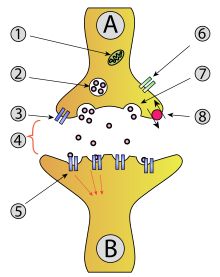
An amino acid neurotransmitter is an amino acid which is able to transmit a nerve message across a synapse. Neurotransmitters (chemicals) are packaged into vesicles that cluster beneath the axon terminal membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse in a process called endocytosis.
Amino acid neurotransmitter release (exocytosis) is dependent upon calcium Ca and is a presynaptic response.
Types
Excitatory amino acids (EAA) will activate post-synaptic cells. inhibitory amino acids (IAA) depress the activity of post-synaptic cells.
| Amino acid | Excitatory or inhibitory |
|---|---|
| Aspartic acid | Excitatory |
| β-alanine | Inhibitory |
| Cysteine | Excitatory |
| GABA (adult human brain) | Inhibitory (adult); excitatory (developing) |
| Glycine | Inhibitory |
| Glutamic acid | Excitatory |
| Homocysteine | Excitatory |
| Taurine | Inhibitory |
See also
References
- "Axon Terminal : on Medical Dictionary Online". Archived from the original on 14 January 2009. Retrieved 2008-12-25.
- ^ D'haenen, Hugo; den Boer, Johan A. (2002). Biological Psychiatry (digitised online by Google books). Paul Willner. John Wiley and Sons. p. 415. ISBN 978-0-471-49198-9. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
- Dalangin, R; Kim, A; Campbell, RE (27 August 2020). "The Role of Amino Acids in Neurotransmission and Fluorescent Tools for Their Detection". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 21 (17): 6197. doi:10.3390/ijms21176197. PMC 7503967. PMID 32867295.
- Foye, William O.; Lemke, Thomas L. (2007). Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. David A. Williams. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 446. ISBN 978-0-7817-6879-5.
| Neurotransmitters | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino acid-derived |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lipid-derived |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nucleobase-derived |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitamin-derived | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Miscellaneous |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Encoded (proteinogenic) amino acids | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General topics |  | ||||||||||
| By properties |
| ||||||||||
| Cell signaling / Signal transduction | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signaling pathways | |||||||||||||
| Agents |
| ||||||||||||
| By distance | |||||||||||||
| Other concepts | |||||||||||||
| Neurotransmitter systems | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetylcholine | |||||||||
| BA/M |
| ||||||||
| AA |
| ||||||||