| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
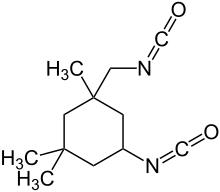
| IUPAC name
5-isocyanato-1- | |
| Other names IPDI | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.021.692 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C12H18N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 222.3 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colourless to slightly yellow liquid |
| Odor | pungent |
| Density | 1.062 g/cm @ 20 °C, liquid |
| Melting point | −60 °C (−76 °F; 213 K) |
| Boiling point | 158 °C (316 °F; 431 K) at 1.33 kPa |
| Vapor pressure | 0.0003 mmHg (20°C) |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 155 °C (311 °F; 428 K) (PMCC) |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
| PEL (Permissible) | none |
| REL (Recommended) | TWA 0.005 ppm (0.045 mg/m) ST 0.02 ppm (0.180 mg/m) |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | N.D. |
| Related compounds | |
| Related isocyanates | Hexamethylene diisocyanate |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI) is an organic compound in the class known as isocyanates. More specifically, it is an aliphatic diisocyanate. It is produced in relatively small quantities, accounting for (with hexamethylene diisocyanate) only 3.4% of the global diisocyanate market in the year 2000. Aliphatic diisocyanates are used, not in the production of polyurethane foam, but in special applications, such as enamel coatings which are resistant to abrasion and degradation from ultraviolet light. These properties are particularly desirable in, for instance, the exterior paint applied to aircraft.
Properties
Isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI) stands out as a cycloaliphatic diisocyanate distinguished by its two reactive isocyanate groups, exhibiting differences in reactivity between primary and secondary NCO groups. This unique property ensures high selectivity in reacting with hydroxyl-bearing compounds.
This distinctive attribute proves advantageous in processing low-viscosity prepolymers, resulting in a notably reduced residual content of monomeric diisocyanate. Furthermore, the low viscosity of IPDI-based prepolymers facilitates a decrease in solvent usage. The presence of methyl groups linked to the cyclohexane ring broadens IPDI's compatibility with resins and solvents.
The inherent cycloaliphatic ring confers heightened rigidity and a notably elevated glass transition temperature to IPDI-based products. IPDI itself is a transparent, slightly yellowish, low-viscosity liquid with a solidification point at -60 °C and boiling point at 158 °C. Semi-finished products like NCO-terminated prepolymers exhibit a low tendency to crystallize, remaining in a liquid state and facilitating easy processing.
Synthesis
Isophorone diisocyanate is produced by phosgenation of isophorone diamine in five-step reaction:
- Reaction of acetone with catalyst to form isophorone.
- Isophorone react with HCN to form isophorone nitrile.
- Isophorone nitrile react with ammonia and hydrogen under the influence of catalyst. This reaction create mixture of isophorone diamine conformers (25% cis, 75% trans).
- Reaction of isophorone diamine with phosgene to form isophorone diisocyanate.
- Purification of product by distillation.

Chemistry
IPDI exists in two stereoisomers, cis and trans. Their reactivities are similar. Each stereoisomer is an unsymmetrical molecule, and thus has isocyanate groups with different reactivities. The primary isocyanate group is more reactive than the secondary isocyanate group.
Application
Isophorone diisocyanate is used in special applications:
- Hard foams and coatings
- Polyurethanes resins (PUR)
- Leather and textile
- Adhesives for battery
- Elastomers and TPU
- PUR fibers and laminates
- Adhesives and glues
- Light-stable PUR
- Aqueous dispersible polymers
Safety
Isophorone diisocyanate is a highly toxic substance if inhaled. It can cause eye irritation and irreversible eye damage, lung and respiratory damage. It is a skin irritant and causes allergic reactions and may cause skin corrosion on prolonged contact. It is highly hazardous to aquatic environment.
H-statements: H315, H317, H319, H331, H334, H335, H411
P-statements: P260, P273, P280, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313



See also
- Hexamethylene diisocyanate
- Methylene diphenyl diisocyanate
- Tetramethylxylene diisocyanate
- Toluene diisocyanate
References
- ^ NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0356". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Randall, David; Lee, Steve (2002). The Polyurethanes Book. New York: Wiley. ISBN 0-470-85041-8.
- ^ "ISOPHORONE DIISOCYANATE". Ataman Kimya (in Turkish). Retrieved 2023-12-20.
- "Isophorone chemistry solutions for resins and elastomers - Evonik Industries". crosslinkers.evonik.com. Retrieved 2023-12-20.
- ^ Kapp, R. W. (2014-01-01), Wexler, Philip (ed.), "Isocyanates", Encyclopedia of Toxicology (Third Edition), Oxford: Academic Press, pp. 1112–1131, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-386454-3.00865-4, ISBN 978-0-12-386455-0, retrieved 2023-12-20
- "IPDI". Vencorex (in French). Retrieved 2023-12-20.
- Molina, P.; Tárraga, A.; Arques, A. (2005-01-01), Katritzky, Alan R.; Taylor, Richard J. K. (eds.), "5.26 - Functions with at Least One Oxygen, YCO", Comprehensive Organic Functional Group Transformations II, Oxford: Elsevier, pp. 949–973, doi:10.1016/b0-08-044655-8/00116-1, ISBN 978-0-08-044655-4, retrieved 2023-12-20
- "www.sigmaaldrich.com".
External links
- NIOSH Safety and Health Topic: Isocyanates, from the website of the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
- Isophorone diisocyanate - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards