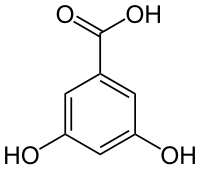
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 3,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid | |
| Other names α-Resorcylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.482 |
| EC Number |
|
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C7H6O4 |
| Molar mass | 154.121 g·mol |
| Melting point | 235.3 °C (455.5 °F; 508.4 K) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.04 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms | 
|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H315, H319, H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds | Gallic acid; 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid; Phloroglucinol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
3,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid (α-resorcylic acid) is a dihydroxybenzoic acid. It is a colorless solid.
Preparation and occurrence
It is prepared by disulfonation of benzoic acid followed by hydrolysis of the disulfonate.
It is a metabolite of alkylresorcinols, first identified in human urine and can be quantified in urine and plasma, and may be an alternative, equivalent biomarker of whole grain wheat intake.
References
- Haynes, p. 5.91
- Haynes, p. 3.190
- Weston, Arthur W.; Suter, C. M. (1941). "3,5-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid". Org. Synth. 21: 27. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.021.0027.
- Ross, A. B.; Åman, P.; Kamal-Eldin, A. (2004). "Identification of cereal alkylresorcinol metabolites in human urine—potential biomarkers of wholegrain wheat and rye intake". Journal of Chromatography B. 809 (1): 125–130. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2004.06.015. PMID 15282102.
- Koskela, A.; Linko-Parvinen, A. -M.; Hiisivuori, P.; Samaletdin, A.; Kamal-Eldin, A.; Tikkanen, M. J.; Adlercreutz, H. (2007). "Quantification of Alkylresorcinol Metabolites in Urine by HPLC with Coulometric Electrode Array Detection". Clinical Chemistry. 53 (7): 1380–1383. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2006.084764. PMID 17495018.
- Koskela, A.; Samaletdin, A.; Aubertin-Leheudre, M. N.; Adlercreutz, H. (2008). "Quantification of Alkylresorcinol Metabolites in Plasma by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Coulometric Electrode Array Detection". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 56 (17): 7678–7681. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.533.1473. doi:10.1021/jf801252s. PMID 18690683.
- Aubertin-Leheudre, M.; Koskela, A.; Marjamaa, A.; Adlercreutz, H. (2008). "Plasma Alkylresorcinols and Urinary Alkylresorcinol Metabolites as Biomarkers of Cereal Fiber Intake in Finnish Women". Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention. 17 (9): 2244–2248. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-08-0215. PMID 18768490.
Cited sources
- Haynes, William M., ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. ISBN 9781498754293.
| Phenolic acids (C6-C1) and their glycosides | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monohydroxybenzoic acids |
| ||||
| Dihydroxybenzoic acids |
| ||||
| Trihydroxybenzoic acids |
| ||||
This article about an aromatic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |