Mean airway pressure typically refers to the mean pressure applied during positive-pressure mechanical ventilation. Mean airway pressure correlates with alveolar ventilation, arterial oxygenation, hemodynamic performance, and barotrauma. It can also match the alveolar pressure if there is no difference between inspiratory and expiratory resistance.
Equations
There are several equations aimed at determining the real mean airway pressure.
Volume control ventilation
In ventilation with a square flow waveform this equation can be used:
where:
- = mean airway pressure
- = peak inspiratory pressure
- = peak end expiratory pressure
- = inspiratory time
- = cycle time
Pressure control ventilation
During pressure control ventilation this variant of the equation can be used:
where:
- = mean airway pressure
- = peak inspiratory pressure
- = peak end expiratory pressure
- = inspiratory time
- = cycle time
Airway pressure release ventilation
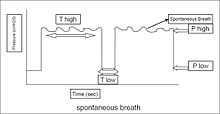
In airway pressure release ventilation (APRV) a variation of the previous equation must be used for the variables:
- where:
- = mean airway pressure
- = peak inspiratory pressure (PIP)
- = peak end expiratory pressure
- = time spent at
- = time spent at
Other equations
Clinical significance
Mean airway pressure has been shown to have a similar correlation as plateau pressure to mortality.
MAP is closely associated with mean alveolar pressure and shows the stresses exerted on the lung parenchyma on mechanical ventilation.
In high frequency oscillatory ventilation, it has been suggested to set the mean airway pressure six above the lower inflection point on the lungs P-V curve.
See also
References
- Stewart AR, Finer NN, Peters KL (1981). "Effects of alterations of inspiratory and expiratory pressures and inspiratory/expiratory ratios on mean airway pressure, blood gases, and intracranial pressure". Pediatrics. 67 (4): 474–81. doi:10.1542/peds.67.4.474. PMID 6789294. S2CID 2214900.
- Marini JJ, Ravenscraft SA (1992). "Mean airway pressure: physiologic determinants and clinical importance--Part 2: Clinical implications". Crit Care Med. 20 (11): 1604–16. doi:10.1097/00003246-199211000-00020. PMID 1424706. S2CID 42496727.
- ^ Hess, Dean (October 21, 2014). "Respiratory Mechanics in Mechanically Ventilated Patients" (PDF). Respiratory Care. 59 (11): 1773–1794. doi:10.4187/respcare.03410. PMID 25336536. S2CID 5706765.
- Daoud, Ehab G. (2007). "Airway pressure release ventilation". Annals of Thoracic Medicine. 2 (4): 176–179. doi:10.4103/1817-1737.36556. ISSN 1817-1737. PMC 2732103. PMID 19727373.
- David W. Chang (1999). Respiratory care calculations. Cengage Learning. pp. 251–. ISBN 978-0-7668-0517-0. Retrieved 30 March 2012.
- Sahetya, Sarina; Wu, David; Brooks, Morgan (May 2020). "Mean Airway Pressure As a Predictor of 90-Day Mortality in Mechanically Ventilated Patients". Critical Care Medicine. 48 (5): 688–695. doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000004268. PMC 8273919. PMID 32079893.
- Su, Longxiang; Pan, Pan; Liu, Dawei; Long, Yun (2021-10-01). "Mean airway pressure has the potential to become the core pressure indicator of mechanical ventilation: Raising to the front from behind the clinical scenes". Journal of Intensive Medicine. 1 (2): 96–98. doi:10.1016/j.jointm.2021.04.002. ISSN 2667-100X. PMC 9923962. PMID 36788801. S2CID 236575021.
- Goddon, Sven; Fujino, Yuji; Hromi, Jonathan M.; Kacmarek, Robert M. (May 2001). "Optimal Mean Airway Pressure during High-frequency Oscillation: Predicted by the Pressure–Volume Curve". Anesthesiology. 94 (5): 862–869. doi:10.1097/00000542-200105000-00026. ISSN 0003-3022. PMID 11388539. S2CID 9604584.
| Mechanical ventilation | |
|---|---|
| Fundamentals | |
| Modes | |
| Related illness | |
| Pressure | |
| Volumes | |
| Other | |

 = mean airway pressure
= mean airway pressure = peak inspiratory pressure
= peak inspiratory pressure = peak end expiratory pressure
= peak end expiratory pressure = inspiratory time
= inspiratory time = cycle time
= cycle time where:
where:

 = peak inspiratory pressure (PIP)
= peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) = peak end expiratory pressure
= peak end expiratory pressure = time spent at
= time spent at  = time spent at
= time spent at 


