Place in Johor, Malaysia
| Muar Bandar Maharani | |
|---|---|
| Municipality, royal capital and district capital | |
| Bandar Maharani, The Royal Town Bandar Maharani Bandar Diraja بندر مهراني بندر دراج | |
| Other transcription(s) | |
| • Jawi | موار |
| • Chinese | 麻坡 Mápō (Hanyu Pinyin) |
| • Tamil | மூவார் Mūvār (Transliteration) |
    Clockwise from top: Muar Clock Tower, colonial-era shophouse, Sultan Ismail Bridge, Sultan Ibrahim Jamek Mosque. Clockwise from top: Muar Clock Tower, colonial-era shophouse, Sultan Ismail Bridge, Sultan Ibrahim Jamek Mosque. | |
 Flag Flag Coat of arms Coat of arms | |
| Motto(s): "Cekap Amanah Dinamik Makmur" (in Malay) "Efficient Trustworthy Dynamic Prosperous" | |
| Location of Muar in Johor | |
    | |
| Coordinates: 2°3′00″N 102°34′00″E / 2.05000°N 102.56667°E / 2.05000; 102.56667 | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Districts | Muar District |
| Township | 1885 |
| Municipality | 2001 |
| Government | |
| • Type | Municipal council |
| • Body | Muar Municipal Council |
| • President | Jamil Hasni Abdullah |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,376 km (531 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 36.88 m (121 ft) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 314,776 |
| • Density | 230/km (590/sq mi) |
| • Demonym | Muarian |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (MST) |
| • Summer (DST) | Not observed |
| Postal code | 84000 |
| National calling code | 06-95xxxxx to 06-98xxxxx |
| License plate prefix | Jxx |
| Website | www www |
Muar (Muarian dialect: Muo; Jawi: موار) or Bandar Maharani, is a historical town and the capital of Muar District, Johor, Malaysia. It is one of the most popular tourist attractions in Malaysia to be visited and explored for its food, coffee and historical prewar buildings. It was recently declared as the royal town of Johor by Sultan Ibrahim Sultan Iskandar and is the fourth largest urban area (after Johor Bahru, Batu Pahat and Kluang) in Johor. It is the main and biggest town of the bigger entity region or area of the same name, Muar which is sub-divided into the Muar district and the new Tangkak district, which was upgraded into a full-fledged district from the Tangkak sub-district earlier. Muar district as the only district covering the whole area formerly borders Malacca in the northern part. Upon the upgrading of Tangkak (formerly Ledang) district, the Muar district now covers only the area south of Sungai Muar, whilst the northern area beyond the river is in within Tangkak district. However, both divided administrative districts are still collectively and fondly called and referred to as the region or area of Muar as a whole by their residents and outsiders. Currently, the new township of Muar is located in the Bakri area.
Muar is one of the cleanest cities in South East Asia, being awarded with Asean Clean Tourist City Standard Award 2017 and 2022.
Etymology
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (April 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Muar also known as Bandar Maharani is said to have had other names earlier and the name itself Muar is believed to have originated and derived from its geographical location at the mouth or estuary of Muar River as the following different version of theories:
- Teluk Dalam: Muar was formerly known as Teluk Dalam meaning "deep bay" due to its location at the estuary or the structure of the mouth of the Muar River which is wide open and deep; based on a sentence in one part of Hikayat Malim Deman; as in :
- Muar belum bernama Muar, Muar bernama Teluk Dalam. (Muar has not been named Muar, Muar is called Teluk Dalam)
- Muara: Muar name is said to be the summary for this old Malay word Muara meaning "the wide open estuary".
- Muak: Means "bored" or "tired" in paddling the boat travelling along the river which is large and curvy by the local people in the early days. The people started calling the river and place Muar deriving from the word Muak after a long time since then.
- Bukit Mor: There is also a hill not far from the Muar near Parit Jawa in the south of the "Padang" area called Mor Hill or Bukit Mor which may be the origin of the name of Muar.
- Bandar Maharani: Modern Muar Town was officially opened and conferred Bandar Maharani title by Maharaja Abu Bakar translated as the Town of Empress the namesake of Maharani Fatimah who also graced the grand inauguration ceremony of the new town on 12 August 1887, to symbolically representing and recognising the prominence status of Muar as the second important and biggest town and district of the state of Johor after Johor Bahru the capital city in those days.
There a few old historic legends which evolved around the area of Muar namely, Hikayat Malim Deman (Epic of Malim Deman), Legenda Lembing Awang Pulang Ke Dayang (Awang's Spear Return to Dayang Legend) and Legenda Puteri Gunung Ledang (Mount Ledang Princess' Legend).
History

Muar is rich in history as mentioned in many historical records and archaeological works. It is believed that the history of Muar started much earlier than the establishment of the Sultanate of Malacca. There were many accounts recorded about the early history of Muar. In 1361, it was claimed that Muar was a part of the Majapahit empire. Another account also stated that Parameswara, upon his exile from Temasik before proceeding to found Melaka, had established some settlements at Kota Buruk, Pagoh, Ulu Muar and Muar before reaching the place that would become Malacca. Historically, Muar was also where the deposed heir of the Malacca Sultanate escaped to in 1511 following the Portuguese invasion launched from Goa by Afonso de Albuquerque. Muar played a role in resisting the Portuguese occupation of Malacca; the Kubu Bentayan fort was built by Sultan Mahmud Shah to repel seaborne invasions, before he was defeated and retreated further to Pagoh, this time witnessing the fall of his empire.
The Portuguese occupied Muar after that and built a fortress named Fortaleza de Muar to defend the colony against the attack of Dutch and Aceh instead at the same strategic site of Bentayan. The colonial British did just about the same thing at the Muar River site near Bentayan in defence against the advance of Japanese Imperial Army in the Battle of Muar in World War II. Muar is also the home for the one and only tomb of the seventh Malacca Sultanate, Sultan Alauddin Riayat Shah I (1477–1488). During the time of the beginning of Bugis immigration from Sulawesi Indonesia and their influence in Johor Sultanate, the five Bugis pioneer prince-brothers sea-warriors or rather pirates from Sulawesi, Indonesia; Daeng Marewah, Daeng Parani, Daeng Celak, Daeng Manambun and Daeng Kemasi said to have come to reside in Liang Batu, Lenga, Muar before they and their descendants become the influential Temenggungs and even rulers later.
Muar, the Bandar Maharani, have been recorded by several historians, scholars and authors and in many important historical materials like old maps, poems, epics, manuscripts and books :
- Prapanca (1361) (Nagarakertagama Poem) :Nagarakertagama poem – written in 1361 Prapanca (a Buddhist monk and priest of Majapahit Palace) told Muar as a colony part of Majapahit empire subdued by Hayam Wuruk and prime minister, Gajah Mada(1350 to 1389).
- João de Barros ("Decades of Asia"), (1553) :João de Barros who wrote in 1553 in his second Décadas da Ásia ("Decades of Asia"), a history of the Portuguese in India and Asia.stated that Parameswara (Paramicura) who were driven away from Temasik after he killed the representative of the King of Siam, Temagi; had escaped in exile and stopped in Muar and built a in rural areas of Muar called Pagoh.
- Tun Sri Lanang (Malay Annals) Shellabear version :In the Malay Annals states that Temasik during the reign of Parameswara (Sultan Iskandar Shah) was defeated by Majapahit Kingdom. But he and his family including his followers had fled to Pagoh, Muar and opened 2 areas on the banks of the Muar River; the Biawak Busuk and another fort called Kota Buruk before moved to Melaka and opened up Melaka. In 1488, the incident of Malacca's Sultan Alauddin Riayat Shah I (1477–1488) who has died and buried in Pagoh, Ulu Muar during a visit, called "Sultan Mangkat Di Muar".
- Tomé Pires (the Suma Oriental) (1512–1515) :Tomé Pires wrote a landmark book on Asian trade, the Suma Oriental que trata do Mar Roxo até aos Chins (Summa of the East, from the Red Sea up to the Chinese) in Malacca and India between 1512 and 1515, completed before the death of Afonso de Albuquerque (December 1515), which highlighted the emergence of Parameswara replacing his father, Raja Sam Agi as the ruler of Palembang and later attacked by the king of Majapahit of Java, King Batara Tamavill for declaring himself as 'Mjeura' (those who dare) before fled to Temasik(Singapore)where he killed Siamese King of Ayutthaya's representative, Temagi and he secretly ruled Temasik for 5 years. But fearing the revenge attack by the King of Ayutthaya, he fled to Pagoh, Muar with his 1,000 followers and lived there for 6 years when the Seletar peoples were still occupying Malacca before he moved to Malacca and opened it later.
- An old Portuguese map shows that Muar had a second Portuguese fort in the Peninsular Malaysia beside Malacca. From the map, it was named Fortaleza de Muar built in 1604 by Emanuel Godinho de Erédia in triangular shape to defend the colony against attacks from the Dutch and Aceh, at the mouth of Bentayan River near the Muar River. It fort has since vanished but it is believed to be located at the present location of Bentayan Express Bus' Station (formerly Pagoh Bus Stand) in Jalan Maharani, Muar.
- Abraham Ortelius (1584) (Old Maps) :Old maps such as Map Ortelius A.D. 1584 shows Muar as a city located to the south of Malacca.
- Jan Huyghen van Linschoten (1595) (Old Maps) :Map Linschoten A.D. 1595 shows Muar as a city close to the state of Malacca.
Sultan Ali's Rule of Muar: Muar was the royal town of northern Johor once. A civil war between the prince of Sultan Hussein Shah; Tengku Ali dan Dato' Temenggong Daeng Ibrahim which was later settled by a treaty of agreement and understanding signed in Singapore between the British and Tengku Ali; that ceded the control of the rest of state of Johor (except Muar region) formally to Temenggong Ibrahim in returns of the sultan title with the condition the title is not hereditary for succession, and recognition of him as Sultan Ali and his reign ruled over the Muar region (state) of the area lies between the Muar River and Kesang River with an annual pension from the British Government under the terms of the treaty. Although Sultan Ali was in fact the real heir of the Johor Sultanate but due to his weakness, the Temenggong became the de facto ruler instead and begin the rule of the Temenggung in Johor onwards. Sultan Ali delegated the administrative affairs of Muar to the Raja Temenggung of Muar (also known by the title of Temenggong Paduka Tuan of Muar) and rather spent most of his time in Malacca. Muar was sparsely populated in 1855 and had a population of 800 and no formal structure of government was formed. In 1860, Sultan Ali reportedly borrowed $53,600 from a Chettiar money lender, Kavana Chana Shellapah and signed an agreement with Shellapah to contribute a portion of his monthly allowance to repay his debt. However, Sultan Ali found himself unable to pay settle his debts in time, and an angry Shellapah wrote to the British government in 1866. Pressured to liquidate his debts in time, Sultan Ali granted Shellapah the right to trade off Muar to the Raja Temenggung of Muar|Temenggong of Johor as mortgage if he is unable to pay off his debts in time. His relations with Temenggong Daeng Ibrahim remained strained; in 1860, Sultan Ali allowed a Bugis adventurer, Suliwatang, the chiefs of Rembau and Sungei Ujong to settle in Muar and prepare themselves for an attack on Johor. Such bad blood between the Sultan Ali and Temenggong Daeng Ibrahim passed down to the Temenggong's son, Temenggong Abu Bakar, who succeeded his father after the former died in 1862. Shortly after Temenggong Abu Bakar became the Temenggong of Johor, he sent a letter to Sultan Ali to reassert of Johor's sovereignty over Segamat. Continued disputes over the sovereignty of Segamat led to an outbreak of a war between the Temenggong's men with the Sultan's. Eleven years later in 1873, attempts made by Suliwatang to collect custom taxes from inhabitants at the Muar estuary led to further conflict with Temenggong Abu Bakar's (who became Maharaja in 1868 and finally Sultan later in 1885, 8 years after death of Sultan Ali) men.
Upon Sultan Ali's death in Umbai, Malacca in 1877, his 11-year-old youngest son, Tengku Mahmood, was named his successor, fuelling anger and dissatisfaction of his oldest son, Tengku Alam Shah. The Raja Temenggung of Muar (also known by the title of Temenggong Paduka Tuan of Muar) and its village chieftains voted in favour of a merger of Muar with Johor following the succession dispute between the two of Sultan Ali's sons. Tengku Alam Shah, disputed the legitimacy of the chieftains' wishes and staked his hereditary claims over Muar, started to instigate and launch the 1879 Jementah Civil War in a bid to reclaim Muar, but was quickly defeated by the Maharaja Abu Bakar's forces and Muar was finally annexed and return as part of the Johor state on 30 December 1879.
During the 1880s, the sovereign rulers of Johor, Temenggong Ibrahim and his successor, Sultan Abu Bakar introduced the Kangchu system and actively encouraged the Chinese leaders to set up new gambier and black pepper plantations and to bring in the Chinese immigrants as agricultural settlers and labourers to open and work in these plantations in Muar. A Western-style contracts (termed as Surat Sungai in Malay, literally "River Documents") to the Kapitan Cina (Chinese leaders) who have established the plantations along river banks in Johor. Letters of authority (Surat Kuasa) were issued when the first Chinese leaders began settling in Johor during the 1850s. The Temenggong quickly established goodwill relations with the Kapitan Cina by appointing one Malay administrator, Muhamad Salleh bin Perang, the Dato' Bentara Luar who was able to speak the Teochew dialect, the language spoken by most Kapitan Cina and settlers and able to read Chinese for these purposes. Influx of these settlers mainly of Teochew origin, and were generally first- or second-generation ethnic Chinese who became an important part and parcel of life and population of Muar until today and helped shape the population demographic and the social economy of Muar. There is even a town called Bukit Gambir meaning Hill of Gambier in Muar.
Modern Muar Town, known as Bandar Maharani, which is the main city center of Muar district, was founded by Dato' Bentara Luar, Muhamad Salleh bin Perang in 1885 and was only officially opened by His Majesty Maharaja Abu Bakar 12 August 1887 (who just became opted Maharaja title on 30 June 1868) and conferred the namesake Bandar Maharani meaning the Town of Empress, the title of Maharani Fatimah who had accompanied to graced the inauguration ceremony of the new town at Tangga Batu a place around Hentian Maharani bus station now where an auspicious "amulet" or "azimat" is said to be buried underground there then. Muar celebrated its centenary in a grand celebration attended by the Sultan of Johor in 1984.
The prosperity and rapid development of Muar made it the only town in Malaysia ever to have had its own local railway network in the early days. The Muar State Railway (MSR) operated from 1889 to 1925, linking Jalan Sulaiman in Bandar Maharani and Sungai Pulai for a distance of 22.5 km. A 1916 plan to extend the line to Batu Pahat was aborted and the service totally stopped in 1925 due to financial and geographical constraints and its reduced importance after the construction of Jalan Abdul Rahman linking the Muar town and Parit Jawa. It remains a memory and is only a part of history of Muar now with just the MSR steam locomotive relic on display at Tanjung Emas Park.

In World War II, the Battle of Muar, 14–22 January 1942, fought around the area from Gemencheh, Muar River and Bukit Bakri in Muar was the last major battle of the Malayan Campaign of the Battle of Malaya, fought by British Allied forces and Japanese forces from 8 December 1941 – 31 January 1942 in British Malaya. The Battle of Bakri or Siege of Bakri was a fierce battle of the fighting troops in Bukit Bakri on 17 January 1942. The battle resulted in the near-annihilation of the Allies' deployed 45th Indian Infantry Brigade, with heavy casualties for its two attached Australian's 2/19th and 2/29th Infantry Battalions and the eventual fall of Muar to the Imperial Japanese forces. During the 1942–45 Japanese occupation of Malaya era, Muar continued to serve as important administration town under the occupying Japanese army with many locals involved in the bulk of anti-Japanese resistance groups such as the Malayan People's Anti-Japanese Army (MPAJA) and Force 136.
During the Malayan Emergency period, in the Bukit Kepong Incident, the police station of Bukit Kepong was ambushed and brutally attacked by members of the Malayan National Liberation Army (MNLA), the military arm of the Malayan Communist Party, on 23 February 1950 killing 26 policemen and family members.
Muar also recorded the history of resistance against the communist attacks and British occupation by Panglima Kiyai Salleh, a religious and martial arts teacher of Banjarese & Javanese origin who founded the resistance guerillas troop Tentera Selempang Merah. The Group of Seven or Orang Tujuh of Muar which consists of Tun Dr Awang Hassan (the former Governor of Penang), father of Tun Dr Ismail Dato Abdul Rahman Mohd Yasin (father of Tun Dr Ismail former Deputy Prime Minister), his brother Datuk Sulaiman Abdul Rahman, Tan Sri Datuk Hassan (former Menteri Besar) and Dato Hj Kosai Mohd Salleh was said to be active fighting the formation of Malayan Union and advocating the independence of Malaya. Muar was declared a municipality in 2001 with the declaration of Muar Municipal Council.
Geography

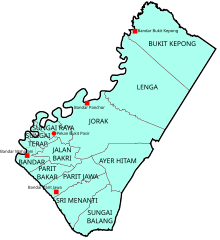
Muar district formerly covers 2346.12 km, with a population of 328,695 (2000). The town of Muar is located at the mouth of Muar River.
The flat terrain of Muar's geographical ground and areas has enable the extensive use of bicycle and tricycle vehicles as the main and major mode of transportation in Muar in the early days. This believe to be the main factor and reason Muar was once the town with the most bicycles and the only town that requires valid license issued by the town council to own and use a bicycle in the country.
Climate
Muar, like the rest of peninsular Malaysia, enjoys a year-round equatorial climate which is warm and sunny, along with plentiful rainfall, especially during the southwest monsoon from April to September. The climate is very much dictated by the adjacent sea and the wind system. In the 2006/2007 floods, unusually heavy rainfall in the states of Johor and Melaka resulted in the worst flooding in southern Peninsular Malaysia in history. Muar was not spared from this dreadful disaster which lasted almost a month. Many areas of Muar such as Pagoh, Lenga, Kundang Ulu, Bukit Gambir and Sawah Ring were seriously flooded with some areas up to 10 feet (3.0 m). About 22,933 people were evacuated to relief centres
| Climate data for Muar | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 32.1 (89.8) |
32.5 (90.5) |
32.6 (90.7) |
32.7 (90.9) |
32.7 (90.9) |
32.4 (90.3) |
32.2 (90.0) |
32.2 (90.0) |
32.2 (90.0) |
32.2 (90.0) |
31.5 (88.7) |
32.2 (90.0) |
32.3 (90.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 26.8 (80.2) |
27.1 (80.8) |
27.1 (80.8) |
27.3 (81.1) |
27.2 (81.0) |
26.9 (80.4) |
26.8 (80.2) |
26.8 (80.2) |
26.8 (80.2) |
26.9 (80.4) |
26.6 (79.9) |
26.8 (80.2) |
26.9 (80.5) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 21.5 (70.7) |
21.7 (71.1) |
21.7 (71.1) |
21.9 (71.4) |
21.7 (71.1) |
21.5 (70.7) |
21.4 (70.5) |
21.5 (70.7) |
21.5 (70.7) |
21.7 (71.1) |
21.7 (71.1) |
21.4 (70.5) |
21.6 (70.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 140 (5.5) |
112 (4.4) |
174 (6.9) |
217 (8.5) |
205 (8.1) |
219 (8.6) |
216 (8.5) |
226 (8.9) |
201 (7.9) |
238 (9.4) |
224 (8.8) |
166 (6.5) |
2,338 (92) |
| Source: Climate-Data.org | |||||||||||||
Demographics
In year 2010, the estimated population of Muar district was 239,027 people. The majority of the Muar's population is of 55.9% Bumiputera (55.3% Malays), 35.7% Chinese descent, 2.4% Indian and others 0.2%.
The city's age distribution (as of 2010):
- 26.6% under 15
- 65.2% from 15 to 64
- 8.2% 65 or older
Administration


Muar District was formerly divided administratively into Muar (Bandar Maharani) municipality and Tangkak township. Upon upgrade of Tangkak sub-district to full-fledged Tangkak district, Bandar Maharani of Muar is now administered by Muar Municipal Council (formerly South Muar Town Council, later Muar Town Council) under the Muar District Office, while Tangkak is administered by Tangkak Town Council (formerly North Muar Town Council) under the Tangkak District Office.
A new administration hub and transportation hub integrated with bus terminal and market called Maharani Sentral are being planned to be built at the location near Muar Bypass in between Jalan Haji Kosai and Jalan Temenggung.
Transportation

Car
Besides federal roads such as Federal Route 5 that runs through Muar town centre, Muar is also accessible via the PLUS Expressway through the Tangkak (EXIT 235), Bukit Gambir (EXIT 236), Pagoh (EXIT 238) and Yong Peng (EXIT 241) interchange exits.
Access to Segamat, the closest railway station to Muar, is possible using Federal Route 23.
Sultan Ismail Bridge, the first bridge across the Muar River is the landmark of the town, built in 1960 and completed in 1962 to replace old ferry services in the 1960s.
The new Muar Second Bridge connecting Parit Bunga at the north and Sabak Awor at the south across the river is part of the 13 km Muar Bypass (highway Federal Route 224) that was completed in 2005. The bridge is the latest landmark of the town. The highway that traverses through the outskirts of the town has ease the journey by diverting the traffic from downtown Muar.
Muar with status as an important trading and administrative town in the state of Johor for both the colonial British and the old Johor Sultanate in the early days has contributed in shaping the landscape of the town.
Public transportation

The state railway KTMB does not serve Muar or its environs; instead the closest station is in Segamat. Train services to the state capital Johor Bahru as well as Kuala Lumpur, Ipoh, Seremban or Tumpat in Kelantan are available.
There are also express bus coaches to all the nearby towns and the major cities of Malaysia including Kuala Lumpur, Johor Bahru, Melaka City, Kuantan, Ipoh, George Town etc. and also Singapore and Hat Yai (south Thailand). There are two bus stations in Muar; Hentian Maharani Bus Station and Bentayan Express Bus Station (formerly Pagoh Bus Station).
Ferry services to Dumai, Sumatra, Indonesia is also available on regular basis, departing from the Custom Jetty. Muar is the only district (besides the state capital Johor Bahru) in Johor that has its own Custom and Excise Duty Department office and checkpoint at its own jetty.
By air, the nearest airport is arguably the Batu Berendam airport (IATA: MKZ, ICAO: WMKM) in Malacca. The Senai Airport (IATA: JHB) is further away, being closer to Johor Bahru than Muar.
Traveling in town easily can be done by walking, or by taking a trishaw, public bus and taxi.
Economy

Muar is internationally well known as the hub of the furniture industry of Malaysia. Industrial estates within Muar district are located at Tanjung Agas, Bukit Bakri, Jorak, Parit Bakar, Pagoh and Tangkak. There are notably three big factories of multinational companies, i.e. STMicroelectronics, Micron Technology and Pioneer Corporation at Tanjung Agas. The town is robust of business and trading activities, with many old traditional Chinese shops offering variety of products at reasonable and attractive prices.
Muar agriculture is mainly made up of the major crops of rubber and oil palm beside some coconut, cocoa, fruits (durian, rambutan, duku, mangosteen, banana, papaya, pineapple, dragon fruit etc.), vegetables and livestock, poultry and fish farming. Fishing is the major economy of some fishing villages like Parit Jawa, Parit Raja, Parit Tiram, and Kesang. There are many cafes that are being open in Muar around the Bakri area to attract tourists and for local enjoyment.
Education
Muar High School (Sekolah Tinggi Muar)(麻坡高级中学) began as a Government English School and it was first housed in an attap (the processed leaves of nypa fruticans) shed known as 'Balai Kuning' which was actually used by the Sultan of Johore as a reception hall whenever he visited Muar. It was located near the site of the former High Court Building. The school was founded in 1902. It was under the charge of C.P. Frois, a Eurasian gentleman from Malacca. He was the first headmaster cum teacher of the school and the enrolment of the school then was about 40 pupils.
It was not until 1904 that the majestic British colonial style historical school building started its construction. Completed in 1915, it is still standing. During the Second World War, the school was used as a Japanese concentration camp. Its alumni include national and state leaders, high-ranking government officials and industrialists, such as Osman Saat, Muhyiddin Yassin, Abdul Ghani Othman, Bahar Munip, and Hussin Hj Ismail.
Chung Hwa High School is one of the oldest Chinese independent high schools in Malaysia. It celebrated its 100th anniversary in July 2012. A fund raising event and dinner was held in conjunction with Chung Hwa High School's 100th anniversary and several million ringgit was raised for the school's fund.
EduHub Pagoh (Bandar Universiti Pagoh)
Pagoh Educational Hub (EduHub Pagoh), the largest public education hub area in Malaysia, is being constructed at Bandar Universiti Pagoh, a new well-planned education township in Muar. The first phase has been launched in the middle of September 2011. The first phase is expected to be completed by 2015. The first phase will see the opening of campuses of four local universities such as:
- Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia (UTHM)
- International Islamic University Malaysia (UIAM)
- Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM)
- Politeknik Tun Syed Nasir
Secondary schools

- Sekolah Tinggi Muar (麻坡高级中学)
- SMK Sultan Alauddin Riayat Shah 1 Pagoh (ALRISHA)
- SMK Saint Andrew (麻坡圣安德烈国民中学)
- SMK Convent (麻坡康文女子国民中学)
- Sultan Abu Bakar Girl School (苏丹阿布峇卡女子国民中学)
- SMK Dato' Sri Amar Diraja (SEDAR) (拿督斯里阿玛国民中学)
- SM Sains Muar (麻坡理科中学)
- Maktab Rendah Sains Mara (MRSM Muar) (麻坡玛拉初级理科学院)
- SM Teknik Muar ( formerly known as Sekolah Menengah Vokasional Muar) (麻坡技术中学)
- SMK Jalan Junid (仲尼路国民中学)
- SMK Sri Muar (斯里麻坡国民中学)
- SMK Bandar Maharani (SMKBM) (香妃城国民中学)
- SMK (A) Ma'ahad Muar
- SMK (Felcra) Bukit Kepong
- SMK Tengku Mahkota (SMTM) (东姑马哥达国民中学)
- SMK Raja Muda (太子国民中学)
- SMK Tun Perak Muar (敦霹雳国民中学)
- SMK Tun Mamat (敦马末国民中学)
- SMJK Pei Hwa (培华国民型中学)
- SMK Bukit Pasir (武吉巴西国民中学)
- SMK Lenga (岭嘉国民中学)
- SMK Parit Bunga (巴力文莪国民中学)
- SMK Tun Dr. Ismail (STUDI), Bakri, Muar. (敦伊斯迈医生国民中学)
- SMK Seri Menanti
- SMK Tengku Mahmud Iskandar, Ledang.
- SMK Bukit Gambir, Ledang.
- SMK Tengku Temenggong Ahmad, Ledang.
- SMK Sungai Abong
- SMK Bukit Naning
Chinese independent schools
- Chung Hwa High School, Jalan Junid (中化中学)
- Pei Hwa High School, Sungai Mati (培华独立中学)
National primary schools
- SK Bakri Batu 5, Bakri, Muar (峇吉里五哩国民小学)
- SK St. Andrew (SAS) (麻坡圣安德鲁国民小学)
- SK Ismail 1 (伊斯迈国民小学一校)
- SK Ismail 2 (伊斯迈国民小学二校)
- SK Convent Infant Jesus (麻坡康文女子国民小学)
- SK Abdullah (阿都拉国民小学)
- SK Sawah Ring
- SK Bukit Gambir (武吉甘蜜国民小学)
- SK Simpang Lima
- SK Serom 3 (实廊国民小学三校)
- SK Parit Bunga (巴力文莪国民小学)
- SK Seri Jong
- SK Simpang 4
- SK Simpang Jeram
- SK Temiang
- SK Parit Setongkat
- SK Air Hitam Batu 18
Tamil primary schools
- SJK(T) Jalan Khalidi (ஐலான் களிடி தேசிய வகை தமிழ்ப்பள்ளி)
Chinese primary schools
- SJK(C) Soon Cheng (训正国民型华文小学)
- SJK(C) Chung Hwa 1A (中化第一华文国民型小学A校)
- SJK(C) Chung Hwa 1B (中化第一华文国民型小学B校)
- SJK(C) Chung Hwa 2A (中化第二华文国民型小学A校)
- SJK(C) Chung Hwa 2B (中化第二华文国民型小学B校)
- SJK(C) Chung Hwa 3 (中化第三华文国民型小学)
- SJK(C) Chung Hwa Presbyterian (中华基督华文国民型小学)
- SJK(C) Sing Hwa (醒华华文国民型小学)
- SJK(C) Chian Kuo (建国华文国民型小学)
- SJK(C) Hwa Ming (华明华文国民型小学)
- SJK(C) Pu Nan 峇吉里吧口(辅南华文国民型小学)
- SJK(C) Pei Yang (培养华文国民型小学)
- SJK(C) Yu Jern (育人华文国民型小学)
- SJK(C) San Chai (善才华文国民型小学)
- SJK(C) Sin Ming (新民华文国民型小学)
- SJK(C) Aik Ming (益民华文国民型小学)
- SJK(C) Yu Eng (育英华文国民型小学)
- SJK(C) Pengkalan Bukit (榜加兰国民型小学)
Architecture
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (April 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |


In the town centre, rows of well-preserved pre-war commercial buildings still dominate the town's architecture.
Further up the town along the river where the main government administrative area located at the Jalan Petrie, Jalan Othman, Jalan Junid and Tanjung Emas area. The Sultan Ibrahim Jamek Mosque, the Sultan Abu Bakar Building, the former High Court Building, the Police Traffic Department building, the Muar High School building, the former Telecom building, the Jabatan Kerja Raya (JKR) building, the 2nd Battalion Regiment 501 AW's territorial army camp building, the Custom Department building and the official District Officer residence and others government official residence houses are among the many old, heritage and historic buildings still standing in the area.
Muar being the royal city of Johor have an official royal palace with a helipad situated at the Muar river bank at Jalan Petrie near Tanjung Emas.
Tourism
There are many local attractions and places of interest of Muar:
Historical places
- Bukit Kepong Police Station – This police station at Bukit Kepong with a history museum is known for the brutal attack by communist terrorists on 23 February 1950 in the Bukit Kepong Incident during the Malayan Emergency period.
- Kubu Bentayan – The last fortress of the retreating last Malacca Sultanate's Sultan Mahmud Shah before it falls during the attack of the Portuguese in the 15th century situated at mouth the Sungai Bentayan, the Bentayan Express Bus Station (formerly Pagoh Bus Stand) location now. Another fortress but built by the Portuguese later, Fortaleza de Muar was also believed to be situated at the same area.
- Panglima Lidah Hitam Mausoleum, Parit Sakai – The grave of a legendary warrior Panglima Lidah Hitam (the Black Tongue Warrior) or Baginda Zahiruddin from Padang Pariaman, Minangkabau, Sumatera, Indonesia; the founder Silat Lintau, whose tongues was black in colour when he died and buried in Parit Sakai Laut, Jalan Junid, Muar.
- Sultan Alauddin Riayat Shah I Mausoleum, Kampung Raja, Pagoh – The tomb of Sultan Alauddin Riayat Shah I, seventh Sultan of Malacca Sultanate from 1477 to 1488 is located at Kampung Raja, Ulu Pagoh.
- Tapak Sejarah Kota Buruk, Jorak – The Kota Buruk fortress historical site located at Tanjung Selabu, Jorak, Bukit Pasir, Pagoh, Muar is where the founder of the Malacca Sultanate, Parameswara, stayed for more than 10 years upon his exile from Temasik before proceeding to open Malacca. It is said another historic fort 'Biawak Busuk', opened by Parameswara, is also located just nearby.
Attractions
- Tanjung Emas - This is a recreational park alongside Muar river. It is common for joggers in the morning and the recreational park is lit up with lights in the night which turn into a place suitable for family activity. The recreational park also has a river cruise for tourists.
- Mural art
- Bangsa Johor Mural
- Loving Sisters
- Ferry Pier
- Opera
Culture and tradition
Muar is the birthplace of ‘Ghazal', Johor’s traditional musical heritage, which has a Persian origin. Muar is also the birthplace of several type of Zapin dances like Zapin Lenga, Zapin Parit Bagan, Zapin Muar and Zapin Putar Alam and also the Ceracap Inai dance. Zapin is a combination of semi-squatting style Malay dance with Arabic influence. The dancers usually perform in pairs and are accompanied by a traditional music ensemble normally consists of the gambus, accordion, violin, marwas (bongos), rebana (drum) and dok. Usually Zapin music is very alive and energetic. Keroncong is a popular musical and songs among the Malays of Javanese descends in Muar.
The traditional Javanese 'Kuda Kepang', a traditional horse dance and 'Barongan' dance originating from Indonesia is believed to be best performed by the Muar Malays of Javanese origin especially the Sg. Balang, Parit Bugis, Parit Yusof, Lenga or Bukit Gambir troupes.
It is generally acknowledged that the local dialect of Malay spoken here (and throughout the state of Johor), the Johor-Riau dialect is the common and standard official version of the Malay language adopted throughout the country.
Other than the above, the Muar is well known for their Chinese community's Lion Dance. Muar "Kun Seng Keng" Lion Dance association had been national champion for 48 times and world champion for 44 times in the International Championship for Lion Dance since 1992 beside many winning other various championship.
Ching Giap See Temple is the largest Buddhist temple in the state of Johor and it is located along Jalan Sulaiman in Muar. Nan Hai Fei Lai Temple was established before 1913 and is considered as the oldest Buddhist temple in the town, it is located at Jalan Salleh.
Gurudwara Sahib Muar is the historical Sikh temple in the state of Johor and it is located along Jalan Mohamadiah, Taman Sri Tanjung, 84000 Muar, Johor, Malaysia. Opening of the Sikh Temple, 3 February 1933
Hospitals

Muar and Tangkak are served by two government hospitals as well as numerous primary health centres. The two hospitals are:
- Sultanah Fatimah Specialist Hospital (Hospital Pakar Sultanah Fatimah). Formerly Muar District Hospital, which has recently been upgraded to specialist hospital status and renamed.
- Tangkak District Hospital
Currently, both hospitals also serve as teaching hospitals for Melaka Manipal Medical College and Asia Metropolitan University.
KPJ Muar Specialist Hospital
Notable people
Politicians and public servants
- Syed Saddiq Syed Abdul Rahman, Member of Parliament Muar 2018-Current.
- Muhyiddin Yassin, eighth Prime Minister of Malaysia.
- Mohamed Khaled Nordin, 15th Menteri Besar of Johor (2013–2018).
- Abdul Ghani Othman, 14th Menteri Besar of Johor (1995–2013).
- Othman Saat, 11th Menteri Besar of Johor (1967–1982).
- Hassan Yunus, tenth Menteri Besar of Johor (1959–1967).
- Abdul Rahman Mohamed Yassin, first President of the Dewan Negara (1959–1968).
- Suleiman Abdul Rahman, first Minister of the Interior (1957–1959) and former Malaysian High Commissioner to Australia (1961–1963).
- Chua Jui Meng, former Bakri's Member of Parliament, former Health Minister of Malaysia and former vice-president of MCA.
- Abdul Kadir Yusuf, former Minister of Law and the Judiciary, Lord President of the Supreme Court and Attorney General of Malaysia, his wife is Fatimah Hashim and their son, Ali Abdul Kadir is former Securities Commission chief.
- Fatimah Hashim, the first woman minister, former Women, Family and Community Development.
- Mohamed Noah Omar, former Minister of Home Affairs and first Speaker of the Dewan Rakyat. Father of Rahah Noah.
- Sulaiman Ninam Shah, former UMNO permanent chairman, former Johor state assemblyman for Parit Jawa (1959–1964).
- Anwar Abdul Malik, a close associate of Onn Jaafar, credited for giving United Malay National Organisation (UMNO) its name, initially United Malay Organisation.
- Awang Hassan, former Member of Parliament of Muar Selatan, former Penang State Governor, the father of Yahya Awang.
- Sellapan Ramanathan, or SR Nathan, President of Singapore, was born in Singapore but grew up in Muar and spent his childhood with his three older sisters and parents in Muar.
- Joshua Benjamin Jeyaretnam, or J. B. Jeyaretnam, a former Singaporean politician, studied in a French convent school in Muar together with his sister in his early life.
- Sam Lim, Member of the Australian House of Representatives
- Dr. Bahar Munip, Secretary-General, African-Asian Rural Development Organisation AARDO (1997-2003)
Medicine
- Yahya Awang, the cardiothoracic surgeon who performed the open heart by-pass surgery on Prime Minister Mahathir Mohamad in 1989; pioneered the establishment of The National Heart Institute of Malaysia in 1992; and performed the first heart transplant in Malaysia in 1998.
- Abu Bakar Suleiman, former Health Ministry Director-General.
Entertainment
- Yasmin Ahmad, esteemed Malaysian Filmmaker/Producer/Director.
- Nurul Hana Che Mahazan or Nana (deejay), of Era.fm/XFM radio station, former student and finalist of Akademi Fantasia AF1 reality show.
- Namewee, Malaysian Chinese hip hop recording artist, composer, filmmaker and actor.
Sportspersons
- Nordin Jadi, former Malaysia track runner athlete, represented in 200m and 400m track events in both Los Angeles 1984 and Seoul 1988 (as Flag Bearer too) Summer Olympics.
- Yap Kim Hock, former top badminton player, silver medal winner in Atlanta 1996 Summer Olympics in men's double with Cheah Soon Kit.
- Malik Sulaiman, former Malaysian yachtsman, silver medalist in Bangkok 1998 Asian Games Regatta sport Super Moth category and Commander (Cdr) of Royal Malaysian Navy (RMN).
- Mazlan Hamzah, former Malaysian track athlete, member of the Malaysian athletic team 1964 Tokyo Olympics
- Teo Ee Yi, a Malaysian badminton player.
Sister cities
References
- "ASEAN TOURISM FORUM 2018" (PDF). asean.org. Archived (PDF) from the original on 1 January 2019. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
- Muar to say goodbye to Tangkak Archived 1 September 2012 at the Wayback Machine, 20 November 2006, The Star (Malaysia)
- "Muar Gets Honoured With Asean Clean Tourist City Award". MIX. Retrieved 29 May 2018.
- "10 PBT rangkul anugerah ASEAN Clean Tourist City Standard". Utusan Borneo. Retrieved 29 May 2018.
- Flag and coat of arms of Johor
- Flag of the State Commissioner for Muar (Bendera Orang Besar Daerah Muar)
- Muar District Office Official Website/Muar Flag Archived 17 February 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- Keyvanfar, Ali; Shafaghat, Arezou; Mohamad, Sapura; Abdullahi, Mu'azu; Ahmad, Hamidah; Mohd Derus, Nurul; Khorami, Majid (2018). "A Sustainable Historic Waterfront Revitalization Decision Support Tool for Attracting Tourists". Sustainability. 10 (2): 215. doi:10.3390/su10020215.
- Brown, C. C. (October 1952). "The Malay Annals". Journal of the Malayan Branch of the Royal Asiatic Society. 25 (2/3 (159)): 5–276.
- The story is recorded in JMBRAS magazine, October 1935, Volume XIII Part 2, page 15 to 16.
- "The History Portuguese Malacca 1511–1641 : History of Colonial Malaysia". Marco Ramerini. Archived from the original on 1 March 2010.
- ^ (Tun) Suzana (Tun) Othman, Ahlul-bait (keluarga) Rasulullah SAW & raja-raja Melayu, pg 182
- ^ R. O. Winstedt, A History of Johore (1365–1941), pg 129
- Studer, American and British Claims Arbitration: William Webster: Appendix to the Memorial of the United States, Vol. III, p. 311-12
- Journal of the Malaysian Branch of the Royal Asiatic Society (1937), p. 74
- Winstedt, A History of Johore (1365–1941), p. 128-29
- Winstedt, A History of Johore (1365–1941), pg 131-2
- Andaya, A History of Malaysia, p. 140
- Sultanah Johor Tanam Azimat di Muar
- The Battle of Muar
- "The Battle of Muar" (PDF). AWM. Retrieved 30 March 2009.
- "Latar Belakang". Portal Rasmi Majlis Perbandaran Muar (MPM) (in Malay). 4 January 2016. Retrieved 18 November 2024.
- The Star, 25 December 2006.
- "Climate: Muar". Climate-Data.org. Retrieved 1 August 2020.
- Department of Statistics, Malaysia: Population Distribution and Basic Demographic Characteristics, 2010, pg 232, Table 18.1: Total population by ethnic group, mukim and state, Malaysia, 2010 (cont'd)
- Department of Statistics, Malaysia: Population Distribution and Basic Demographic Characteristics, 2010, pg 11, Table 1 : Key summary statistics for Local Authority areas, Malaysia, 2010 (cont'd)
- Khairul Ashraf Kammed (16 November 2017). "The rise of Pagoh". New Straits Times. Retrieved 5 September 2019.
- Muhyiddin launches phase one of Pagoh education hub Archived 29 December 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- FARIDAH BEGUM (7 October 2007), "Regal coastal town", The Star, Muar: Sundaymetro, retrieved 10 April 2010
- HAMDAN RAJA ABDULLAH (4 March 2010), "Boosting Muar tours", The Star, Muar: Metro/South & East, retrieved 8 April 2010
- Makam Sultan Alauddin Riayat Shah I|Tour Malaysia
- "6 Mural Paling Cantik Bergambar di Muar, Johor. Salah Satunya Paling Besar di Malaysia". 21 August 2020.
- Showcase folk dances on regular basis|Fauziah Ismail|2009/06/22|JohorBuzz|MyJohor|Johor Street Reaching Out|NST Archived 30 May 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- Tarian Tradisional|Johor State Government Official Portal Archived 23 March 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- Muar Lion Dance Troupe is World Champion | New Straits Times | 11 Feb, 1994
- Nan Hai Fei Lai Temple
External links
- Municipal Council of Muar/Majlis Perbandaran Muar(MPM)
- Muar Food and Tourism Portal with Muar city maps
| State of Johor | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||
| General topics |
|  | |||||||||||||
| Administrative divisions |
| ||||||||||||||
| City councils (Majlis Bandaraya) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Municipal councils (Majlis Perbandaran) |
| ||||||||||||||
| District councils (Majlis Daerah) |
| ||||||||||||||