This is an old revision of this page, as edited by George (talk | contribs) at 05:09, 8 December 2006 (rv edits by Shamir1. Please be careful not to revert useful changes when making changes.). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 05:09, 8 December 2006 by George (talk | contribs) (rv edits by Shamir1. Please be careful not to revert useful changes when making changes.)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Template:Campaignbox Arab-Israeli conflict | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict, known in Lebanon as the July War and in Israel as the Second Lebanon War, was a military conflict in Lebanon and northern Israel, primarily between Hezbollah paramilitary forces and Israel. It started on 12 July 2006 and continued until a United Nations-brokered ceasefire went into effect on 14 August 2006, though it formally ended on 8 September 2006, when Israel lifted their naval blockade against Lebanon.
The conflict began when Hezbollah fired Katyusha rockets and mortars at Israeli military positions and border villages to divert attention from another Hezbollah unit that crossed the border and kidnapped two Israeli soldiers (Ehud Goldwasser and Eldad Regev) and killed three. Israel attempted to rescue the abducted soldiers and five more were killed during the rescue mission. Israel responded with massive airstrikes and artillery fire on Lebanese civilian infrastructure, which Israel said Hezbollah was using, an air and naval blockade, and a ground invasion of southern Lebanon. Hezbollah in turn launched rockets into northern Israel and engaged the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) in guerrilla warfare from hardened positions.
The conflict killed over 1,500 people, most of whom were Lebanese civilians (although a Israeli research group report has suggested that some of these, perhaps up to 650, were Hezbollah fighters in civilian dress), severely damaged Lebanese infrastructure, displaced about 900,000 Lebanese and 300,000 Israelis and disrupted normal life across all of Lebanon and northern Israel. Even after the ceasefire, 256,000 Lebanese remained internally displaced, and much of South Lebanon remained uninhabitable due to unexploded cluster bombs.
On 11 August 2006 the United Nations Security Council unanimously approved UN Resolution 1701 in an effort to end the hostilities. The resolution, which was approved by both Lebanese and Israeli governments the following days, also called for the disarming of Hezbollah, for Israel to withdraw, and for the deployment of Lebanese soldiers and an enlarged United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon (UNIFIL) force in southern Lebanon. The Lebanese army began deploying in southern Lebanon on 17 August 2006. The blockade was lifted on 8 September 2006. On 1 October 2006 the Israeli army reported that it had completed its withdrawal, but UNIFIL denied these assertions. When asked about the UNIFIL report, the IDF confirmed its forces were still operating near Ghajar, a village split in two by the border.
Background
Main article: Israel-Lebanon conflictLebanon has long failed to control militancy within its borders, and Israel has had a history of using force in Lebanon in response to militant attacks. The Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) was committing cross border attacks from Southern Lebanon into Israel as far back as 1968, but the area became a significant base following the arrival of the PLO leadership and its Fatah brigade after their 1971 expulsion from Jordan. This situation exacerbated demographic tensions over the Lebanese National Pact which divided governmental powers among religious groups, leading in part to the Lebanese Civil War (1975-1990). Concurrently, Syria began a 29 year military occupation. Israel's 1978 invasion of Lebanon failed to stem the Palestinian attacks, but Israel invaded Lebanon again in 1982 and forcibly expelled the PLO. Israel withdrew to a slim borderland buffer zone in Southern Lebanon, held with the aid of proxy militants in the South Lebanon Army (SLA). In 1985, a Lebanese Shi'a militia calling itself Hezbollah declared armed struggle to end the Israeli occupation of Lebanese territory. When the Lebanese civil war ended and other warring factions agreed to disarm, Hezbollah and the SLA refused. Combat with Hezbollah weakened Israeli resolve and led to a collapse of the SLA and an early Israeli withdrawal in 2000 to their side of the UN designated border. Citing Israeli control of the Shebaa farms territory and the incarceration of Lebanese prisoners in Israel, Hezbollah continued cross border attacks, and successfully used the tactic of capturing soldiers from Israel as leverage for a prisoner exchange in 2004, though it also continues to call for Israel's destruction.
Beginning of conflict
Main article: Zar'it-Shtula incident See also: Timeline of the 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflictAt around 9:00 AM local time (06:00 UTC), on 12 July 2006, Hezbollah initiated diversionary rocket attacks toward Israeli military positions near the coast and near the border village of Zar'it as well as on the Israeli town of Shlomi. At the same time, a ground contingent of Hezbollah crossed the border into Israeli territory and attacked two Israeli armoured Humvees patrolling on the Israeli side of the Israel-Lebanon border, near Zar'it, killing three, injuring two, and capturing two Israeli soldiers. Five more Israeli soldiers were killed later on the Lebanese side of the border during an attempt to rescue the two kidnapped soldiers.
Hezbollah named the attack "Operation Truthful Promise" after leader Hassan Nasrallah's public pledges over the prior year and a half to capture Israeli soldiers and swap them for convicted murderer Samir Kuntar, convicted spy Nasim Nisr, alleged terrorist Yahya Skaf who Hezbollah claims was arrested in Israel (Israel denies this), and Ali Faratan, who is being held for reasons unknown, among any other Lebanese prisoners incarcerated in Israel. Nasrallah claimed that Israel had broken an agreement to release these prisoners in a previous deal, and that, diplomacy having failed, violence was the only remaining option. Nasrallah declared: "No military operation will return the Israeli captured soldiers…The prisoners will not be returned except through one way: indirect negotiations and a trade of prisoners."
Israeli Prime Minister Ehud Olmert described the capture of the soldiers as an "act of war" by the sovereign country of Lebanon and promised Lebanon a "very painful and far-reaching response." Israel quickly blamed the Lebanese government for the raid, as it was carried out from Lebanese territory and Hezbollah had two ministers serving in the Lebanese cabinet at that time.
In response, Lebanese Prime Minister Fouad Siniora denied any knowledge of the raid and stated that he did not condone it. An emergency meeting of the Lebanese government reaffirmed this position.
The Israel Defense Forces attacked targets within Lebanon with artillery and airstrikes hours before the Israeli Cabinet met to discuss a response. Israel's chief of staff Dan Halutz said, "if the soldiers are not returned, we will turn Lebanon's clock back 20 years," while the head of Israel's Northern Command Udi Adam said, "this affair is between Israel and the state of Lebanon. Where to attack? Once it is inside Lebanon, everything is legitimate -- not just southern Lebanon, not just the line of Hezbollah posts." The Israeli Cabinet authorized "severe and harsh" retaliation on Lebanon. A retired Israeli Army Colonel explained that the rationale behind the attack was to create a rift between the Lebanese population and Hezbollah supporters by exacting a heavy price from the elite in Beirut.
When asked in August about the proportionality of the response, Prime Minister Olmert stated that the "war started not only by killing eight Israeli soldiers and abducting two but by shooting Katyusha and other rockets on the northern cities of Israel on that same morning. Indiscriminately." He added "no country in Europe would have responded in such a restrained manner as Israel did."
Israeli action
Main article: Military operations of the 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict See also: Timeline of Military Operations in the 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict See also: Military equipment of IsraelDuring the campaign, Israel's Air Force flew more than 12,000 combat missions. The Navy fired 2,500 shells, and the Army fired over 100,000 shells , destroying large parts of the Lebanese civilian infrastructure. 400 miles of roads, 73 bridges and 31 targets such as Beirut International Airport, ports, water and sewage treatment plants, electrical facilities, 25 fuel stations, 900 commercial structures, up to 350 schools and two hospitals were destroyed, as well as some 15,000 homes. Some 130,000 more homes were damaged.
Israeli Defense Minister Amir Peretz ordered commanders to prepare civil defense plans. One million Israelis had to stay near or in bomb shelters or security rooms, with some 250,000 civilians evacuating the north and relocating to other areas of the country.
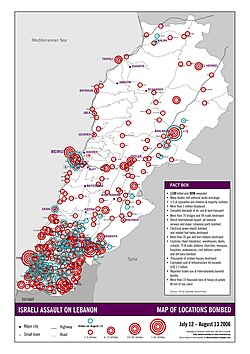
Timeline
- Early on 13 July 2006 Israel began attacks on civilian targets with the bombing of Beirut International Airport, forcing its closure and diversion of incoming flights to Cyprus. Israel subsequently imposed an air and sea blockade on Lebanon, and bombed the main Beirut–Damascus highway.
- On 14 July 2006 the IDF bombed Nasrallah's offices in Beirut.Nasrallah addressed Israel, saying “You wanted an open war, and we are heading for an open war. We are ready for it.”
- On 23 July 2006 Israeli land forces crossed into Lebanon in the Maroun al-Ras area, which overlooks several other locations said to have been used as launch sites for Hezbollah rockets.
- On 25 July 2006 IDF engaged Hezbollah forces in the Battle of Bint Jbeil.
- On 26 July 2006 Israeli forces attacked and destroyed an UN observer post. Described as a nondeliberate attack by Israel, the post was shelled for hours before being bombed. UN forces made repeated calls to alert Israeli forces of the danger to the UN observers, all four of whom were killed. Rescuers were shelled as they attempted to reach the post. According to an e-mail sent earlier by one of the UN observers killed in the attack, there had been numerous occasions on a daily basis where the post had come under fire from both Israeli artillery and aerial bombing. The UN observer reportedly wrote that previous Israeli bombing near the post had not been deliberate targeting, but rather due to "tactical necessity," military jargon which retired Canadian Major General Lewis MacKenzie later interpreted as indicating that Israeli strikes were aimed at Hezbollah targets extremely close to the post.

- On 27 July 2006 Hezbollah ambushed the Israeli forces in Bint Jbeil and killed eight soldiers. Israel said it also inflicted heavy losses on Hezbollah.
- On 28 July 2006 Israeli paratroopers killed 26 of Hezbollah's commando elite in Bint Jbeil. In total, the IDF claimed that 80 fighters were killed in the battles at Bint Jbeil.
- On 30 July 2006 Israeli airstrikes hit an apartment building in Qana, killing at least 28 civilians, of which 16 were children, with 13 more missing. The airstrike was widely condemned.
- On 31 July 2006 the Israeli military and Hezbollah forces engaged Hezbollah in the Battle of Ayta ash-Shab.
- On 1 August 2006 Israeli commandos launched Operation Sharp and Smooth and landed in Baalbek and captured five civilians including one bearing the same name as Hezbollah's leader, "Hassan Nasrallah". All of the civilians were released after the ceasefire. Troops landed near Dar al-Himkeh hospital west of Baalbeck as part of a widescale operation in the area.
- On 4 August 2006 the IAF attacked a building in the area of al-Qaa around 10 kilometers (six miles) from Hermel in the Bekaa Valley, Lebanon. Thirty-three farm workers, mostly Syrian and Lebanese Kurds, were killed during the airstrike.
- On 5 August 2006 Israeli commandos carried out a nighttime raid in Tyre.
- On 7 August 2006 the IAF attacked the Shiyyah suburb in the Lebanese capital of Beirut, destroying three apartment buildings in the suburb, killing at least 50 people.
- On 11 August 2006 the IAF attacked a convoy of approximately 750 vehicles containing Lebanese police, army, civilians, and one Associated Press journalist, killing at least seven people and wounding at least 36.
- On 12 August 2006 the IDF established its hold in Lebanon. Over the weekend Israeli forces in southern Lebanon nearly tripled in size. and were ordered to advance towards the Litani River.
- On 14 August 2006 the Israeli Air Force reported that they had killed the head of Hezbollah’s Special Forces, whom they identified as Sajed Dewayer, while Hezbollah denied this claim. 80 minutes before the cessation of hostilities, the IDF targeted a Palestinian faction in the Ain al-Hilweh refugee camp in Sidon, killing a UNRWA staff member. Two refugees had been killed in an attack on this camp six days prior to the incident.
Hezbollah action
Main article: Military operations of the 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict See also: Timeline of Military Operations in the 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict See also: Hezbollah rocket force
During the campaign, Hezbollah fired between 3,970 and 4,228 rockets, about 95% of which were 122 mm (4.8 in) Katyusha artillery rockets carrying an up to 30 kg (66 lb) warhead and having a range of up to 30 km (19 mi). An estimated 23% of these rockets hit built-up areas, primarily civilian in nature. Cities hit included Haifa, Hadera, Nazareth, Tiberias, Nahariya, Safed, Afula, Kiryat Shmona, Beit She'an, Karmiel, and Maalot, and dozens of Kibbutzim, Moshavim, and Druze and Arab villages, as well as the northern West Bank. Hezbollah also engaged in guerrilla warfare from well fortified positions with the IDF. These attacks by small, well-armed units caused serious problems for the IDF, especially where hundreds of sophisticated Russian-made anti-tank guided missiles (ATGMs) were used. Hezbollah destroyed 14 Israeli Merkava main battle tanks and damaged 50. Six tanks were destroyed by anti-tank mines. Hezbollah caused additional casualties using ATGMs to collapse buildings onto Israeli troops sheltering inside.
After the initial Israeli response, Hezbollah declared an all-out military alert. Hezbollah was estimated to have 13,000 missiles at the beginning of the conflict.. Israeli newspaper Haaretz reported that it was a trained, skilled, well-organized, highly motivated infantry that was equipped with the cream of the crop of modern weaponry from the arsenals of Syria, Iran, Russia, and China. Lebanese satellite TV station Al-Manar reported that the attacks had included a Fajr-3 and a Ra'ad 1, both liquid-fuel missiles developed by Iran.
Timeline
- On 13 July 2006 in response to Israel's retaliatory attacks in which civilians were killed, Hezbollah launched rockets at Haifa for the first time, hitting a cable car station along with a few other buildings.
- On 14 July 2006 Hezbollah attacked the INS Hanit, an Israeli Sa'ar 5-class missile boat enforcing the naval blockade, with a radar guided C-802 anti-ship missile. 4 sailors were killed and the warship was severely damaged and towed back to port.
- On 17 July 2006 Hezbollah hit a railroad repair depot, killing eight workers. Hezbollah claimed that this attack was aimed at a large Israeli fuel storage plant adjacent to the railway facility. Haifa is home to many strategically valuable facilities such as shipyards and oil refineries.
- On 27 July 2006 Hezbollah ambushed the Israeli forces in Bint Jbeil and killed eight soldiers. Israel said it also inflicted heavy losses on Hezbollah.
- On 3 August 2006 Nasrallah warned Israel against hitting Beirut and promised retaliation against Tel Aviv in this case. He also stated that Hezbollah would stop its rocket campaign if Israel ceased aerial and artillery strikes of Lebanese towns and villages.
- On 4 August 2006 Israel targetted the southern outskirts of Beirut, and later in the day, Hezbollah launched rockets at the Hadera region.
- On 9 August 2006 nine Israeli soldiers were killed when the building they were taking cover in was struck by a Hezbollah anti-tank missile and collapsed.
- On 12 August 2006 24 Israeli soldiers were killed; the worst Israeli loss in a single day. Out of those 24, five soldiers were killed when Hezbollah shot down an Israeli helicopter, a first for the militia.. Hezbollah claimed the helicopter had been attacked with a Wa'ad missile.
Position of Lebanon
Main article: Position of Lebanon in the 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict See also: Siniora Plan See also: Foreign relations of LebanonWhile Israel initially held the Lebanese government responsible for the Hezbollah attacks due to Lebanon's failure to implement Resolution 1559 and disarm Hezbollah, Lebanon disavowed the raids, stating that the government of Lebanon did not condone them, and that Israel had its own history of disregarding inconvenient UN resolutions. On 13 July 2006 Hezbollah hit Haifa for the first time, targeting a cable car station along with a few other buildings .On 14 July 2006 the Prime Minister's office issued a statement that called on US President George W. Bush to exert all his efforts on Israel to stop its attacks on Lebanon, reach a comprehensive ceasefire and lift its blockade. On the next day, Siniora called for "an immediate ceasefire backed by the United Nations" in a televised speech. A US-France draft for a resolution that was influenced by the Lebanese Siniora Plan and which contained conditions on Israeli withdrawal, military actions and mutual prisoner release, was later rejected as inadequate. Many Lebanese accused the US government of stalling the ceasefire resolution and support of Israel. In a poll conducted two weeks into the conflict, 8% of the respondents felt that the US would support Lebanon, while 87% supported Hezbollah's fight against Israel. After the attack on Qana, Siniora snubbed US Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice by cancelling a meeting with her and thanked Hezbollah for its "sacrifices for the independence and sovereignty of Lebanon." On 7 August 2006 the 7-point plan was extended to include the deployment of 15,000 Lebanese Army troops to fill the void between an Israeli withdrawal and UNIFIL deployment.
During Israel's raid on Tyre, the Lebanese Army reportedly fired surface-to-air missiles at Israeli helicopters, which returned fire and destroyed a Lebanese M113 Armored Personnel Carrier.
Targeting of civilian areas
Main article: Targeting of civilian areas in the 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict
The high number of civilian deaths in the conflict has been one of its most controversial aspects; The vast majority of casualties were civilians, around 1,056 Lebanese (although Israeli research group report suggest that up to 650 of these were Hezbollah fighters) and 44 Israelis. Almost one third of the Lebanese civilian casualties were children under 13 years of age.
The United Nations Development Program (UNDP) initially estimated about 35,000 homes and businesses in Lebanon were destroyed by Israel in the conflict, while a quarter of the country's road bridges or overpasses were damaged. Jean Fabre, a UNDP spokesman, estimated that overall economic losses for Lebanon from the month-long conflict between Israel and Hezbollah totaled "at least $15 billion, if not more." Israel, however, says that it only attacked buildings and infrastructure used by Hezbollah to launch rockets or receive re-supply from Iran and Syria.
Hezbollah also fired hundreds of rockets, sometimes more than 200 per day throughout the conflict, which landed in all major cities of northern Israel, including Haifa, Nazareth, and Tiberias, as well as dozens of kibbutzim, moshavim, Druze, and Arab villages, while Israel destroyed large parts of the Lebanese civilian infrastructure with airstrikes and heavy artillery fire. Hezbollah leader Hassan Nasrallah defended the attacks, saying that Hezbollah had "started to act calmly, we focused on Israel military bases and we didn’t attack any settlement, however, since the first day, the enemy attacked Lebanese towns and murdered civilians—Hezbollah militants had destroyed military bases, while the Israelis killed civilians and targeted Lebanon's infrastructure."
Various agencies have criticised both Israel and Hezbollah; Amnesty International condemned both Hezbollah and Israel for attacks on civilians, in addition to the confirmed use of white phosphorus by the IDF, and published a report suggesting that the attacks on civilian property were a deliberate part of the Israeli military strategy, rather than collateral damage; Human Rights Watch condemned the indiscriminate use of force against civilians by both Israel and Hezbollah. They blamed Israel for systematically failing to distinguish between combatants and civilians, which may constitute a war crime, and accused Hezbollah of committing war crimes by the deliberate and indiscriminate killing of civilians by firing rockets into populated areas. The organization also strongly criticized Hezbollah and Israel for using cluster bombs too close to civilians because of their inaccuracy and unreliability, suggesting that Hezbollah may have gone as far as deliberately targeting civilian areas with such munitions. Hezbollah was also criticized by Human Rights Watch for filling its rockets with ball bearings, which "suggests a desire to maximize harm to civilians"; the U.N has criticised Israel for it's use of cluster munitions and disproportionate attacks. Both sides have been accused of violations of international law and war crimes.
Israeli officials accused Hezbollah of intentionally using the civilian population as human shields, and several reports have alleged that Hezbollah fired rockets from residential areas to draw Israeli fire on those areas, which maximised civilian casualties. Moreover, the IDF said that Hezbollah had blocked village exits to prevent residents from leaving the warzone. The Association for Civil Rights in Israel points to Israeli attacks on roads, bridges and vehicles transporting refugees as preventing civilian evacuation.
Environmental damage
See also: Jiyeh power station oil spill
The Israeli Air Force bombed the Jiyeh power station, 30 km (19 mi) south of Beirut, on 13 July 2005 and 15 July 2006, resulting in an environmental disaster. The plant's damaged storage tanks leaked an estimated 12,000 to 15,000 tonnes (more than 4 million gallons) of oil into the eastern Mediterranean Sea A 10 km (6 mi) wide oil slick covered 170 km (105 statute miles) of coastline at one point, and threatened Turkey and Cyprus. The slick reportedly killed fish, threatened the habitat of the endangered green sea turtle, as well as potentially increased the risk of cancer. An additional 25,000 tons of oil burned at the power station, creating a "toxic cloud" that rained oil downwind. The Lebanese government estimated the time necessary for a complete recovery to be 10 years. The UN estimated the cost for the initial clean-up at $64m.
Hezbollah rocket attacks caused numerous forest fires inside northern Israel, particularly on the Naftali mountain range near Kiryat Shmona. As of 8 August as many as 9,000 acres, including 3,000 acres of Israel’s few forests, were damaged by fires caused by Hezbollah rockets, and at least one forest lost nearly 75% of its trees. The Jewish National Fund estimated that it would take 50 to 60 years to rehabilitate the forests.
International action and reaction

The conflict engendered worldwide concerns over infrastructure damage and the risks of escalation of the crisis, as well as mixed support and criticism of both Hezbollah and Israel. Governments of the United States, United Kingdom, GermanyAustralia, and Canada, asserted Israel's right to self-defense. The United States government further responded by authorizing Israel's request for expedited shipment of precision-guided bombs, but did not announce the decision publicly.
Among neighboring Middle Eastern nations, Iran, Syria, and Yemen voiced strong support for Hezbollah, while the Arab League issued statements condemning Israel’s response and criticizing Hezbollah’s action.
Many worldwide protests and demonstrations appealed for an immediate ceasefire on both sides and expressed concern for the heavy loss of civilian life on all sides. Other demonstrations were held exclusively in favor of Lebanon or Israel. Numerous newspaper advertising campaigns, SMS and email appeals, and online petitions also occurred.
Various foreign governments assisted the evacuation of their citizens from Lebanon.
Ceasefire
See also: Ceasefire attempts during the 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflictTerms for a ceasefire had been drawn and revised several times over the course of the conflict, yet successful agreement between the two sides took several weeks. Hezbollah maintained the desire for an unconditional ceasefire, while Israel insisted upon a conditional ceasefire, including the return of the two kidnapped soldiers. Lebanon frequently pled for the United Nations Security Council to call for an immediate, unconditional ceasefire between Israel and Hezbollah.
On 11 August 2006 the United Nations Security Council unanimously approved UN Security Council Resolution 1701, in an effort to end the hostilities. It was accepted by the Lebanese government and Hezbollah on 12 August 2006, and by the Israeli government on 13 August 2006. The ceasefire took effect at 8:00 AM (5:00 AM GMT) on 14 August 2006.
Before the ceasefire, the two Hezbollah members of cabinet said that their militia would not disarm south of the Litani River, according to another senior member of the Lebanese cabinet, while a top Hezbollah official similarly denied any intention of disarming in the south. Israel said it would stop withdrawing from Southern Lebanon if Lebanese troops were not deployed there within a matter of days.
Reviews of the conflict

Following the UN-brokered ceasefire, there were mixed responses on who had gained most in the war. Iran and Syria proclaimed a victory for Hezbollah while the Israeli and United States administrations declared that Hezbollah lost the conflict. Initially, in a poll by an Israeli radio station, Israelis were split on the outcome with the majority believing that no one won. By 25 August, 63% of Israelis polled wanted Olmert to resign due to his handling of the war. The Economist concluded that by surviving this asymmetrical military conflict with Israel, Hezbollah effectively emerged with a military and political victory from this conflict. They cite the facts that Hezbollah was able to sustain defenses on Lebanese soil and inflict unmitigated rocket attacks on Israeli civilians in the face of a punishing air and land campaign by the IDF. Also, Israel's stated goals entering the conflict were to retrieve its two captured soldiers and destroy the military capability of Hezbollah - neither goal was accomplished. Hezbollah is leading the rebuilding effort in south Beirut and Lebanon using "unlimited" support from Iran, thereby awarding Hezbollah further political clout. However, given the response from Israeli military forces, which caused widespread destruction in southern Lebanon, as well as a new UN force to occupy what was formerly a Hezbollah controlled area, the conflict is generally seen as weakening Hezbollah militarily. On 27 August, Hassan Nasrallah apologised to the Lebanese people for the incident that sparked the war, saying "Had we known that the kidnapping of the soldiers would have led to this, we would definitely not have done it." This was the day before UN Secretary-General Kofi Annan's visit to Lebanon, On 22 September, some eight hundred thousand Hezbollah supporters gathered in Beirut for victory rally. Nasrallah said that Hezbollah should celebrate the "divine and strategic victory."
Israeli Prime Minister Olmert admitted to the Knesset that there were mistakes in the war in Lebanon, though he framed UN Security Council resolution 1701 as an accomplishment for Israel that would bring home the kidnapped soldiers, and said that the operations had altered the regional strategic balance vis-à-vis Hezbollah. Israeli chief of staff Dan Halutz admitted to failings in the conflict. On 15 August, Israeli government and defense officials called for Halutz' resignation following a stock scandal in which he admitted selling stocks hours before the start of the Israeli offensive.
On 21 August, a group of demobilized Israel reserve soldiers and parents of soldiers killed in the fighting started a movement calling for the resignation of Ehud Olmert and the establishment of a state commission of inquiry. They set up a protest tent opposite the Knesset and grew to over 2,000 supporters by 25 August , including the influential Movement for Quality Government. On 28 August, Olmert announced that there would be no independent state or governmental commission of inquiry, but two internal inspection probes, one to investigate the political echelon and one to examine IDF, and likely a third commission to examine the Home Front, to be announced at a later date. These would have a more limited mandate and less authority than a single inquiry commission headed by a retired judge. The political and military committees were to be headed by former director of Mossad Nahum Admoni and former Chief of Staff Amnon Lipkin-Shahak, respectively. Critics argued that these committees amount to a whitewash, due to their limited authority, limited investigatory scope, their self-appointed basis, and that neither would be headed by a retired judge.
Due to these pressures, on 11 October, Admoni was replaced by retired justice Eliyahu Winograd as chair of the political probe, and the probe itself was elevated to the status of governmental commission with near-state commission mandate: the Winograd Commission. On 12 September, former defense minister Moshe Arens spoke of "the defeat of Israel" in calling for a state committee of inquiry. He said that Israel had lost "to a very small group of people, 5000 Hezbollah fighters, which should have been no match at all for the IDF," and stated that the conflict could have "some very fateful consequences for the future." Disclosing his intent to shortly resign, Ilan Harari, the IDF's chief education officer, stated at a conference of senior IDF officers that Israel lost the war, becoming the first senior active duty officer to publicly state such an opinion. IDF Major General Yiftah Ron Tal, on Oct 4, 2006 became the second and highest ranking serving officer to express his opinion that the IDF failed "to win the day in the battle against Hezbollah," as well as calling for Lt. Gen. Dan Halutz' resignation. Ron-Tal was subsequently fired for making those and other critical comments.
US President George W. Bush questioned Hezbollah's declarations of victory "when at one time were a state within a state, safe within southern Lebanon, and now going to be replaced by a Lebanese army and an international force." UNIFIL has been given an expanded mandate, including the ability to use force to ensure that their area of operations is not used for hostile activities, and to resist attempts by force to prevent them from discharging their duties.
The fighting resulted in a huge financial setback for Lebanon, with estimates ranging from US$7 to US$15 billion in direct costs while the cost for Israel is put at US$1.6 - US$3 billion. This has prompted a commentator in the London-based Arabic newspaper Asharq Al-Awsat to question the claims of victory by Hezbollah. According to one analyst in the Associated Press, the main casualty was the fragile unity between Lebanon's sectarian and political groups, though an Asia Times piece points to Free Patriotic Movement head Michel Aoun's support for Hezbollah and provision of housing for displaced Shi'a as evidence for strengthened relations.
Media controversy
Main article: 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict photographs controversies See also: Adnan Hajj photographs controversySeveral media commentators and journalists have alleged an intentionally distorted coverage of the events, in favour of Hezbollah, by means of photo manipulation, staging by Hezbollah or by journalists, and false or misleading captioning.
On 18 July 2006 Hezbollah Press Officer Hussein Nabulsi took CNN's Nic Robertson on an exclusive tour of southern Beirut. Robertson noted that despite his minder's anxiety about explosions in the area, it was clear that Hezbollah had sophisticated media relations and were in control of the situation. Hezbollah designated the places that they went to, and the journalists "certainly didn't have time to go into the houses or lift up the rubble to see what was underneath." According to his reports, there was no doubt that the bombs were hitting Hezbollah facilities, and while there appeared to be "a lot of civilian damage, a lot of civilian properties," he reiterated that he couldn't verify the civilian nature of the destroyed buildings.
CNN's Charlie Moore described a Hezbollah press tour of a bombed-out area in southern Beirut on 23 July 2006 as a "dog-and-pony show" due to perceived staging, misrepresentation of the nature of the destroyed areas, and strict directives about when and with whom interviews could take place.
In the same interview aired on 23 July 2006, CNN's John Roberts, who was reporting from an Israeli artillery battery on the Lebanese border, stated that he had to take everything he was told—either by the IDF or Hezbollah—"with a grain of salt," citing mutual recriminations of civilian targeting which he was unable to verify independently.
Reuters withdrew over 900 photographs by Adnan Hajj, a Lebanese freelance photographer, after he admitted to digitally adding and darkening smoke spirals in photographs of an attack on Beirut.
Photographs submitted to Reuters and Associated Press showed one Lebanese woman mourning on two different pictures taken by two photographers, allegedly taken two weeks apart. While it is "common practice to send more than one photographer to an incident", questions remained as to whether the images were wrongly captioned or deliberately staged.
Post-ceasefire events
- On 14 August 2006, hours after the beginning of the ceasefire, about four mortars were fired inside southern Lebanon. An Israeli military spokesman said that Israel would not respond to their firing. On that day four more incidents were recorded when armed Hezbollah members said to have approached Israeli positions were killed.
- On 15 August 2006 "Israeli soldiers opened fire when four Hezbollah fighters came toward them," three of the Hezbollah fighters were killed. The same day, about 10 rockets were fired by Hezbollah inside southern Lebanon. Israel reiterated it wouldn't respond since the rockets did not cross border.
- On 18 August 2006 Lebanese police sources reported that Israeli Defense Force warplanes launched four missiles toward targets in the eastern Lebanese village of Baalbek. Israeli sources acknowledge that its air force performs sorties over Lebanese territory, but denied breaking the ceasefire. Lebanese officials later contradicted the police sources stating that no missiles were fired by the Israeli planes. The Associated Press reported that Hezbollah had fired at least 10 Katyusha rockets into southern Lebanon. The IDF stated that as none had crossed the border and there were no casualties, they did not respond. Earlier, skirmishes between Israeli forces and Hezbollah left six guerrillas dead. UNIFIL also reported that the IDF fired a tank shell at the Lebanese village of Markaba but that there was no response from the other side.
- On 19 August 2006 Israel launched a raid in Lebanon's eastern Bekaa Valley it says was aimed to disrupt weapons supplies to Hezbollah from Syria and Iran. Lebanese officials "said the Israelis were apparently seeking a guerrilla target in a school." One Israeli soldier was killed, another mortally wounded, while 3 Hezbollah fighters were wounded. Hezbollah said it wouldn't respond to the attack. U.N. Secretary-General Kofi Annan said he was "deeply concerned" about an Israeli commando raid in eastern Lebanon Saturday, calling it a violation of a U.N.-backed ceasefire. The statement also cites UNIFIL troops as saying there have "also been several air violations by Israeli military aircraft." Israeli Foreign Ministry spokesman Mark Regev told the Associated Press that “he cease-fire is based on (U.N. resolution) 1701 which calls for an international arms embargo against Hezbollah.” Regev was referring to article 8 of the resolution which calls for an end to all weapons transfers to Hezbollah.
- On 27 August 2006 UN Secretary-General Kofi Annan said that U.N. troops would not intercept Syrian arms shipments to Hezbollah unless requested to do so by the Lebanese Government.
- On 29 August 2006 UN Secretary-General Kofi Annan said that Israel had committed most of the truce violations and described Israel's continuing embargo as "a humiliation and an infringement on Lebanese sovereignty." Israeli Prime Minister Ehud Olmert reiterated Israel's willingness to lift the blockade after full implementation of the U.N.-brokered cease fire.
- On 6 September 2006 the Israeli government announced that it would lift the blockade the following day at 6:00 PM local time (3:00 PM GMT).
- On 7 September 2006 the aviation blockade was lifted.
- On 8 September 2006 the naval blockade was lifted.
- On 21 September 2006 Hezbollah supporters throw stones over border fence at Israeli patrols, seen as part of Hezbollah redeployments
- On 22 September 2006 Nasrallah claimed in a victory rally that Hezbollah possessed over 20,000 rockets and that it was stronger than before 12 July. According to various estimates, the organisation had fewer than 20,000 rockets before and fired about 4,000 rockets during the conflict.
- On 1 October 2006, the Israeli army reported that it had completed its withdrawal. The UN has said Israel has withdrawn the bulk of its troops from Lebanon, fulfilling a key condition of the UN ceasefire ending war with Hezbollah, but that some Israeli troops remained in Ghajar. The IDF confirmed its forces were still operating near Ghajar, a village split in two by the border. Because of the volatile nature of the place, Israel says it will maintain presence in Ghajar until a security agreement is reached with the UN and the Lebanese army.
- On 3 October, Israeli jet planes conducted mock exercises over Southern Lebanon. The first group conducted series of mock air raids over Nabatiyeh, Khiam and Marjayoun. The second group conducted similar manouvres over Iqlim al-Tuffah region and Western Bekaa Valley.
- On 22 October, Israel admitted to using white phosphorus in Lebanon. Although Israel continues to deny the use of phosphorus on civilians, doctors in southern Lebanon have suspected some injuries were caused by contact with the chemical.
- On 23 October, Lebanese police reported Israeli "most intensive overflight" of Lebanon after the ceasefire. Two jets flew low over Beirut, while four more aircraft conducted sonic boom raid in Tyre. France who leads UNIFIL troops called the continuing overflights "extremely dangerous".
- On 24 October, six Israeli F-16 flew over Germany vessel patrolling off Israel's coast just south of the Lebanese border. The German Defence Ministry said that the planes had given off infrared decoys and one of the aircraft had fired two shots into the air, which had not been specifically aimed. The Israeli military said that a German helicopter took off from the vessel without having coordinated this with Israel, and denied vehemently having fired any shots at the vessel and said "as of now" it also had no knowledge of the jets launching flares over it. Israeli Defence Minister Amir Peretz telephoned his German counterpart Franz Josef Jung to clarify that 'Israel has no intention to carry out any aggressive actions' against the German peacekeeping forces in Lebanon, who are there as part of UNIFIL to enforce an arms embargo against Hezbollah. Germany confirmed the consultations, and that both sides were interested in maintaining good cooperation.
- On 31 October 8 Israeli F-15's flew over Beirut and many areas in Lebanon. Israeli jets also flew over French peacekeeper position in Lebanon, in a threatening dive-bomb position. The peacekeepers "almost" fired at IAF jets
- On 1 December, Annan submitted a report to the Security Council president, detailing evidence of the presence of unauthorized armed personnel, assets and weapons in Lebanon. In one case, a UNIFIL de-mining team was challenged by two armed Hezbollah members in combat uniforms. UNIFIL notified the Lebanese army who arrested them. There were also 13 instances where UNIFIL came across unauthorized arms or related material in its area of operation, including the discovery of 17 katyusha rockets and several improvised explosive devices in Rachaiya El-Foukhar, and the discovery of a weapons cache cotaining seven missiles, three rocket launchers and a substantial amount of ammunition in the area of Bourhoz.
See also
- 2006 Israel-Gaza conflict
- Views of the Arab-Israeli conflict
- International law and the Arab-Israeli conflict
- Arab-Israeli conflict facts, figures, and statistics
- History of Lebanon
- History of Israel
- History of the Middle East
- Israel-United States relations
- May 17 Agreement 1980s prospective peace agreement
- United Nations Security Council Resolution 1559
- United Nations Security Council Resolution 1697
- Canadians of convenience
References
- http://allafrica.com/stories/200611200092.html
- "Arafat's 'fox' running rocket unit", Jerusalem Post, 29 July 2006; See also, "Imad Mughniyeh: Hezbollah's Phantom"
- "Two Northern Command chiefs?", Ynetnews, 8 August 2006; See also, "IDF officials: Maj. Gen. Adam must quit post after war"; "Israel swaps commanders"; "Impatient Israel appoints new battle chief"; "New Israeli General Oversees Lebanon "; "Israel names new commander to head offensive"; "Israel changes command structure"
- International Institute for Strategic Studies
- "Some 30,000 Israeli troops in Lebanon - army radio". Reuters via Yahoo! News Asia. 2006-08-13.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Fragile truce begins in Lebanon". Reuters. 200614 September.
Hizbollah has acknowledged only about 80 dead
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Analysis: Hezbollah's recovery timetable". UPI. "Israel identified 440 dead guerrillas by name and address, ... Amidror estimated, Hezbollah's death toll might be as high as 700."
- Peacekeeping force won't disarm Hizbollah, ''Telegraph.co.uk'', "A UN official estimated the deaths at 500"
- "Hezb's political regrouping efforts in full swing". "Sources in Lebanon claim Hezbollah has buried more than 700 fighters so far, with many more to go."
- Wheeler, Carolynne (August 16, 2006). "Israel begins pullout as ceasefire holds". The Globe and Mail. pp. A13.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) "Israeli army officials indicated they have 13 captured Hezbollah fighters " - ^ "Israel-Hizbullah conflict: Victims of rocket attacks and IDF casualties". Israel, Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Cite error: The named reference "MFA" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ "Humanitarian Assistance to Lebanon". United States Agency for International Development Disaster Assistance. November 3 2006. Retrieved 2006-11-17.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Offering Video, Israel Answers Critics on War". New York Times. December 4 2006. Retrieved 2006-12-06.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Listing of all Israeli casualties in 2006 Lebanon war with links to corresponding reports on the circumstances of their deaths". ynet.co.il. 14 August 2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Some 1,300 Israelis hurt since fighting began". Ynetnews. 2006-07-23.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - AFP (2006). "Timeline of the July War 2006". Lebanon: The Daily Star. Retrieved 15 September.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - See, e.g., Yaakov Katz, "Halutz officers discuss war strategy," Jerusalem Post, Sept. 5, 2006, p. 2
- Greg Myre and Steven Erlanger, "Clashes spread to Lebanon as Hezbollah Raids Israel," New York Times, July 13, 2006 ("The Israeli military confirmed the strike , saying that was a target because Hezbollah receives weapons shipments there").
- "Lebanese Premier Seeks U.S. Help in Lifting Blockade". Washington Post. 24 August 2006.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Urquhart, Conal (August 11, 2006). "Computerised weaponry and high morale". The Guardian. Retrieved 2006-10-08.
- "Mideast War, by the numbers". Guardian Unlimited / Associated Press. 2006-08-18. Retrieved 2006-08-25.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Hizbullah attacks northern Israel and Israel's response". Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs. August, 2006. Retrieved 2006-10-02.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Pannell, Ian (9 September 2006). "Lebanon breathes after the blockade". BBC News. Retrieved 2006-09-09.
- AFP - Israel pulls remaining troops out of Lebanon
- UN peacekeepers: Israeli troops still in Lebanon, CNN
- ^ "Report of the Secretary-General on the United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon (For the period from 21 January 2006 to 18 July 2006)". United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon. July 21, 2006.
- "Day-by-day: Lebanon crisis - week one". BBC. July 19, 2006.
- "Israel/Lebanon Under fire: Hizbullah's attacks on northern Israel". Amnesty International. September 14, 2006. Retrieved 2006-09-27.
- ^ "Press Conference with Hasan Nasrallah". UNDERSTANDING THE PRESENT CRISIS. UPC. 12 July 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "J Who are the Mid-East prisoners?". BBC. 26 July. Retrieved 6 October.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=,|date=, and|year=/|date=mismatch (help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - "Hizbullah leader calls for prisoner exchange". Al Bawaba. 12 July 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israelis invade Lebanon after soldiers are seized". Guardian Unlimited. July 12, 2006. Retrieved September 26, 2006.
- "Olmert: We were attacked by a sovereign country". Ynetnews. July 12, 2006. Retrieved September 26, 2006.
- Fletcher, Martin (12 July 2006). "Regional tensions fuel Lebanon-Israel clashes". MSNBC. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Alon, Gideon (13 July 2006). "Israel holds Lebanon government responsible for Hezbollah attack". Haaretz. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - "Statement by Prime Minister Fouad Siniora". The Manila Times. July 17, 2006. Retrieved 2006-09-26.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Statement by Prime Minister Fouad Siniora". Daily Star (Lebanon) (registration required). 17 July 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-20.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Qawas, Nafez (13 July 2006). "Simiora's Cabinet makes clear it had nothing to do with 'what happened'". Daily Star (Lebanon) (registration required). Retrieved 2006-08-20.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - "Israel authorizes 'severe' response to abductions". CNN. July 12, 2006. Retrieved 2006-09-26.
- Wright, Robin (19 July 2006). "Bush Supports Israel's Move Against Hezbollah". Washington Post. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Farrel, Stephen (2 August 2006). "The Times interview with Ehud Olmert: full transcript". The Times. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "The war in numbers". Jane's Defence Weekly. 23 August 2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Mideast War, by the numbers". Guardian / Associated Press. 2006-08-18. Retrieved 2006-08-25.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Lebanon Refuses Contact With Israel". Guardian / Associated Press. 2006-08-30. Retrieved 2006-09-04.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Amnesty report accuses Israel of war crimes". Guardian. 2006-08-23. Retrieved 2006-09-03.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Crayons, glass, litter floor of Lebanese school". Reuters AlertNet. 2006-08-30. Retrieved 2006-09-03.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Hizballah's Rocket Campaign Against Northern Israel: A Preliminary Report". Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs. 2006-08-31. Retrieved 2006-09-14.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Hasson, Nir (14 July 2006). "Israel targets Hezbollah stronghold in Beirut suburb". Haaretz. Retrieved 2006-08-20.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - "Hezbollah leader vows 'open war'". BBC News. 07-15-06.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israeli Attacks Increase; Hezbollah Vows 'Open War'". NPR. 2006-07-14.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israel 'seizes' Hezbollah village". BBC News. 2006-07-23.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/5215366.stm
- "Soldier missing at UN border post, presumed dead". CTV television network. July 26, 2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Bint Jbeil: Hezbollah heartland". BBC News. 2006-07-27.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Ynet (Hebrew)
- Human Rights Watch puts Qana death toll at 28, Reuters, August 3, 2006.
- KIFNER, John (23 August 2006). "What's in a Name? Not, It Seems, a Leader of Hezbollah in Lebanon". The New York Times. Retrieved 2006-08-23.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Greenberg, Hanan (12 August 2006). "Chief of staff: We tripled our forces in southern Lebanon". Haaretz. Retrieved 2006-08-20.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Katz, Yaakov (12 August 2006). "IDF troops advancing to Litani River". Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 2006-08-20.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Greenberg, Hanan (16 August 2006). "IDF: Senior Hizbullah man killed before truce". Ynetnews. Retrieved 2006-08-20.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Hezbollah's rocket force". BBC. 2006-07-18. Retrieved 2006-09-14.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Mideast War, by the numbers". Guardian / Associated Press. 2006-08-18. Retrieved 2006-08-25.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Major Attacks in Lebanon, Israel and the Gaza Strip". New York Times. 14 August 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-23.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Greenberg, Hannan (14 July 2006). "Woman, grandson killed in Meron rocket attack". Ynetnews. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - "Long-range rocket lands near Jenin". Ynetnews. 2006-08-02.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Tal, Avraham (31 July 2006). "Justified, essential and timely". Haaretz. Retrieved 2006-08-14.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Hezbollah rockets kill 9 in Israeli city". Associated Press. 2006-07-16.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Hizballah Rockets". GlobalSecurity.org. 200630 July.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|accessed=ignored (help) - "Hizbullah: One of the rockets is a Ra'ad 1". Ynetnews. 2006-07-16.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "2 wounded in Hezbollah strike on Haifa". The News-Sentinel. 2006-07-17.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israel hammers at Lebanese infrastructure". The Associated Press. 2006-07-17.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Siegel-Itzkovich, Judy (2006). "Hizbollah rocket hits hospital" (Abstract). British Medical Journal. 333 (7561): 217-b-. doi:10.1136/bmj.333.7561.217-b. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - "Lebanese Hezbollah warns of rocket attacks at Tel Aviv if Beirut struck", People's Daily, 4 August 2005
- Template:He icon"Mabat", IBA, 3 August 2006
- Raved, Ahiya (4 August 2006). "For first time: Hizbullah targets Hadera area". Ynetnews. Retrieved 2006-08-15.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "24 soldiers killed in South Lebanon Saturday". Jerusalem Post. 2006-08-12.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Hezbollah downs Israeli helicopter". Al Jazeera. 2006-03-16.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Lebanon says Bush to press Israel to limit attacks". Reuters. 2006-07-14.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Lebanese PM demands ceasefire". ABC News. 2006-09-15.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Israeli strikes may boost Hezbollah base
- Civilian Deaths in Lebanon Provoke International Outcry, Israel Suspends Aerial Bombardment
- Israeli commandos raid Tyre, USATODAY.com
- "UN likely to cut request for Lebanon emergency aid". Reuters. 2006-07-23.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Lebanon: Key Facts - BBC News. "Attacks by air, land and sea targeted Lebanese cities, roads and infrastructure, killing about 1,100 civilians"
- "Lebanon says 1,000 dead or missing". Reuters. 2006-08-07.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Lebanon Reports 1,130 Dead". IsraelNationalNews. 2006-08-12.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "War wiped out 15 years of Lebanese recovery - UNDP". The Daily Star. 24 August 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-24.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Finer, Jonathan (8 August 2006). "Israeli Soldiers Find a Tenacious Foe in Hezbollah". Washington Post. p. A1. Retrieved 2006-08-23.
Israeli commanders say Hezbollah has obtained its sophisticated weaponry from its main backers, Syria and Iran… Hezbollah chooses to fight in and among civilian centers, making it difficult to target its fighters without killing bystanders.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Cody, Edward (5 August 2006). "Israeli Warplanes Hit Lebanon's Christian Areas". Washington Post. p. A12. Retrieved 2006-08-23.
An Israeli military spokesman, Capt. Jacob Dallal, said Israeli planes attacked a building in Qaa suspected of 'being used as a weapons depot of some sort'.…Israeli aircraft also hit Beirut's southern suburbs, at Ouzai near Beirut's international airport.…The targets were buildings with Hezbollah offices and other installations, they claimed.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help); Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - "Hizbullah attacks northern Israel and Israel's response". MFA. 2006-07-12.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Anxious northern Israel endures rocket fire". CNN.
{{cite news}}: Text "date2006-07-14" ignored (help) - "Hizbullah leader promises enemy 'more surprises'". Islamic Resistance Lebanon. 17 July 2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "UN: Security Council must adopt urgent measures to protect civilians in Israel-Lebanon conflict". Amnesty International.
- "Obligations under international humanitarian law of the parties to the conflict in Israel and Lebanon". Amnesty International. 26 July 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-15.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Deliberate destruction or "collateral damage"? Israeli attacks on civilian infrastructure". Amnesty International. 2006-08-23.
- http://www.hrw.org/english/docs/2006/10/18/lebano14412.htm
- "U.N.: Open Independent Inquiry into Civilian Deaths". Human Rights Watch. 2006-08-08.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israeli Cluster Munitions Hit Civilians in Lebanon". Human Rights Watch. 2006-07-24.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Lebanon: Hezbollah Rocket Attacks on Haifa Designed to Kill Civilians". Human Rights Watch. 18 July 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "UN warning on Mid-East war crimes". BBC News. 2006-07-20.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Might in the air will not defeat guerillas in this bitter conflict". The Times. 2006-06-02.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Verma, Sonia (August 5, 2006). "Hezbollah's deadly hold on heartland: Loved by many, accused by others of sacrificing civilians". CanWest Interactive. Retrieved 2006-08-07.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - http://www.ynetnews.com/articles/0,7340,L-3278026,00.html
- "ACRI calls for state inquiry into Lebanese civilian deaths". Association for Civil Rights in Israel. . Retrieved 2006-09-07.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "UN sounds Lebanon oil spill alarm". Al Jazeera. 2006-08-08.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Seattle Post-Intelligencer (September 10, 2006). "After the bombs, environmental calamity". Retrieved December 8, 2006.
- "Crisis talks on Lebanon oil spill". BBC News. 2006-08-16.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "'Damage is done' to Lebanon coast". BBC News. 2006-08-08.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Middle East crisis: Facts and figures". BBC News.
- "In pictures: Conflict enters fourth week: Picture 8: "Some Hezbollah rockets have started forest fires in Israel"". BBC News. 2006-08-02.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Kraft, Dina (8 August 2006). "Dry Forests in Northern Israel Are Damaged as Hezbollah's Rocket Attacks Ignite Fires". The Environment. New York Times. Retrieved 2006-08-08.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "More Press for JNF's Work in the North" (Press release). Jewish National Fund. 2006-08-09. Retrieved 2006-08-14.
- "Developments in Israel-Lebanon Crisis". Forbes. 07-13-06.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Office of the Press Secretary (2006-07-13). "President Bush and German Chancellor Merkel Participate in Press Availability". The White House. Retrieved 2006-07-15.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Interview with Federal Foreign Minister Steinmeier on the Middle East". German Foreign Office. 2006-07-13.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Reuters (2006-07-22). "US Rushes Precision-Guided Bombs to Israel". Reuters.
{{cite news}}:|author=has generic name (help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Arab League declares support for Lebanon, calls on UN to step in". Haaretz. 16 July 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Fattah, Hassan M. (17 July 2006). "Arab League criticizes Hezbollah for attacks". International Herald Tribune. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Press Association (28 July 2006). "Ads urge call for Lebanon ceasefire". The Guardian. Retrieved 2006-08-16.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Save the Lebanese Civilians Petition". E-petitions.net. 15 July 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-16.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Lebanon evacuation gathers pace". BBC News. 2006-07-18.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Hezbollah wants an unconditional ceasefire". CTV.ca. 2006-07-17.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israel sends instructions to Lebanon through Italy". Jerusalem Post. 2006-07-16.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "U.N.: Cease-fire begins Monday". CNN. 2006-08-12.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "U.N.: Cease-fire begins Monday". CNN. 12 August 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-13.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israel to halt pullout unless Lebanon army deploys". Reuters. 16 August 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-16.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Hizbullah's shallow victory". The Economist. 19 August 2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - http://www.denverpost.com/nationworld/ci_4180464
- Syria and Iran claim victory over West
- "With guns silent, wartime unity unravels in Israel". International Herald Tribune. 18/08/2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Israeli war protests echo 1973
- "Hizbullah's shallow victory". The Economist. 19 August 2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israeli MPs urge full war inquiry". BBC News. 2006-09-05. Retrieved 2006-09-06.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Hezbollah Leads Work to Rebuild, Gaining Stature". The New York Times. 16 August 2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Nasrallah sorry for scale of war". BBC News. 27 August2006. Retrieved 2006-08-27.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - http://multimedia.repubblica.it/home/425272?ref=hpmm
- http://haaretz.com/hasen/spages/766373.html
- http://edition.cnn.com/2006/WORLD/meast/09/22/lebanon.rally/
- Bassam, Laila (Sep 21, 2006). "Hizbollah backers gather for Lebanon "victory" rally". Reuters.
- http://edition.cnn.com/2006/WORLD/meast/09/22/lebanon.rally/
- "Olmert: Mistakes made in Lebanon war". United Press International. 14 August 2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israel army chief admits failures". 24 August 2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Stocks scandal spells doom of embattled Israeli army chief". Agence France-Presse. 16 August 2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Yoman", Israel Broadcasting Authority, 25 August 2006 Template:He icon
- "Hundreds support protesting reservists", Ynetnews, 24 August 2006
- "Olmert: An inquiry commission will not be formed, we do not have the luxury to submerge in investigating the past", Haaretz, 28 August 2006 Template:He icon
- "Mabat", Israel Broadcasting Authority, 28 August 2006 Template:He icon
- "Halutz disputes officer's remarks that Israel lost war". Haaretz. 2006-09-22.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Peretz backs Halutz on dismissal of Major General Yiftah Ron-Tal, Haaretz
- http://www.whitehouse.gov/news/releases/2006/08/20060814-3.html
- "Lebanon: UN peacekeepers lay out rules of engagement, including use of force". UN News Centre. 2006-10-03.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - West Asia war by numbers
- Bloomberg
- Between Victory and Defeat
- Lebanon's fragile unity shatters - Kuwaittimes.net
- Media Missiles
- "CNN RELIABLE SOURCES (transcript)". CNN. 2006-07-23.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Our very strange day with Hezbollah". CNN. 2006-07-23.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "CNN RELIABLE SOURCES, Coverage of Mideast Conflict". CNN. 2006-07-23.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Reuters withdraws all photos by Lebanese freelance, Reuters
- http://www.bbc.co.uk/blogs/theeditors/2006/08/trusting_photos.html
- http://blogs.usatoday.com/ondeadline/2006/08/reuters_adnan_h.html
- "IDF: Hours after cease-fire, 4 clashes between Hezbollah and Israeli troops; 4 Hezbollah fighters killed". CNN.com. 14 August 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-23.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "IDF: Israeli soldiers kill 3 Hezbollah fighters". CNN.com. 15 August 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-23.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Janelle, Chantelle (18 August 2006). "Israel flies over Lebanon, but no airstrikes". WIS-TV. Retrieved 2006-08-21.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Hurst, Stephen R. (15 August2006). "Rockets hit Lebanon despite cease-fire". Associated Press. Retrieved 2006-08-15.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Four Hezbollah fighters killed in ceasefire breaches: UN - Agence France-Presse (via Yahoo!). 16 August 2006
- ^ "Israel: Raid targets weapons transfer". CNN. 19 August 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-21.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israeli Commando Dies in Lebanon Raid". The Associated Press. 19 August 2006. Retrieved 2006-08-27.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Morales, Alex (20 August 2006). "Kofi Annan declares Israeli raid violation of ceasefire". CNN. Retrieved 2006-08-21.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "UN will not stop Syria sending weapons to Lebanon". The Daily Telegraph. 27 August 2006.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/5296314.stm
- http://news.yahoo.com/s/ap/20060831/ap_on_re_mi_ea/mideast
- Israel to lift Lebanon blockade
- Dakroub, Hussein (9 September 2006). "Israel ends naval blockade of Lebanon". Toronto Star/AP. Retrieved 2006-09-09.
- Ynet report, Yahoo news, Haaretz report
- We still have 20,000 rockets, says Nasrallah, The Guardian
- AFP - Israel pulls remaining troops out of Lebanon
- UN peacekeepers: Israeli troops still in Lebanon, CNN
- http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/middle_east/5396966.stm
- Israel violates Lebanese airspace, launches mock raids
- Israeli warplanes violate Lebanese airspace again
- "Israel To Continue Lebanon Overflights". All Headline News. October 4, 2006. Retrieved 2006-10-06.
- [http://english.aljazeera.net/NR/exeres/9491C6CD-868E-4780-9C5F-EFCDFC5DA6C8.htm
- http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/middle_east/6075408.stm
- "Israel jets fly over Lebanon despite French appeal". Reuters. 2006-10-23. Retrieved 25 October.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help); Unknown parameter|accessyear=ignored (|access-date=suggested) (help) - Israel continues overflights of Lebanon. Al Jazeera
- France calls IAF overflights in Lebanon 'extremely dangerous', Haaretz.
- "Germany, Israel confirm naval vessel-planes incident". Telugu Portal. 200628 October.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Germany, Israel confirm naval vessel-planes incident". Middle East News. 200628 October.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - "Israel denies firing shots at German ship". Ynetnews. 200628 October.
{{cite news}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - Israeli jets fly low over Beirut, BBC
- Israeli warplanes fly low over Beirut, suburbs, Reuters
- IDF checking French claim its UN troops almost fired at IAF jets, AP in Haaretz
- Annan: Israel's actions compromise efforts to stabilize the Israeli-Lebanon border
External links
International organizations
- United Nations Interim Forces In Lebanon, including deployment maps
- The International Committee of the Red Cross in Lebanon
- US Humanitarian Assistance to Lebanon
International media
- CNN - Crisis in the Middle East
- BBC News - Middle East Crisis in depth
- JURIST - Legal news and resources on the Middle East conflict
- MOSAIC - World news from the Middle East
- ABC News - The Middle East Conflict
- CTV News - Mideast Crisis
- New York Times - Interactive map
Israeli media
Lebanese media
Hezbollah media
Category: