 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
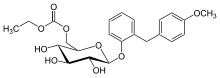
| Formula | C23H28O9 |
| Molar mass | 448.468 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
Sergliflozin etabonate (INN/USAN, codenamed GW869682X) is an investigational anti-diabetic drug being developed by GlaxoSmithKline. It did not undergo further development after phase II.
Method of action
Sergliflozin inhibits subtype 2 of the sodium-glucose transport proteins (SGLT2), which is responsible for at least 90% of the glucose reabsorption in the kidney. Blocking this transporter causes blood glucose to be eliminated through the urine.
Chemistry
Etabonate refers to the ethyl carbonate group. The remaining structure, which is the active substance, is called sergliflozin.

References
- World Health Organization (2008). "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Recommended International Nonproprietary Names: List 59" (PDF). WHO Drug Information. 22 (1): 66. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 19, 2009.
- "Statement on a nonproprietary name adopted by the USAN council: Sergliflozin etabonate" (PDF). American Medical Association. Retrieved 2008-08-10.
- Katsuno K, Fujimori Y, Takemura Y, et al. (January 2007). "Sergliflozin, a novel selective inhibitor of low-affinity sodium glucose cotransporter (SGLT2), validates the critical role of SGLT2 in renal glucose reabsorption and modulates plasma glucose level". J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 320 (1): 323–30. doi:10.1124/jpet.106.110296. PMID 17050778. S2CID 8306408.
- "Prous Science: Molecule of the Month November 2007". Archived from the original on 2007-11-05. Retrieved 2008-10-28.
| Sodium-glucose transporter modulators | |
|---|---|
| SGLT1Tooltip Sodium-glucose transporter 1 | |
| SGLT2Tooltip Sodium-glucose transporter 2 |
|
| SGLT1Tooltip Sodium-glucose transporter 1 & SGLT2Tooltip Sodium-glucose transporter 2 |
|
| See also: Receptor/signaling modulators | |
This drug article relating to the gastrointestinal system is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |