, etc.. See also Spanish Antioquia.
The Spaniards in Antioquia
The first Spaniard that came to Antioquia was Rodrigo de Bastidas who was in Darién in the year 1500. Ten years later, Alonso de Ojeda founded San Sebastián de Urabá, 2 km from the present-day town of Necoclí, which would be destroyed later by the natives. However, the first Spanish incursion in Antioquia only took place in 1537, when an expedition commanded by Francisco César traveled the lands of Indian chief Dabeiba, arriving at the Cauca River and taking an important treasure from the indigenous tombs. However, men of chief Nutibara harassed the Spaniards, forcing them to return to Urabá.
In 1541, Marshal Jorge Robledo left the now-gone Spanish establishment of Arma, a little below Aguadas in the south of Antioquia, for an expedition toward the north on the Cauca River.
Farther north, in 1541, Robledo would found Santa Fe de Antioquia. In 1813, Santa Fe de Antioquia was declared the capital of the County of Antioquia, and this lasted until 1826 when Medellin was made the capital.
Toponymy
The reason behind the chosen name for the Department is not historically clear. The most accepted explanation is that the name for the, then Syrian (now Turkish), Hellenistic city of Antioch on the Orontes (Arabic: Antākiyyah, today Antakya) was used, as the region known as the Coffee Zone in Colombia, in which many towns and cities are named after cities in the middle east, has a very strong Judeo-Arabic influence, both demographically and culturally; Additionally the city in mention played a significant role in the development of early Christian communities thus religiously important for Roman Catholic Spaniard conquerors. Others state that it is named after some of the other many Hellenistic ancient cities in the middle east named Antiochia which were founded as well by some of the Antiochus Kings during the Seleucid Empire (312-63 BC).
History of Antioquia from the 16th to the 21st centuries
Due to its geographical isolation (as it is located among mountains), Antioquia suffered supply problems. Its topography did not allow for much agriculture, so Antioquia became dependent upon trade, especially of gold and gin for the colonization of new land, although much of this trade was due to reformations passed after a visit from an inspector of the Spanish crown, Juan Antonio Mon y Velarde in 1785. The Antioquia became colonizers and traders, contributing to the Antioquian culture.
Administrative divisions
Regions and Municipalities
Antioquia is divided into 9 subregions to facilitate the Department's administration. These 9 regions contain a total of 126 municipalities. The 9 subregions with their municipalities are:
| Southwestern Antioquia | Eastern Antioquia | Northeastern Antioquia |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
| Northern Antioquia | Western Antioquia | Bajo Cauca Antioquia |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
| Magdalena Medio Antioquia | Urabá Antioquia | Medellín Metropolitan Area |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
Demography
The population of Antioquia is 5,819,358 (2005 estimate), of which more than half live in the metropolitan area of Medellin. The racial composition is:
- White
- Mestizos Mixed Indigenous
- Black or Afro-Colombian (10.83%)
- Amerindian or Indigenous (0.51%)
- Gypsies (7.00%)
The local inhabitants of Antioquia are known as antioqueños. Of the five main regional groups in Colombia, the predominant group in Antioquia are known as paisa, referring to those living in the Paisa region, which covers most of Antioquia, as well as the departments of Caldas, Risaralda and Quindío.
See also
References
Further reading
- Template:Es icon Secretary of Education - Government of Colombia
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. {{cite encyclopedia}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) The article is available here
| Capital: Medellín | |||||||||||||||||||
| Regions and municipalities |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Related topics | |||||||||||||||||||
| Departments of Colombia | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||