| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | N3−N=O |
| Molar mass | 72.027 g·mol |
| Appearance | Pale yellow solid below −50 °C (−58 °F). Above that temperature it decomposes. |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Nitrosyl azide is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and oxygen with the chemical formula N3−N=O. It is a highly labile nitrogen oxide with the empirical formula N4O.
Synthesis
Nitrosyl azide can be synthesized via the following reaction of sodium azide and nitrosyl chloride at low temperatures:
Properties
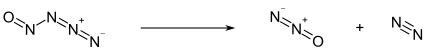
Below −50 °C, nitrosyl azide exists as a pale yellow solid. Above this temperature, it decomposes into nitrous oxide N2O and molecular nitrogen N2:
Characterization of the compound with IR and Raman spectroscopy show absorption bands that agree well with calculated values for a trans-structure. Quantum chemical calculations show a cis-form higher in energy by 4.2 kJ/mol and an aromatic ring form (oxatetrazole N4O) that is more stable by 205 kJ/mol. However, the cyclization to the ring form would have to surpass the 205 kJ/mol activation energy barrier require to bend the azide group, which might explain why nitrosyl azide is stable enough to be isolated at low temperature.
References
- ^ Schulz, Axel; Tornieporth-Oetting, Inis C.; Klapötke, Thomas M. (1993). "Nitrosyl Azide, N4O, an Intrinsically Unstable Oxide of Nitrogen". Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 32 (11): 1610–1612. doi:10.1002/anie.199316101.
- Lucien, Harold W. (1958). "The Preparation and Properties of Nitrosyl Azide". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 80 (17): 4458–4460. doi:10.1021/ja01550a004.
- Cotton, F. Albert & Geoffrey Wilkinson (1999). Advanced Inorganic Chemistry (6th ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons. p. 331. ISBN 0-471-19957-5.
| Salts and covalent derivatives of the azide ion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||