This is the current revision of this page, as edited by LegionMammal978 (talk | contribs) at 23:13, 30 April 2023 (move systematic name). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 23:13, 30 April 2023 by LegionMammal978 (talk | contribs) (move systematic name)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)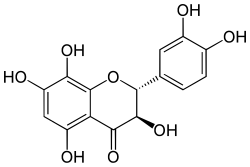
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name (2R,3R)-3,3′,4′,5,7,8-Hexahydroxyflavan-4-one | |
| Systematic IUPAC name (2R,3R)-2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7,8-tetrahydroxy-2,3-dihydro-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Other names
2,3-Dihydrogossypetin 3′,4′,5,7,8-pentahydroxyflavanonol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C15H12O8 |
| Molar mass | 320.25 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Dihydrogossypetin is a flavanonol, a type of flavonoid.
Biosynthesis
The enzyme Taxifolin 8-monooxygenase hydroxylates taxifolin using NADH, NADPH, H, and O2 to produce 2,3-dihydrogossypetin, NAD, NADP, and H2O.
References
- Jeffrey, A. M.; Jerina, D. M.; Self, R.; Evans, W. C. (1972). "The bacterial degradation of flavonoids. Oxidative fission of the A-ring of dihydrogossypetin by a Pseudomonas sp". The Biochemical Journal. 130 (2): 383–90. doi:10.1042/bj1300383. PMC 1174417. PMID 4198081.
| Flavanonols and their glycosides | |
|---|---|
| 3-Hydroxyflavanones: |
|
| O-methylated flavanonols | |
| dihydroflavonol 3-O-glycosides | |
| Glycosides |
|
| Acetylated glycosides | |
This article about an aromatic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |