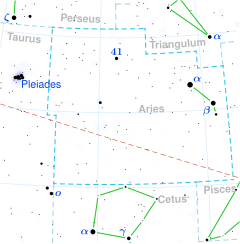
Star in the constellation Aries
For other stars with this Bayer designation , see τ Arietis .
Tau Arietis , Latinized from τ Arietis, is the Bayer designation for a binary star in the northern constellation on Aries . The combined apparent visual magnitude of this system is +5.09, which is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. With an annual parallax shift of 10.27 mas , it is located at a distance of approximately 320 light-years (98 parsecs ) from Earth , give or take a 20 light-year margin of error . At this distance the brightness of the star is diminished by 0.18 in magnitude because of extinction from interstellar gas and dust .
The primary component is an evolved giant star with a stellar classification of K3 III. It has expanded to 19 times the radius of the Sun, from which it is radiating 120 times the Sun's luminosity. This energy is being emitted into outer space from the outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of 4,406 K, giving it the cool orange glow of a K-type star . At an angular separation of 0.53 arcseconds is a magnitude 8.50 companion.
References
^ van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics , 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv :0708.1752 , Bibcode :2007A&A...474..653V , doi :10.1051/0004-6361:20078357 , S2CID 18759600 .
^ Argue, A. N. (1966), "UBV photometry of 550 F, G and K type stars", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society , 133 (4): 475, Bibcode :1966MNRAS.133..475A , doi :10.1093/mnras/133.4.475 .
Cenarro, A. J.; et al. (January 2007), "Medium-resolution Isaac Newton Telescope library of empirical spectra - II. The stellar atmospheric parameters", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 374 (2): 664–690, arXiv :astro-ph/0611618 , Bibcode :2007MNRAS.374..664C , doi :10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.11196.x , S2CID 119428437 .
^ Massarotti, Alessandro; et al. (January 2008), "Rotational and Radial Velocities for a Sample of 761 HIPPARCOS Giants and the Role of Binarity", The Astronomical Journal , 135 (1): 209–231, Bibcode :2008AJ....135..209M , doi :10.1088/0004-6256/135/1/209 , S2CID 121883397 .
Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters , 38 (5): 331, arXiv :1108.4971 , Bibcode :2012AstL...38..331A , doi :10.1134/S1063773712050015 , S2CID 119257644 .
"63 Ari" . SIMBAD Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg . Retrieved 2012-07-18.{{cite web }}: CS1 maint: postscript (link )
^ Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (September 2008). "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems" . Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society . 389 (2): 869–879. arXiv :0806.2878 . Bibcode :2008MNRAS.389..869E . doi :10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x . S2CID 14878976 .
Famaey, B.; et al. (January 2005), "Local kinematics of K and M giants from CORAVEL/Hipparcos/Tycho-2 data. Revisiting the concept of superclusters", Astronomy and Astrophysics , 430 (1): 165–186, arXiv :astro-ph/0409579 , Bibcode :2005A&A...430..165F , doi :10.1051/0004-6361:20041272 , S2CID 17804304
Roman, Nancy G. (July 1952), "The Spectra of the Bright Stars of Types F5-K5", Astrophysical Journal , 116 : 122, Bibcode :1952ApJ...116..122R , doi :10.1086/145598 .
External links
Categories :
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.
**DISCLAIMER** We are not affiliated with Wikipedia, and Cloudflare.
The information presented on this site is for general informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice.
You should always have a personal consultation with a healthcare professional before making changes to your diet, medication, or exercise routine.
AI helps with the correspondence in our chat.
We participate in an affiliate program. If you buy something through a link, we may earn a commission 💕
↑