This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Kosmopolis (talk | contribs) at 17:20, 5 September 2006 (reintroduced summarization of efforts). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 17:20, 5 September 2006 by Kosmopolis (talk | contribs) (reintroduced summarization of efforts)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)| This article documents a current event. Information may change rapidly as the event progresses, and initial news reports may be unreliable. The latest updates to this article may not reflect the most current information. Feel free to improve this article or discuss changes on the talk page, but please note that updates without valid and reliable references will be removed. (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| 2006 Israel-Lebanon War (Arab-Israeli conflict) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the 2006 Middle East conflict | |||||||
| File:2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict titlepic.png | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| File:Flag of Hezbollah.svg Hezbollah |
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
Hassan Nasrallah (Secretary General) | Dan Halutz (CoS), Moshe Kaplinsky, Udi Adam (Regional) | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
600-1,000 fighters |
30,000 ground troops (plus IAF & ISC) | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
Hezbollah militia: Allied militia: |
IDF: | ||||||
|
Lebanese civilians: Israeli civilians: UN personnel: | |||||||
| See also: Casualties of the 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict | |||||||
| 2006 Lebanon War | |
|---|---|
| Timeline
Military engagements and attacks
Evacuations Response
Related topics |
The 2006 Israel-Lebanon War is a military conflict in Lebanon and northern Israel, primarily between Hezbollah militia and Israel, which started on 12 July 2006. A United Nations-brokered ceasefire went into effect on 14 August 2006.
The conflict began when a Hezbollah unit conducted a cross-border raid into Israel and captured two Israeli soldiers to enforce a prisoner trade. Three Israeli soldiers were killed in the operation, and a diversionary Katyusha rocket and mortar attack on Israeli military positions and border villages was initiated. Israel responded with massive airstrikes throughout Lebanon, an air and naval blockade and a ground invasion of southern Lebanon, while Hezbollah continued to launch rockets against mostly civilian targets in northern Israel and engaged the Israeli Army in guerrilla warfare. The conflict engendered worldwide concerns over infrastructure damage and the risks of escalation of the crisis, as well as mixed support and criticism of both Hezbollah and Israel.
Killed in the conflict were 211 members of Hezbollah militia and allied factions, 119 Israeli soldiers, 1,187 Lebanese civilians and 44 Israeli civilians. Israel's Air Force flew more than 12,000 combat missions while its Navy fired 2,500 shells; these efforts destroyed 400 miles of roads, 73 bridges, 31 strategic targets such as Beirut International Airport, ports, water and sewage treatment plants, electrical facilities, 900 commercial structures, 25 fuel stations, up to 350 schools, and two hospitals. They destroyed some 15,000 Lebanese homes and damaged 130,000 more. Lebanon's electrical and water service were severely interrupted. Hezbollah launched about 4,000 rockets, of which 900 fell in cities, causing much less damage.
Over 900,000 Lebanese (about one-fourth of the population) were displaced, as were about 300,000 Israelis (about 4% of the population). Even after the ceasefire, 256,000 Lebanese have remained internally displaced. The Israeli bombing of a Lebanese power station released heavy fuel oil into the Mediterranean Sea. Hezbollah rockets caused numerous forest fires in northern Israel.
On 11 August 2006 the United Nations Security Council unanimously approved United Nations Security Council Resolution 1701, in an effort to end the hostilities. The resolution, which was approved by both Lebanese and Israeli governments the following days, also called for the disarming of Hezbollah, for Israel to withdraw its forces and for the deployment of Lebanese soldiers and an enlarged UNIFIL force in southern Lebanon. The Lebanese army began deploying its forces in southern Lebanon on 17 August 2006, and Israel began to withdraw some of its forces from the country.
Background
Israel-Lebanon conflict
The history of conflict between the two countries began with the establishment of the state of Israel in 1948, which provoked massive opposition in the Arab world. Palestinians who fled the newly formed state entered neighboring countries, including Lebanon. After the 1967 Six Day War, in which the armies of various Arab countries failed to defeat the Israeli army, and following the Black September in Jordan, over 110,000 Palestinian refugees migrated to Lebanon, making up, with their descendants, over 400,000 people today. By 1975, they numbered more than 300,000, creating an informal state-within-a-state in South Lebanon. The PLO became a powerful force and played an important role in the Lebanese Civil War. In response to numerous attacks launched from southern Lebanon, Israel invaded in 1978 in an attempt to rout out Palestinian militants. As a result the United Nations passed UN Resolutions 425 and 426, which called for the immediate withdrawal of Israeli forces and an end to military action in Lebanon.
At the end of the operation, Israeli forces withdrew from Lebanon, replaced by a UNIFIL force. Israel military forces entered again four years later in 1982, forcing PLO forces out of Lebanon (mostly to Tunisia), and Israel occupied the southern part of the country. A US brokered peace treaty was ratified by the Lebanese parliament in 1983, but President Amine Gemayel decided against signing in 1984. In 1985, Israel withdrew its forces from parts of Lebanon and remained in a 4–6 kilometre (2.5–3.75 mi) deep strip of southern Lebanon, described by Israel as a "security zone" which it justified as a protective measure to defend its northern towns against Hezbollah attacks. This occupation lasted until 2000. On 24 May 2000 Israel withdrew its troops from southern Lebanon.
The South Lebanon Army's equipment and positions in South Lebanon largely fell into the hands of Hezbollah, which has put considerable effort into fortifying the former security zone and establishing new firing positions. Since then, Hezbollah has repeatedly attacked Israeli military positions, whilst Israel has carried out numerous attacks aimed at striking Hezbollah bases (see Hezbollah activities). Most recently, on 26 May 2006, a car bomb in southern Lebanon killed Palestinian Islamic Jihad leader Mahmoud Majzoub, and his brother Nidal. Lebanon's Prime Minister Fouad Siniora declared Israel the primary suspect. Israel denied involvement, but two days later, a barrage of rockets were fired from Lebanon into Israel. Israel responded by bombing suspected militant targets inside Lebanon, and exchanging fire across the border. Before the end of the day, the UN negotiated a ceasefire.
On 2 September 2004 the United Nations Security Council adopted United Nations Security Council Resolution 1559 calling for the disbanding of all Lebanese militias, among other things, and an armed Hezbollah in South Lebanon is seen by many to be a contravention of the resolution. The Lebanese government differs from this interpretation, and the United Nations has not ruled on this matter.
Beginning of conflict
Main article: Zar'it-Shtula incident See also: Timeline of the 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict See also: Military operations of the 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflictAt around 9:00 AM local time (06:00 UTC), on 12 July 2006, Hezbollah initiated a diversionary Katyusha rocket and mortar attack on Israeli military positions and border villages. At the same time, a ground contingent of Hezbollah crossed the border into Israeli territory and attacked two Israeli armoured Humvees patrolling on the Israeli side of the Israel-Lebanon border, near the village of Zar'it, capturing two Israeli soldiers and killing three. Five others were killed later on the Lebanese side of the border during a mission to rescue the two kidnapped soldiers. The UN, the EU, the G8, the US, and prominent news agencies, including Al Jazeera, have characterized the Hezbollah action as "cross-border". Israeli Prime Minister Ehud Olmert said that "the war started not only by killing eight Israeli soldiers and abducting two, but by shooting Katyusha and other rockets on the northern cities of Israel on that same morning. Indiscriminately."
Hezbollah's attack was named "Operation Truthful Promise", after its leader Hassan Nasrallah had announced to kidnap Israeli soldiers and swap them for Arab prisoners in Israeli jails. It also include some of the four Lebanese prisoners in Israel, including convicted murderer Samir Kuntar. Later on, Nasrallah declared: “No military operation will return the Israeli captured soldiers…The prisoners will not be returned except through one way: indirect negotiations and a trade of prisoners.”
Israeli action
Main article: Israeli military action in the 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict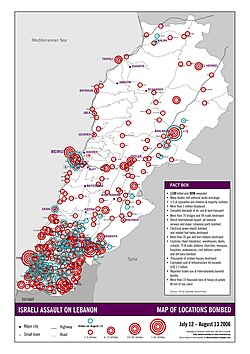
Israeli Prime Minister Ehud Olmert declared the attack by Hezbollah’s military wing an "act of war", and promised Lebanon a "very painful and far-reaching response". It was reported that the Israeli cabinet authorized "severe and harsh" retaliation on Lebanon. , while Israel’s chief of staff, Lt. Gen. Dan Halutz, stated that “f the soldiers are not returned, we will turn Lebanon’s clock back 20 years." A retired Israeli Army Colonel Gal Luft explained that the rationale behind the attack was to create a rift between the Lebanese population and Hezbollah supporters by exacting a heavy price from the elite in Beirut.
The Israeli government held the Beirut government responsible for the attack, as it was carried out from Lebanese territory and Hezbollah had two ministers serving in the Lebanese cabinet at that time. In response, Lebanese Prime Minister Fouad Siniora denied any knowledge of the raid and stated that he did not condone it. An emergency meeting of the Lebanese government reaffirmed this position.

Early on 13 July 2006 Israel sent IAF jets to bomb Beirut International Airport, forcing its closure and diversion of incoming flights to Cyprus. Israel subsequently imposed an air and sea blockade on Lebanon, and bombed the main Beirut–Damascus highway.
On 23 July 2006 Israeli land forces crossed into Lebanon in the Maroun al-Ras area, which overlooks several other locations that were supposedly used as rocket launch sites.
On 25 July 2006 IDF forces attacked Bint Jbeil, a Hezbollah stronghold opposite the Israeli border. On 27 July 2006 Hezbollah ambushed the Israelis and killed eight soldiers. The Israeli Army stated that it inflicted heavy losses on Hezbollah.
On 1 August 2006 Israeli commandos landed in Baalbek in Operation Sharp and Smooth, and captured five civilians including one bearing the same name as Hezbollah's leader, "Hassan Nasrallah". All of the civilians were released after the ceasefire. Troops landed near Dar al-Himkeh hospital west of Baalbeck as part of a widescale operation in the area.
On 5 August 2006 Israeli commandos carried out a raid in Tyre.
On 12 August 2006, one day after United Nations Security Council had approved Resolution 1701, the IDF established its hold in Lebanon. Over the weekend Israeli forces in southern Lebanon nearly tripled in size and were ordered to advance towards the Litani River.
On 14 August 2006, moments before the ceasefire went into effect, the Israeli Air Force reported that they had killed the head of Hezbollah’s Special Forces, whom they identified as Sajed Dewayer, while Hezbollah denied this claim. On the same day, the IDF targeted what it said was a Palestinian faction in the Ein el-Hilweh refugee camp in Saida. Two missiles were fired into a civilian residential area and killed UNRWA staff member Abdel Saghir. Two civilians had been killed in this camp a few days prior to the incident.
As of 15 August 2006, the Israeli Air Force had 15,500 sorties flown over Lebanon, hitting 7,000 targets. The Israeli Sea Corps also conducted 2,500 bombardments of targets along the Lebanese coast, including missile launch sites, missile launchers and weapons storage sites. IDF had focussed on targeting transportation infrastructure, as they were said to be essential to Hezbollah's rocket-launching capability. Over 100,000 artillery shells had been fired.
Hezbollah action
Main article: Hezbollah rocket campaign in the 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict See also: Hezbollah rocket force
Hezbollah fired at least 3,970 rockets, mostly hitting civilian targets throughout the conflict. Cities targeted included Haifa, Hadera, Nazareth, Tiberias, Nahariya, Safed, Afula, Kiryat Shmona, Beit She'an, Karmiel, and Maalot, and dozens of Kibbutzim, Moshavim, and Druze and Arab villages, as well as the northern West Bank. It also hit a hospital in Safed in northern Galilee on 18 July, wounding eight. One of the attacks hit a railroad repair depot, killing eight workers. Hezbollah claimed that this attack was aimed at a large Israeli fuel storage plant adjacent to the railway facility. Haifa is home to many strategically valuable facilities such as shipyards and oil refineries. Hezbollah also engaged in guerilla warfare with the IDF. These attacks by small, well-armed units caused serious problems for the IDF, especially where hundreds of sophisticated Russian-made anti-tank guided missiles (ATGMs) were used. They enabled Hezbollah to destroy 14 Israeli Merkava main battle tanks. Six tanks were destroyed by anti-tank mines. Additional casualties were caused by Hezbollah using ATGMs to collapse buildings onto Israeli troops sheltering inside.
Israeli newspaper Haaretz reported that Hezbollah was "a trained, skilled, well-organized, highly motivated infantry that is equipped with the cream of the crop of modern weaponry from the arsenals of Syria, Iran, Russia, and China." Lebanese satellite TV station Al-Manar reported that the attack had included a Fajr-3 and a Ra'ad 1, both liquid-fuel missiles developed by Iran.
After the initial Israeli response, Hezbollah declared an all-out military alert, and said it had 13,000 rockets capable of hitting towns and installations far into northern Israel. As a result, Israeli Defense Minister Peretz told commanders to prepare civil defense plans, and many civilians living in Northern Israel were sent to bomb shelters or fled their homes to other parts of the country. Hezbollah continued to fire rockets into northern Israel's towns, cities, and numerous small agricultural villages.
On 14 July 2006, following Israeli bombing raids on Lebanon that killed 60 civilians, Nasrallah addressed Israel, saying “You wanted an open war, and we are heading for an open war. We are ready for it.”
On 3 August 2006 Nasrallah warned Israel against hitting Beirut and promised retalation against Tel Aviv in this case. He also stated that Hezbollah would stop its rocket campaign if Israel ceased aerial and artillery strikes of Lebanese towns and villages. On 4 August Israel attacked the southern outskirts of Beirut, and later in the day, Hezbollah launched rockets at the Hadera region.
On 7 August 2006 the Israeli Air Force claimed that it had shot down an Iranian-made unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) over Lebanese territory. According to the IAF, the same type of UAV had been sent towards Israel before.
On 12 August 2006 Hezbollah killed 24 Israeli soldiers; the worst Israeli loss in a single day. Five soldiers were killed when Hezbollah apparently shot down an Israeli helicopter..
On 27 August 2006 Hassan Nasrallah apologised to the Lebanese people for the incident that sparked the war, saying "Had we known that the kidnapping of the soldiers would have led to this, we would definitely not have done it."
Initial reviews of the conflict after the ceasefire
Following the UN-brokered ceasefire, there were mixed responses on who had gained most in the war. Iran and Syria proclaimed a victory for Hezbollah while the Israeli and United States administrations declared that Hezbollah lost the conflict. Initially, in a poll by an Israeli radio station, Israelis were split on the outcome with the majority believing that no one won.. By 25 August 63% of Israelis polled wanted Olmert to resign due to his handling of the war. Some analysts, like The Economist, concluded that by surviving this unsymmetrical military conflict with Israel, Hezbollah effectively emerged with a military and political victory from this conflict. They cite the facts that Hezbollah was able to sustain defenses on Lebanese soil and inflict unmitigated rocket attacks on Israeli civilians in the face of a punishing air and land campaign by the IDF. Also, Israel's stated goals entering the conflict were to retrieve its kidnapped soldiers and destroy the military capability of Hezbollah - neither goal was accomplished. Furthermore, Hezbollah is also leading the rebuilding effort in south Beirut and Lebanon using "unlimited" support from Iran, thereby awarding Hezbollah further political clout.
In contrast, Israeli Prime Minister Olmert admitted to the Knesset that there were mistakes in the war in Lebanon, though he framed UN Security Council resolution 1701 as an accomplishment for Israel that it would bring home the kidnapped soldiers, and said that the operations had altered the regional strategic balance vis-à-vis Hezbollah. Israeli chief of staff Dan Halutz, has publicly admitted to failings in the conflict. On 15 August Israeli government and defense officials have called for the resignation of Halutz following a stock scandal in which he admitted selling stocks hours before the start of the Israeli offensive; the magnitude of the affair is considered linked to the lack of a "clearcut victory" for Israel.
On 21 August a group of demobolized Israel reserve soldiers and parents of soldiers killed in the fighting started a movement calling for the resignation of Ehud Olmert and the establishment of a national commission of inquiry. They have set up a protest tent opposite the Knesset and have grown significantly in numbers, reaching over 2,000 by 25 August and including support from the influential Movement for Quality Government. On 28 August Olmert announced that there will be no independent national or governmental commission of inquiry. Instead, there will be two internal inspection commissions, one to investigate the political echelon and one to examine IDF, and likely a third commission to examine the Home Front, to be announced at a later date. These will have a far more limited mandate and authority than a single inquiry commission headed by a retired judge. The political and military committees are to be headed by former director of Mossad, Nahum Admoni, and former Chief of Staff, Amnon Lipkin-Shahak, respectively. Critics argued that these committees amount to a whitewash, due to their limited authority, limited investigatory scope, their self-appointed basis, and that neither will be headed by a retired judge.
US President George W. Bush has questioned Hezbollah's declarations of victory "when at one time were a state within a state, safe within southern Lebanon, and now going to be replaced by a Lebanese army and an international force." It seems unlikely, however, that the army or the international force will attempt to disarm Hezbollah. Economic aftermath indicate that the fighting had resulted in a huge financial setback for Lebanon, with estimates ranging from US$7 to US$10 billion in direct costs while the cost for Israel is put at US$1.6 - US$3 billion. This, and other factors has prompted a commentator in the London-based Arabic newspaper Asharq Al-Awsat to question the claims of victory by Hezbollah. According to one analyst in the Associated Press, the main casualty was the fragile unity between Lebanon's sectarian and political groups. The American and Lebanese relationship has been strained by the war. After the attack on Qana, the typically pro-American Lebanese prime minister Fuad Seniora snubbed Condoleezza Rice by cancelling a meeting with her and thanked Hezbollah for its "sacrifices for the independence and sovereignty of Lebanon." Many in Lebanon viewed the US harshly in the conflict for stalling the cease-fire resolution in the UN and for its support of Israel. On 28 July only 8% of Lebanese felt that the US supports Lebanon, while 87% supported Hezbollah's fight with Israel.
Targets in civilian areas
Main article: Targeting of civilian areas in the 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict
Each side has complained about the other's artillery and missiles being fired into civilian areas. Both sides have reported civilian casualties.
The United Nations Development Program (UNDP) initially estimated about 35,000 homes and businesses in Lebanon were destroyed by Israel in the conflict, while a quarter of the country's road bridges or overpasses were damaged. Jean Fabre, a UNDP spokesman, estimated that overall economic losses for Lebanon from the month-long conflict between Israel and Hezbollah totaled "at least $15 billion, if not more." Israel says that it attacked buildings and infrastructure used by Hezbollah to launch rockets or receive re-supply from Iran and Syria.
Hezbollah fired hundreds of rockets, sometimes more than 200 per day throughout the conflict. These landed in all major cities of northern Israel including Haifa, Nazareth, and Tiberias, as well as dozens of kibbutzim, moshavim, Druze, and Arab villages.
Hezbollah leader Hassan Nasrallah defended their rocket attacks, saying “In the beginning, we started to act calmly, we focused on Israel military bases and we didn’t attack any settlement, however, since the first day, the enemy attacked Lebanese towns and murdered civilians—Hezbollah militants had destroyed military bases, while the Israelis killed civilians and targeted Lebanon's infrastructure”.
Amnesty International published findings from a research mission that pointed to an Israeli policy of deliberate destruction of Lebanese civilian infrastructure during the conflict, which included war crimes. Their findings "indicate that such destruction was deliberate and part of a military strategy, rather than 'collateral damage."' Amnesty researcher Donatella Rovera, who visited Lebanon during the war and co-authored the report stated "There is clear evidence of disproportionate and indiscriminate attacks." The organisation nevertheless condemned both Hezbollah and Israel for attacks on civilians, in addition to the reported use of white phosphorus by the IDF. In the report Amnesty International presented facts suggesting that Israel deliberately attacked the civilian population and government of Lebanon in a conscious effort to turn them against Hezbollah. The report also stated the need for an independent and impartial inquiry appointed by UN, to investigate alleged war crimes by both Hezbollah and Israel.
Human Rights Watch issued many reports documenting indiscriminate use of force against civilians by both Israel and Hezbollah. They blamed Israel for systematically failing to distinguish between combatants and civilians and accused Hezbollah of the deliberate and indiscriminate killing of civilians by firing rockets into populated areas. The organization has also strongly criticized Israel for using cluster bombs and Hezbollah for filling its rockets with ball bearings. The US government is investigating whether Israel's use of American-made cluster bombs in southern Lebanon violated secret agreements that restrict the use of these weapons. Unexploded cluster bombs dropped by Israeli warplanes or duds fired by artillery remain in much of South Lebanon, and have killed 12 people and wounded 39, according to the U.N. Mine Action Coordination Center. 90 percent of the cluster bomb strikes occurred in the last 72 hours of the war.
Israeli officials accused Hezbollah of intentionally using the civilian population as human shields. They alleged that Hezbollah fired rockets from residential areas to draw Israeli fire on those areas, in an attempt to maximize civilian casualties and garner more sympathy. The IDF claimed that Hezbollah blocked village exits to prevent residents from leaving the warzone. It declared that the IAF drops leaflets warning civilians to leave the area before it attacks. Israeli Justice Minister Haim Ramon stated civilians remaining in South Lebanon after being issued such leaflets should be considered "terrorists". Israel asserted that its attacks on infrastructure such as the airport were justified, as such infrastructure was used to re-supply Hezbollah with missiles and other ordnance from Syria and Iran, and could have been used to smuggle the two kidnapped Israeli soldiers into Iran.
Jan Egeland, United Nations Undersecretary-General for Humanitarian Affairs and Emergency Relief Coordinator called Hezbollah rocket attacks into northern Israel and Israeli aerial bombing of Beirut violations of humanitarian law. He accused Hezbollah of “cowardly blending…among women and children” and condemned their rumored pride at "having many more children and women dead than armed men."
Louise Arbour, United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights, expressed “grave concern over the continued killing and maiming of civilians in Lebanon, Israel and the occupied Palestinian territory.” She suggested that the actions of Israel and Hezbollah may constitute war crimes. Arbour called for Israel to obey a “principle of proportionality” and said, “indiscriminate shelling of cities constitutes a foreseeable and unacceptable targeting of civilians.…Similarly, the bombardment of sites with alleged military significance, but resulting invariably in the killing of innocent civilians, is unjustifiable”.
Killed in the conflict were 1,187 Lebanese civilians and 44 Israeli civilians.. Almost one third of the Lebanese civilian casualties were children under 13 years of age.
Environmental consequences
See also: Jiyeh power station oil spill
An environmental disaster resulted from the Israeli Airforce bombing the Jiyeh power station, 30 km (19 mi) south of Beirut, on 13 July and 15 July. The plant's damaged storage tanks leaked 20,000 to 30,000 tonnes of oil into the eastern Mediterranean Sea, comparable in size to the Exxon Valdez oil spill. A 10 km wide oil slick covers 170 km of coastline, and was threatening Turkey and Cyprus. The slick was reportedly causing breathing problems, killing fish, and threatened the habitat of the endangered green sea turtle, as well as increasing the risk of cancer. It may take at least 10 years to recover from this spill.
Hezbollah rocket attacks caused numerous and fierce forest fires inside northern Israel, particularly on the Naftali mountain range near Kiryat Shmona. As of 8 August as many as 9,000 acres including 3,000 acres of Israel’s few forests, were damaged by fires caused by Hezbollah rockets, and at least one forest has lost nearly 75% of its trees. Estimates are that it will take at least 60 years to rehabilitate the forests.
Amnesty International called on Israel to consider refraining from the use of depleted uranium munitions, due to health risks, after press reports claiming its delivery to Israel. The effect of the radioactive dust created on impact is debated, though the weapon itself is considered "toxic and constitutes a health risk independent of any residual radioactivity" due to the nature of heavy metals.
Position of Lebanon
Main article: Position of Lebanon in the 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflictWhile Israel holds the Lebanese government responsible for the Hezbollah attacks due to Lebanon’s failure to implement Resolution 1559 calling on it to disarm Hezbollah, Lebanon disavows the raids, stating that the government of Lebanon does not condone them, and that in any case Israel has its own history of disregarding inconvenient UN resolutions. An emergency meeting of the Lebanese government reaffirmed this position. Almost immediately after hostilities began, Lebanon's Prime Minister Fouad Siniora called for a ceasefire. On 14 July 2006, following a phone call between Siniora and President Bush, the Prime Minister’s office issued the statement that “Prime Minister Siniora called on President Bush to exert all his efforts on Israel to stop its aggression on Lebanon, reach a comprehensive ceasefire and lift its blockade.”
The next day, in a televised message to the Lebanese people, and afterwards in an interview with CNN, Siniora said “We call for an immediate ceasefire backed by the United Nations.”
During Israeli raid on Tyre, it was reported that the Lebanese Army fired surface-to-air missiles at the Israeli helicopters, which returned fire, hitting a Lebanese M113 Armored Personnel Carrier and destroying it.
Ceasefire
Previous attempts
Main article: Ceasefire attempts during the 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflictTerms for a ceasefire had been drawn and revised several times over the course of the conflict, yet successful agreement between the two sides took several weeks. Hezbollah maintained the desire for an unconditional ceasefire, while Israel insisted upon a conditional ceasefire, including the return of the two kidnapped soldiers. Lebanon frequently pled for the United Nations Security Council to call for an immediate, unconditional ceasefire between Israel and Hezbollah.
Status quo
On 11 August the United Nations Security Council unanimously approved UN Security Council Resolution 1701, in an effort to end the hostilities. It was accepted by the Lebanese government and Hezbollah on 12 August, and by the Israeli government on 13 August. The ceasefire took effect in the region at 8:00 AM (5:00 AM GMT) on 14 August 2006.
Before the ceasefire, two Hezbollah members said that their militia would not disarm south of the Litani River, according to a senior member of the Lebanese cabinet, while a top Hezbollah official has similarly denied any intention of disarming in the south. Israel has said it will stop withdrawing from Southern Lebanon if Lebanese troops aren't deployed there within a matter of days.
Both sides promised to retaliate when placed on the defensive
Post-ceasefire conflict
- On 14 August 2006, hours after the beginning of the ceasefire, about four mortars were fired inside southern Lebanon. An Israeli military spokesperson said that Israel will not respond to their firing. On that day four more incidents were recorded when armed Hezbollah members said to have approached Israeli positions were killed.
- On 15 August 2006 "Israeli soldiers opened fire when four Hezbollah fighters came toward them," three of the Hezbollah fighters were killed. The same day, about 10 rockets were fired by Hezbollah inside southern Lebanon. Israel reiterated it wouldn't respond since the rockets did not cross the border.
- On 18 August Lebanese police sources reported that Israeli Defense Force warplanes launched four missiles toward targets in an eastern Lebanese village of Baalbek. Israeli sources acknowledge that its air force performs sorties over Lebanese territory, but denied breaking the ceasefire. Lebanese officials later contradicted the police sources stating that no missiles were fired by the Israeli planes.
- On 19 August, six days after the beginning of the cease-fire, Israel launched a raid in Lebanon's eastern Bekaa Valley it says was aimed to disrupt weapons supplies to Hezbollah from Syria and Iran.. Syria and Iran immediately denied supplying Hezbollah with weapons. Lebanese officials said, "the Israelis were apparently seeking a guerrilla target in a school." One Israeli soldier was killed, another mortally wounded, while three Hezbollah fighters were wounded. Hezbollah said it would not respond to the attack.
- On 19 August UN Secretary-General Kofi Annan said he was "deeply concerned" about an Israeli commando raid in eastern Lebanon Saturday, calling it a violation of a UN-backed ceasefire. Israeli Foreign Ministry spokesman Mark Regev told the Associated Press that “he ceasefire is based on (U.N. resolution) 1701 which calls for an international arms embargo against Hezbollah.” Regev was referring to article 8 of the resolution which calls for an end to all weapons transfers to Hezbollah.
- On 27 August the UN Secretary-General Kofi Annan said that UN troops would not intercept Syrian arms shipments to Hizbollah unless requested to do so by the Lebanese Government.
- On 29 August Annan said that Israel had committed most of the truce violations and described Israel's continuing embargo as "a humiliation and an infringement on sovereignty". Israeli Prime Minister Ehud Olmert reiterated Israel's willingness to lift the blockade after full implementation of the UN-brokered ceasefire.
International reaction

The conflict engendered worldwide concerns over infrastructure damage and the risks of escalation of the crisis, as well as mixed support and criticism of both Hezbollah and Israel. A number of governments, including the United States, United Kingdom, Germany, Australia, and Canada, asserted Israel's right to self-defense. The United States government further responded by authorizing Israel's request for expedited shipment of precision-guided bombs, but did not announce the decision publicly.
Spokespersons from the United Nations, the European Union, the Organization of Islamic Conference, and an assortment of human rights organizations condemned Israel for its disproportionate response to Hezbollah’s attacks.
Among neighboring Middle Eastern nations, Iran, Syria, and Yemen voiced strong support for Hezbollah, while the Arab League issued statements condemning both Hezbollah’s attack and Israel’s response.
Many worldwide protests and demonstrations appealed for an immediate ceasefire on both sides and expressed concern for the heavy loss of civilian life on all sides. Other demonstrations were held exclusively in favor of Lebanon or Israel. Numerous newspaper advertising campaigns, SMS and email appeals, and online petitions also occurred.
Various foreign governments assisted the evacuation of their citizens from Lebanon.
Previous prisoner exchanges
See also: Israeli MIA prisoner exchangesOver the last 30 years, Israel has released about 7,000 prisoners to secure freedom for 19 Israelis and to retrieve the bodies of eight others. In October 2000, Hezbollah captured three IDF soldiers who were killed either during the operation or in its immediate aftermath at Shebaa Farms, and kidnapped an Israeli businessman and former army colonel Elchanan Tenenbaum in Kuwait. A prisoner swap was carried out on 29 January 2004: 30 Lebanese and Arab prisoners, the remains of 59 Lebanese militants and civilians, 400 Palestinian prisoners for Tenenbaum and the remains of the three soldiers. Hezbollah requested that maps showing Israeli mines in South Lebanon be included as part of the exchange. On 23 August 2006, one such a mine killed an Israeli soldier in South Lebanon.
See also
Template:Campaignbox Arab-Israeli conflict
- 2006 Israel-Gaza conflict
- Israel-United States relations
- History of Lebanon
- History of Israel
- May 17 Agreement 1980s prospective peace agreement
- Arab-Israeli conflict
- Multinational Force in Lebanon in 1982
- United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon - UNIFIL (1978-current)
- History of the Middle East
- Views of the Arab-Israeli conflict
- International law and the Arab-Israeli conflict
- Arab-Israeli conflict facts, figures, and statistics
- United Nations Security Council Resolution 1559
- United Nations Security Council Resolution 1701
References
- "Two Northern Command chiefs?", Ynetnews, 8 August 2006; See also, "IDF officials: Maj. Gen. Adam must quit post after war"; "Israel swaps commanders"; "Impatient Israel appoints new battle chief"; "New Israeli General Oversees Lebanon "; "Israel names new commander to head offensive"; "Israel changes command structure"
- The International Institute For Strategic Studies (2006-07-21). "Agence France Presse - Lebanese army faces no-win situation". Retrieved 2006-08-01.
- "Some 30,000 Israeli troops in Lebanon - army radio". Reuters via Yahoo! News Asia. 2006-08-13.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Israeli offensive killed 1,287 in Lebanon: official tolls". Daily Star (Lebanon). 2006-08-19.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Israel Defense Forces (2006-08-14). "List of 180 dead Hezbollah terrorists released of an estimated 530 killed since start of fighting".
- ^ "Israel-Hizbullah conflict: Victims of rocket attacks and IDF casualties". Israel, Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
- ^ "Humanitarian Assistance to Lebanon". United States Agency for International Development Disaster Assistance. 1 September 2006. Retrieved 2006-09-03.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Listing of all Israeli casualties in 2006 Lebanon war with a photo of each deceased person". Israel, Prime Minister's Office. unknown.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Listing of all Israeli casualties in 2006 Lebanon war with links to corresponding reports on the circumstances of their deaths". ynet.co.il. 14 August 2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Some 1,300 Israelis hurt since fighting began". Ynetnews. 2006-07-23.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Lebanese Premier Seeks U.S. Help in Lifting Blockade". Washington Post. 24 August 2006.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Mideast War, by the numbers". Guardian / Associated Press. 2006-08-18. Retrieved 2006-08-25.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Lebanon Refuses Contact With Israel". Guardian / Associated Press. 2006-08-30. Retrieved 2006-09-04.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Amnesty report accuses Israel of war crimes". Guardian. 2006-08-23. Retrieved 2006-09-03.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Crayons, glass, litter floor of Lebanese school". Reuters AlertNet. 2006-08-30. Retrieved 2006-09-03.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Refugees and internally displaced persons". Lebanon. The CIA World Factbook. 8 August 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-16.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Lebanon – UNIFIL Background". United Nations. 2005. Retrieved 2006-07-14.
- Israel-Lebanon border, June 1982
- "Israeli jets hit Lebanon targets". BBC News. 2004-01-20. Retrieved 2006-07-13.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Mroue, Bassem (26 May 2006). "Islamic Jihad leader killed in Lebanon". The Boston Globe. Retrieved 14 August 2006.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=and|date=(help) - Klein, Aaron (29 May 2006). "Syria, Iran directed rocket barrage against Israel". World News Daily. Retrieved 14 August 2006.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=and|date=(help) - "Security Council Notes Significant Progress in Lebanon ..." United Nations Security Council. 01-23-06.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Hezbollah rejects call to disarm". ABC (AU). 2005-04-27.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Harel, Amos (14 July 2006). "IDF retrieves bodies of four tank soldiers killed in south Lebanon". Haaretz. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - "Clashes Spread to Lebanon as Hezbollah Raids Israel". The New York Times. 2006-07-13.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Lebanon divided over Hezbollah raid". Al Jazeera. 2006-07-14.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Hezbollah kidnaps two Israeli soldiers". Yahoo! News. 12 July 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Farrel, Stephen (2 August 2006). "The Times interview with Ehud Olmert: full transcript". The Times. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Press Conference with Hasan Nasrallah". UNDERSTANDING THE PRESENT CRISIS. UPC. 12 July 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Hizbullah leader calls for prisoner exchange". Al Bawaba. 12 July 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Fletcher, Martin (12 July 2006). "Regional tensions fuel Lebanon-Israel clashes". MSNBC. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Labott, Elise (12 July 2006). "Israel authorizes 'severe' response to kidnapped". CNN. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Wright, Robin (19 July 2006). "Bush Supports Israel's Move Against Hezbollah". Washington Post. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Alon, Gideon (13 July 2006). "Israel holds Lebanon government responsible for Hezbollah attack". Haaretz. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "Statement by Prime Minister Fouad Siniora". Daily Star (Lebanon) (registration required). 17 July 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-20.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Qawas, Nafez (13 July 2006). "Simiora's Cabinet makes clear it had nothing to do with 'what happened'". Daily Star (Lebanon) (registration required). Retrieved 2006-08-20.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Hasson, Nir (14 July 2006). "Israel targets Hezbollah stronghold in Beirut suburb". Haaretz. Retrieved 2006-08-20.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - "Israel 'seizes' Hezbollah village". BBC News. 2006-07-23.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Bint Jbeil: Hezbollah heartland". BBC News. 2006-07-27.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - KIFNER, John (23 August 2006). "What's in a Name? Not, It Seems, a Leader of Hezbollah in Lebanon". The New York Times. Retrieved 2006-08-23.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Greenberg, Hanan (12 August 2006). "Chief of staff: We tripled our forces in southern Lebanon". Haaretz. Retrieved 2006-08-20.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Katz, Yaakov (12 August 2006). "IDF troops advancing to Litani River". Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 2006-08-20.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Greenberg, Hanan (16 August 2006). "IDF: Senior Hizbullah man killed before truce". Ynetnews. Retrieved 2006-08-20.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "7,000 Targets in Lebanon". Israel Defense Force. 15 August 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-18.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "IDF Attacks Over 60 Targets in Lebanese Territory". Israeli Defense Forces. 29 July 2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "The war in numbers". Jane's Defence Weekly. 23 August 2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Major Attacks in Lebanon, Israel and the Gaza Strip". New York Times. 14 August 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-23.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Greenberg, Hannan (14 July 2006). "Woman, grandson killed in Meron rocket attack". Ynetnews. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - "Long-range rocket lands near Jenin". Ynetnews. 2006-08-02.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Siegel-Itzkovich, Judy (2006). "Hizbollah rocket hits hospital" (Abstract). British Medical Journal. 333 (7561): 217-b-. doi:10.1136/bmj.333.7561.217-b. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - "2 wounded in Hezbollah strike on Haifa". The News-Sentinel. 2006-07-17.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israel hammers at Lebanese infrastructure". The Associated Press. 2006-07-17.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Tal, Avraham (31 July 2006). "Justified, essential and timely". Haaretz. Retrieved 2006-08-14.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Hezbollah rockets kill 9 in Israeli city". Associated Press. 2006-07-16.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Hizbullah: One of the rockets is a Ra'ad 1". Ynetnews. 2006-07-16.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israeli Couple Weds in Bomb Shelter". Associated Press. 2006-07-22.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Katyusha rockets hit Galilee". Ynetnews. 2006-07-13.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Hezbollah leader vows 'open war'". BBC News. 07-15-06.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israeli Attacks Increase; Hezbollah Vows 'Open War'". NPR. 2006-07-14.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Lebanese Hezbollah warns of rocket attacks at Tel Aviv if Beirut struck", People's Daily, 4 August 2005
- Cite error: The named reference
mabatwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - Raved, Ahiya (4 August 2006). "For first time: Hizbullah targets Hadera area". Ynetnews. Retrieved 2006-08-15.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Air Force Shoots Down Hezbollah UAV". Israel Defence Forces. 8 August 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-15.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Katz, Yaacov (8 August 2006). "Hizbullah UAV shot down off Acre coast". Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 2006-08-15.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "24 soldiers killed in South Lebanon Saturday". Jerusalem Post. 2006-08-12.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Nasrallah sorry for scale of war". BBC News. 27 August2006. Retrieved 2006-08-27.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Hizbullah's shallow victory". The Economist. 19 August 2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Syria and Iran claim victory over West
- "With guns silent, wartime unity unravels in Israel". International Herald Tribune. 18/08/2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Israeli war protests echo 1973
- "Hizbullah's shallow victory". The Economist. 19 August 2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Hezbollah Leads Work to Rebuild, Gaining Stature". The New York Times. 16 August 2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Olmert: Mistakes made in Lebanon war". United Press International. 14 August 2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israel army chief admits failures". 24 August 2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Stocks scandal spells doom of embattled Israeli army chief". Agence France-Presse. 16 August 2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Yoman", Israel Broadcasting Authority, 25 August 2006 Template:He icon
- "Hundreds support protesting reservists", Ynetnews, 24 August 2006
- "Olmert: An inquiry commission will not be formed, we do not have the luxury to submerge in investigating the past", Haaretz, 28 August 2006 Template:He icon
- "Mabat", Israel Broadcasting Authority, 28 August 2006 Template:He icon
- http://www.whitehouse.gov/news/releases/2006/08/20060814-3.html
- The army is back, but don't expect it to disarm Hizbollah
- Lebanon and Israel: A chance for peace?
- West Asia war by numbers
- Bloomberg
- Between Victory and Defeat
- Lebanon's fragile unity shatters - Kuwaittimes.net
- Civilian Deaths in Lebanon Provoke International Outcry, Israel Suspends Aerial Bombardment
- Israeli strikes may boost Hezbollah base
- "War wiped out 15 years of Lebanese recovery - UNDP". The Daily Star. 24 August 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-24.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Finer, Jonathan (8 August 2006). "Israeli Soldiers Find a Tenacious Foe in Hezbollah". Washington Post. p. A1. Retrieved 2006-08-23.
Israeli commanders say Hezbollah has obtained its sophisticated weaponry from its main backers, Syria and Iran… Hezbollah chooses to fight in and among civilian centers, making it difficult to target its fighters without killing bystanders.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Cody, Edward (5 August 2006). "Israeli Warplanes Hit Lebanon's Christian Areas". Washington Post. p. A12. Retrieved 2006-08-23.
An Israeli military spokesman, Capt. Jacob Dallal, said Israeli planes attacked a building in Qaa suspected of 'being used as a weapons depot of some sort'.…Israeli aircraft also hit Beirut's southern suburbs, at Ouzai near Beirut's international airport.…The targets were buildings with Hezbollah offices and other installations, they said.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - "Hizbullah attacks northern Israel and Israel's response". MFA. 2006-07-12.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Anxious northern Israel endures rocket fire". CNN.
{{cite news}}: Text "date2006-07-14" ignored (help) - "Hizbullah leader promises enemy 'more surprises'". Islamic Resistance Lebanon. 17 July 2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Lebanon: Destruction of civilian infrastructure". Amnesty International. 23 August 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-23.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Amnesty International Accuses Israel of War Crimes". Fox News. 2006-08-23.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "UN: Security Council must adopt urgent measures to protect civilians in Israel-Lebanon conflict". Amnesty International.
- "Obligations under international humanitarian law of the parties to the conflict in Israel and Lebanon". Amnesty International. 26 July 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-15.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Deliberate destruction or "collateral damage"? Israeli attacks on civilian infrastructure". Amnesty International. 2006-08-23.
- "U.N.: Open Independent Inquiry into Civilian Deaths". Human Rights Watch. 2006-08-08.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israeli Cluster Munitions Hit Civilians in Lebanon". Human Rights Watch. 2006-07-24.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Lebanon: Hezbollah Rocket Attacks on Haifa Designed to Kill Civilians". Human Rights Watch. 18 July 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Inquiry Opened Into Israeli Use of U.S. Bombs". New York Times. 2006-08-24. Retrieved 2006-08-25.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "In Lebanon's Rubble, Aftershocks of War". Washington Post. 2006-08-26. Retrieved 2006-08-26.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israel spewed cluster bombs over Lebanon in last days of war : UN". Yahoo News / AFP. 2006-08-30. Retrieved 2006-09-05.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - http://www.ynetnews.com/articles/0,7340,L-3278026,00.html
- de Quetteville, Harry (28 July 2006). "You're all targets, Israel tells Lebanese in South". The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Condoleezza Rice meets with Mid-East leaders (transcript)". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 2006-07-25.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israel bombing breaks humanitarian law - UN official". Reuters. 23 July2006.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|1=(help) - "UN warning on Mid-East war crimes". BBC News. 2006-07-20.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "UN likely to cut request for Lebanon emergency aid". Reuters. 2006-07-23.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Lebanon says 1,000 dead or missing". Reuters. 2006-08-07.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Lebanon Reports 1,130 Dead". IsraelNationalNews. 2006-08-12.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "UN sounds Lebanon oil spill alarm". Al Jazeera. 2006-08-08.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Crisis talks on Lebanon oil spill". BBC News url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/4798965.stm. 2006-08-16.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Missing pipe in:|publisher=(help) - "'Damage is done' to Lebanon coast". BBC News. 2006-08-08.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "In pictures: Conflict enters fourth week: Picture 8: "Some Hezbollah rockets have started forest fires in Israel"". BBC News. 2006-08-02.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Kraft, Dina (8 August 2006). "Dry Forests in Northern Israel Are Damaged as Hezbollah's Rocket Attacks Ignite Fires". The Environment. New York Times. Retrieved 2006-08-08.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "More Press for JNF's Work in the North" (Press release). Jewish National Fund. 2006-08-09. Retrieved 2006-08-14.
- "ISRAEL/LEBANON ISRAEL AND HIZBULLAH MUST SPARE CIVILIANS: Obligations under international humanitarian law of the parties to the conflict in Israel and Lebanon". Amnesty International. 26 July 2006. Retrieved 29 August 2006.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=and|date=(help) - "Lebanon says Bush to press Israel to limit attacks". Reuters. 2006-07-14.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Lebanese PM demands ceasefire". ABC News. 2006-07-15.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Hezbollah wants an unconditional ceasefire". CTV. 2006-07-17.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israel sends instructions to Lebanon through Italy". Jerusalem Post. 2006-07-16.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "U.N.: Cease-fire begins Monday". CNN. 2006-08-12.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "U.N.: Cease-fire begins Monday". CNN. 12 August 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israel to halt pullout unless Lebanon army deploys". Reuters. 16 August 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-16.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "IDF: Hours after cease-fire, 4 clashes between Hezbollah and Israeli troops; 4 Hezbollah fighters killed". CNN. 14 August 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-23.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "IDF: Israeli soldiers kill 3 Hezbollah fighters". CNN. 15 August 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-23.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Janelle, Chantelle (18 August 2006). "Israel flies over Lebanon, but no airstrikes". WIS-TV. Retrieved 2006-08-21.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Israel: Raid targets weapons transfer". CNN. 19 August 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-21.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israeli Commando Dies in Lebanon Raid". Associated Press. 19 August 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-27.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Morales, Alex (20 August 2006). "Kofi Annan declares Israeli raid violation of ceasefire". CNN. Retrieved 2006-08-21.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/main.jhtml?xml=/news/2006/08/27/wleb27.xml
- http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/5296314.stm
- http://news.yahoo.com/s/ap/20060831/ap_on_re_mi_ea/mideast
- "Developments in Israel-Lebanon Crisis". Forbes. 07-13-06.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Office of the Press Secretary (2006-07-13). "President Bush and German Chancellor Merkel Participate in Press Availability". The White House. Retrieved 2006-07-15.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Reuters (2006-07-22). "US Rushes Precision-Guided Bombs to Israel". Reuters.
{{cite news}}:|author=has generic name (help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Malignant Neglect". Front Page Magazine. 7-24-06.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Fattah, Hassan M. (17 July 2006). "Arab League criticizes Hezbollah for attacks". International Herald Tribune. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Arab League declares support for Lebanon, calls on UN to step in". Haaretz. 16 July 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Press Association (28 July 2006). "Ads urge call for Lebanon ceasefire". The Guardian. Retrieved 2006-08-16.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Save the Lebanese Civilians Petition". E-petitions.net. 15 July 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-16.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Lebanon evacuation gathers pace". BBC News. 2006-07-18.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Factfile: Hezbollah". Aljazeera. 2006-07-12.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israel, Hezbollah swap prisoners". CNN. 2004-01-29.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "IDF soldier killed, two officers hurt, in South Lebanon". Haaretz. 2004-08-23.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help)
External links
- United Nations Interim Forces In Lebanon, including maps of the UN deployment
- Human Rights Watch report: Israel's Indiscriminate Attacks Against Civilians in Lebanon
- JURIST - Legal news and resources on the conflict
- Google Earth layer
- video about photo fraud at the war
- How did Hezzbollah remain in full control after 35 days of fighting?
- Nasrallah supports decision to send army to South Lebanon Ya Libnan
- “We are fighting against people with inhuman mentality”, Israeli ambassador to Russia interview to Kommersant, August 30, 2006
- Artcle describing Hezbollah tactics in Lebanon
- Psychological warfare in the 2006 Israel-Lebanon Conflict
- Who attacked Israel? HIR
War photography
- Lebanon Photo Gallery - Features hundreds of photos of war torn Lebanon
- Video showing degree of structural damage in major Lebanese cities (no casualties)
Warning: Extremely graphic wartime imagery below
- Graphic photographs of Lebanese civilian casualties hosted at the Embassy of Lebanon in Washington, DC
- Graphic photographs of Lebanese civilian casualties from the 2006 Qana airstrike
- Graphic photographs of Israeli military and civilian casualties
- "ISRAELI AIR ATTACK KILLS CIVILIANS". CNN. 2006-07-30.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help)