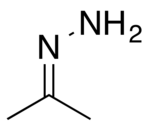
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Propan-2-ylidenehydrazine | |
| Other names Isopropylidenehydrazine | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C3H8N2 |
| Molar mass | 72.111 g·mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |     
|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H226, H301, H311, H314, H331, H351, H411 |
| Precautionary statements | P203, P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+P316, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P302+P361+P354, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P354+P338, P316, P318, P321, P330, P361+P364, P363, P370+P378, P391, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, P501 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Acetone hydrazone (isopropylidenehydrazine) is the product of condensation of acetone and hydrazine, as typical for hydrazone formation. It is an intermediate in the synthesis of 2-diazopropane [fr].
Acetone hydrazone can be produced on large scale by reaction of acetone azine with hydrazine, a more convenient reaction than direct reaction of acetone and hydrazine. Likewise, it is susceptible to disproportionation to revert to acetone azine and hydrazine, especially in the presence of water.
The chemical is one of the metabolic products of the antihypertensive pharmaceutical hydralazine, and itself also have antihypertensive effects.
References
- "Acetone hydrazone". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- Andrews, S. D.; Day, A. C.; Raymond, P.; Whiting, M. C. (1970). "2-Diazopropane". Organic Syntheses: 27; Collected Volumes, vol. 6, 1988, p. 392.
- ^ Day, A. C.; Whiting, M. C. "Acetone Hydrazone". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 6, p. 10.
- Cohn JN, McInnes GT, Shepherd AM (2011). "Direct-acting vasodilators". Journal of Clinical Hypertension. 13 (9): 690–692. doi:10.1111/j.1751-7176.2011.00507.x. PMC 8108999. PMID 21896152.
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |

