This is the current revision of this page, as edited by BegbertBiggs (talk | contribs) at 17:11, 28 October 2023 (removed hatnote). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this version.
Revision as of 17:11, 28 October 2023 by BegbertBiggs (talk | contribs) (removed hatnote)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 1-Methyl-4-(propan-2-yl)benzene | |||
| Other names
para-Cymene 4-Isopropyltoluene 4-Methylcumene Paracymene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number | |||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| 3DMet | |||
| Beilstein Reference | 1903377 | ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.542 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| Gmelin Reference | 305912 | ||
| KEGG | |||
| PubChem CID | |||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2046 | ||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
InChI
| |||
SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | C10H14 | ||
| Molar mass | 134.222 g·mol | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Density | 0.857 g/cm | ||
| Melting point | −68 °C (−90 °F; 205 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 177 °C (351 °F; 450 K) | ||
| Solubility in water | 23.4 mg/L | ||
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | −1.028×10 cm/mol | ||
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.4908 (at 20 °C) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
| Pictograms |   
| ||
| Signal word | Danger | ||
| Hazard statements | H226, H304, H411 | ||
| Precautionary statements | P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P273, P280, P301+P310, P303+P361+P353, P331, P370+P378, P391, P403+P235, P405, P501 | ||
| Flash point | 47 °C (117 °F; 320 K) | ||
| Autoignition temperature |
435 °C (815 °F; 708 K) | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |||
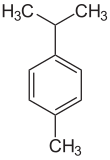
p-Cymene is a naturally occurring aromatic organic compound. It is classified as an alkylbenzene related to monocyclic monoterpenes. Its structure consists of a benzene ring para-substituted with a methyl group and an isopropyl group. p-Cymene is insoluble in water, but miscible with organic solvents.
Isomers and production
In addition to p-cymene, two less common geometric isomers are o-cymene, in which the alkyl groups are ortho-substituted, and m-cymene, in which they are meta-substituted. p-Cymene is the only natural isomer, as expected from the terpene rule. All three isomers form the group of cymenes.
Cymene is also produced by alkylation of toluene with propene.
Related compounds
It is a constituent of a number of essential oils, most commonly the oil of cumin and thyme. Significant amounts are formed in sulfite pulping process from the wood terpenes.
p-Cymene is a common ligand for ruthenium. The parent compound is 2. This half-sandwich compound is prepared by the reaction of ruthenium trichloride with the terpene α-phellandrene. The osmium complex is also known.
Hydrogenation gives the saturated derivative p-menthane.
References
- Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. pp. 139, 597. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- Pabst, Florian; Blochowicz, Thomas (December 2022). "On the intensity of light scattered by molecular liquids - Comparison of experiment and quantum chemical calculations". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 157 (24): 244501. Bibcode:2022JChPh.157x4501P. doi:10.1063/5.0133511. PMID 36586992.
- Balahbib, Abdelaali; El Omari, Nasreddine; Hachlafi, Naoufal EL.; Lakhdar, Fatima; El Menyiy, Naoual; Salhi, Najoua; Mrabti, Hanae Naceiri; Bakrim, Saad; Zengin, Gokhan; Bouyahya, Abdelhakim (2021-07-01). "Health beneficial and pharmacological properties of p-cymene". Food and Chemical Toxicology. 153: 112259. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2021.112259. ISSN 0278-6915.
- Vora, Bipin V.; Kocal, Joseph A.; Barger, Paul T.; Schmidt, Robert J.; Johnson, James A. (2003). "Alkylation". Kirk‐Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. doi:10.1002/0471238961.0112112508011313.a01.pub2. ISBN 0471238961.
- Bennett, M. A.; Huang, T.-N.; Matheson, T. W.; Smith, A. K. (1982). "(η-Hexamethylbenzene)Ruthenium Complexes". Inorganic Syntheses. 21: 74–78. doi:10.1002/9780470132524.ch16. ISBN 9780470132524.
| Hydrocarbons | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saturated aliphatic hydrocarbons |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aromatic hydrocarbons |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||