| Revision as of 11:43, 24 July 2011 editChuispastonBot (talk | contribs)100,206 editsm r2.7.1) (robot Adding: simple:Pentene← Previous edit | Revision as of 13:27, 29 November 2011 edit undoLamro (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users84,236 edits linkNext edit → | ||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| '''Pentene''' refers to all the ] with ] {{ |
'''Pentene''' refers to all the ] with ] {{chem|C|5|H|10}}. Each contains one ] within its molecular structure. There are a total of five different compounds in this class, differing from each other by whether the carbon atoms are attached linearly or in a branched structure, and whether the double bond has a ] form. | ||
| == Straight-chain isomers == | == Straight-chain isomers == | ||
| 1-Pentene is an ]. Most often 1-pentene is made as a byproduct of catalytic or |
1-Pentene is an ]. Most often 1-pentene is made as a byproduct of ] or ] of ], or during production of ] and ] via thermal cracking of hydrocarbon fractions. It is rarely isolated as a separate compound. Instead, it is most often blended into ] or, in a mixture with other hydrocarbons, ] with ] to make gasoline. | ||
| The only commercial manufacturer of 1-pentene{{Citation needed|date=April 2011}} is ], where it is separated from crude made by the ]. | The only commercial manufacturer of 1-pentene{{Citation needed|date=April 2011}} is ], where it is separated from crude made by the ]. | ||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
| {{Alkenes}} | {{Alkenes}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Revision as of 13:27, 29 November 2011
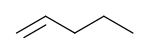 1-Pentene | |
 cis-2-Pentene | |
 trans-2-Pentene | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.636 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C5H10 |
| Molar mass | 70.135 g·mol |
| Density | 0.64 g/cm (1-pentene) |
| Melting point | -165.2 °C (1-pentene) |
| Boiling point | 30 °C (1-pentene) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Pentene refers to all the alkenes with chemical formula C
5H
10. Each contains one double bond within its molecular structure. There are a total of five different compounds in this class, differing from each other by whether the carbon atoms are attached linearly or in a branched structure, and whether the double bond has a cis or trans form.
Straight-chain isomers
1-Pentene is an alpha-olefin. Most often 1-pentene is made as a byproduct of catalytic or thermal cracking of petroleum, or during production of ethylene and propylene via thermal cracking of hydrocarbon fractions. It is rarely isolated as a separate compound. Instead, it is most often blended into gasoline or, in a mixture with other hydrocarbons, alkylated with isobutane to make gasoline.
The only commercial manufacturer of 1-pentene is Sasol Ltd, where it is separated from crude made by the Fischer-Tropsch process.
2-Pentene has two geometric isomers, cis-2-pentene and trans-2-pentene. cis-2-Pentene is used in olefin metathesis.
Alternative names for 1-pentene include amylene, n-amylene, and n-pentene. Alternative names for 2-pentene include beta-n-amylene and sym-methylethylethylene.
Branched-chain isomers
The branched isomers are 2-methylbut-1-ene, 3-methylbut-1-ene (isopentene), and 2-methylbut-2-ene (isoamylene).
Isoamylene is one of three main byproducts of deep catalytic cracking (DCC), a relatively new concept that is very similar to the operation of the fluid catalytic cracking (FCC). The DCC uses vacuum gas oil (VGO) as a feedstock to produce primarily propylene, isobutylene, and isoamylene. The rise in demand for polypropylene has encouraged the growth of the DCCU, which is operated very much like an FCCU. Isobutylene and isoamylene are feedstocks necessary for the production of the much debated gasoline blending components methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) and tert-amyl methyl ether (TAME).