| Amphibious Training Base Morro Bay | |
|---|---|
| Part of US Navy | |
| Morro Bay, California, U.S. | |
 Amphibious Training Base Morro Bay, U.S. Army Signal Corps training in 1943 Amphibious Training Base Morro Bay, U.S. Army Signal Corps training in 1943 | |
| Coordinates | 35°22′19″N 120°51′25″W / 35.37194°N 120.85694°W / 35.37194; -120.85694 |
| Type | Military training base |
| Site information | |
| Owner | |
| Controlled by | |
| Site history | |
| Built | 1941 |
| In use | 1941–1945 |
| Fate | Closed in 31 October 1945 |
| Demolished | 1947 |
| Events | Amphibious Training for World War II |

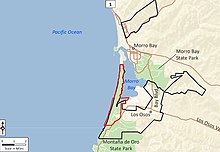
Amphibious Training Base Morro Bay also called Camp Morro Bay and Morro Bay Section Base was a US Navy training base for amphibious beach assault during World War II. The base opened in 1941 to train troops for the Pacific theater of operations' island leapfrogging using landing craft and LCVP. The base was located in Morro Bay, California in San Luis Obispo County. The base was on 250 acres (100 ha) of leased land. Ships for the base were based at the Avila's Port San Luis in San Luis Bay. Which was also leased with the yacht club and its warehouse. Added to the leased land was: two piers, mess hall, gallon water storage tanks, roads, buildings, garages, and ammo storage area. The Navy also extended the bay's breakwater. A wooden trestle bridge was built to get to the nearby sandspit (now Morro Bay State Park), the bridge was removed in 1946 and some pillars still remain. The near Estero Bay was the site of training assault also, by the Navy, US Army, US Marine Corps and United States Coast Guard also taking over the unused vacation hotel there. Nearby United States Army Air Corps fields had fighter aircraft fire flour shot to make the training more real. Up to 175 landing craft were at the base and 16,000 troops a day trained. In the base and in nearby Los Osos and Baywood live fire bombing, machine gun, bazookas, and flamethrowers were used for training. The training ended on 31 October 1945 and the site is now a Duke Energy power plant built in 1955, site of three large smoke stacks. North of the former base in the notable Morro Rock. Avila Beach was also a Union Oil plant with many oil storage tanks, use for Navy ships.
Baywood Park Training Area
Baywood Park Training Area opened in July 1943 as a branch of the Camp San Luis Obispo and Amphibious Training Base Morro Bay. The site was on 8,810 acres (3,570 ha) of leased land. The site is in the current town of Baywood-Los Osos, California and the Morro Bay State Park. The lease ended in 1947.




See also
- California during World War II
- Camp San Luis Obispo
- NAAS Monterey, a supporting airfield
- NAS Alameda, a supporting airfield
- Naval Auxiliary Air Station, San Luis Obispo, the main supporting airfield
- SS Montebello, a tanker that was sunk after departing the base by Japanese submarine I-21
References
- Historic Posts, Camps, Stations and Air Fields: Amphibious Training Base, Morro Bay (Morro Bay Section Base, Camp Morro Bay)
- The Morro Bay Amphibious Training Base, 1941-1947
- South Pacific Army/Navy WWII amphibian landing craft Morro Bay training base, By Tom Wilmer, 18 Aug 2017
- By Tom Wilmer, WWII Morro Bay Amphib training base 30 May 2018
- Harbor Development During World War Two, THE SUN, 5 December 1941--June4, 1943
- San Luis Yacht Club 1941 - 1945
- World War 2 collection, 7 March 1944
- sanluisobispo.com Amphibious Training Base Morro Bay
- pasoroblesdailynews.com Amphibious Training Base Morro Bay
- US Army Baywood Park Training Area
- US Army Baywood Park Training Area, FUDS
| Operational military installations in California | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Army |
|  | |||||||||||||
| Marines |
| ||||||||||||||
| Navy |
| ||||||||||||||
| Air Force |
| ||||||||||||||
| Space Force |
| ||||||||||||||
| National Guard |
| ||||||||||||||
| Coast Guard |
| ||||||||||||||
| State of California | |
|---|---|
| Sacramento (capital) | |
| Topics | |
| Regions |
|
| Metro regions | |
| Counties |
|
| Most populous cities | |
| States |
|   |
|---|---|---|
| Federal district and territories |
| |
| Leadership |  | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structure |
| ||||||||||
| Personnel and training |
| ||||||||||
| Equipment | |||||||||||
| History and traditions |
| ||||||||||
| United States Armed Forces | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||
| Leadership |
| ||||||||||||
| Components |
| ||||||||||||
| Structure | |||||||||||||
| Operations and history |
| ||||||||||||
| Personnel |
| ||||||||||||
| Equipment |
| ||||||||||||
| United States naval ship classes of World War II | |
|---|---|
| Aircraft carriers | |
| Light aircraft carriers | |
| Escort carriers | |
| Battleships | |
| Large cruisers | |
| Heavy cruisers | |
| Light cruisers | |
| Gunboats | |
| Destroyers | |
| Destroyer escorts | |
| Patrol frigates | |
| Patrol boats | |
| Minelayers | |
| Minesweepers | |
| Submarines | |
| Tankers | |
| Cargo ships | |
| Auxiliary ships | |
| |
