| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Khopyor" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Khopyor | |
|---|---|
 | |
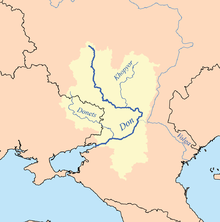 The Khopyor in the Don river basin. The Khopyor in the Don river basin. | |
| Native name | Хопёр (Russian) |
| Location | |
| Country | Russia |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mouth | Don |
| • coordinates | 49°36′23″N 42°18′29″E / 49.60639°N 42.30806°E / 49.60639; 42.30806 |
| Length | 979 km (608 mi) |
| Basin size | 61,100 km (23,600 sq mi) |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | Don→ Sea of Azov |
The Khopyor (Russian: Хопёр, also transliterated as Khoper) is a river in European Russia, the biggest left tributary of the river Don. It is 979 kilometres (608 mi) long, with a watershed of 61,100 square kilometres (23,600 sq mi). The mouth width is 300 metres (980 ft). The Khopyor is navigable up to 323 kilometres (201 mi) from the mouth. The maximum discharge is 3,720 cubic metres per second (131,000 cu ft/s); the average discharge is 150 cubic metres per second (5,300 cu ft/s), and the minimum discharge is 45 cubic metres per second (1,600 cu ft/s).
Fish in the river include bream, zander, common roach, rudd, European chub, ide, bleak, catfish, pike, perch, asp and burbot.
Found near the river elks, hares, herons, swans, eagles, falcons, owls, nightingales, ducks, beavers, pond turtles, snakes (vipers), etc. Previously, there were bison, now exterminated.
The unique nature made Khopyor a favorite place for tourists.
Tributaries
The largest tributaries of the Khopyor are, from source to mouth:
Towns
Towns on the Khopyor River in orographic sequence (from source to mouth) are:
Downstream from Borisoglebsk, is the Khopyor Nature Reserve, populated with protected beavers, wisents and Russian desman. It also has various protected flora including Iris tenuifloia.
Cultural associations
In 1834, Mikhail Zagoskin published a collection of ghost stories entitled An Evening on the Khoper River.
According to legend, an oldman Hopper lived in these places of Penza Oblast. One day he went by steppe and saw 12 springs. The old man took a shovel and assembled all the springs in one big stream. On this stream oldman Hopper built a mill to grind grain for the peasants from nearby villages. Later the river was given the name of its creator.
The river gave its name to the Khoper-Invest company, infamous for its pyramid scheme fraud.
References
- ^ Хопёр, Great Soviet Encyclopedia
- ^ «Река Хопер», Russian State Water Registry
- "The exhibition "Iris Russia"". flower-iris.ru. Retrieved 23 January 2015.