| This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (June 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Perineal artery | |
|---|---|
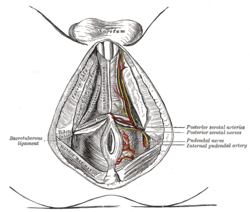 The superficial branches of the internal pudendal artery. (Perineal artery visible but not labeled.) The superficial branches of the internal pudendal artery. (Perineal artery visible but not labeled.) | |
| Details | |
| Source | Internal pudendal artery |
| Branches | Transverse perineal artery and posterior scrotal arteries |
| Vein | Perineal vein |
| Supplies | Bulbospongiosus and ischiocavernosus muscles, and skin and dartos tunic of the scrotum |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria perinealis |
| TA98 | A12.2.15.040 |
| TA2 | 4343 |
| FMA | 20836 |
| Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] | |
The perineal artery (superficial perineal artery) arises from the internal pudendal artery, and turns upward, crossing either over or under the superficial transverse perineal muscle, and runs forward, parallel to the pubic arch, in the interspace between the bulbospongiosus and ischiocavernosus muscles, both of which it supplies, and finally divides into several posterior scrotal branches which are distributed to the skin and dartos tunic of the scrotum.
As it crosses the superficial transverse perineal muscle it gives off the transverse perineal artery which runs transversely on the cutaneous surface of the muscle, and anastomoses with the corresponding vessel of the opposite side and with the perineal and inferior hemorrhoidal arteries.
It supplies the transverse perineal muscles and the structures between the anus and the urethral bulb.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 619 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 619 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This cardiovascular system article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |