| This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (May 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Splenius capitis muscle | |
|---|---|
 Muscles connecting the upper extremity to the vertebral column (splenius capitis et cervicis labeled at upper right). Muscles connecting the upper extremity to the vertebral column (splenius capitis et cervicis labeled at upper right). | |
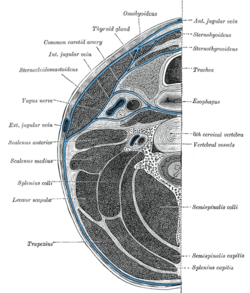 Section of the neck at about the level of the sixth cervical vertebra. Showing the arrangement of the deep cervical fascia (splenius capitis labeled at bottom right). Section of the neck at about the level of the sixth cervical vertebra. Showing the arrangement of the deep cervical fascia (splenius capitis labeled at bottom right). | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Nuchal ligament and spinous process of C7-T3 |
| Insertion | Mastoid process of temporal and occipital bone |
| Artery | Muscular branches of the aorta |
| Nerve | Posterior ramus of spinal nerves C3 and C4 |
| Actions | Extend, rotate, and laterally flex the head |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus splenius capitis |
| TA98 | A04.3.02.103 |
| TA2 | 2273 |
| FMA | 22653 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle[edit on Wikidata] | |
The splenius capitis (/ˈspliːniəs ˈkæpɪtɪs/) (from Greek splēníon 'bandage' and Latin caput 'head') is a broad, straplike muscle in the back of the neck. It pulls on the base of the skull from the vertebrae in the neck and upper thorax. It is involved in movements such as shaking the head.
Structure
It arises from the lower half of the nuchal ligament, from the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra, and from the spinous processes of the upper three or four thoracic vertebrae.
The fibers of the muscle are directed upward and laterally and are inserted, under cover of the sternocleidomastoideus, into the mastoid process of the temporal bone, and into the rough surface on the occipital bone just below the lateral third of the superior nuchal line. The splenius capitis is deep to sternocleidomastoideus at the mastoid process, and to the trapezius for its lower portion. It is one of the muscles that forms the floor of the posterior triangle of the neck.
The splenius capitis muscle is innervated by the posterior ramus of spinal nerves C3 and C4.
Function
The splenius capitis muscle is a prime mover for head extension. The splenius capitis can also allow lateral flexion and rotation of the cervical spine.
Additional images
-
 Muscles of the neck. Lateral view.
Muscles of the neck. Lateral view.
-
Splenius capitis muscle
-
 Splenius muscle
Splenius muscle
-
 Splenius and Semispinalis
Splenius and Semispinalis
See also
This article uses anatomical terminology.References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 397 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 397 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Arnold, MA; Bryce, Deborah. "Arnold's Glossary of Anatomy". The University of Sydney.
- "Splenius capitis muscle - definition of Splenius capitis muscle in the Medical dictionary". Medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com. Retrieved 2011-08-18.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 01:03-01 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Superficial layer of the extrinsic muscles of the back."
- Anatomy figure: 01:05-01 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Intermediate layer of the extrinsic muscles of the back, deep muscles."
- Anatomy figure: 24:01-02 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Identification of the muscles associated with the posterolateral triangle."
- PTCentral
| Muscles of the thorax and back | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Back |
| ||||||||||
| Thorax |
| ||||||||||