| Giroc | |
|---|---|
| Commune | |
 St. Demetrius Orthodox church in Giroc St. Demetrius Orthodox church in Giroc | |
 Coat of arms Coat of arms | |
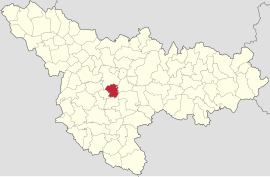 Location in Timiș County Location in Timiș County | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 45°42′N 21°14′E / 45.700°N 21.233°E / 45.700; 21.233 | |
| Country | Romania |
| County | Timiș |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2020–2024) | Iosif Ionel Toma (PSD) |
| Area | 52.77 km (20.37 sq mi) |
| Population | 22,270 |
| • Density | 420/km (1,100/sq mi) |
| Time zone | EET/EEST (UTC+2/+3) |
| Postal code | 307220–307221 |
| Vehicle reg. | TM |
| Website | www |
Giroc (Hungarian: Gyüreg; German: Girok) is a commune in Timiș County, Romania. It is composed of two villages, Chișoda and Giroc (commune seat). It is located near Timișoara, south of the city.
Location
Giroc is a suburban commune of Timișoara, located three kilometers south of it. In recent years, by building and developing the neighborhood in Planiște and Ogrindova areas, Giroc has virtually joined Timișoara. It is bordered on the east by Urseni, on the southwest by Șag and on the west by Utvin. Timiș River flows through the south of the commune, which separates Giroc from Pădureni and Unip.
History
The first recorded mention of Giroc dates back to 1371, in a document by which Sigismund of Luxembourg donated the Gyüreg estate to Vladislau, son of Ștefan de Taar. Throughout the Middle Ages, Giroc continued to be sporadically mentioned in various documents. Between 1453 and 1497 it appears under the Hungarian name Szent György (Saint George). What is certain is that, in 1456, Chișoda is mentioned as the property of John Hunyadi, which is why it is possible that Giroc had the same status. Later, Marsigli's conscriptions from 1690–1700 speak of Gyirog. After the Austrian conquest of Banat, Giroc appears on the 1717 map with the name Jurok, listed with 70 houses and later on Mercy's map from 1723 with the name Jurak.
After the Hungarian Revolution of 1848 and the abolition of serfdom, Giroc experienced a marked development, although it also suffered heavy flooding in 1859 and a severe drought between 1863 and 1864. As a result of the floods, Timiș River was dammed in Giroc; damming works began in 1874. In the second half of the 19th century, Giroc benefited from the general modernization that included Banat, being in turn connected to the postal network, to the telegraphic one and then to the Timișoara–Baziaș railway, one of the first railways in Banat, connecting Timișoara to the Danubian port Baziaș, put into use in 1858. In 1897, Atanasie Baicu founded the people's bank Giroceana, a rural credit institution that supported Romanian peasants to buy agricultural land, offering them much more advantageous loans that they could receive from Timișoara banks. The bank has played a key role in modernizing agriculture and significantly increasing general welfare.
After the union of Banat with Romania, in 1921, the Hungarian barons were expropriated and the land was redistributed to the peasants. During the same period, the official name changed from Gyüreg to the Romanian Giroc. After World War II, Giroc underwent nationalization and collectivization, then partial industrialization and experienced an increase in migration and commuting. The first years after the Romanian Revolution marked a period of stagnation, but Giroc currently benefits from a favorable position and conjuncture, being one of the richest communes in Timiș County.
Demographics
Giroc had 8,388 inhabitants at the 2011 census, up 95% from the 2002 census. More recent estimates show that the population has exceeded 14,000 inhabitants.
Until World War I, there was a general increase in population due to both natural and migratory growth. During World War I the population decreases, then goes through a period of relative stagnation until World War II, when it decreases again. After that, it started to grow, especially after 1960, when several families from the rest of the country began to settle in Giroc, especially from Caraș-Severin County and Transylvania (especially Bihor).
The development of Timișoara's industry, the need for labor and the impossibility of settling in Timișoara, this being a closed city, determined many families to settle in Giroc, where they buy houses or live in rent and from where they commute to Timișoara, especially after, in 1963, the bus from Timișoara to Giroc is established. In January 1977, 145 households and 545 inhabitants outside the actual hearth of Giroc are detached and administratively transferred to Timișoara, to form the current Fratelia B neighborhood, attached to the city.
After declining in the late 1980s and early 1990s, the population stabilized and began to rise again. Both Germans and Hungarians were significantly reduced in number, and the Romanian majority strengthened. Especially after 2000, amid the development of the local economy, there is an increased development of the real estate industry, which also entails a significant increase of the population.
Ethnic composition
Ethnic composition (2011)
Romanians (90.44%) Hungarians (1.8%) Unknown (4.64%) Others (3.12%)Religious composition (2011)
Orthodox (81.75%) Roman Catholics (3.84%) Pentecostals (3.51%) Baptists (3.12%) Unknown (4.84%) Others (2.94%)According to the 2011 census, the majority of the inhabitants are Romanians (90.44%), with a minority of Hungarians (1.8%). For 4.64% of the population, ethnicity is unknown. The inhabitants were for a long time mostly Romanian Orthodox. Between 1865 and 1870, the first colonization of Giroc took place with German families from Grabaț, Lenauheim and Variaș. Between 1910 and 1912, a new wave of German settlers from Nițchidorf arrived in Giroc.
| Census | Ethnic composition | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Population | Romanians | Hungarians | Germans | ||
| 1880 | 3,033 | 2,813 | 31 | 173 | ||
| 1890 | 3,467 | 3,006 | 51 | 402 | ||
| 1900 | 3,903 | 3,195 | 192 | 492 | ||
| 1910 | 5,368 | 3,233 | 846 | 1,155 | ||
| 1920 | 3,574 | 2,862 | 164 | 513 | ||
| 1930 | 3,610 | 2,799 | 167 | 576 | ||
| 1941 | 3,702 | 2,856 | 228 | 570 | ||
| 1956 | 3,393 | 2,760 | 162 | 430 | ||
| 1966 | 4,452 | 3,601 | 298 | 499 | ||
| 1977 | 4,891 | 4,168 | 182 | 440 | ||
| 1992 | 3,951 | 3,645 | 128 | 96 | ||
| 2002 | 4,295 | 4,060 | 112 | 61 | ||
| 2011 | 8,388 | 7,586 | 151 | 66 | ||
Religious composition
According to the 2011 census, most of the inhabitants are Eastern Orthodox (81.75%), but there are also minorities of Roman Catholics (3.84%), Pentecostals (3.51%) and Baptists (3.12%). For 4.84% of the population, religious affiliation is unknown. There are two Romanian Orthodox churches, two Pentecostal churches and two Baptist churches in the commune.
Economy
Giroc plays an important role for the economy of Timișoara, as it has established itself as a labor force reserve, and in recent years has begun to host several firms attracted by the economy of Timișoara, but which have settled in neighboring areas. In Giroc and Chișoda there are a total of almost 2,000 firms. On the territory belonging to Chișoda is the Șagului industrial platform. The economic development of the commune is also reflected in the size of the built-up area, which increased sixfold between 2009 and 2019.
Notable people
- Aurel Jivi (1943–2002), professor and priest
- Petrică Moise (1947–2021), singer and composer of folk music
References
- "Results of the 2020 local elections". Central Electoral Bureau. Retrieved 16 June 2021.
- "Primăria Giroc". Ghidul Primăriilor.
- "Populaţia rezidentă după grupa de vârstă, pe județe și municipii, orașe, comune, la 1 decembrie 2021" (XLS). National Institute of Statistics.
- ^ "Descrierea comunei Giroc". Primăria comunei Giroc.
- ^ Gruița, Octavian (1996). Giroc. Monografie istorică. Timișoara: Editura Marineasa. ISBN 973-9185-49-5.
- "Fișa Primăriei comunei Giroc pe anul 2020". Consiliul Județean Timiș.
- ^ Szabó, Attila M. (2003). Erdély, Bánság és Partium történeti és közigazgatási helységnévtára. Miercurea Ciuc: Pro-Print Kiadó. ISBN 973-8468-01-9.
- ^ "Tab8. Populația stabilă după etnie – județe, municipii, orașe, comune". Institutul Național de Statistică. Archived from the original on 2016-01-18. Retrieved 2021-09-02.
- ^ "Tab13. Populația stabilă după religie – județe, municipii, orașe, comune". Institutul Național de Statistică. Archived from the original on 2020-08-07. Retrieved 2021-09-02.
- Varga, E. Árpád. "Temes megye településeinek etnikai (anyanyelvi/nemzetiségi) adatai 1880-1992" (PDF).
- "Giroc / Gyüreg / Girok". Structura etno-demografică a României. Centrul de Resurse pentru Diversitate Etnoculturală.
- "Biserici și monumente". Primăria comunei Giroc.
- Ledrer, Caterina (8 September 2019). "Giroc, comuna lipită de Timișoara și preferată de mulți timișoreni. Avantaje și dezavantaje". Banatul Azi.
- ^ Diaconu, Raluca (14 February 2019). "Comuna din România care atrage tinerii ca un magnet! În 25 de ani, numărul de locuitori a crescut de 5 ori!". Libertatea.
