This is the current revision of this page, as edited by M97uzivatel (talk | contribs) at 17:34, 8 June 2022. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 17:34, 8 June 2022 by M97uzivatel (talk | contribs)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 3-hydroxy-2-phosphonooxypropanoic acid | |
| Other names 2PG | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C3H7O7P |
| Molar mass | 186.06 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
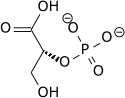
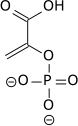
2-Phosphoglyceric acid (2PG), or 2-phosphoglycerate, is a glyceric acid which serves as the substrate in the ninth step of glycolysis. It is catalyzed by enolase into phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), the penultimate step in the conversion of glucose to pyruvate.
In glycolysis
| 3-phospho-D-glycerate | Phosphoglyceromutase | 2-phospho-D-glycerate | Enolase | phosphoenolpyruvate | ||

|
|
| ||||
| H2O | ||||||

|
| |||||
| H2O | ||||||
| Phosphoglyceromutase | Enolase | |||||
Compound C00197 at KEGG Pathway Database. Enzyme 5.4.2.1 at KEGG Pathway Database. Compound C00631 at KEGG Pathway Database. Enzyme 4.2.1.11 at KEGG Pathway Database. Compound C00074 at KEGG Pathway Database.
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles.
[[File:

- The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "GlycolysisGluconeogenesis_WP534".
See also
References
| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "2-Phosphoglyceric acid" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2007) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Glycolysis metabolic pathway | |
|---|---|
 ATP
ADP
ATP
ADP

 ATP
ADP
ATP
ADP


+ +
2 × Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate 2 ×
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate  ADP
ATP
ADP
ATP


Phosphopyruvate  ADP
ATP
ADP
ATP
2 × Pyruvate 2 × |
This article about metabolism is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |