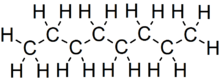(Redirected from N-octane )
Hydrocarbon compound with the formula C8H18
Not to be confused with octene or octyne .
For the gasoline rating system, see Octane rating . For other uses, see Octane (disambiguation) .
Octane
Names
Systematic IUPAC name
Octane
Other names
n -Octane
Identifiers
CAS Number
3D model (JSmol )
3DMet
Beilstein Reference
1696875
ChEBI
ChEMBL
ChemSpider
DrugBank
ECHA InfoCard
100.003.539
EC Number
Gmelin Reference
82412
KEGG
MeSH
octane
PubChem CID
RTECS number
UNII
UN number
1262
CompTox Dashboard (EPA )
InChI
InChI=1S/C8H18/c1-3-5-7-8-6-4-2/h3-8H2,1-2H3Key: TVMXDCGIABBOFY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
SMILES
Properties
Chemical formula
CH3 (CH2 )6 CH3
Molar mass
114.232 g·mol
Appearance
Colourless liquid
Odor
Gasoline-like
Density
0.703 g/cm
Melting point
−57.1 to −56.6 °C; −70.9 to −69.8 °F; 216.0 to 216.6 K
Boiling point
125.1 to 126.1 °C; 257.1 to 258.9 °F; 398.2 to 399.2 K
Solubility in water
0.007 mg/dm (at 20 °C)
log P
4.783
Vapor pressure
1.47 kPa (at 20.0 °C)
Henry's law (k H )
29 nmol/(Pa·kg)
Conjugate acid
Octonium
Magnetic susceptibility (χ)
−96.63·10 cm/mol
Refractive index (n D )
1.398
Viscosity
0.509 mPa·s (25 °C)
0.542 mPa·s (20 °C)
Thermochemistry
Heat capacity (C )
255.68 J/(K·mol)
Std molar (S 298 )
361.20 J/(K·mol)
Std enthalpy of (Δf H 298 )
−252.1 to −248.5 kJ/mol
Std enthalpy of (Δc H 298 )
−5.53 to −5.33 MJ/mol
Hazards
GHS labelling
Pictograms
Signal word
Danger
Hazard statements
H225 , H304 , H315 , H336 , H410
Precautionary statements
P210 , P261 , P273 , P301+P310 , P331
NFPA 704
1
3
0
Flash point
13.0 °C (55.4 °F; 286.1 K)
Autoignition
220.0 °C (428.0 °F; 493.1 K)
Explosive limits
0.96 – 6.5%
Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC):
LDLo (lowest published )
428 mg/kg (mouse, intravenous)
NIOSH
PEL (Permissible)
TWA 500 ppm (2350 mg/m)
REL (Recommended)
TWA 75 ppm (350 mg/m) C 385 ppm (1800 mg/m)
IDLH (Immediate danger)
1000 ppm
Related compounds
Related alkanes
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
verify (what is ?)
Infobox references
Chemical compound
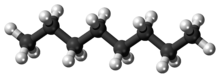
Octane is a hydrocarbon and an alkane with the chemical formula C8 H18 , and the condensed structural formula CH3 (CH2 )6 CH3 . Octane has many structural isomers that differ by the location of branching in the carbon chain . One of these isomers, 2,2,4-trimethylpentane (commonly called iso-octane), is used as one of the standard values in the octane rating scale.
Octane is a component of gasoline and petroleum. Under standard temperature and pressure , octane is an odorless, colorless liquid. Like other short-chained alkanes with a low molecular weight, it is volatile , flammable, and toxic. Octane is 1.2 to 2 times more toxic than heptane .
Isomers
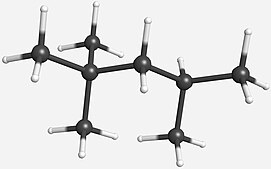
N-octane has 23 constitutional isomers . 8 of these isomers have one stereocenter ; 3 of them have two stereocenters.
(3S ,4S )-3,4-Dimethylhexane (top left) and (3R ,4R )-3,4-Dimethylhexane (top right) are non-superimposable mirror images, so they are chiral enantiomers . (meso )-3,4-Dimethylhexane (bottom) has a superimposable mirror image, so it is an achiral meso compound .Achiral Isomers:
2-Methylheptane 4-Methylheptane 3-Ethylhexane 2,2-Dimethylhexane 2,5-Dimethylhexane (meso )-3,4-Dimethylhexane 3,3-Dimethylhexane 3-Ethyl-2-methylpentane 3-Ethyl-3-methylpentane 2,2,4-Trimethylpentane (i.e. iso-octane)2,3,3-Trimethylpentane 2,3,4-Trimethylpentane 2,2,3,3-Tetramethylbutane Chiral Isomers:
(3R )-3-Methylheptane (3S )-3-Methylheptane (3R )-2,3-Dimethylhexane (3S )-2,3-Dimethylhexane (4R )-2,4-Dimethylhexane (4S )-2,4-Dimethylhexane (3R ,4R )-3,4-Dimethylhexane (3S ,4S )-3,4-Dimethylhexane (3R )-2,2,3-Trimethylpentane (3S )-2,2,3-Trimethylpentane Production and Use
In petrochemistry, octanes are not typically differentiated or purified as specific compounds. Octanes are components of particular boiling fractions.
A common route to such fractions is the alkylation reaction between iso-butane and 1-butene, which forms iso-octane.
Octane is commonly used as a solvent in paints and adhesives.
N-octane is the octane isomer that has the longest carbon skeleton. Unlike its constitutional isomers, it has a very low knock resistance.The octane isomer, iso-octane , is used as one of the standards for octane ratings. It has a rating of 100 by definition. The octane isomer 2,3,3-Trimethylpentane has an octane rating exceeding 100.
References
"octane - Compound Summary" . PubChem Compound . USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 16 September 2004. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 6 January 2012.^ NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0470" . National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
Dymond, J. H.; Oye, H. A. (1994). "Viscosity of Selected Liquid n -Alkanes". Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data . 23 (1): 41–53. Bibcode :1994JPCRD..23...41D . doi :10.1063/1.555943 . ISSN 0047-2689 .
"Octane" . Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH) . National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)."1988 OSHA PEL Project - Octane | NIOSH | CDC" . www.cdc.gov . 2020-02-27. Retrieved 2024-04-19."Fractionation" . www.appliedcontrol.com . Retrieved 2024-04-19.Ross, Julian (January 1986). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of industrial chemistry" . Applied Catalysis . 27 (2): 403–404. doi :10.1016/s0166-9834(00)82943-7 . ISSN 0166-9834 .
External links
Categories :
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.
**DISCLAIMER** We are not affiliated with Wikipedia, and Cloudflare.
The information presented on this site is for general informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice.
You should always have a personal consultation with a healthcare professional before making changes to your diet, medication, or exercise routine.
AI helps with the correspondence in our chat.
We participate in an affiliate program. If you buy something through a link, we may earn a commission 💕
↑