| This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (April 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

In mathematics and physics, the centroid, also known as geometric center or center of figure, of a plane figure or solid figure is the arithmetic mean position of all the points in the surface of the figure. The same definition extends to any object in -dimensional Euclidean space.
In geometry, one often assumes uniform mass density, in which case the barycenter or center of mass coincides with the centroid. Informally, it can be understood as the point at which a cutout of the shape (with uniformly distributed mass) could be perfectly balanced on the tip of a pin.
In physics, if variations in gravity are considered, then a center of gravity can be defined as the weighted mean of all points weighted by their specific weight.
In geography, the centroid of a radial projection of a region of the Earth's surface to sea level is the region's geographical center.
History
The term "centroid" is of recent coinage (1814). It is used as a substitute for the older terms "center of gravity" and "center of mass" when the purely geometrical aspects of that point are to be emphasized. The term is peculiar to the English language; French, for instance, uses "centre de gravité" on most occasions, and other languages use terms of similar meaning.
The center of gravity, as the name indicates, is a notion that arose in mechanics, most likely in connection with building activities. It is uncertain when the idea first appeared, as the concept likely occurred to many people individually with minor differences. Nonetheless, the center of gravity of figures was studied extensively in Antiquity; Bossut credits Archimedes (287–212 BCE) with being the first to find the centroid of plane figures, although he never defines it. A treatment of centroids of solids by Archimedes has been lost.
It is unlikely that Archimedes learned the theorem that the medians of a triangle meet in a point—the center of gravity of the triangle—directly from Euclid, as this proposition is not in the Elements. The first explicit statement of this proposition is due to Heron of Alexandria (perhaps the first century CE) and occurs in his Mechanics. It may be added, in passing, that the proposition did not become common in the textbooks on plane geometry until the nineteenth century.
Properties
The geometric centroid of a convex object always lies in the object. A non-convex object might have a centroid that is outside the figure itself. The centroid of a ring or a bowl, for example, lies in the object's central void.
If the centroid is defined, it is a fixed point of all isometries in its symmetry group. In particular, the geometric centroid of an object lies in the intersection of all its hyperplanes of symmetry. The centroid of many figures (regular polygon, regular polyhedron, cylinder, rectangle, rhombus, circle, sphere, ellipse, ellipsoid, superellipse, superellipsoid, etc.) can be determined by this principle alone.
In particular, the centroid of a parallelogram is the meeting point of its two diagonals. This is not true of other quadrilaterals.
For the same reason, the centroid of an object with translational symmetry is undefined (or lies outside the enclosing space), because a translation has no fixed point.
Examples
The centroid of a triangle is the intersection of the three medians of the triangle (each median connecting a vertex with the midpoint of the opposite side).
For other properties of a triangle's centroid, see below.
Determination
See also: Center of mass § DeterminationPlumb line method
The centroid of a uniformly dense planar lamina, such as in figure (a) below, may be determined experimentally by using a plumbline and a pin to find the collocated center of mass of a thin body of uniform density having the same shape. The body is held by the pin, inserted at a point, off the presumed centroid in such a way that it can freely rotate around the pin; the plumb line is then dropped from the pin (figure b). The position of the plumbline is traced on the surface, and the procedure is repeated with the pin inserted at any different point (or a number of points) off the centroid of the object. The unique intersection point of these lines will be the centroid (figure c). Provided that the body is of uniform density, all lines made this way will include the centroid, and all lines will cross at exactly the same place.
 |
 |
 |
| (a) | (b) | (c) |
This method can be extended (in theory) to concave shapes where the centroid may lie outside the shape, and virtually to solids (again, of uniform density), where the centroid may lie within the body. The (virtual) positions of the plumb lines need to be recorded by means other than by drawing them along the shape.
Balancing method
For convex two-dimensional shapes, the centroid can be found by balancing the shape on a smaller shape, such as the top of a narrow cylinder. The centroid occurs somewhere within the range of contact between the two shapes (and exactly at the point where the shape would balance on a pin). In principle, progressively narrower cylinders can be used to find the centroid to arbitrary precision. In practice air currents make this infeasible. However, by marking the overlap range from multiple balances, one can achieve a considerable level of accuracy.
Of a finite set of points
The centroid of a finite set of points in is This point minimizes the sum of squared Euclidean distances between itself and each point in the set.
By geometric decomposition
The centroid of a plane figure can be computed by dividing it into a finite number of simpler figures computing the centroid and area of each part, and then computing
Holes in the figure overlaps between the parts, or parts that extend outside the figure can all be handled using negative areas Namely, the measures should be taken with positive and negative signs in such a way that the sum of the signs of for all parts that enclose a given point is if belongs to and otherwise.
For example, the figure below (a) is easily divided into a square and a triangle, both with positive area; and a circular hole, with negative area (b).
 (a) 2D Object
(a) 2D Object (b) Object described using simpler elements
(b) Object described using simpler elements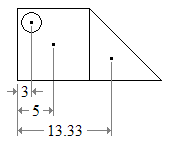 (c) Centroids of elements of the object
(c) Centroids of elements of the object
The centroid of each part can be found in any list of centroids of simple shapes (c). Then the centroid of the figure is the weighted average of the three points. The horizontal position of the centroid, from the left edge of the figure is The vertical position of the centroid is found in the same way.
The same formula holds for any three-dimensional objects, except that each should be the volume of rather than its area. It also holds for any subset of for any dimension with the areas replaced by the -dimensional measures of the parts.
By integral formula
The centroid of a subset of can also be computed by the formula
where the integrals are taken over the whole space and is the characteristic function of the subset of if and otherwise. Note that the denominator is simply the measure of the set This formula cannot be applied if the set has zero measure, or if either integral diverges.
Another formula for the centroid is
where is the th coordinate of and is the measure of the intersection of with the hyperplane defined by the equation Again, the denominator is simply the measure of
For a plane figure, in particular, the barycentric coordinates are
where is the area of the figure is the length of the intersection of with the vertical line at abscissa and is the length of the intersection of with the horizontal line at ordinate
Of a bounded region
The centroid of a region bounded by the graphs of the continuous functions and such that on the interval is given by
where is the area of the region (given by ).
With an integraph
An integraph (a relative of the planimeter) can be used to find the centroid of an object of irregular shape with smooth (or piecewise smooth) boundary. The mathematical principle involved is a special case of Green's theorem.
Of an L-shaped object
This is a method of determining the centroid of an L-shaped object.
- Divide the shape into two rectangles, as shown in fig 2. Find the centroids of these two rectangles by drawing the diagonals. Draw a line joining the centroids. The centroid of the shape must lie on this line
- Divide the shape into two other rectangles, as shown in fig 3. Find the centroids of these two rectangles by drawing the diagonals. Draw a line joining the centroids. The centroid of the L-shape must lie on this line
- As the centroid of the shape must lie along and also along it must be at the intersection of these two lines, at The point might lie inside or outside the L-shaped object.
Of a triangle
Main article: Triangle center 
|
The centroid of a triangle is the point of intersection of its medians (the lines joining each vertex with the midpoint of the opposite side). The centroid divides each of the medians in the ratio which is to say it is located of the distance from each side to the opposite vertex (see figures at right). Its Cartesian coordinates are the means of the coordinates of the three vertices. That is, if the three vertices are and then the centroid (denoted here but most commonly denoted in triangle geometry) is
The centroid is therefore at in barycentric coordinates.
In trilinear coordinates the centroid can be expressed in any of these equivalent ways in terms of the side lengths and vertex angles :
The centroid is also the physical center of mass if the triangle is made from a uniform sheet of material; or if all the mass is concentrated at the three vertices, and evenly divided among them. On the other hand, if the mass is distributed along the triangle's perimeter, with uniform linear density, then the center of mass lies at the Spieker center (the incenter of the medial triangle), which does not (in general) coincide with the geometric centroid of the full triangle.
The area of the triangle is times the length of any side times the perpendicular distance from the side to the centroid.
A triangle's centroid lies on its Euler line between its orthocenter and its circumcenter exactly twice as close to the latter as to the former:
In addition, for the incenter and nine-point center we have
If is the centroid of the triangle then
The isogonal conjugate of a triangle's centroid is its symmedian point.
Any of the three medians through the centroid divides the triangle's area in half. This is not true for other lines through the centroid; the greatest departure from the equal-area division occurs when a line through the centroid is parallel to a side of the triangle, creating a smaller triangle and a trapezoid; in this case the trapezoid's area is that of the original triangle.
Let be any point in the plane of a triangle with vertices and centroid Then the sum of the squared distances of from the three vertices exceeds the sum of the squared distances of the centroid from the vertices by three times the squared distance between and :
The sum of the squares of the triangle's sides equals three times the sum of the squared distances of the centroid from the vertices:
A triangle's centroid is the point that maximizes the product of the directed distances of a point from the triangle's sidelines.
Let be a triangle, let be its centroid, and let be the midpoints of segments respectively. For any point in the plane of
Of a polygon
The centroid of a non-self-intersecting closed polygon defined by vertices is the point where
and
and where is the polygon's signed area, as described by the shoelace formula:
In these formulae, the vertices are assumed to be numbered in order of their occurrence along the polygon's perimeter; furthermore, the vertex is assumed to be the same as meaning on the last case must loop around to (If the points are numbered in clockwise order, the area computed as above, will be negative; however, the centroid coordinates will be correct even in this case.)
Of a cone or pyramid
The centroid of a cone or pyramid is located on the line segment that connects the apex to the centroid of the base. For a solid cone or pyramid, the centroid is the distance from the base to the apex. For a cone or pyramid that is just a shell (hollow) with no base, the centroid is the distance from the base plane to the apex.
Of a tetrahedron and n-dimensional simplex
A tetrahedron is an object in three-dimensional space having four triangles as its faces. A line segment joining a vertex of a tetrahedron with the centroid of the opposite face is called a median, and a line segment joining the midpoints of two opposite edges is called a bimedian. Hence there are four medians and three bimedians. These seven line segments all meet at the centroid of the tetrahedron. The medians are divided by the centroid in the ratio The centroid of a tetrahedron is the midpoint between its Monge point and circumcenter (center of the circumscribed sphere). These three points define the Euler line of the tetrahedron that is analogous to the Euler line of a triangle.
These results generalize to any -dimensional simplex in the following way. If the set of vertices of a simplex is then considering the vertices as vectors, the centroid is
The geometric centroid coincides with the center of mass if the mass is uniformly distributed over the whole simplex, or concentrated at the vertices as equal masses.
Of a hemisphere
The centroid of a solid hemisphere (i.e. half of a solid ball) divides the line segment connecting the sphere's center to the hemisphere's pole in the ratio (i.e. it lies of the way from the center to the pole). The centroid of a hollow hemisphere (i.e. half of a hollow sphere) divides the line segment connecting the sphere's center to the hemisphere's pole in half.
See also
- Chebyshev center
- Circular mean
- Fréchet mean
- k-means algorithm
- List of centroids
- Medoid
- Pappus's centroid theorem
Notes
- ^ Protter & Morrey (1970, p. 520)
- Protter & Morrey (1970, p. 521)
- Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London at Google Books
- Court, Nathan Altshiller (1960). "Notes on the centroid". The Mathematics Teacher. 53 (1): 33–35. doi:10.5951/MT.53.1.0033. JSTOR 27956057.
- Knorr, W. (1978). "Archimedes' lost treatise on the centers of gravity of solids". The Mathematical Intelligencer. 1 (2): 102–109. doi:10.1007/BF03023072. ISSN 0343-6993. S2CID 122021219.
- ^ Altshiller-Court (1925, p. 66)
- ^ Protter & Morrey (1970, p. 526)
- Protter & Morrey (1970, p. 527)
- Protter & Morrey (1970, p. 528)
- Larson (1998, pp. 458–460)
- Sangwin
- Altshiller-Court (1925, p. 65)
- Kay (1969, p. 184)
- Clark Kimberling's Encyclopedia of Triangles "Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers". Archived from the original on 2012-04-19. Retrieved 2012-06-02.
- Johnson (2007, p. 173)
- Altshiller-Court (1925, p. 101)
- Kay (1969, pp. 18, 189, 225–226)
- Bottomley, Henry. "Medians and Area Bisectors of a Triangle". Retrieved 27 September 2013.
- ^ Altshiller-Court (1925, pp. 70–71)
- Kimberling, Clark (201). "Trilinear distance inequalities for the symmedian point, the centroid, and other triangle centers". Forum Geometricorum. 10: 135–139.
- Gerald A. Edgar, Daniel H. Ullman & Douglas B. West (2018) Problems and Solutions, The American Mathematical Monthly, 125:1, 81-89, DOI: 10.1080/00029890.2018.1397465
- ^ Bourke (1997)
- Leung, Kam-tim; and Suen, Suk-nam; "Vectors, matrices and geometry", Hong Kong University Press, 1994, pp. 53–54
References
- Altshiller-Court, Nathan (1925), College Geometry: An Introduction to the Modern Geometry of the Triangle and the Circle (2nd ed.), New York: Barnes & Noble, LCCN 52013504
- Bourke, Paul (July 1997). "Calculating the area and centroid of a polygon".
- Johnson, Roger A. (2007), Advanced Euclidean Geometry, Dover
- Kay, David C. (1969), College Geometry, New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston, LCCN 69012075
- Larson, Roland E.; Hostetler, Robert P.; Edwards, Bruce H. (1998), Calculus of a Single Variable (6th ed.), Houghton Mifflin Company
- Protter, Murray H.; Morrey, Charles B. Jr. (1970), College Calculus with Analytic Geometry (2nd ed.), Reading: Addison-Wesley, LCCN 76087042
- Sangwin, C.J., Locating the centre of mass by mechanical means (PDF), archived from the original (PDF) on November 13, 2013
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Geometric Centroid". MathWorld.
- Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers by Clark Kimberling. The centroid is indexed as X(2).
- Characteristic Property of Centroid at cut-the-knot
- Interactive animations showing Centroid of a triangle and Centroid construction with compass and straightedge
- Experimentally finding the medians and centroid of a triangle at Dynamic Geometry Sketches, an interactive dynamic geometry sketch using the gravity simulator of Cinderella.
 -
- points
points  in
in  is
is
 This point minimizes the sum of squared Euclidean distances between itself and each point in the set.
This point minimizes the sum of squared Euclidean distances between itself and each point in the set.
 can be computed by dividing it into a finite number of simpler figures
can be computed by dividing it into a finite number of simpler figures  computing the centroid
computing the centroid  and area
and area  of each part, and then computing
of each part, and then computing

 overlaps between the parts, or parts that extend outside the figure can all be handled using negative areas
overlaps between the parts, or parts that extend outside the figure can all be handled using negative areas  Namely, the measures
Namely, the measures  is
is  if
if  otherwise.
otherwise.
 The vertical position of the centroid is found in the same way.
The vertical position of the centroid is found in the same way.
 rather than its area. It also holds for any subset of
rather than its area. It also holds for any subset of  for any dimension
for any dimension  with the areas replaced by the
with the areas replaced by the  -dimensional
-dimensional 
 and
and  is the
is the  if
if  and
and  otherwise. Note that the denominator is simply the
otherwise. Note that the denominator is simply the  This formula cannot be applied if the set
This formula cannot be applied if the set 
 is the
is the  and
and  is the measure of the intersection of
is the measure of the intersection of  Again, the denominator is simply the measure of
Again, the denominator is simply the measure of 
 is the area of the figure
is the area of the figure  is the length of the intersection of
is the length of the intersection of  and
and  is the length of the intersection of
is the length of the intersection of 
 of a region bounded by the graphs of the
of a region bounded by the graphs of the  and
and  on the interval
on the interval 
 is given by
is given by

 ).
).



 and also along
and also along  it must be at the intersection of these two lines, at
it must be at the intersection of these two lines, at  The point
The point  might lie inside or outside the L-shaped object.
might lie inside or outside the L-shaped object. which is to say it is located
which is to say it is located  of the distance from each side to the opposite vertex (see figures at right). Its
of the distance from each side to the opposite vertex (see figures at right). Its 
 and
and  then the centroid (denoted
then the centroid (denoted  here but most commonly denoted
here but most commonly denoted  in
in 
 in
in  and vertex angles
and vertex angles  :
:

 times the length of any side times the perpendicular distance from the side to the centroid.
times the length of any side times the perpendicular distance from the side to the centroid.
 and its
and its  exactly twice as close to the latter as to the former:
exactly twice as close to the latter as to the former:

 and
and  we have
we have

 then
then

 that of the original triangle.
that of the original triangle.
 be any point in the plane of a triangle with vertices
be any point in the plane of a triangle with vertices  and centroid
and centroid  Then the sum of the squared distances of
Then the sum of the squared distances of 

 be a triangle, let
be a triangle, let  be the midpoints of segments
be the midpoints of segments  respectively. For any point
respectively. For any point 


 is the point
is the point  where
where



 is assumed to be the same as
is assumed to be the same as  meaning
meaning  on the last case must loop around to
on the last case must loop around to  (If the points are numbered in clockwise order, the area
(If the points are numbered in clockwise order, the area  computed as above, will be negative; however, the centroid coordinates will be correct even in this case.)
computed as above, will be negative; however, the centroid coordinates will be correct even in this case.)
 the distance from the base to the apex. For a cone or pyramid that is just a shell (hollow) with no base, the centroid is
the distance from the base to the apex. For a cone or pyramid that is just a shell (hollow) with no base, the centroid is  The centroid of a tetrahedron is the midpoint between its
The centroid of a tetrahedron is the midpoint between its  then considering the vertices as
then considering the vertices as 
 equal masses.
equal masses.
 (i.e. it lies
(i.e. it lies  of the way from the center to the pole).
The centroid of a hollow hemisphere (i.e. half of a hollow sphere) divides the line segment connecting the sphere's center to the hemisphere's pole in half.
of the way from the center to the pole).
The centroid of a hollow hemisphere (i.e. half of a hollow sphere) divides the line segment connecting the sphere's center to the hemisphere's pole in half.