| This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (March 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Mathematical analysis → Complex analysis |
| Complex analysis |
|---|
 |
| Complex numbers |
| Complex functions |
| Basic theory |
| Geometric function theory |
| People |
Complex analysis, traditionally known as the theory of functions of a complex variable, is the branch of mathematical analysis that investigates functions of complex numbers. It is helpful in many branches of mathematics, including algebraic geometry, number theory, analytic combinatorics, and applied mathematics, as well as in physics, including the branches of hydrodynamics, thermodynamics, quantum mechanics, and twistor theory. By extension, use of complex analysis also has applications in engineering fields such as nuclear, aerospace, mechanical and electrical engineering.
As a differentiable function of a complex variable is equal to the sum function given by its Taylor series (that is, it is analytic), complex analysis is particularly concerned with analytic functions of a complex variable, that is, holomorphic functions. The concept can be extended to functions of several complex variables.
History

Complex analysis is one of the classical branches in mathematics, with roots in the 18th century and just prior. Important mathematicians associated with complex numbers include Euler, Gauss, Riemann, Cauchy, Gösta Mittag-Leffler, Weierstrass, and many more in the 20th century. Complex analysis, in particular the theory of conformal mappings, has many physical applications and is also used throughout analytic number theory. In modern times, it has become very popular through a new boost from complex dynamics and the pictures of fractals produced by iterating holomorphic functions. Another important application of complex analysis is in string theory which examines conformal invariants in quantum field theory.
Complex functions

A complex function is a function from complex numbers to complex numbers. In other words, it is a function that has a (not necessarily proper) subset of the complex numbers as a domain and the complex numbers as a codomain. Complex functions are generally assumed to have a domain that contains a nonempty open subset of the complex plane.
For any complex function, the values from the domain and their images in the range may be separated into real and imaginary parts:
where are all real-valued.
In other words, a complex function may be decomposed into
- and
i.e., into two real-valued functions (, ) of two real variables (, ).
Similarly, any complex-valued function f on an arbitrary set X (is isomorphic to, and therefore, in that sense, it) can be considered as an ordered pair of two real-valued functions: (Re f, Im f) or, alternatively, as a vector-valued function from X into
Some properties of complex-valued functions (such as continuity) are nothing more than the corresponding properties of vector valued functions of two real variables. Other concepts of complex analysis, such as differentiability, are direct generalizations of the similar concepts for real functions, but may have very different properties. In particular, every differentiable complex function is analytic (see next section), and two differentiable functions that are equal in a neighborhood of a point are equal on the intersection of their domain (if the domains are connected). The latter property is the basis of the principle of analytic continuation which allows extending every real analytic function in a unique way for getting a complex analytic function whose domain is the whole complex plane with a finite number of curve arcs removed. Many basic and special complex functions are defined in this way, including the complex exponential function, complex logarithm functions, and trigonometric functions.
Holomorphic functions
Main article: Holomorphic functionComplex functions that are differentiable at every point of an open subset of the complex plane are said to be holomorphic on . In the context of complex analysis, the derivative of at is defined to be
Superficially, this definition is formally analogous to that of the derivative of a real function. However, complex derivatives and differentiable functions behave in significantly different ways compared to their real counterparts. In particular, for this limit to exist, the value of the difference quotient must approach the same complex number, regardless of the manner in which we approach in the complex plane. Consequently, complex differentiability has much stronger implications than real differentiability. For instance, holomorphic functions are infinitely differentiable, whereas the existence of the nth derivative need not imply the existence of the (n + 1)th derivative for real functions. Furthermore, all holomorphic functions satisfy the stronger condition of analyticity, meaning that the function is, at every point in its domain, locally given by a convergent power series. In essence, this means that functions holomorphic on can be approximated arbitrarily well by polynomials in some neighborhood of every point in . This stands in sharp contrast to differentiable real functions; there are infinitely differentiable real functions that are nowhere analytic; see Non-analytic smooth function § A smooth function which is nowhere real analytic.
Most elementary functions, including the exponential function, the trigonometric functions, and all polynomial functions, extended appropriately to complex arguments as functions , are holomorphic over the entire complex plane, making them entire functions, while rational functions , where p and q are polynomials, are holomorphic on domains that exclude points where q is zero. Such functions that are holomorphic everywhere except a set of isolated points are known as meromorphic functions. On the other hand, the functions , , and are not holomorphic anywhere on the complex plane, as can be shown by their failure to satisfy the Cauchy–Riemann conditions (see below).
An important property of holomorphic functions is the relationship between the partial derivatives of their real and imaginary components, known as the Cauchy–Riemann conditions. If , defined by , where , is holomorphic on a region , then for all ,
In terms of the real and imaginary parts of the function, u and v, this is equivalent to the pair of equations and , where the subscripts indicate partial differentiation. However, the Cauchy–Riemann conditions do not characterize holomorphic functions, without additional continuity conditions (see Looman–Menchoff theorem).
Holomorphic functions exhibit some remarkable features. For instance, Picard's theorem asserts that the range of an entire function can take only three possible forms: , , or for some . In other words, if two distinct complex numbers and are not in the range of an entire function , then is a constant function. Moreover, a holomorphic function on a connected open set is determined by its restriction to any nonempty open subset.
Conformal map
This section is an excerpt from Conformal map.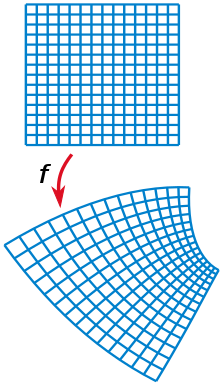
In mathematics, a conformal map is a function that locally preserves angles, but not necessarily lengths.
More formally, let and be open subsets of . A function is called conformal (or angle-preserving) at a point if it preserves angles between directed curves through , as well as preserving orientation. Conformal maps preserve both angles and the shapes of infinitesimally small figures, but not necessarily their size or curvature.
The conformal property may be described in terms of the Jacobian derivative matrix of a coordinate transformation. The transformation is conformal whenever the Jacobian at each point is a positive scalar times a rotation matrix (orthogonal with determinant one). Some authors define conformality to include orientation-reversing mappings whose Jacobians can be written as any scalar times any orthogonal matrix.
For mappings in two dimensions, the (orientation-preserving) conformal mappings are precisely the locally invertible complex analytic functions. In three and higher dimensions, Liouville's theorem sharply limits the conformal mappings to a few types.
The notion of conformality generalizes in a natural way to maps between Riemannian or semi-Riemannian manifolds.Major results
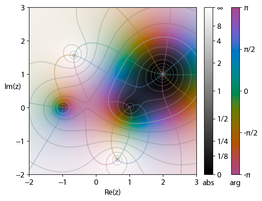
Hue represents the argument, brightness the magnitude.
One of the central tools in complex analysis is the line integral. The line integral around a closed path of a function that is holomorphic everywhere inside the area bounded by the closed path is always zero, as is stated by the Cauchy integral theorem. The values of such a holomorphic function inside a disk can be computed by a path integral on the disk's boundary (as shown in Cauchy's integral formula). Path integrals in the complex plane are often used to determine complicated real integrals, and here the theory of residues among others is applicable (see methods of contour integration). A "pole" (or isolated singularity) of a function is a point where the function's value becomes unbounded, or "blows up". If a function has such a pole, then one can compute the function's residue there, which can be used to compute path integrals involving the function; this is the content of the powerful residue theorem. The remarkable behavior of holomorphic functions near essential singularities is described by Picard's theorem. Functions that have only poles but no essential singularities are called meromorphic. Laurent series are the complex-valued equivalent to Taylor series, but can be used to study the behavior of functions near singularities through infinite sums of more well understood functions, such as polynomials.
A bounded function that is holomorphic in the entire complex plane must be constant; this is Liouville's theorem. It can be used to provide a natural and short proof for the fundamental theorem of algebra which states that the field of complex numbers is algebraically closed.
If a function is holomorphic throughout a connected domain then its values are fully determined by its values on any smaller subdomain. The function on the larger domain is said to be analytically continued from its values on the smaller domain. This allows the extension of the definition of functions, such as the Riemann zeta function, which are initially defined in terms of infinite sums that converge only on limited domains to almost the entire complex plane. Sometimes, as in the case of the natural logarithm, it is impossible to analytically continue a holomorphic function to a non-simply connected domain in the complex plane but it is possible to extend it to a holomorphic function on a closely related surface known as a Riemann surface.
All this refers to complex analysis in one variable. There is also a very rich theory of complex analysis in more than one complex dimension in which the analytic properties such as power series expansion carry over whereas most of the geometric properties of holomorphic functions in one complex dimension (such as conformality) do not carry over. The Riemann mapping theorem about the conformal relationship of certain domains in the complex plane, which may be the most important result in the one-dimensional theory, fails dramatically in higher dimensions.
A major application of certain complex spaces is in quantum mechanics as wave functions.
See also
- Complex geometry
- Hypercomplex analysis
- Vector calculus
- List of complex analysis topics
- Monodromy theorem
- Real analysis
- Riemann–Roch theorem
- Runge's theorem
References
- "Industrial Applications of Complex Analysis". Newton Gateway to Mathematics. October 30, 2019. Retrieved November 20, 2023.
- Rudin, Walter (1987). Real and Complex Analysis (PDF). McGraw-Hill Education. p. 197. ISBN 978-0-07-054234-1.
- Blair, David (2000-08-17). Inversion Theory and Conformal Mapping. The Student Mathematical Library. Vol. 9. Providence, Rhode Island: American Mathematical Society. doi:10.1090/stml/009. ISBN 978-0-8218-2636-2. S2CID 118752074.
Sources
- Ablowitz, M. J. & A. S. Fokas, Complex Variables: Introduction and Applications (Cambridge, 2003).
- Ahlfors, L., Complex Analysis (McGraw-Hill, 1953).
- Cartan, H., Théorie élémentaire des fonctions analytiques d'une ou plusieurs variables complexes. (Hermann, 1961). English translation, Elementary Theory of Analytic Functions of One or Several Complex Variables. (Addison-Wesley, 1963).
- Carathéodory, C., Funktionentheorie. (Birkhäuser, 1950). English translation, Theory of Functions of a Complex Variable (Chelsea, 1954).
- Carrier, G. F., M. Krook, & C. E. Pearson, Functions of a Complex Variable: Theory and Technique. (McGraw-Hill, 1966).
- Conway, J. B., Functions of One Complex Variable. (Springer, 1973).
- Fisher, S., Complex Variables. (Wadsworth & Brooks/Cole, 1990).
- Forsyth, A., Theory of Functions of a Complex Variable (Cambridge, 1893).
- Freitag, E. & R. Busam, Funktionentheorie. (Springer, 1995). English translation, Complex Analysis. (Springer, 2005).
- Goursat, E., Cours d'analyse mathématique, tome 2. (Gauthier-Villars, 1905). English translation, A course of mathematical analysis, vol. 2, part 1: Functions of a complex variable. (Ginn, 1916).
- Henrici, P., Applied and Computational Complex Analysis (Wiley).
- Kreyszig, E., Advanced Engineering Mathematics. (Wiley, 1962).
- Lavrentyev, M. & B. Shabat, Методы теории функций комплексного переменного. (Methods of the Theory of Functions of a Complex Variable). (1951, in Russian).
- Markushevich, A. I., Theory of Functions of a Complex Variable, (Prentice-Hall, 1965).
- Marsden & Hoffman, Basic Complex Analysis. (Freeman, 1973).
- Needham, T., Visual Complex Analysis. (Oxford, 1997). http://usf.usfca.edu/vca/
- Remmert, R., Theory of Complex Functions. (Springer, 1990).
- Rudin, W., Real and Complex Analysis. (McGraw-Hill, 1966).
- Shaw, W. T., Complex Analysis with Mathematica (Cambridge, 2006).
- Stein, E. & R. Shakarchi, Complex Analysis. (Princeton, 2003).
- Sveshnikov, A. G. & A. N. Tikhonov, Теория функций комплексной переменной. (Nauka, 1967). English translation, The Theory Of Functions Of A Complex Variable (MIR, 1978).
- Titchmarsh, E. C., The Theory of Functions. (Oxford, 1932).
- Wegert, E., Visual Complex Functions. (Birkhäuser, 2012).
- Whittaker, E. T. & G. N. Watson, A Course of Modern Analysis. (Cambridge, 1902). 3rd ed. (1920)
External links
| Major topics in mathematical analysis | |
|---|---|
| Mathematics portal |
 from the domain and their images
from the domain and their images  in the range may be separated into
in the range may be separated into 
 are all real-valued.
are all real-valued.
 may be decomposed into
may be decomposed into
 and
and 
 ,
,  ) of two real variables (
) of two real variables ( ,
,  ).
).

 of the complex plane are said to be holomorphic on
of the complex plane are said to be holomorphic on  at
at  is defined to be
is defined to be

 , are holomorphic over the entire complex plane, making them entire functions, while rational functions
, are holomorphic over the entire complex plane, making them entire functions, while rational functions  , where p and q are polynomials, are holomorphic on domains that exclude points where q is zero. Such functions that are holomorphic everywhere except a set of isolated points are known as meromorphic functions. On the other hand, the functions
, where p and q are polynomials, are holomorphic on domains that exclude points where q is zero. Such functions that are holomorphic everywhere except a set of isolated points are known as meromorphic functions. On the other hand, the functions  ,
,  , and
, and  are not holomorphic anywhere on the complex plane, as can be shown by their failure to satisfy the Cauchy–Riemann conditions (see below).
are not holomorphic anywhere on the complex plane, as can be shown by their failure to satisfy the Cauchy–Riemann conditions (see below).
 , where
, where  , is holomorphic on a
, is holomorphic on a  ,
,

 and
and  , where the subscripts indicate partial differentiation. However, the Cauchy–Riemann conditions do not characterize holomorphic functions, without additional continuity conditions (see
, where the subscripts indicate partial differentiation. However, the Cauchy–Riemann conditions do not characterize holomorphic functions, without additional continuity conditions (see  ,
,  , or
, or  for some
for some  . In other words, if two distinct complex numbers
. In other words, if two distinct complex numbers  are not in the range of an entire function
are not in the range of an entire function  and
and  be open subsets of
be open subsets of  . A function
. A function  is called conformal (or angle-preserving) at a point
is called conformal (or angle-preserving) at a point  if it preserves angles between directed
if it preserves angles between directed  , as well as preserving orientation. Conformal maps preserve both angles and the shapes of infinitesimally small figures, but not necessarily their size or
, as well as preserving orientation. Conformal maps preserve both angles and the shapes of infinitesimally small figures, but not necessarily their size or