| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Methyl(trioxo)rhenium(VII) | |
| Other names Methyltrioxorhenium(VII) | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Abbreviations | MTO |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.202.821 |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | CH3ReO3 |
| Molar mass | 249.239 g·mol |
| Appearance | white powder |
| Melting point | 112 °C (234 °F; 385 K) |
| Solubility in water | highly soluble in water |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  
|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H272, H315, H319, H335, H413 |
| Precautionary statements | P210, P220, P221, P261, P264, P271, P273, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P370+P378, P403+P233, P405, P501 |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
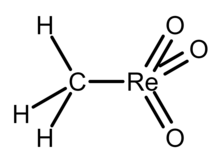
Methylrhenium trioxide, also known as methyltrioxorhenium(VII), is an organometallic compound with the formula CH3−ReO3. It is a volatile, colourless solid that has been used as a catalyst in some laboratory experiments. In this compound, rhenium has a tetrahedral coordination geometry with one methyl and three oxo ligands. The oxidation state of rhenium is +7.
Synthesis
Methylrhenium trioxide is commercially available. It can be prepared by many routes, a typical method is the reaction of rhenium heptoxide and tetramethyltin:
- Re2O7 + (CH3)4Sn → CH3ReO3 + (CH3)3Sn−O−ReO3
Analogous alkyl and aryl derivatives are known. Compounds of the type R−ReO3 are Lewis acids, forming both 1:1 and 1:2 adducts with halides and amines.
Uses
Methylrhenium trioxide serves as a heterogeneous catalyst for a variety of transformations. Supported on alumina/silica, it catalyzes olefin metathesis at 25 °C.
In solution, methylrhenium trioxide catalyses for the oxidations with hydrogen peroxide. Terminal alkynes yield the corresponding carboxylic acid or ester, internal alkynes yield diketones, and alkenes give epoxides. Methylrhenium trioxide also catalyses the conversion of aldehydes and diazoalkanes into an alkene, and the oxidation of amines to N-oxides with sodium percarbonate.
References
- Herrmann, W. A.; Kratzer R. M.; Fischer R. W. (1997). "Alkylrhenium Oxides from Perrhenates: A New, Economical Access to Organometallic Oxide Catalysts". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 36 (23): 2652–2654. doi:10.1002/anie.199726521.
- Hudson, Andrew; Betz, Daniel; Kühn, Fritz E.; Jiménez-Alemán, Guillermo H.; Boland, Wilhelm (2013-09-16). "Methyltrioxorhenium". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. doi:10.1002/047084289x.rn00017.pub3. ISBN 978-0-471-93623-7.
- Jain, Suman L.; Joseph, Jomy K.; Sain, Bir (2006). "Rhenium-Catalyzed Highly Efficient Oxidations of Tertiary Nitrogen Compounds to N-Oxides Using Sodium Percarbonate as Oxygen Source". Synlett: 2661–2663. doi:10.1055/s-2006-951487.
| Rhenium compounds | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rhenium(0) |
| ||||
| Rhenium(I) |
| ||||
| Rhenium(II) | |||||
| Rhenium(III) | |||||
| Rhenium(IV) | |||||
| Rhenium(V) | |||||
| Rhenium(VI) | |||||
| Rhenium(VII) |
| ||||