| Governor of Guam | |
|---|---|
| I Maga'låhi / Maga'håga Guåhan | |
 Territory seal Territory seal | |
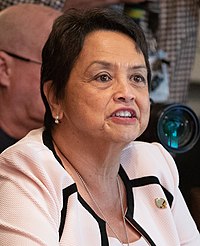 Incumbent IncumbentLou Leon Guerrero since January 7, 2019 | |
| Style | The Honorable (formal) |
| Residence | Government House (Agaña Heights) |
| Seat | Ricardo J. Bordallo Governor's Complex (Adelup) |
| Term length | Four-year term, renewable once |
| Constituting instrument | Organic Act of Guam |
| Inaugural holder | Carlos Camacho |
| Formation | January 4, 1971 |
| Deputy | Lieutenant Governor of Guam (Josh Tenorio) |
| Salary | $90,000 (2013) |
| Politics of Guam |
|---|
 |
The governor of Guam (Chamorro: I Maga'låhen / Maga'håga Guåhan) is the head of government of Guam and the commander-in-chief of the Guam National Guard, whose responsibilities also include making the annual State of the Island (formerly the State of the Territory) addresses to the Guam Legislature, submitting the budget, and ensuring that Guam's public laws are enforced. The position was created in 1968, through the passage of the Guam Elected Governors Act which took effect in 1970. Guam elected its first civilian governor in 1970 with the inauguration of former governor Carlos Camacho.
The current governor is Lou Leon Guerrero, a Democrat who was inaugurated on January 7, 2019, following her election in 2018.
Powers and duties
The governor has a duty to enforce Guam's public laws, the power to either approve or veto bills passed by the Guam Legislature, to convene the legislature, and to commute or grant pardons to criminal sentences, except in cases of treason and impeachment. The governor is given the power to control government budgeting and appoint many officials (including many judges).
Unlike the other government departments that compose the executive branch of government, the governor is themselves head of the state executive department. The governor may also perform ceremonial roles, such as greeting dignitaries, issuing symbolic proclamations or commencing the Liberation Day parade.
As the commander-in-chief of the Guam National Guard, the governor, as well as the president, may call on the Guard at a moment's notice to provide defense for the island, in a state of emergency.
The governor also delivers the annual State of the Island address (similar to the State of the State address in the US) to a special session of the Guam Legislature. The speech is given to satisfy a constitutional stipulation that a governor must report annually, or in older constitutions described as being "from time to time", on the state or condition of the territory.
Seat and residence
Sitting along Route 1, the governor's seat of power is located in Adelup in the Ricardo J. Bordallo Governor's Complex, named after the island's 2nd and 4th governor, Ricardo Bordallo.
The governor lives in their official residence at the Government House in Agaña Heights. The island's former Spanish and American military governors had lived in the Governor's Palace in the Plaza de España (Hagåtña) until its destruction in the shelling of Hagåtña during the reconquest of Guam in World War II.
Election process
Eligibility
According to the Elective Governors Act:
"No person shall be eligible for election to the office of Governor or Lieutenant Governor unless he/she is an eligible voter and has been for five consecutive years immediately preceding the election a citizen of the United States and a bona fide resident of Guam and will be, at the time of taking office, at least thirty years of age. The Governor shall maintain his/her official residence in Guam during his/her incumbency."
To be eligible, a candidate for Governor of Guam must:
- an eligible voter of Guam
- a United States citizen
- at least thirty years of age.
- has lived in Guam for five years, preceding the general election.
Election
According to the Elective Governor Acts of 1968, the Governor of Guam, together with the Lieutenant Governor, shall be elected by a majority of the votes cast by the people who are qualified to vote for the members of the Legislature of Guam. The Governor and Lieutenant Governor shall be chosen jointly, by the casting by each voter of a single vote applicable to both offices. The first election for Governor and Lieutenant Governor was held on November 3, 1970, with the election of Governor Carlos Camacho and Lt. Governor Kurt Moylan. Beginning in 1974, Guam's Governor and Lieutenant Governor is elected by direct vote, on the first Tuesday of November. The Governor and Lieutenant Governor shall hold office for a term of four years and until their successors are elected and qualified.
Inauguration
The Governor of Guam usually takes the oath of office on the first Monday of January. In past inaugurations, however, the governor-elect and lieutenant governor-elect would take the oath of office past midnight on Monday morning.
Traditionally, the lieutenant governor-elect takes the oath first and delivers his inaugural remarks, followed then by the incoming governor-elect. As soon as the governor takes the oath of office, four ruffles and flourishes are played then followed by "The Stars and Stripes Forever" and a 21-gun salute. The newly inaugurated governor delivers his inaugural address, an opportunity for the new leader to state his goals for the next 4 years.
Oath of office
Pursuant to the Guam Organic Act, the governor's term of office begins at midnight on the first Monday of January of the year following the election. The day marks the beginning of the four-year term of the Governor and Lieutenant Governor of Guam. Before executing the powers as the Governor of Guam, the governor must take an oath of office:
I, (name), duly elected Governor of Guam, do solemnly swear, in the presence of the Almighty God, that I will well and faithfully support the Constitution of the United States, the laws of the United States applicable to Guam, and the laws of Guam, and that I will conscientiously and impartially discharge my duties as the Governor of Guam.
In line with traditional oath-takings, governors have traditionally palmed a Bible and have added, "So help me God!" at the end of their oaths. The Governor of Guam is sworn in by the Chief Justice of Guam.
Succession
Main article: Gubernatorial lines of succession in the United States § GuamTenure and term limits
The Governor of Guam is only limited two terms as prescribed in the Elective Governors Act:
- No person who has been elected Governor for two full successive terms shall again be eligible to hold that office until one full term has intervened.
- The term of the elected Governor and Lieutenant Governor shall commence on the first Monday of January following the date of election.
However, a former governor can be re-elected once again only after a full term has passed.
History
Spanish era
Main article: List of governors of the Spanish Mariana IslandsIn 1565, Miguel López de Legazpi formally declared Spanish sovereignty over the Mariana Islands. However, there was no permanent Spanish presence on the island and it was ruled from the Philippines as part of the Spanish East Indies by the Governor-General of the Philippines. Diego Luis de San Vitores established a mission on Guam in 1668, but Francisco de Irrisari was the first person to take the title "Governor" in June 1676, amidst the Spanish-Chamorro Wars. Antonio de Saravia, who arrived in June 1681, was the first to receive his appointment as governor from the Spanish throne, meaning that, technically, he was no longer subordinate to rule from the Philippines or Mexico.
American capture of the territory (1898)
| Image | Name | Term start | Term end |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Henry Glass, Admiral | June 12, 1898 | June 22, 1898 |
 |
Francisco Martínez Portusach | June 22, 1898 | December 12, 1898 |
Political instability (1898–1899)
| Image | Name | Term start | Term end | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
José Sisto | December 12, 1898 | December 31, 1898 | overthrew Portusach |
 |
Venancio Roberto | December 31, 1898 | January 2, 1899 | overthrew Sisto |
 |
José Sisto | January 2, 1899 | February 1, 1899 | put back in power by US Navy |
 |
Edward D. Taussig | February 1, 1899 | February 13, 1899 | re-asserted USN authority, put a local council in place |
 |
Don Joaquin Perez y Cruz | February 13, 1899 | April 20, 1899 | local council |
 |
William Coe | April 20, 1899 | May 9, 1899 | local council |
 |
Louis A. Kaiser | May 9, 1899 | August 7, 1899 | local council |
American Naval governors (1899–1941)
| # | Image | Name | Term start | Term end |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |
Richard Phillips Leary | August 7, 1899 | July 12, 1900 |
| – |  |
William Edwin Safford Acting |
June 12, 1900 | July 19, 1900 |
| 2 |  |
Seaton Schroeder | July 12, 1900 | January 25, 1903 |
| – |  |
William Swift Acting |
January 25, 1903 | February 6, 1903 |
| 3 |  |
William Elbridge Sewell | February 6, 1903 | May 16, 1904 |
| – |  |
Frank Herman Schofield Acting |
January 11, 1904 | January 28, 1904 |
| – |  |
Raymond Stone Acting |
January 28, 1904 | May 16, 1904 |
| 4 |  |
George Leland Dyer | May 16, 1904 | November 2, 1905 |
| 5 |  |
Luke McNamee | November 2, 1905 | December 3, 1906 |
| 6 |  |
Templin Morris Potts | December 3, 1906 | October 3, 1907 |
| – |  |
Luke McNamee Acting |
October 3, 1907 | December 28, 1907 |
| 7 |  |
Edward John Dorn | December 28, 1907 | November 5, 1910 |
| 8 |  |
Frank Freyer | November 5, 1910 | January 21, 1911 |
| 9 |  |
George Salisbury | January 21, 1911 | January 30, 1912 |
| 10 |  |
Robert Edward Coontz | January 30, 1912 | September 23, 1913 |
| 11 |  |
Alfred Walton Hinds | September 23, 1913 | March 28, 1914 |
| 12 |  |
William John Maxwell | March 28, 1914 | April 29, 1916 |
| – |  |
William P. Cronan Acting |
April 29, 1916 | May 18, 1916 |
| – |  |
Edward E. Simpson Acting |
May 18, 1916 | May 30, 1916 |
| 13 |  |
Roy Campbell Smith | May 30, 1916 | November 18, 1918 |
| 14 |  |
William Gilmer | November 18, 1918 | November 22, 1919 |
| – |  |
William A. Hodgman | November 22, 1919 | December 21, 1919 |
| 15 |  |
William Gilmer | December 21, 1919 | July 7, 1920 |
| 16 |  |
Ivan Wettengel | July 7, 1920 | February 27, 1921 |
| 17 |  |
James Sutherland Spore | February 27, 1921 | February 7, 1922 |
| – |  |
Adelbert Althouse Acting |
February 7, 1922 | December 8, 1922 |
| – |  |
John P. Miller Acting |
December 8, 1922 | December 14, 1922 |
| 18 |  |
Adelbert Althouse | December 14, 1922 | August 4, 1923 |
| 19 |  |
Henry Bertram Price | August 4, 1923 | August 26, 1924 |
| 20 |  |
Alfred Winsor Brown | August 26, 1924 | August 7, 1926 |
| 23 |  |
Lloyd Stowell Shapley | August 7, 1926 | June 11, 1929 |
| 24 |  |
Willis W. Bradley | June 11, 1929 | March 15, 1931 |
| 25 |  |
Edmund Root | March 15, 1931 | June 21, 1933 |
| 26 |  |
George A. Alexander | June 21, 1933 | March 27, 1936 |
| 27 |  |
Benjamin McCandlish | March 27, 1936 | February 8, 1938 |
| 28 |  |
James Thomas Alexander | February 8, 1938 | April 20, 1940 |
| 29 |  |
George McMillin | April 20, 1940 | December 10, 1941 |
Japanese military governors (1941–1944)
| Name (Birth–Death) |
Took office | Left office | |
|---|---|---|---|

|
Tomitarō Horii (1890–1942) |
December 10, 1941 | January 1942 |
| Hayashi Hiromu | January 1942 | June 1942 | |
| Homura Teiichi | June 1942 | March 1944 | |

|
Takeshi Takashina (1891–1944) |
March 1944 | July 28, 1944 |

|
Hideyoshi Obata (1890–1944) |
July 28, 1944 | August 11, 1944 |
American military governors (1944–1949)
| Name (Birth–Death) |
Took office | Left office | |
|---|---|---|---|

|
Roy Stanley Geiger (1885–1947) |
July 21, 1944 | August 10, 1944 |

|
Henry Louis Larsen (1890–1962) |
August 10, 1944 | May 30, 1946 |

|
Charles Alan Pownall (1887–1975) |
May 30, 1946 | September 27, 1949 |
Appointed civilian governors (1949–1971)
| # | Governor (Birth–Death) |
Start | End | Appointed by | Acting Governor | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
|
Carlton Skinner (1913–2004) |
September 17, 1949 | April 22, 1953 | Harry S. Truman | Randall Herman (February 20, 1953 – April 22, 1953) | |
| 2 | 
|
Ford Elvidge (1892–1980) |
April 23, 1953 | October 2, 1956 | Dwight D. Eisenhower | William Corbett (May 19, 1956 – October 2, 1956) | |
| 3 | 
|
Richard Lowe (1902–1972) |
October 2, 1956 | July 9, 1960 | Marcellus Boss (November 14, 1959 – August 22, 1960) | ||
| 4 | 
|
Joseph Flores (1900–1981) |
July 9, 1960 | May 20, 1961 | |||
| 5 | 
|
Bill Daniel (1915–2006) |
May 20, 1961 | March 9, 1963 | John F. Kennedy | Carson Guerrero (January 20, 1963 – March 9, 1963) | |
| 6 | 
|
Carson Guerrero (1914–1985) |
March 9, 1963 | July 20, 1969 | |||
| 7 | 
|
Carlos Camacho (1924–1979) |
July 20, 1969 | January 4, 1971 | Richard Nixon | ||
Elected governors (1971–present)
|
Democratic (4) Republican (5) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Governor | Start | End | Party | Elected | Prior Office | Lieutenant Governor | ||||
| 1 | 
|
Carlos Camacho (1924–1979) |
January 4, 1971 | January 6, 1975 (lost election) |
Republican | 1970 | Appointed Governor of Guam | Kurt Moylan | ||
| 2 | 
|
Ricardo Bordallo (1927–1990) |
January 6, 1975 | January 1, 1979 (lost election) |
Democratic | 1974 | Senator of the Guam Legislature | Rudy Sablan | ||
| 3 | 
|
Paul Calvo (1934–2024) |
January 1, 1979 | January 3, 1983 (lost election) |
Republican | 1978 | Senator of the Guam Legislature | Joseph Ada | ||
| 4 | 
|
Ricardo Bordallo (1927–1990) |
January 3, 1983 | January 5, 1987 (lost election) |
Democratic | 1982 | Senator of the Guam Legislature | Eddie Reyes | ||
| 5 | 
|
Joseph Ada (born 1943) |
January 5, 1987 | January 2, 1995 (lost election) |
Republican | 1986 1990 |
Lieutenant Governor of Guam | Frank Blas | ||
| 6 | 
|
Carl Gutierrez (born 1941) |
January 2, 1995 | January 6, 2003 (lost renomination) |
Democratic | 1994 1998 |
Senator of the Guam Legislature | Madeleine Bordallo | ||
| 7 | 
|
Felix Camacho (born 1957) |
January 6, 2003 | January 3, 2011 (term limited) |
Republican | 2002 2006 |
Senator of the Guam Legislature | Kaleo Moylan | ||
| Michael Cruz | ||||||||||
| 8 | 
|
Eddie Calvo (born 1961) |
January 3, 2011 | January 7, 2019 (term limited) |
Republican | 2010 2014 |
Senator of the Guam Legislature | Ray Tenorio | ||
| 9 | 
|
Lou Leon Guerrero (born 1950) |
January 7, 2019 | present | Democratic | 2018 2022 |
Senator of the Guam Legislature | Josh Tenorio | ||
See also
- List of governors of the Spanish Mariana Islands
- List of governors of the Northern Mariana Islands
- First ladies and gentlemen of Guam
References
- "CSG Releases 2013 Governor Salaries". The Council of State Governments. June 25, 2013. Archived from the original on October 22, 2014. Retrieved November 23, 2014.
- "48 U.S. Code § 1422 - Governor and Lieutenant Governor; term of office; qualifications; powers and duties; annual report to Congress".
- Hezel, Francis X. (2015). When cultures clash: revisiting the 'Spanish-Chamorro Wars'. Richard F. Taitano Micronesian Area Research Center, University of Guam. ISBN 978-1-935198-04-8. Retrieved 19 June 2020.
External links
| Territory of Guam | |
|---|---|
| Hagåtña (capital) | |
| Topics | |
| Geography | |
| Villages | |
| History | |
| Culture |
|
| Bases | |
| Healthcare | |
| Governors of Guam | ||
|---|---|---|
| Commissioner (1898–1899) |  | |
| Naval (1899–1941) | ||
| Military (1944–1949) | ||
| Civilian (1949–1969) | ||
| Elected (since 1969) | ||