| This article may require cleanup to meet Misplaced Pages's quality standards. The specific problem is: Some links missing, also check for overlink. Please help improve this article if you can. (February 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

Endogenous retroviruses (ERVs) are endogenous viral elements in the genome that closely resemble and can be derived from retroviruses. They are abundant in the genomes of jawed vertebrates, and they comprise up to 5–8% of the human genome (lower estimates of ~1%).
An ERV is a vertically inherited proviral sequence and a subclass of a type of gene called a transposon, which can normally be packaged and moved within the genome to serve a vital role in gene expression and in regulation. ERVs, however, lack most transposon functions, are typically not infectious, and are often defective genomic remnants of the retroviral replication cycle. They are distinguished as germline provirus retroelements due to their integration and reverse-transcription into the nuclear genome of the host cell.
Researchers have suggested that retroviruses evolved from a type of transposon called a retrotransposon, a Class I element; these genes can mutate and instead of moving to another location in the genome, they can become exogenous or pathogenic. This means that not all ERVs may have originated as an insertion by a retrovirus but that some may have been the source for the genetic information in the retroviruses they resemble. When integration of viral DNA occurs in the germ-line, it can give rise to an ERV, which can later become fixed in the gene pool of the host population.
Formation
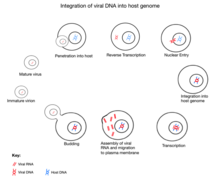
The replication cycle of a retrovirus entails the insertion ("integration") of a DNA copy of the viral genome into the nuclear genome of the host cell. Most retroviruses infect somatic cells, but occasional infection of germline cells (cells that produce eggs and sperm) can also occur. Rarely, retroviral integration may occur in a germline cell that goes on to develop into a viable organism. This organism will carry the inserted retroviral genome as an integral part of its own genome—an "endogenous" retrovirus (ERV) that may be inherited by its offspring as a novel allele. Many ERVs have persisted in the genome of their hosts for millions of years. However, most of these have acquired inactivating mutations during host DNA replication and are no longer capable of producing the virus. ERVs can also be partially excised from the genome by a process known as recombinational deletion, in which recombination between the identical sequences that flank newly integrated retroviruses results in deletion of the internal, protein-coding regions of the viral genome.
The general retrovirus genome consists of three genes vital for the invasion, replication, escape, and spreading of its viral genome. These three genes are gag (encodes for structural proteins for the viral core), pol (encodes for reverse transcriptase, integrase, and protease), and env (encodes for coat proteins for the virus's exterior). These viral proteins are encoded as polyproteins. In order to carry out their life cycle, the retrovirus relies heavily on the host cell's machinery. Protease degrades peptide bonds of the viral polyproteins, making the separate proteins functional. Reverse transcriptase functions to synthesize viral DNA from the viral RNA in the host cell's cytoplasm before it enters the nucleus. Integrase guides the integration of viral DNA into the host genome.
Over time, the genome of ERVs not only acquire point mutations, but also shuffle and recombine with other ERVs. ERVs with a decayed sequence for the env become more likely to propagate.
Role in genomic evolution
Endogenous retroviruses can play an active role in shaping genomes. Most studies in this area have focused on the genomes of humans and higher primates, but other vertebrates, such as mice and sheep, have also been studied in depth. The long terminal repeat (LTR) sequences that flank ERV genomes frequently act as alternate promoters and enhancers, often contributing to the transcriptome by producing tissue-specific variants. In addition, the retroviral proteins themselves have been co-opted to serve novel host functions, particularly in reproduction and development. Recombination between homologous retroviral sequences has also contributed to gene shuffling and the generation of genetic variation. Furthermore, in the instance of potentially antagonistic effects of retroviral sequences, repressor genes have co-evolved to combat them.
About 90% of endogenous retroviruses are solo LTRs, lacking all open reading frames (ORFs). Solo LTRs and LTRs associated with complete retroviral sequences have been shown to act as transcriptional elements on host genes. Their range of action is mainly by insertion into the 5' untranslated regions (UTRs) of protein coding genes; however, they have been known to act upon genes up to 70–100 kb away. The majority of these elements are inserted in the sense direction (5' to 3') to their corresponding genes, but there has been evidence of LTRs acting in the antisense direction (3' to 5') and as a bidirectional promoter for neighboring genes. In a few cases, the LTR functions as the major promoter for the gene.
For example, in humans, amylase alpha 1C (AMY1C) has a complete ERV sequence in its promoter region; the associated LTR confers salivary specific expression of the digestive enzyme amylase. Also, the primary promoter for bile acid-CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase (BAAT), which codes for an enzyme that is integral in bile metabolism, is of LTR origin.
The insertion of a solo ERV-9 LTR may have produced a functional open reading frame, causing the rebirth of the human immunity related GTPase gene (IRGM). ERV insertions have also been shown to generate alternative splice sites either by direct integration into the gene, as with the human leptin hormone receptor, or driven by the expression of an upstream LTR, as with the phospholipase A-2 like protein.
Most of the time, however, the LTR functions as one of many alternate promoters, often conferring tissue-specific expression related to reproduction and development. In fact, 64% of known LTR-promoted transcription variants are expressed in reproductive tissues. For example, the gene CYP19 codes for aromatase P450, an important enzyme for estrogen synthesis, that is normally expressed in the brain and reproductive organs of most mammals. However, in primates, an LTR-promoted transcriptional variant confers expression to the placenta and is responsible for controlling estrogen levels during pregnancy. Furthermore, the neuronal apoptosis inhibitory protein (NAIP), normally widespread, has an LTR of the human ERV-P (HERV-P) family acting as a promoter that confers expression to the testis and prostate. Other proteins, such as nitric oxide synthase 3 (NOS3), interleukin-2 receptor B (IL-2RB), and another mediator of estrogen synthesis, HSD17B1, are also alternatively regulated by LTRs that confer placental expression, but their specific functions are not yet known. The high degree of reproductive expression is thought to be an after effect of the method by which they were endogenized; however, this also may be due to a lack of DNA methylation in germ-line tissues.
The best-characterized instance of placental protein expression comes not from an alternatively promoted host gene but from a complete co-option of a retroviral protein. Retroviral fusogenic env proteins, which play a role in the entry of the virion into the host cell, have had an important impact on the development of the mammalian placenta. In mammals, intact env proteins called syncytins are responsible for the formation and function of syncytiotrophoblasts. These multinucleated cells are mainly responsible for maintaining nutrient exchange and separating the fetus from the mother's immune system. It has been suggested that the selection and fixation of these proteins for this function have played a critical role in the evolution of viviparity.
In addition, the insertion of ERVs and their respective LTRs have the potential to induce chromosomal rearrangement due to recombination between viral sequences at inter-chromosomal loci. These rearrangements have been shown to induce gene duplications and deletions that largely contribute to genome plasticity and dramatically change the dynamic of gene function. Furthermore, retroelements in general are largely prevalent in rapidly evolving, mammal-specific gene families whose function is largely related to the response to stress and external stimuli. In particular, both human class I and class II MHC genes have a high density of HERV elements as compared to other multi-locus-gene families. It has been shown that HERVs have contributed to the formation of extensively duplicated duplicon blocks that make up the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class 1 family of genes. More specifically, HERVs primarily occupy regions within and between the break points of these blocks, suggesting that considerable duplication and deletion events, typically associated with unequal crossover, facilitated their formation. The generation of these blocks, inherited as immunohaplotypes, act as a protective polymorphism against a wide range of antigens that may have imbued humans with an advantage over other primates.
The characteristic of placentas being very evolutionary distinct organs between different species has been suggested to result from the co-option of ERV enhancers. Regulatory mutations, instead of mutations in genes that encode for hormones and growth factors, support the known evolution of placental morphology, especially since the majority of hormone and growth factor genes are expressed in response to pregnancy, not during placental development. Researchers studied the regulatory landscape of placental development between the rat and mouse, two closely related species. This was done by mapping all regulatory elements of the rat trophoblast stem cells (TSCs) and comparing them to their orthologs in mouse TSCs. TSCs were observed because they reflect the initial cells that develop in the fetal placenta. Regardless of their tangible similarities, enhancer and repressed regions were mostly species-specific. However, most promoter sequences were conserved between mouse and rat. In conclusion to their study, researchers proposed that ERVs influenced species-specific placental evolution through mediation of placental growth, immunosuppression, and cell fusion.
Another example of ERV exploiting cellular mechanisms is p53, a tumor suppressor gene (TSG). DNA damage and cellular stress induces the p53 pathway, which results in cell apoptosis. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation with sequencing, thirty-percent of all p53-binding sites were located within copies of a few primate-specific ERV families. A study suggested that this benefits retroviruses because p53's mechanism provides a rapid induction of transcription, which leads to the exit of viral RNA from the host cell.
Finally, the insertion of ERVs or ERV elements into genic regions of host DNA, or overexpression of their transcriptional variants, has a much higher potential to produce deleterious effects than positive ones. Their appearance into the genome has created a coevolutionary dynamic that proliferated the duplication and expansion of repressor genes. The most clear-cut example of this involves the rapid duplication and proliferation of tandem zinc-finger genes in mammal genomes. Zinc-finger genes, particularly those that include a (Krüppel associated box) KRAB domain, exist in high copy number in vertebrate genomes, and their range of functions are limited to transcriptional roles. It has been shown in mammals, however, that the diversification of these genes was due to multiple duplication and fixation events in response to new retroviral sequences or their endogenous copies to repress their transcription.
Role in disease
The majority of ERVs that occur in vertebrate genomes are ancient, inactivated by mutation, and have reached genetic fixation in their host species. For these reasons, they are extremely unlikely to have negative effects on their hosts except under unusual circumstances. Nevertheless, it is clear from studies in birds and non-human mammal species including mice, cats and koalas, that younger (i.e., more recently integrated) ERVs can be associated with disease. The number of active ERVs in the genome of mammals is negatively related to their body size, suggesting a contribution to Peto's paradox through cancer pathogenesis. This has led researchers to propose a role for ERVs in several forms of human cancer and autoimmune disease, although conclusive evidence is lacking.
Neurological disorders
In humans, ERVs have been proposed to be involved in multiple sclerosis (MS). A specific association between MS and the ERVWE1, or "syncytin" gene, which is derived from an ERV insertion, has been reported, along with the presence of an "MS-associated retrovirus" (MSRV), in patients with the disease. HERVs have also been implicated in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and addiction.
In 2004 it was reported that antibodies to HERVs were found in greater frequency in the sera of people with schizophrenia. Additionally, the cerebrospinal fluid of people with recent onset schizophrenia contained levels of a retroviral marker, reverse transcriptase, four times higher than control subjects. Researchers continue to look at a possible link between HERVs and schizophrenia, with the additional possibility of a triggering infection inducing schizophrenia.
Immunity
ERVs have been found to be associated to disease not only through disease-causing relations, but also through immunity. The frequency of ERVs in LTRs likely correlates to viral adaptations to take advantage of immunity signaling pathways that promote viral transcription and replication. A study done in 2016 investigated the benefit of ancient viral DNA integrated into a host through gene regulation networks induced by interferons, a branch of innate immunity. These cytokines are first to respond to viral infection and are also important in immunosurveillance for malignant cells. ERVs are predicted to act as cis-regulatory elements, but much of the adaptive consequences for certain physiological functions is still unknown. There is data that supports the general role of ERVs in the regulation of human interferon (IFN) response, specifically to interferon-gamma (IFN-G). For example, IFN-stimulated genes were found to be greatly enriched with ERVs bound by signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) and/or Interferon regulatory factor (IRF1) in CD14+ macrophages.
HERVs also play various roles shaping the human innate immunity response, with some sequences activating the system and others suppressing it. They may also protect from exogenous retroviral infections: the virus-like transcripts can activate pattern recognition receptors, and the proteins can interfere with active retroviruses. A gag protein from HERV-K(HML2) is shown to mix with HIV Gag, impairing HIV capsid formation as a result.
Gene regulation
Another idea proposed was that ERVs from the same family played a role in recruiting multiple genes into the same network of regulation. It was found that MER41 elements provided additional redundant regulatory enhancement to the genes located near STAT1 binding sites.
Role in medicine
Porcine endogenous retrovirus
See also: Xenotransplantation § Porcine endogenous retrovirusesFor humans, porcine endogenous retroviruses (PERVs) pose a concern when using porcine tissues and organs in xenotransplantation, the transplanting of living cells, tissues, and organs from an organism of one species to an organism of different species. Although pigs are generally the most suitable donors to treat human organ diseases due to practical, financial, safety, and ethical reasons, PERVs previously could not be removed from pigs, due to their viral ability to integrate into the host genome and passed into offspring, until the 2017, when one lab, using CRISPR-Cas9, removed all 62 retroviruses from the pig genome. The consequences of cross-species transmission remain unexplored and have dangerous potential.
Researchers have indicated that infection of human tissues by PERVs is very possible, especially in immunosuppressed individuals. An immunosuppressed condition could potentially permit a more rapid and tenacious replication of viral DNA, and would later have less difficulty adapting to human-to-human transmission. Although known infectious pathogens present in the donor organ/tissue can be eliminated by breeding pathogen-free herds, unknown retroviruses can be present in the donor. These retroviruses are often latent and asymptomatic in the donor, but can become active in the recipient. Some examples of endogenous viruses that can infect and multiply in human cells are from baboons (BaEV), cats (RD114), and mice.
There are three different classes of PERVs, PERV-A, PERV-B, and PERV-C. PERV-A and PERV-B are polytropic and can infect human cells in vitro, while PERV-C is ecotropic and does not replicate on human cells. The major differences between the classes is in the receptor binding domain of the env protein and the LTRs that influence the replication of each class. PERV-A and PERV-B display LTRs that have repeats in the U3 region. However, PERV-A and PERV-C show repeatless LTRs. Researchers found that PERVs in culture actively adapted to the repeat structure of their LTR in order to match the best replication performance a host cell could perform. At the end of their study, researchers concluded that repeatless PERV LTR evolved from the repeat-harboring LTR. This was likely to have occurred from insertional mutation and was proven through use of data on LTR and env/Env. It is thought that the generation of repeatless LTRs could be reflective of an adaptation process of the virus, changing from an exogenous to an endogenous lifestyle.
A clinical trial study performed in 1999 sampled 160 patients who were treated with different living pig tissues and observed no evidence of a persistent PERV infection in 97% of the patients from whom a sufficient amount of DNA was available to PCR for amplification of PERV sequences. This study stated found that retrospective studies are limited to finding the true incidence of infection or associated clinical symptoms. It suggested using closely monitored prospective trials which would provide a more complete and detailed evaluation of the possible cross-species PERV transmission and a comparison of the PERV.
Human endogenous retroviruses
"HERV" redirects here. For other uses, see Herv (disambiguation).HERVs comprise a significant part of the human genome, with approximately 98,000 ERV elements and fragments making up 5–8%. According to a study published in 2005, no HERVs capable of replication had been identified; all appeared to be defective, containing major deletions or nonsense mutations (not true for HERV-K). This is because most HERVs are merely traces of original viruses, having first integrated millions of years ago. An analysis of HERV integrations is ongoing as part of the 100,000 Genomes Project.
A 2023 study found HERV can become awakened from dormant states and contribute to aging which could be blocked by neutralizing antibodies.
HERVs were originally discovered when human genomic libraries were screened under low-stringency conditions using either probes from animal retroviruses or by using oligonucleotides with similarity to virus sequences.
Classification
HERVs are classified based on their homologies to animal retroviruses. Families belonging to Class I are similar in sequence to mammalian Gammaretroviruses (type C) and Epsilonretroviruses (Type E). Families belonging to Class II show homology to mammalian Betaretroviruses (Type B) and Deltaretroviruses (Type D). Families belonging to Class III are similar to foamy viruses. For all classes, if homologies appear well conserved in the gag, pol, and env gene, they are grouped into a superfamily. There are more Class I families known to exist. The families themselves are named in a less uniform manner, with a mixture of naming based on an exogenous retrovirus, the priming tRNA (HERV-W, HERV-K), or some neighboring gene (HERV-ADP), clone number (HERV-S71), or some amino acid motif (HERV-FRD). A proposed nomenclature aims to clean up the sometimes paraphyletic standards.
Origin
Sometime during human evolution, exogenous progenitors of HERV inserted themselves into germ line cells and then replicated along with the host's genes using and exploiting the host's cellular mechanisms. Because of their distinct genomic structure, HERVs were subjected to many rounds of amplification and transposition, which led to a more widespread distribution of retroviral DNA.
Nevertheless, one family of viruses has been active since the divergence of humans and chimpanzees. This family, termed HERV-K (HML2), makes up less than 1% of HERV elements but is one of the most studied. There are indications it has even been active in the past few hundred thousand years, e.g., some human individuals carry more copies of HML2 than others. Traditionally, age estimates of HERVs are performed by comparing the 5' and 3' LTR of a HERV; however, this method is only relevant for full-length HERVs. A recent method, called cross-sectional dating, uses variations within a single LTR to estimate the ages of HERV insertions. This method is more precise in estimating HERV ages and can be used for any HERV insertions. Cross-sectional dating has been used to suggest that two members of HERV-K (HML2), HERV-K106 and HERV-K116, were active in the last 800,000 years and that HERV-K106 may have infected modern humans 150,000 years ago. However, the absence of known infectious members of the HERV-K (HML2) family, and the lack of elements with a full coding potential within the published human genome sequence, suggests to some that the family is less likely to be active at present. In 2006 and 2007, researchers working independently in France and USA recreated functional versions of HERV-K (HML2).
Expression of HERV proteins
The expression of HERV-K, a biologically active family of HERV, produces proteins found in placenta. Furthermore, the expression of the envelope genes of HERV-W (ERVW-1 Archived 2013-09-19 at the Wayback Machine) and HERV-FRD (ERVFRD-1 Archived 2012-10-26 at the Wayback Machine) produces syncytins which are important for the generation of the syncytiotrophoblast cell layer during placentogenesis by inducing cell-cell fusion. The HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC) approves gene symbols for transcribed human ERVs.
Functional impact
MER41.AIM2 is an HERV that regulates the transcription of AIM2 (Absent in Melanoma 2) which encodes for a sensor of foreign cytosolic DNA. This acts as a binding site for AIM2, meaning that it is necessary for the transcription of AIM2. Researchers had shown this by deleting MER41.AIM2 in HeLa cells using CRISPR/Cas9, leading to an undetectable transcript level of AIM2 in modified HeLa cells. The control cells, which still contained the MER41.AIM2 ERV, were observed with normal amounts of AIM2 transcript. In terms of immunity, researchers concluded that MER41.AIM2 is necessary for an inflammatory response to infection.
Activation by exogenous viruses
Considerable evidence indicates that HERVs can be reactivated by viral infections, such as:
- retroviruses – human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1), human T-lymphotropic virus 1 (HTLV-1);
- RNA viruses – influenza A virus, hepatitis C virus (HCV), severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARSCoV-2);
- DNA viruses – herpes simplex virus type-1 (HSV-1), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), human cytomegalovirus (CMV), Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV)
Several studies have shown that EBV is able to transactivate the expression of the normally inactive HERV-K18 Env protein, e.g., interacting with resting B cells via the CD21 receptor. Further studies revealed that the mechanism of transactivation depends on the expression of the major EBV late gene transactivator, EBNA-2. In-depth analysis completed the picture identifying the EBV latent membrane protein LMP-2A as a strong candidate for the HERV-K18 transactivation. HERV-K18 has also been reported to have superantigen activity (i.e., polyclonal T and B cell activation regardless of the specificity of their antigen receptor).
It has also been shown that in vitro binding of the EBV gp350 protein caused activation of MSRVenv and syncytin-1 in B-cells, monocytes, macrophages, and astrocytes - cells that are involved in pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Monocytes, especially after their differentiation into macrophages, appeared to be the most responsive to EBVgp350, expressing even higher levels of HERV-Wenv than B cells. This finding is concordant with another study, which demonstrated that during infectious mononucleosis, EBV promoted the strongest activation of HERV-W/MSRV expression in monocytes compared to other blood cell types.
Immune response to HERVs
Despite having been integrated into genomes of vertebrates for millions of years, ERVs represent an intermediate stage between exogenous viruses and the host genome; it is suggested that immunological tolerance to HERV-derived proteins and peptides is imperfect due to the epigenetic silencing of HERV in the thymus and bone marrow, which prevents deletion of all HERV-specific T and B cells. As evidence of this, immunization of non-human primates with ERV-derived antigens mounted robust polyfunctional cytotoxic T cell response as well as high antibody titers. According to phylogenetic studies, among 30 HERV families existing in the human genome, HERV-K (HML-2) elements which integrated most recently are the most intact and biologically active forms. HERV-K env and HERV-H env, considered to be a new class of tumor-associated antigens, have been found to promote strong cytotoxic T-cell responses in patients with various types of cancers.
On a level of the innate immune sensing of nucleic acids, single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) and double-stranded RNA
(dsRNA) derived from endogenous retroviruses are recognized by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs).
SsRNAs can be sensed by Toll-like receptors TLR-7 and TLR-8, resulting in secretion of IFN-α by stimulated dendritic cells (DCs) and macrophages, which was observed for ssRNAs derived from HIV-1.
DsRNAs might be one of the most immunogenic nucleic acid pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), since they are not found in cells in a normal state. HERV-derived dsRNA can be recognized by TLR-3, RIG-I, and MDA5; RIG-I and MDA5 are known to induce a type I IFN response.
When retrotranscribed into DNA, retroviruses can be sensed by cyclic guanosine monophosphate (GMP)-adenosine monophosphate (AMP) synthase-stimulator of interferon genes (cGAS-STING) pathway, leading to the activation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kB) and IFN regulatory factor 3 (IRF3), which in turn trigger a type I IFN response. DsDNA could also be sensed by DNA-dependent activator of IFN-regulatory factors (DAI); DNA:RNA hybrids could be recognized by TLR-9
The recognition of nucleic acids through PRRs provides a very efficient strategy to fight against viral infections, at the same time exposing the host to a risk due to the possibility of recognizing self-nucleic acids and promotion of autoimmunity. Not surprisingly, HERVs have been found to be associated with different autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, such as multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumathoid arthritis (RA), and Sjögren syndrome (SS).
On a protein level, a direct interaction between TLRs and certain HERV proteins has been shown. For example, the surface unit of HERV-W Env (also known as multiple sclerosis-associated retroviral element (MSRV) env) was found to bind to TLR4 and CD14, stimulating the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines including IL-1β, IL-6, and TNFα. HERV-W Env can trigger a maturation process in human dendritic cells, endowing them with the capacity to support a Th1-like type of Th cell differentiation.
Immunological studies have shown some evidence for T cell immune responses against HERVs in HIV-infected individuals. The hypothesis that HIV induces HERV expression in HIV-infected cells led to the proposal that a vaccine targeting HERV antigens could specifically eliminate HIV-infected cells. The potential advantage of this novel approach is that, by using HERV antigens as surrogate markers of HIV-infected cells, it could circumvent the difficulty inherent in directly targeting notoriously diverse and fast-mutating HIV antigens.
Techniques for characterizing ERVs
Whole genome sequencing
Example: A PERV Chinese-born minipig isolate, PERV-A-BM, was sequenced completely and along with different breeds and cell lines in order to understand its genetic variation and evolution. The observed number of nucleotide substitutions and among the different genome sequences helped researchers determine an estimated age that PERV-A-BM was integrated into its host genome, which was found to be of an evolutionary age earlier than the European-born pigs isolates.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation with sequencing (ChIP-seq)
This technique is used to find histone marks indicative of promoters and enhancers, which are binding sites for DNA proteins, and repressed regions and trimethylation. DNA methylation has been shown to be vital to maintain silencing of ERVs in mouse somatic cells, while histone marks are vital for the same purpose in embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and early embryogenesis.
Applications
Constructing phylogenies
Because most HERVs have no function, are selectively neutral, and are very abundant in primate genomes, they easily serve as phylogenetic markers for linkage analysis. They can be exploited by comparing the integration site polymorphisms or the evolving, proviral, nucleotide sequences of orthologs. To estimate when integration occurred, researchers used distances from each phylogenetic tree to find the rate of molecular evolution at each particular locus. It is also useful that ERVs are abundant within the genomes of many species (i.e., plants, insects, mollusks, fish, rodents, domestic pets, and livestock) and the application of this ERV approach can be used to answer a variety of phylogenetic questions.
Designating the age of provirus and the time points of species separation events
This is accomplished by comparing the different HERV from different evolutionary periods. For example, this study was done for different hominoids, which ranged from humans to apes and to monkeys. This is difficult to do with PERV because of the large diversity present.
Further research
Epigenetic variability
Researchers could analyze individual epigenomes and transcriptomes to study the reactivation of dormant transposable elements through epigenetic release and their potential associations with human disease and exploring the specifics of gene regulatory networks.
Immunological problems of xenotransplantation
Little is known about an effective way to overcoming hyperacute rejection (HAR), which follows the activation of complement initiated by xenoreactive antibodies recognizing galactosyl-alpha1-3galatosyl (alpha-Gal) antigens on the donor epithelium.
Risk factors of HERVs in gene therapy
Because retroviruses are able to recombine with each other and with other endogenous DNA sequences, it would be beneficial for gene therapy to explore the potential risks HERVs can cause, if any. Also, this ability of HERVs to recombine can be manipulated for site-directed integration by including HERV sequences in retroviral vectors.
HERV gene expression
Researchers believe that RNA and proteins encoded for by HERV genes should continue to be explored for putative function in cell physiology and in pathological conditions. These studies would examine and more deeply define the biological significance of the proteins synthesized.
See also
- Avian sarcoma leukosis virus (ASLV)
- Endogenous viral element
- Endogeny (biology)
- ERV3
- HERV-FRD
- Horizontal gene transfer
- Jaagsiekte sheep retrovirus (JSRV)
- Koala retrovirus (KoRV)
- Mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV)
- Murine leukemia virus (MLV) and xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus (XMRV)
- Paleovirology
References
- ^ Belshaw R, Pereira V, Katzourakis A, Talbot G, Paces J, Burt A, Tristem M (April 2004). "Long-term reinfection of the human genome by endogenous retroviruses". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 101 (14): 4894–4899. Bibcode:2004PNAS..101.4894B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0307800101. PMC 387345. PMID 15044706.
- Nelson PN, Hooley P, Roden D, Davari Ejtehadi H, Rylance P, Warren P, et al. (October 2004). "Human endogenous retroviruses: transposable elements with potential?". Clinical and Experimental Immunology. 138 (1): 1–9. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02592.x. PMC 1809191. PMID 15373898.
- Khodosevich K, Lebedev Y, Sverdlov E (October 2002). "Endogenous retroviruses and human evolution". Comparative and Functional Genomics. 3 (6): 494–498. doi:10.1002/cfg.216. PMC 2448423. PMID 18629260.
- Kim FJ, Battini JL, Manel N, Sitbon M (January 2004). "Emergence of vertebrate retroviruses and envelope capture". Virology. 318 (1): 183–191. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2003.09.026. PMID 14972546.
- Stoye JP, Boeke JD (1997). "Retrotransposons, Endogenous Retroviruses, and the Evolution of Retroelements". Retroviruses. Cold Spring Harbor (NY): Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. p. 343. ISBN 9780879695712. PMID 21433351. NBK19468. Retrieved 2021-02-22.
- ^ Gifford RJ, Blomberg J, Coffin JM, Fan H, Heidmann T, Mayer J, et al. (August 2018). "Nomenclature for endogenous retrovirus (ERV) loci". Retrovirology. 15 (1): 59. doi:10.1186/s12977-018-0442-1. PMC 6114882. PMID 30153831.
- ^ Rebollo R, Romanish MT, Mager DL (2012-01-01). "Transposable elements: an abundant and natural source of regulatory sequences for host genes". Annual Review of Genetics. 46 (1): 21–42. doi:10.1146/annurev-genet-110711-155621. PMID 22905872.
- Cotton, J. (2001). "Retroviruses from retrotransposons". Genome Biology. 2 (2): 6. doi:10.1186/gb-2001-2-2-reports0006.
It appears that the transition from nonviral retrotransposon to retrovirus has occurred independently at least eight times, and the source of the envelope gene responsible for infectious ability can now be traced to a virus in at least four of these instances. This suggests that potentially, any LTR retrotransposon can become a virus through the acquisition of existing viral genes.
- ^ Johnson WE, Coffin JM (August 1999). "Constructing primate phylogenies from ancient retrovirus sequences". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 96 (18): 10254–10260. Bibcode:1999PNAS...9610254J. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.18.10254. PMC 17875. PMID 10468595.
- Fujiwara T, Mizuuchi K (August 1988). "Retroviral DNA integration: structure of an integration intermediate". Cell. 54 (4): 497–504. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(88)90071-2. PMID 3401925. S2CID 37801365.
- ^ Vargiu L, Rodriguez-Tomé P, Sperber GO, Cadeddu M, Grandi N, Blikstad V, et al. (January 2016). "Classification and characterization of human endogenous retroviruses; mosaic forms are common". Retrovirology. 13: 7. doi:10.1186/s12977-015-0232-y. PMC 4724089. PMID 26800882.
- Magiorkinis G, Gifford RJ, Katzourakis A, De Ranter J, Belshaw R (May 2012). "Env-less endogenous retroviruses are genomic superspreaders". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 109 (19): 7385–7390. doi:10.1073/pnas.1200913109. PMC 3358877. PMID 22529376.
- ^ Li J, Akagi K, Hu Y, Trivett AL, Hlynialuk CJ, Swing DA, et al. (May 2012). "Mouse endogenous retroviruses can trigger premature transcriptional termination at a distance". Genome Research. 22 (5): 870–884. doi:10.1101/gr.130740.111. PMC 3337433. PMID 22367191.
- Spencer TE, Palmarini M (2012). "Endogenous retroviruses of sheep: a model system for understanding physiological adaptation to an evolving ruminant genome". The Journal of Reproduction and Development. 58 (1): 33–37. doi:10.1262/jrd.2011-026. PMID 22450282.
- ^ Black SG, Arnaud F, Palmarini M, Spencer TE (October 2010). "Endogenous retroviruses in trophoblast differentiation and placental development". American Journal of Reproductive Immunology. 64 (4): 255–264. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0897.2010.00860.x. PMC 4198168. PMID 20528833.
- Ryan FP (December 2004). "Human endogenous retroviruses in health and disease: a symbiotic perspective". Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine. 97 (12): 560–565. doi:10.1177/014107680409701202. PMC 1079666. PMID 15574851.
- Pi W, Zhu X, Wu M, Wang Y, Fulzele S, Eroglu A, et al. (July 2010). "Long-range function of an intergenic retrotransposon". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 107 (29): 12992–12997. Bibcode:2010PNAS..10712992P. doi:10.1073/pnas.1004139107. PMC 2919959. PMID 20615953.
- ^ van de Lagemaat LN, Landry JR, Mager DL, Medstrand P (October 2003). "Transposable elements in mammals promote regulatory variation and diversification of genes with specialized functions". Trends in Genetics. 19 (10): 530–536. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2003.08.004. PMID 14550626.
- ^ Kovalskaya E, Buzdin A, Gogvadze E, Vinogradova T, Sverdlov E (March 2006). "Functional human endogenous retroviral LTR transcription start sites are located between the R and U5 regions". Virology. 346 (2): 373–378. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2005.11.007. PMID 16337666.
- Hata K, Okano M, Lei H, Li E (April 2002). "Dnmt3L cooperates with the Dnmt3 family of de novo DNA methyltransferases to establish maternal imprints in mice". Development. 129 (8): 1983–1993. doi:10.1242/dev.129.8.1983. PMID 11934864.
- Dunn CA, Romanish MT, Gutierrez LE, van de Lagemaat LN, Mager DL (February 2006). "Transcription of two human genes from a bidirectional endogenous retrovirus promoter". Gene. 366 (2): 335–342. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2005.09.003. PMID 16288839.
- Gogvadze E, Stukacheva E, Buzdin A, Sverdlov E (June 2009). "Human-specific modulation of transcriptional activity provided by endogenous retroviral insertions". Journal of Virology. 83 (12): 6098–6105. doi:10.1128/JVI.00123-09. PMC 2687385. PMID 19339349.
- Ting CN, Rosenberg MP, Snow CM, Samuelson LC, Meisler MH (August 1992). "Endogenous retroviral sequences are required for tissue-specific expression of a human salivary amylase gene". Genes & Development. 6 (8): 1457–1465. doi:10.1101/gad.6.8.1457. PMID 1379564.
- ^ Cohen CJ, Lock WM, Mager DL (December 2009). "Endogenous retroviral LTRs as promoters for human genes: a critical assessment". Gene. 448 (2): 105–114. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2009.06.020. PMID 19577618.
- Bekpen C, Marques-Bonet T, Alkan C, Antonacci F, Leogrande MB, Ventura M, et al. (March 2009). "Death and resurrection of the human IRGM gene". PLOS Genetics. 5 (3): e1000403. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000403. PMC 2644816. PMID 19266026.
- ^ Jern P, Coffin JM (2008). "Effects of retroviruses on host genome function". Annual Review of Genetics. 42: 709–732. doi:10.1146/annurev.genet.42.110807.091501. PMID 18694346.
- Oliver KR, Greene WK (May 2011). "Mobile DNA and the TE-Thrust hypothesis: supporting evidence from the primates". Mobile DNA. 2 (1): 8. doi:10.1186/1759-8753-2-8. PMC 3123540. PMID 21627776.
- Romanish MT, Lock WM, van de Lagemaat LN, Dunn CA, Mager DL (January 2007). "Repeated recruitment of LTR retrotransposons as promoters by the anti-apoptotic locus NAIP during mammalian evolution". PLOS Genetics. 3 (1): e10. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.0030010. PMC 1781489. PMID 17222062.
- Huh JW, Ha HS, Kim DS, Kim HS (July 2008). "Placenta-restricted expression of LTR-derived NOS3". Placenta. 29 (7): 602–608. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2008.04.002. PMID 18474398.
- Villarreal LP, Villareal LP (February 1997). "On viruses, sex, and motherhood". Journal of Virology. 71 (2): 859–865. doi:10.1128/JVI.71.2.859-865.1997. PMC 191132. PMID 8995601.
- Hughes JF, Coffin JM (December 2001). "Evidence for genomic rearrangements mediated by human endogenous retroviruses during primate evolution". Nature Genetics. 29 (4): 487–489. doi:10.1038/ng775. PMID 11704760. S2CID 20262212.
- ^ Dawkins R, Leelayuwat C, Gaudieri S, Tay G, Hui J, Cattley S, et al. (February 1999). "Genomics of the major histocompatibility complex: haplotypes, duplication, retroviruses and disease". Immunological Reviews. 167: 275–304. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.1999.tb01399.x. PMID 10319268. S2CID 9924684.
- Doxiadis GG, de Groot N, Bontrop RE (July 2008). "Impact of endogenous intronic retroviruses on major histocompatibility complex class II diversity and stability". Journal of Virology. 82 (13): 6667–6677. doi:10.1128/JVI.00097-08. PMC 2447082. PMID 18448532.
- ^ Chuong EB, Rumi MA, Soares MJ, Baker JC (March 2013). "Endogenous retroviruses function as species-specific enhancer elements in the placenta". Nature Genetics. 45 (3): 325–329. doi:10.1038/ng.2553. PMC 3789077. PMID 23396136.
- Thomas JH, Schneider S (November 2011). "Coevolution of retroelements and tandem zinc finger genes". Genome Research. 21 (11): 1800–1812. doi:10.1101/gr.121749.111. PMC 3205565. PMID 21784874.
- McEwen GK, Alquezar-Planas DE, Dayaram A, Gillett A, Tarlinton R, Mongan N, et al. (February 2021). "Retroviral integrations contribute to elevated host cancer rates during germline invasion". Nature Communications. 12 (1): 1316. Bibcode:2021NatCo..12.1316M. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-21612-7. PMC 7910482. PMID 33637755.
- Katzourakis A, Magiorkinis G, Lim AG, Gupta S, Belshaw R, Gifford R (July 2014). "Larger mammalian body size leads to lower retroviral activity". PLOS Pathogens. 10 (7): e1004214. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1004214. PMC 4102558. PMID 25033295.
- Bannert N, Kurth R (October 2004). "Retroelements and the human genome: new perspectives on an old relation". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 101 (Suppl 2): 14572–14579. Bibcode:2004PNAS..10114572B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404838101. PMC 521986. PMID 15310846.
- Nelson PN, Carnegie PR, Martin J, Davari Ejtehadi H, Hooley P, Roden D, et al. (February 2003). "Demystified. Human endogenous retroviruses". Molecular Pathology. 56 (1): 11–18. doi:10.1136/mp.56.1.11. PMC 1187282. PMID 12560456.
- Singh SK (June 2007). "Endogenous retroviruses: suspects in the disease world". Future Microbiology. 2 (3): 269–275. doi:10.2217/17460913.2.3.269. PMID 17661701.
- Magiorkinis G, Belshaw R, Katzourakis A (September 2013). "'There and back again': revisiting the pathophysiological roles of human endogenous retroviruses in the post-genomic era". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences. 368 (1626): 20120504. doi:10.1098/rstb.2012.0504. PMC 3758188. PMID 23938753.
- Mameli G, Astone V, Arru G, Marconi S, Lovato L, Serra C, et al. (January 2007). "Brains and peripheral blood mononuclear cells of multiple sclerosis (MS) patients hyperexpress MS-associated retrovirus/HERV-W endogenous retrovirus, but not Human herpesvirus 6". The Journal of General Virology. 88 (Pt 1): 264–274. doi:10.1099/vir.0.81890-0. PMID 17170460.
- Serra C, Mameli G, Arru G, Sotgiu S, Rosati G, Dolei A (December 2003). "In vitro modulation of the multiple sclerosis (MS)-associated retrovirus by cytokines: implications for MS pathogenesis". Journal of Neurovirology. 9 (6): 637–643. doi:10.1080/714044485. PMID 14602576.
- "Reactivated Virus May Contribute to ALS". 2016-01-23.
- Karamitros T, Hurst T, Marchi E, Karamichali E, Georgopoulou U, Mentis A, et al. (October 2018). "Human Endogenous Retrovirus-K HML-2 integration within RASGRF2 is associated with intravenous drug abuse and modulates transcription in a cell-line model". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 115 (41): 10434–10439. Bibcode:2018PNAS..11510434K. doi:10.1073/pnas.1811940115. PMC 6187174. PMID 30249655.
- Rob Picheta (25 September 2018). "Addiction may stem from ancient retrovirus, study says". CNN. Retrieved 2019-10-13.
- "An ancient virus may promote addiction in modern people". The Economist. 2018-10-02. ISSN 0013-0613. Retrieved 2019-10-13.
- Yolken R (June 2004). "Viruses and schizophrenia: a focus on herpes simplex virus". Herpes. 11 (Suppl 2): 83A–88A. PMID 15319094.
- Fox D (2010). "The Insanity Virus". Discover. Retrieved 2011-02-17.
- ^ Patience C, Takeuchi Y, Weiss RA (March 1997). "Infection of human cells by an endogenous retrovirus of pigs". Nature Medicine. 3 (3): 282–286. doi:10.1038/nm0397-282. PMID 9055854. S2CID 33977939.
- Platanias LC (May 2005). "Mechanisms of type-I- and type-II-interferon-mediated signalling". Nature Reviews. Immunology. 5 (5): 375–386. doi:10.1038/nri1604. PMID 15864272.
- Grandi N, Tramontano E (2018). "Human Endogenous Retroviruses Are Ancient Acquired Elements Still Shaping Innate Immune Responses". Frontiers in Immunology. 9: 2039. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.02039. PMC 6139349. PMID 30250470.
- Niu D, Wei HJ, Lin L, George H, Wang T, Lee IH, et al. (September 2017). "Inactivation of porcine endogenous retrovirus in pigs using CRISPR-Cas9". Science. 357 (6357): 1303–1307. Bibcode:2017Sci...357.1303N. doi:10.1126/science.aan4187. PMC 5813284. PMID 28798043.
- ^ Tang HB, Ouyang K, Rao GB, Ma L, Zhong H, Bai A, et al. (2016-01-01). "Characterization of Complete Genome Sequences of a Porcine Endogenous Retrovirus Isolated From China Bama Minipig Reveals an Evolutionary Time Earlier Than That of Isolates From European Minipigs". Transplantation Proceedings. 48 (1): 222–228. doi:10.1016/j.transproceed.2015.12.005. PMID 26915872.
- ^ Tönjes RR, Niebert M (November 2003). "Relative age of proviral porcine endogenous retrovirus sequences in Sus scrofa based on the molecular clock hypothesis". Journal of Virology. 77 (22): 12363–12368. doi:10.1128/JVI.77.22.12363-12368.2003. PMC 254287. PMID 14581574.
- Paradis K, Langford G, Long Z, Heneine W, Sandstrom P, Switzer WM, et al. (August 1999). "Search for cross-species transmission of porcine endogenous retrovirus in patients treated with living pig tissue. The XEN 111 Study Group". Science. 285 (5431): 1236–1241. doi:10.1126/science.285.5431.1236. PMID 10455044.
- "Genomics England › Integrated Pathogens and Mobile Elements GeCIP Domain". Archived from the original on 2019-10-13. Retrieved 2019-10-13.
- "Aging and Retroviruses". Science. Archived from the original on 17 February 2023. Retrieved 17 February 2023.
- Liu, Xiaoqian; Liu, Zunpeng; Wu, Zeming; Ren, Jie; Fan, Yanling; Sun, Liang; Cao, Gang; Niu, Yuyu; Zhang, Baohu; Ji, Qianzhao; Jiang, Xiaoyu; Wang, Cui; Wang, Qiaoran; Ji, Zhejun; Li, Lanzhu; Esteban, Concepcion Rodriguez; Yan, Kaowen; Li, Wei; Cai, Yusheng; Wang, Si; Zheng, Aihua; Zhang, Yong E.; Tan, Shengjun; Cai, Yingao; Song, Moshi; Lu, Falong; Tang, Fuchou; Ji, Weizhi; Zhou, Qi; Belmonte, Juan Carlos Izpisua; Zhang, Weiqi; Qu, Jing; Liu, Guang-Hui (19 January 2023). "Resurrection of endogenous retroviruses during aging reinforces senescence". Cell. 186 (2): 287–304.e26. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2022.12.017. ISSN 0092-8674. PMID 36610399. S2CID 232060038.
- Belshaw R, Dawson AL, Woolven-Allen J, Redding J, Burt A, Tristem M (October 2005). "Genomewide screening reveals high levels of insertional polymorphism in the human endogenous retrovirus family HERV-K(HML2): implications for present-day activity". Journal of Virology. 79 (19): 12507–12514. doi:10.1128/JVI.79.19.12507-12514.2005. PMC 1211540. PMID 16160178.
- Jha AR, Pillai SK, York VA, Sharp ER, Storm EC, Wachter DJ, et al. (November 2009). "Cross-sectional dating of novel haplotypes of HERV-K 113 and HERV-K 115 indicate these proviruses originated in Africa before Homo sapiens". Molecular Biology and Evolution. 26 (11): 2617–2626. doi:10.1093/molbev/msp180. PMC 2760466. PMID 19666991.
- Jha AR, Nixon DF, Rosenberg MG, Martin JN, Deeks SG, Hudson RR, et al. (May 2011). "Human endogenous retrovirus K106 (HERV-K106) was infectious after the emergence of anatomically modern humans". PLOS ONE. 6 (5): e20234. Bibcode:2011PLoSO...620234J. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020234. PMC 3102101. PMID 21633511.
- Lee YN, Bieniasz PD (January 2007). "Reconstitution of an infectious human endogenous retrovirus". PLOS Pathogens. 3 (1): e10. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.0030010. PMC 1781480. PMID 17257061.
- Dewannieux M, Harper F, Richaud A, Letzelter C, Ribet D, Pierron G, Heidmann T (December 2006). "Identification of an infectious progenitor for the multiple-copy HERV-K human endogenous retroelements". Genome Research. 16 (12): 1548–1556. doi:10.1101/gr.5565706. PMC 1665638. PMID 17077319.
- Morozov VA, Dao Thi VL, Denner J (2013). "The transmembrane protein of the human endogenous retrovirus--K (HERV-K) modulates cytokine release and gene expression". PLOS ONE. 8 (8): e70399. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...870399M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0070399. PMC 3737193. PMID 23950929.
- Mayer J, Blomberg J, Seal RL (May 2011). "A revised nomenclature for transcribed human endogenous retroviral loci". Mobile DNA. 2 (1): 7. doi:10.1186/1759-8753-2-7. PMC 3113919. PMID 21542922.
- Chuong EB, Elde NC, Feschotte C (March 2016). "Regulatory evolution of innate immunity through co-option of endogenous retroviruses". Science. 351 (6277): 1083–1087. Bibcode:2016Sci...351.1083C. doi:10.1126/science.aad5497. PMC 4887275. PMID 26941318.
- Li Y, Fan T, Cui J (March 2022). "Human endogenous retroviruses in viral disease and therapy". Clinical and Translational Discovery. 2 (1). doi:10.1002/ctd2.38. ISSN 2768-0622. S2CID 247750447.
- ^ Gröger V, Cynis H (2018-02-20). "Human Endogenous Retroviruses and Their Putative Role in the Development of Autoimmune Disorders Such as Multiple Sclerosis". Frontiers in Microbiology. 9: 265. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2018.00265. PMC 5826199. PMID 29515547.
- Mameli G, Poddighe L, Mei A, Uleri E, Sotgiu S, Serra C, et al. (2012-09-27). "Expression and activation by Epstein Barr virus of human endogenous retroviruses-W in blood cells and astrocytes: inference for multiple sclerosis". PLOS ONE. 7 (9): e44991. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...744991M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0044991. PMC 3459916. PMID 23028727.
- Mameli G, Madeddu G, Mei A, Uleri E, Poddighe L, Delogu LG, et al. (2013-11-13). "Activation of MSRV-type endogenous retroviruses during infectious mononucleosis and Epstein-Barr virus latency: the missing link with multiple sclerosis?". PLOS ONE. 8 (11): e78474. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...878474M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0078474. PMC 3827255. PMID 24236019.
- ^ Bannert N, Hofmann H, Block A, Hohn O (2018-02-13). "HERVs New Role in Cancer: From Accused Perpetrators to Cheerful Protectors". Frontiers in Microbiology. 9: 178. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2018.00178. PMC 5816757. PMID 29487579.
- Rycaj K, Plummer JB, Yin B, Li M, Garza J, Radvanyi L, et al. (January 2015). "Cytotoxicity of human endogenous retrovirus K-specific T cells toward autologous ovarian cancer cells". Clinical Cancer Research. 21 (2): 471–483. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0388. PMID 25370465. S2CID 2651471.
- Mullins CS, Linnebacher M (July 2012). "Endogenous retrovirus sequences as a novel class of tumor-specific antigens: an example of HERV-H env encoding strong CTL epitopes". Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy. 61 (7): 1093–1100. doi:10.1007/s00262-011-1183-3. PMC 11029769. PMID 22187063. S2CID 28485656.
- ^ Alcazer V, Bonaventura P, Depil S (March 2020). "Human Endogenous Retroviruses (HERVs): Shaping the Innate Immune Response in Cancers". Cancers. 12 (3): 610. doi:10.3390/cancers12030610. PMC 7139688. PMID 32155827.
- Hurst TP, Magiorkinis G (June 2015). "Activation of the innate immune response by endogenous retroviruses". The Journal of General Virology. 96 (Pt 6): 1207–1218. doi:10.1099/jgv.0.000017. PMID 26068187.
- Rolland A, Jouvin-Marche E, Viret C, Faure M, Perron H, Marche PN (June 2006). "The envelope protein of a human endogenous retrovirus-W family activates innate immunity through CD14/TLR4 and promotes Th1-like responses". Journal of Immunology. 176 (12): 7636–7644. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.176.12.7636. PMID 16751411. S2CID 24492010.
- ^ Garrison KE, Jones RB, Meiklejohn DA, Anwar N, Ndhlovu LC, Chapman JM, et al. (November 2007). "T cell responses to human endogenous retroviruses in HIV-1 infection". PLOS Pathogens. 3 (11): e165. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.0030165. PMC 2065876. PMID 17997601.
Further reading
- Löwer R, Löwer J, Kurth R (May 1996). "The viruses in all of us: characteristics and biological significance of human endogenous retrovirus sequences". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 93 (11): 5177–5184. Bibcode:1996PNAS...93.5177L. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.11.5177. PMC 39218. PMID 8643549.
- Molès JP, Tesniere A, Guilhou JJ (July 2005). "A new endogenous retroviral sequence is expressed in skin of patients with psoriasis". The British Journal of Dermatology. 153 (1): 83–89. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06555.x. PMID 16029331. S2CID 6642536.
- Seifarth W, Frank O, Zeilfelder U, Spiess B, Greenwood AD, Hehlmann R, Leib-Mösch C (January 2005). "Comprehensive analysis of human endogenous retrovirus transcriptional activity in human tissues with a retrovirus-specific microarray". Journal of Virology. 79 (1): 341–352. doi:10.1128/JVI.79.1.341-352.2005. PMC 538696. PMID 15596828.
- Knerr I, Beinder E, Rascher W (February 2002). "Syncytin, a novel human endogenous retroviral gene in human placenta: evidence for its dysregulation in preeclampsia and HELLP syndrome". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 186 (2): 210–213. doi:10.1067/mob.2002.119636. PMID 11854637.
- Gifford R, Tristem M (May 2003). "The evolution, distribution and diversity of endogenous retroviruses" (PDF). Virus Genes. 26 (3): 291–315. doi:10.1023/A:1024455415443. PMID 12876457. S2CID 34639116. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-02-15. Retrieved 2008-01-16.
External links
- Endogenous+Retroviruses at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- HERVd – human endogenous retrovirus database
| Self-replicating organic structures | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cellular life | |||||||||||
| Virus | |||||||||||
| Subviral agents |
| ||||||||||
| Nucleic acid self-replication |
| ||||||||||
| Endosymbiosis | |||||||||||
| Abiogenesis | |||||||||||
| See also | |||||||||||