
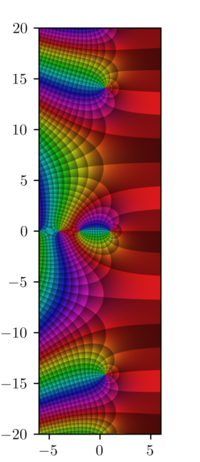
The Riemann zeta function or Euler–Riemann zeta function, denoted by the Greek letter ζ (zeta), is a mathematical function of a complex variable defined as for , and its analytic continuation elsewhere.
The Riemann zeta function plays a pivotal role in analytic number theory and has applications in physics, probability theory, and applied statistics.
Leonhard Euler first introduced and studied the function over the reals in the first half of the eighteenth century. Bernhard Riemann's 1859 article "On the Number of Primes Less Than a Given Magnitude" extended the Euler definition to a complex variable, proved its meromorphic continuation and functional equation, and established a relation between its zeros and the distribution of prime numbers. This paper also contained the Riemann hypothesis, a conjecture about the distribution of complex zeros of the Riemann zeta function that many mathematicians consider the most important unsolved problem in pure mathematics.
The values of the Riemann zeta function at even positive integers were computed by Euler. The first of them, ζ(2), provides a solution to the Basel problem. In 1979 Roger Apéry proved the irrationality of ζ(3). The values at negative integer points, also found by Euler, are rational numbers and play an important role in the theory of modular forms. Many generalizations of the Riemann zeta function, such as Dirichlet series, Dirichlet L-functions and L-functions, are known.
Definition

The Riemann zeta function ζ(s) is a function of a complex variable s = σ + it, where σ and t are real numbers. (The notation s, σ, and t is used traditionally in the study of the zeta function, following Riemann.) When Re(s) = σ > 1, the function can be written as a converging summation or as an integral:
where
is the gamma function. The Riemann zeta function is defined for other complex values via analytic continuation of the function defined for σ > 1.
Leonhard Euler considered the above series in 1740 for positive integer values of s, and later Chebyshev extended the definition to
The above series is a prototypical Dirichlet series that converges absolutely to an analytic function for s such that σ > 1 and diverges for all other values of s. Riemann showed that the function defined by the series on the half-plane of convergence can be continued analytically to all complex values s ≠ 1. For s = 1, the series is the harmonic series which diverges to +∞, and Thus the Riemann zeta function is a meromorphic function on the whole complex plane, which is holomorphic everywhere except for a simple pole at s = 1 with residue 1.
Euler's product formula
In 1737, the connection between the zeta function and prime numbers was discovered by Euler, who proved the identity
where, by definition, the left hand side is ζ(s) and the infinite product on the right hand side extends over all prime numbers p (such expressions are called Euler products):
Both sides of the Euler product formula converge for Re(s) > 1. The proof of Euler's identity uses only the formula for the geometric series and the fundamental theorem of arithmetic. Since the harmonic series, obtained when s = 1, diverges, Euler's formula (which becomes Πp p/p − 1) implies that there are infinitely many primes. Since the logarithm of p/p − 1 is approximately 1/p, the formula can also be used to prove the stronger result that the sum of the reciprocals of the primes is infinite. On the other hand, combining that with the sieve of Eratosthenes shows that the density of the set of primes within the set of positive integers is zero.
The Euler product formula can be used to calculate the asymptotic probability that s randomly selected integers are set-wise coprime. Intuitively, the probability that any single number is divisible by a prime (or any integer) p is 1/p. Hence the probability that s numbers are all divisible by this prime is 1/p, and the probability that at least one of them is not is 1 − 1/p. Now, for distinct primes, these divisibility events are mutually independent because the candidate divisors are coprime (a number is divisible by coprime divisors n and m if and only if it is divisible by nm, an event which occurs with probability 1/nm). Thus the asymptotic probability that s numbers are coprime is given by a product over all primes,
Riemann's functional equation
This zeta function satisfies the functional equation where Γ(s) is the gamma function. This is an equality of meromorphic functions valid on the whole complex plane. The equation relates values of the Riemann zeta function at the points s and 1 − s, in particular relating even positive integers with odd negative integers. Owing to the zeros of the sine function, the functional equation implies that ζ(s) has a simple zero at each even negative integer s = −2n, known as the trivial zeros of ζ(s). When s is an even positive integer, the product sin( π s / 2 ) Γ(1 − s) on the right is non-zero because Γ(1 − s) has a simple pole, which cancels the simple zero of the sine factor.
Proof of Riemann's functional equationA proof of the functional equation proceeds as follows: We observe that if then
As a result, if then with the inversion of the limiting processes justified by absolute convergence (hence the stricter requirement on ).
For convenience, let
which is a special case of the theta function. Then
By the Poisson summation formula we have
so that
Hence
This is equivalent to or
So
which is convergent for all s, so holds by analytic continuation. Furthermore, note by inspection that the RHS remains the same if s is replaced by 1 − s . Hence
which is the functional equation attributed to Bernhard Riemann. The functional equation above can now be obtained using the duplication formula for the gamma function.
The functional equation was established by Riemann in his 1859 paper "On the Number of Primes Less Than a Given Magnitude" and used to construct the analytic continuation in the first place.
Equivalencies
An equivalent relationship had been conjectured by Euler over a hundred years earlier, in 1749, for the Dirichlet eta function (the alternating zeta function):
Incidentally, this relation gives an equation for calculating ζ(s) in the region 0 < ℛℯ(s) < 1 , i.e. where the η-series is convergent (albeit non-absolutely) in the larger half-plane s > 0 (for a more detailed survey on the history of the functional equation, see e.g. Blagouchine).
Riemann also found a symmetric version of the functional equation applying to the ξ-function: which satisfies:
(Riemann's original ξ(t) was slightly different.)
The factor was not well-understood at the time of Riemann, until John Tate's (1950) thesis, in which it was shown that this so-called "Gamma factor" is in fact the local L-factor corresponding to the Archimedean place, the other factors in the Euler product expansion being the local L-factors of the non-Archimedean places.
Zeros, the critical line, and the Riemann hypothesis
Main article: Riemann hypothesis


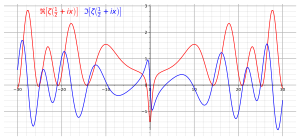
The functional equation shows that the Riemann zeta function has zeros at −2, −4,.... These are called the trivial zeros. They are trivial in the sense that their existence is relatively easy to prove, for example, from sin πs/2 being 0 in the functional equation. The non-trivial zeros have captured far more attention because their distribution not only is far less understood but, more importantly, their study yields important results concerning prime numbers and related objects in number theory. It is known that any non-trivial zero lies in the open strip , which is called the critical strip. The set is called the critical line. The Riemann hypothesis, considered one of the greatest unsolved problems in mathematics, asserts that all non-trivial zeros are on the critical line. In 1989, Conrey proved that more than 40% of the non-trivial zeros of the Riemann zeta function are on the critical line.
For the Riemann zeta function on the critical line, see Z-function.
| Zero |
|---|
| 1/2 ± 14.134725 i |
| 1/2 ± 21.022040 i |
| 1/2 ± 25.010858 i |
| 1/2 ± 30.424876 i |
| 1/2 ± 32.935062 i |
| 1/2 ± 37.586178 i |
| 1/2 ± 40.918719 i |
Number of zeros in the critical strip
Let be the number of zeros of in the critical strip , whose imaginary parts are in the interval . Trudgian proved that, if , then
- .
The Hardy–Littlewood conjectures
In 1914, G. H. Hardy proved that ζ (1/2 + it) has infinitely many real zeros.
Hardy and J. E. Littlewood formulated two conjectures on the density and distance between the zeros of ζ (1/2 + it) on intervals of large positive real numbers. In the following, N(T) is the total number of real zeros and N0(T) the total number of zeros of odd order of the function ζ (1/2 + it) lying in the interval (0, T].
- For any ε > 0, there exists a T0(ε) > 0 such that when
- For any ε > 0, there exists a T0(ε) > 0 and cε > 0 such that the inequality
These two conjectures opened up new directions in the investigation of the Riemann zeta function.
Zero-free region
The location of the Riemann zeta function's zeros is of great importance in number theory. The prime number theorem is equivalent to the fact that there are no zeros of the zeta function on the Re(s) = 1 line. A better result that follows from an effective form of Vinogradov's mean-value theorem is that ζ (σ + it) ≠ 0 whenever and |t| ≥ 3.
In 2015, Mossinghoff and Trudgian proved that zeta has no zeros in the region
for |t| ≥ 2. This is the largest known zero-free region in the critical strip for .
The strongest result of this kind one can hope for is the truth of the Riemann hypothesis, which would have many profound consequences in the theory of numbers.
Other results
It is known that there are infinitely many zeros on the critical line. Littlewood showed that if the sequence (γn) contains the imaginary parts of all zeros in the upper half-plane in ascending order, then
The critical line theorem asserts that a positive proportion of the nontrivial zeros lies on the critical line. (The Riemann hypothesis would imply that this proportion is 1.)
In the critical strip, the zero with smallest non-negative imaginary part is 1/2 + 14.13472514...i (OEIS: A058303). The fact that
for all complex s ≠ 1 implies that the zeros of the Riemann zeta function are symmetric about the real axis. Combining this symmetry with the functional equation, furthermore, one sees that the non-trivial zeros are symmetric about the critical line Re(s) = 1/2.
It is also known that no zeros lie on the line with real part 1.
Specific values
Main article: Particular values of the Riemann zeta functionFor any positive even integer 2n, where B2n is the 2n-th Bernoulli number. For odd positive integers, no such simple expression is known, although these values are thought to be related to the algebraic K-theory of the integers; see Special values of L-functions.
For nonpositive integers, one has for n ≥ 0 (using the convention that B1 = 1/2). In particular, ζ vanishes at the negative even integers because Bm = 0 for all odd m other than 1. These are the so-called "trivial zeros" of the zeta function.
Via analytic continuation, one can show that This gives a pretext for assigning a finite value to the divergent series 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + ⋯, which has been used in certain contexts (Ramanujan summation) such as string theory. Analogously, the particular value can be viewed as assigning a finite result to the divergent series 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + ⋯.
The value is employed in calculating kinetic boundary layer problems of linear kinetic equations.
Although diverges, its Cauchy principal value exists and is equal to the Euler–Mascheroni constant γ = 0.5772....
The demonstration of the particular value is known as the Basel problem. The reciprocal of this sum answers the question: What is the probability that two numbers selected at random are relatively prime? The value is Apéry's constant.
Taking the limit through the real numbers, one obtains . But at complex infinity on the Riemann sphere the zeta function has an essential singularity.
Various properties
For sums involving the zeta function at integer and half-integer values, see rational zeta series.
Reciprocal
The reciprocal of the zeta function may be expressed as a Dirichlet series over the Möbius function μ(n):
for every complex number s with real part greater than 1. There are a number of similar relations involving various well-known multiplicative functions; these are given in the article on the Dirichlet series.
The Riemann hypothesis is equivalent to the claim that this expression is valid when the real part of s is greater than 1/2.
Universality
The critical strip of the Riemann zeta function has the remarkable property of universality. This zeta function universality states that there exists some location on the critical strip that approximates any holomorphic function arbitrarily well. Since holomorphic functions are very general, this property is quite remarkable. The first proof of universality was provided by Sergei Mikhailovitch Voronin in 1975. More recent work has included effective versions of Voronin's theorem and extending it to Dirichlet L-functions.
Estimates of the maximum of the modulus of the zeta function
Let the functions F(T;H) and G(s0;Δ) be defined by the equalities
Here T is a sufficiently large positive number, 0 < H ≪ log log T, s0 = σ0 + iT, 1/2 ≤ σ0 ≤ 1, 0 < Δ < 1/3. Estimating the values F and G from below shows, how large (in modulus) values ζ(s) can take on short intervals of the critical line or in small neighborhoods of points lying in the critical strip 0 ≤ Re(s) ≤ 1.
The case H ≫ log log T was studied by Kanakanahalli Ramachandra; the case Δ > c, where c is a sufficiently large constant, is trivial.
Anatolii Karatsuba proved, in particular, that if the values H and Δ exceed certain sufficiently small constants, then the estimates
hold, where c1 and c2 are certain absolute constants.
The argument of the Riemann zeta function
The function
is called the argument of the Riemann zeta function. Here arg ζ(1/2 + it) is the increment of an arbitrary continuous branch of arg ζ(s) along the broken line joining the points 2, 2 + it and 1/2 + it.
There are some theorems on properties of the function S(t). Among those results are the mean value theorems for S(t) and its first integral
on intervals of the real line, and also the theorem claiming that every interval (T, T + H] for
contains at least
points where the function S(t) changes sign. Earlier similar results were obtained by Atle Selberg for the case
Representations
Dirichlet series
An extension of the area of convergence can be obtained by rearranging the original series. The series
converges for Re(s) > 0, while
converge even for Re(s) > −1. In this way, the area of convergence can be extended to Re(s) > −k for any negative integer −k.
The recurrence connection is clearly visible from the expression valid for Re(s) > −2 enabling further expansion by integration by parts.
Mellin-type integrals
The Mellin transform of a function f(x) is defined as
in the region where the integral is defined. There are various expressions for the zeta function as Mellin transform-like integrals. If the real part of s is greater than one, we have
- and ,
where Γ denotes the gamma function. By modifying the contour, Riemann showed that
for all s (where H denotes the Hankel contour).
We can also find expressions which relate to prime numbers and the prime number theorem. If π(x) is the prime-counting function, then
for values with Re(s) > 1.
A similar Mellin transform involves the Riemann function J(x), which counts prime powers p with a weight of 1/n, so that
Now
These expressions can be used to prove the prime number theorem by means of the inverse Mellin transform. Riemann's prime-counting function is easier to work with, and π(x) can be recovered from it by Möbius inversion.
Theta functions
The Riemann zeta function can be given by a Mellin transform
in terms of Jacobi's theta function
However, this integral only converges if the real part of s is greater than 1, but it can be regularized. This gives the following expression for the zeta function, which is well defined for all s except 0 and 1:
Laurent series
The Riemann zeta function is meromorphic with a single pole of order one at s = 1. It can therefore be expanded as a Laurent series about s = 1; the series development is then
The constants γn here are called the Stieltjes constants and can be defined by the limit
The constant term γ0 is the Euler–Mascheroni constant.
Integral
For all s ∈ ℂ, s ≠ 1, the integral relation (cf. Abel–Plana formula)
holds true, which may be used for a numerical evaluation of the zeta function.
Rising factorial
Another series development using the rising factorial valid for the entire complex plane is
This can be used recursively to extend the Dirichlet series definition to all complex numbers.
The Riemann zeta function also appears in a form similar to the Mellin transform in an integral over the Gauss–Kuzmin–Wirsing operator acting on x; that context gives rise to a series expansion in terms of the falling factorial.
Hadamard product
On the basis of Weierstrass's factorization theorem, Hadamard gave the infinite product expansion
where the product is over the non-trivial zeros ρ of ζ and the letter γ again denotes the Euler–Mascheroni constant. A simpler infinite product expansion is
This form clearly displays the simple pole at s = 1, the trivial zeros at −2, −4, ... due to the gamma function term in the denominator, and the non-trivial zeros at s = ρ. (To ensure convergence in the latter formula, the product should be taken over "matching pairs" of zeros, i.e. the factors for a pair of zeros of the form ρ and 1 − ρ should be combined.)
Globally convergent series
A globally convergent series for the zeta function, valid for all complex numbers s except s = 1 + 2πi/ln 2n for some integer n, was conjectured by Konrad Knopp in 1926 and proven by Helmut Hasse in 1930 (cf. Euler summation):
The series appeared in an appendix to Hasse's paper, and was published for the second time by Jonathan Sondow in 1994.
Hasse also proved the globally converging series
in the same publication. Research by Iaroslav Blagouchine has found that a similar, equivalent series was published by Joseph Ser in 1926.
In 1997 K. Maślanka gave another globally convergent (except s = 1) series for the Riemann zeta function:
where real coefficients are given by:
Here are the Bernoulli numbers and denotes the Pochhammer symbol.
Note that this representation of the zeta function is essentially an interpolation with nodes, where the nodes are points , i.e. exactly those where the zeta values are precisely known, as Euler showed. An elegant and very short proof of this representation of the zeta function, based on Carlson's theorem, was presented by Philippe Flajolet in 2006.
The asymptotic behavior of the coefficients is rather curious: for growing values, we observe regular oscillations with a nearly exponentially decreasing amplitude and slowly decreasing frequency (roughly as ). Using the saddle point method, we can show that
where stands for:
(see for details).
On the basis of this representation, in 2003 Luis Báez-Duarte provided a new criterion for the Riemann hypothesis. Namely, if we define the coefficients as
then the Riemann hypothesis is equivalent to
Rapidly convergent series
Peter Borwein developed an algorithm that applies Chebyshev polynomials to the Dirichlet eta function to produce a very rapidly convergent series suitable for high precision numerical calculations.
Series representation at positive integers via the primorial
Here pn# is the primorial sequence and Jk is Jordan's totient function.
Series representation by the incomplete poly-Bernoulli numbers
The function ζ can be represented, for Re(s) > 1, by the infinite series
where k ∈ {−1, 0}, Wk is the kth branch of the Lambert W-function, and B
n, ≥2 is an incomplete poly-Bernoulli number.
The Mellin transform of the Engel map
The function is iterated to find the coefficients appearing in Engel expansions.
The Mellin transform of the map is related to the Riemann zeta function by the formula
Thue-Morse sequence
Certain linear combinations of Dirichlet series whose coefficients are terms of the Thue-Morse sequence give rise to identities involving the Riemann Zeta function (Tóth, 2022 ). For instance:
where is the term of the Thue-Morse sequence. In fact, for all with real part greater than , we have
In nth dimensions
The zeta function can also be represented as an nth amount of integrals:
and it only works for
Numerical algorithms
A classical algorithm, in use prior to about 1930, proceeds by applying the Euler-Maclaurin formula to obtain, for n and m positive integers,
where, letting denote the indicated Bernoulli number,
and the error satisfies
with σ = Re(s).
A modern numerical algorithm is the Odlyzko–Schönhage algorithm.
Applications
The zeta function occurs in applied statistics including Zipf's law, Zipf–Mandelbrot law, and Lotka's law.
Zeta function regularization is used as one possible means of regularization of divergent series and divergent integrals in quantum field theory. In one notable example, the Riemann zeta function shows up explicitly in one method of calculating the Casimir effect. The zeta function is also useful for the analysis of dynamical systems.
Musical tuning
In the theory of musical tunings, the zeta function can be used to find equal divisions of the octave (EDOs) that closely approximate the intervals of the harmonic series. For increasing values of , the value of
peaks near integers that correspond to such EDOs. Examples include popular choices such as 12, 19, and 53.
Infinite series
The zeta function evaluated at equidistant positive integers appears in infinite series representations of a number of constants.
In fact the even and odd terms give the two sums
and
Parametrized versions of the above sums are given by
and
with and where and are the polygamma function and Euler's constant, respectively, as well as
all of which are continuous at . Other sums include
where denotes the imaginary part of a complex number.
Another interesting series that relates to the natural logarithm of the lemniscate constant is the following
There are yet more formulas in the article Harmonic number.
Generalizations
There are a number of related zeta functions that can be considered to be generalizations of the Riemann zeta function. These include the Hurwitz zeta function
(the convergent series representation was given by Helmut Hasse in 1930, cf. Hurwitz zeta function), which coincides with the Riemann zeta function when q = 1 (the lower limit of summation in the Hurwitz zeta function is 0, not 1), the Dirichlet L-functions and the Dedekind zeta function. For other related functions see the articles zeta function and L-function.
The polylogarithm is given by
which coincides with the Riemann zeta function when z = 1. The Clausen function Cls(θ) can be chosen as the real or imaginary part of Lis(e).
The Lerch transcendent is given by
which coincides with the Riemann zeta function when z = 1 and q = 1 (the lower limit of summation in the Lerch transcendent is 0, not 1).
The multiple zeta functions are defined by
One can analytically continue these functions to the n-dimensional complex space. The special values taken by these functions at positive integer arguments are called multiple zeta values by number theorists and have been connected to many different branches in mathematics and physics.
See also
- 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + ···
- Arithmetic zeta function
- Generalized Riemann hypothesis
- Lehmer pair
- Prime zeta function
- Riemann Xi function
- Renormalization
- Riemann–Siegel theta function
- ZetaGrid
References
- "Jupyter Notebook Viewer". Nbviewer.ipython.org. Retrieved 4 January 2017.
- ^ Steuding, Jörn; Suriajaya, Ade Irma (1 November 2020). "Value-Distribution of the Riemann Zeta-Function Along Its Julia Lines". Computational Methods and Function Theory. 20 (3): 389–401. doi:10.1007/s40315-020-00316-x. hdl:2324/4483207. ISSN 2195-3724. S2CID 216323223.
Theorem 2 implies that ζ has an essential singularity at infinity
- Bombieri, Enrico. "The Riemann Hypothesis – official problem description" (PDF). Clay Mathematics Institute. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 December 2015. Retrieved 8 August 2014.
- Devlin, Keith (2002). The Millennium Problems: The seven greatest unsolved mathematical puzzles of our time. New York: Barnes & Noble. pp. 43–47. ISBN 978-0-7607-8659-8.
- Sandifer, Charles Edward (2007). How Euler Did It. Mathematical Association of America. p. 193. ISBN 978-0-88385-563-8.
- Titchmarsh, E.C. (1986). The Theory of the Riemann Zeta Function (2nd ed.). Oxford, UK: Oxford Science Publications. pp. 21–22. ISBN 0-19-853369-1.
- Blagouchine, I.V. (1 March 2018). The history of the functional equation of the zeta-function. Seminar on the History of Mathematics. St. Petersburg, RU: Steklov Institute of Mathematics; "online PDF". Archived from the original on 2 May 2018. Retrieved 2 May 2018.
- Blagouchine, I.V. (2014). "Rediscovery of Malmsten's integrals, their evaluation by contour integration methods and some related results". The Ramanujan Journal. 35 (1): 21–110. doi:10.1007/s11139-013-9528-5. S2CID 120943474.
Blagouchine, I.V. (2017). "Addendum". The Ramanujan Journal. 42: 777–781. doi:10.1007/s11139-015-9763-z. S2CID 125198685. Archived from the original on 2 May 2018. Retrieved 2 May 2018. - Conrey, J. B. (1989). "More than two fifths of the zeros of the Riemann zeta function are on the critical line". J. Reine Angew. Math. 1989 (399): 1–26. doi:10.1515/crll.1989.399.1. MR 1004130. S2CID 115910600.
- Eric Weisstein. "Riemann Zeta Function Zeros". Retrieved 24 April 2021.
- The L-functions and Modular Forms Database. "Zeros of ζ(s)".
- Trudgian, Timothy S. (2014). "An improved upper bound for the argument of the Riemann zeta function on the critical line II". J. Number Theory. 134: 280–292. arXiv:1208.5846. doi:10.1016/j.jnt.2013.07.017.
- Hardy, G.H. (1914). "Sur les zeros de la fonction ζ(s)". Comptes rendus de l'Académie des Sciences. 158. French Academy of Sciences: 1012–1014.
- Hardy, G. H.; Fekete, M.; Littlewood, J. E. (1 September 1921). "The Zeros of Riemann's Zeta-Function on the Critical Line". Journal of the London Mathematical Society. s1-1: 15–19. doi:10.1112/jlms/s1-1.1.15.
- Diamond, Harold G. (1982). "Elementary methods in the study of the distribution of prime numbers". Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society. 7 (3): 553–89. doi:10.1090/S0273-0979-1982-15057-1. MR 0670132.
- Ford, K. (2002). "Vinogradov's integral and bounds for the Riemann zeta function". Proc. London Math. Soc. 85 (3): 565–633. arXiv:1910.08209. doi:10.1112/S0024611502013655. S2CID 121144007.
- Mossinghoff, Michael J.; Trudgian, Timothy S. (2015). "Nonnegative trigonometric polynomials and a zero-free region for the Riemann zeta-function". J. Number Theory. 157: 329–349. arXiv:1410.3926. doi:10.1016/J.JNT.2015.05.010. S2CID 117968965.
- Polchinski, Joseph (1998). An Introduction to the Bosonic String. String Theory. Vol. I. Cambridge University Press. p. 22. ISBN 978-0-521-63303-1.
- Kainz, A. J.; Titulaer, U. M. (1992). "An accurate two-stream moment method for kinetic boundary layer problems of linear kinetic equations". J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 25 (7): 1855–1874. Bibcode:1992JPhA...25.1855K. doi:10.1088/0305-4470/25/7/026.
- Further digits and references for this constant are available at OEIS: A059750.
- Sondow, Jonathan (1998). "An antisymmetric formula for Euler's constant". Mathematics Magazine. 71 (3): 219–220. doi:10.1080/0025570X.1998.11996638. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011. Retrieved 29 May 2006.
- Ogilvy, C. S.; Anderson, J. T. (1988). Excursions in Number Theory. Dover Publications. pp. 29–35. ISBN 0-486-25778-9.
- Voronin, S. M. (1975). "Theorem on the Universality of the Riemann Zeta Function". Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Matem. 39: 475–486. Reprinted in Math. USSR Izv. (1975) 9: 443–445.
- Ramūnas Garunkštis; Antanas Laurinčikas; Kohji Matsumoto; Jörn Steuding; Rasa Steuding (2010). "Effective uniform approximation by the Riemann zeta-function". Publicacions Matemàtiques. 54 (1): 209–219. doi:10.5565/PUBLMAT_54110_12. JSTOR 43736941.
- Bhaskar Bagchi (1982). "A Joint Universality Theorem for Dirichlet L-Functions". Mathematische Zeitschrift. 181 (3): 319–334. doi:10.1007/bf01161980. ISSN 0025-5874. S2CID 120930513.
- Steuding, Jörn (2007). Value-Distribution of L-Functions. Lecture Notes in Mathematics. Vol. 1877. Berlin: Springer. p. 19. arXiv:1711.06671. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-44822-8. ISBN 978-3-540-26526-9.
- Karatsuba, A. A. (2001). "Lower bounds for the maximum modulus of ζ(s) in small domains of the critical strip". Mat. Zametki. 70 (5): 796–798.
- Karatsuba, A. A. (2004). "Lower bounds for the maximum modulus of the Riemann zeta function on short segments of the critical line". Izv. Ross. Akad. Nauk, Ser. Mat. 68 (8): 99–104. Bibcode:2004IzMat..68.1157K. doi:10.1070/IM2004v068n06ABEH000513. S2CID 250796539.
- Karatsuba, A. A. (1996). "Density theorem and the behavior of the argument of the Riemann zeta function". Mat. Zametki (60): 448–449.
- Karatsuba, A. A. (1996). "On the function S(t)". Izv. Ross. Akad. Nauk, Ser. Mat. 60 (5): 27–56.
- ^ Knopp, Konrad (1947). Theory of Functions, Part Two. New York, Dover publications. pp. 51–55.
- Riemann, Bernhard (1859). "On the number of primes less than a given magnitude". Monatsberichte der Königlich Preußischen Akademie der Wissenschaften zu Berlin. translated and reprinted in Edwards, H. M. (1974). Riemann's Zeta Function. New York: Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-232750-0. Zbl 0315.10035.
- Trivial exceptions of values of s that cause removable singularities are not taken into account throughout this article.
- Neukirch, Jürgen (1999). Algebraic number theory. Springer. p. 422. ISBN 3-540-65399-6.
- Hashimoto, Yasufumi; Iijima, Yasuyuki; Kurokawa, Nobushige; Wakayama, Masato (2004). "Euler's constants for the Selberg and the Dedekind zeta functions". Bulletin of the Belgian Mathematical Society, Simon Stevin. 11 (4): 493–516. doi:10.36045/bbms/1102689119. MR 2115723.
- "A series representation for the Riemann Zeta derived from the Gauss-Kuzmin-Wirsing Operator" (PDF). Linas.org. Retrieved 4 January 2017.
- ^ Blagouchine, Iaroslav V. (2018). "Three Notes on Ser's and Hasse's Representations for the Zeta-functions". INTEGERS: The Electronic Journal of Combinatorial Number Theory. 18A: 1–45. arXiv:1606.02044. Bibcode:2016arXiv160602044B.
- ^ Hasse, Helmut (1930). "Ein Summierungsverfahren für die Riemannsche ζ-Reihe" [A summation method for the Riemann ζ series]. Mathematische Zeitschrift (in German). 32 (1): 458–464. doi:10.1007/BF01194645. S2CID 120392534.
- Sondow, Jonathan (1994). "Analytic continuation of Riemann's zeta function and values at negative integers via Euler's transformation of series" (PDF). Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society. 120 (2): 421–424. doi:10.1090/S0002-9939-1994-1172954-7.
- Blagouchine, Iaroslav V. (2016). "Expansions of generalized Euler's constants into the series of polynomials in π and into the formal enveloping series with rational coefficients only". Journal of Number Theory. 158: 365–396. arXiv:1501.00740. doi:10.1016/j.jnt.2015.06.012.
- Ser, Joseph (1926). "Sur une expression de la fonction ζ(s) de Riemann" [Upon an expression for Riemann's ζ function]. Comptes rendus hebdomadaires des séances de l'Académie des Sciences (in French). 182: 1075–1077.
- Maślanka, Krzysztof (1997). "The Beauty of Nothingness". Acta Cosmologica. XXIII–I: 13–17.
- Báez-Duarte, Luis (2010). "On Maslanka's Representation for the Riemann Zeta Function". International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences. 2010: 1–9. arXiv:math/0307214. doi:10.1155/2010/714147.
- Flajolet, Philippe; Vepstas, Linas (2008). "On Differences of Zeta Values". Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics. 220 (1-2 October): 58–73. arXiv:math/0611332. Bibcode:2008JCoAM.220...58F. doi:10.1016/j.cam.2007.07.040.
- Maślanka, Krzysztof; Koleżyński, Andrzej (2022). "The High Precision Numerical Calculation of Stieltjes Constants. Simple and Fast Algorithm". Computational Methods in Science and Technology. 28 (2): 47–59. arXiv:2210.04609. doi:10.12921/cmst.2022.0000014. S2CID 252780397.
- Báez-Duarte, Luis (2003). "A New Necessary and Sufficient Condition for the Riemann Hypothesis". Number Theory. arXiv:math/0307215. Bibcode:2003math......7215B.
- Maślanka, Krzysztof (2006). "Báez-Duarte's Criterion for the Riemann Hypothesis and Rice's Integrals". Number Theory. arXiv:math/0603713v2. Bibcode:2006math......3713M.
- Wolf, Marek (2014). "Some remarks on the Báez-Duarte criterion for the Riemann Hypothesis". Computational Methods in Science and Technology. 20 (2): 39–47. doi:10.12921/cmst.2014.20.02.39-47.
- Borwein, Peter (2000). "An Efficient Algorithm for the Riemann Zeta Function" (PDF). In Théra, Michel A. (ed.). Constructive, Experimental, and Nonlinear Analysis. Conference Proceedings, Canadian Mathematical Society. Vol. 27. Providence, RI: American Mathematical Society, on behalf of the Canadian Mathematical Society. pp. 29–34. ISBN 978-0-8218-2167-1. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 July 2011. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- Mező, István (2013). "The primorial and the Riemann zeta function". The American Mathematical Monthly. 120 (4): 321.
- Komatsu, Takao; Mező, István (2016). "Incomplete poly-Bernoulli numbers associated with incomplete Stirling numbers". Publicationes Mathematicae Debrecen. 88 (3–4): 357–368. arXiv:1510.05799. doi:10.5486/pmd.2016.7361. S2CID 55741906.
- "A220335 - OEIS". oeis.org. Retrieved 17 April 2019.
- Tóth, László (2022). "Linear Combinations of Dirichlet Series Associated with the Thue-Morse Sequence". Integers. 22 (article 98). arXiv:2211.13570.
- Odlyzko, A. M.; Schönhage, A. (1988). "Fast algorithms for multiple evaluations of the Riemann zeta function". Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 309 (2): 797–809. doi:10.2307/2000939. JSTOR 2000939. MR 0961614..
- "Work on spin-chains by A. Knauf, et. al". Empslocal.ex.ac.uk. Retrieved 4 January 2017.
- Gene Ward Smith. "Nearest integer to locations of increasingly large peaks of abs(zeta(0.5 + i*2*Pi/log(2)*t)) for increasing real t". The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. Retrieved 4 March 2022.
- William A. Sethares (2005). Tuning, Timbre, Spectrum, Scale (2nd ed.). Springer-Verlag London. p. 74.
...there are many different ways to evaluate the goodness, reasonableness, fitness, or quality of a scale...Under some measures, 12-tet is the winner, under others 19-tet appears best, 53-tet often appears among the victors...
- Most of the formulas in this section are from § 4 of J. M. Borwein et al. (2000)
Sources
- Apostol, T.M. (2010). "Zeta and Related Functions". In Olver, Frank W. J.; Lozier, Daniel M.; Boisvert, Ronald F.; Clark, Charles W. (eds.). NIST Handbook of Mathematical Functions. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-19225-5. MR 2723248..
- Borwein, Jonathan; Bradley, David M.; Crandall, Richard (2000). "Computational Strategies for the Riemann Zeta Function" (PDF). J. Comput. Appl. Math. 121 (1–2): 247–296. Bibcode:2000JCoAM.121..247B. doi:10.1016/S0377-0427(00)00336-8. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 December 2013 – via University of Exeter (maths.ex.ac.uk).
- Cvijović, Djurdje; Klinowski, Jacek (2002). "Integral representations of the Riemann zeta function for odd-integer arguments". J. Comput. Appl. Math. 142 (2): 435–439. Bibcode:2002JCoAM.142..435C. doi:10.1016/S0377-0427(02)00358-8. MR 1906742.
- Cvijović, Djurdje; Klinowski, Jacek (1997). "Continued-fraction expansions for the Riemann zeta function and polylogarithms". Proc. Amer. Math. Soc. 125 (9): 2543–2550. doi:10.1090/S0002-9939-97-04102-6.
- Edwards, H.M. (1974). Riemann's Zeta Function. Academic Press. ISBN 0-486-41740-9 – via archive.org. Has an English translation of Riemann's paper.
- Hadamard, Jacques (1896). "Sur la distribution des zéros de la fonction ζ(s) et ses conséquences arithmétiques" [Regarding the distribution of the zeros of the function ζ(s) and the arithmetical consequences]. Bulletin de la Société Mathématique de France (in French). 14: 199–220. doi:10.24033/bsmf.545.
- Hardy, G.H. (1949). Divergent Series. Oxford, UK: Clarendon Press.
- Hasse, Helmut (1930). "Ein Summierungsverfahren für die Riemannsche ζ-Reihe" [A summation method for the Riemann ζ series]. Math. Z. (in German). 32: 458–464. doi:10.1007/BF01194645. MR 1545177. S2CID 120392534. (Globally convergent series expression.)
- Ivic, Aleksandar (1985). The Riemann Zeta Function. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-80634-X.
- Motohashi, Y. (1997). Spectral Theory of the Riemann Zeta-Function. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521445205.
- Karatsuba, A.A.; Voronin, S.M. (1992). The Riemann Zeta-Function. Berlin, DE: W. de Gruyter.
- Mező, István; Dil, Ayhan (2010). "Hyperharmonic series involving Hurwitz zeta function". Journal of Number Theory. 130 (2): 360–369. doi:10.1016/j.jnt.2009.08.005. hdl:2437/90539. MR 2564902. S2CID 122707401.
- Montgomery, Hugh L.; Vaughan, Robert C. (2007). Multiplicative Number Theory. I. Classical theory. Cambridge tracts in advanced mathematics. Vol. 97. Cambridge University Press. Chapter 10. ISBN 978-0-521-84903-6.
- Newman, Donald J. (1998). Analytic Number Theory. Graduate Texts in Mathematics. Vol. 177. Springer-Verlag. Ch. 6. ISBN 0-387-98308-2.
- Raoh, Guo (1996). "The distribution of the logarithmic derivative of the Riemann zeta function". Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society. S3–72: 1–27. doi:10.1112/plms/s3-72.1.1.
- Riemann, Bernhard (1859). "Über die Anzahl der Primzahlen unter einer gegebenen Grösse". Monatsberichte der Berliner Akademie (in German and English) – via Trinity College, Dublin (maths.tcd.ie). Also available in Riemann, Bernhard (1953) . Gesammelte Werke [Collected Works] (in German) (reprint ed.). New York, NY / Leipzig, DE: Dover (1953) / Teubner (1892).
- Sondow, Jonathan (1994). "Analytic continuation of Riemann's zeta function and values at negative integers via Euler's transformation of series" (PDF). Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society. 120 (2): 421–424. doi:10.1090/S0002-9939-1994-1172954-7 – via American Mathematical Society (ams.org).
- Titchmarsh, E.C. (1986). Heath-Brown (ed.). The Theory of the Riemann Zeta Function (2nd rev. ed.). Oxford University Press.
- Whittaker, E.T.; Watson, G.N. (1927). A Course in Modern Analysis (4th ed.). Cambridge University Press. Chapter 13.
- Zhao, Jianqiang (1999). "Analytic continuation of multiple zeta functions". Proceedings of the American Mathematical Society. 128 (5): 1275–1283. doi:10.1090/S0002-9939-99-05398-8. MR 1670846.
External links
 Media related to Riemann zeta function at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Riemann zeta function at Wikimedia Commons- "Zeta-function". Encyclopedia of Mathematics. EMS Press. 2001 .
- Riemann Zeta Function, in Wolfram Mathworld — an explanation with a more mathematical approach
- Tables of selected zeros Archived 17 May 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- Prime Numbers Get Hitched A general, non-technical description of the significance of the zeta function in relation to prime numbers.
- X-Ray of the Zeta Function Visually oriented investigation of where zeta is real or purely imaginary.
- Formulas and identities for the Riemann Zeta function functions.wolfram.com
- Riemann Zeta Function and Other Sums of Reciprocal Powers, section 23.2 of Abramowitz and Stegun
- Frenkel, Edward. "Million Dollar Math Problem" (video). Brady Haran. Archived from the original on 11 December 2021. Retrieved 11 March 2014.
- Mellin transform and the functional equation of the Riemann Zeta function—Computational examples of Mellin transform methods involving the Riemann Zeta Function
- Visualizing the Riemann zeta function and analytic continuation a video from 3Blue1Brown
| L-functions in number theory | |
|---|---|
| Analytic examples | |
| Algebraic examples | |
| Theorems | |
| Analytic conjectures | |
| Algebraic conjectures | |
| p-adic L-functions | |
| Sequences and series | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Integer sequences |
|  | ||||
| Properties of sequences | ||||||
| Properties of series |
| |||||
| Explicit series | ||||||
| Kinds of series | ||||||
| Hypergeometric series | ||||||
 and two zeros on the critical line.
and two zeros on the critical line. for
for  , and its
, and its 


 Thus the Riemann zeta function is a
Thus the Riemann zeta function is a 


 where Γ(s) is the
where Γ(s) is the  then
then

 then
then
 with the inversion of the limiting processes justified by absolute convergence (hence the stricter requirement on
with the inversion of the limiting processes justified by absolute convergence (hence the stricter requirement on  ).
).





 or
or




 where the η-series is
where the η-series is  which satisfies:
which satisfies:

 factor was not well-understood at the time of Riemann, until
factor was not well-understood at the time of Riemann, until  , which is called the critical strip. The set
, which is called the critical strip. The set  is called the critical line. The
is called the critical line. The  be the number of zeros of
be the number of zeros of  in the critical strip
in the critical strip  , whose imaginary parts are in the interval
, whose imaginary parts are in the interval  .
Trudgian proved that, if
.
Trudgian proved that, if  , then
, then
 .
.


 and |t| ≥ 3.
and |t| ≥ 3.

 .
.


 where B2n is the 2n-th
where B2n is the 2n-th  for n ≥ 0 (using the convention that B1 = 1/2).
In particular, ζ vanishes at the negative even integers because Bm = 0 for all odd m other than 1. These are the so-called "trivial zeros" of the zeta function.
for n ≥ 0 (using the convention that B1 = 1/2).
In particular, ζ vanishes at the negative even integers because Bm = 0 for all odd m other than 1. These are the so-called "trivial zeros" of the zeta function.
 This gives a pretext for assigning a finite value to the divergent series
This gives a pretext for assigning a finite value to the divergent series  can be viewed as assigning a finite result to the divergent series
can be viewed as assigning a finite result to the divergent series  is employed in calculating kinetic boundary layer problems of linear kinetic equations.
is employed in calculating kinetic boundary layer problems of linear kinetic equations.
 diverges, its
diverges, its  exists and is equal to the
exists and is equal to the  is known as the
is known as the  is
is  through the real numbers, one obtains
through the real numbers, one obtains  . But at
. But at 











 and
and  ,
,















 are given by:
are given by:

 are the Bernoulli numbers and
are the Bernoulli numbers and  denotes the Pochhammer symbol.
denotes the Pochhammer symbol.
 , i.e. exactly those where the zeta values are precisely known, as Euler showed. An elegant and very short proof of this representation of the zeta function, based on Carlson's theorem, was presented by Philippe Flajolet in 2006.
, i.e. exactly those where the zeta values are precisely known, as Euler showed. An elegant and very short proof of this representation of the zeta function, based on Carlson's theorem, was presented by Philippe Flajolet in 2006.
 values, we observe regular oscillations with a nearly exponentially decreasing amplitude and slowly decreasing frequency (roughly as
values, we observe regular oscillations with a nearly exponentially decreasing amplitude and slowly decreasing frequency (roughly as  ). Using the saddle point method, we can show that
). Using the saddle point method, we can show that

 stands for:
stands for:

 as
as




 is iterated to find the coefficients appearing in
is iterated to find the coefficients appearing in  is related to the Riemann zeta function by the formula
is related to the Riemann zeta function by the formula


 is the
is the  term of the Thue-Morse sequence. In fact, for all
term of the Thue-Morse sequence. In fact, for all  , we have
, we have




 denote the indicated
denote the indicated 

 , the value of
, the value of






 and where
and where  and
and  are the
are the 
 . Other sums include
. Other sums include





 denotes the
denotes the 



