| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 3′-O-Phosphonoadenosine 5′-ethyl}amino)-3-oxopropyl]amino}-4-oxobutyl dihydrogen diphosphate] | |
| Preferred IUPAC name O-{methyl} O-ethyl}amino)-3-oxopropyl]amino}-4-oxobutyl] dihydrogen diphosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | isovaleryl-coenzyme+A |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
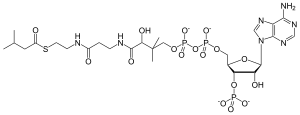
| Chemical formula | C26H44N7O17P3S |
| Molar mass | 851.652 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Isovaleryl-coenzyme A, also known as isovaleryl-CoA, is an intermediate in the metabolism of branched-chain amino acids.
Leucine metabolism
Leucine metabolism in humans
 L-Leucine
Branched-chain amino
L-Leucine
Branched-chain aminoacid aminotransferase α-Ketoglutarate Glutamate Glutamate Alanine Pyruvate Muscle: α-Ketoisocaproate (α-KIC) Liver: α-Ketoisocaproate (α-KIC) Branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase (mitochondria) KIC-dioxygenase (cytosol) Isovaleryl-CoA β-Hydroxy β-methylbutyrate (HMB) Excreted in urine (10–40%)
(HMG-CoA) β-Methylcrotonyl-CoA (MC-CoA) β-Methylglutaconyl-CoA (MG-CoA) CO2 CO2 O2 CO2 H2O CO2 H2O (liver) HMG-CoA lyase Enoyl-CoA hydratase Isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase MC-CoA carboxylase MG-CoA hydratase HMG-CoA reductase HMG-CoA synthase β-Hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase Mevalonate pathway Thiolase Unknown enzyme β-Hydroxybutyrate Acetoacetyl-CoA Acetyl-CoA Acetoacetate Mevalonate Cholesterol |
See also
References
- ^ Wilson JM, Fitschen PJ, Campbell B, Wilson GJ, Zanchi N, Taylor L, Wilborn C, Kalman DS, Stout JR, Hoffman JR, Ziegenfuss TN, Lopez HL, Kreider RB, Smith-Ryan AE, Antonio J (February 2013). "International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate (HMB)". Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 10 (1): 6. doi:10.1186/1550-2783-10-6. PMC 3568064. PMID 23374455.
- Zanchi NE, Gerlinger-Romero F, Guimarães-Ferreira L, de Siqueira Filho MA, Felitti V, Lira FS, Seelaender M, Lancha AH (April 2011). "HMB supplementation: clinical and athletic performance-related effects and mechanisms of action". Amino Acids. 40 (4): 1015–1025. doi:10.1007/s00726-010-0678-0. PMID 20607321. S2CID 11120110.
HMB is a metabolite of the amino acid leucine (Van Koverin and Nissen 1992), an essential amino acid. The first step in HMB metabolism is the reversible transamination of leucine to that occurs mainly extrahepatically (Block and Buse 1990). Following this enzymatic reaction, may follow one of two pathways. In the first, HMB is produced from by the cytosolic enzyme KIC dioxygenase (Sabourin and Bieber 1983). The cytosolic dioxygenase has been characterized extensively and differs from the mitochondrial form in that the dioxygenase enzyme is a cytosolic enzyme, whereas the dehydrogenase enzyme is found exclusively in the mitochondrion (Sabourin and Bieber 1981, 1983). Importantly, this route of HMB formation is direct and completely dependent of liver KIC dioxygenase. Following this pathway, HMB in the cytosol is first converted to cytosolic β-hydroxy-β-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA), which can then be directed for cholesterol synthesis (Rudney 1957) (Fig. 1). In fact, numerous biochemical studies have shown that HMB is a precursor of cholesterol (Zabin and Bloch 1951; Nissen et al. 2000).
- ^ Kohlmeier M (May 2015). "Leucine". Nutrient Metabolism: Structures, Functions, and Genes (2nd ed.). Academic Press. pp. 385–388. ISBN 978-0-12-387784-0. Retrieved 6 June 2016.
Energy fuel: Eventually, most Leu is broken down, providing about 6.0kcal/g. About 60% of ingested Leu is oxidized within a few hours ... Ketogenesis: A significant proportion (40% of an ingested dose) is converted into acetyl-CoA and thereby contributes to the synthesis of ketones, steroids, fatty acids, and other compounds
Figure 8.57: Metabolism of L-leucine - ^ Zanchi NE, Gerlinger-Romero F, Guimarães-Ferreira L, de Siqueira Filho MA, Felitti V, Lira FS, Seelaender M, Lancha AH (April 2011). "HMB supplementation: clinical and athletic performance-related effects and mechanisms of action". Amino Acids. 40 (4): 1015–1025. doi:10.1007/s00726-010-0678-0. PMID 20607321. S2CID 11120110.
HMB is a metabolite of the amino acid leucine (Van Koverin and Nissen 1992), an essential amino acid. The first step in HMB metabolism is the reversible transamination of leucine to that occurs mainly extrahepatically (Block and Buse 1990). Following this enzymatic reaction, may follow one of two pathways. In the first, HMB is produced from by the cytosolic enzyme KIC dioxygenase (Sabourin and Bieber 1983). The cytosolic dioxygenase has been characterized extensively and differs from the mitochondrial form in that the dioxygenase enzyme is a cytosolic enzyme, whereas the dehydrogenase enzyme is found exclusively in the mitochondrion (Sabourin and Bieber 1981, 1983). Importantly, this route of HMB formation is direct and completely dependent of liver KIC dioxygenase. Following this pathway, HMB in the cytosol is first converted to cytosolic β-hydroxy-β-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA), which can then be directed for cholesterol synthesis (Rudney 1957) (Fig. 1). In fact, numerous biochemical studies have shown that HMB is a precursor of cholesterol (Zabin and Bloch 1951; Nissen et al. 2000).
This biochemistry article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |